Page 17 of 279

Ford Mondeo maintenance schedule
1•3
1
Maintenance schedule
The manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for these
vehicles is as described below - note that the schedule starts from the
vehicle’s date of registration. These are the minimum maintenance
intervals recommended by the factory for Mondeos driven daily, but
subjected only to “normal” use. If you wish to keep your vehicle in
peak condition at all times, you may wish to perform some of these
procedures even more often. Because frequent maintenance
enhances the efficiency, performance and resale value of your vehicle,
we encourage you to do so. If your usage is not “normal”, shorter
intervals are also recommended - the most important examples of
these are noted in the schedule. These shorter intervals apply
particularly if you drive in dusty areas, tow a caravan or trailer, sit with
the engine idling or drive at low speeds for extended periods (ie, in
heavy traffic), or drive for short distances (less than four miles) in
below-freezing temperatures.
When your vehicle is new, it should be serviced by a Ford dealer
service department to protect the factory warranty. In many cases, the
initial maintenance check is done at no cost to the owner. Note that
this first free service (carried out by the selling dealer 1500 miles or 3
months after delivery), although an important check for a new vehicle,
is not part of the regular maintenance schedule, and is therefore not
mentioned here.
Weekly checks
m mCheck the engine oil level, and top-up if necessary
(Section 3)
m mCheck the brake fluid level, and top-up if necessary
(Section 3). If repeated topping-up is required, check the
system for leaks or damage at the earliest possible
opportunity (Sections 12 and 22)
m mCheck the windscreen/tailgate washer fluid level, and top-
up if necessary (Section 3)
m mCheck the tyre pressures, including the spare (Section 4)
m mVisually check the tyres for excessive tread wear, or
damage (Section 4)
m mCheck the operation of all (exterior and interior) lights and
the horn, wipers and windscreen/tailgate washer system
(Sections 6 and 8). Renew any blown bulbs (Chapter 12),
and clean the lenses of all exterior lights
Monthly checks
m mCheck the coolant level, and top-up if necessary (Sec-
tion 3)
m mCheck the battery electrolyte level, where applicable
(Section 3)
m mCheck the power steering fluid level, and top-up if
necessary (Section 5)
m mVisually check all reservoirs, hoses and pipes for leakage
(Section 12)
m mCheck the operation of the air conditioning system
(Section 14)
m mCheck the operation of the handbrake (Section 23)
m mCheck the aim of the windscreen/tailgate/headlight
washer jets, correcting them if required (Section 6)
m mCheck the condition of the wiper blades, renewing them if
worn or no longer effective - note that the manufacturer
recommends renewing the blades as a safety precaution,
irrespective of their apparent condition, at least once a
year (Section 6)
Every 10 000 miles or 12 months,
whichever occurs first
Note:If the vehicle is used regularly for very short (less than
10 miles), stop/go journeys, the oil and filter should be renewed
between services (ie, every 5000 miles/6 months).
m mCheck the electrical system (Section 8)
m mCheck the battery (Section 9)
m mCheck the seat belts (Section 10)
m mCheck the auxiliary drivebelt (Section 11)
m mCheck for fluid leaks and hose condition (Section 12)
m mCheck the condition of all wiring (Section 13)
m mCheck all air conditioning components (Section 14)
m mChange the engine oil and filter (Section 15)
m mCheck the manual transmission oil level (Section 16)
m mCheck the adjustment of the clutch pedal (Section 17)
m mLubricate the automatic transmission linkage (Section 18)
m mCheck the steering, suspension and wheels (Section 19)
m mCheck the driveshaft gaiters and CV joints (Section 20)
m mCheck the exhaust system (Section 21)
m mCheck the underbody, and all fuel/brake lines (Section 22)
m mCheck the brake system (Section 23)
m mCheck and lubricate the doors and bonnet (Section 24)
m mCheck the security of all roadwheel nuts (Section 25)
m mRoad test (Section 26). Check the level of the automatic
transmission fluid with the engine still hot, after the road
test (Section 7)
Every 20 000 miles or 2 years,
whichever occurs first
Carry out all operations listed above, plus the following:
m mRenew the ventilation system pollen filter (Section 27)
m mRenew the coolant (Sections 2 and 28)
Every 30 000 miles or 3 years,
whichever occurs first
Carry out all operations listed above, plus the following:
m mRenew the air filter element (Section 29). Note that this
task must be carried out at more frequent intervals if the
vehicle is used in dusty or polluted conditions
m mCheck the Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system,
and clean the filter (Section 30)
m mRenew the spark plugs (Section 31)
Every 60 000 miles
Carry out all operations listed above, plus the following:
m
mRenew the timing belt (Section 32)
m mRenew the fuel filter (Section 33)
Every 3 years
(regardless of mileage)
m mRenew the brake fluid (Section 34)
procarmanuals.com
Page 18 of 279
1•4
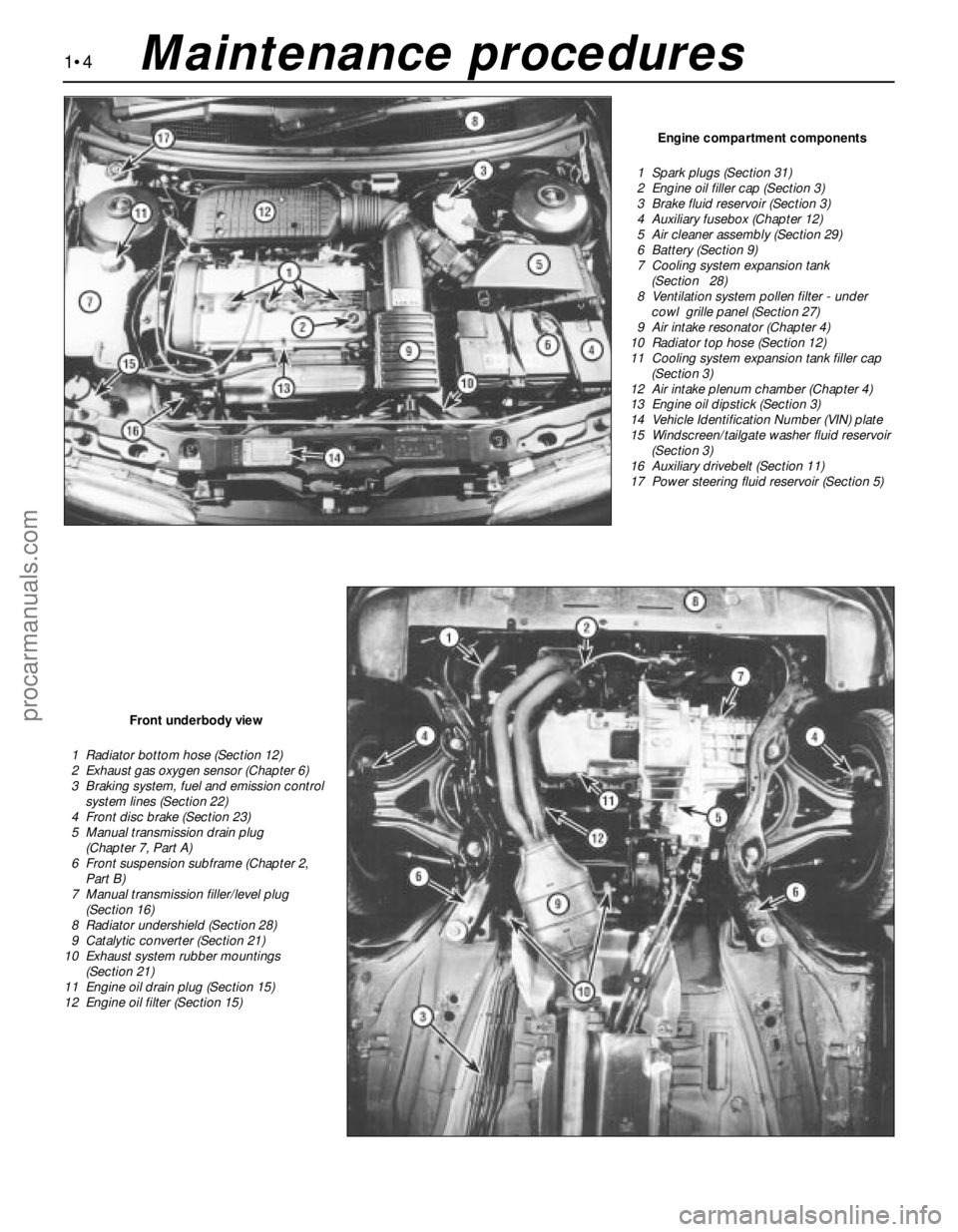
Engine compartment components
1 Spark plugs (Section 31)
2 Engine oil filler cap (Section 3)
3 Brake fluid reservoir (Section 3)
4 Auxiliary fusebox (Chapter 12)
5 Air cleaner assembly (Section 29)
6 Battery (Section 9)
7 Cooling system expansion tank
(Section 28)
8 Ventilation system pollen filter - under
cowl grille panel (Section 27)
9 Air intake resonator (Chapter 4)
10 Radiator top hose (Section 12)
11 Cooling system expansion tank filler cap
(Section 3)
12 Air intake plenum chamber (Chapter 4)
13 Engine oil dipstick (Section 3)
14 Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) plate
15 Windscreen/tailgate washer fluid reservoir
(Section 3)
16 Auxiliary drivebelt (Section 11)
17 Power steering fluid reservoir (Section 5)
Front underbody view
1 Radiator bottom hose (Section 12)
2 Exhaust gas oxygen sensor (Chapter 6)
3 Braking system, fuel and emission control
system lines (Section 22)
4 Front disc brake (Section 23)
5 Manual transmission drain plug
(Chapter 7, Part A)
6 Front suspension subframe (Chapter 2,
Part B)
7 Manual transmission filler/level plug
(Section 16)
8 Radiator undershield (Section 28)
9 Catalytic converter (Section 21)
10 Exhaust system rubber mountings
(Section 21)
11 Engine oil drain plug (Section 15)
12 Engine oil filter (Section 15)
Maintenance procedures
procarmanuals.com
Page 19 of 279
1•5
1
Maintenance procedures
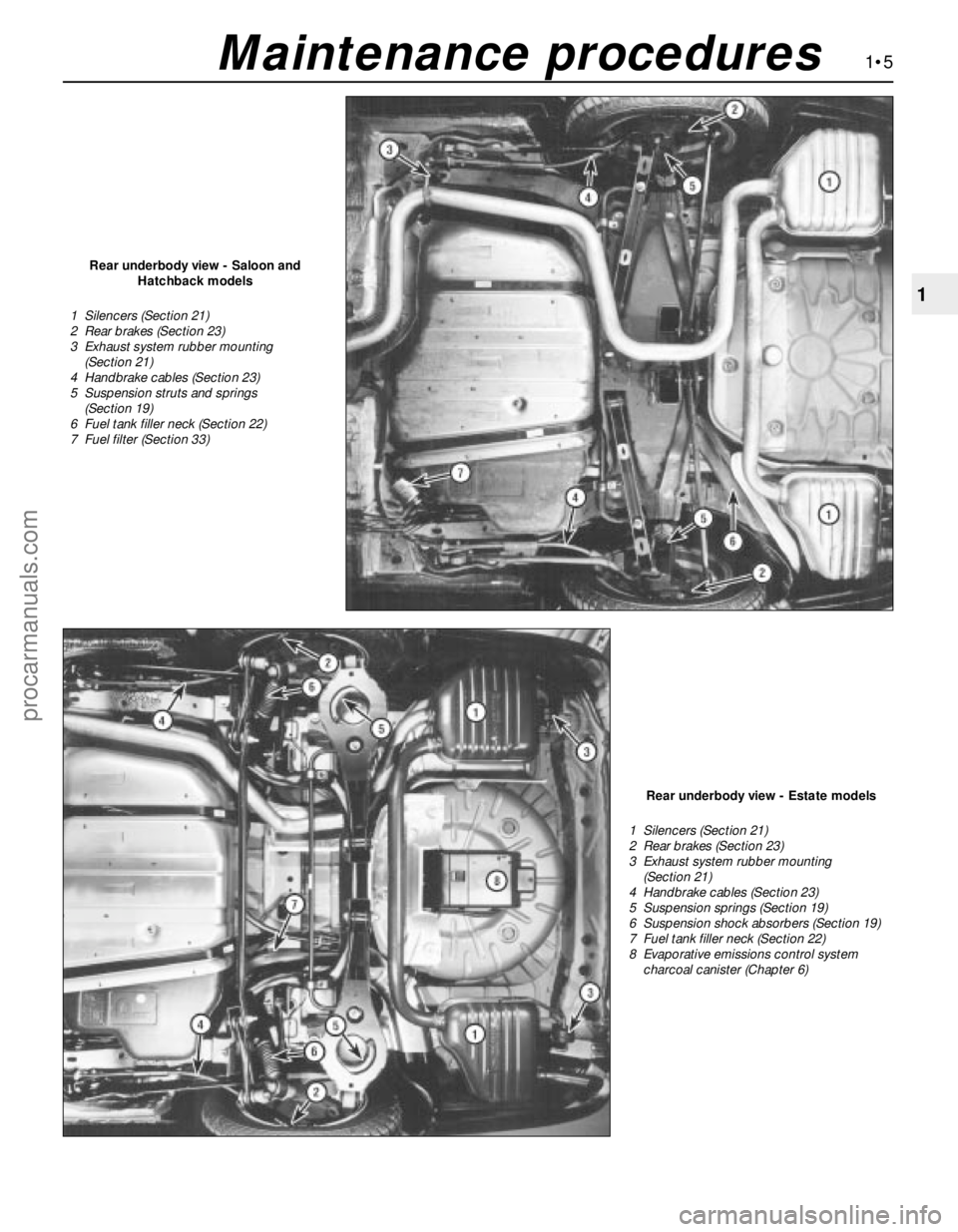
Rear underbody view - Saloon and
Hatchback models
1 Silencers (Section 21)
2 Rear brakes (Section 23)
3 Exhaust system rubber mounting
(Section 21)
4 Handbrake cables (Section 23)
5 Suspension struts and springs
(Section 19)
6 Fuel tank filler neck (Section 22)
7 Fuel filter (Section 33)
Rear underbody view - Estate models
1 Silencers (Section 21)
2 Rear brakes (Section 23)
3 Exhaust system rubber mounting
(Section 21)
4 Handbrake cables (Section 23)
5 Suspension springs (Section 19)
6 Suspension shock absorbers (Section 19)
7 Fuel tank filler neck (Section 22)
8 Evaporative emissions control system
charcoal canister (Chapter 6)
procarmanuals.com
Page 20 of 279

This Chapter is designed to help the home
mechanic maintain the Ford Mondeo models
for peak performance, economy, safety and
long life.
On the following pages are Sections
dealing specifically with each item on the
maintenance schedule. Visual checks,
adjustments, component replacement and
other helpful items are included. Refer to the
accompanying illustrations of the engine
compartment and the underside of the vehicle
for the location of various components.
Servicing your Mondeo in accordance with
the mileage/time maintenance schedule and
the following Sections will provide it with a
planned maintenance programme, which
should result in a long and reliable service life.
This is a comprehensive plan, so maintaining
some items but not others at the specified
service intervals will not produce the same
results.
As you service your Mondeo, you will
discover that many of the procedures can -
and should - be grouped together, because of
the nature of the particular procedure you’re
performing, or because of the close proximity
to one another of two otherwise-unrelated
components.
For example, if the vehicle is raised for anyreason, you should inspect the exhaust,
suspension, steering and fuel systems while
you’re under the vehicle. When you’re
checking the tyres, it makes good sense to
check the brakes and wheel bearings,
especially if the roadwheels have already
been removed.
Finally, let’s suppose you have to borrow or
hire a torque wrench. Even if you only need to
tighten the spark plugs, you might as well
check the torque of as many critical fasteners
as time allows.
The first step of this maintenance
programme is to prepare yourself before the
actual work begins. Read through all the
Sections which are relevant to the procedures
you’re planning to carry out, then make a list
of, and gather together, all the parts and tools
you will need to do the job. If it looks as if you
might run into problems during a particular
segment of some procedure, seek advice
from your local parts man or dealer service
department.
Ford state that, where antifreeze to
specification ESD-M97B-49-A (the type with
which the vehicle’s cooling system would
have been filled on production at the factory)
is used, it will last the lifetime of the vehicle.This is subject to it being used in the
recommended concentration, unmixed with
any other type of antifreeze or additive, and
topped-up when necessary using only that
antifreeze mixed 50/50 with clean water. If any
other type of antifreeze is added, the lifetime
guarantee no longer applies; to restore the
lifetime protection, the system must be
drained and thoroughly reverse-flushed
before fresh coolant mixture is poured in.
If the vehicle’s history (and therefore the
quality of the antifreeze in it) is unknown,
owners who wish to follow Ford’s
recommendations are advised to drain and
thoroughly reverse-flush the system, as
outlined in Section 28, before refilling with
fresh coolant mixture. If the appropriate
quality of antifreeze is used, the coolant can
then be left for the life of the vehicle.
If any antifreeze other than Ford’s is to be
used, the coolant must be renewed at regular
intervals to provide an equivalent degree of
protection; the conventional recommendation
is to renew the coolant every two years.
The above assumes the use of a mixture (in
exactly the specified concentration) of clean,
soft water and of antifreeze to Ford’s
specification or equivalent. It is also assumed
that the cooling system is maintained in a
scrupulously-clean condition, by ensuring that
only clean coolant is added on topping-up,
and by thorough reverse-flushing whenever
the coolant is drained (Section 28).
2 Coolant renewal
1 Introduction
1•6Weekly checks
Weekly checks
General
1Fluids are an essential part of the
lubrication, cooling, braking and other
systems. Because these fluids gradually
become depleted and/or contaminated during
normal operation of the vehicle, they must be
periodically replenished. See “Lubricants and
fluids and capacities”at the beginning of this
Chapter before adding fluid to any of the
following components. Note:The vehicle
must be on level ground before fluid levels can
be checked.
Engine oil
2The engine oil level is checked with a
dipstick located at the front of the engine; it
can be identified by its yellow/black plastic
grip (see illustration). The dipstick extends
through a metal tube, from which it protrudes
down into the sump at the bottom of the
engine.
3The oil level should be checked before the
vehicle is driven, or about 5 minutes after the
engine has been switched off.4Pull the dipstick from the tube, and wipe all
the oil from the end with a clean rag or paper
towel; note the dipstick’s maximum and
minimum levels, indicated by notches (seeillustration). Insert the clean dipstick all the way
back into its metal tube, and pull it out again.
Observe the oil on the end of the dipstick; its
level should be between these two notches.
5Do not allow the level to drop below the
minimum level notch, or oil starvation may
cause engine damage. Conversely, overfilling
the engine (adding oil above the maximum
level notch) may cause oil-fouled spark plugs,
oil leaks or oil seal failures.
6The yellow/black plastic oil filler cap is
screwed into the left-hand front end of the
3 Fluid level checks
3.2 The engine oil dipstick (arrowed) is
located at the front of the engine - note
yellow/black plastic grip
3.4 The oil level should be at or near the
maximum level notch (A) - if not, add
enough oil to correct the level. It takes
approximately 0.5 to 1.0 litre of oil to raise
the level from the minimum level notch (B)
to the maximum
If the level is checked
immediately after driving the
vehicle, some of the oil will
remain in the engine upper
components, producing an inaccurate
dipstick reading.
procarmanuals.com
Page 21 of 279
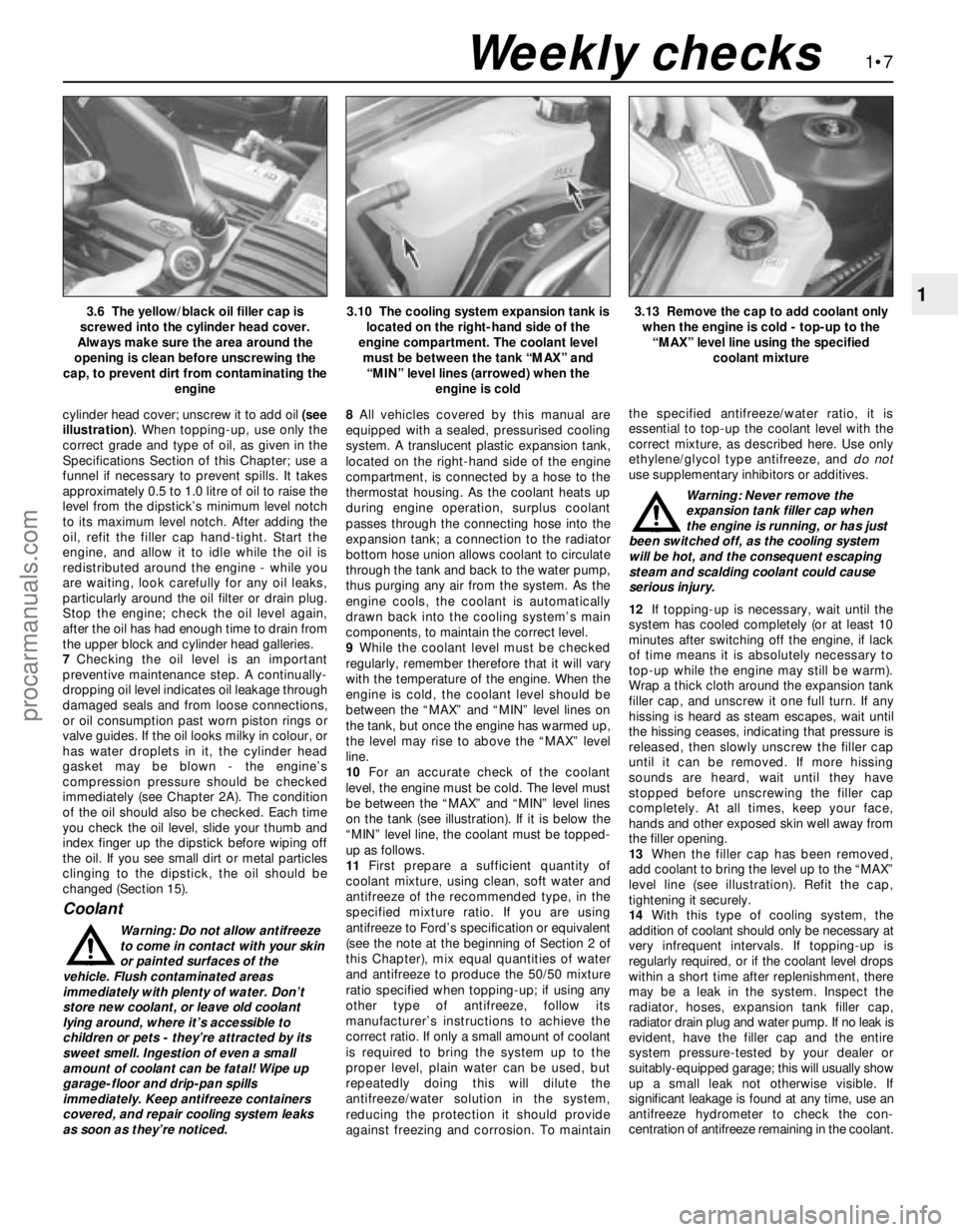

cylinder head cover; unscrew it to add oil (see
illustration). When topping-up, use only the
correct grade and type of oil, as given in the
Specifications Section of this Chapter; use a
funnel if necessary to prevent spills. It takes
approximately 0.5 to 1.0 litre of oil to raise the
level from the dipstick’s minimum level notch
to its maximum level notch. After adding the
oil, refit the filler cap hand-tight. Start the
engine, and allow it to idle while the oil is
redistributed around the engine - while you
are waiting, look carefully for any oil leaks,
particularly around the oil filter or drain plug.
Stop the engine; check the oil level again,
after the oil has had enough time to drain from
the upper block and cylinder head galleries.
7Checking the oil level is an important
preventive maintenance step. A continually-
dropping oil level indicates oil leakage through
damaged seals and from loose connections,
or oil consumption past worn piston rings or
valve guides. If the oil looks milky in colour, or
has water droplets in it, the cylinder head
gasket may be blown - the engine’s
compression pressure should be checked
immediately (see Chapter 2A). The condition
of the oil should also be checked. Each time
you check the oil level, slide your thumb and
index finger up the dipstick before wiping off
the oil. If you see small dirt or metal particles
clinging to the dipstick, the oil should be
changed (Section 15).
Coolant
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze
to come in contact with your skin
or painted surfaces of the
vehicle. Flush contaminated areas
immediately with plenty of water. Don’t
store new coolant, or leave old coolant
lying around, where it’s accessible to
children or pets - they’re attracted by its
sweet smell. Ingestion of even a small
amount of coolant can be fatal! Wipe up
garage-floor and drip-pan spills
immediately. Keep antifreeze containers
covered, and repair cooling system leaks
as soon as they’re noticed.8All vehicles covered by this manual are
equipped with a sealed, pressurised cooling
system. A translucent plastic expansion tank,
located on the right-hand side of the engine
compartment, is connected by a hose to the
thermostat housing. As the coolant heats up
during engine operation, surplus coolant
passes through the connecting hose into the
expansion tank; a connection to the radiator
bottom hose union allows coolant to circulate
through the tank and back to the water pump,
thus purging any air from the system. As the
engine cools, the coolant is automatically
drawn back into the cooling system’s main
components, to maintain the correct level.
9While the coolant level must be checked
regularly, remember therefore that it will vary
with the temperature of the engine. When the
engine is cold, the coolant level should be
between the “MAX” and “MIN” level lines on
the tank, but once the engine has warmed up,
the level may rise to above the “MAX” level
line.
10For an accurate check of the coolant
level, the engine must be cold. The level must
be between the “MAX” and “MIN” level lines
on the tank (see illustration). If it is below the
“MIN” level line, the coolant must be topped-
up as follows.
11First prepare a sufficient quantity of
coolant mixture, using clean, soft water and
antifreeze of the recommended type, in the
specified mixture ratio. If you are using
antifreeze to Ford’s specification or equivalent
(see the note at the beginning of Section 2 of
this Chapter), mix equal quantities of water
and antifreeze to produce the 50/50 mixture
ratio specified when topping-up; if using any
other type of antifreeze, follow its
manufacturer’s instructions to achieve the
correct ratio. If only a small amount of coolant
is required to bring the system up to the
proper level, plain water can be used, but
repeatedly doing this will dilute the
antifreeze/water solution in the system,
reducing the protection it should provide
against freezing and corrosion. To maintainthe specified antifreeze/water ratio, it is
essential to top-up the coolant level with the
correct mixture, as described here. Use only
ethylene/glycol type antifreeze, and do not
use supplementary inhibitors or additives.
Warning: Never remove the
expansion tank filler cap when
the engine is running, or has just
been switched off, as the cooling system
will be hot, and the consequent escaping
steam and scalding coolant could cause
serious injury.
12If topping-up is necessary, wait until the
system has cooled completely (or at least 10
minutes after switching off the engine, if lack
of time means it is absolutely necessary to
top-up while the engine may still be warm).
Wrap a thick cloth around the expansion tank
filler cap, and unscrew it one full turn. If any
hissing is heard as steam escapes, wait until
the hissing ceases, indicating that pressure is
released, then slowly unscrew the filler cap
until it can be removed. If more hissing
sounds are heard, wait until they have
stopped before unscrewing the filler cap
completely. At all times, keep your face,
hands and other exposed skin well away from
the filler opening.
13When the filler cap has been removed,
add coolant to bring the level up to the “MAX”
level line (see illustration). Refit the cap,
tightening it securely.
14With this type of cooling system, the
addition of coolant should only be necessary at
very infrequent intervals. If topping-up is
regularly required, or if the coolant level drops
within a short time after replenishment, there
may be a leak in the system. Inspect the
radiator, hoses, expansion tank filler cap,
radiator drain plug and water pump. If no leak is
evident, have the filler cap and the entire
system pressure-tested by your dealer or
suitably-equipped garage; this will usually show
up a small leak not otherwise visible. If
significant leakage is found at any time, use an
antifreeze hydrometer to check the con-
centration of antifreeze remaining in the coolant.
1•7
13.13 Remove the cap to add coolant only
when the engine is cold - top-up to the
“MAX” level line using the specified
coolant mixture3.6 The yellow/black oil filler cap is
screwed into the cylinder head cover.
Always make sure the area around the
opening is clean before unscrewing the
cap, to prevent dirt from contaminating the
engine3.10 The cooling system expansion tank is
located on the right-hand side of the
engine compartment. The coolant level
must be between the tank “MAX” and
“MIN” level lines (arrowed) when the
engine is cold
Weekly checks
procarmanuals.com
Page 22 of 279
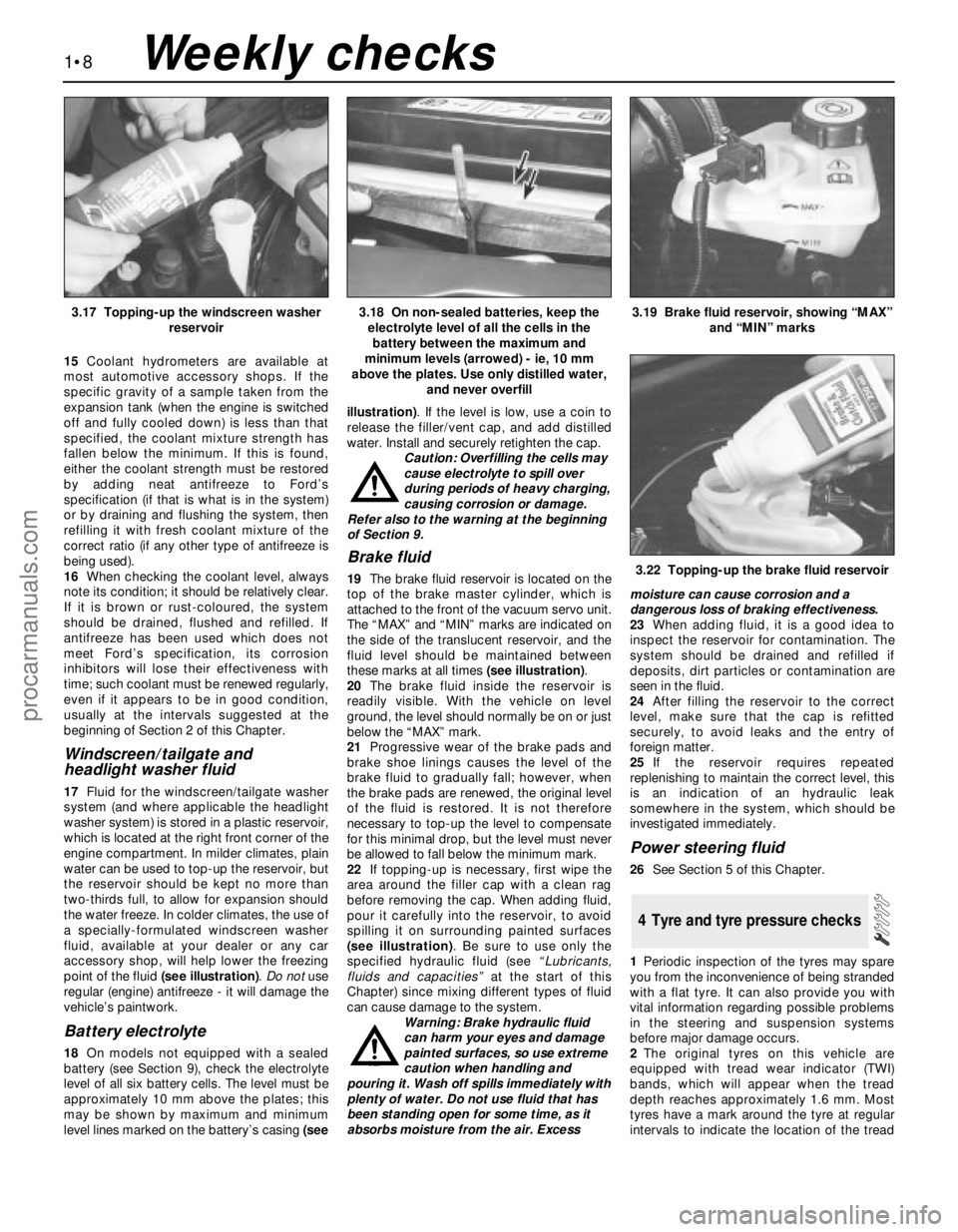
15Coolant hydrometers are available at
most automotive accessory shops. If the
specific gravity of a sample taken from the
expansion tank (when the engine is switched
off and fully cooled down) is less than that
specified, the coolant mixture strength has
fallen below the minimum. If this is found,
either the coolant strength must be restored
by adding neat antifreeze to Ford’s
specification (if that is what is in the system)
or by draining and flushing the system, then
refilling it with fresh coolant mixture of the
correct ratio (if any other type of antifreeze is
being used).
16When checking the coolant level, always
note its condition; it should be relatively clear.
If it is brown or rust-coloured, the system
should be drained, flushed and refilled. If
antifreeze has been used which does not
meet Ford’s specification, its corrosion
inhibitors will lose their effectiveness with
time; such coolant must be renewed regularly,
even if it appears to be in good condition,
usually at the intervals suggested at the
beginning of Section 2 of this Chapter.
Windscreen/tailgate and
headlight washer fluid
17Fluid for the windscreen/tailgate washer
system (and where applicable the headlight
washer system) is stored in a plastic reservoir,
which is located at the right front corner of the
engine compartment. In milder climates, plain
water can be used to top-up the reservoir, but
the reservoir should be kept no more than
two-thirds full, to allow for expansion should
the water freeze. In colder climates, the use of
a specially-formulated windscreen washer
fluid, available at your dealer or any car
accessory shop, will help lower the freezing
point of the fluid (see illustration). Do notuse
regular (engine) antifreeze - it will damage the
vehicle’s paintwork.
Battery electrolyte
18On models not equipped with a sealed
battery (see Section 9), check the electrolyte
level of all six battery cells. The level must be
approximately 10 mm above the plates; this
may be shown by maximum and minimum
level lines marked on the battery’s casing (seeillustration). If the level is low, use a coin to
release the filler/vent cap, and add distilled
water. Install and securely retighten the cap.
Caution: Overfilling the cells may
cause electrolyte to spill over
during periods of heavy charging,
causing corrosion or damage.
Refer also to the warning at the beginning
of Section 9.
Brake fluid
19The brake fluid reservoir is located on the
top of the brake master cylinder, which is
attached to the front of the vacuum servo unit.
The “MAX” and “MIN” marks are indicated on
the side of the translucent reservoir, and the
fluid level should be maintained between
these marks at all times (see illustration).
20The brake fluid inside the reservoir is
readily visible. With the vehicle on level
ground, the level should normally be on or just
below the “MAX” mark.
21Progressive wear of the brake pads and
brake shoe linings causes the level of the
brake fluid to gradually fall; however, when
the brake pads are renewed, the original level
of the fluid is restored. It is not therefore
necessary to top-up the level to compensate
for this minimal drop, but the level must never
be allowed to fall below the minimum mark.
22If topping-up is necessary, first wipe the
area around the filler cap with a clean rag
before removing the cap. When adding fluid,
pour it carefully into the reservoir, to avoid
spilling it on surrounding painted surfaces
(see illustration). Be sure to use only the
specified hydraulic fluid (see “Lubricants,
fluids and capacities”at the start of this
Chapter) since mixing different types of fluid
can cause damage to the system.
Warning: Brake hydraulic fluid
can harm your eyes and damage
painted surfaces, so use extreme
caution when handling and
pouring it. Wash off spills immediately with
plenty of water. Do not use fluid that has
been standing open for some time, as it
absorbs moisture from the air. Excessmoisture can cause corrosion and a
dangerous loss of braking effectiveness.
23When adding fluid, it is a good idea to
inspect the reservoir for contamination. The
system should be drained and refilled if
deposits, dirt particles or contamination are
seen in the fluid.
24After filling the reservoir to the correct
level, make sure that the cap is refitted
securely, to avoid leaks and the entry of
foreign matter.
25If the reservoir requires repeated
replenishing to maintain the correct level, this
is an indication of an hydraulic leak
somewhere in the system, which should be
investigated immediately.
Power steering fluid
26See Section 5 of this Chapter.
1Periodic inspection of the tyres may spare
you from the inconvenience of being stranded
with a flat tyre. It can also provide you with
vital information regarding possible problems
in the steering and suspension systems
before major damage occurs.
2The original tyres on this vehicle are
equipped with tread wear indicator (TWI)
bands, which will appear when the tread
depth reaches approximately 1.6 mm. Most
tyres have a mark around the tyre at regular
intervals to indicate the location of the tread
4 Tyre and tyre pressure checks
1•8
3.17 Topping-up the windscreen washer
reservoir3.18 On non-sealed batteries, keep the
electrolyte level of all the cells in the
battery between the maximum and
minimum levels (arrowed) - ie, 10 mm
above the plates. Use only distilled water,
and never overfill3.19 Brake fluid reservoir, showing “MAX”
and “MIN” marks
3.22 Topping-up the brake fluid reservoir
Weekly checks
procarmanuals.com
Page 23 of 279
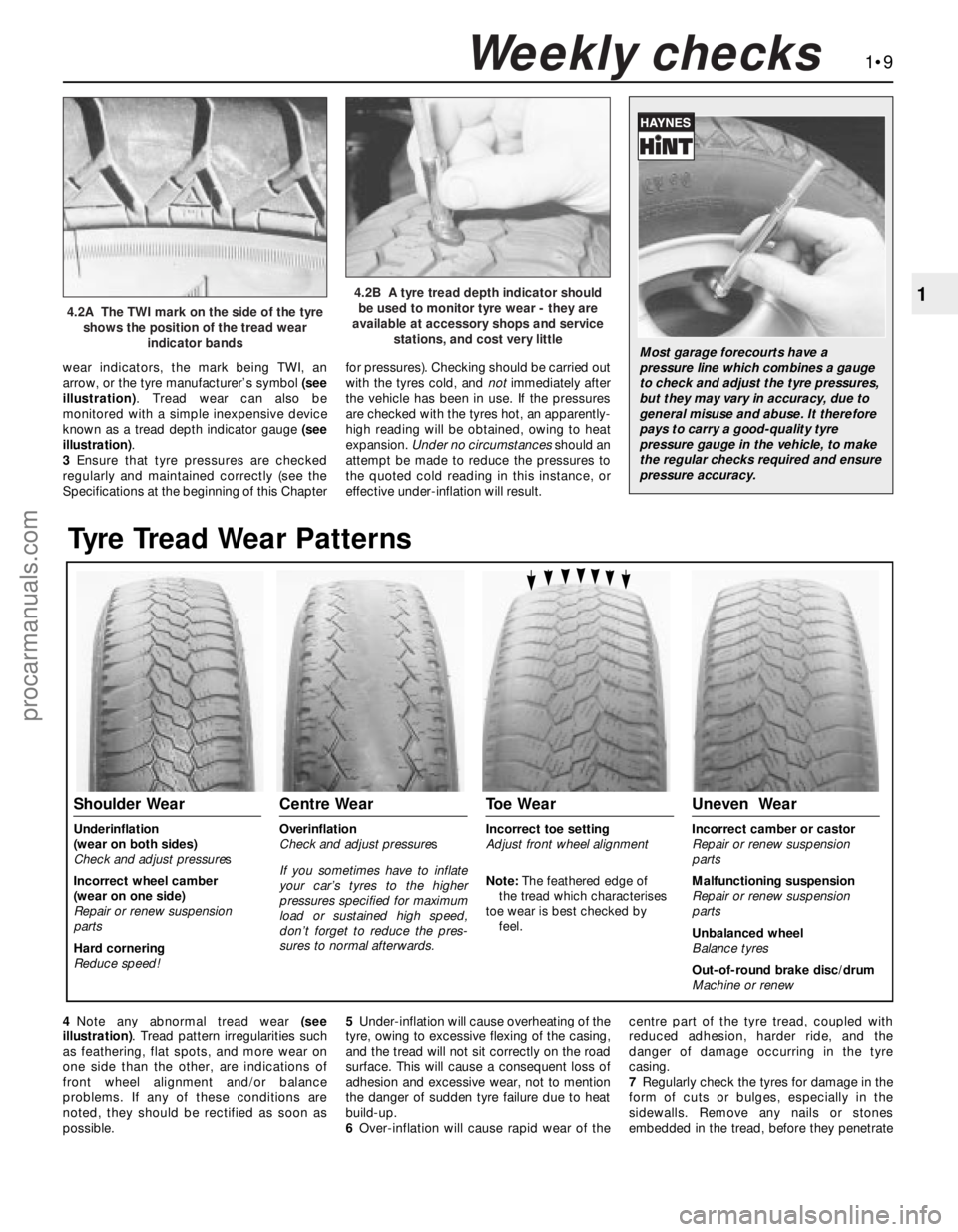
wear indicators, the mark being TWI, an
arrow, or the tyre manufacturer’s symbol (see
illustration). Tread wear can also be
monitored with a simple inexpensive device
known as a tread depth indicator gauge (see
illustration).
3Ensure that tyre pressures are checked
regularly and maintained correctly (see the
Specifications at the beginning of this Chapterfor pressures). Checking should be carried out
with the tyres cold, and notimmediately after
the vehicle has been in use. If the pressures
are checked with the tyres hot, an apparently-
high reading will be obtained, owing to heat
expansion. Under no circumstancesshould an
attempt be made to reduce the pressures to
the quoted cold reading in this instance, or
effective under-inflation will result.
1•9
1
Tyre Tread Wear Patterns
Shoulder Wear
Underinflation
(wear on both sides)
Check and adjust pressures
Incorrect wheel camber
(wear on one side)
Repair or renew suspension
parts
Hard cornering
Reduce speed!
Centre Wear
Overinflation
Check and adjust pressures
If you sometimes have to inflate
your car’s tyres to the higher
pressures specified for maximum
load or sustained high speed,
don’t forget to reduce the pres-
sures to normal afterwards.
Toe Wear
Incorrect toe setting
Adjust front wheel alignment
Note: The feathered edge of
the tread which characterises
toe wear is best checked by
feel.
Uneven Wear
Incorrect camber or castor
Repair or renew suspension
parts
Malfunctioning suspension
Repair or renew suspension
parts
Unbalanced wheel
Balance tyres
Out-of-round brake disc/drum
Machine or renew
4.2A The TWI mark on the side of the tyre
shows the position of the tread wear
indicator bands
4.2B A tyre tread depth indicator should
be used to monitor tyre wear - they are
available at accessory shops and service
stations, and cost very little
Weekly checks
Most garage forecourts have a
pressure line which combines a gauge
to check and adjust the tyre pressures,
but they may vary in accuracy, due to
general misuse and abuse. It therefore
pays to carry a good-quality tyre
pressure gauge in the vehicle, to make
the regular checks required and ensure
pressure accuracy.
4Note any abnormal tread wear (see
illustration). Tread pattern irregularities such
as feathering, flat spots, and more wear on
one side than the other, are indications of
front wheel alignment and/or balance
problems. If any of these conditions are
noted, they should be rectified as soon as
possible.5Under-inflation will cause overheating of the
tyre, owing to excessive flexing of the casing,
and the tread will not sit correctly on the road
surface. This will cause a consequent loss of
adhesion and excessive wear, not to mention
the danger of sudden tyre failure due to heat
build-up.
6Over-inflation will cause rapid wear of thecentre part of the tyre tread, coupled with
reduced adhesion, harder ride, and the
danger of damage occurring in the tyre
casing.
7Regularly check the tyres for damage in the
form of cuts or bulges, especially in the
sidewalls. Remove any nails or stones
embedded in the tread, before they penetrate
procarmanuals.com
Page 24 of 279
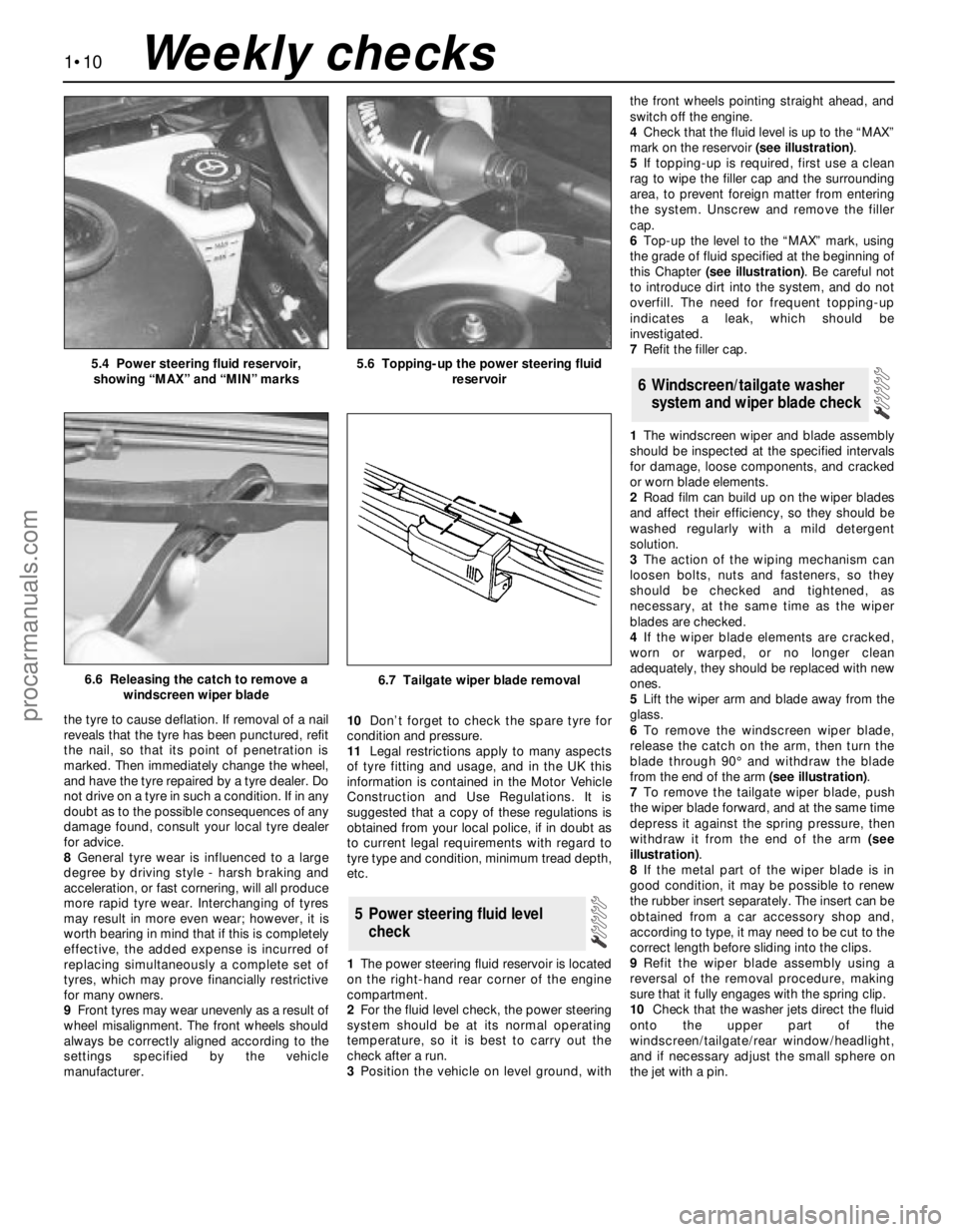
the tyre to cause deflation. If removal of a nail
reveals that the tyre has been punctured, refit
the nail, so that its point of penetration is
marked. Then immediately change the wheel,
and have the tyre repaired by a tyre dealer. Do
not drive on a tyre in such a condition. If in any
doubt as to the possible consequences of any
damage found, consult your local tyre dealer
for advice.
8General tyre wear is influenced to a large
degree by driving style - harsh braking and
acceleration, or fast cornering, will all produce
more rapid tyre wear. Interchanging of tyres
may result in more even wear; however, it is
worth bearing in mind that if this is completely
effective, the added expense is incurred of
replacing simultaneously a complete set of
tyres, which may prove financially restrictive
for many owners.
9Front tyres may wear unevenly as a result of
wheel misalignment. The front wheels should
always be correctly aligned according to the
settings specified by the vehicle
manufacturer.10Don’t forget to check the spare tyre for
condition and pressure.
11Legal restrictions apply to many aspects
of tyre fitting and usage, and in the UK this
information is contained in the Motor Vehicle
Construction and Use Regulations. It is
suggested that a copy of these regulations is
obtained from your local police, if in doubt as
to current legal requirements with regard to
tyre type and condition, minimum tread depth,
etc.
1The power steering fluid reservoir is located
on the right-hand rear corner of the engine
compartment.
2For the fluid level check, the power steering
system should be at its normal operating
temperature, so it is best to carry out the
check after a run.
3Position the vehicle on level ground, withthe front wheels pointing straight ahead, and
switch off the engine.
4Check that the fluid level is up to the “MAX”
mark on the reservoir (see illustration).
5If topping-up is required, first use a clean
rag to wipe the filler cap and the surrounding
area, to prevent foreign matter from entering
the system. Unscrew and remove the filler
cap.
6Top-up the level to the “MAX” mark, using
the grade of fluid specified at the beginning of
this Chapter (see illustration). Be careful not
to introduce dirt into the system, and do not
overfill. The need for frequent topping-up
indicates a leak, which should be
investigated.
7Refit the filler cap.
1The windscreen wiper and blade assembly
should be inspected at the specified intervals
for damage, loose components, and cracked
or worn blade elements.
2Road film can build up on the wiper blades
and affect their efficiency, so they should be
washed regularly with a mild detergent
solution.
3The action of the wiping mechanism can
loosen bolts, nuts and fasteners, so they
should be checked and tightened, as
necessary, at the same time as the wiper
blades are checked.
4If the wiper blade elements are cracked,
worn or warped, or no longer clean
adequately, they should be replaced with new
ones.
5Lift the wiper arm and blade away from the
glass.
6To remove the windscreen wiper blade,
release the catch on the arm, then turn the
blade through 90° and withdraw the blade
from the end of the arm (see illustration).
7To remove the tailgate wiper blade, push
the wiper blade forward, and at the same time
depress it against the spring pressure, then
withdraw it from the end of the arm (see
illustration).
8If the metal part of the wiper blade is in
good condition, it may be possible to renew
the rubber insert separately. The insert can be
obtained from a car accessory shop and,
according to type, it may need to be cut to the
correct length before sliding into the clips.
9Refit the wiper blade assembly using a
reversal of the removal procedure, making
sure that it fully engages with the spring clip.
10Check that the washer jets direct the fluid
onto the upper part of the
windscreen/tailgate/rear window/headlight,
and if necessary adjust the small sphere on
the jet with a pin.
6 Windscreen/tailgate washer
system and wiper blade check
5 Power steering fluid level
check
1•10
5.4 Power steering fluid reservoir,
showing “MAX” and “MIN” marks5.6 Topping-up the power steering fluid
reservoir
6.7 Tailgate wiper blade removal6.6 Releasing the catch to remove a
windscreen wiper blade
Weekly checks
procarmanuals.com
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11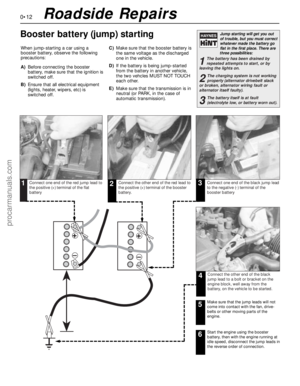 12
12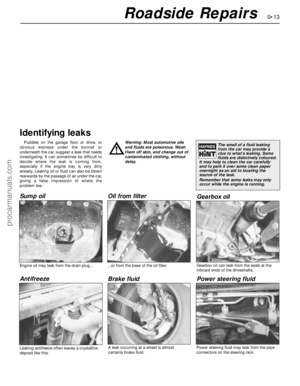 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17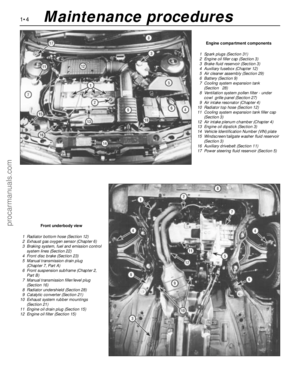 18
18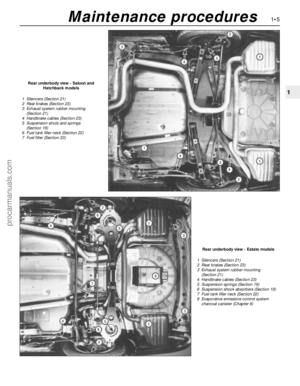 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22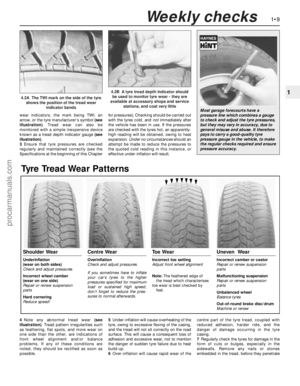 23
23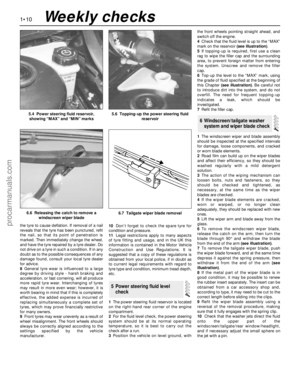 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27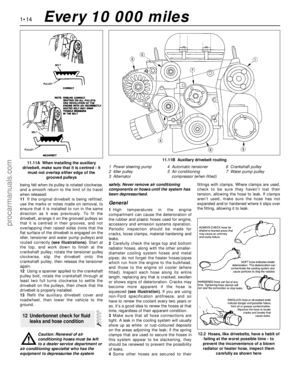 28
28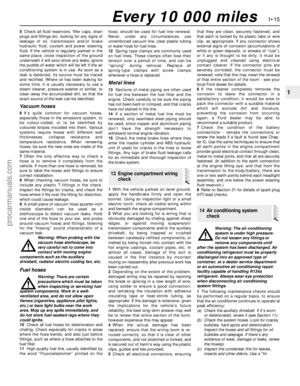 29
29 30
30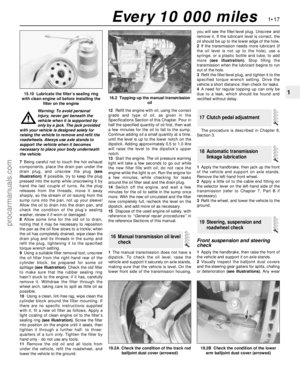 31
31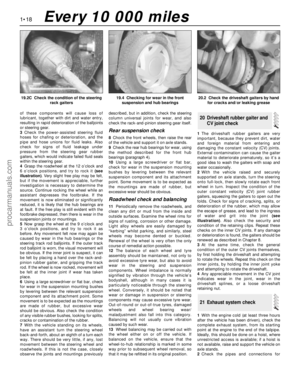 32
32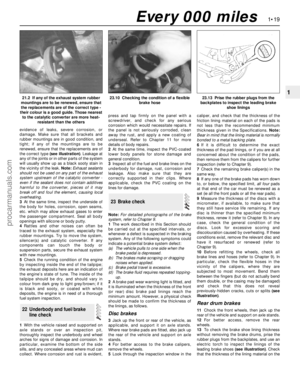 33
33 34
34 35
35 36
36 37
37 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41 42
42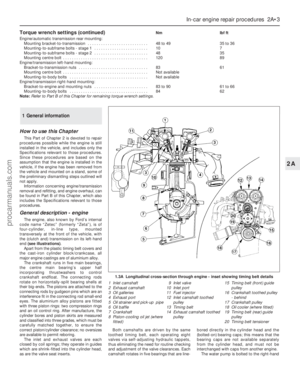 43
43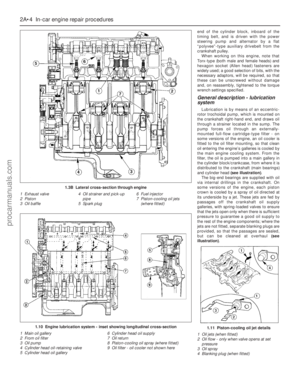 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50 51
51 52
52 53
53 54
54 55
55 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59 60
60 61
61 62
62 63
63 64
64 65
65 66
66 67
67 68
68 69
69 70
70 71
71 72
72 73
73 74
74 75
75 76
76 77
77 78
78 79
79 80
80 81
81 82
82 83
83 84
84 85
85 86
86 87
87 88
88 89
89 90
90 91
91 92
92 93
93 94
94 95
95 96
96 97
97 98
98 99
99 100
100 101
101 102
102 103
103 104
104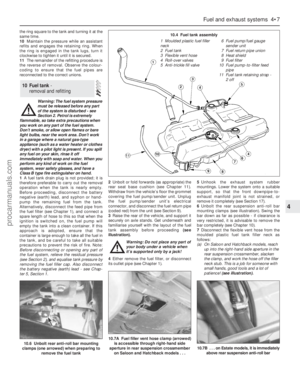 105
105 106
106 107
107 108
108 109
109 110
110 111
111 112
112 113
113 114
114 115
115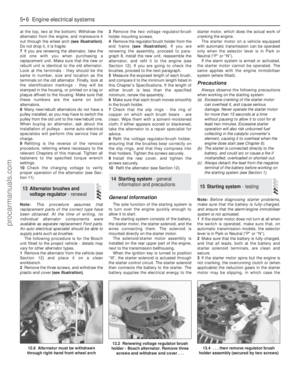 116
116 117
117 118
118 119
119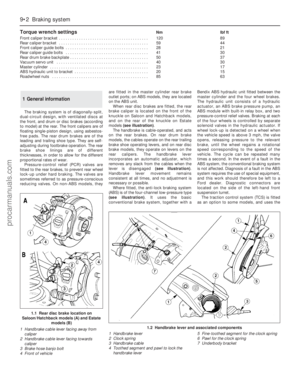 120
120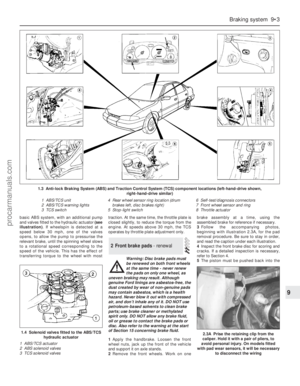 121
121 122
122 123
123 124
124 125
125 126
126 127
127 128
128 129
129 130
130 131
131 132
132 133
133 134
134 135
135 136
136 137
137 138
138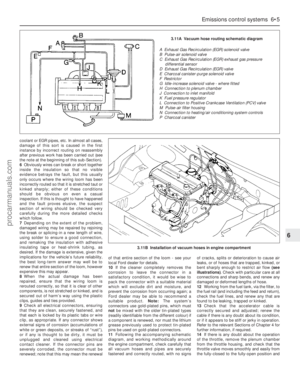 139
139 140
140 141
141 142
142 143
143 144
144 145
145 146
146 147
147 148
148 149
149 150
150 151
151 152
152 153
153 154
154 155
155 156
156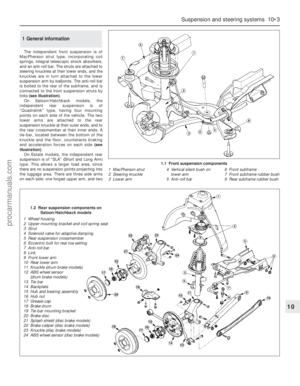 157
157 158
158 159
159 160
160 161
161 162
162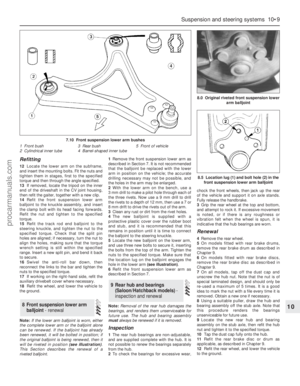 163
163 164
164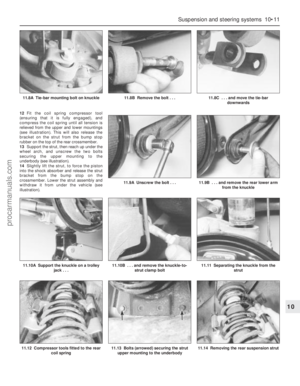 165
165 166
166 167
167 168
168 169
169 170
170 171
171 172
172 173
173 174
174 175
175 176
176 177
177 178
178 179
179 180
180 181
181 182
182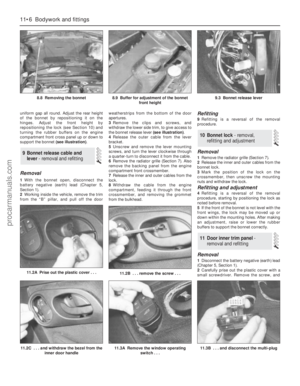 183
183 184
184 185
185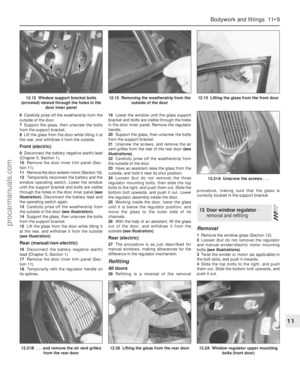 186
186 187
187 188
188 189
189 190
190 191
191 192
192 193
193 194
194 195
195 196
196 197
197 198
198 199
199 200
200 201
201 202
202 203
203 204
204 205
205 206
206 207
207 208
208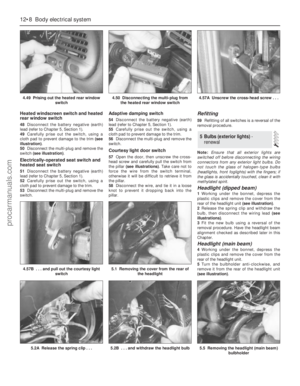 209
209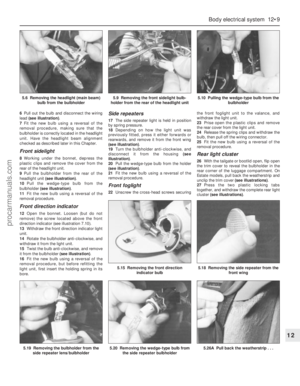 210
210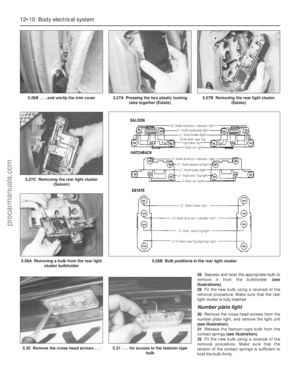 211
211 212
212 213
213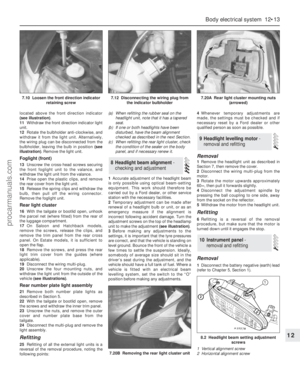 214
214 215
215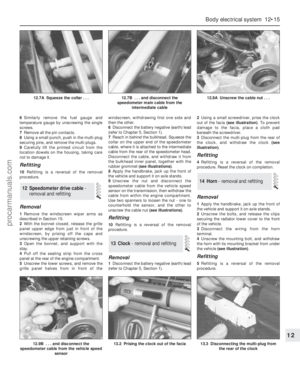 216
216 217
217 218
218 219
219 220
220 221
221 222
222 223
223 224
224 225
225 226
226 227
227 228
228 229
229 230
230 231
231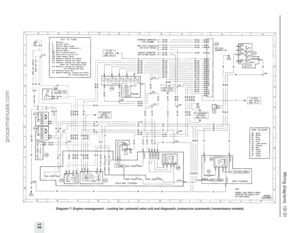 232
232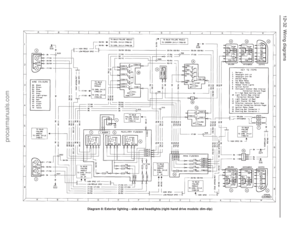 233
233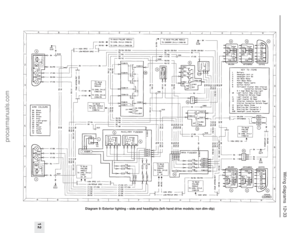 234
234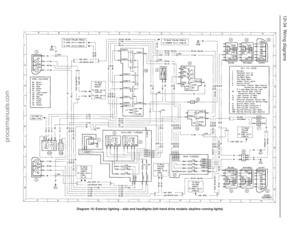 235
235 236
236 237
237 238
238 239
239 240
240 241
241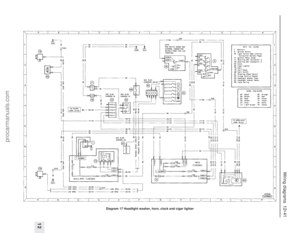 242
242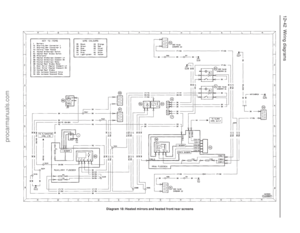 243
243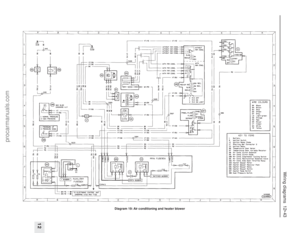 244
244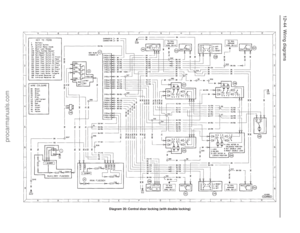 245
245 246
246 247
247 248
248 249
249 250
250 251
251 252
252 253
253 254
254 255
255 256
256 257
257 258
258 259
259 260
260 261
261 262
262 263
263 264
264 265
265 266
266 267
267 268
268 269
269 270
270 271
271 272
272 273
273 274
274 275
275 276
276 277
277 278
278