2006 DODGE RAM SRT-10 Compression
[x] Cancel search: CompressionPage 1505 of 5267
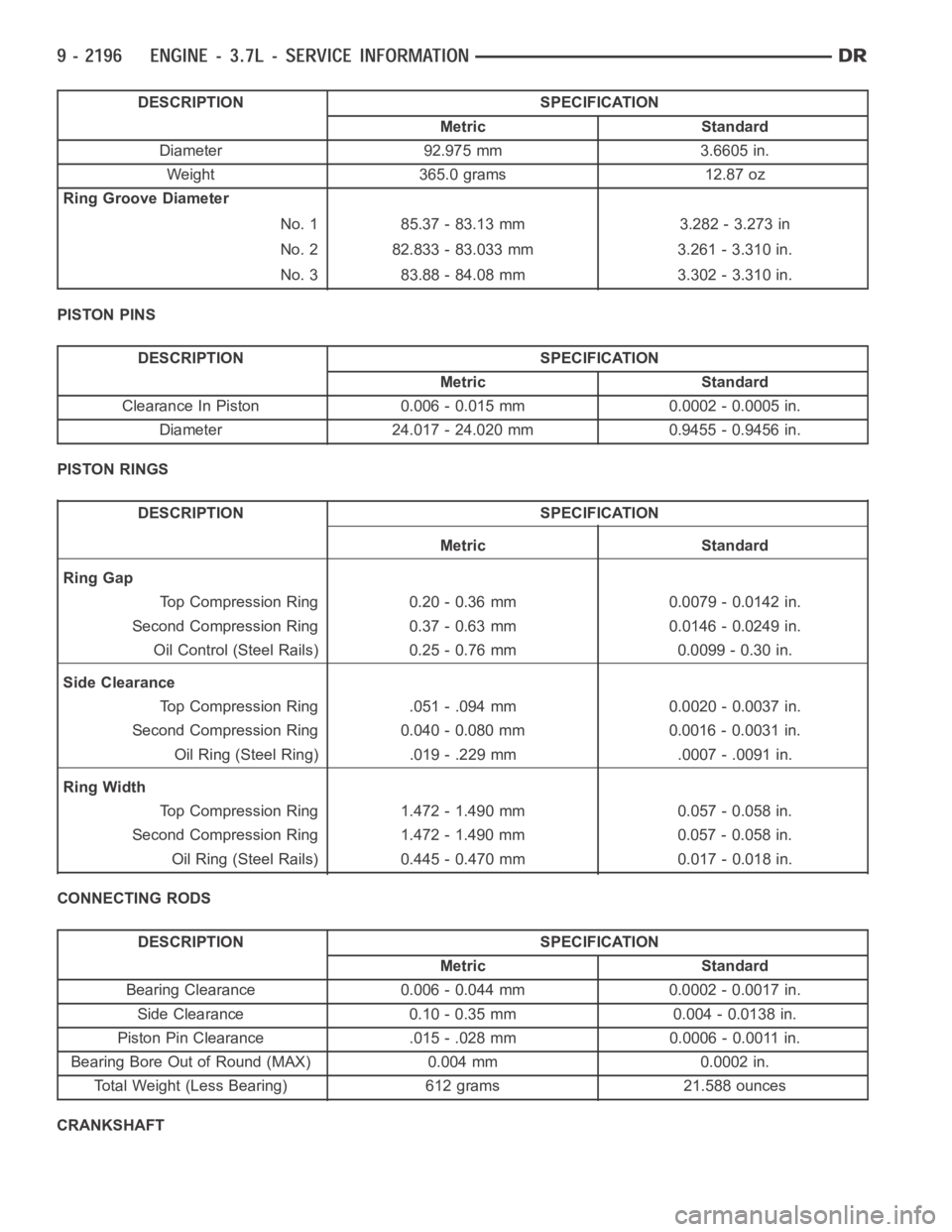
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Diameter 92.975 mm 3.6605 in.
Weight 365.0 grams 12.87 oz
Ring Groove Diameter
No. 1 85.37 - 83.13 mm 3.282 - 3.273 in
No. 2 82.833 - 83.033 mm 3.261 - 3.310 in.
No. 3 83.88 - 84.08 mm 3.302 - 3.310 in.
PISTON PINS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Clearance In Piston 0.006 - 0.015 mm 0.0002 - 0.0005 in.
Diameter 24.017 - 24.020 mm 0.9455 - 0.9456 in.
PISTON RINGS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Ring Gap
Top Compression Ring 0.20 - 0.36 mm 0.0079 - 0.0142 in.
Second Compression Ring 0.37 - 0.63 mm 0.0146 - 0.0249 in.
Oil Control (Steel Rails) 0.25 - 0.76 mm 0.0099 - 0.30 in.
Side Clearance
Top Compression Ring .051 - .094 mm 0.0020 - 0.0037 in.
Second Compression Ring 0.040 - 0.080 mm 0.0016 - 0.0031 in.
Oil Ring (Steel Ring) .019 - .229 mm .0007 - .0091 in.
Ring Width
Top Compression Ring 1.472 - 1.490 mm 0.057 - 0.058 in.
Second Compression Ring 1.472 - 1.490 mm 0.057 - 0.058 in.
Oil Ring (Steel Rails) 0.445 - 0.470 mm 0.017 - 0.018 in.
CONNECTING RODS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Bearing Clearance 0.006 - 0.044 mm 0.0002 - 0.0017 in.
Side Clearance 0.10 - 0.35 mm 0.004 - 0.0138 in.
Piston Pin Clearance .015 - .028 mm 0.0006 - 0.0011 in.
Bearing Bore Out of Round (MAX) 0.004 mm 0.0002 in.
Total Weight (Less Bearing) 612 grams 21.588 ounces
CRANKSHAFT
Page 1517 of 5267

HEAD-CYLINDER-LEFT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER HEAD GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the adjacent
water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
Loss of engine power
Engine misfiring
Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water jacket are:
Engine overheating
Loss of coolant
Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from exhaust
Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is leaking between adjacentcylinders, follow the procedures in Cyl-
inder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An engine cylinder head
gasket leaking between adjacent cylinders will result in approximately a50 - 70% reduction in compression pres-
sure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRESSURE CAP
REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure cap. Start the engine andallow it to warm up until thermostat
opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST.EXCESSIVE
PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A SAFE PRESSURE
POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRESSURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the tester’s
pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or equivalent.
Perform test following the procedures supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
1. Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
2. Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
3. Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the left side exhaust manifold.
4. Drain the engine coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
5. Lower the vehicle.
6. Remove the intake manifold (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - REMOVAL).
Page 1608 of 5267

2. Using a mirror, locate the TDC arrow on the front cover. Rotate the crankshaft until the mark on the crankshaft
damper (2) is aligned with the TDC arrow on the front cover (2). The engine isnow at TDC.
3. Note the location of the V6 mark stamped into the camshaft drive gears (1,2). If the V6 mark on each camshaft
drive gear is at the twelve o’clock position, the engine is at TDC on the exhaust stroke. If the V6 mark on each
gear is at the six o’clock position, the engine is at TDC on the compression stroke.
4. If both of the camshaft drive gears are off in the same or opposite directions, the primary chain or both second-
ary chains are at fault. Refer to Timing Chain and Sprockets procedure in this section.
5. If only one of the camshaft drive gears is off and the other is correct, theproblem is confined to one secondary
chain. Refer to Single camshaft timing, in this procedure.
6. If both camshaft drive gear V6 marks are at the twelve o’clock or the six o’clock position the engine base timing
is correct. Reinstall the cylinder head covers.
COUNTER BALANCE SHAFT TIMING
1. Ensure that the engine is at TDC with both cam-
shaft sprocket V6 marks in the 12 o’clock position.
2. Look down the left cylinder head chain cavity. The
timing dot (2) on the counter balance shaft drive
gear should be in the 6 o’clock position.
Page 1623 of 5267

page page
ENGINE - 4.7L - SERVICE INFORMATION
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE............. 2316
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL............... 2318
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE............... 2318
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE...... 2319
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION............. 2320
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS.......... 2320
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-
PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS.......... 2320
REMOVAL ................................. 2321
INSTALLATION ............................. 2327
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - 4.7L ENGINE .......... 2331
TORQUE ................................. 2336
SPECIAL TOOLS
4.7L ENGINE ............................. 2338
ELEMENT - AIR CLEANER
REMOVAL ................................. 2342
INSTALLATION ............................. 2343
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - CYLINDER HEAD ......... 2344
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES ........... 2344
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CYLINDER HEAD GASKET................ 2344
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - LEFT CYLINDER HEAD ........ 2345
REMOVAL - RIGHT CYLINDER HEAD ...... 2348
CLEANING ................................. 2350
INSPECTION ............................... 2350
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - LEFT CYLINDER HEAD . . . 2351
INSTALLATION - RIGHT CYLINDER HEAD . . 2353
CAMSHAFT - LEFT
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2357
REMOVAL ................................. 2357
INSTALLATION ............................. 2359
CAMSHAFT - RIGHT
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2362
REMOVAL ................................. 2362
INSTALLATION ............................. 2365
COVER - CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2369REMOVAL
REMOVAL - RIGHT SIDE .................. 2369
REMOVAL - LEFT SIDE ................... 2369
CLEANING ................................. 2369
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - RIGHT SIDE .............. 2370
INSTALLATION - LEFT SIDE ............... 2370
VALVES & SEATS - INTAKE/EXHAUST
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2371
REMOVAL ................................. 2371
INSTALLATION ............................. 2372
ROCKER ARM - VALVE
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2374
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
LASH ADJUSTER ......................... 2374
REMOVAL ................................. 2374
INSTALLATION ............................. 2375
SPRINGS-VALVE
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2376
REMOVAL ................................. 2376
INSTALLATION ............................. 2377
SEALS-VALVE GUIDE
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2378
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2379
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING ................................. 2379
CLEANING ................................. 2379
INSPECTION............................... 2380
BEARINGS - CONNECTING ROD
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CONNECTING
ROD BEARING FITTING ................... 2381
PLUGS - CORE
REMOVAL ................................. 2384
INSTALLATION ............................. 2384
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2385
REMOVAL ................................. 2385
INSPECTION............................... 2386
INSTALLATION ............................. 2386
BEARINGS - CRANKSHAFT MAIN
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CRANKSHAFT
MAIN BEARING - FITTING ................. 2389
INSPECTION............................... 2390
SEAL - CRANKSHAFT OIL - FRONT
REMOVAL ................................. 2391
INSTALLATION ............................. 2392
SEAL - CRANKSHAFT OIL - REAR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR SEAL
AREA LEAKS . ............................ 2393
REMOVAL ................................. 2393
Page 1626 of 5267

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE LOSS OF POWER 1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Dirt or water in fuel system. 2. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump. 3. Refer to the Appropriate
Diagnostic Information
4. Blown cylinder head gasket. 4. Replace cylinder head gasket.
5. Low compression. 5. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
6. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system.7. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
8. Faulty coil. 8. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Dirt in fuel system. 2. Clean fuel system.
3. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 3. Replcae as necessary.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
ENGINE MISSES AT HIGH SPEED 1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Faulty coil. 2. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
3. Dirt or water in fuel system. 3. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
Page 1627 of 5267
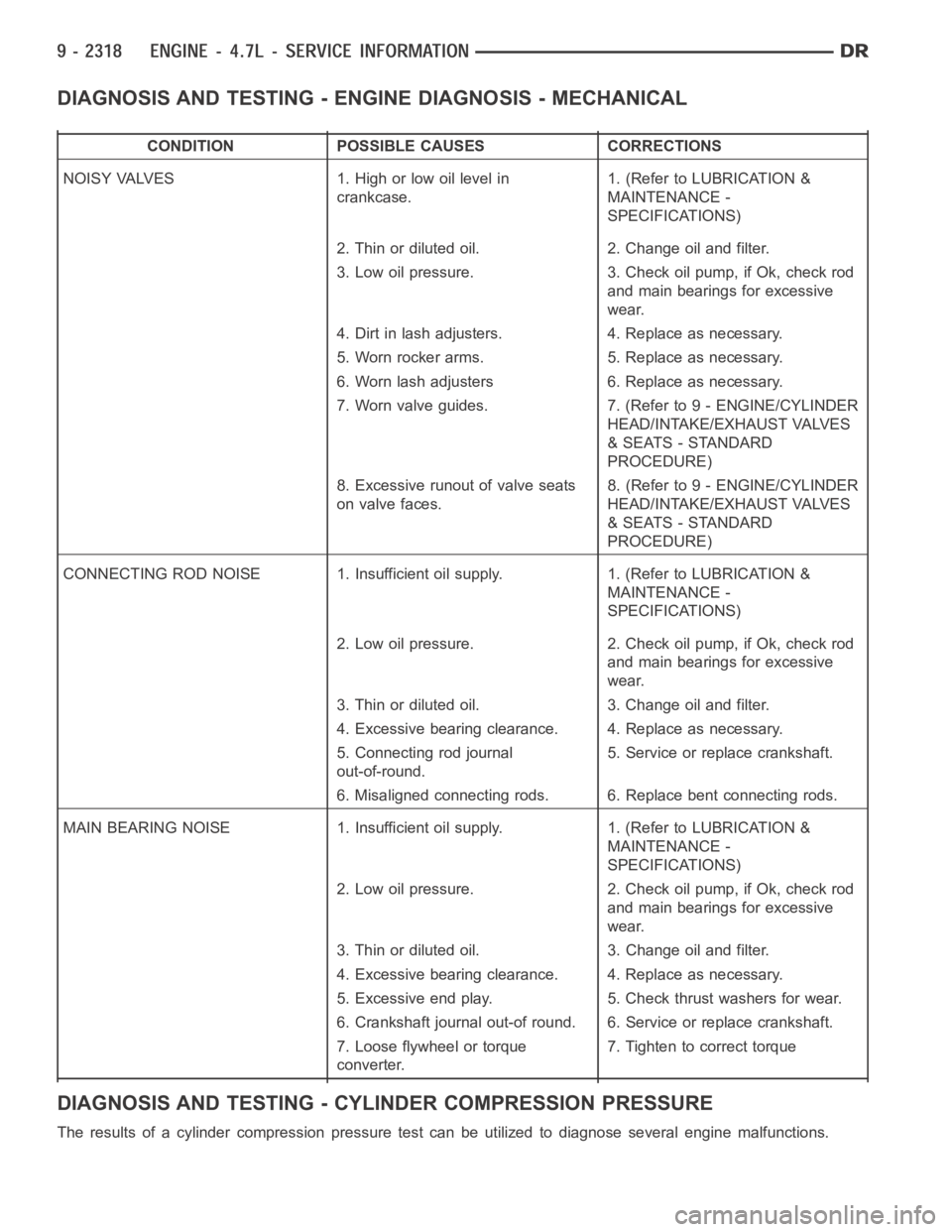
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil and filter.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
4. Dirt in lash adjusters. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Worn rocker arms. 5. Replace as necessary.
6. Worn lash adjusters 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Worn valve guides. 7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
8. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.8. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION&
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.5. Service or replace crankshaft.
6. Misaligned connecting rods. 6. Replace bent connecting rods.
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Excessive end play. 5. Check thrust washers for wear.
6. Crankshaft journal out-of round. 6. Service or replace crankshaft.
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.7. Tighten to correct torque
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compressionpressure test can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunctions.
Page 1628 of 5267

Ensurethebatteryiscompletelychargedandtheenginestartermotorisingood operating condition. Otherwise the
indicated compression pressures may not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
1. Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed air.
2. Remove the spark plugs.
3. Disable the fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DESCRIPTION).
4. Remove the ASD relay (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/AUTO SHUTDOWNRELAY-
REMOVAL).
5. Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate the engine with the engine starter motor for three revolutions.
6. Record the compression pressure on the 3rd revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylinders.
7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for the correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDERCOMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seating).
Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water jacket.
Any causes for combustion/compression pressure loss.
1. Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO NOT install the radiatorcap.
2. Start and operate the engine until it attains normal operating temperature, then turn the engine OFF.
3. Remove the spark plugs.
4. Remove the oil filler cap.
5. Remove the air cleaner hose.
6. Calibrate the tester according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The shop air source for testing should maintain
483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379 kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recommended.
7. Perform the test procedures on each cylinder according to the tester manufacturer’s instructions. Set piston of
cylinder to be tested at TDC compression,While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping through the throttle
body, tailpipe and oil filler cap opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal, with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pressure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be maintained in the
cylinder.
Refer to CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART .
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
THROTTLE BODYIntake valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary.
Inspect valve springs. Replace as
necessary.
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
TAILPIPEExhaust valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary.
Inspect valve springs. Replace as
necessary.
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
RADIATORHead gasket leaking or cracked
cylinder head or blockRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace defective part
MORE THAN 50% LEAKAGE
FROM ADJACENT CYLINDERSHead gasket leaking or crack in
cylinder head or block between
adjacent cylindersRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace gasket, head, or block as
necessary
Page 1629 of 5267

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
MORE THAN 25% LEAKAGE AND
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH OIL
FILLER CAP OPENING ONLYStuckorbrokenpistonrings;
cracked piston; worn rings and/or
cylinder wallInspect for broken rings or piston.
Measure ring gap and cylinder
diameter, taper and out-of-round.
Replace defective part as necessary
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the causes of malfunctions notdetected and remedied by routine main-
tenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either performance (e.g., engineidles rough and stalls) or mechanical
(e.g., a strange noise).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) - PERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)—MECHANICAL for possible causes and corrections of malfunctions. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be necessary for specificengine malfunctions that can not be iso-
lated with the Service Diagnosis charts. Information concerning additional tests and diagnosis is provided within the
following diagnosis:
Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Cylinder Combustion Pressure LeakageTest (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSISAND TESTING).
Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKEMANIFOLD - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essentially, this repair consistsof:
Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or equivalent.
Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken when apply-
ing form-in-place gaskets to assure obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-place gasket material
unless specified.Bead size, continuity, and location are of great importance. Too thin a bead can result in leakage
while too much can result in spill-overwhich can break off and obstruct fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the
proper width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket materials that are used in the engine area. Mopar
Engine RTV
GEN II, Mopar
ATF-RTV, and MoparGasket Maker gasket materials, each have different properties and can not
be used in place of the other.
MOPAR
ENGINE RTV GEN II
Mopar
Engine RTV GEN II is used to seal components exposed to engine oil. This material is a specially designed
black silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and sealing properties when exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the
air causes the material to cure. This material is available in three ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After
one year this material will not properly cure. Always inspect the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPAR
AT F R T V
Mopar
ATF RTV is a specifically designed black silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and sealing properties
to seal components exposed to automatic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and moisture. This material is avail-