1993 FORD MONDEO automatic transmission
[x] Cancel search: automatic transmissionPage 3 of 279

REPAIRS & OVERHAUL
Engine and Associated Systems
In-car engine repair procedures Page 2A•1
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures Page 2B•1
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems Page3•1
Fuel and exhaust systems Page 4•1
Engine electrical systems Page 5•1
Emissions control systems Page 6•1
Transmission
Manual transmission Page 7A•1
Automatic transmission Page7B•1
Clutch and driveshafts Page 8•1
Brakes
Braking systemPage 9•1
Suspension
Suspension and steering systems Page 10•1
Body Equipment
Bodywork and fittings Page 11•1
Electrical
Body electrical systems Page 12•1
Wiring DiagramsPage 12•24
REFERENCE
Tools and Working Facilities Page REF• 1
General Repair Procedures Page REF• 4
Buying spare parts and vehicle identification numbers PageREF• 5
Fault FindingPage REF• 6
Glossary of Technical Terms PageREF•13
IndexPage REF•17
Contents
procarmanuals.com
Page 4 of 279

0•4Introduction
Introduced in March 1993, the Ford
Mondeo models are available in four-door
Saloon, five-door Hatchback and five-door
Estate configurations. All feature a high
standard of equipment, with driver/passenger
safety in accidents being a particularly high
design priority; all models are fitted with
features such as side impact bars in all doors,
“anti-submarine” seats combined with “seatbelt grabbers” and pre-tensioners, and an
airbag fitted to the steering wheel. Vehicle
security is enhanced, with an in-built alarm
system and engine immobiliser being fitted as
standard, as well as double-locking doors
with shielded locks, and security-coded audio
equipment.
The four-cylinder petrol engine is a new
design, available in 1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 litrecapacities. It is controlled by a sophisticated
engine management system, which combines
multi-point sequential fuel injection and
distributorless ignition systems with
evaporative emissions control, exhaust gas
recirculation and a three-way regulated
catalytic converter (with a pulse-air system for
rapid warm-up) to ensure that the vehicle
complies with the most stringent of the
emissions control standards currently in force,
and yet provides the levels of performance
and fuel economy expected.
The transversely-mounted engine drives
the front roadwheels through either a five-
speed manual transmission with a cable-
operated clutch, or through an electronically-
controlled four-speed automatic transmission.
The fully-independent suspension is by
MacPherson strut on all four roadwheels,
located by transverse lower arms at the front,
and by transverse and trailing arms at the rear;
anti-roll bars are fitted at front and rear. The
Estate rear suspension is of a different design,
to give maximum loadspace inside the
vehicle, with self-levelling suspension units
available as an option. On some models, the
suspension is electronically-controlled
through the Adaptive Damping System.
The steering is power-assisted, the pump
being belt-driven from the engine, and the
rack-and-pinion steering gear mounted
behind the engine.
The vacuum servo-assisted brakes are disc
at the front, with drums at the rear on most
models; disc rear brakes and an
electronically-controlled Anti-lock Braking
System (ABS) are available on some models,
with a Traction Control System (TCS) available
as a further option where ABS is fitted.
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to Champion Spark Plug,
who supplied the illustrations showing spark
plug conditions. Certain other illustrations are
the copyright of the Ford Motor Company,
and are used with their permission. Thanks
are also due to Sykes-Pickavant Limited, who
provided some of the workshop tools, and to
all those people at Sparkford who helped in
the production of this manual.
Project vehicles
The main project vehicle used in the
preparation of this manual, and appearing in
many of the photographic sequences, was a
1993-model Ford Mondeo 2.0 Si Hatchback.
Additional work was carried out and
photographed on a 1993-model 2.0 Si Saloon
and a 1993-model 2.0 Ghia Estate (with
automatic transmission).
Introduction to the Ford Mondeo
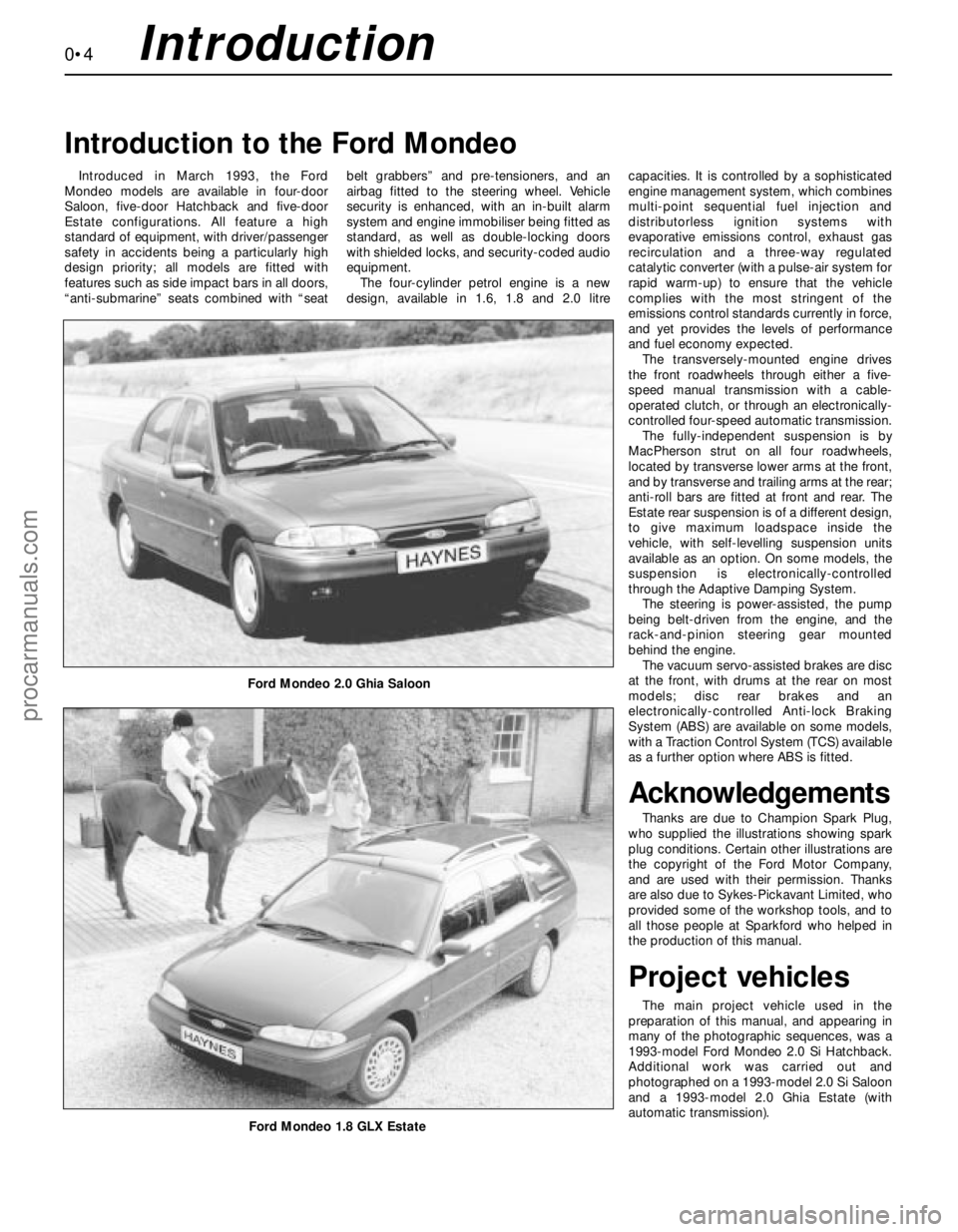
Ford Mondeo 2.0 Ghia Saloon
Ford Mondeo 1.8 GLX Estate
procarmanuals.com
Page 5 of 279

Working on your car can be dangerous.
This page shows just some of the potential
risks and hazards, with the aim of creating a
safety-conscious attitude.
General hazards
Scalding
• Don’t remove the radiator or expansion
tank cap while the engine is hot.
• Engine oil, automatic transmission fluid or
power steering fluid may also be dangerously
hot if the engine has recently been running.
Burning
• Beware of burns from the exhaust system
and from any part of the engine. Brake discs
and drums can also be extremely hot
immediately after use.
Crushing
• When working under or near
a raised vehicle, always
supplement the
jack with axle
stands, or use
drive-on ramps.
Never venture
under a car
which is only
supported by
a jack.
• Take care if loosening or tightening high-
torque nuts when the vehicle is on stands.
Initial loosening and final tightening should
be done with the wheels on the ground.
Fire
• Fuel is highly flammable; fuel vapour is
explosive.
• Don’t let fuel spill onto a hot engine.
• Do not smoke or allow naked lights
(including pilot lights) anywhere near a
vehicle being worked on. Also beware of
creating sparks
(electrically or by use of tools).
• Fuel vapour is heavier than air, so don’t
work on the fuel system with the vehicle over
an inspection pit.
• Another cause of fire is an electrical
overload or short-circuit. Take care when
repairing or modifying the vehicle wiring.
• Keep a fire extinguisher handy, of a type
suitable for use on fuel and electrical fires.
Electric shock
• Ignition HT
voltage can be
dangerous,
especially to
people with
heart problems
or a pacemaker.
Don’t work on or
near the ignition
system with the
engine running or the
ignition switched on.• Mains voltage is also dangerous. Make
sure that any mains-operated equipment is
correctly earthed. Mains power points should
be protected by a residual current device
(RCD) circuit breaker.
Fume or gas intoxication
• Exhaust fumes are
poisonous; they often
contain carbon
monoxide, which is
rapidly fatal if inhaled.
Never run the
engine in a
confined space
such as a garage
with the doors shut.
• Fuel vapour is also
poisonous, as are the vapours from some
cleaning solvents and paint thinners.
Poisonous or irritant substances
• Avoid skin contact with battery acid and
with any fuel, fluid or lubricant, especially
antifreeze, brake hydraulic fluid and Diesel
fuel. Don’t syphon them by mouth. If such a
substance is swallowed or gets into the eyes,
seek medical advice.
• Prolonged contact with used engine oil can
cause skin cancer. Wear gloves or use a
barrier cream if necessary. Change out of oil-
soaked clothes and do not keep oily rags in
your pocket.
• Air conditioning refrigerant forms a
poisonous gas if exposed to a naked flame
(including a cigarette). It can also cause skin
burns on contact.
Asbestos
• Asbestos dust can cause cancer if inhaled
or swallowed. Asbestos may be found in
gaskets and in brake and clutch linings.
When dealing with such components it is
safest to assume that they contain asbestos.
Special hazards
Hydrofluoric acid
• This extremely corrosive acid is formed
when certain types of synthetic rubber, found
in some O-rings, oil seals, fuel hoses etc, are
exposed to temperatures above 400
0C. The
rubber changes into a charred or sticky
substance containing the acid. Once formed,
the acid remains dangerous for years. If it
gets onto the skin, it may be necessary to
amputate the limb concerned.
• When dealing with a vehicle which has
suffered a fire, or with components salvaged
from such a vehicle, wear protective gloves
and discard them after use.
The battery
• Batteries contain sulphuric acid, which
attacks clothing, eyes and skin. Take care
when topping-up or carrying the battery.
• The hydrogen gas given off by the battery
is highly explosive. Never cause a spark or
allow a naked light nearby. Be careful when
connecting and disconnecting battery
chargers or jump leads.
Air bags
• Air bags can cause injury if they go off
accidentally. Take care when removing the
steering wheel and/or facia. Special storage
instructions may apply.
Diesel injection equipment
• Diesel injection pumps supply fuel at very
high pressure. Take care when working on
the fuel injectors and fuel pipes.
Warning: Never expose the
hands, face or any other part of
the body to injector spray; the
fuel can penetrate the skin with
potentially fatal results.
Remember...
DO
• Do use eye protection when using power
tools, and when working under the vehicle.
• Do wear gloves or use barrier cream to
protect your hands when necessary.
• Do get someone to check periodically
that all is well when working alone on the
vehicle.
• Do keep loose clothing and long hair well
out of the way of moving mechanical parts.
• Do remove rings, wristwatch etc, before
working on the vehicle – especially the
electrical system.
• Do ensure that any lifting or jacking
equipment has a safe working load rating
adequate for the job.
A few tips
DON’T
• Don’t attempt to lift a heavy component
which may be beyond your capability – get
assistance.
• Don’t rush to finish a job, or take
unverified short cuts.
• Don’t use ill-fitting tools which may slip
and cause injury.
• Don’t leave tools or parts lying around
where someone can trip over them. Mop
up oil and fuel spills at once.
• Don’t allow children or pets to play in or
near a vehicle being worked on.
0•5Safety First!
procarmanuals.com
Page 6 of 279

0•6General Dimensions & Weights
Dimensions
Overall length:
Saloon, Hatchback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4481 mm
Estate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4631 mm
Overall width - including mirrors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1925 mm
Overall height - at kerb weight:
Saloon, Hatchback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1403 to 1435 mm
Estate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1416 to 1501 mm
Wheelbase . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2704 mm
Front track - all models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1503 mm
Rear track:
Saloon, Hatchback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1486 to 1487 mm
Estate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1504 mm
Turning circle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.9 m
Weights
Kerb weight:
1.6 Saloon, Hatchback models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1215 to 1250 kg
1.6 Estate models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1265 to 1275 kg
1.8 Saloon, Hatchback models:
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1225 to 1260 kg
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1260 to 1280 kg
1.8 Estate models:
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1275 to 1285 kg
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1305 kg
2.0 Saloon, Hatchback models:
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1250 to 1310 kg
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1285 to 1340 kg
2.0 Estate models:
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1295 to 1335 kg
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1330 to 1415 kg
Maximum gross vehicle weight:
Saloon, Hatchback:
1.6 models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1725 kg
1.8 Saloon models, automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1750 kg
2.0 models, automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1800 kg
All others . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1775 kg
Estate:
1.6 models, 2.0 models with manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . 1900 kg
All others . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1925 kg
Maximum roof rack load:
Estate models with integral roof rack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100 kg
All others . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75 kg
Maximum towing weight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1500 kg
Trailer nose weight limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75 kg
procarmanuals.com
Page 11 of 279
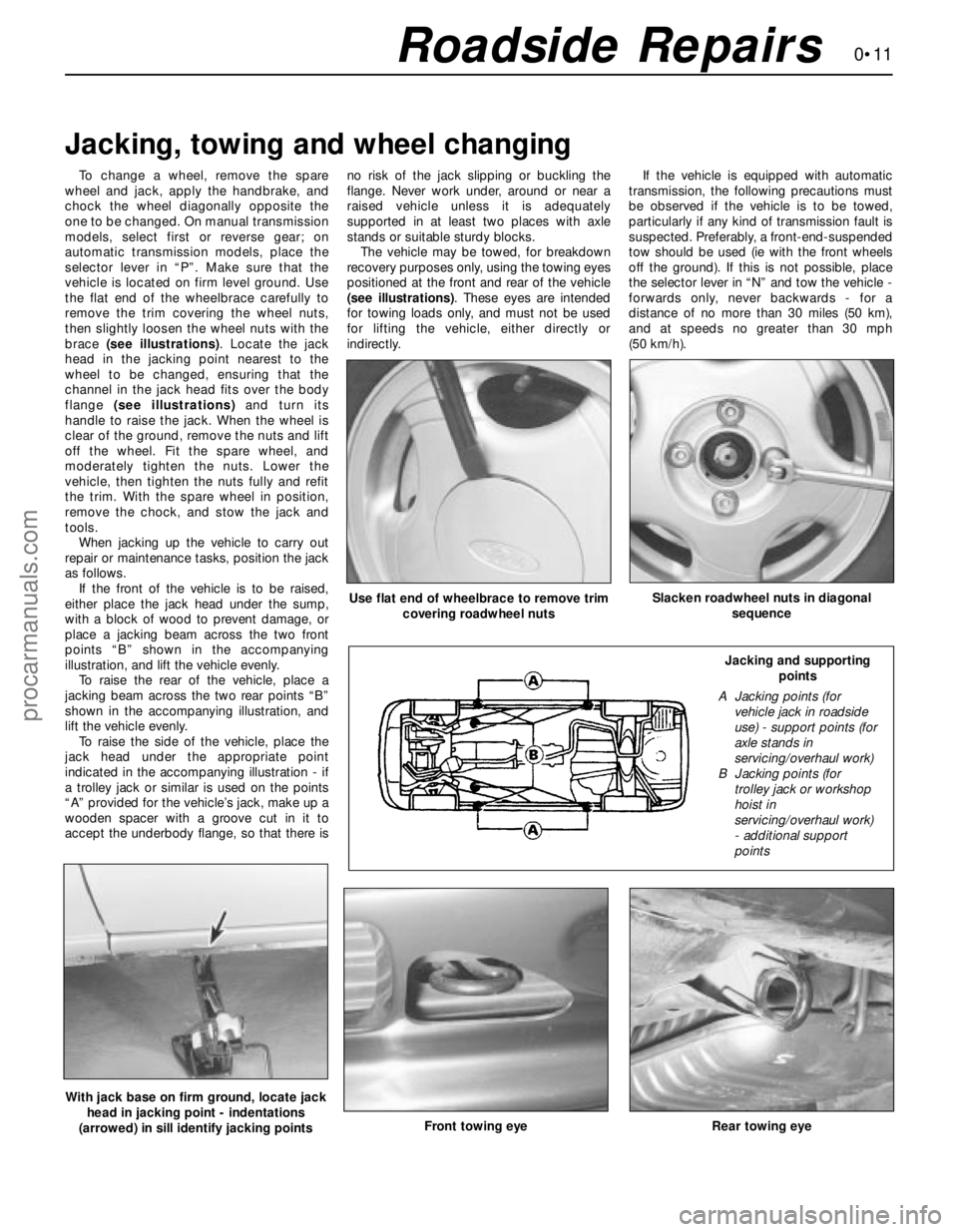
0•11Roadside Repairs
To change a wheel, remove the spare
wheel and jack, apply the handbrake, and
chock the wheel diagonally opposite the
one to be changed. On manual transmission
models, select first or reverse gear; on
automatic transmission models, place the
selector lever in “P”. Make sure that the
vehicle is located on firm level ground. Use
the flat end of the wheelbrace carefully to
remove the trim covering the wheel nuts,
then slightly loosen the wheel nuts with the
brace (see illustrations). Locate the jack
head in the jacking point nearest to the
wheel to be changed, ensuring that the
channel in the jack head fits over the body
flange (see illustrations)and turn its
handle to raise the jack. When the wheel is
clear of the ground, remove the nuts and lift
off the wheel. Fit the spare wheel, and
moderately tighten the nuts. Lower the
vehicle, then tighten the nuts fully and refit
the trim. With the spare wheel in position,
remove the chock, and stow the jack and
tools.
When jacking up the vehicle to carry out
repair or maintenance tasks, position the jack
as follows.
If the front of the vehicle is to be raised,
either place the jack head under the sump,
with a block of wood to prevent damage, or
place a jacking beam across the two front
points “B” shown in the accompanying
illustration, and lift the vehicle evenly.
To raise the rear of the vehicle, place a
jacking beam across the two rear points “B”
shown in the accompanying illustration, and
lift the vehicle evenly.
To raise the side of the vehicle, place the
jack head under the appropriate point
indicated in the accompanying illustration - if
a trolley jack or similar is used on the points
“A” provided for the vehicle’s jack, make up a
wooden spacer with a groove cut in it to
accept the underbody flange, so that there isno risk of the jack slipping or buckling the
flange. Never work under, around or near a
raised vehicle unless it is adequately
supported in at least two places with axle
stands or suitable sturdy blocks.
The vehicle may be towed, for breakdown
recovery purposes only, using the towing eyes
positioned at the front and rear of the vehicle
(see illustrations). These eyes are intended
for towing loads only, and must not be used
for lifting the vehicle, either directly or
indirectly.If the vehicle is equipped with automatic
transmission, the following precautions must
be observed if the vehicle is to be towed,
particularly if any kind of transmission fault is
suspected. Preferably, a front-end-suspended
tow should be used (ie with the front wheels
off the ground). If this is not possible, place
the selector lever in “N” and tow the vehicle -
forwards only, never backwards - for a
distance of no more than 30 miles (50 km),
and at speeds no greater than 30 mph
(50 km/h).
Jacking, towing and wheel changing
Front towing eyeRear towing eye
Use flat end of wheelbrace to remove trim
covering roadwheel nutsSlacken roadwheel nuts in diagonal
sequence
With jack base on firm ground, locate jack
head in jacking point - indentations
(arrowed) in sill identify jacking points
Jacking and supporting
points
A Jacking points (for
vehicle jack in roadside
use) - support points (for
axle stands in
servicing/overhaul work)
B Jacking points (for
trolley jack or workshop
hoist in
servicing/overhaul work)
- additional support
points
procarmanuals.com
Page 12 of 279
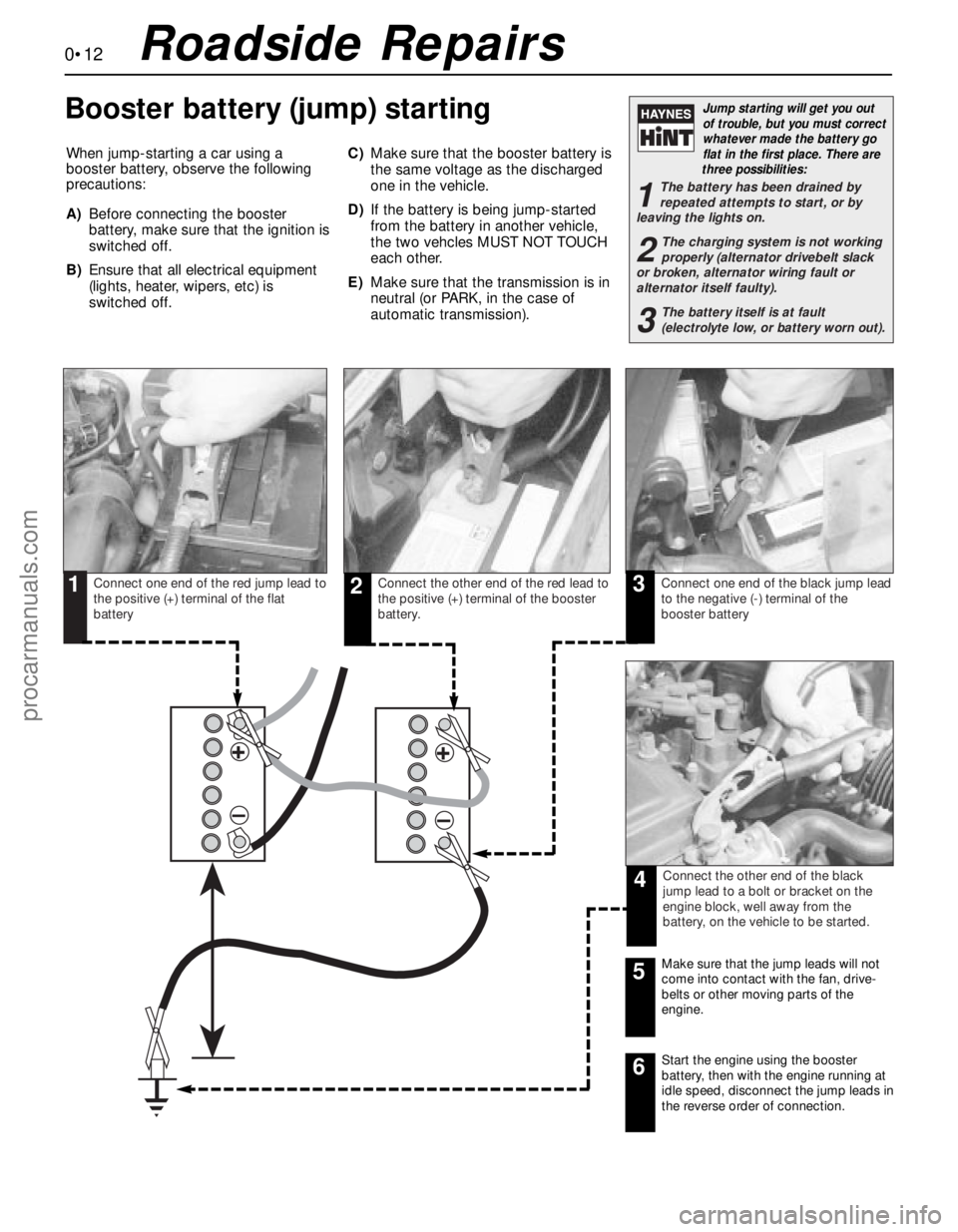
0•12
When jump-starting a car using a
booster battery, observe the following
precautions:
A)Before connecting the booster
battery, make sure that the ignition is
switched off.
B)Ensure that all electrical equipment
(lights, heater, wipers, etc) is
switched off.C)Make sure that the booster battery is
the same voltage as the discharged
one in the vehicle.
D)If the battery is being jump-started
from the battery in another vehicle,
the two vehcles MUST NOT TOUCH
each other.
E)Make sure that the transmission is in
neutral (or PARK, in the case of
automatic transmission).
Jump starting will get you out
of trouble, but you must correct
whatever made the battery go
flat in the first place. There are
three possibilities:
1The battery has been drained by
repeated attempts to start, or by
leaving the lights on.
2The charging system is not working
properly (alternator drivebelt slack
or broken, alternator wiring fault or
alternator itself faulty).
3The battery itself is at fault
(electrolyte low, or battery worn out).
Connect one end of the red jump lead to
the positive (+) terminal of the flat
batteryConnect the other end of the red lead to
the positive (+) terminal of the booster
battery.Connect one end of the black jump lead
to the negative (-) terminal of the
booster battery
Connect the other end of the black
jump lead to a bolt or bracket on the
engine block, well away from the
battery, on the vehicle to be started.
123
4
Make sure that the jump leads will not
come into contact with the fan, drive-
belts or other moving parts of the
engine.5
Start the engine using the booster
battery, then with the engine running at
idle speed, disconnect the jump leads in
the reverse order of connection.6
Roadside Repairs
Booster battery (jump) starting
procarmanuals.com
Page 15 of 279

Chapter 1 Routine maintenance and servicing
Air conditioning system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Air filter element renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Automatic transmission fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Automatic transmission linkage lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Auxiliary drivebelt check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Battery check, maintenance and charging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Brake check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Brake fluid renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Clutch pedal adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Coolant renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2, 28
Door and bonnet check and lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Driveshaft rubber gaiter and CV joint check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Electrical system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Engine compartment wiring check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Engine oil and filter change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Exhaust system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Fluid level checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Fuel filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Idle speed and mixture check and adjustment . . . . . . See Chapter 4Ignition timing check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 5
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Manual transmission oil level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system check
and filter cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Power steering fluid level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Road test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Roadwheel nut tightness check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Seat belt check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Spark plug renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See end of Chapter
Steering, suspension and roadwheel check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Timing belt renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Tyre and tyre pressure checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Underbody and fuel/brake line check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Underbonnet check for fluid leaks and hose condition . . . . . . . . . . 12
Ventilation system pollen filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Windscreen/tailgate washer system and wiper blade check . . . . . . 6
1•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,suitable
for competent DIY
mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty Contents
1
procarmanuals.com
Page 16 of 279
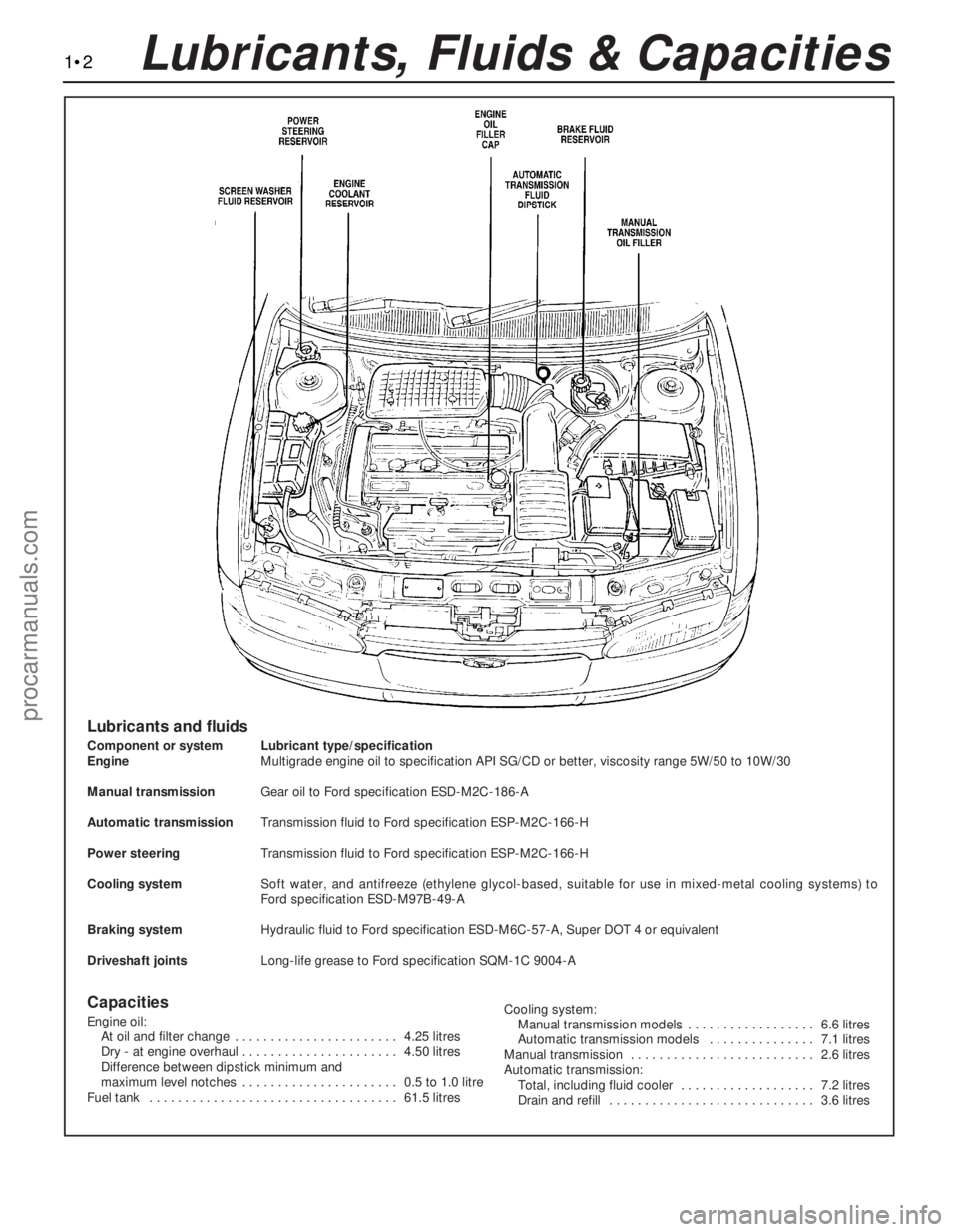
1•2Lubricants, Fluids & Capacities
Lubricants and fluids
Component or system Lubricant type/specification
EngineMultigrade engine oil to specification API SG/CD or better, viscosity range 5W/50 to 10W/30
Manual transmissionGear oil to Ford specification ESD-M2C-186-A
Automatic transmissionTransmission fluid to Ford specification ESP-M2C-166-H
Power steeringTransmission fluid to Ford specification ESP-M2C-166-H
Cooling systemSoft water, and antifreeze (ethylene glycol-based, suitable for use in mixed-metal cooling systems) to
Ford specification ESD-M97B-49-A
Braking systemHydraulic fluid to Ford specification ESD-M6C-57-A, Super DOT 4 or equivalent
Driveshaft jointsLong-life grease to Ford specification SQM-1C 9004-A
Capacities
Engine oil:
At oil and filter change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.25 litres
Dry - at engine overhaul . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.50 litres
Difference between dipstick minimum and
maximum level notches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5 to 1.0 litre
Fuel tank . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61.5 litresCooling system:
Manual transmission models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.6 litres
Automatic transmission models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.1 litres
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.6 litres
Automatic transmission:
Total, including fluid cooler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7.2 litres
Drain and refill . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.6 litres
procarmanuals.com