2006 DODGE RAM SRT-10 Compression
[x] Cancel search: CompressionPage 1640 of 5267

28. Install starter (4) (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLATION).
CAUTION: The structural cover requires a specific
torque sequence. Failure to follow this sequence
may cause severe damage to the cover.
29. Install structural cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/STRUCTURAL COVER - INSTAL-
LATION) .
30. Install exhaust crossover pipe.
31. Install engine block heater power cable, If
equipped.
32.4X4 vehiclesConnect axle vent tube to left side
engine mount.
33. Lower vehicle.
34. Check and fill engine oil.
35. Recharge the A/C system (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
36. Refill the engine cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
37. Connect the battery positive and negative cables.
38. Start the engine and check for leaks.
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - 4.7L ENGINE
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Engine Type 90° SOHC V-8 16-Valve
Displacement 4.7 Liters / 4701 cc
287 ( Cubic Inches)
Bore 93.0 mm (3.66 in.)
Stroke 86.5 mm (3.40 in.)
Compression Ratio 9.0:1
Horsepower 235 BHP @ 4800 RPM
Torque 295 LB-FT @ 3200 RPM
Lead Cylinder #1 Left Bank
Page 1641 of 5267
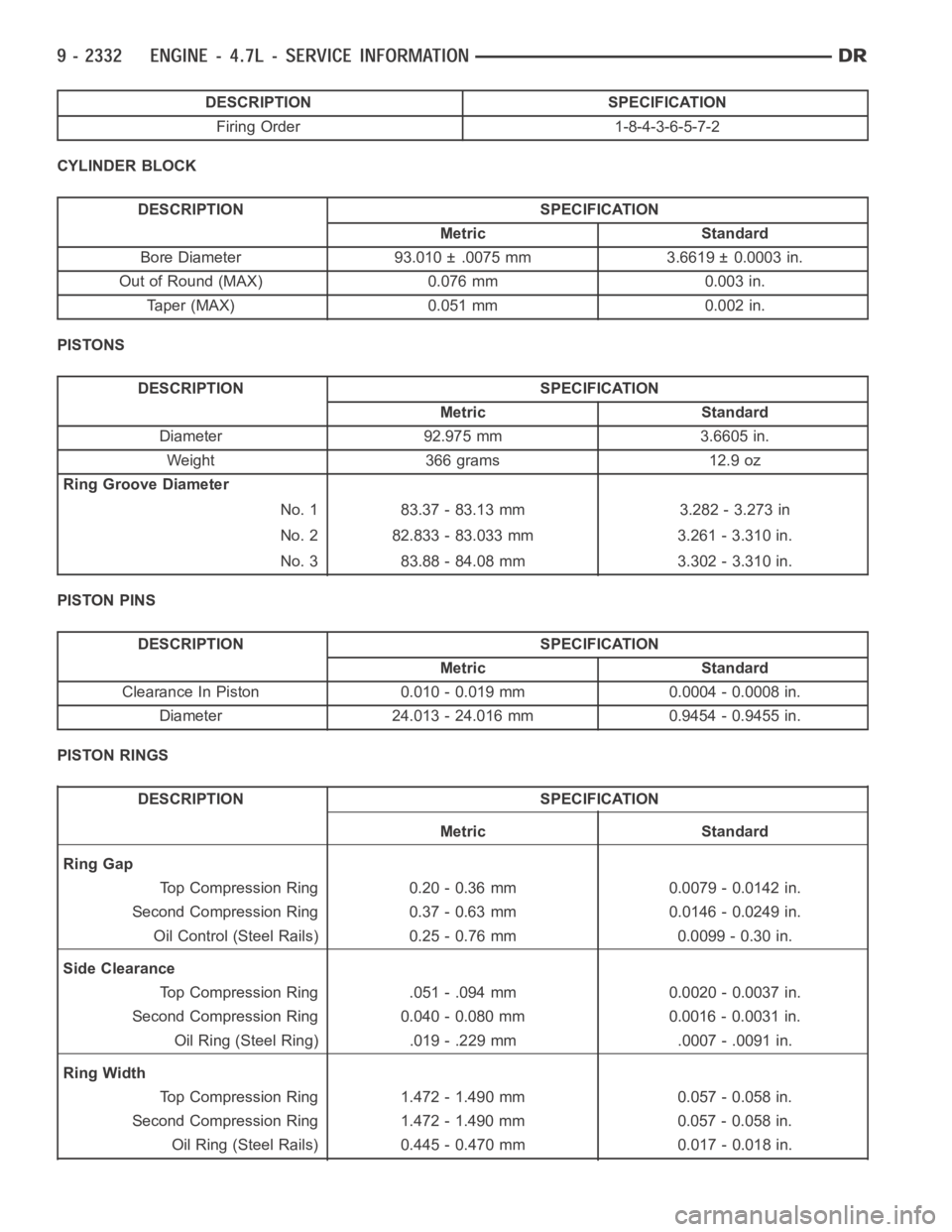
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Firing Order 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2
CYLINDER BLOCK
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Bore Diameter 93.010 ± .0075 mm 3.6619 ± 0.0003 in.
Out of Round (MAX) 0.076 mm 0.003 in.
Taper (MAX) 0.051 mm 0.002 in.
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Diameter 92.975 mm 3.6605 in.
Weight 366 grams 12.9 oz
Ring Groove Diameter
No. 1 83.37 - 83.13 mm 3.282 - 3.273 in
No. 2 82.833 - 83.033 mm 3.261 - 3.310 in.
No. 3 83.88 - 84.08 mm 3.302 - 3.310 in.
PISTON PINS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Clearance In Piston 0.010 - 0.019 mm 0.0004 - 0.0008 in.
Diameter 24.013 - 24.016 mm 0.9454 - 0.9455 in.
PISTON RINGS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Ring Gap
Top Compression Ring 0.20 - 0.36 mm 0.0079 - 0.0142 in.
Second Compression Ring 0.37 - 0.63 mm 0.0146 - 0.0249 in.
Oil Control (Steel Rails) 0.25 - 0.76 mm 0.0099 - 0.30 in.
Side Clearance
Top Compression Ring .051 - .094 mm 0.0020 - 0.0037 in.
Second Compression Ring 0.040 - 0.080 mm 0.0016 - 0.0031 in.
Oil Ring (Steel Ring) .019 - .229 mm .0007 - .0091 in.
Ring Width
Top Compression Ring 1.472 - 1.490 mm 0.057 - 0.058 in.
Second Compression Ring 1.472 - 1.490 mm 0.057 - 0.058 in.
Oil Ring (Steel Rails) 0.445 - 0.470 mm 0.017 - 0.018 in.
Page 1653 of 5267

CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - CYLINDER HEAD
The cylinder heads are made of an aluminum alloy. The cylinder head features two valves per cylinder with pressed
in powdered metal valve guides. The cylinder heads also provide enclosures for the timing chain drain, necessitating
unique left and right cylinder heads.
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES
The valve guides are made of powered metal and are pressed into the cylinderhead. The guides are not replace-
able or serviceable, and valve guide reaming is not recommended. If the guides are worn beyond acceptable limits,
replace the cylinder heads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CYLINDER HEAD GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the adjacent
water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
Loss of engine power
Engine misfiring
Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water jacket are:
Engine overheating
Loss of coolant
Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from exhaust
Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is leaking between adjacentcylinders, follow the procedures in Cyl-
inder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An engine cylinder head
gasket leaking between adjacent cylinders will result in approximately a50 - 70% reduction in compression pres-
sure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRESSURE CAP
REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure cap. Start the engine andallow it to warm up until thermostat
opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST.EXCESSIVE
PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A SAFE PRESSURE
POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRESSURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Page 1683 of 5267

ROCKER ARM - VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The rocker arms are steel stampings with an integral roller bearing. The rocker arms incorporate an 0.5 mm (0.019
inch) oil hole in the ball socket forroller and camshaft lubrication.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several items. Check the followingitems.
1. Engine oil level too high or too low. This may cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause them to be
spongy.
2. Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylinder head. Low speed runningupto1hourmayberequired.
3. Turn engine off and let set for a few minutes before restarting. Repeat this several times after engine has
reached normal operating temperature.
4. Low oil pressure.
5. The oil restrictor in cylinder head gasket or the oil passage to the cylinder head is plugged with debris.
6. Airingestedintooilduetobrokenorcrackedoilpumppickup.
7. Worn valve guides.
8. Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring retainer.
9. Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maximum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
10. Oil leak or excessive cam bore wear in cylinder head.
11. Faulty lash adjuster.
a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while installed in cylinder head and cam on camshaft at base circle.
Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster. Normal adjusters should feel very firm. Spongy adjusters can be bot-
tomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
c. Before installation, make sure adjusters are at least partially full ofoil. This can be verified by little or no
plunger travel when lash adjuster is depressed.
REMOVAL
NOTE: Disconnect the battery negative cable to
prevent accidental starter engagement.
1. Remove the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
2. For rocker arm removal on cylinders 3 and 5
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
exhaust stroke.
3. For rocker arm removal on cylinders 2 and 8
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC
compression stroke.
4. For rocker arm removal on cylinders 4 and 6
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #3 is at TDC
compression stroke.
5. For rocker arm removal on cylinders 1 and 7
Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #2 is at TDC
compression stroke.
6. Using special tool 8516 Rocker Arm Remover (2),
press downward on the valve spring, remove
rocker arm.
Page 1684 of 5267

INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Make sure the rocker arms are installed with the concave pocket over the lash adjusters. Failure
to do so may cause severe damage to the rocker arms and/or lash adjusters.
NOTE: Coat the rocker arms with clean engine oil prior to installation.
1. For rocker arm installation on cylinders 3 and 5 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC exhaust stroke.
2. For rocker arm installation on cylinders 2 and 8 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #1 is at TDC compression
stroke.
3. For rocker arm installation on cylinders 4 and 6 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #3 is at TDC compression
stroke.
4. For rocker arm installation on cylinders 1 and 7 Rotate the crankshaft until cylinder #2 is at TDC compression
stroke.
5. Using special tool 8516 press downward on the valve spring, install rocker arm.
6. Install the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTAL-
LATION).
Page 1741 of 5267

2. Using a mirror, locate the TDC arrow on the front
cover. Rotate the crankshaft until the mark on the
crankshaft damper is aligned with the TDC arrow
on the front cover. The engine is now at TDC.
3. Note the location of the V8 mark stamped into the camshaft drive gears. IftheV8markoneachcamshaftdrive
gear is at the twelve o’clock position, the engine is at TDC (cylinder #1) onthe exhaust stroke. If the V8 mark on
each gear is at the six o’clock position, the engine is at TDC (cylinder #1) on the compression stroke.
4. If both of the camshaft drive gears are off in the same or opposite directions, the primary chain or both second-
ary chains are at fault. Refer to Timing Chain and Sprockets procedure in this section.
5. If only one of the camshaft drive gears is off and the other is correct, theproblem is confined to one secondary
chain. Refer to Single camshaft timing, in this procedure.
6. If both camshaft drive gear V8 marks are at the twelve o’clock or the six o’clock position the engine base timing
is correct. Reinstall the cylinder head covers.
SINGLE CAMSHAFT TIMING
NOTE: to adjust the timing on one camshaft, peform the following procedure.
Page 1756 of 5267

page page
ENGINE - 5.7L - SERVICE INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2449
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION............. 2449
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE............. 2449
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL............... 2451
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE............... 2451
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE...... 2452
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - LUBRICATION............... 2453
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL............... 2453
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS.......... 2456
STANDARD PROCEDURE—HYDROSTATIC
LOCK.................................... 2456
REMOVAL ................................. 2457
INSTALLATION ............................. 2462
SPECIFICATIONS
5.7L ENGINE ............................. 2467
TORQUE ................................. 2472
SPECIAL TOOLS
5.7L ENGINE ............................. 2475
ELEMENT - AIR CLEANER
REMOVAL ................................. 2478
INSTALLATION ............................. 2479
CYLINDER HEAD
OPERATION—CYLINDER HEAD ............. 2481
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING—CYLINDER HEAD
GASKET FAILURE........................ 2481
REMOVAL ................................. 2482
CLEANING ................................. 2484
INSPECTION ............................... 2484
INSTALLATION ............................. 2485
COVER - CYLINDER HEAD
REMOVAL ................................. 2490
INSTALLATION ............................. 2493
VALVES & SEATS - INTAKE/EXHAUST
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - VALVE GUIDES ........... 2496
DESCRIPTION ........................... 2496
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFACING ....... 2496
REMOVAL ................................. 2497
INSTALLATION ............................. 2497ROCKER ARM
REMOVAL ................................. 2498
INSTALLATION ............................. 2500
SEALS - VALVE GUIDE
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2503
SPRINGS - VALVE
REMOVAL ................................. 2504
INSTALLATION ............................. 2510
ENGINE BLOCK
CLEANING ................................. 2515
INSPECTION............................... 2515
CAMSHAFT
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CAMSHAFT CORE HOLE PLUG . 2516
REMOVAL - CAMSHAFT ................... 2516
INSPECTION............................... 2520
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CAMSHAFT CORE HOLE
PLUG.................................... 2520
INSTALLATION - CAMSHAFT .............. 2521
CRANKSHAFT
REMOVAL ................................. 2527
INSTALLATION ............................. 2531
BEARINGS - CRANKSHAFT MAIN
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CRANKSHAFT
MAIN BEARING - FITTING ................. 2536
INSPECTION............................... 2536
SEAL - CRANKSHAFT OIL - FRONT
REMOVAL ................................. 2537
INSTALLATION ............................. 2538
SEAL - CRANKSHAFT OIL - REAR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR SEAL
AREA LEAKS . ............................ 2539
REMOVAL ................................. 2539
INSTALLATION ............................. 2540
RETAINER - CRANK REAR OIL - SEAL
REMOVAL ................................. 2541
INSTALLATION ............................. 2541
FLEX PLATE
REMOVAL ................................. 2542
INSTALLATION ............................. 2542
TAPPETS - HYDRAULIC ROLLER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
TAPPETS ................................ 2543
REMOVAL ................................. 2543
INSTALLATION ............................. 2544
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION ............................. 2546
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON FITTING . 2546
REMOVAL ................................. 2547
CLEANING ................................. 2548
Page 1758 of 5267

ENGINE - 5.7L - SERVICE INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION
The 5.7L engine (345 CID) eight-cylinder engine is a 90° V-Type lightweight, deep skirt cast iron block, aluminum
heads, single cam, overhead valve engine with hydraulic roller tappets. The heads incorporate splayed valves with
a hemispherical style combustion chamber and dual spark plugs. The cylinders are numbered from front to rear; 1,
3, 5, 7 on the left bank and 2, 4, 6, 8 on the right bank. The firing order is 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the causes of malfunctions notdetected and remedied by routine main-
tenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either performance (e.g., engineidles rough and stalls) or mechanical
(e.g., a strange noise).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) - PERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)—MECHANICAL for possible causes and corrections of malfunctions. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be necessary for specificengine malfunctions that can not be iso-
lated with the Service Diagnosis charts. Information concerning additional tests and diagnosis is provided within the
following diagnosis:
Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Cylinder Combustion Pressure LeakageTest (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSISAND TESTING).
Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKEMANIFOLD - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
4. Faulty coil or control unit. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
6. Dirt or water in fuel system. 6. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
7. Faulty fuel pump, relay or wiring. 7. Repair or replace as necessary.