1993 FORD MONDEO coolant
[x] Cancel search: coolantPage 15 of 279

Chapter 1 Routine maintenance and servicing
Air conditioning system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Air filter element renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Automatic transmission fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Automatic transmission linkage lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Auxiliary drivebelt check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Battery check, maintenance and charging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Brake check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Brake fluid renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Clutch pedal adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Coolant renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2, 28
Door and bonnet check and lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Driveshaft rubber gaiter and CV joint check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Electrical system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Engine compartment wiring check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Engine oil and filter change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Exhaust system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Fluid level checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Fuel filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Idle speed and mixture check and adjustment . . . . . . See Chapter 4Ignition timing check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 5
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Manual transmission oil level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system check
and filter cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Power steering fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Road test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Roadwheel nut tightness check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Seat belt check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Spark plug renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See end of Chapter
Steering, suspension and roadwheel check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Timing belt renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Tyre and tyre pressure checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Underbody and fuel/brake line check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Underbonnet check for fluid leaks and hose condition . . . . . . . . . . 12
Ventilation system pollen filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Windscreen/tailgate washer system and wiper blade check . . . . . . 6
1•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,suitable
for competent DIY
mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty Contents
1
procarmanuals.com
Page 17 of 279

Ford Mondeo maintenance schedule
1•3
1
Maintenance schedule
The manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for these
vehicles is as described below - note that the schedule starts from the
vehicle’s date of registration. These are the minimum maintenance
intervals recommended by the factory for Mondeos driven daily, but
subjected only to “normal” use. If you wish to keep your vehicle in
peak condition at all times, you may wish to perform some of these
procedures even more often. Because frequent maintenance
enhances the efficiency, performance and resale value of your vehicle,
we encourage you to do so. If your usage is not “normal”, shorter
intervals are also recommended - the most important examples of
these are noted in the schedule. These shorter intervals apply
particularly if you drive in dusty areas, tow a caravan or trailer, sit with
the engine idling or drive at low speeds for extended periods (ie, in
heavy traffic), or drive for short distances (less than four miles) in
below-freezing temperatures.
When your vehicle is new, it should be serviced by a Ford dealer
service department to protect the factory warranty. In many cases, the
initial maintenance check is done at no cost to the owner. Note that
this first free service (carried out by the selling dealer 1500 miles or 3
months after delivery), although an important check for a new vehicle,
is not part of the regular maintenance schedule, and is therefore not
mentioned here.
Weekly checks
m mCheck the engine oil level, and top-up if necessary
(Section 3)
m mCheck the brake fluid level, and top-up if necessary
(Section 3). If repeated topping-up is required, check the
system for leaks or damage at the earliest possible
opportunity (Sections 12 and 22)
m mCheck the windscreen/tailgate washer fluid level, and top-
up if necessary (Section 3)
m mCheck the tyre pressures, including the spare (Section 4)
m mVisually check the tyres for excessive tread wear, or
damage (Section 4)
m mCheck the operation of all (exterior and interior) lights and
the horn, wipers and windscreen/tailgate washer system
(Sections 6 and 8). Renew any blown bulbs (Chapter 12),
and clean the lenses of all exterior lights
Monthly checks
m mCheck the coolant level, and top-up if necessary (Sec-
tion 3)
m mCheck the battery electrolyte level, where applicable
(Section 3)
m mCheck the power steering fluid level, and top-up if
necessary (Section 5)
m mVisually check all reservoirs, hoses and pipes for leakage
(Section 12)
m mCheck the operation of the air conditioning system
(Section 14)
m mCheck the operation of the handbrake (Section 23)
m mCheck the aim of the windscreen/tailgate/headlight
washer jets, correcting them if required (Section 6)
m mCheck the condition of the wiper blades, renewing them if
worn or no longer effective - note that the manufacturer
recommends renewing the blades as a safety precaution,
irrespective of their apparent condition, at least once a
year (Section 6)
Every 10 000 miles or 12 months,
whichever occurs first
Note:If the vehicle is used regularly for very short (less than
10 miles), stop/go journeys, the oil and filter should be renewed
between services (ie, every 5000 miles/6 months).
m mCheck the electrical system (Section 8)
m mCheck the battery (Section 9)
m mCheck the seat belts (Section 10)
m mCheck the auxiliary drivebelt (Section 11)
m mCheck for fluid leaks and hose condition (Section 12)
m mCheck the condition of all wiring (Section 13)
m mCheck all air conditioning components (Section 14)
m mChange the engine oil and filter (Section 15)
m mCheck the manual transmission oil level (Section 16)
m mCheck the adjustment of the clutch pedal (Section 17)
m mLubricate the automatic transmission linkage (Section 18)
m mCheck the steering, suspension and wheels (Section 19)
m mCheck the driveshaft gaiters and CV joints (Section 20)
m mCheck the exhaust system (Section 21)
m mCheck the underbody, and all fuel/brake lines (Section 22)
m mCheck the brake system (Section 23)
m mCheck and lubricate the doors and bonnet (Section 24)
m mCheck the security of all roadwheel nuts (Section 25)
m mRoad test (Section 26). Check the level of the automatic
transmission fluid with the engine still hot, after the road
test (Section 7)
Every 20 000 miles or 2 years,
whichever occurs first
Carry out all operations listed above, plus the following:
m mRenew the ventilation system pollen filter (Section 27)
m mRenew the coolant (Sections 2 and 28)
Every 30 000 miles or 3 years,
whichever occurs first
Carry out all operations listed above, plus the following:
m mRenew the air filter element (Section 29). Note that this
task must be carried out at more frequent intervals if the
vehicle is used in dusty or polluted conditions
m mCheck the Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system,
and clean the filter (Section 30)
m mRenew the spark plugs (Section 31)
Every 60 000 miles
Carry out all operations listed above, plus the following:
m
mRenew the timing belt (Section 32)
m mRenew the fuel filter (Section 33)
Every 3 years
(regardless of mileage)
m mRenew the brake fluid (Section 34)
procarmanuals.com
Page 20 of 279

This Chapter is designed to help the home
mechanic maintain the Ford Mondeo models
for peak performance, economy, safety and
long life.
On the following pages are Sections
dealing specifically with each item on the
maintenance schedule. Visual checks,
adjustments, component replacement and
other helpful items are included. Refer to the
accompanying illustrations of the engine
compartment and the underside of the vehicle
for the location of various components.
Servicing your Mondeo in accordance with
the mileage/time maintenance schedule and
the following Sections will provide it with a
planned maintenance programme, which
should result in a long and reliable service life.
This is a comprehensive plan, so maintaining
some items but not others at the specified
service intervals will not produce the same
results.
As you service your Mondeo, you will
discover that many of the procedures can -
and should - be grouped together, because of
the nature of the particular procedure you’re
performing, or because of the close proximity
to one another of two otherwise-unrelated
components.
For example, if the vehicle is raised for anyreason, you should inspect the exhaust,
suspension, steering and fuel systems while
you’re under the vehicle. When you’re
checking the tyres, it makes good sense to
check the brakes and wheel bearings,
especially if the roadwheels have already
been removed.
Finally, let’s suppose you have to borrow or
hire a torque wrench. Even if you only need to
tighten the spark plugs, you might as well
check the torque of as many critical fasteners
as time allows.
The first step of this maintenance
programme is to prepare yourself before the
actual work begins. Read through all the
Sections which are relevant to the procedures
you’re planning to carry out, then make a list
of, and gather together, all the parts and tools
you will need to do the job. If it looks as if you
might run into problems during a particular
segment of some procedure, seek advice
from your local parts man or dealer service
department.
Ford state that, where antifreeze to
specification ESD-M97B-49-A (the type with
which the vehicle’s cooling system would
have been filled on production at the factory)
is used, it will last the lifetime of the vehicle.This is subject to it being used in the
recommended concentration, unmixed with
any other type of antifreeze or additive, and
topped-up when necessary using only that
antifreeze mixed 50/50 with clean water. If any
other type of antifreeze is added, the lifetime
guarantee no longer applies; to restore the
lifetime protection, the system must be
drained and thoroughly reverse-flushed
before fresh coolant mixture is poured in.
If the vehicle’s history (and therefore the
quality of the antifreeze in it) is unknown,
owners who wish to follow Ford’s
recommendations are advised to drain and
thoroughly reverse-flush the system, as
outlined in Section 28, before refilling with
fresh coolant mixture. If the appropriate
quality of antifreeze is used, the coolant can
then be left for the life of the vehicle.
If any antifreeze other than Ford’s is to be
used, the coolant must be renewed at regular
intervals to provide an equivalent degree of
protection; the conventional recommendation
is to renew the coolant every two years.
The above assumes the use of a mixture (in
exactly the specified concentration) of clean,
soft water and of antifreeze to Ford’s
specification or equivalent. It is also assumed
that the cooling system is maintained in a
scrupulously-clean condition, by ensuring that
only clean coolant is added on topping-up,
and by thorough reverse-flushing whenever
the coolant is drained (Section 28).
2 Coolant renewal
1 Introduction
1•6Weekly checks
Weekly checks
General
1Fluids are an essential part of the
lubrication, cooling, braking and other
systems. Because these fluids gradually
become depleted and/or contaminated during
normal operation of the vehicle, they must be
periodically replenished. See “Lubricants and
fluids and capacities”at the beginning of this
Chapter before adding fluid to any of the
following components. Note:The vehicle
must be on level ground before fluid levels can
be checked.
Engine oil
2The engine oil level is checked with a
dipstick located at the front of the engine; it
can be identified by its yellow/black plastic
grip (see illustration). The dipstick extends
through a metal tube, from which it protrudes
down into the sump at the bottom of the
engine.
3The oil level should be checked before the
vehicle is driven, or about 5 minutes after the
engine has been switched off.4Pull the dipstick from the tube, and wipe all
the oil from the end with a clean rag or paper
towel; note the dipstick’s maximum and
minimum levels, indicated by notches (seeillustration). Insert the clean dipstick all the way
back into its metal tube, and pull it out again.
Observe the oil on the end of the dipstick; its
level should be between these two notches.
5Do not allow the level to drop below the
minimum level notch, or oil starvation may
cause engine damage. Conversely, overfilling
the engine (adding oil above the maximum
level notch) may cause oil-fouled spark plugs,
oil leaks or oil seal failures.
6The yellow/black plastic oil filler cap is
screwed into the left-hand front end of the
3 Fluid level checks
3.2 The engine oil dipstick (arrowed) is
located at the front of the engine - note
yellow/black plastic grip
3.4 The oil level should be at or near the
maximum level notch (A) - if not, add
enough oil to correct the level. It takes
approximately 0.5 to 1.0 litre of oil to raise
the level from the minimum level notch (B)
to the maximum
If the level is checked
immediately after driving the
vehicle, some of the oil will
remain in the engine upper
components, producing an inaccurate
dipstick reading.
procarmanuals.com
Page 21 of 279
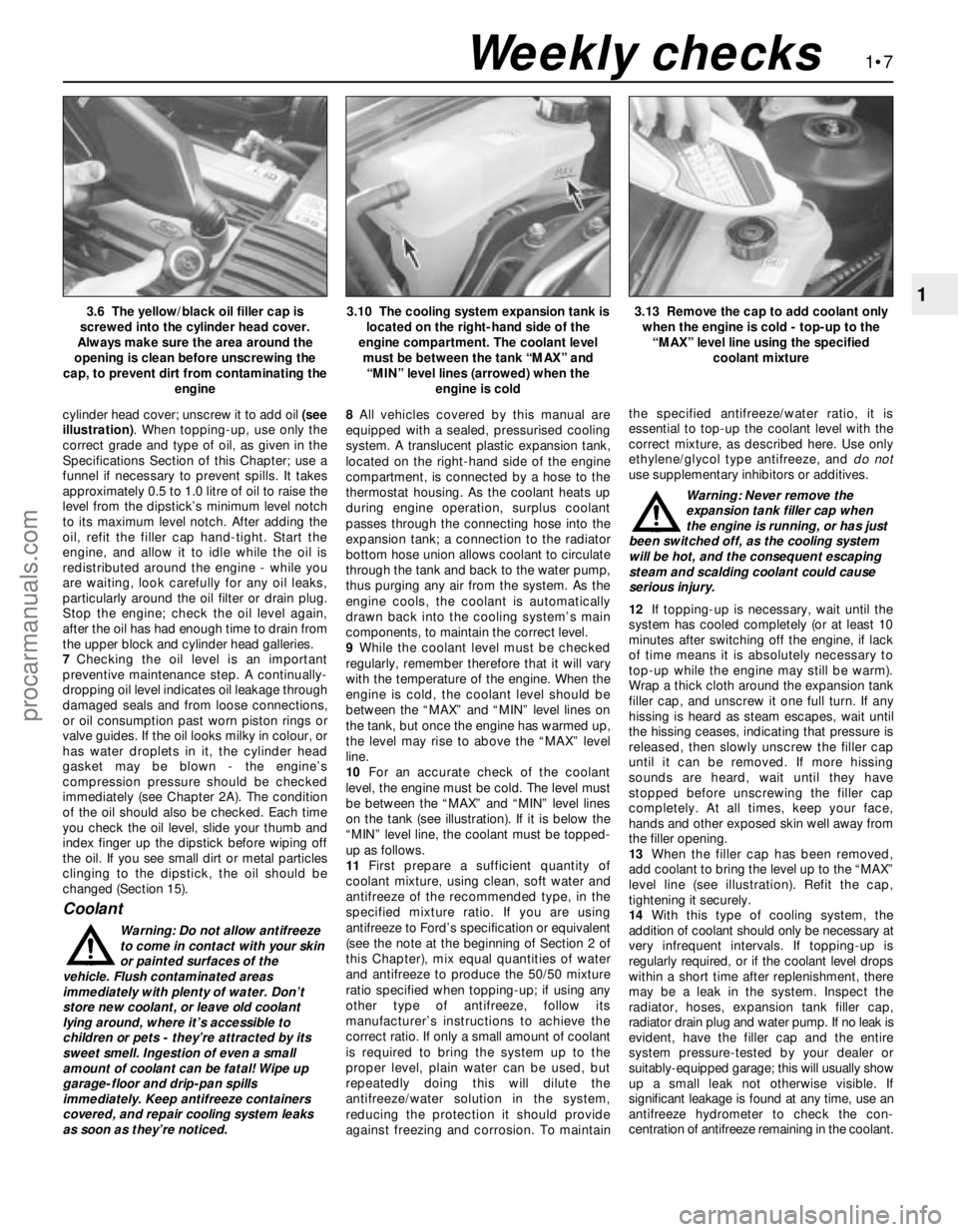

cylinder head cover; unscrew it to add oil (see
illustration). When topping-up, use only the
correct grade and type of oil, as given in the
Specifications Section of this Chapter; use a
funnel if necessary to prevent spills. It takes
approximately 0.5 to 1.0 litre of oil to raise the
level from the dipstick’s minimum level notch
to its maximum level notch. After adding the
oil, refit the filler cap hand-tight. Start the
engine, and allow it to idle while the oil is
redistributed around the engine - while you
are waiting, look carefully for any oil leaks,
particularly around the oil filter or drain plug.
Stop the engine; check the oil level again,
after the oil has had enough time to drain from
the upper block and cylinder head galleries.
7Checking the oil level is an important
preventive maintenance step. A continually-
dropping oil level indicates oil leakage through
damaged seals and from loose connections,
or oil consumption past worn piston rings or
valve guides. If the oil looks milky in colour, or
has water droplets in it, the cylinder head
gasket may be blown - the engine’s
compression pressure should be checked
immediately (see Chapter 2A). The condition
of the oil should also be checked. Each time
you check the oil level, slide your thumb and
index finger up the dipstick before wiping off
the oil. If you see small dirt or metal particles
clinging to the dipstick, the oil should be
changed (Section 15).
Coolant
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze
to come in contact with your skin
or painted surfaces of the
vehicle. Flush contaminated areas
immediately with plenty of water. Don’t
store new coolant, or leave old coolant
lying around, where it’s accessible to
children or pets - they’re attracted by its
sweet smell. Ingestion of even a small
amount of coolant can be fatal! Wipe up
garage-floor and drip-pan spills
immediately. Keep antifreeze containers
covered, and repair cooling system leaks
as soon as they’re noticed.8All vehicles covered by this manual are
equipped with a sealed, pressurised cooling
system. A translucent plastic expansion tank,
located on the right-hand side of the engine
compartment, is connected by a hose to the
thermostat housing. As the coolant heats up
during engine operation, surplus coolant
passes through the connecting hose into the
expansion tank; a connection to the radiator
bottom hose union allows coolant to circulate
through the tank and back to the water pump,
thus purging any air from the system. As the
engine cools, the coolant is automatically
drawn back into the cooling system’s main
components, to maintain the correct level.
9While the coolant level must be checked
regularly, remember therefore that it will vary
with the temperature of the engine. When the
engine is cold, the coolant level should be
between the “MAX” and “MIN” level lines on
the tank, but once the engine has warmed up,
the level may rise to above the “MAX” level
line.
10For an accurate check of the coolant
level, the engine must be cold. The level must
be between the “MAX” and “MIN” level lines
on the tank (see illustration). If it is below the
“MIN” level line, the coolant must be topped-
up as follows.
11First prepare a sufficient quantity of
coolant mixture, using clean, soft water and
antifreeze of the recommended type, in the
specified mixture ratio. If you are using
antifreeze to Ford’s specification or equivalent
(see the note at the beginning of Section 2 of
this Chapter), mix equal quantities of water
and antifreeze to produce the 50/50 mixture
ratio specified when topping-up; if using any
other type of antifreeze, follow its
manufacturer’s instructions to achieve the
correct ratio. If only a small amount of coolant
is required to bring the system up to the
proper level, plain water can be used, but
repeatedly doing this will dilute the
antifreeze/water solution in the system,
reducing the protection it should provide
against freezing and corrosion. To maintainthe specified antifreeze/water ratio, it is
essential to top-up the coolant level with the
correct mixture, as described here. Use only
ethylene/glycol type antifreeze, and do not
use supplementary inhibitors or additives.
Warning: Never remove the
expansion tank filler cap when
the engine is running, or has just
been switched off, as the cooling system
will be hot, and the consequent escaping
steam and scalding coolant could cause
serious injury.
12If topping-up is necessary, wait until the
system has cooled completely (or at least 10
minutes after switching off the engine, if lack
of time means it is absolutely necessary to
top-up while the engine may still be warm).
Wrap a thick cloth around the expansion tank
filler cap, and unscrew it one full turn. If any
hissing is heard as steam escapes, wait until
the hissing ceases, indicating that pressure is
released, then slowly unscrew the filler cap
until it can be removed. If more hissing
sounds are heard, wait until they have
stopped before unscrewing the filler cap
completely. At all times, keep your face,
hands and other exposed skin well away from
the filler opening.
13When the filler cap has been removed,
add coolant to bring the level up to the “MAX”
level line (see illustration). Refit the cap,
tightening it securely.
14With this type of cooling system, the
addition of coolant should only be necessary at
very infrequent intervals. If topping-up is
regularly required, or if the coolant level drops
within a short time after replenishment, there
may be a leak in the system. Inspect the
radiator, hoses, expansion tank filler cap,
radiator drain plug and water pump. If no leak is
evident, have the filler cap and the entire
system pressure-tested by your dealer or
suitably-equipped garage; this will usually show
up a small leak not otherwise visible. If
significant leakage is found at any time, use an
antifreeze hydrometer to check the con-
centration of antifreeze remaining in the coolant.
1•7
13.13 Remove the cap to add coolant only
when the engine is cold - top-up to the
“MAX” level line using the specified
coolant mixture3.6 The yellow/black oil filler cap is
screwed into the cylinder head cover.
Always make sure the area around the
opening is clean before unscrewing the
cap, to prevent dirt from contaminating the
engine3.10 The cooling system expansion tank is
located on the right-hand side of the
engine compartment. The coolant level
must be between the tank “MAX” and
“MIN” level lines (arrowed) when the
engine is cold
Weekly checks
procarmanuals.com
Page 22 of 279
15Coolant hydrometers are available at
most automotive accessory shops. If the
specific gravity of a sample taken from the
expansion tank (when the engine is switched
off and fully cooled down) is less than that
specified, the coolant mixture strength has
fallen below the minimum. If this is found,
either the coolant strength must be restored
by adding neat antifreeze to Ford’s
specification (if that is what is in the system)
or by draining and flushing the system, then
refilling it with fresh coolant mixture of the
correct ratio (if any other type of antifreeze is
being used).
16When checking the coolant level, always
note its condition; it should be relatively clear.
If it is brown or rust-coloured, the system
should be drained, flushed and refilled. If
antifreeze has been used which does not
meet Ford’s specification, its corrosion
inhibitors will lose their effectiveness with
time; such coolant must be renewed regularly,
even if it appears to be in good condition,
usually at the intervals suggested at the
beginning of Section 2 of this Chapter.
Windscreen/tailgate and
headlight washer fluid
17Fluid for the windscreen/tailgate washer
system (and where applicable the headlight
washer system) is stored in a plastic reservoir,
which is located at the right front corner of the
engine compartment. In milder climates, plain
water can be used to top-up the reservoir, but
the reservoir should be kept no more than
two-thirds full, to allow for expansion should
the water freeze. In colder climates, the use of
a specially-formulated windscreen washer
fluid, available at your dealer or any car
accessory shop, will help lower the freezing
point of the fluid (see illustration). Do notuse
regular (engine) antifreeze - it will damage the
vehicle’s paintwork.
Battery electrolyte
18On models not equipped with a sealed
battery (see Section 9), check the electrolyte
level of all six battery cells. The level must be
approximately 10 mm above the plates; this
may be shown by maximum and minimum
level lines marked on the battery’s casing (seeillustration). If the level is low, use a coin to
release the filler/vent cap, and add distilled
water. Install and securely retighten the cap.
Caution: Overfilling the cells may
cause electrolyte to spill over
during periods of heavy charging,
causing corrosion or damage.
Refer also to the warning at the beginning
of Section 9.
Brake fluid
19The brake fluid reservoir is located on the
top of the brake master cylinder, which is
attached to the front of the vacuum servo unit.
The “MAX” and “MIN” marks are indicated on
the side of the translucent reservoir, and the
fluid level should be maintained between
these marks at all times (see illustration).
20The brake fluid inside the reservoir is
readily visible. With the vehicle on level
ground, the level should normally be on or just
below the “MAX” mark.
21Progressive wear of the brake pads and
brake shoe linings causes the level of the
brake fluid to gradually fall; however, when
the brake pads are renewed, the original level
of the fluid is restored. It is not therefore
necessary to top-up the level to compensate
for this minimal drop, but the level must never
be allowed to fall below the minimum mark.
22If topping-up is necessary, first wipe the
area around the filler cap with a clean rag
before removing the cap. When adding fluid,
pour it carefully into the reservoir, to avoid
spilling it on surrounding painted surfaces
(see illustration). Be sure to use only the
specified hydraulic fluid (see “Lubricants,
fluids and capacities”at the start of this
Chapter) since mixing different types of fluid
can cause damage to the system.
Warning: Brake hydraulic fluid
can harm your eyes and damage
painted surfaces, so use extreme
caution when handling and
pouring it. Wash off spills immediately with
plenty of water. Do not use fluid that has
been standing open for some time, as it
absorbs moisture from the air. Excessmoisture can cause corrosion and a
dangerous loss of braking effectiveness.
23When adding fluid, it is a good idea to
inspect the reservoir for contamination. The
system should be drained and refilled if
deposits, dirt particles or contamination are
seen in the fluid.
24After filling the reservoir to the correct
level, make sure that the cap is refitted
securely, to avoid leaks and the entry of
foreign matter.
25If the reservoir requires repeated
replenishing to maintain the correct level, this
is an indication of an hydraulic leak
somewhere in the system, which should be
investigated immediately.
Power steering fluid
26See Section 5 of this Chapter.
1Periodic inspection of the tyres may spare
you from the inconvenience of being stranded
with a flat tyre. It can also provide you with
vital information regarding possible problems
in the steering and suspension systems
before major damage occurs.
2The original tyres on this vehicle are
equipped with tread wear indicator (TWI)
bands, which will appear when the tread
depth reaches approximately 1.6 mm. Most
tyres have a mark around the tyre at regular
intervals to indicate the location of the tread
4 Tyre and tyre pressure checks
1•8
3.17 Topping-up the windscreen washer
reservoir3.18 On non-sealed batteries, keep the
electrolyte level of all the cells in the
battery between the maximum and
minimum levels (arrowed) - ie, 10 mm
above the plates. Use only distilled water,
and never overfill3.19 Brake fluid reservoir, showing “MAX”
and “MIN” marks
3.22 Topping-up the brake fluid reservoir
Weekly checks
procarmanuals.com
Page 28 of 279
being felt when its pulley is rotated clockwise,
and a smooth return to the limit of its travel
when released.
11If the original drivebelt is being refitted,
use the marks or notes made on removal, to
ensure that it is installed to run in the same
direction as it was previously. To fit the
drivebelt, arrange it on the grooved pulleys so
that it is centred in their grooves, and not
overlapping their raised sides (note that the
flat surface of the drivebelt is engaged on the
idler, tensioner and water pump pulleys) and
routed correctly (see illustrations). Start at
the top, and work down to finish at the
crankshaft pulley; rotate the tensioner pulley
clockwise, slip the drivebelt onto the
crankshaft pulley, then release the tensioner
again.
12Using a spanner applied to the crankshaft
pulley bolt, rotate the crankshaft through at
least two full turns clockwise to settle the
drivebelt on the pulleys, then check that the
drivebelt is properly installed.
13Refit the auxiliary drivebelt cover and
roadwheel, then lower the vehicle to the
ground.
Caution: Renewal of air
conditioning hoses must be left
to a dealer service department or
air conditioning specialist who has the
equipment to depressurise the systemsafely. Never remove air conditioning
components or hoses until the system has
been depressurised.
General
1High temperatures in the engine
compartment can cause the deterioration of
the rubber and plastic hoses used for engine,
accessory and emission systems operation.
Periodic inspection should be made for
cracks, loose clamps, material hardening and
leaks.
2Carefully check the large top and bottom
radiator hoses, along with the other smaller-
diameter cooling system hoses and metal
pipes; do not forget the heater hoses/pipes
which run from the engine to the bulkhead,
and those to the engine oil cooler (where
fitted). Inspect each hose along its entire
length, replacing any that is cracked, swollen
or shows signs of deterioration. Cracks may
become more apparent if the hose is
squeezed (see illustration). If you are using
non-Ford specification antifreeze, and so
have to renew the coolant every two years or
so, it’s a good idea to renew the hoses at that
time, regardless of their apparent condition.
3Make sure that all hose connections are
tight. A leak in the cooling system will usually
show up as white- or rust-coloured deposits
on the areas adjoining the leak; if the spring
clamps that are used to secure the hoses in
this system appear to be slackening, they
should be renewed to prevent the possibility
of leaks.
4Some other hoses are secured to theirfittings with clamps. Where clamps are used,
check to be sure they haven’t lost their
tension, allowing the hose to leak. If clamps
aren’t used, make sure the hose has not
expanded and/or hardened where it slips over
the fitting, allowing it to leak.
12 Underbonnet check for fluid
leaks and hose condition
1•14
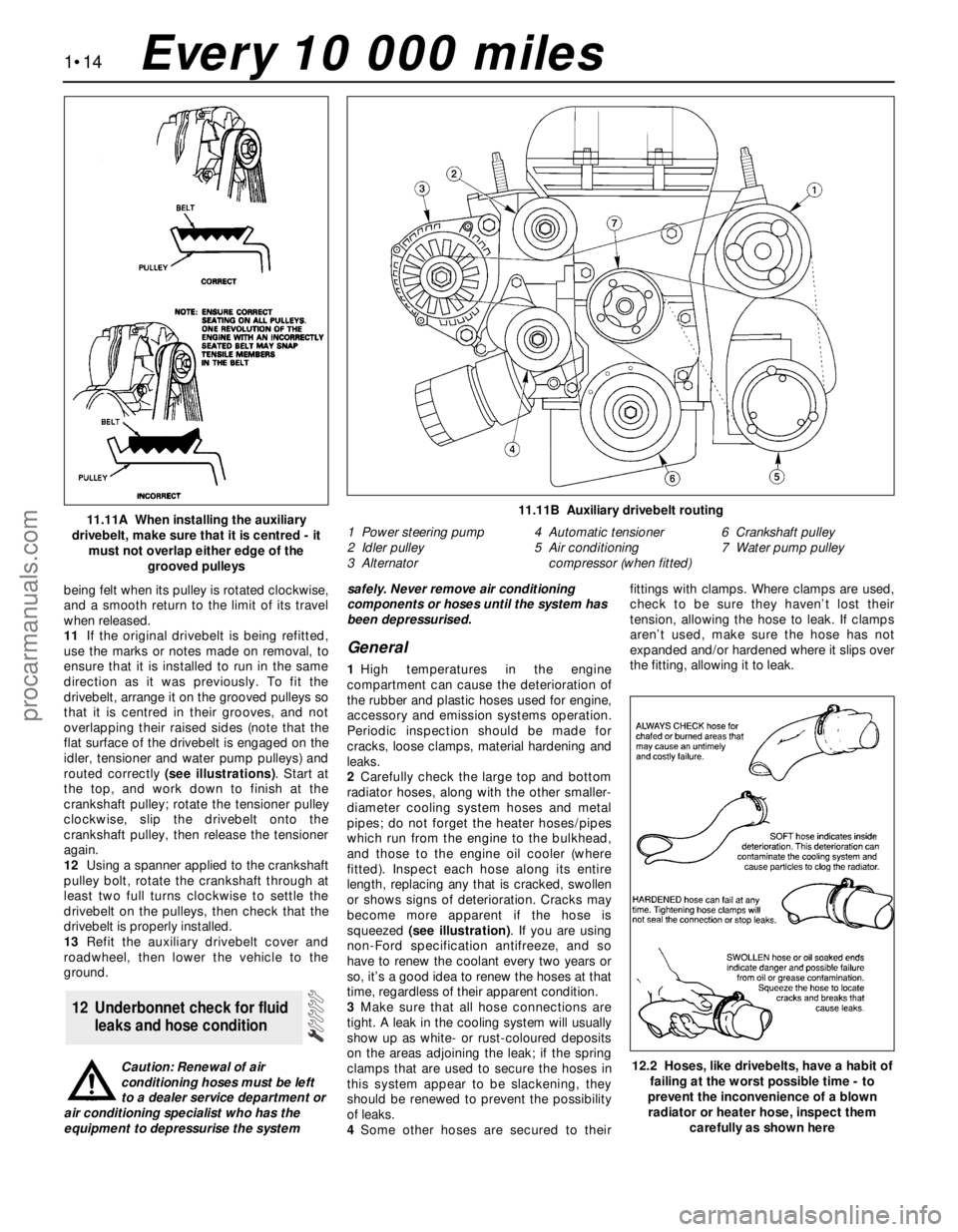
11.11A When installing the auxiliary
drivebelt, make sure that it is centred - it
must not overlap either edge of the
grooved pulleys11.11B Auxiliary drivebelt routing
1 Power steering pump
2 Idler pulley
3 Alternator4 Automatic tensioner
5 Air conditioning
compressor (when fitted)6 Crankshaft pulley
7 Water pump pulley
12.2 Hoses, like drivebelts, have a habit of
failing at the worst possible time - to
prevent the inconvenience of a blown
radiator or heater hose, inspect them
carefully as shown here
Every 10 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 29 of 279
5Check all fluid reservoirs, filler caps, drain
plugs and fittings etc, looking for any signs of
leakage of oil, transmission and/or brake
hydraulic fluid, coolant and power steering
fluid. If the vehicle is regularly parked in the
same place, close inspection of the ground
underneath it will soon show any leaks; ignore
the puddle of water which will be left if the air
conditioning system is in use. As soon as a
leak is detected, its source must be traced
and rectified. Where oil has been leaking for
some time, it is usually necessary to use a
steam cleaner, pressure washer or similar, to
clean away the accumulated dirt, so that the
exact source of the leak can be identified.
Vacuum hoses
6It’s quite common for vacuum hoses,
especially those in the emissions system, to
be colour-coded, or to be identified by
coloured stripes moulded into them. Various
systems require hoses with different wall
thicknesses, collapse resistance and
temperature resistance. When renewing
hoses, be sure the new ones are made of the
same material.
7Often the only effective way to check a
hose is to remove it completely from the
vehicle. If more than one hose is removed, be
sure to label the hoses and fittings to ensure
correct installation.
8When checking vacuum hoses, be sure to
include any plastic T-fittings in the check.
Inspect the fittings for cracks, and check the
hose where it fits over the fitting for distortion,
which could cause leakage.
9A small piece of vacuum hose (quarter-inch
inside diameter) can be used as a
stethoscope to detect vacuum leaks. Hold
one end of the hose to your ear, and probe
around vacuum hoses and fittings, listening
for the “hissing” sound characteristic of a
vacuum leak.
Warning: When probing with the
vacuum hose stethoscope, be
very careful not to come into
contact with moving engine
components such as the auxiliary
drivebelt, radiator electric cooling fan, etc.
Fuel hoses
Warning: There are certain
precautions which must be taken
when inspecting or servicing fuel
system components. Work in a well-
ventilated area, and do not allow open
flames (cigarettes, appliance pilot lights,
etc.) or bare light bulbs near the work
area. Mop up any spills immediately, and
do not store fuel-soaked rags where they
could ignite.
10Check all fuel hoses for deterioration and
chafing. Check especially for cracks in areas
where the hose bends, and also just before
fittings, such as where a hose attaches to the
fuel filter.
11High-quality fuel line, usually identified by
the word “Fluoroelastomer” printed on thehose, should be used for fuel line renewal.
Never, under any circumstances, use
unreinforced vacuum line, clear plastic tubing
or water hose for fuel lines.
12Spring-type clamps are commonly used
on fuel lines. These clamps often lose their
tension over a period of time, and can be
“sprung” during removal. Replace all
spring-type clamps with screw clamps
whenever a hose is replaced.
Metal lines
13Sections of metal piping are often used
for fuel line between the fuel filter and the
engine. Check carefully to be sure the piping
has not been bent or crimped, and that cracks
have not started in the line.
14If a section of metal fuel line must be
renewed, only seamless steel piping should
be used, since copper and aluminium piping
don’t have the strength necessary to
withstand normal engine vibration.
15Check the metal brake lines where they
enter the master cylinder and ABS hydraulic
unit (if used) for cracks in the lines or loose
fittings. Any sign of brake fluid leakage calls
for an immediate and thorough inspection of
the brake system.
1With the vehicle parked on level ground,
apply the handbrake firmly and open the
bonnet. Using an inspection light or a small
electric torch, check all visible wiring within
and beneath the engine compartment.
2What you are looking for is wiring that is
obviously damaged by chafing against sharp
edges, or against moving suspension/
transmission components and/or the auxiliary
drivebelt, by being trapped or crushed
between carelessly-refitted components, or
melted by being forced into contact with the
hot engine castings, coolant pipes, etc. In
almost all cases, damage of this sort is
caused in the first instance by incorrect
routing on reassembly after previous work has
been carried out.
3Depending on the extent of the problem,
damaged wiring may be repaired by rejoining
the break or splicing-in a new length of wire,
using solder to ensure a good connection,
and remaking the insulation with adhesive
insulating tape or heat-shrink tubing, as
appropriate. If the damage is extensive, given
the implications for the vehicle’s future
reliability, the best long-term answer may well
be to renew that entire section of the loom,
however expensive this may appear.
4When the actual damage has been
repaired, ensure that the wiring loom is re-
routed correctly, so that it is clear of other
components, and not stretched or kinked, and
is secured out of harm’s way using the plastic
clips, guides and ties provided.
5Check all electrical connectors, ensuringthat they are clean, securely fastened, and
that each is locked by its plastic tabs or wire
clip, as appropriate. If any connector shows
external signs of corrosion (accumulations of
white or green deposits, or streaks of “rust”),
or if any is thought to be dirty, it must be
unplugged and cleaned using electrical
contact cleaner. If the connector pins are
severely corroded, the connector must be
renewed; note that this may mean the renewal
of that entire section of the loom - see your
local Ford dealer for details.
6If the cleaner completely removes the
corrosion to leave the connector in a
satisfactory condition, it would be wise to
pack the connector with a suitable material
which will exclude dirt and moisture,
preventing the corrosion from occurring
again; a Ford dealer may be able to
recommend a suitable product.
7Check the condition of the battery
connections - remake the connections or
renew the leads if a fault is found (see Chap-
ter 5). Use the same techniques to ensure that
all earth points in the engine compartment
provide good electrical contact through clean,
metal-to-metal joints, and that all are securely
fastened. (In addition to the earth connection
at the engine lifting eye, and that from the
transmission to the body/battery, there are
one or two earth points behind each headlight
assembly, and one below the power steering
fluid reservoir.)
8Refer to Section 31 for details of spark plug
(HT) lead checks.
Warning: The air conditioning
system is under high pressure.
Do not loosen any fittings or
remove any components until
after the system has been discharged. Air
conditioning refrigerant must be properly
discharged into an approved type of
container, at a dealer service department
or an automotive air conditioning repair
facility capable of handling R134a
refrigerant. Always wear eye protection
when disconnecting air conditioning
system fittings.
1The following maintenance checks should
be performed on a regular basis, to ensure
that the air conditioner continues to operate at
peak efficiency:
(a) Check the auxiliary drivebelt. If it’s worn
or deteriorated, renew it (see Section 11).
(b) Check the system hoses. Look for cracks,
bubbles, hard spots and deterioration.
Inspect the hoses and all fittings for oil
bubbles and seepage. If there’s any
evidence of wear, damage or leaks, renew
the hose(s).
(c) Inspect the condenser fins for leaves,
insects and other debris. Use a “fin
14 Air conditioning system
check
13 Engine compartment wiring
check
1•15
1
Every 10 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 35 of 279

pleated-paper type filter, it cannot be washed
or re-oiled. If it cannot be cleaned
satisfactorily with compressed air, discard
and renew it.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
8Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure; ensure that the element and
housing are securely seated, so that unfiltered
air cannot enter the passenger compartment.
Note:If the antifreeze used is Ford’s own, or of
similar quality, the coolant need not be
renewed for the life of the vehicle. If the
vehicle’s history is unknown, if antifreeze of
lesser quality is known to be in the system, or
simply if you prefer to follow conventional
servicing intervals, the coolant should be
changed periodically (typically, every 2 years)
as described here. Refer also to the
information in Section 2 of this Chapter.
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze
to come in contact with your skin
or painted surfaces of the
vehicle. Flush contaminated areas
immediately with plenty of water. Don’t
store new coolant, or leave old coolant
lying around, where it’s accessible to
children or pets - they’re attracted by its
sweet smell. Ingestion of even a small
amount of coolant can be fatal! Wipe up
garage-floor and drip-pan spills
immediately. Keep antifreeze containers
covered, and repair cooling system leaks
as soon as they’re noticed.
Warning: Never remove the
expansion tank filler cap when
the engine is running, or has just
been switched off, as the cooling system
will be hot, and the consequent escaping
steam and scalding coolant could cause
serious injury.
Coolant draining
Warning: Wait until the engine is
cold before starting this
procedure.1To drain the system, first remove the
expansion tank filler cap (see Section 3).
2If the additional working clearance is
required, raise the front of the vehicle and
support it securely on axle stands.
3Remove the radiator undershield (eight or
nine screws), then place a large drain tray
underneath, and unscrew the radiator drain
plug; direct as much of the escaping coolant
as possible into the tray (see illustrations).
System flushing
4With time, the cooling system may
gradually lose its efficiency, as the radiator
core becomes choked with rust, scale
deposits from the water, and other sediment
(refer also to the information at the start of
Section 2). To minimise this, as well as using
only good-quality antifreeze and clean soft
water, the system should be flushed as
follows whenever any part of it is disturbed,
and/or when the coolant is renewed.
5With the coolant drained, refit the drain plug
and refill the system with fresh water. Refit the
expansion tank filler cap, start the engine and
warm it up to normal operating temperature,
then stop it and (after allowing it to cool down
completely) drain the system again. Repeat as
necessary until only clean water can be seen
to emerge, then refill finally with the specified
coolant mixture.
6If only clean, soft water and good-quality
antifreeze (even if not to Ford’s specification)
has been used, and the coolant has been
renewed at the suggested intervals, the above
procedure will be sufficient to keep clean the
system for a considerable length of time. If,however, the system has been neglected, a
more thorough operation will be required, as
follows.
7First drain the coolant, then disconnect the
radiator top and bottom hoses. Insert a
garden hose into the top hose, and allow
water to circulate through the radiator until it
runs clean from the bottom outlet.
8To flush the engine, insert the garden hose
into the thermostat water outlet, and allow
water to circulate until it runs clear from the
bottom hose. If, after a reasonable period, the
water still does not run clear, the radiator
should be flushed with a good proprietary
cleaning agent.
9In severe cases of contamination, reverse-
flushing of the radiator may be necessary. To
do this, remove the radiator (Chapter 3), invert
it, and insert the garden hose into the bottom
outlet. Continue flushing until clear water runs
from the top hose outlet. A similar procedure
can be used to flush the heater matrix.
10The use of chemical cleaners should be
necessary only as a last resort. Normally,
regular renewal of the coolant will prevent
excessive contamination of the system.
Coolant filling
11With the cooling system drained and
flushed, ensure that all disturbed hose unions
28 Coolant renewal
1•21
1
28.3A Remove the screws (arrowed) and
withdraw the radiator undershield . . .
28.3B . . . to unscrew the radiator drain
plug (arrowed) and empty the cooling
system. Try to protect yourself from
coolant splashing into your eyes or onto
your skin, catching as much of it as
possible in the drain tray
27.3 Remove screws (arrowed) to release
cowl grille panel . . .27.5A . . . release clips to lift out pollen
filter housing . . .27.5B . . . then withdraw pollen filter
element
Every 20 000 miles
procarmanuals.com