1988 PONTIAC FIERO stop start
[x] Cancel search: stop startPage 135 of 1825

3-10 STEERING, SUSPENSION, TIRES AND WHEELS DIAGNOSIS
Reminder Keeps Operating With Key In Lock
Cylinder, Driver's Door Open Or Closed; Ceases
When Key Is Removed
Inspect
s Door jamb switch on driver's side misadjusted or
inoperative.
e Wire from signal switch to door jamb switch
shorted.
A. This condition indicates the lock cylinder or
the reminder switch is at fault. To verify,
check for continuity at the
"E" and "F"
male column connector contacts, with the
key removed from the lock cylinder. If
continuity exists, the fault is in the column.
B. Insert the key into the lock, then turn the
lock toward the "Start" position. If the
reminder stops when the key is in the
"Run" position or when it is turned past
"Run" toward "Start," the problem is a
sticky lock cylinder actuator.
COLUMN-MOUNTED DIMMER SWITCH
No "Low" or "High" Beam
Inspect
e Loose connector at dimmer switch
e Improper adjustment
e Internally damaged or worn switch. Check the
continuity on the switch at the It. green and at the
tan switch terminals by pushing in the plunger all
the way.
A click should be heard. If there is no
continuity, replace the dimmer switch. If there is
continuity, refer
to'section 8A for electricaldiag-
nosis.
PIVOT AND SWITCH ASSEMBLY
Switch Inoperative: No "Low," "High" and/or
"Wash"
e Loose body-to-switch connector
a Broken or damaged switch
Internally damaged or worn switch. Connect a
new switch without removing the old one. If the
system functions, replace the switch. If the
system doesn't function, refer to Section
8A for
electrical diagnosis.
STEERING GEAR AND PUMP LEAKS
General Procedure
Inspect
s Overfilled reservoir
s Fluid aeration and overflow
e , Hose connections
Verify exact point of leakage Example:
Torsion bar, stub shaft and
adjuster seals are close together; the exact
spot where the system is leaking may not be
clear.
Example: The point from which the fluid is
dripping is not necessarily the point where
the system is leaking; fluid overflowing from
the reservoir, for instance.
e When service is required:
A. Clean leakage area upon disassembly.
B. Replace leaking seal.
C. Check component sealing surfaces for
damage.
D. Reset bolt torque to specifications, where
required.
Some complaints about the power steering system
may be reported as:
A. Fluid leakage on garage floor
B. Fluid leaks visible on steering gear or pump
C. Growling noise, especially when parking or
when engine is cold
D. Loss of power steering when parking
E. Heavy steering effort
When troubleshooting these kinds of complaints,
check for an external leak in the power steering system.
For further diagnosis of leaks, refer to External
Leakage Check in this section.
External Leakage Check
Fig. 12
The purpose of this procedure is to pinpoint the
location of the leak.
In some cases, the leak can easily be located. But,
seepage-type leaks may be more difficult to isolate. To
locate seepage leaks, use the following method.
1. With the engine off, wipe dry the complete power
steering system.
2. Check the fluid level in the pump's reservoir. Add
fluid if necessary.
3. Start the engine, then turn the steering wheel
from stop to stop several times. Do not hold it at
a stop for any length of time, as this can damage
the power steering pump. It is easier if someone
else operates the steering wheel while you search
for the seepage.
4. Find the exact area of the leak and repair leak.
SEAL REPLACEMENT
RECOMMENDATIONS
Lip seals, which seal rotating shafts, require
special treatment. This type of seal is used on the
steering gear and on the drive shaft of the pump. When
there is a leak in one of these areas, always replace the
seal(s), after inspecting and thoroughly cleaning the
sealing surfaces. Replace the shaft only if very severe
pitting is found. If the corrosion in the lip seal contact
zone is slight, clean the surface of the shaft with crocus
cloth. Replace the shaft only if the leakage cannot be
stopped by first smoothing with crocus cloth.
Page 137 of 1825

3-1 2 STEERING, SUSPENSION, TIRES AND WHEELS DIAGNOSIS
POWER STEERlNG SYSTEM "TEST
PROCEDURE
Fig. 13 1. J-5176-D 2. LlNE TO STEERING GEAR
1. Disconnect pressure hose at pump. Use a small 3. LINE TO POWER STEERING PUMP
container to catch any fluid which might leak.
2. Connect a spare pressure hose to pump.
3. Connect pressure gage
J 5176-D
to both hoses.
e The power steering system may be tested
using
J 5 176-D as described here. It can also
be tested with available tool
J 25323 Power
Steering Analyzer, which will measure flow
rate as well as pressure.
4. Open valve on gage.
5. Start the engine. Allow the system to reach
operating temperature, then check the fluid level
and add fluid if required.
6. When the engine is at normal operating
temperature, the pressure reading on the gage
(valve open) should be in the 552-862
kPa (80-125
psi) range. If the pressure is more than 1 380
kPa
(200 psi), check the hoses for restrictions and the
poppet valve on the steering gear for proper
assembly.
7. Fully close the valve 3 times. (Do not leave the
valve fully closed for more than 5 seconds, as the
pump could be damaged.) Record the pressure
reading each time the valve is closed. Each
reading should show at least 6 895
kPa (1,000
psi), or at least 8 619 kPa (1,250 psi) on the TC
series pumps. The three readings should be within
345
kPa (50 psi) of each other.
A. If the pressure readings are high enough,
and are within 345
kPa (50 psi) of each
other, the pump is functioning properly.
B. If the pressure readings are high enough,
but are not within 345
kPa (50 psi) of each
other, the flow control valve in the pump is
sticking. Remove the valve; clean it and
remove any burrs using crocus cloth or fine
hone. If the system contains some dirt, flush
it. If it is exceptionally dirty, both the pump
and the steering gear must be completely
disassembled, cleaned and reassembled.
C. If the pressure readings are less than
6 895
kPa (1,000 psi), or are less than 8 619 kPa
(1,250 psi) on the TC series pumps, replace
the flow control valve and recheck. If the
pressures are still low, replace the rotor and
vanes.
8. If the pump checks to specification, leave the
valve open and turn (or have turned) the steering
wheel to both stops. Record the highest pressures
and compare with the highest pump pressure
recorded. If the pressure at both stops is not the
same as the maximum pressure, the steering gear
is leaking internally and must be disassembled
and repaired.
9. Turn off the engine, then remove the testing gage
and the spare hose. Reconnect the pressure hose,
check the fluid level or make needed repairs.
Fig. 13 Power Steering Pressure Gage
STRUT DAMPENER AND SHOCK
ABSORBER DIAGNOSIS
The strut dampener is basically a shock absorber.
Strut dampeners are easier to extend and retract by
hand than are shock absorbers.
The following procedure includes both on-car
and bench checks to be done when evaluating the
performance of strut dampeners and shock absorbers.
ON-CAR CHECKS
Weak
For struts, follow Steps 1 through 4.
1. Check
and adjust tire pressures to the pressures
shown on the Tire Placard.
2. Note the load conditions under which the car is
normally driven.
3. If practical, ride with the owner to be sure you
understand the complaint before proceeding to
next step.
4. Test each strut
dampener/shock in turn by
quickly pushing down, then lifting up, the corner
of the bumper nearest the strut
dampener/shock
being checked. Use the same amount of effort on
each test and note the resistance on compression
and rebound. Compare this with a similar car
having acceptable ride quality. Both strut
dampeners/shocks should provide the same
feeling of resistance.
If there is much difference between the right and
left rear shocks, go to the next step.
5. Support the rear axle at least enough to unload
the shock mounts.
6. Disconnect the lower shock mountings. Stroke
the shocks at various rates of speed, through
maximum travel in both directions. Compare the
two sides for rebound and compression
resistance. Rebound resistance is normally
stronger than compression (about 2 to 1). The
right and left shocks must feel comparable.
Differences between front and rear are normal. If
Page 194 of 1825

POWER Sf EERING 387-1
SECTION 3B7
POWER STEER NG GEAR AND PUMP
The following notice applies to one or more steps in the assembly procedure of components in this portion
of the manual as indicated at appropriate locations. "See Notice on Page
1 of this Section".
NOTICE: Steering column fasteners are important attaching parts in that they may affect the performance
of vital components and systems, and/or could result in major repair expense. They must be replaced with one
of the same part number or with an equivalent part if replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a replacement
part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque values must be used as specified during reassembly to assure
proper retention of these parts. For prevailing torque
nut(s) and bolt(s), refer to the "Reuse of Prevailing Torque
Nut(s) and Bolt(s)" chart in Section 10.
CONTENTS
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
Bleeding Hydraulic System
................................................................................................. 3B7- 1
Fluid Level ......................................................................................................................... 3B7- 1
Power Steering Gear Adj. ..................................................................................................... 3B7- 1
Drive Belt Tension .............................................................................................................. 3B7-2
Hydraulic System Checks .................................................................................................. 3B7-2
Hydraulic System Test ......................................................................................................... 3B7-2
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
Steering Gear Removal
...................................................................................................... 3B7-3
Pitman Shaft Seal .................................................................................................................. 3B7-3
Pump Removal ..... , ................................................................................................................ 3B7-4
................................................................................................................... Hoses and Pipes 3B7-4
Pump Pulley ....................................................................................................................... 3B7-4
.................................................................................. Pump Brackets/Hoses/Cooling Pipes 3B7-5
........................................................................................ Pump Overhaul .................... ..... 3B7- 12
Gear Overhaul .................................................................................................................... 3B7- 13
SPECIAL TOOLS ............................................................................................................ 3B7-17 ......................... .......................................................... GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS .. 3B7- 18
MAlNKNANGE AND ADJUSTMENTS
BLEEDING HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
Fill fluid reservoir to proper level and let remain
undisturbed for at least two minutes.
Start engine and run momentarily.
Shut engine off to add fluid.
Repeat above procedure until fluid level remains
constant after running engine.
Raise front end of vehicle so that wheels are off
the ground.
Start engine and increase engine speed to
approximately
1500 rpm.
Turn the wheels (off ground) right and left,
lightly contacting the wheel stops.
Lower the car and turn wheels right and left on
the ground.
Shut engine off, check fluid level and refill as
required.
If fluid is extremely foamy, allow vehicle to stand
a few minutes with engine off while you run
through the following:
a. Check belt
tightness and check for a bent or
loose pulley. (Pulley should not wobble with
engine running.) b.
Check
to make sure hoses are not touching
any other parts of the car, particularly sheet
metal and exhaust manifold.
c. Check fluid
level, filling to proper level if
necessary. Air in the fluid is the most
frequent cause of objectionable pump noise.
d. When air is present, bleed system as
described in operations 1 through 10. If the
pump will not bleed after a few trials,
proceed as outlined under Hydraulic
System Checks. FLUID LEVEL
1. Check fluid level in the reservoir by checking the
dip stick when fluid is at operating temperature.
2. Fill, if necessary, to proper level with GM Power
Steering Fluid, or equivalent.
POWER STEERING GEAR ADJUSTMENTS
Adjustment of the power steering gear in the
vehicle is discouraged because of the difficulty involved
in adjusting the worm thrust bearing preload and the
confusing effects of the hydraulic fluid in the gear. The
steering gear adjustment is made only as a correction
and not as a required periodic adjustment.
Page 195 of 1825

387-2 POWER STEERING
The effect of improperly adjusted worm thrust
bearings or an improperly adjusted over-center preload
could cause a handling stability complaint.
To properly adjust the power steering gear, the
assembly MUST be removed from the vehicle and
adjustments performed as outlined.
For removal of the power steering gear assembly
see "Power Steering Gear".
DRIVE BELT TENSION
All drive belt tension specifications can be found
in the Engine Cooling Section 6B.
When adjusting a power steering pump belt,
never pry against the pump reservoir or pull against the
filler neck. Two systems are used for belt adjustment.
On some
models, the pump is loosened from the
bracket and moved outward to increase the tension. On
other models, a half-inch square drive hole is located
in the bracket, and this hole is used to rotate the
pump-and-bracket assembly outward to increase belt
tension.
Place belt tension gage, J-23600 or equivalent
midway between the pulleys on drive belt being
checked.
POWER SKERING ADAPER GAGE J-5176-01 J-22326
PRESSURE HOSE TO
P/S GEAR PRESSURE HOSE
Figure 387-1 Test Gage Installation
To adjust pump:
1.
Loosen the pump attaching bolts and adjust the
belt to correct tension by moving the pump
outward, away from the engine.
2. Snug all pump mounting bolts and remove pry
bar.
3. Tighten all pump mounting bolts to specified
torque.
4. Check belt tension using the tension gage.
NOTICE: Do not move pump by prying against
reservoir or by pulling on filler neck, or damage
may occur.
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CHECKS
The following procedure outlines methods to
identify and isolate power steering hydraulic circuit difficulties.
The test provides means of determining
whether power steering system hydraulic parts are
actually
defective.
Before performing hydraulic circuit test,
carefully check belt tension, fluid level and condition
of driving pulley.
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM TEST
(Figure 387- lj
Fluid must be at normal operating temperature.
Check front tires for correct pressure. All tests are
made with engine idling. If necessary, adjust engine
idle speed to correct specifications listed in Section 6C
and proceed as follows:
1. Stop engine, disconnect pressure hose from pump
and install Tool
5-5176 using a spare pressure
hose between gage and pump. Gage must be
between shut-off valve and pump. Open shut-off
valve.
2. Remove filler cap from pump reservoir and check
fluid level. Fill pump reservoir to full mark on dip
stick. Start engine and, momentarily holding
steering wheel against stop, check connections at
Tool J-5 176 for leakage.
3. Bleed system as outlined under Maintenance and
Adjustments.
4. Insert thermometer (Tool J-5421) in reservoir
filler opening. Move
/steering (wheel/ from stop to
stop several times until thermometer indicates
that hydraulic fluid in reservoir has reached
temperature of
150" to 170°F (65" to 77°C).
N OTI G E: To prevent scrubbing flat spots on tires,
do not turn steering wheel more than five times
without rolling vehicle to change tire-to-floor
contact area. Front end of vehicle can be lifted for
this test.
5. Start engine and check fluid level, adding fluid if
required. When engine is at normal operating
temperature, the initial pressure read on the gage
(valve open) should be in the 80-125 psi (550-860
kPa) range. Should this pressure be in excess of
200 psi (1380
kPa) - check the hoses for
restrictions and the poppet valve for proper
assembly.
6. Close gate valve fully
3 times. Record the highest
pressures attained each time.
N OTI C E: Do not leave valve fully closed for more
than
5 seconds as the pump could be damaged
internally.
a. If
the pressures recorded are within the
listed specs and the range of readings are
within 50 psi (345
kPa), the pump is
functioning within specs.
b. If the pressures recorded are high, but do
not repeat within 50 PSI (345
kPa), the flow
controlling valve is sticking. Remove the
valve, clean it and remove any burrs using
Page 196 of 1825
POWER STEERING 387-3
crocus cloth or fine hone. If the system 4. If the pump checks within specifications, leave
contains some dirt, flush it. If it is the valve open and turn (or have turned) the
exceptionally dirty, both the pump and the steering wheel into both corners. Record the
gear must be completely disassembled, highest pressures and compare with the
cleaned, flushed and reassembled before maximum pump pressure recorded. If this
further usage. pressure cannot be built in either (or one) side of
- the gear, the gear is leaking internally and must
c. If
the pressures recorded are constant, but
be disassembled and repaired. See "Unit Repair"
more than
100 PSI (690 kPa), below the
at the end of this section.
spec.9 rep1ace the flow 8. Shut off engine, remove testing gage, spare hose,
valve and recheck. If the pressures are still
low, replace the rotating group in the pump. reconnect pressure hose, check fluid
level and/or
make needed repairs.
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
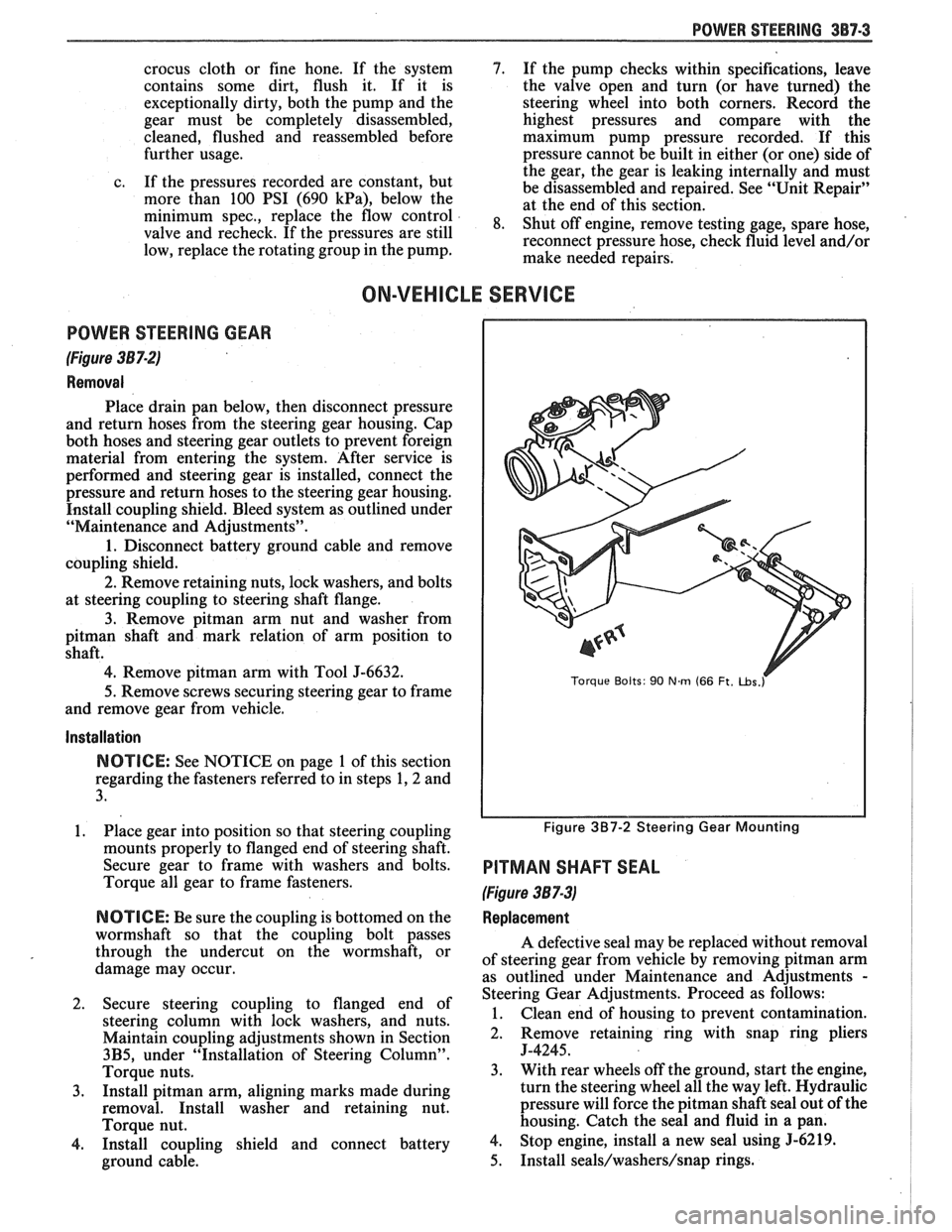
POWER STEERING GEAR
(Figure 387-2)
Removal
Place drain pan below, then disconnect pressure
and return hoses from the steering gear housing. Cap
both hoses and steering gear outlets to prevent foreign
material from entering the system. After service is
performed and steering gear is installed, connect the
pressure and return hoses to the steering gear housing.
Install coupling shield. Bleed system as outlined under
"Maintenance and Adjustments".
1. Disconnect battery ground cable and remove
coupling shield.
2. Remove retaining nuts, lock washers, and bolts
at steering coupling to steering shaft flange.
3. Remove pitman arm nut and washer from
pitman shaft and mark relation of arm position to
shaft.
4. Remove pitman arm with Tool J-6632.
5.
Remove screws securing steering gear to frame
and remove gear from vehicle.
Installation
NOTICE: See NOTICE on page 1 of this section
regarding the fasteners referred to in steps 1,2 and
3.
1. Place gear into position so that steering coupling
mounts properly to flanged end of steering shaft.
Secure gear to frame with washers and bolts.
Torque all gear to frame fasteners.
NOTICE: Be sure the coupling is bottomed on the
wormshaft so that the coupling bolt passes
through the undercut on the wormshaft, or
damage may occur.
2. Secure steering coupling to flanged end of
steering column with lock washers, and nuts.
Maintain coupling adjustments shown in Section
3B5, under "Installation of Steering Column".
Torque nuts.
3. Install pitman arm, aligning marks made during
removal. Install washer and retaining nut.
Torque nut.
4. Install coupling shield and connect battery
ground cable.
Torque Bolts: 90 Nm (66 Ft. ~bs.r
Figure 3B7-2 Steering Gear Mounting
PITMAN SHAFT SEAL
(Figure 387-3)
Replacement
A defective seal may be replaced without removal
of steering gear from vehicle by removing
pitman arm
as outlined under Maintenance and Adjustments
-
Steering Gear Adjustments. Proceed as follows:
1. Clean end of housing to prevent contamination.
2. Remove retaining
ring with snap ring pliers
J-4245.
3. With rear wheels off the ground, start the engine,
turn the steering wheel all the way left. Hydraulic
pressure will force the
pitman shaft seal out of the
housing. Catch the seal and fluid in a pan.
4. Stop engine, install a new seal using 5-6219.
5. Install seals/washers/snap rings.
Page 245 of 1825

4A-4 PROPELLER SHAFT
PROPELLER SHAFT BALANCING
Hose Clamp Method
Figures 4A- 1 1 thru 4A-13
1. Place the vehicle on a twin post hoist so that the
rear of the vehicle is supported on the rear axle
housing and the rear wheels are free to rotate.
Remove both rear wheel assemblies and reinstall
wheel lug nuts with flat sides next to
drums/discs.
2. Mark and number propeller shaft at four (4)
points 90 degrees apart at rear of shaft just
forward of balance weight, as shown.
3. Install two (2) hose clamps on the rear of the
propeller shaft and slide them rearward until the
clamps stop at the nearest balance weight welded
to the tube. Align both clamps at any one of the
four marks made on shaft in Step 2 and tighten.
Be sure sufficient clearance is maintained so that
clamp heads do not contact floor pan of vehicle
when axle is in contact with rebound bumper in
frame. In order to gain sufficient clearance, it
may be necessary to position the clamps over the
balance weights.
4. Run the vehicle through the speed range to 80-90
MPH (130-145
Km/h) and note amount of
imbalance.
CAUTION: All persons should stay
clear of universal joint and balance
weight areas to avoid possible injury.
Do not run on hoist for extended
periods due to the danger of
overheating the transmission or
engine.
5. Loosen clamps and rotate clamp heads 90 degrees
to the next mark on a propeller shaft. Tighten
clamps and repeat Step 4.
6. Repeat Step 5 until car has been run with clamp
heads located at all four marks on shaft.
7. Position clamps at point of least imbalance.
Rotate the clamp heads away from each other 45
degrees (one on each side of the position), as
shown. Run the vehicle and note if imbalance has
improved.
In some cases it may be necessary to use one
clamp or possibly three clamps in order to obtain
a good balance. Replace shaft if three hose clamps
do not improve the imbalance.
8. Continue to rotate the clamps apart in smaller
angular increments until the imbalance is at its
minimum.
9. Reinstall wheel assemblies and road test the
vehicle for final check of balance. A minimal
vibration felt in the vehicle on the hoist may not
show up during a road test.
Strobe Light Method
Figures 461- 1 1, $A- 14, and 4A- 15
If a wheel balancer of the strobe light type is
available, the use of such a unit will facilitate the
balancing of the propeller shaft. The balance pick-up
unit should be placed directly under the nose of the
rear axle carrier and as far forward as possible. 1.
Place
the vehicle on a twin post hoist so the rear of
the vehicle is supported on the rear axle housing and
the rear wheels are free to rotate. Lower rear hoist
and allow axle to rest on jackstands. The groove in
the rear hoist fixture could clamp the axle and de-
stroy the sensitivity of the operation. Remove both
rear wheel assemblies and reinstall wheel lug nuts
with flat sides next to the
drums/rotors.
2.
Mark and number drive shaft at 4 points 90
degrees apart at rear of shaft just forward of
balance weights, as shown.
3. Place the strobe light wheel balancer pick-up
under the nose of the carrier.
4. Run vehicle in gear at the speed where the
distrubance is at its peak, allow the driveline to
stabilize by holding at a constant speed. Point
strobe light up at the spinning propeller shaft and
note position of one of the reference numbers.
Shut off engine and position the propeller shaft so
the reference numbers will be in the same position
as was noted while the shaft was rotating.
When strobe light flashed, the heaviest point of
the shaft was at the bottom (6 o'clock). To
balance the propeller shaft, it would be necessary
to apply the balancing weights (hose clamps) 180
degrees away from the heaviest point or at the top
of the propeller shaft (12 o'clock).
5. Install two screw-type hose clamps on the
propeller shaft as close to the rear as possible.
Position both clamp heads 180 degrees from the
heaviest point of drive shaft as indicated by strobe
light. Tighten clamps.
NOTICE: Be sure sufficient clearance is
maintained so clamp heads do not contact floor
pan of vehicle when axle is in contact with rebound
bumper on frame. In order to gain. sufficient
clearance, it may be necessary to position the
clamps over the balance weights.
6. Run vehicle through the speed range 80-90
M.P.
H. (130-145 Km/h). If disturbance is gone,
nothing further need be done on the hoist. If the
disturbance is not gone and the strobe light shows
the clamp heads at the bottom (6 o'clock) of the
shaft, go to Step
7. If the strobe light shows the
two clamp heads at the top of the shaft, add one
more hose clamp and recheck. If the strobe light
shows the three clamp heads at the top of the
shaft, remove the propeller shaft and
reindex it
180 degrees on the rear axle pinion companion
flange. Recheck with no clamps. Repeat balance
starting with Step 5. If the shaft still needs more
than three hose clamps at the same clock position,
replace it. If the clamps are also 180 degrees from
their original position after the propeller shaft
was reindexed 180 degrees, the rear axle pinion
companion flange is out of balance and must be
replaced. DO NOT use more than three hose
clamps to balance the shaft. If the strobe light
shows the hose clamps at the bottom of the shaft,
but the disturbance still exists, go to Step
7.
Page 252 of 1825
I
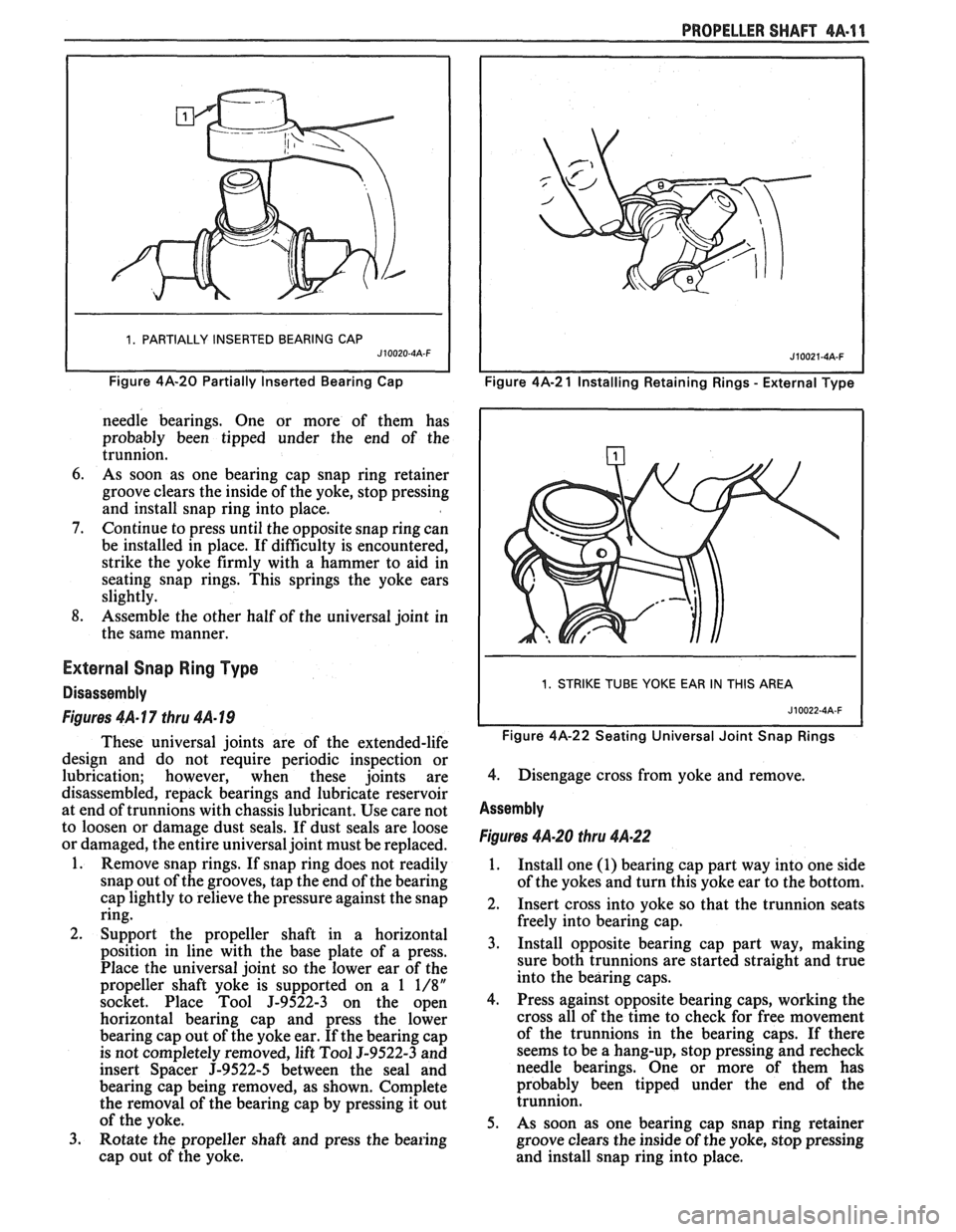
1. PARTIALLY INSERTED BEARING CAP J10020-4A-F I
Figure 4A-20 Partially Inserted eari in^ Cap
needle bearings. One or more of them has
probably been tipped under the end of the
trunnion.
6. As soon as one bearing cap snap ring retainer
groove clears the inside of the yoke, stop pressing
and install snap ring into place.
7. Continue to press until the opposite snap ring can
be installed in place. If difficulty is encountered,
strike the yoke firmly with a hammer to aid in
seating snap rings. This springs the yoke ears
slightly.
8. Assemble the other half of the universal joint in
the same manner.
External Snap Ring Type
Disassembly
Figures 4A- 17 thru 4A- 19
These universal joints are of the extended-life
design and do not require periodic inspection or
lubrication; however, when these joints are
disassembled, repack bearings and lubricate reservoir
at end of trunnions with chassis lubricant. Use care not
to loosen or damage dust seals. If dust seals are loose
or damaged, the entire universal joint must be replaced.
1. Remove snap rings. If snap ring does not readily
snap out of the grooves, tap the end of the bearing
cap lightly to relieve the pressure against the snap
ring.
2. Support the propeller shaft in a horizontal
position in line with the base plate of a press.
Place the universal joint so the lower ear of the
propeller shaft yoke is supported on a
1 1/8"
socket. Place Tool J-9522-3 on the open
horizontal bearing cap and press the lower
bearing cap out of the yoke ear. If the bearing cap
is not completely removed, lift Tool
9-9522-3 and
insert Spacer
J-9522-5 between the seal and
bearing cap being removed, as shown. Complete
the removal of the bearing cap by pressing it out
of the yoke.
3. Rotate the propeller shaft and press the bearing
cap out of the yoke.
PROPELLER SHAFT 4A-11
I I Figure 4A-2 1 Installing Retaining Rings - External Type
I 1. STRIKE TUBE YOKE EAR IN THIS AREA I
Figure 4A-22 Seating Universal Joint Snap Rings
4. Disengage cross from yoke and remove.
Assembly
Figures 4A-20 thru 4A.22
1. Install one (1) bearing cap part way into one side
of the yokes and turn this yoke ear to the bottom.
2. Insert cross into yoke so that the trunnion seats
freely into bearing cap.
3. Install opposite bearing cap part way, making
sure both trunnions are started straight and true
into the bearing caps.
4. Press against opposite bearing caps, working the
cross all of the time to check for free movement
of the trunnions in the bearing caps. If there
seems to be a hang-up, stop pressing and recheck
needle bearings. One or more of them has
probably been tipped under the end of the
trunnion.
5. As soon as one bearing cap snap ring retainer
groove clears the inside of the yoke, stop pressing
and install snap ring into place.
Page 296 of 1825

BRAKES 5-3
DIAGNOSIS AND INSPECTION
BRAKE SYSTEM TESTING
(Figures
2 through 4)
Brakes should be tested on dry, clean, reasonably
smooth and level roadway. A true test of brake performance
cannot be made if the roadway is wet, greasy or covered
with loose dirt so that all tires do not grip the road equally.
Testing will also be affected if the roadway is crowned
which would throw the weight of the car toward the wheels
on one side. If the roadway is too rough, the wheels will tend
to bounce. Test brakes at different car speeds with both light and
heavy pedal pressure, avoid locking the brakes and sliding
the tires. Locked brakes and sliding tires do not indicate
brake efficiency, because heavily braked, but turning
wheels will stop the car in less distance than locked brakes.
More tire-to-road friction is present with a heavily braked
turning tire than with a sliding tire. The brake system is designed and balanced to avoid
locking the wheels, except at very high deceleration levels.
The shortest stopping distance and best control is achieved
without brake lock-up.
Because of high deceleration capability, a firmer pedal
may be felt at higher deceleration levels.
External Conditions That Affect Brake Performance
1. Tires. Tires having unequal contact and grip on road
will cause unequal braking. Tires must be equally
inflated and tread pattern of right and left tires must
be approximately equal.
2. Car Loading. A heavily loaded car requires more
braking effort. When a car has unequal loading, the
most heavily loaded wheels require more braking
power than others.
3. Wheel Alignment. Misalignment of the wheels, par-
ticularly excessive camber and caster, will cause the
brakes to pull to one side.
4. Front Wheel Bearings. A loose front wheel bearing
BRAKE FLUID LEAKS
With engine running at idle and the transmission in neu-
tral, depress the brake pedal and hold a constant foot pres-
sure.
If the pedal gradually falls away with the constant
pressure, the hydraulic system may be leaking. Perform a
visual check to confirm any suspected leak.
Check the master cylinder fluid levels. While a slight drop
in reservoir level does result from normal lining wear, an
abnormally low level in either reservoir indicates
a leak in
the system. The hydraulic system may be leaking either
internally or externally. See "Master Cylinder Check."
Also, the system may appear to pass this test but still have
slight leakage.
If fluid levels are normal, check the vacuum booster
pushrod length. If an incorrect length pushrod is found,
adjust or replace the
pushrod. Check the service brake
pedal travel and the parking brake adjustment.
When checking the fluid levels, the master cylinder reser-
voir may be as low as
25 mm (1 inch) from the top if the front
linings are worn. This is not abnormal.
MASTER CYLINDER CHECK
These checks will help locate some master cylinder mal-
functions. Use the Brake Diagnosis Charts to help isolate
the problem if it is not found by using these tests.
1. Check for a cracked master cylinder casting or brake
fluid around the master cylinder. Leaks are indicated
only if there is at least a drop of fluid. A damp condi-
tion is not abnormal.
2. Check for a binding pedal linkage.
3. Disassemble the master cylinder and check for swol-
len or stretched piston
seal(s). If swollen seals are
found, substandard or contaminated brake fluid
should be suspected.
If contaminated, all compo-
nents should be disassembled and cleaned. All rub-
ber components should be replaced and all the pipes
should be flushed.
permits the front wheel to tilt and lose contact with the
SUBSTANDARD OR CONTAMINATED brake shoe linings causing erratic brake operation. BRAKE FLUID
WARNING LAMP OPERATION
The brake system uses a single red "BRAKE" warning
lamp located in the instrument panel cluster. When the
ignition switch is in the "START" position, the "BRAKE"
warning lamp should come on. It should go off when the
ignition switch returns to the "RUN" position.
The following conditions will activate the "BRAKE"
warning lamp:
1. Parking brake applied. The lamp should be on when
tfie parking brake is applied and the ignition switch is
"ON."
2. Pressure differential switch detects a failure. See
"Brake Pressure Differential Warning Switch" in this
section. Improper
brake fluid, mineral oil or water in the fluid may
cause the brake fluid to boil or the rubber components to
deteriorate.
If piston cups are swollen, the rubber parts have dete-
riorated. This deterioration may also be seen by swollen
wheel cylinder piston cups on the drum brake wheels or a
swollen master cylinder cover diaphragm.
If rubber deterioration is evident, disassemble all hydrau-
lic parts and wash with alcohol. Dry these parts with com-
pressed air before assembly to keep alcohol out of the
system. Replace all rubber parts in the system, including
hoses. Check for fluid on the linings. If excessive fluid is
found, replace the linings.
If master cylinder piston seals are satisfactory, check for
leakage or excessive heat conditions. If condition is not
found, drain fluid, flush with brake fluid, fill and bleed the
system.