1988 PONTIAC FIERO mileage
[x] Cancel search: mileagePage 286 of 1825
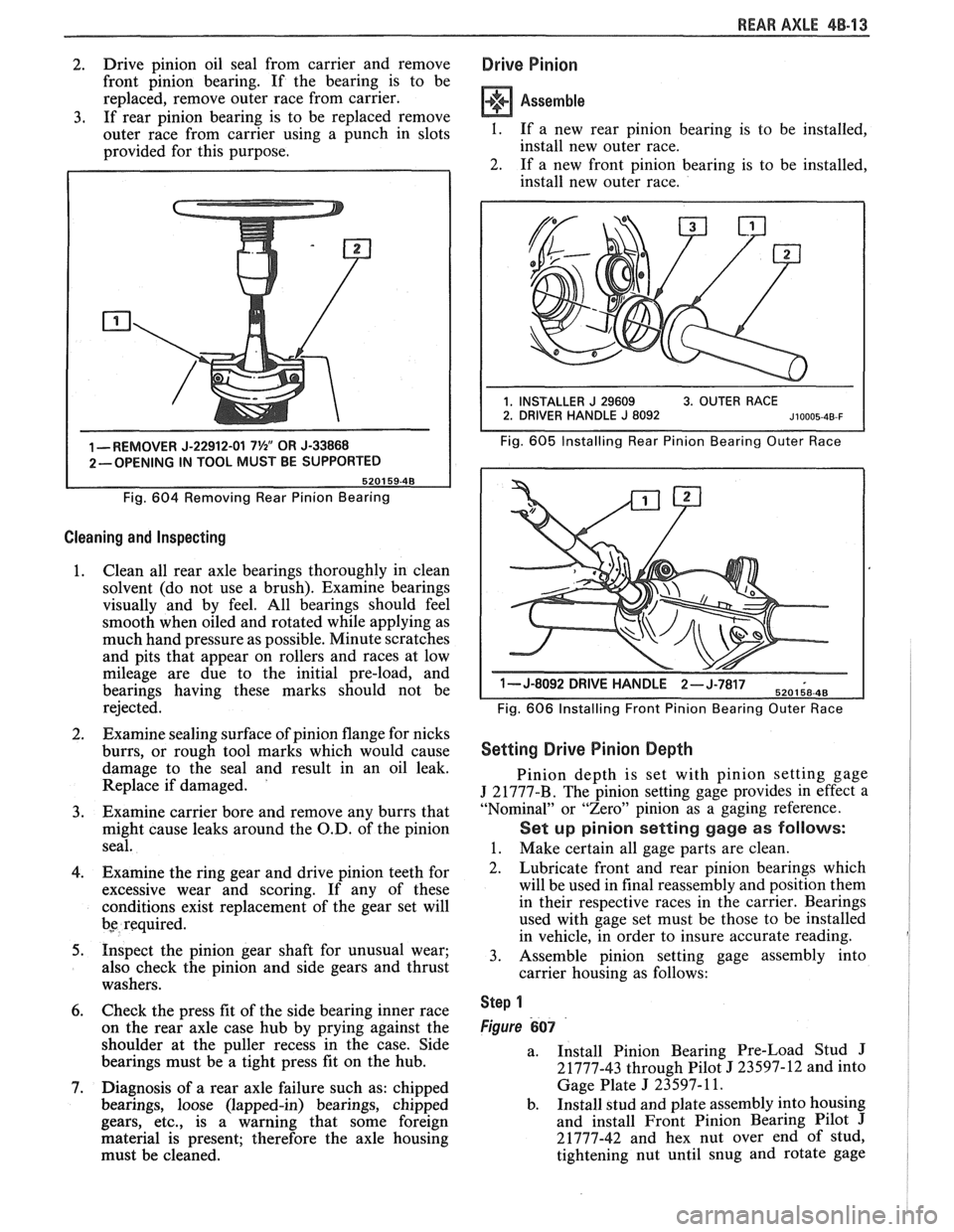
REAR AXLE 48-13
2. Drive
pinion oil seal from carrier and remove
front pinion bearing. If the bearing is to be
replaced, remove outer race from carrier.
3. If rear pinion bearing is to be replaced remove
outer race from carrier using a punch in slots
provided for this purpose.
1 -REMOVER J-22912-01 7%" OR J-33868
2-OPENING IN TOOL MUST BE SUPPORTED
Fig.
604 Removing Rear Pinion Bearing
Cleaning and Inspecting
1. Clean
all rear axle bearings thoroughly in clean
solvent (do not use a brush). Examine bearings
visually and by feel. All bearings should feel
smooth when oiled and rotated while applying as
much hand pressure as possible. Minute scratches
and pits that appear on rollers and races at low
mileage are due to the initial pre-load, and
bearings having these marks should not be
rejected.
2. Examine sealing surface of pinion flange for nicks
burrs, or rough tool marks which would cause
damage to the seal and result in an oil leak.
Replace if damaged.
'
3. Examine carrier bore and remove any burrs that
might cause leaks around the O.D. of the pinion
seal.
4. Examine the ring gear and drive pinion teeth for
excessive wear and scoring. If any of these
conditions exist replacement of the gear set will
bs required.
5. Inspect the pinion gear shaft for unusual wear;
also check the pinion and side gears and thrust
washers.
6. Check the press fit of the side bearing inner race
on the rear axle case hub by prying against the
shoulder at the puller recess in the case. Side
bearings must be a tight press fit on the hub.
7. Diagnosis of a rear axle failure such as: chipped
bearings, loose (lapped-in) bearings, chipped
gears, etc., is a warning that some foreign
material is present; therefore the axle housing
must be cleaned.
Drive Pinion
Assemble
I. If a new rear pinion bearing is to be installed,
install new outer race.
2. If a new front pinion bearing is to be installed,
install new outer race.
Fig. 605 Installing Rear Pinion Bearing Outer Race
1- J-8092 DRIVE H-,.wb- 6
Fig. 606 Installing Front Pinion Bearing Outer Race
Setting Drive Pinion Depth
Pinion depth is set with pinion setting gage
J 21777-B. The pinion setting gage provides in effect a
"Nominal" or "Zero" pinion as a gaging reference.
Set up pinion setting gage as follows:
1. Make certain all gage parts are clean.
2. Lubricate front and rear pinion bearings which
will be used in final reassembly and position them
in their respective races in the carrier. Bearings
used with gage set must be those to be installed
in vehicle, in order to insure accurate reading.
3. Assemble pinion setting gage assembly into
carrier housing as follows:
Step 1
Figure 607
a.
Install Pinion Bearing Pre-Load Stud J
21777-43 through Pilot J 23597-12 and into
Gage Plate
J 23597- 11.
b. Install stud and plate assembly into housing
and install Front Pinion Bearing Pilot
J
21777-42 and hex nut over end of stud,
tightening nut until snug and rotate gage
Page 347 of 1825

6-2 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION
6E3 - Fuel Injection (Ported) This section has information
on all exhaust
system parts, such as tailpipes, mufflers, and the
SECTION 6F - EXHAUST SYSTEM catalytic converter.
GENERAL INFORMAflION
CLEANLINESS AND CARE
An automobile engine is a combination of many
machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with
tolerances that are measured in the ten-thousandths of
an inch. When any internal engine parts are serviced,
care and cleanliness are important. A liberal coating of
engine oil should be applied to friction areas during
assembly, to protect and lubricate the surfaces on
initial operation. Throughout this section, it should be
understood that proper cleaning and protection of
machined surfaces and friction areas is part of the
repair procedure. This is considered standard shop
practice, even if not specifically stated. PREVENTING
DAMAGE AND IN
CONTRIBUTING TO RELIABLE ENGINE
PERFORMANCE.
When raising or supporting the engine for any
reason, do not use a jack under the oil pan. Due to the
small clearance between the oil pan and the oil pump
screen, jacking against the oil pan may cause it to be
bent against the pump screen resulting in a damaged
oil pick-up unit.
When working on the engine, remember that the
12-volt electrical system is capable of causing short
circuits. When performing any work where electrical terminals could possibly be grounded, the ground cable
of the battery should be disconnected at the battery.
Any time the carburetor or air cleaner is
train components are removed removed, the intake opening should be covered. This for service, they should be in order' will protect against entrance of foreign be installed in the same locations, and with the same material, which could follow the intake passage into mating surfaces, as when removed
the cylinder and cause extensive damage when the -
Battery cables should be disconnected before any engin; is started.
major work is performed on the engine. Failure to IN THE MECHANICAL PROCEDURES
disconnect cables may result in damage to wire harness DESCRIBED IN THIS SECTION, GENERALLY
or other electrical parts. NO
REFERENCES WILL BE MADE TO THE
REMOVAL OF OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT SUCH
ENGINE SERVICE AS POWER STEERING PUMP, AIR
CONDITIONING COMPRESSOR, ETC.
THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION ON SHOULD IT BECOME NECESSARY TO
ENGINE SERVICE SHOULD BE NOTED REMOVE ANY SUCH ITEM TO
PERFORM
CAREFULLY, AS IT IS IMPORTANT IN OTHER SERVICE, REFER TO THE
APPROPRIATE SECTION OF THIS SERVICE
MANUAL FOR SPECIFIC INFORMATION.
ENGINE PERFORMANCE DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTION interchangeably for so long, it was necessary to decide
on the most common usage and then define them. If the
Engine Performance procedures are definition is not understood, and the exact Symptom is
guides that will lead to the most probable causes of not used, the Diagnostic procedure will not work. engine performance complaints. They cover the
components of the fuel, ignition, and mechanical It
is important to keep two facts in mind:
systems that could cause a particular
complaint, and 1. The procedures are written to diagnose problems
then outline repairs in a logical sequence. on cars
that have
"run well at one time" and
that time and wear have created the condition.
It is important to determine if the
"Service ~~~i~~ soon- light is "ON,~' or has come for 2. All possible causes cannot be covered,
a short interval while driving. If the
"Service Engine particularly with regard to emission controls. If
Soon" light has come "ON," the Computer doing the work prescribed does not correct the
Command Control System or DECS should be complaint, then either the wrong Symptom was
checked for stored
"Trouble Codes" (See Diagnostic used, or a more detailed analysis will have to be
Circuit Check, Section 6E, for the engine you are made.
working on) which may indicate the cause for the All of the Symptoms can be caused by worn out
performance
complaint.Each Symptom is defined, and or defective parts such as Spark Plugs, Ignition
it is important that the correct one be selected, based Wiring, etc. If time and/or mileage indicate that
on the complaints reported or found. The definition of parts should be replaced, it is recommended that
each symptom is included with the symptom. it
be done.
The words used may not be what you are used to Refer to:
in all cases, but because these terms have been used
@ Section 6E - Driveability and Emissions
Page 348 of 1825

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION 6-3
B, Section 6E2 - Fuel Injection (TBI)
B, Section 6E3 - Fuel Injection (Ported)
ENGINE MECHANICAL DIAGNOSIS
The following diagnostic information covers common problems and possible causes. When
the proper diagnosis is made, the problem should be corrected by adjustment, repair or part
replacement as required. Refer to the appropriate section of the manual for these procedures.
EXCESSIVE OIL LOSS
B, External oil leaks. Tighten bolts and/or replace o Continuous high speed driving, and/or severe
gaskets and seals as necessary. usage
such as trailer hauling, will normally cause
decreased oil mileage.
e Improper reading of dipstick. Check oil with car PCV system malfunctioning. on a level surface and allow adequate drain-down Valve guides and/or valve stem seals worn, or time.
seals omitted. Ream guides and install oversize
service valves and/or new valve stem seals.
Improper Use S.A'E' Piston rings broken, worn, or not seateded. Allow viscosity for prevailing temperatures. See
adequate time for rings to seat. Replace broken
Owner's Manual for proper specifications.
or worn rings, as necessary.
Piston improperly installed or misfitted.
LOW OIL PRESSURE
Slow idle speed. Set idle speed to correct
specification, if not ECM controlled.
Incorrect, or malfunctioning, oil pressure switch.
Incorrect, or malfunctioning, oil pressure gage.
Replace with proper gage.
.*
Improper oil viscosity, or diluted oil. install oil of
proper viscosity for expected temperature, or
install new oil if diluted with moisture or
unburned fuel mixtures.
o Oil pump worn or dirty.
e Plugged oil filter.
e Oil pickup screen loose or plugged.
B, Hole in oil pickup tube.
e Excessive bearing clearance. Replace if necessary.
o Cracked, porous or plugged oil galleys. Repair or
replace block.
o Galley plugs missing or misinstalled. Install
plugs, or repair as necessary.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE
e Low oil pressure. Repair as necessary. (See o Broken valve spring.
preceding diagnosis for low oil pressure.)
o Sticking valves.
o Loose rocker arm attachments. Inspect and B, Lifters worn, dirty, or defective. Clean, inspect,
test and replace as necessary.
repair as necessary.
o Camshaft worn, or poor machining. Replace
o Worn rocker arm and/or pushrod. camshaft.
B, Worn valve guides.
ENGINE KNOCK DIAGNOSIS
KNOCKS COLD AND CONTINUES FOR TWO TO THREE MINUTES
INCREASES
WITH TORQUE
o Vacuum operated EFE engines may have valve o Excessive piston to bore clearance. Replace
knock. Replace EFE valve. piston.
e Flywheel contacting splash shield. Reposition
splash shield.
e Loose or broken balancer or drive pulleys.
Tighten, or replace as necessary. Cold engine piston knock usually
disappears when the cylinder is grounded
out. Cold engine piston knock which
disappears in 1.5 minutes should be
considered acceptable.
Page 472 of 1825

IGNITION SYSTEM 6B4-3
flash-over, which causes engine misfiring. Do not
mistake corona discharge for flash-over, or a shorted
insulator. Corona is a steady blue light appearing
around the insulator, just above the shell crimp. It is
the visible evidence of a high-tension field and has no
effect on ignition performance. Usually it can be
detected only in darkness. This discharge may repel
dust particles, leaving a clear ring on the insulator just
above the shell. This ring is sometimes mistakenly
regarded as evidence that combustion gases have blown
out between shell and insulator.
lgnition Switch
The mechanical switch is located in the steering
column on the right hand side just below the steering
wheel. The electrical switching portion of the assembly
is separate from the key and lock cylinder. However,
both are synchronized and work in conjunction with
each other through the action of the actuator rod
assembly.
For a complete explanation of the key and lock
cylinder, and the actuator rod assembly, see
STEERING, Section
38. See Section 8 for electrical
switching.
DIAGNOSIS
IGNITION SYSTEM
Spark Plugs
Worn or dirty plugs may give satisfactory
operation at idling speed, but at higher RPM they
frequently fail. Faulty plugs are indicated in a number
of ways: poor fuel economy, power loss, loss of speed,
hard starting and generally poor engine performance.
Spark plugs may also fail due to carbon fouling,
excessive gap, or a broken insulator. Fouled plugs may
be indicated by black carbon
deposits. The black deposits are usually the result of
slow-speed driving and short runs, where sufficient
engine operating temperature is seldom reached. Worn
pistons, rings, faulty ignition, over-rich carburetion
and spark plugs which are too cold will also result in
carbon deposits.
Excessive gap wear, on plugs of low mileage,
usually indicates the engine is operating at high speeds,
or loads that are consistently greater than normal, or
that a plug which is too hot is being used. Electrode
wear may also be the result of plug overheating,
causcd
by combustion gases leaking past the threads due to
insufficient torquing of the spark plug. Excessively lean
carburetion will also result in accelerated electrode
wear.
Broken insulators are usually the result of
improper installation, or carelessness when regapping
the plug. Broken upper insulators usually result from
a poor fitting wrench, or an outside blow. The cracked
insulator may not show up right away, but will as soon
as oil or moisture penetrates the crack. The crack is
usually just below the crimped part of shell and may
not be visible.
Broken lower insulators usually result from
carelessness when regapping and generally are visible.
This type of break may result from the plug operating
too "hot", which may happen in periods of high-speed
operation or under heavy loads. When regapping a
spark plug, always make the gap adjustment by
bending the ground (side) electrode. Spark plugs with
broken insulators should always be replaced.
HE1 Distributor
See Unit Repair for distributor disassembly, test
and reassembly of individual distributor components,
when the distributor is removed from the vehicle. See
On-Car Service for distributor removal and installation
and for component removal with distributor in car. See
Section 6E for
HE1 and EST diagnosis.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
IGNITION SYSTEM
Distributor Ignition
NOTICE: This procedure is generally true for
most carlines. Where procedure is different, or
where additional information is required, see
"ON-CAR SERVICE" for specific
carline.
HE1 DISTRIBUTOR
Service Precautions
1. When making compression checks, disconnect
the ignition switch feed wire at the distributor.
When disconnecting this connector,
do not use
a screwdriver or tool to release the locking tab, as
it may break.
2. No periodic lubrication is required. Engine oil
lubricates the lower bushing and an oil-filled
reservoir provides lubrication for the upper
bushing. 3.
The tachometer (TACH) terminal is next to the
ignition switch (BAT) connector on the
distributor cap.
NOTICE: The tachometer terminal must
NEVER be allowed to touch ground, as damage
to the module and/or ignition coil can result.
Some tachometers currently in use may NOT be
compatible with the High Energy Ignition System.
Consult the manufacturer of the tachometer if
questions arise.
4. Dwell adjustment is controlled by the module,
and cannot be adjusted.
5. The material used to construct the spark plug
cables is very soft. This cable will withstand more
heat and carry a higher voltage, but scuffing and
cutting become easier. The spark plug cables
must be routed correctly to prevent
chafing or
cutting. See Spark Plug Section. When removing
Page 1613 of 1825

842-2 INSTRUMENT PANEL. GAGES & CONSOLE
Pinion Gear
The PINION GEAR is attached to the
traaasmission/transaxle output shaft and rotates in
proportion to the speed of the car. This rotation is
transferred from the pinion gear to the speedometer
head by the speedometer cable.
Photo Speed Sensor
On vehicles that use a mechanical drag-cup
speedometer, the PHOTO SPEED SENSOR is
inserted into the frame of the mechanical speedometer
to provide an electrical feedback to the ECM that
represents vehicle speed. The ECM needs to know how
fast the car is traveling in order to control and operate
the cruise control, cooling fan, and transmission and
evaporative systems.
The photo speed sensor is made up of two special
electronic devices: a Eight-Emitting Diode (LED) and
a photo transistor (a light-sensitive amplifying device).
In the mechanical speedometer, there is a reflective
blade attached to the rotating magnet that is polished
to
reflect light from the LED back to the photo
transistor. Whenever the light strikes the photo
transistor, it conducts electricity. The rate that the
transistor conducts and does not conduct is
proportional to the speed of the magnet, which reflects
the speed of the vehicle. This voltage signal from the
photo transistor is sent to a buffer amplifier (part of the
speed sensor) to be conditioned to a signal the ECM
can understand and use.
PM Generator
The PM (Permanent Magnet) GENERATOR is
a small
AC generator used to sense vehicle speed. The
shaft of the generator fits into a pinion gear in the
transmission/transaxle output shaft (as does the cable
in
a mechanical system).
When the output shaft rotates, the magnet rotates
and generates a voltage. Except for the permanent
magnet, the
PM Generator is exactly like a miniature
alternator. The PM generator is constructed to provide
a voltage whose frequency is about
1.1 cycles per
second for every mile per hour of vehicle speed. This
signal is sent to a buffer amplifier, and then to the
speedometer and the
EGM.
SPEEDOMETER
The speedometer is a road speed indicator with
an odometer to record total mileage, and, on some cars,
a resettable trip odometer.
The major types of speedometers in use are
mechanical instruments and electronic instruments.
Mechanical speedometers use a dial needle to indicate
road speed. Electronic speedometers include
instruments that use a dial indicator and those using
bar-graph
LCD's (Liquid Crystal Displays) or VTF
(Vacuum Tube Fluorescent) displays.
Meehanice! Speedometers
A mechanical speedometer uses a cable driven
(through a pinion gear) by the transmission output
shaft. The cable connects to a magnetic drag-cup inside the
speedometer, which rotates the speedometer
needle. The end of the rotating cable causes a small bar
magnet to rotate within a metal cup. As the magnet
rotates within the cup, it magnetically attracts (drags)
the metal cup along behind it. Two things work to
prevent the cup from rotating as quickly as the magnet.
1. The distance of the magnet from the cup reduces
its effect on the cup.
2. A counterspring is wound around the shaft of the
cup in such a way as to oppose the normal
rotation of the cup. The counterspring loads the
drag-cup to give correct indication of the speed,
prevent needle overshoot, and also to return the
drag cup to a zero point.
Mechanical speedometers require a photo speed
sensor to provide road speed information for the ECM
and other systems, such as Cruise Control and the TCC
(Torque Converter Clutch).
The odometer on these instruments consists of
numbered wheels that are rotated by the speedometer
cable through worm gears.
Quartz Speedometer
The quartz speedometer is an electrically driven
instrument. The indicator needle is driven by a
precision DC motor, and is countersprung to provide
a mechanical load, prevent overshoot of the needle, and
return the indicator to zero when the road speed is
zero.
The source of speed information for a quartz
speedometer is the PM generator. From the PM
generator, speed information goes to the buffer
amplifier to be converted to digital voltage, and then
to the cluster circuitry, which interprets the speed of
the vehicle and produces small voltage to apply to the
speedometer motor.
The odometer on this instrument consists of
numbered wheels that are electrically driven by a
special precision DC motor called a stepper motor.
Digital Speedometer
Digital clusters utilize two types of displays: LCD
(Liquid Crystal Display) and VTF (Vacuum Tube
Fluorescent). They are used in digital speedometers
and bar-graph tachometers, fuel gages, etc.
Speed information entering the cluster from the
buffer amplifier is interpreted by a microcomputer
which controls the speed indication, the tachometer
display and the odometer reading.
The odometers associated with these instruments
utilize either numbered wheels driven by a small motor
or electronic displays. With an electronic display, the
mileage reading is stored in a computer chip (called a
non-volatile RAM chip; NVRAM) that does not
become 'erased' when the vehicle is turned off,
as the
display does not retain the information.
FUEL GAGE
An electrical fuel gage is used on all models,
consisting of an instrument panel gage and a fuel tank
pick-up. The fuel gage indicates the quantity of fuel in
Page 1614 of 1825

INSTRUMENT PANEL. GAGES & CONSOLE 8C-3
tank only when ignition switch is turned to "ON" or
"ACCESSORY" positions.
When ignition is turned to "OFF" or "START"
positions, the pointer may come to rest at any position.
The letters
"E" and "F" on the fuel gage are used to
point out direction of indicator travel only.
TEMPERATURE WARNING LIGHT
The engine temperature warning light is
controlled by a thermal switch which senses engine
coolant temperatures.
When the ignition switch is turned to "START"
position, a test circuit is closed and the light will come
on to indicate whether the light is functioning properly.
It is important to note that with low boiling-point
coolants (such as plain water) the temperature light
may not come on even though the coolant is boiling.
GENERATOR WARNING LIGHT
The generator warning light, located in the
instrument cluster, should come on when the ignition
switch is turned
"ON" and engine is not running. If
not, either the bulb is burned out or wiring to generator
has an open circuit.
When the generator voltage output becomes
greater than the battery voltage, the
"GEN" light
should go out. This does not, however, indicate
whether the battery is being charged or if the voltage
regulator is functioning properly.
Checks of the charging system are covered in
Section 6D, 'Engine Electrical'.
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE LIGHT
The engine oil pressure warning light is mounted
in the instrument cluster and controlled by a pressure
operated switch located on the engine block. When the ignition switch is
in the
"run" or "start9' position, the
oil pressure light should come on. If not, the bulb is
burned out, there is an open circuit between the bulb
and the oil pressure switch, or there is an open circuit
between the oil pressure switch and the choke heater.
After the engine is running, the oil pressure light
should go out when the oil pressure reaches the correct
specification. If not an oil pressure problem, a faulty oil
pressure switch or an open circuit from the choke
heater fuse to the oil pressure switch is indicated.
"SERVICE ENGINE SOON" LIGHT
All cars have a "SERVICE ENGINE SOON"
light mounted in the instrument cluster. The
"SERVICE ENGINE SOON9' light should come on
during engine starting. The light may stay on
a short
time after the engine starts.
If the light comes on while
driving, service to the emission control system may be
required. See Section
6E and Section 8A-80,
'Instrument Cluster', for complete diagnosis and
wiring diagrams of the
""P;RVICE ENGINE SOON"
light circuit.
UPSHIFT INDICATOR LIGHT
If your vehicle has a manual transmission, there
may be an
''Upshift" light on the instrument panel.
This light is illuminated to indicate optimum shift
points throughout the range from optimum fuel
economy to optimum performance. When this light is
on, shift your transmission to the next higher gear
range if conditions permit. For fuel economy,
accelerate slowly and shift when the light goes on. For
performance, accelerate as desired and shift when the
light goes on.
Safe operation of the vehicle may require shifting
differently than indicated by the "Upshift" light to
adapt to weather, road or traffic conditions.
Downshifting one or more gears may be required
to keep the engine running smoothly or to maintain
satisfactory performance.
DIAGNOSIS
Diagnostic information for all instrument panel
electrical systems is found in Section
8A-80,
'Instrument Panel'.
CAUTION: When removing or
installing any electrical units,
disconnect the negative battery cable
to prevent possible short circuits
which could lead to personal injury
and/or property damage. When
replacing a speedometer or
odometer assembly, the law requires the
odometer reading of the replacement unit to
be set to register the same mileage as the
prior odometer.
if the same mileage cannot be
set, the
law requires that the replacement
odometer be set to zero and a label be
installed on the driver's door frame to show
the previous odometer reading and the date
of replacement.
GENERAL BNFORMATlOM
INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAGES
The instrument panel is a single unit design and
and screws. To service the instrument panel and
all parts attach to the main instrument panel with clips components see Figs. 601 through 610.