2006 DODGE RAM SRT-10 fuel pump
[x] Cancel search: fuel pumpPage 1388 of 5267
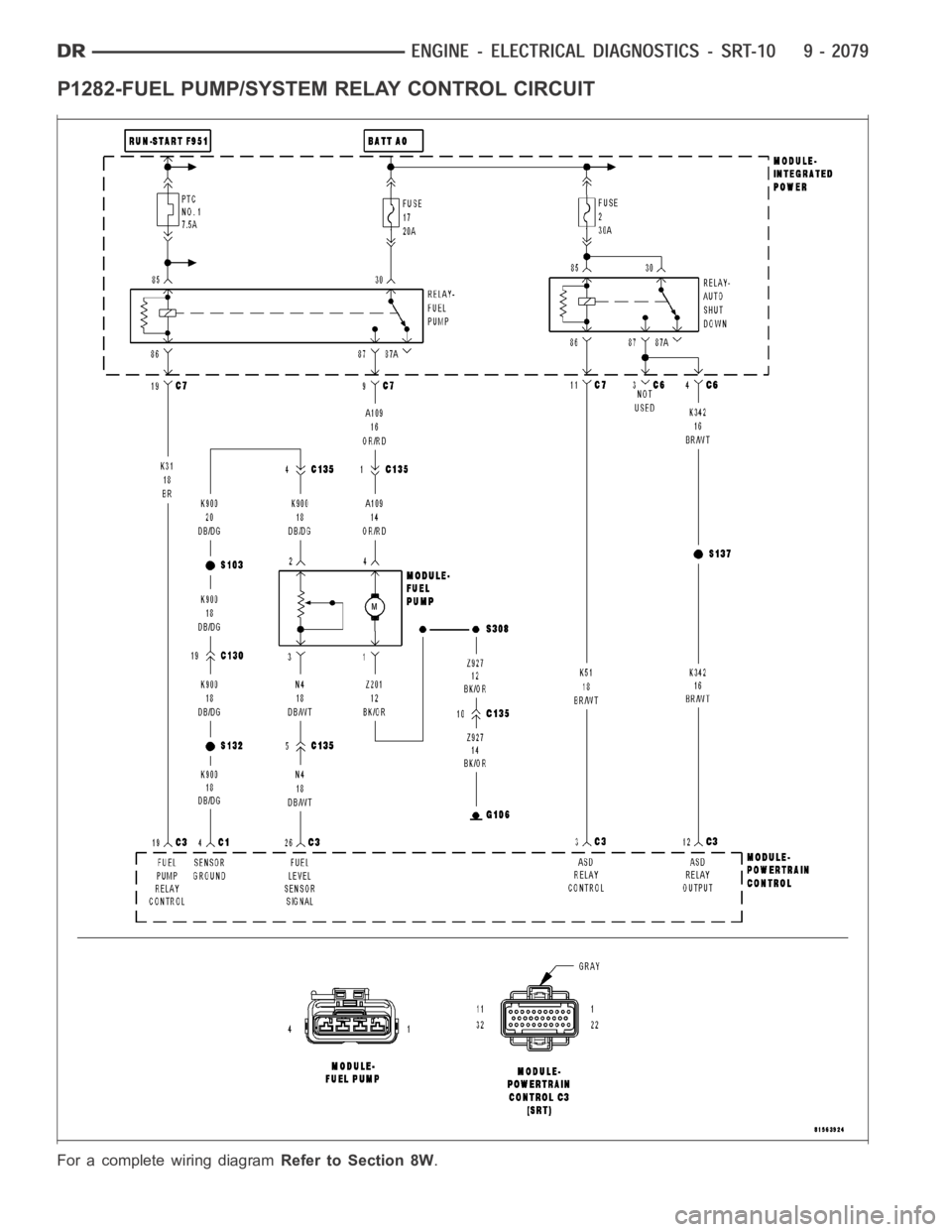
P1282-FUEL PUMP/SYSTEM RELAY CONTROL CIRCUIT
For a complete wiring diagramRefer to Section 8W.
Page 1389 of 5267

When Monitored:
With the ignition on and battery voltage above 10.4 volts.
Set Condition:
An open or shorted condition is detected in the Fuel Pump Relay Control circuit.
Possible Causes
FUEL PUMP RELAY OPERATION
FUEL PUMP RELAY
FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT CIRCUIT
(K31) FUEL PUMP RELAY CONTROL CIRCUIT OPEN
(K31) FUEL PUMP RELAY CONTROL CIRCUIT SHORTED TO GROUND
PCM
Always perform the Pre-Diagnostic Troubleshooting procedure before proceeding. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
1.FUEL PUMP RELAY OPERATION
Ignition on, engine not running.
With the scan tool, read DTCs and record the related Freeze Frame data.
With the scan tool, actuate the Fuel Pump Relay.
Is the Fuel Pump Relay clicking?
Ye s>>
Refer to the INTERMITTENT CONDITIONSymptom (Diagnostic Procedure).
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
No>>
Go To 2
2.FUEL PUMP RELAY
Turn the ignition off.
Remove the Fuel Pump Relay.
NOTE: Check connectors - Clean/repair as necessary.
Measure the resistance between the coil terminals of the Fuel Pump Relay.
Is the resistance between 50 and 90 ohms?
Ye s>>
Go To 3
No>>
Replace the Fuel Pump Relay.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
3.FUSED IGNITION SWITCH CIRCUIT OPEN
Ignition on, engine not running.
Using a 12-volt test light connected to ground, probe the Fused Ignition Switch Output circuit in the Fuel Pump
Relay connector.
Does the test light illuminate brightly?
Ye s>>
Go To 4
No>>
Repair the open or short to ground in the Fused Ignition Switch Output circuit. Inspect the related fuse
and repair as necessary.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Page 1390 of 5267

4.(K31) FUEL PUMP RELAY CONTROL CIRCUIT OPEN
Turn the ignition off.
Disconnect the PCM harness connectors.
Measure the resistance of the (K31) Fuel Pump Relay Control circuit from the Fuel Pump Relay connector to the
PCM harness connector.
Is the resistance below 5.0 ohms?
Ye s>>
Go To 5
No>>
Repair the open in the (K31) Fuel Pump Relay Control circuit.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
5.(K31) FUEL PUMP RELAY CONTROL CIRCUIT SHORT TO GROUND
Measure the resistance between ground and the (K31) Fuel Pump Relay Control circuit at the PDC.
Istheresistancebelow100ohms?
Ye s>>
Repair the short to ground in the (K31) Fuel Pump Relay Control circuit.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
No>>
Go To 6
6.PCM
NOTE: Before continuing, check the PCM harness connector terminals for corrosion, damage, or terminal
push out. Repair as necessary.
Using the schematics as a guide, inspect the wire harness and connectors. Pay particular attention to all Power and
Ground circuits.
If there are no possible causes remaining, view repair.
Repair
Replace and program the Powertrain Control Module per Service Information.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Page 1417 of 5267

3.EVAP PURGE SOLENOID VACUUM LINE
Turn the ignition off.
Inspect the Purge Solenoid Vacuum line that runs from the Evap Purge Solenoid to the throttle body or intake man-
ifold.
Is the vacuum line plugged or kinked?
Ye s>>
Repair or replace the vacuum line from the solenoid to the throttle body / intake manifold.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
No>>
Go To 4
NOTE: Reconnect the vacuum line before continuing.
4.CHECKED FOR OTHER BLOCKED HOSES
To continue testing you will need Miller Tool #6872A (Evap System PressurePump) and #8382 (Gas Cap Tester [
]Adapter).
WARNING: The test equipment is designed to be used to pressurize the vehicles Evaporative System only.
Using the equipment in a manner for which it was not designed could be harmful.
WARNING: Keep lit cigarettes, sparks, flames, and other ignition sourcesaway from the test area to prevent
the ignition of explosive gases. Keep the test area well ventilated.
NOTE: The fuel tank should have between 20% and 80% of full to properly test the Evap System.
Attach the power source clip (red) of Miller Tool #6872A to Battery (+) and the ground clip (black) to Battery (-).
Perform the Evaporative System Pressure Pump self test that is specified on the tester cover.
Remove gas cap and install Miller Tool #8382 on the vehicle. Install gas capto Miller Tool #8382. Attach the pres-
sure supply hose from Miller Tool #6872A to the fitting on #8382.
Disconnect the vacuum supply hose at the Leak Detection Pump.
Connect and apply a continuous vacuum supply (i.e. 20”Hg) to the Leak Detection Pump. A vacuum pump such as
an A/C Recovery unit works well.
Ignition on, engine not running.
With the scan tool perform the “Leak Detect Pump Test”. Follow the scan toolinstructions and then press ENTER.
Select#3–HOLDPSI.
On Miller Tool #6872A, set the Pressure/Hold switch to Open and set the Ventswitch to Closed. Turn the pump
timer On and watch the gauge.
When the gauge pressure reaches 14”H2O, turn the Pressure/Hold Valve to Closed.
Turn the pump timer off.
Disconnect the hose at the Evap Canister that goes to the Fuel Tank.
Did the pressure drop when the hose was disconnected?
Ye s>>
Go To 5
No>>
Repair the obstruction in the Evap System between the Evap Canister and thefuel tank.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
5.EVAP CANISTER FUNCTION
NOTE: Connect all previously disconnected hoses.
Re-pressurize the Evap System. On Miller Tool #6872A, set the Pressure/Hold switch to Open and set the Vent
switch to Closed.
Turn the pump timer On and watch the gauge.
When the gauge pressure reaches 14” H2O, turn the Pressure/Hold Valve Closed.
Turn the pump timer off.
Page 1418 of 5267

Disconnect the LDP Pressure hose at the Evap Canister. The LDP Pressure hose is the hose that connects the
Evap Canister to the Leak Detection Pump.
Did pressure drop when the hose was disconnected?
Ye s>>
Go To 6
No>>
Replace the Evap Canister.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
6.EVAP CANISTER FUNCTION
NOTE: Connect all previously disconnected hoses.
Re-pressurize the Evap System. On Miller Tool #6872A, set the Pressure/Hold switch to Open and set the Vent
switch to Closed.
Turn the pump timer On and watch the gauge.
When the gauge pressure reaches 14” H2O, turn the Pressure/Hold Valve Closed.
Turn the pump timer off.
Disconnect the Evap hoses at the Evap Purge Solenoid.
Did pressure drop when the hose was disconnected?
Ye s>>
Go To 7
No>>
Repair or replace the hose / tube assembly as necessary.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
7.LEAK DETECTION PUMP HOSE
Disconnect and remove the LDP pressure hose. The LDP pressure hose is the hose that connects the Evap Can-
ister to the Leak Detection Pump.
Inspect the LDP pressure hose for anyobstructions or physical damage.
Is the LDP pressure hose free of defects?
Ye s>>
Replace the Leak Detection Pump.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
No>>
Repair or replace the hose / tube assembly as necessary.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
8.LDP MONITOR TEST
At this time, the conditions required to set the DTC are not present.
NOTE: Use the Freeze Frame data to help you duplicate the conditions that set the DTC. Pay particular
attention to the DTC setconditions, such as, VSS, MAP, ECT, and Load.
NOTE: A thorough visual inspection of the Evap system hoses, tubes, and connections may save time in
you diagnosis. Look for any physical damage or signs of wetness at connections. The strong smell of fuel
vapors may aid diagnosis also.
NOTE: Refer to any Service Bulletins that may apply
With the scan tool, perform the LDP Monitor Test. This will force the PCM to run the LDP Monitor. If the monitor
fails, further diagnosis is required to find a faulty component. If the monitor passes, the condition is not present at
this time.
Did the monitor test fail?
Ye s>>
Check the one trip faults to determine the DTC that was set during the LDP monitor test. Continue
diagnosis as necessary.
No>>
Te s t C o m p l e t e .
Page 1490 of 5267

(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) - PERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)—MECHANICAL for possible causes and corrections of malfunctions. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be necessary for specificengine malfunctions that can not be iso-
lated with the Service Diagnosis charts. Information concerning additional tests and diagnosis is provided within the
following diagnosis:
Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Cylinder Combustion Pressure LeakageTest (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSISAND TESTING).
Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKEMANIFOLD - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
4. Faulty coil or control unit. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
6. Incorrect right bank cam timing. 6. Refer to engine timing in this
section.
7. Dirt or water in fuel system. 7. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
8.Faulty fuel pump, relay or wiring. 8.Repair or replace as necessary.
9. Faulty cam or crank sensor 9. Refer to Ignition system.
ENGINE STALLS OR ROUGH IDLE 1. Vacuum leak. 1. Inspect intake manifold and
vacuum hoses, repair or replace as
necessary.
2. Faulty crank position sensor 2. Replace crank position sensor.
3. Faulty coil. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
4. Incorrect cam timing. 4. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE
TIMING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
Page 1491 of 5267

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
1. ENGINE LOSS OF POWER 1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Dirt or water in fuel system. 2. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump. 3. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL PUMP -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
4. Blown cylinder head gasket. 4. Replace cylinder head gasket.
5. Low compression. 5. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING), repair
as necessary.
6. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system.7. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
8. Faulty coil. 8. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
9. Incorrect cam timing. 9. Refer to Engine TIming in this
section.
1. ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Dirt in fuel system. 2. Clean fuel system.
3. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 3. Replcae as necessary.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
1. ENGINE MISSES AT HIGH
SPEED1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Faulty coil. 2. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
3. Dirt or water in fuel system. 3. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
Page 1494 of 5267

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL PUMPING AT RINGS; SPARK
PLUGS FOULING1. Worn or damaged rings. 1. Hone cylinder bores and replace
rings.
2. Carbon in oil ring slots. 2. Replace rings (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON
RINGS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
3. Incorrect ring size installed. 3. Replace rings (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON
RINGS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
4. Worn valve guides. 4. Ream guides and replace valves
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
5. Leaking valve guide seals. 5. Replace valve guide seals.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compressionpressure test can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunctions.
Ensurethebatteryiscompletelychargedandtheenginestartermotorisingood operating condition. Otherwise the
indicated compression pressures may not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
1. Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed air.
2. Remove the spark plugs.
3. Disable the fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DESCRIPTION).
4. Remove the ASD relay (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/AUTO SHUTDOWNRELAY-
REMOVAL).
5. Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate the engine with the engine starter motor for three revolutions.
6. Record the compression pressure on the 3rd revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylinders.
7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for the correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDERCOMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seating).
Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water jacket.
Any causes for combustion/compression pressure loss.
1. Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO NOT install the radiatorcap.
2. Start and operate the engine until it attains normal operating temperature, then turn the engine OFF.
3. Remove the spark plugs.
4. Remove the oil filler cap.
5. Remove the air cleaner hose.
6. Calibrate the tester according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The shop air source for testing should maintain
483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379 kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recommended.
7. Perform the test procedures on each cylinder according to the tester manufacturer’s instructions. Set piston of
cylinder to be tested at TDC compression,While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping through the throttle
body, tailpipe and oil filler cap opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal, with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pressure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be maintained in the
cylinder.