1993 FORD MONDEO open bonnet
[x] Cancel search: open bonnetPage 27 of 279

amperage charger, but don’t use one rated
more than 1/10th the amp/hour rating of the
battery (ie no more than 5 amps, typically).
Rapid boost charges that claim to restore the
power of the battery in one to two hours are
hardest on the battery, and can damage
batteries not in good condition. This type of
charging should only be used in emergency
situations.
14The average time necessary to charge a
battery should be listed in the instructions that
come with the charger. As a general rule, a
trickle charger will charge a battery in 12 to
16 hours.
1Check the seat belts for satisfactory
operation and condition. Inspect the webbing
for fraying and cuts. Check that they retract
smoothly and without binding into their reels.
2Check that the seat belt mounting bolts are
tight, and if necessary tighten them to the
specified torque wrench setting.
General
1The auxiliary drivebelt is of the flat, multi-
ribbed (or “polyvee”) type, and is located on
the right-hand end of the engine. It drives the
alternator, water pump, power steering pump
and (when fitted) the air conditioning
compressor from the engine’s crankshaft
pulley.
2The good condition and proper tension of
the auxiliary drivebelt is critical to the
operation of the engine. Because of their
composition and the high stresses to which
they are subjected, drivebelts stretch anddeteriorate as they get older. They must,
therefore, be regularly inspected.
Check
3With the engine switched off, open and
support the bonnet, then locate the auxiliary
drivebelt on the right-hand end of the engine,
under the engine right-hand mounting
bracket. (Be very careful, and wear protective
gloves to minimise the risk of burning your
hands on hot components, if the engine has
recently been running.) For improved access,
jack up the front right-hand side of the
vehicle, support it securely on an axle stand,
remove the roadwheel, then remove the
auxiliary drivebelt cover (two fasteners) from
inside the wheel arch (see illustration).
4Using an inspection light or a small electric
torch, and rotating the engine when necessary
with a spanner applied to the crankshaft
pulley bolt, check the whole length of the
drivebelt for cracks, separation of the rubber,
and torn or worn ribs (see illustration). Also
check for fraying and glazing, which gives the
drivebelt a shiny appearance. Both sides of
the drivebelt should be inspected, which
means you will have to twist the drivebelt to
check the underside. Use your fingers to feel
the drivebelt where you can’t see it. If you are
in any doubt as to the condition of the
drivebelt, renew it (go to paragraph 7).
Drivebelt tension
5The auxiliary drivebelt is tensioned by an
automatic tensioner; regular checks are not
required, and manual “adjustment” is not
possible.
6If you suspect that the drivebelt is slipping
and/or running slack, or that the tensioner is
otherwise faulty, it must be renewed. To do
this, remove the drivebelt as described below,
then unbolt the tensioner (two Torx-type
screws accessible from underneath, via the
wheel arch) from the alternator mounting
bracket (see illustration). On fitting the new
tensioner, ensure it is aligned correctly on its
mountings, and tighten the screws to the
specified torque wrench setting.
Renewal
7Open the bonnet. Jack up the front right-
hand side of the vehicle and support it
securely on an axle stand, remove the
roadwheel, then remove the auxiliary drivebelt
cover (two fasteners) from inside the wheel
arch.
8If the existing drivebelt is to be refitted,
mark it, or note the maker’s markings on its
flat surface, so that it can be installed the
same way round.
9Reaching up between the body and the
engine (above and to the rear of the
crankshaft pulley), apply a spanner to the
hexagon in the centre of the automatic
tensioner’s pulley. Rotate the tensioner pulley
clockwise to release its pressure on the
drivebelt, then slip the drivebelt off the
crankshaft pulley, and release the tensioner
again (see illustration). Working from the
wheel arch or engine compartment as
necessary, and noting its routing, slip the
drivebelt off the remaining pulleys and
withdraw it.
10Check all the pulleys, ensuring that their
grooves are clean, and removing all traces of
oil and grease. Check that the tensioner
works properly, with strong spring pressure
11 Auxiliary drivebelt check and
renewal
10 Seat belt check
1•13
1
11.9 Rotate the tensioner pulley clockwise
to release its pressure on the drivebelt,
then slip the drivebelt off the crankshaft
pulley
11.3 Removing the auxiliary drivebelt
cover - it is secured by a fastener at each
end (arrowed) - from inside the right-hand
front wheel arch
11.4 Check the auxiliary drivebelt for signs
of wear like these. Very small cracks across
the drivebelt ribs are acceptable. If the
cracks are deep, or if the drivebelt looks
worn or damaged in any other way, renew it
11.6 The auxiliary drivebelt is tensioned by
an automatic tensioner; Torx screws
(arrowed) secure it to alternator mounting
bracket
Every 10 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 29 of 279
5Check all fluid reservoirs, filler caps, drain
plugs and fittings etc, looking for any signs of
leakage of oil, transmission and/or brake
hydraulic fluid, coolant and power steering
fluid. If the vehicle is regularly parked in the
same place, close inspection of the ground
underneath it will soon show any leaks; ignore
the puddle of water which will be left if the air
conditioning system is in use. As soon as a
leak is detected, its source must be traced
and rectified. Where oil has been leaking for
some time, it is usually necessary to use a
steam cleaner, pressure washer or similar, to
clean away the accumulated dirt, so that the
exact source of the leak can be identified.
Vacuum hoses
6It’s quite common for vacuum hoses,
especially those in the emissions system, to
be colour-coded, or to be identified by
coloured stripes moulded into them. Various
systems require hoses with different wall
thicknesses, collapse resistance and
temperature resistance. When renewing
hoses, be sure the new ones are made of the
same material.
7Often the only effective way to check a
hose is to remove it completely from the
vehicle. If more than one hose is removed, be
sure to label the hoses and fittings to ensure
correct installation.
8When checking vacuum hoses, be sure to
include any plastic T-fittings in the check.
Inspect the fittings for cracks, and check the
hose where it fits over the fitting for distortion,
which could cause leakage.
9A small piece of vacuum hose (quarter-inch
inside diameter) can be used as a
stethoscope to detect vacuum leaks. Hold
one end of the hose to your ear, and probe
around vacuum hoses and fittings, listening
for the “hissing” sound characteristic of a
vacuum leak.
Warning: When probing with the
vacuum hose stethoscope, be
very careful not to come into
contact with moving engine
components such as the auxiliary
drivebelt, radiator electric cooling fan, etc.
Fuel hoses
Warning: There are certain
precautions which must be taken
when inspecting or servicing fuel
system components. Work in a well-
ventilated area, and do not allow open
flames (cigarettes, appliance pilot lights,
etc.) or bare light bulbs near the work
area. Mop up any spills immediately, and
do not store fuel-soaked rags where they
could ignite.
10Check all fuel hoses for deterioration and
chafing. Check especially for cracks in areas
where the hose bends, and also just before
fittings, such as where a hose attaches to the
fuel filter.
11High-quality fuel line, usually identified by
the word “Fluoroelastomer” printed on thehose, should be used for fuel line renewal.
Never, under any circumstances, use
unreinforced vacuum line, clear plastic tubing
or water hose for fuel lines.
12Spring-type clamps are commonly used
on fuel lines. These clamps often lose their
tension over a period of time, and can be
“sprung” during removal. Replace all
spring-type clamps with screw clamps
whenever a hose is replaced.
Metal lines
13Sections of metal piping are often used
for fuel line between the fuel filter and the
engine. Check carefully to be sure the piping
has not been bent or crimped, and that cracks
have not started in the line.
14If a section of metal fuel line must be
renewed, only seamless steel piping should
be used, since copper and aluminium piping
don’t have the strength necessary to
withstand normal engine vibration.
15Check the metal brake lines where they
enter the master cylinder and ABS hydraulic
unit (if used) for cracks in the lines or loose
fittings. Any sign of brake fluid leakage calls
for an immediate and thorough inspection of
the brake system.
1With the vehicle parked on level ground,
apply the handbrake firmly and open the
bonnet. Using an inspection light or a small
electric torch, check all visible wiring within
and beneath the engine compartment.
2What you are looking for is wiring that is
obviously damaged by chafing against sharp
edges, or against moving suspension/
transmission components and/or the auxiliary
drivebelt, by being trapped or crushed
between carelessly-refitted components, or
melted by being forced into contact with the
hot engine castings, coolant pipes, etc. In
almost all cases, damage of this sort is
caused in the first instance by incorrect
routing on reassembly after previous work has
been carried out.
3Depending on the extent of the problem,
damaged wiring may be repaired by rejoining
the break or splicing-in a new length of wire,
using solder to ensure a good connection,
and remaking the insulation with adhesive
insulating tape or heat-shrink tubing, as
appropriate. If the damage is extensive, given
the implications for the vehicle’s future
reliability, the best long-term answer may well
be to renew that entire section of the loom,
however expensive this may appear.
4When the actual damage has been
repaired, ensure that the wiring loom is re-
routed correctly, so that it is clear of other
components, and not stretched or kinked, and
is secured out of harm’s way using the plastic
clips, guides and ties provided.
5Check all electrical connectors, ensuringthat they are clean, securely fastened, and
that each is locked by its plastic tabs or wire
clip, as appropriate. If any connector shows
external signs of corrosion (accumulations of
white or green deposits, or streaks of “rust”),
or if any is thought to be dirty, it must be
unplugged and cleaned using electrical
contact cleaner. If the connector pins are
severely corroded, the connector must be
renewed; note that this may mean the renewal
of that entire section of the loom - see your
local Ford dealer for details.
6If the cleaner completely removes the
corrosion to leave the connector in a
satisfactory condition, it would be wise to
pack the connector with a suitable material
which will exclude dirt and moisture,
preventing the corrosion from occurring
again; a Ford dealer may be able to
recommend a suitable product.
7Check the condition of the battery
connections - remake the connections or
renew the leads if a fault is found (see Chap-
ter 5). Use the same techniques to ensure that
all earth points in the engine compartment
provide good electrical contact through clean,
metal-to-metal joints, and that all are securely
fastened. (In addition to the earth connection
at the engine lifting eye, and that from the
transmission to the body/battery, there are
one or two earth points behind each headlight
assembly, and one below the power steering
fluid reservoir.)
8Refer to Section 31 for details of spark plug
(HT) lead checks.
Warning: The air conditioning
system is under high pressure.
Do not loosen any fittings or
remove any components until
after the system has been discharged. Air
conditioning refrigerant must be properly
discharged into an approved type of
container, at a dealer service department
or an automotive air conditioning repair
facility capable of handling R134a
refrigerant. Always wear eye protection
when disconnecting air conditioning
system fittings.
1The following maintenance checks should
be performed on a regular basis, to ensure
that the air conditioner continues to operate at
peak efficiency:
(a) Check the auxiliary drivebelt. If it’s worn
or deteriorated, renew it (see Section 11).
(b) Check the system hoses. Look for cracks,
bubbles, hard spots and deterioration.
Inspect the hoses and all fittings for oil
bubbles and seepage. If there’s any
evidence of wear, damage or leaks, renew
the hose(s).
(c) Inspect the condenser fins for leaves,
insects and other debris. Use a “fin
14 Air conditioning system
check
13 Engine compartment wiring
check
1•15
1
Every 10 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 30 of 279

comb” or compressed air to clean the
condenser.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
(d) Check that the drain tube from the front
of the evaporator is clear - note that it is
normal to have clear fluid (water) dripping
from this while the system is in operation,
to the extent that quite a large puddle can
be left under the vehicle when it is parked.
2It’s a good idea to operate the system forabout 30 minutes at least once a month,
particularly during the winter. Long term
non-use can cause hardening, and
subsequent failure, of the seals.
3Because of the complexity of the air
conditioning system and the special
equipment necessary to service it, in-depth
fault diagnosis and repairs are not included in
this manual. For more complete information
on the air conditioning system, refer to the
Haynes Automotive Heating and Air
Conditioning Manual.
4The most common cause of poor cooling is
simply a low system refrigerant charge. If a
noticeable drop in cool air output occurs, the
following quick check will help you determine
if the refrigerant level is low.
5Warm the engine up to normal operating
temperature.
6Place the air conditioning temperature
selector at the coldest setting, and put the
blower at the highest setting. Open the doors
- to make sure the air conditioning system
doesn’t cycle off as soon as it cools the
passenger compartment.
7With the compressor engaged - the clutch
will make an audible click, and the centre of
the clutch will rotate - feel the inlet and outlet
pipes at the compressor. One side should be
cold, and one hot. If there’s no perceptible
difference between the two pipes, there’s
something wrong with the compressor or the
system. It might be a low charge - it might be
something else. Take the vehicle to a dealer
service department or an automotive air
conditioning specialist.1Make sure that you have all the necessary
tools before you begin this procedure (see
illustration). You should also have plenty of
rags or newspapers handy, for mopping up
any spills.
2To avoid any possibility of scalding, and to
protect yourself from possible skin irritants
and other harmful contaminants in used
engine oils, it is advisable to wear gloves
when carrying out this work.
3Access to the underside of the vehicle is
greatly improved if the vehicle can be lifted on
a hoist, driven onto ramps, or supported by
axle stands.
Warning: Do not work under a
vehicle which is supported only
by an hydraulic or scissors-type
jack, or by bricks, blocks of
wood, etc.
4If this is your first oil change, get under the
vehicle and familiarise yourself with the
position of the engine oil drain plug, which is
located at the rear of the sump. The engine
and exhaust components will be warm during
the actual work, so try to anticipate any
potential problems while the engine and
accessories are cool.
5The oil should preferably be changed when
the engine is still fully warmed-up to normal
operating temperature, just after a run (the
needle on the temperature gauge should be in
the “Normal” sector of the gauge); warm oil
and sludge will flow out more easily. Park the
vehicle on firm, level ground, apply the
handbrake firmly, then select 1st or reverse
gear (manual transmission) or the “P” position
(automatic transmission). Open the bonnet
and remove the engine oil filler cap from the
cylinder head cover, then remove the oil level
dipstick from its tube (see Section 3).
6Raise the front of the vehicle, and support it
securely on axle stands. Remove the front
right-hand roadwheel to provide access to the
oil filter; if the additional working clearance is
required, remove also the auxiliary drivebelt
cover (two fasteners).
15 Engine oil and filter change
1•16
15.1 These tools are required when
changing the engine oil and filter
1Drain pan- It should be fairly shallow in
depth, but wide to prevent spills
2Rubber gloves- When removing the drain
plug and filter, it is inevitable that you will get
oil on your hands (the gloves will prevent
burns from hot oil)
3Breaker bar- Sometimes the oil drain plug
is pretty tight, and a long breaker bar is
needed to loosen it
4Socket- To be used with the breaker bar
or a ratchet (must be the correct size to fit the
drain plug)
5Filter wrench- This is a metal band-type
wrench, which requires clearance around the
filter to be effective
6Filter wrench- This type fits on the
bottom of the filter, and can be turned with a
ratchet or breaker bar (different size wrenches
are available for different types of filters)
15.7 Use the correct-size spanner or
socket to remove the oil drain plug and
avoid rounding it off15.9 Since the oil filter is usually on very
tight, you’ll need a special wrench for
removal. DO NOT use the wrench to
tighten the new filter. Pack rag under the
filter before removal to minimise the mess
Every 10 000 miles
Frequent oil changes are the
best preventive maintenance
the home mechanic can give
the engine, because ageing
oil becomes diluted and contaminated,
which leads to premature engine wear.
Note: It is
antisocial and
illegal to dump
oil down the
drain. To find
the location of
your local oil
recycling bank,
call this
number free.
procarmanuals.com
Page 34 of 279

brake shoes is not less than the
recommendation given in the Specifications.
14If it is difficult to determine the exact
thickness of the brake shoe linings, or if you
are at all concerned about the condition of the
shoes, then remove the rear drums for a more
comprehensive inspection (refer to Chapter 9)
(see illustration).
15With the drum removed, check the shoe
return and hold-down springs for correct
installation, and check the wheel cylinders for
leakage of brake fluid. Check the friction
surface of the brake drums for scoring and
discoloration. If excessive, the drum should
be resurfaced or renewed.
16Before refitting the wheels, check all
brake lines and hoses (refer to Chapter 9). On
completion, apply the handbrake and check
that the rear wheels are locked. The
handbrake is self-adjusting, and no manual
adjustment is possible.
1Check that the doors, bonnet and
tailgate/boot lid close securely. Check that
the bonnet safety catch operates correctly.
Check the operation of the door check straps.
2Lubricate the hinges, door check straps,
the striker plates and the bonnet catch
sparingly with a little oil or grease.1Apply the handbrake.
2Remove the wheel covers, using the flat
end of the wheelbrace supplied in the tool kit
(on models with the RS trim kit, it will be
necessary to unscrew the retaining bolts with
the special key).
3Check that the roadwheel nuts are tightened
to the specified torque wrench setting.
4Refit the wheel covers.
Check the operation and
performance of the braking
system
1Make sure that the vehicle does not pull to
one side when braking, and that the wheels
do not lock prematurely when braking hard.
2Check that there is no vibration through the
steering when braking.
3Check that the handbrake operates
correctly, without excessive movement of the
lever, and that it holds the vehicle stationary
on a slope.
4With the engine switched off, test the
operation of the brake servo unit as follows.
Depress the footbrake four or five times to
exhaust the vacuum, then start the engine. As
the engine starts, there should be a noticeable
“give” in the brake pedal as vacuum builds
up. Allow the engine to run for at least two
minutes, and then switch it off. If the brake
pedal is now depressed again, it should be
possible to detect a hiss from the servo as the
pedal is depressed. After about four or five
applications, no further hissing should be
heard, and the pedal should feel considerably
harder.
Steering and suspension
5Check for any abnormalities in the steering,
suspension, handling or road “feel”.
6Drive the vehicle, and check that there are
no unusual vibrations or noises.
7Check that the steering feels positive, with
no excessive sloppiness or roughness, andcheck for any suspension noises when
cornering and driving over bumps.
Drivetrain
8Check the performance of the engine,
transmission and driveshafts.
9Check that the engine starts correctly, both
when cold and when hot.
10Listen for any unusual noises from the
engine and transmission.
11Make sure that the engine runs smoothly
when idling, and that there is no hesitation
when accelerating.
12On manual transmission models, check
that all gears can be engaged smoothly
without noise, and that the gear lever action is
not abnormally vague or “notchy”.
13On automatic transmission models, make
sure that all gearchanges occur smoothly
without snatching, and without an increase in
engine speed between changes. Check that
all the gear positions can be selected with the
vehicle at rest. If any problems are found, they
should be referred to a Ford dealer.
14Listen for a metallic clicking sound from
the front of the vehicle as the vehicle is driven
slowly in a circle with the steering on full-lock.
Carry out this check in both directions. If a
clicking noise is heard, this indicates wear in a
driveshaft joint, in which case renew the joint
if necessary.
Clutch
15Check that the clutch pedal moves
smoothly and easily through its full travel, and
that the clutch itself functions correctly, with
no trace of slip or drag. If the movement is
uneven or stiff in places, check that the cable
is routed correctly, with no sharp turns.
16Inspect both ends of the clutch inner
cable, both at the gearbox end and inside the
car, for signs of wear and fraying.
17Check the pedal stroke as described in
Chapter 8, Section 3, and adjust if necessary.
Instruments and electrical
equipment
18Check the operation of all instruments
and electrical equipment.
19Make sure that all instruments read
correctly, and switch on all electrical
equipment in turn, to check that it functions
properly.
26 Road test
25 Roadwheel nut tightness
check
24 Door and bonnet check and
lubrication
1•20
23.14 If the lining is bonded to the brake
shoe, measure the lining thickness from
the outer surface to the metal shoe, as
shown here; if the lining is riveted to the
shoe, measure from the lining outer
surface to the rivet head
Every 20 000 miles
Every 20 000 miles or 2 years
1The air entering the vehicle’s ventilation
system is passed through a very fine pleated-
paper air filter element, which removes
particles of pollen, dust and other airborne
foreign matter. To ensure its continued
effectiveness, this filter’s element must be
renewed at regular intervals.2Remove the left-hand side windscreen
wiper arm (Chapter 12).
3Prise off their trim caps, then unscrew the two
screws securing the windscreen edge of the cowl
grille panel; open the bonnet and remove the
remaining three retaining screws (see illustration).
4Peel back the rubber seal and withdraw the
cowl grille panel.
5Releasing the clip at each end, lift out the
pollen filter housing, and withdraw the
element (see illustrations).6Wipe out the ventilation system intake and
the filter housing, removing any leaves, dead
insects etc.
7If carrying out a routine service, the element
must be renewed regardless of its apparent
condition. If you are checking the element for
any other reason, inspect its front surface; if it
is very dirty, renew the element. If it is only
moderately dusty, it can be re-used by
blowing it clean from the rear to the front
surface with compressed air. Because it is a
27 Ventilation system pollen
filter renewal
procarmanuals.com
Page 36 of 279

are correctly secured, and that the radiator
drain plug is securely tightened. Refit the
radiator undershield, noting that it is located
by three clips at its front edge; tighten the
retaining screws securely (see illustration). If
it was raised, lower the vehicle to the ground.
12Prepare a sufficient quantity of the
specified coolant mixture (see below); allow
for a surplus, so as to have a reserve supply
for topping-up.
13Slowly fill the system through the
expansion tank; since the tank is the highest
point in the system, all the air in the system
should be displaced into the tank by the rising
liquid. Slow pouring reduces the possibility of
air being trapped and forming air-locks.
14Continue filling until the coolant level
reaches the expansion tank “MAX” level line,
then cover the filler opening to prevent
coolant splashing out.
15Start the engine and run it at idle speed,
until it has warmed-up to normal operating
temperature and the radiator electric cooling
fan has cut in; watch the temperature gauge
to check for signs of overheating. If the level in
the expansion tank drops significantly, top-up
to the “MAX” level line, to minimise the
amount of air circulating in the system.
16Stop the engine, allow it to cool down
completely(overnight, if possible), then
uncover the expansion tank filler opening and
top-up the tank to the “MAX” level line. Refit
the filler cap, tightening it securely, and washoff any spilt coolant from the engine
compartment and bodywork.
17After refilling, always check carefully all
components of the system (but especially any
unions disturbed during draining and flushing)
for signs of coolant leaks. Fresh antifreeze has
a searching action, which will rapidly expose
any weak points in the system.
18 Note:If, after draining and refilling the
system, symptoms of overheating are found
which did not occur previously, then the fault
is almost certainly due to trapped air at some
point in the system, causing an air-lock and
restricting the flow of coolant; usually, the air
is trapped because the system was refilled too
quickly. In some cases, air-locks can be
released by tapping or squeezing the various
hoses. If the problem persists, stop the engine
and allow it to cool down completely, before
unscrewing the expansion tank filler cap or
disconnecting hoses to bleed out the trapped
air.
Antifreeze mixture
19If the antifreeze used is not to Ford’s
specification, it should always be renewed at
the suggested intervals. This is necessary not
only to maintain the antifreeze properties, but
also to prevent the corrosion which would
otherwise occur as the corrosion inhibitors
become progressively less effective. Always
use an ethylene glycol-based antifreeze which
is suitable for use in mixed-metal cooling
systems.
20If the antifreeze used is to Ford’s
specification, the levels of protection it affords
are indicated in the Specifications Section of
this Chapter. To give the recommended
standardmixture ratio for this antifreeze, 40%
(by volume) of antifreeze must be mixed with
60% of clean, soft water; if you are using any
other type of antifreeze, follow its
manufacturer’s instructions to achieve the
correct ratio. It is best to make up slightly
more than the system’s specified capacity, so
that a supply is available for subsequent
topping-up.
21Before adding antifreeze, the cooling
system should be completely drained,
preferably flushed, and all hoses checked forcondition and security. As noted earlier, fresh
antifreeze will rapidly find any weaknesses in
the system.
22After filling with antifreeze, a label should
be attached to the expansion tank, stating the
type and concentration of antifreeze used,
and the date installed. Any subsequent
topping-up should be made with the same
type and concentration of antifreeze. If
topping-up using antifreeze to Ford’s
specification, note that a 50/50 mixture is
permissible, purely for convenience.
23Do not use engine antifreeze in the
windscreen/tailgate washer system, as it will
damage the vehicle’s paintwork. A screen
wash additive should be added to the washer
system in its maker’s recommended
quantities.
General cooling system checks
24The engine should be cold for the cooling
system checks, so perform the following
procedure before driving the vehicle, or after it
has been shut off for at least three hours.
25Remove the expansion tank filler cap (see
Section 3), and clean it thoroughly inside and
out with a rag. Also clean the filler neck on the
expansion tank. The presence of rust or
corrosion in the filler neck indicates that the
coolant should be changed. The coolant
inside the expansion tank should be relatively
clean and transparent. If it is rust- coloured,
drain and flush the system, and refill with a
fresh coolant mixture.
26Carefully check the radiator hoses and
heater hoses along their entire length; renew
any hose which is cracked, swollen or
deteriorated (see Section 12).
27Inspect all other cooling system
components (joint faces, etc.) for leaks. A leak
in the cooling system will usually show up as
white- or rust-coloured deposits on the area
adjoining the leak. Where any problems of this
nature are found on system components,
renew the component or gasket with
reference to Chapter 3.
28Clean the front of the radiator with a soft
brush to remove all insects, leaves, etc,
embedded in the radiator fins. Be careful not
to damage the radiator fins, or cut your fingers
on them.
1•22
28.11 Ensure radiator undershield is
located securely in three clips at front
edge (arrowed) when refitting
Every 30 000 miles
Every 30 000 miles or 3 years
1The air filter element is located in the air
cleaner assembly on the left-hand side of the
engine compartment. Release the clips, and
lift the air cleaner cover (see illustrations). If
the additional working clearance is required,
unclip the cover from the air mass meter, and
withdraw it completely.
2Lift out the element, and wipe out thehousing (see illustration). Check that no
foreign matter is visible, either in the air intake
or in the air mass meter.
3If carrying out a routine service, the element
must be renewed regardless of its apparent
condition; note that the small foam filter in the
rear right-hand corner of the air cleaner
housing must be cleaned whenever the air
filter element is renewed (see Section 30).
4If you are checking the element for any
other reason, inspect its lower surface; if it is
oily or very dirty, renew the element. If it is
only moderately dusty, it can be re-used byblowing it clean from the upper to the lower
surface with compressed air. Because it is a
pleated-paper type filter, it cannot be washed
or re-oiled. If it cannot be cleaned
satisfactorily with compressed air, discard
and renew it.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
Caution: Never drive the vehicle
with the air cleaner filter element
removed. Excessive engine wear could
result, and backfiring could even cause a
fire under the bonnet.
29 Air filter element renewal
procarmanuals.com
Page 37 of 279

5Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure. Ensure that the element and cover
are securely seated, so that unfiltered air
cannot enter the engine.
1The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV)
system components are located at the front of
the engine, underneath the exhaust manifold
and air intake resonator. Refer to Chapter 6
for further information.
2Check that all components of the system
are securely fastened, correctly routed (with
no kinks or sharp bends to restrict flow) and in
sound condition; renew any worn or damaged
components.
3If oil leakage is noted, disconnect the
various hoses and pipes, and check that all
are clear and unblocked. Remove the air
cleaner assembly cover, air mass meter and
resonator, then check that the hose from the
cylinder head cover to the air cleaner housing
is clear and undamaged. Disconnect the
rubber T-piece both from the union on the
inlet manifold left-hand end, and from the
metal crankcase breather pipe under the
ignition coil. Connect a spare, clean, length of
hose to the breather pipe. Suck on the end of
the hose, then blow through it - little or norestriction to airflow should be felt in either
direction. A similar test can be applied to
check that the inlet manifold passages are
clear - air should be heard hissing out of the
plenum chamber mouth as you blow.
4The PCV valve is designed to allow gases
to flow out of the crankcase only, so that a
depression is created in the crankcase under
most operating conditions, particularly at idle.
Therefore, if either the oil separator or the PCV
valve are thought to be blocked, they must be
renewed (see Chapter 6). In such a case,
however, there is nothing to be lost by
attempting to flush out the blockage using a
suitable solvent. The PCV valve should rattle
when shaken.
5While the air filter element is removed (see
Section 29), wipe out the housing, and
withdraw the small foam filter from its location
in the rear right-hand corner of the housing
(see illustration). If the foam is badly clogged
with dirt or oil, it must be cleaned by soaking it
in a suitable solvent, and allowed to dry
before being refitted.
Spark plug check and renewal
1It is vital for the correct running, full
performance and proper economy of the
engine that the spark plugs perform with
maximum efficiency. The most important
factor in ensuring this is that the plugs fitted
are appropriate for the engine. The suitable
type is given in the Specifications Section at
the beginning of this Chapter, on the Vehicle
Emissions Control Information (VECI) label
located on the underside of the bonnet (only
on models sold in some areas) or in the
vehicle’s Owner’s Handbook. If these sources
specify different plugs, purchase the spark
plug type specified on the VECI label (where
appropriate), as that information is provided
specifically for your engine. If this type is used
and the engine is in good condition, the spark
plugs should not need attention between
scheduled renewal intervals. Spark plug
cleaning is rarely necessary, and should notbe attempted unless specialised equipment is
available, as damage can easily be caused to
the firing ends.
2Spark plug removal and refitting requires a
spark plug socket, with an extension which
can be turned by a ratchet handle or similar.
This socket is lined with a rubber sleeve, to
protect the porcelain insulator of the spark
plug, and to hold the plug while you insert it
into the spark plug hole. You will also need a
wire-type feeler gauge, to check and adjust
the spark plug electrode gap, and a torque
wrench to tighten the new plugs to the
specified torque (see illustration).
3To remove the spark plugs, first open the
bonnet; the plugs are easily reached at the
top of the engine. Note how the spark plug
(HT) leads are routed and secured by clips
along the channel in the cylinder head cover.
31 Spark plug renewal
30 Positive Crankcase
Ventilation (PCV) system
check and filter cleaning
1•23
1
30.5 The Positive Crankcase Ventilation
(PCV) system filter in the air cleaner
assembly must be cleaned whenever the
air filter element is renewed
31.2 Tools required for changing spark
plugs
1Spark plug socket- This will have special
padding inside, to protect the spark plug
porcelain insulator
2Torque wrench- Although not essential,
use of this tool is the best way to ensure that
the plugs are tightened properly
3Ratchet- Standard hand tool to fit the
plug socket
4Extension- Depending on the other tools
available, you may need an extension to reach
the plugs
5Spark plug gap gauge- This gauge for
checking the gap comes in a variety of styles.
Make sure the gap for your engine is included
29.1A Release the wire clips to detach the
cover from the air cleaner assembly . . .29.1B . . . noting the long clip normally
hidden by the battery . . .29.2 . . . lift the element out of the housing,
and wipe out its interior before fitting the
new element
Every 30 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 45 of 279

The cylinder head is provided with two oil
galleries, one on the inlet side and one on the
exhaust, to ensure constant oil supply to the
camshaft bearings and hydraulic tappets. A
retaining valve (inserted into the cylinder
head’s top surface, in the middle, on the inlet
side) prevents these galleries from being
drained when the engine is switched off. The
valve incorporates a ventilation hole in its
upper end, to allow air bubbles to escape
from the system when the engine is restarted.
While the crankshaft and camshaft
bearings and the hydraulic tappets receive a
pressurised supply, the camshaft lobes and
valves are lubricated by splash, as are all
other engine components.
Valve clearances - general
It is necessary for a clearance to exist
between the tip of each valve stem and the
valve operating mechanism, to allow for the
expansion of the various components as the
engine reaches normal operating
temperature.
On most older engine designs, this meant
that the valve clearances (also known as
“tappet” clearances) had to be checked and
adjusted regularly. If the clearances were
allowed to be too slack, the engine would be
very noisy, its power output would suffer, and
its fuel consumption would increase. If the
clearances were allowed to be too tight, the
engine’s power output would be reduced,
and the valves and their seats could be
severely damaged.
The engines covered in this manual,
however, employ hydraulic tappets which use
the lubricating system’s oil pressure
automatically to take up the clearance
between each camshaft lobe and its
respective valve stem. Therefore, there is no
need for regular checking and adjustment of
the valve clearances, but it is essential that
onlygood-quality oil of the recommended
viscosity and specification is used in the
engine, and that this oil is always changed at
the recommended intervals. If this advice is
not followed, the oilways and tappets may
become clogged with particles of dirt, or
deposits of burnt (inferior) engine oil, so that
the system cannot work properly; ultimately,
one or more of the tappets may fail, and
expensive repairs may be required.
On starting the engine from cold, there will
be a slight delay while full oil pressure builds
up in all parts of the engine, especially in the
tappets; the valve components, therefore,
may well “rattle” for about 10 seconds or so,
and then quieten. This is a normal state of
affairs, and is nothing to worry about,
provided that all tappets quieten quickly and
stay quiet.
After the vehicle has been standing for
several days, the valve components may
“rattle” for longer than usual, as nearly all the
oil will have drained away from the engine’s
top end components and bearing surfaces.
While this is only to be expected, care mustbe taken not to damage the engine under
these circumstances - avoid high speed
running until all the tappets are refilled with oil
and operating normally. With the vehicle
stationary, hold the engine at no more than a
fast idle speed (maximum 2000 to 2500 rpm)
for 10 to 15 seconds, or until the noise
ceases. Do not run the engine at more than
3000 rpm until the tappets are fully recharged
with oil and the noise has ceased.
If the valve components are thought to be
noisy, or if a light rattle persists from the top
end after the engine has warmed up to
normal operating temperature, take the
vehicle to a Ford dealer for expert advice.
Depending on the mileage covered and the
usage to which each vehicle has been put,
some vehicles may be noisier than others;
only a good mechanic experienced in these
engines can tell if the noise level is typical for
the vehicle’s mileage, or if a genuine fault
exists. If any tappet’s operation is faulty, it
must be renewed (Section 13).
The following major repair operations can
be accomplished without removing the
engine from the vehicle. However, owners
should note that any operation involving the
removal of the sump requires careful
forethought, depending on the level of skill
and the tools and facilities available; refer to
the relevant text for details.
(a) Compression pressure - testing.
(b) Cylinder head cover - removal and
refitting.
(c) Timing belt covers - removal and refitting.
(d) Timing belt - renewal.
(e) Timing belt tensioner and toothed pulleys
- removal and refitting.
(f) Camshaft oil seals - renewal.
(g) Camshafts and hydraulic tappets -
removal and refitting.
(h) Cylinder head - removal, overhaul and
refitting.
(i) Cylinder head and pistons -
decarbonising.
(j) Sump - removal and refitting.
(k) Crankshaft oil seals - renewal.
(l) Oil pump - removal and refitting.
(m) Piston/connecting rod assemblies -
removal and refitting (but see note below).
(n) Flywheel/driveplate - removal and
refitting.
(o) Engine/transmission mountings - removal
and refitting.
Clean the engine compartment and the
exterior of the engine with some type of
degreaser before any work is done. It will
make the job easier, and will help to keep dirt
out of the internal areas of the engine.
Depending on the components involved, it
may be helpful to remove the bonnet, to
improve access to the engine as repairs are
performed (refer to Chapter 11 if necessary).Cover the wings to prevent damage to the
paint; special covers are available, but an old
bedspread or blanket will also work.
If vacuum, exhaust, oil or coolant leaks
develop, indicating a need for component/
gasket or seal replacement, the repairs can
generally be made with the engine in the
vehicle. The intake and exhaust manifold
gaskets, sump gasket, crankshaft oil seals
and cylinder head gasket are all accessible
with the engine in place.
Exterior components such as the intake
and exhaust manifolds, the sump, the oil
pump, the water pump, the starter motor, the
alternator and the fuel system components
can be removed for repair with the engine in
place.
Since the cylinder head can be removed
without lifting out the engine, camshaft and
valve component servicing can also be
accomplished with the engine in the vehicle,
as can renewal of the timing belt and toothed
pulleys.
In extreme cases caused by a lack of
necessary equipment, repair or renewal of
piston rings, pistons, connecting rods and
big-end bearings is possible with the engine
in the vehicle. However, this practice is not
recommended, because of the cleaning and
preparation work that must be done to the
components involved, and because of the
amount of preliminary dismantling work
required - these operations are therefore
covered in Part B of this Chapter.
1When engine performance is down, or if
misfiring occurs which cannot be attributed to
the ignition or fuel systems, a compression
test can provide diagnostic clues as to the
engine’s condition. If the test is performed
regularly, it can give warning of trouble before
any other symptoms become apparent.
2The engine must be fully warmed-up to
normal operating temperature, the oil level
must be correct, the battery must be fully
charged, and the spark plugs must be
removed. The aid of an assistant will be
required also.
3Disable the ignition system by unplugging
the ignition coil’s electrical connector, and
remove fuse 14 to disconnect the fuel pump.
4Fit a compression tester to the No 1
cylinder spark plug hole - the type of tester
which screws into the plug thread is to be
preferred.
5Have the assistant hold the throttle wide
open and crank the engine on the starter
motor; after one or two revolutions, the
compression pressure should build up to a
maximum figure, and then stabilise. Record
the highest reading obtained.
6Repeat the test on the remaining cylinders,
recording the pressure developed in each.
7At the time of writing, no compression
3 Compression test -
description and interpretation
2 Repair operations possible with
the engine in the vehicle
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•5
2A
procarmanuals.com
Page 51 of 279
1With the vehicle parked on firm level
ground, open the bonnet and disconnect the
battery negative (earth) lead - see Chapter 5,
Section 1 (see illustration).
2Unbolt the power steering high-pressure
pipe from the cylinder head rear support
plate/engine lifting eye, and from the front
support plate/pump bracket.
3Unscrew the six nuts securing the
engine/transmission right-hand mounting
bracket, then withdraw the bracket.
4Slacken the water pump pulley bolts.5Remove the cylinder head cover (see
Section 5).
6Remove the spark plugs, covering their
holes with clean rag, to prevent dirt or other
foreign bodies from dropping in (see Chap-
ter 1).
7Remove the auxiliary drivebelt (see Chap-
ter 1).
8Rotate the crankshaft clockwise until the
second pair of notches in the pulley rim align
with the edge of the sump mark, so that Nos
1 and 4 cylinders are at TDC (see Section 4).9Unbolt and remove the water pump pulley
and the auxiliary drivebelt idler pulley.
10Obtain Ford service tool 21-162, or
fabricate a substitute from a strip of metal
5 mm thick (while the strip’s thickness is
critical, its length and width are not, but
should be approximately 180 to 230 mm by
20 to 30 mm). Check that Nos 1 and 4
cylinders are at Top Dead Centre (TDC) - No 1
on the compression stroke - by resting this
tool on the cylinder head mating surface, and
sliding it into the slot in the left-hand end of
both camshafts (see illustration). The tool
should slip snugly into both slots while resting
on the cylinder head mating surface; if one
camshaft is only slightly out of alignment, it is
permissible to use an open-ended spanner to
rotate the camshaft gently and carefully until
the tool will fit.
11If both camshaft slots (they are machined
significantly off-centre) are below the level of
the cylinder head mating surface, rotate the
crankshaft through one full turn clockwise
and fit the tool again; it should now fit as
described in the previous paragraph.
12With the camshaft aligning tool remaining
in place, remove the crankshaft pulley. Do not
use the locked camshafts to prevent the
crankshaft from rotating - use only the locking
methods described in Section 8.
13Remove the timing belt lower and middle
covers (see Section 9).
14With the camshaft aligning tool still in
place, slacken the tensioner bolt, and use an
Allen key inserted into its centre to rotate the
tensioner clockwise as far as possible away
from the belt; retighten the bolt to secure the
tensioner clear of the timing belt (see
illustration).
15If the timing belt is to be re-used, use
white paint or similar to mark its direction of
rotation, and note from the manufacturer’s
markings which way round it is fitted.
Withdraw the belt (see illustration). Do not
rotate the crankshaft until the timing belt is
refitted.
16If the belt is being removed for reasons
other than routine renewal, check it carefully
for any signs of uneven wear, splitting, cracks
(especially at the roots of the belt teeth) or
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•11
2A
10.10 Fit camshaft aligning tool to ensure
engine is locked with Nos 1 and 4 cylinders
at TDC10.14 Slacken tensioner bolt, and use
Allen key to rotate tensioner away from
timing belt . . .10.15 . . . then withdraw timing belt
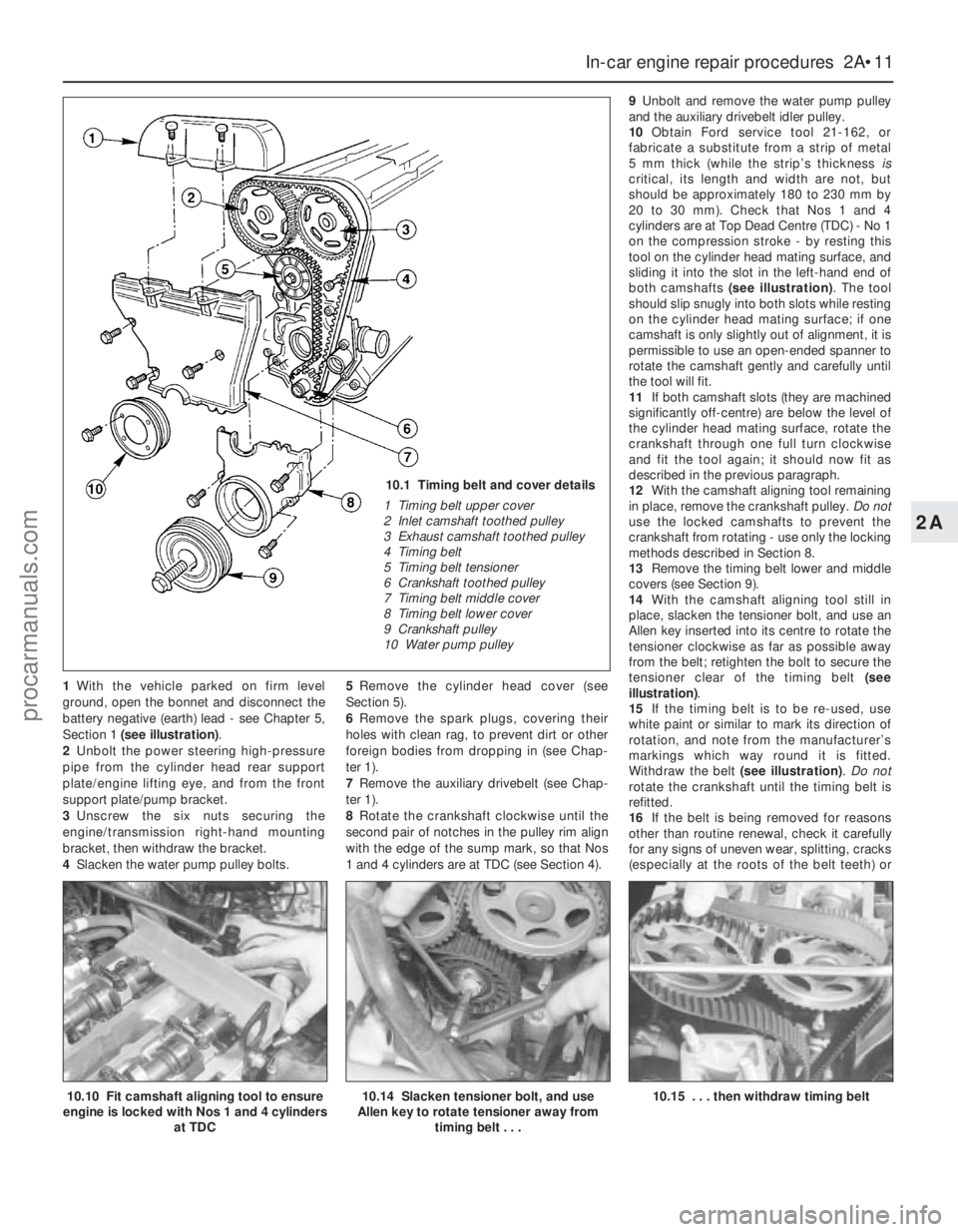
10.1 Timing belt and cover details
1 Timing belt upper cover
2 Inlet camshaft toothed pulley
3 Exhaust camshaft toothed pulley
4 Timing belt
5 Timing belt tensioner
6 Crankshaft toothed pulley
7 Timing belt middle cover
8 Timing belt lower cover
9 Crankshaft pulley
10 Water pump pulley
procarmanuals.com