Page 9 of 255

6Over-inflation will cause rapid wear of the
centre part of the tyre tread, coupled with
reduced adhesion, harsher ride, and the
danger of shock damage occurring in the tyre
casing.
7Regularly check the tyres for damage in the
form of cuts or bulges, especially in the
sidewalls. Remove any nails or stones
embedded in the tread before they penetrate the
tyre to cause deflation. If removal of a nail does
reveal that the tyre has been punctured, refit the
nail so that its point of penetration is marked.
Then immediately change the wheel, and have
the tyre repaired by a tyre dealer. Do not drive on
a tyre in such a condition. If in any doubt as to
the possible consequences of any damage
found, consult your local tyre dealer for advice.
8Periodically remove the wheels, and clean
any dirt or mud from the inside and outside
surfaces. Examine the wheel rims for signs of
rusting, corrosion or other damage. Light alloy
wheels are easily damaged by “kerbing” whilst
parking, and similarly steel wheels may
become dented or buckled. Renewal of the
wheel is very often the only course of remedial
action possible.
9The balance of each wheel and tyre
assembly should be maintained to avoid
excessive wear, not only to the tyres but also
to the steering and suspension components.
Wheel imbalance is normally signified by
vibration through the vehicle’s bodyshell,
although in many cases it is particularly
noticeable through the steering wheel.
Conversely, it should be noted that wear ordamage in suspension or steering
components may cause excessive tyre wear.
Out-of-round or out-of-true tyres, damaged
wheels, and wheel bearing wear also fall into
this category. Balancing will not usually cure
vibration caused by such wear.
10Wheel balancing may be carried out with
the wheel either on or off the vehicle. If
balanced on the vehicle, ensure that the
wheel-to-hub relationship is marked in some
way prior to subsequent wheel removal, so
that it may be refitted in its original position.
11General tyre wear is influenced to a large
degree by driving style - harsh braking and
acceleration, or fast cornering, will all produce
more rapid tyre wear. Interchanging of tyres
may result in more even wear. However, if this
is completely effective, the added expense is
incurred of replacing all four tyres at once,
which may prove financially-restrictive for
many owners.
12Front tyres may wear unevenly as a result
of wheel misalignment. The front wheels
should always be correctly aligned according
to the settings specified by the vehicle
manufacturer.
13Legal restrictions apply to many aspects
of tyre fitting and usage, and in the UK this
information is contained in the Motor Vehicle
Construction and Use Regulations. It is
suggested that a copy of these regulations is
obtained from your local police, if in doubt as
to current legal requirements with regard to
tyre type and condition, minimum tread depth,
etc.Check the operation of all the electrical
equipment, ie. lights, direction indicators,
horn, washers, etc. Refer to the appropriate
Sections of Chapter 13 for details if any of the
circuits are found to be inoperative.
Visually check all accessible wiring
connectors, harnesses and retaining clips for
security, and for signs of chafing or damage.
Rectify any faults found.
Caution: Before carrying out any work on the
vehicle battery, read through the precautions
given in “Safety first!” at the beginning of this
manual.
1The battery fitted as original equipment is
“maintenance-free”, and requires no
maintenance apart from having the case kept
clean, and the terminals clean and tight.
2If a “traditional” type battery is fitted as a
replacement, remove the old cell covers and
check that the plate separators in each cell are
covered by approximately 6 mm (0.25 in) of
electrolyte. If the battery case is translucent,
the cell covers need not be removed to check
the level. Top-up if necessary with distilled or
de-ionized water; do not overfill, and mop up
any spillage at once(see illustration).
6Battery electrolyte level check
5Electrical system check
1•8Weekly checks
Tyre Tread Wear Patterns
Shoulder Wear
Underinflation
(wear on both sides)
Check and adjust pressures
Incorrect wheel camber
(wear on one side)
Repair or renew suspension
parts
Hard cornering
Reduce speed!
Centre Wear
Overinflation
Check and adjust pressures
If you sometimes have to inflate
your car’s tyres to the higher
pressures specified for maximum
load or sustained high speed,
don’t forget to reduce the
pressures to normal afterwards.
Toe Wear
Incorrect toe setting
Adjust front wheel alignment
Note: The feathered edge of
the tread which characterises
toe wear is best checked by
feel.
Uneven Wear
Incorrect camber or castor
Repair or renew suspension
parts
Malfunctioning suspension
Repair or renew suspension
parts
Unbalanced wheel
Balance tyres
Out-of-round brake disc/drum
Machine or renew
procarmanuals.com
Page 10 of 255

3Persistent need for topping-up the battery
electrolyte suggests either that the alternator
output is excessive. or that the battery is
approaching the end of its life.
4Further information on the battery, charging
and jump-starting can be found in Chapter 5,
and in the preliminary Sections of this manual.1Clean the wiper blades and the windscreen,
using a solution of concentrated washer fluid
or methylated spirit. Similarly clean the
headlight lens and wiper blades.
2Check the condition of the wiper blades; if
they are cracked or show any signs of
deterioration, or if the glass swept area is
smeared, renew them. At the same time,
check the headlight wiper blades (where fitted)
for condition, and renew if necessary.
3To remove a blade, hinge the arm and blade
away from the screen. Press the tab on the
spring clip in the middle of the blade and
unhook the blade from the arm. 4Refit the blade by sliding it onto the hook on
the arm(see illustration).
5Check that the windscreen washer jets
operate correctly, and direct the washer fluid
towards the upper area of the wiper blade
stroke. If necessary, use a pin to reposition the
washer jets.
7Wiper blade check
1Before starting this procedure, gather
together all the necessary tools and materials.
Also make sure that you have plenty of clean
rags and newspapers handy, to mop up any
spills. Ideally, the engine oil should be warm,
as it will drain better, and more built-up sludge
will be removed with it. Take care, however,
not to touch the exhaust or any other hot parts
of the engine when working under the vehicle.
To avoid any possibility of scalding, and toprotect yourself from possible skin irritants
and other harmful contaminants in used
engine oils, it is advisable to wear gloves when
carrying out this work.
2Access to the underside of the vehicle will be
greatly improved if it can be raised on a lift,
driven onto ramps, or jacked up and supported
on axle stands (see “Jacking”). Whichever
method is chosen, make sure that the vehicle
remains level, or if it is at an angle, that the drain
plug is at the lowest point.
3Slacken the drain plug about half a turn.
Position the draining container under the drain
plug, then remove the plug completely. If
possible, try to keep the plug pressed into the
sump while unscrewing it by hand the last
couple of turns. As the plug releases from the
threads, move it away sharply so the stream of
oil issuing from the sump runs into the
container, not up your sleeve. Recover the
sealing washer from the drain plug.
4Allow some time for the old oil to drain,
noting that it may be necessary to reposition
the container as the oil flow slows to a trickle.
5After all the oil has drained, wipe off the
drain plug with a clean rag. Check the sealing
washer for condition, and renew it if
necessary. Clean the area around the drain
plug opening, and refit the plug. Tighten the
plug to the specified torque.
6Move the container into position under the
oil filter. On SOHC engines, the filter is located
on the left-hand side of the cylinder block in
front of the engine bearer. On DOHC and V6
engines, the filter is located on the right-hand
side of the cylinder block (see illustration).
7Using an oil filter removal tool if necessary,
slacken the filter, then unscrew it by hand the
rest of the way. Empty the oil from the old filter
into the container, and discard the filter.8Use a clean rag to remove all oil, dirt and
sludge from the filter sealing area on the
engine. Check the old filter to make sure that
the rubber sealing ring hasn’t stuck to the
engine. If it has, carefully remove it.
9Apply a light coating of clean engine oil to
the sealing ring on the new filter, then screw it
into position on the engine. Tighten the filter
firmly by hand only - do notuse any tools.
Wipe clean the filter and sump drain plug.
10Remove the old oil and all tools from
under the car, then lower the car to the ground
(if applicable).
11Remove the oil filler cap and withdraw the
dipstick from the top of the filler tube. Fill the
engine, using the correct grade and type of oil
(see “Lubricants and fluids”). An oil can spout
or funnel may help to reduce spillage. Pour in
half the specified quantity of oil first, then wait
a few minutes for the oil to fall to the sump.
Continue adding oil a small quantity at a time
until the level is up to the lower mark on the
dipstick. Finally, bring the level up to the upper
mark on the dipstick. Insert the dipstick, and
refit the filler cap.
12Start the engine and run it for a few
minutes; check for leaks around the oil filter
seal and the sump drain plug. Note that there
may be a delay of a few seconds before the oil
pressure warning light goes out when the
engine is first started, as the oil circulates
through the engine oil galleries and the new oil
filter, before the pressure builds up.
13Switch off the engine, and wait a few
minutes for the oil to settle in the sump once
more. With the new oil circulated and the filter
completely full, recheck the level on the
dipstick, and add more oil as necessary.
14Dispose of the used engine oil safely, with
reference to “General repair procedures”in the
reference Sections of this manual.
8Engine oil and filter renewal
1•9
1
Every 6000 miles or 6 months
8.6 Fitting an oil filter
6.2 Topping up the battery7.4 Fitting a windscreen wiper blade
Every 6000 miles or 6 months
For maximum clarity of vision,
windscreen wiper blades
should be renewed annually,
as a matter of course.
Frequent oil and filter changes
are the most important
preventative maintenance
procedures which can be
undertaken by the DIY owner. As
engine oil ages, it becomes diluted and
contaminated, which leads to
premature engine wear.
procarmanuals.com
Page 11 of 255

1Firmly apply the handbrake, then jack up the
front and rear of the car and support it
securely on axle stands (see “Jacking”).
2For a quick check, the front brake disc pads
can be inspected without removing the front
wheels, using a mirror and a torch through the
aperture in the rear face of the caliper. If any
one pad is worn down to the minimum
specified, all four pads (on both front wheels)
must be renewed.
3It is necessary to remove the rear wheels in
order to inspect the rear pads. The pads can
be viewed through the top of the caliper after
removing the spring clip. If any one pad is
worn down to the minimum specified, all four
pads (on both rear wheels) must be renewed.
4For a comprehensive check, the brake pads
should be removed and cleaned. The
operation of the caliper can then also be
checked, and the condition of the brake discs
can be fully examined on both sides. Refer to
Chapter 10 for further information.
5At the same interval, check the function of
the brake fluid level warning light. Chock the
wheels, release the handbrake and switch on
the ignition. Unscrew and raise the brake fluid
reservoir cap whilst an assistant observes the
warning light: it should come on as the level
sensor is withdrawn from the fluid. Refit the
cap.
6On completion, refit the wheels and lower
the car to the ground.
1Visually inspect the engine joint faces,
gaskets and seals for any signs of water or oil
leaks. Pay particular attention to the areas
around the rocker cover, cylinder head, oil
filter and sump joint faces. Bear in mind that
over a period of time some very slight seepage
from these areas is to be expected but what
you are really looking for is any indication of a
serious leak. Should a leak be found, renew
the offending gasket or oil seal by referring to
the appropriate Chapter(s) in this manual.
2Similarly, check the transmission for oil
leaks, and investigate and rectify and
problems found.
3Check the security and condition of all the
engine related pipes and hoses. Ensure that all
cable-ties or securing clips are in place and in
good condition. Clips which are broken or
missing can lead to chafing of the hoses,
pipes or wiring which could cause more
serious problems in the future.
4Carefully check the condition of all coolant,
fuel and brake hoses. Renew any hose which
is cracked, swollen or deteriorated. Cracks will
show up better if the hose is squeezed. Pay
close attention to the hose clips that secure
the hoses to the system components. Hoseclips can pinch and puncture hoses, resulting
in leaks. If wire type hose clips are used, it
may be a good idea to replace them with
screw-type clips.
5With the vehicle raised, inspect the fuel tank
and filler neck for punctures, cracks and other
damage. The connection between the filler neck
and tank is especially critical. Sometimes a
rubber filler neck or connecting hose will leak due
to loose retaining clamps or deteriorated rubber.
6Similarly, inspect all brake hoses and metal
pipes. If any damage or deterioration is
discovered, do not drive the vehicle until the
necessary repair work has been carried out.
Renew any damaged sections of hose or pipe.
7Carefully check all rubber hoses and metal
fuel lines leading away from the petrol tank.
Check for loose connections, deteriorated
hoses, crimped lines and other damage. Pay
particular attention to the vent pipes and
hoses which often loop up around the filler
neck and can become blocked or crimped.
Follow the lines to the front of the vehicle
carefully inspecting them all the way. Renew
damaged sections as necessary.
8From within the engine compartment, check
the security of all fuel hose attachments and
pipe unions, and inspect the fuel hoses and
vacuum hoses for kinks, chafing and
deterioration.
9Where applicable, check the condition of
the oil cooler hoses and pipes.
10Check the condition of all exposed wiring
harnesses.
11Also check the engine and transmission
components for signs of fluid leaks.
Periodically check the belts for fraying or
other damage. If evident, renew the belt.
If the belts become dirty, wipe them with a
damp cloth using a little detergent only.
Check the tightness of the anchor bolts and
if they are ever disconnected, make quite sure
that the original sequence of fitting of washers,
bushes and anchor plates is retained.With the vehicle raised on a hoist or
supported on axle stands (see “Jacking”),
check the exhaust system for signs of leaks,
corrosion or damage and check the rubber
mountings for condition and security. Where
damage or corrosion are evident, renew the
system complete or in sections, as applicable,
using the information given in Chapter 4.
With the wheels on the ground, slacken
each wheel nut by a quarter turn, then
retighten it immediately to the specified
torque.
Remove and clean the oil filler cap of any
sludge build-up using paraffin.
Inspect the vent hose for blockage or
damage. A blocked hose can cause a build-up
of crankcase pressure, which in turn can
cause oil leaks.
An accurate tachometer (rev. counter) will
be needed to adjust the idle speed. The
engine must be at operating temperature, the
air cleaner element must be clean and the
vacuum hoses fitted, and the engine valve
clearances must be correct. The ignition
system must also be in good condition.
Connect the tachometer to the engine as
instructed by the manufacturers. Start the
engine and allow it to idle. Read the speed
from the tachometer and compare it with the
value in the Specifications of Chapter 4
(Pierburg 2V carburettor).
If adjustment is necessary, turn the idle
speed adjustment screw. Turn the screw
clockwise to increase the speed, and anti-
clockwise to decrease the speed (see
illustration).
1.8 litre engine
1An exhaust gas analyser (CO meter) or other
proprietary device will be needed to adjust the
idle mixture.
2The engine must be at operating
temperature, the air cleaner element must be
clean and the vacuum hoses fitted, and the
16Idle mixture check -
carburettor models only
15Idle speed check - 1.8 litre
SOHC
14Oil filler cap check
13Roadwheel security check
12Exhaust system check
11Seat belt check10Fluid leak check
9Front and rear brake pad
check
1•10Every 6000 miles or 6 months
15.3 Idle adjustment screws - Pierburg 2V
carburettor
A Idle speedB Idle mixture
procarmanuals.com
Page 12 of 255

engine valve clearances must be correct. The
ignition system must also be in good
condition.
3Mixture adjustment is not usual on a routine
basis. If the CO level is incorrect, proceed as
follows.
4Connect the exhaust gas analyser as
instructed by the manufacturers.
5Raise the engine speed to 3000 rpm
approximately and hold it at this speed for
30 seconds, then allow it to idle. Repeat this
procedure every 60 seconds until adjustment
is complete.6Read the CO level when it has stabilised
after the 3000 rpm burst. The desired level is
given in the Specifications of Chapter 4
(Pierburg 2V carburettor).
7If the idle mixture needs adjustment, turn
the mixture adjusting screw. The screw may
be covered by a tamperproof plug.
8Recheck the idle speed after adjusting the
mixture.
9Stop the engine and disconnect the test
gear. 10Fit a new tamperproof plug to the mixture
adjusting screw if required.
2.0 litre SOHC engine
11If mixture adjustment is required, proceed
as described for the 1.8 litre engine above.
12See illustrationfor the location of the
mixture adjusting screw on the Weber 2V
carburettor fitted to this engine
DOHC engine
13Proceed as described for the 1.8 litre
engine, noting the following points (see
illustration).
14Refer to the Specification for the Weber 2V
(TLD) carburettor in Chapter 4.
15The air cleaner must be removed for
access to the mixture adjustment screw.
16Prise the tamperproof seal from the
mixture screw.
17Loosely refit the air cleaner, ensuring that
the vacuum pipe and the camshaft cover
breather hose are securely connected and free
from restrictions (there is no need to secure
the air cleaner in position).
18On completion, fit a new tamperproof seal
to the mixture screw (the service replacement
plug is coloured blue) and refit the air cleaner
assembly.
1Fluid level should be checked with the
transmission at operating temperature (after a
run) and with the vehicle parked on level
ground.
2Open and prop the bonnet. With the engine
idling and the handbrake and footbrake
applied, move the gear selector through all
positions three times, finishing up in position
P.
3Wait one minute. With the engine still idling,
withdraw the transmission dipstick (see
illustration).Wipe the dipstick with a clean
lint-free rag, re-insert it fully and withdraw itagain. Read the fluid level at the end of the
dipstick: it should be between the two
notches.
4If topping-up is necessary, do so via the
dipstick tube, using clean transmission fluid of
the specified type (see illustration).Do not
overfill.
5Stop the engine, refit the dipstick and close
the bonnet.
6Note that if the fluid level was below the
minimum mark when checked or is in constant
need oftopping-up, check around the
transmission for any signs of excessive fluid
leaks.If present, leaks must be rectified
without delay.
7If the colour of the fluid is dark brown or
black this denotes the sign of a worn brakeband or transmission clutches, in which case
have your Ford dealer check the transmission
at the earliest opportunity.
1Place the vehicle over a pit, or raise and
support it at front and rear. The vehicle must
be level for an accurate check.
2If the transmission is hot after a run, allow it
to cool for a few minutes. This is necessary
because the oil can foam when hot and give a
false level reading.
3Wipe clean around the filler/level plug,
which is located on the left-hand side of the
gearbox. Unscrew the plug with a square drive
key and remove it
4Using a piece of bent wire as a dipstick,
check that the oil level is up to the bottom of
the filler/level plug hole, or no more than 5 mm
(0.2 in) below it.
5Top-up if necessary using clean oil of the
specified type. Do not overfill; allow excess oil
to drip out of the plug hole if necessary. Refit
and tighten the filler/level plug.
6Frequent need for topping-up can only be
due to leaks, which should be rectified. The
rear extension oil seal can be renewedin situ
after removing the propeller shaft (N type
only).
7No periodic oil changing is specified, and no
drain plug is fitted.
18Manual gearbox oil level
check
17Automatic transmission fluid
level check
1•11
1
Every 12 000 miles or 12 months
16.13 Idle adjustment screws- Weber 2V
TLD carburettor
A Idle mixtureB Idle speed
16.12 Idle mixture adjustment screw
(arrowed) - Weber 2V carburettor
17.4 Topping up the transmission fluid17.3 The automatic transmission dipstick
Every 12 000 miles or 12 months
procarmanuals.com
Page 13 of 255

1Work around the vehicle, and lubricate the
hinges and locks with a light machine oil.
2Lightly lubricate the bonnet release
mechanism and exposed sections of inner
cable with a smear of grease.
3Check the security and operation of all
hinges, latches and locks, adjusting them
where required. Where applicable, check the
operation of the central locking system.
4Check the condition and operation of the
tailgate struts, renewing them if either is
leaking or is no longer able to support the
tailgate securely when raised.
SOHC and V6 engines
1The correct functioning of the spark plugs is
vital for the correct running and efficiency of
the engine. It is essential that the plugs fitted
are appropriate for the engine.
2Make sure that the ignition is switched off
before inspecting the HT leads to see if they
carry their cylinder numbers - if not, number
each lead using sticky tape or paint.
3Pull the HT lead connectors off the plugs.
Pull on the connectors, not on the leads.
4Blow away any dirt from around the spark
plug recesses in the cylinder head(s).
5Unscrew and remove the plugs, using a
proprietary plug spanner or a spark plug
socket, extension and ratchet.
6The condition of the plugs will tell much
about the overall condition of the engine. If the
insulator nose of the spark plug is clean and
white, with no deposits, this is indicative of a
weak mixture or too hot a plug (a hot plug
transfers heat away from the electrode slowly,
a cold plug transfers heat away quickly).
7If the tip and insulator nose are covered with
hard black-looking deposits, then this is
indicative that the mixture is too rich. Should
the plug be black and oily, then it is likely that
the engine is fairly worn, as well as the mixture
being too rich.
8If the insulator nose is covered with light tan
to greyish-brown deposits, then the mixture is
correct, and it is likely that the engine is in
good condition.
9Apply a smear of anti-seize compound to
the threads of the new plugs. Make sure that
theinsulators are clean and that the screwed
HT lead adapters are tight. Pay particular
attention to the plug seating surfaces on OHC
engines, since these plugs have no sealing
washers (“taper seat” type) and any dirt will
cause a bad seal.
10Screw each plug into its hole by hand. If a
plug is reluctant to go in, do not force it with a
spanner, but unscrew it and try again. If the
plug is cross-threaded, it is the cylinder head
which will be damaged.11Final tightening of the spark plugs should
ideally be carried out using a torque wrench.
The tightening torques are given in the
Specifications. If a torque wrench is not
available, tighten the plugs beyond the point
where they contact the head as follows:
OHC (taper seat plugs) - One-sixteenth of a
turn maximum
V6 (plugs with washers) - One-quarter of a
turn maximum
12If the taper seat type of plug is
overtightened, the sealing faces will bite
together and removal will be very difficult.
13Refit the HT leads to the plugs, paying
attention to the cylinder numbers. Push each
connector firmly onto its plug.
14Run the engine to verify that the HT leads
have been refitted correctly.
DOHC engines
15Proceed as described above whilst noting
the following points.
a)Remove the air cleaner as described in
Chapter 4.
b)The minimal length of number 3 HT lead
makes removal from the spark plug
difficult. It is advisable to remove this lead
from the distributor prior to removing it
from the spark plug.
c)The spark plugs are deeply recessed in
the cylinder head and it will be necessary
to use a spark plug socket with a long
extension bar. If possible, use a spark plug
socket with a rubber grip inside as this will
hold onto the spark plug once loosened
and will enable the spark plugs to be
withdrawn and refitted more easily.
SOHC and all V6 engines
1All of these engines have one or two
drivebelts which drive the water pump and
alternator from the crankshaft pulley. When
power steering is fitted, the same belts drive
the steering pump. The air conditioning
compressor, when fitted, is driven
independently.
2Periodically inspect the drivebelt(s) for
fraying, cracks, glazing or other damage. Turn
the engine so that the full length of the belt(s)
can be viewed. Renew belts which are in poor
condition. When twin drivebelts are fitted, both
must be renewed together, even if only one is
damaged.
3Check the tension of the drivebelt(s) by
pressing firmly with the fingers in the middle of
the longest belt run (engine stopped). Tension
is correct when the belt can be deflected by
10 mm (0.4 in) under firm finger pressure (see
illustration).
4Renewal and adjustment procedures for
models with power steering are given in
Chapter 11. For other models proceed as
follows.
5Disconnect the battery negative lead.
6On models with air conditioning, remove the
compressor drivebelt.
7Slacken the alternator pivot and adjusting
bolts. Swing the alternator towards the engine
and slip the belt(s) off the pulleys.
8Fit the new belt(s) over the pulleys. Move
the alternator away from the engine until the
belt tension is correct, then tighten the
alternator adjusting strap and pivot bolts. If it
is necessary to lever against the alternator to
achieve the correct tension, only do so using a
wooden or plastic lever(seeillustration).
9Refit and tension the air conditioning
compressor drivebelt, when applicable.
10Reconnect the battery. If a new drivebelt
has been fitted, run the engine for a few
minutes, then stop it and recheck the tension.
11Check the tension of new belts again after
a few hundred miles.
21Auxiliary drivebelt check
20Spark plug renewal
19Hinge and lock check and
lubrication
1•12Every 12 000 miles or 12 months
21.3 Checking drivebelt tension
It is very often difficult to insert spark
plugs into their holes without cross-
threading them. To avoid this
possibility, fit a short length of 5/16-
inch internal diameter rubber hose over
the end of the spark plug. The flexible
hose acts as a universal joint to help
align the plug with the plug hole.
Should the plug begin to cross-thread,
the hose will slip on the spark plug,
preventing thread damage to the
aluminium cylinder head. Remove the
rubber hose, and tighten the plug to the
specified torque using the spark plug
socket and a torque wrench. Fit the
remaining spark plugs in the same
manner.
procarmanuals.com
Page 14 of 255

DOHC engines
12On this engine, the coolant/alternator
drivebelt also drives the power steering pump
and (where applicable) the air conditioning
compressor. The drivebelt tension is set by an
automatic tensioner assembly.
13The condition of the drivebelt should be
checked as described above.
14An idea of the amount of wear which has
taken place on the belt can be gained from the
position of indicator mark (A) on the mounting
bracket in relation to the block (B) on the
tensioner arm (see illustration).When the belt
is new the mark should be aligned with the top
of the tensioner block. As the belt wears, the
tensioner arm moves and the block on the arm
will move slowly up in relation to the mark on
the bracket. When the mark aligns with the
bottom of the tensioner arm block the belt can
be regarded as worn and should be replaced
(see illustration).
15To renew the belt, turn the automatic
tensioner arm clockwise, using a 17 mm
socket and a wrench on the boss in the centre
of the pulley, and slide the belt from the
pulleys, then slowly release the tensioner.
16To fit a new belt, rotate the tensioner
clockwise as during removal, then slide the
belt over the pulleys. With the belt correctly
located, slowly release the tensioner; the
tensioner will automatically set the correct
drivebelt tension.
Caution:Before carrying out any work on the
vehicle battery, read through the precautions
given in “Safety first!” at the beginning of this
manual.
1The battery fitted as original equipment is
“maintenance-free”, and requires no
maintenance apart from having the case kept
clean, and the terminals clean and tight.
2To clean the battery terminals disconnect
them, after having first removed the cover
(later models) -negative earth first. Use a wire
brush or abrasive paper to clean the terminals.
Bad corrosion should be treated with a
solution of bicarbonate of soda, applied with
an old toothbrush. Do not let this solution get
inside the battery.3Coat the battery terminals with petroleum
jelly or a proprietary anti-corrosive compound
before reconnecting them. Reconnect and
tighten the positive (live) lead first, followed by
the negative (earth) lead. Do not overtighten.
4Keep the top of the battery clean and dry.
Periodically inspect the battery tray for
corrosion, and make good as necessary.
5Further information on the battery, charging
and jump-starting can be found in Chapter 5,
and in the preliminary Sections of this manual.
SOHC engines
1Valve clearances are checked with the
engine cold.
2On carburettor models, remove the air cleaner.
3On fuel-injection models, remove the
bracing strap which connects the inlet
manifold to the right-hand side of the engine.
4On all models, identify the HT leads and
disconnect them from the spark plugs. Unclip
the leads from the rocker cover.
5Although not essential, it will make the
engine easier to turn if the spark plugs are
removed.
6Remove the ten bolts which secure the
rocker cover, noting the location of the
different shapes of reinforcing plates. Remove
the cover and gasket.7One of the cam lobes will be seen to be
pointing upwards. Measure the clearance
between the base of this cam and the cam
follower, finding the thickness of feeler blade
which gives a firm sliding fit(see illustration).
8The desired valve clearances are given in
the Specifications. Note that the clearances
for inlet and exhaust valves are different.
Numbering from the front (sprocket) end of the
camshaft, the exhaust valves are 1, 3, 5 and 7,
and the inlet valves 2, 4, 6 and 8.
9If adjustment is necessary, slacken the ball-
pin locknut and screw the ball-pin up or down
until the clearance is correct. Hold the ball-pin
stationary and tighten the locknut(see
illustration).Recheck the clearance after
tightening the locknut in case the ball-pin has
moved.
10Turn the engine to bring another cam lobe
to the vertical position and repeat the above
procedure. Carry on until all eight valves have
been checked.
11Access to some of the ball-pins is made
difficult by the carburettor or fuel-injection inlet
manifold. To avoid having to remove the
offending components, double cranked
spanners or cutaway socket spanners can be
used (see illustration).
12When adjustment is complete, refit the
rocker cover using a new gasket. Make sure
that the dovetail sections of the gasket fit
together correctly.
13Fit the rocker cover bolts and reinforcing
plates. Tighten the bolts as described in
Chapter 2A Section 44, paragraph 11.
23Engine valve clearance check
22Battery terminal check
1•13
1
Every 12 000 miles or 12 months
21.14a Water pump/alternator drivebelt
tensioner indicator position - DOHC engine
A Indicator markB Block
21.14b Water pump/alternator drivebelt
tensioner wear indicator location (arrowed)
- DOHC engine21.8 Tightening the alternator strap bolt
23.7 Measuring a valve clearance - SOHC
engine23.9 Adjusting a valve clearance - SOHC
engine
procarmanuals.com
Page 15 of 255

14Refit the other disturbed components.
15Run the engine and check that there are
no oil leaks from the rocker cover.
2.8 litre engine
16If the engine is in the vehicle, carry out the
preliminary steps:
a)Disconnect the battery negative lead
b)Remove the throttle mechanism cover, air
cleaner cover, airflow meters and inlet
trunking
c)Remove the HT leads from the spark plugs
and unclip them from the rocker cover
d)Unbolt and remove the rocker covers
17Although not essential, it will be easier to
turn the engine if the spark plugs are removed.
18Valve clearances must be adjusted with
the engine cold (less than 40°C/104°F).
19Turn the engine, using a spanner on the
crankshaft pulley bolt, until the crankshaft
pulley timing mark is aligned with the TDC
(zero) pointer on the timing cover and the
valves of No 5 cylinder are overlapping, ie the
exhaust valve is closing and the inlet valve is
opening. (No 5 cylinder is the middle one on
the left-hand bank - left being the vehicle’s
left, not necessarily to operator’s.) (see
illustration).
20When the valves of No 5 cylinder are in
this position, check the valve clearances of
No1 cylinder by inserting a feeler blade of the
specified thickness between the rocker arm
and the valve stem. Adjust the clearance, if
necessary, by turning the rocker arm adjustingscrew until the specified clearance is obtained
(see illustration).Inlet and exhaust valve are
different.
21If the engine is now rotated one-third of a
turn clockwise at the crankshaft, the valves of
No 3 cylinder will be overlapping and the
valves of No4 cylinder can be checked and
adjusted.
22Proceed to adjust the clearances
according to the firing order as follows. The
cylinders are numbered (see illustration)and
the valves are listed in their correct order,
working from the front of the engine:
Valves overlappingValves to adjust
No 5 cylinderNo 1 cylinder (in, ex)
No 3 cylinderNo 4 cylinder (in, ex)
No 6 cylinderNo 2 cylinder (in, ex)
No 1 cylinderNo 5 cylinder (ex, in)
No 4 cylinderNo 3 cylinder (ex, in)
No 2 cylinderNo 6 cylinder (ex, in)
23Refit the rocker covers, using new gaskets
if necessary. Tighten the rocker cover bolts to
the specified torque.
24If the engine is in the vehicle, refit the other
displaced components.
2.4 & 2.9 litre engines
25The operation for these engines is
essentially as described for the 2.8 litre
engine, noting that the valve arrangement is
changed (see illustrations).
Using a spanner of the appropriate size,
check each manifold securing nut in turn
whilst referring to the appropriate Sections in
Chapter 2C for tightening sequences and
torque loading figures.
Remove the radiator grille and clean any
leaves, insects etc. from the condenser coil
and fins. Be very careful not to damage the
condenser fins: use a soft brush, or a
compressed air jet, along (not across) the fins
(see illustration).
25Air conditioner condenser
check
24Engine inlet manifold security
check - V6 only
1•14Every 12 000 miles or 12 months
23.19 Inlet and exhaust valve location -
2.8 litre V6 engine
23.20 Adjusting a valve clearance -
V6 engine
23.11 Cutaway socket spanner
23.25a Valve arrangement for RH cylinder
head - 2.4 & 2.9 litre engines
Upper arrow points to front of engine23.25b Valve arrangement for LH cylinder
head - 2.4 & 2.9 litre engines
Upper arrow points to front of engine
23.22 Cylinder numbering and HT lead
connections - V6 engine
White arrow points to front of engine
25.1 Cleaning the air conditioner
condenser fins
procarmanuals.com
Page 16 of 255

1Remove the radiator grille being careful not
to damage the condenser fins.
2Check the refrigerant charge as follows. The
engine should be cold and the ambient
temperature should be between 18°and 25°C
(64°and 77°F).
3Start the engine and allow it to idle. Observe
the refrigerant sight glass(see illustration)
and have an assistant switch on the air
conditioning to fan speed III. A few bubbles
should be seen in the sight glass as the
system starts up, but all bubbles should
disappear within 10 seconds. Persistent
bubbles, or no bubbles at all, mean that the
refrigerant charge is low. Switch off the
system immediately if the charge is low and do
not use it again until it has been recharged.
4Inspect the refrigerant pipes, hoses and
unions for security and good condition. Refit
the radiator grille.
5The air conditioning system will lose a
proportion of its charge through normal
seepage typically up to 100 g (4 oz) per year -
so it is as well to regard periodic recharging as
a maintenance operation.
1Check the final drive oil level as follows.
2Position the vehicle over a pit, or raise it at
front and rear on ramps or axle stands (see
“Jacking”). The vehicle must be level.
3Wipe clean around the final drive filler/level
plug (see illustration).Unscrew the plug with
a hexagon key. Using a piece of bent wire as
a dipstick, check that the oil is no more than
10 mm (0.4 in) below the plug hole.
4If topping-up is necessary, use clean gear
oil of the specified type. Do not overfill.
Frequent need for topping-up can only be due
to leaks, which should be rectified.
5When the level is correct, refit the filler/level
plug and tighten it.
6There is no requirement for periodic oil
changing, and no drain plug is provided. Lubricate the transmission selector and
kickdown linkages with engine oil or aerosol
lubricant.
1Examine all steering and suspension
components for wear and damage. Pay
particular attention to dust covers and gaiters,
which if renewed promptly when damaged can
save further damage to the component
protected.
2At the same intervals, check the front
suspension lower arm balljoints for wear by
levering up the arms(see illustration).
Balljoint free movement must not exceed
0.5 mm (0.02 in). The track rod end balljoints
can be checked in a similar manner, or by
observing them whilst an assistant rocks the
steering wheel back and forth. If the lower arm
balljoint is worn, the complete lower arm must
be renewed.
3Check the shock absorbers by bouncing the
vehicle up and down at each corner in turn.
When released, it should come to rest within
one complete oscillation. Continued
movement, or squeaking and groaning noises
from the shock absorber suggests that
renewal is required.Position the vehicle over a pit, or raise it at
front and rear on ramps or axle stands.
Examine the driveshaft joint rubber gaiters.
Flex the gaiters by hand and inspect the folds
and clips. Damaged or leaking gaiters must be
renewed without delay to avoid damage
occurring to the joint itself
Check the tightness of the final drive
mounting bolts and the driveshaft flange
screws.
1Except on vehicles with a wax-based
underbody protective coating, have the whole
of the underframe of the vehicle steam-
cleaned, engine compartment included, so
that a thorough inspection can be carried out
to see what minor repairs and renovations are
necessary.
2Steam-cleaning is available at many
garages, and is necessary for the removal of
the accumulation of oily grime, which
sometimes is allowed to become thick in
certain areas. If steam-cleaning facilities are
not available, there are some excellent grease
solvents available which can be brush-applied;
the dirt can then be simply hosed off.
3After cleaning, position the vehicle over a
pit, or raise it at front and rear on ramps or axle
stands.
4Using a strong light, work around the
underside of the vehicle, inspecting it for
corrosion or damage. If either is found, refer to
Chapter 12 for details of repair.
Periodically inspect the rigid brake pipes for
rust and other damage, and the flexible hoses
for cracks, splits or “ballooning”. Have an
assistant depress the brake pedal (ignition on)
and inspect the hose and pipe unions for
leaks. Renew any defective item without delay.
On 2.0 litre engines, good electrical contact
between the carburettor stepper motor
plunger and the adjusting screw is essential to
maintain a regular idle speed.
Clean the plunger and adjusting screw
contact faces with abrasive paper followed by
switch cleaning fluid. Switch cleaning fluid is
available from electronic component shops.
33Idle speed linkage clean
32Brake pipe and hose check
31Underbody inspection
30Driveshaft check
29Steering and suspension
security check
28Automatic transmission
selector linkage lubrication
27Final drive oil level check
26Air conditioner refrigerant
charge check
1•15
1
Every 12 000 miles or 12 months
27.3 Final drive oil filler/level plug (arrowed)
29.2 Checking a front suspension lower
arm balljoint
26.3 Refrigerant sight glass (arrowed)
procarmanuals.com
 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 11
11 12
12 13
13 14
14 15
15 16
16 17
17 18
18 19
19 20
20 21
21 22
22 23
23 24
24 25
25 26
26 27
27 28
28 29
29 30
30 31
31 32
32 33
33 34
34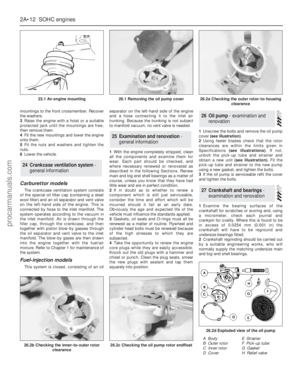 35
35 36
36 37
37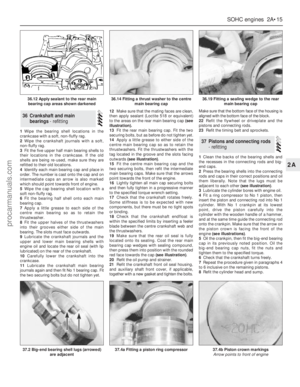 38
38 39
39 40
40 41
41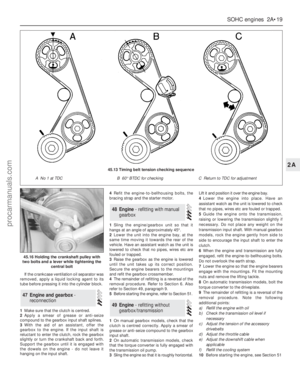 42
42 43
43 44
44 45
45 46
46 47
47 48
48 49
49 50
50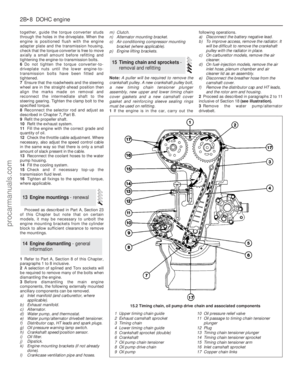 51
51 52
52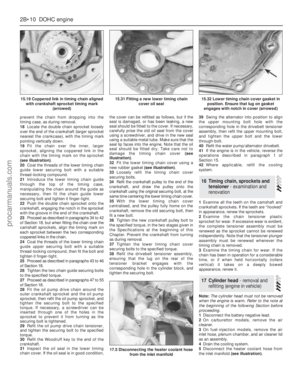 53
53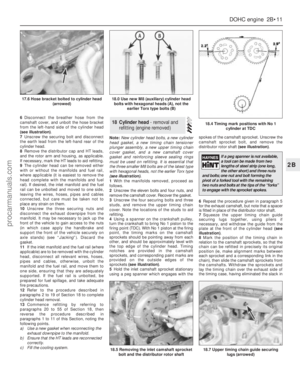 54
54 55
55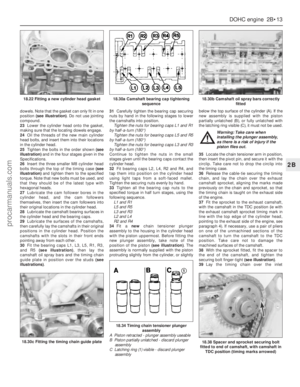 56
56 57
57 58
58 59
59 60
60 61
61 62
62 63
63 64
64 65
65 66
66 67
67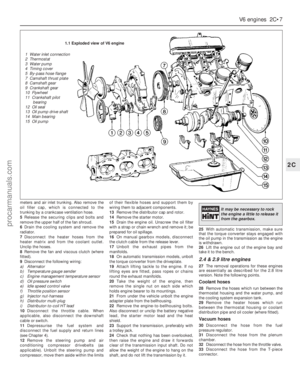 68
68 69
69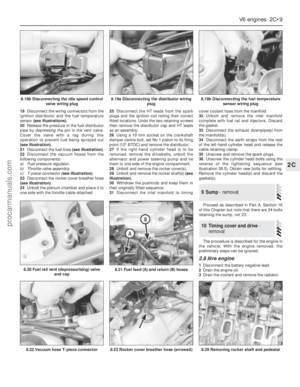 70
70 71
71 72
72 73
73 74
74 75
75 76
76 77
77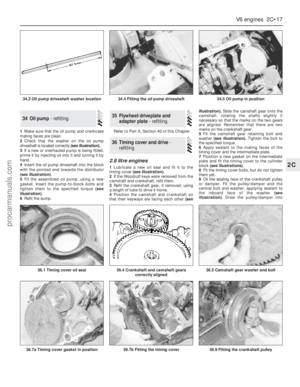 78
78 79
79 80
80 81
81 82
82 83
83 84
84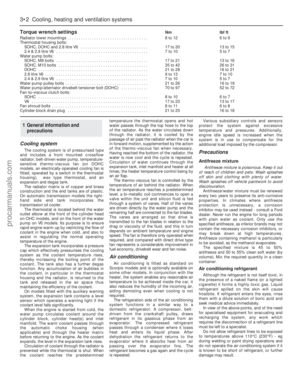 85
85 86
86 87
87 88
88 89
89 90
90 91
91 92
92 93
93 94
94 95
95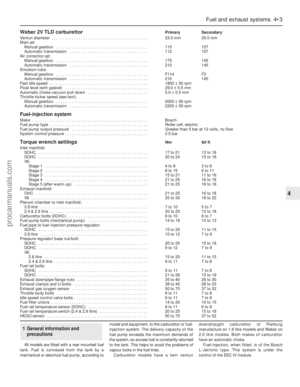 96
96 97
97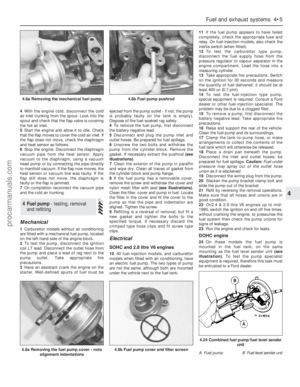 98
98 99
99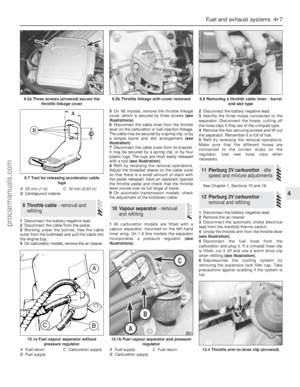 100
100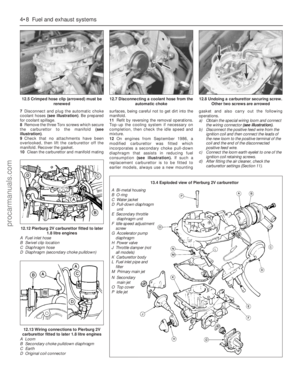 101
101 102
102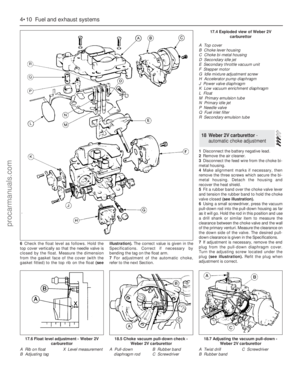 103
103 104
104 105
105 106
106 107
107 108
108 109
109 110
110 111
111 112
112 113
113 114
114 115
115 116
116 117
117 118
118 119
119 120
120 121
121 122
122 123
123 124
124 125
125 126
126 127
127 128
128 129
129 130
130 131
131 132
132 133
133 134
134 135
135 136
136 137
137 138
138 139
139 140
140 141
141 142
142 143
143 144
144 145
145 146
146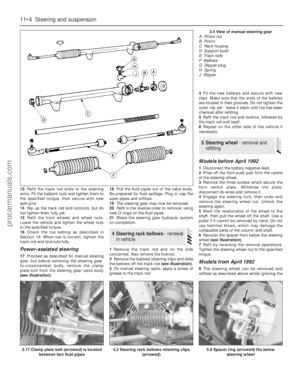 147
147 148
148 149
149 150
150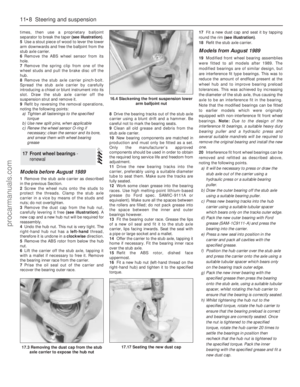 151
151 152
152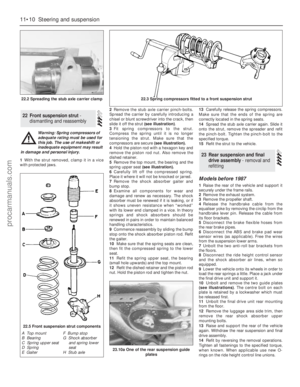 153
153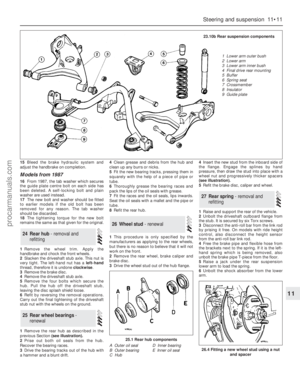 154
154 155
155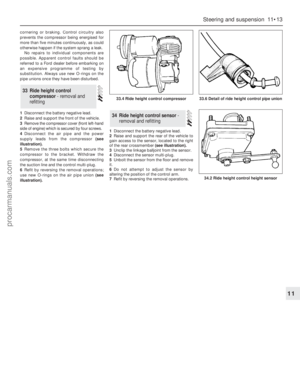 156
156 157
157 158
158 159
159 160
160 161
161 162
162 163
163 164
164 165
165 166
166 167
167 168
168 169
169 170
170 171
171 172
172 173
173 174
174 175
175 176
176 177
177 178
178 179
179 180
180 181
181 182
182 183
183 184
184 185
185 186
186 187
187 188
188 189
189 190
190 191
191 192
192 193
193 194
194 195
195 196
196 197
197 198
198 199
199 200
200 201
201 202
202 203
203 204
204 205
205 206
206 207
207 208
208 209
209 210
210 211
211 212
212 213
213 214
214 215
215 216
216 217
217 218
218 219
219 220
220 221
221 222
222 223
223 224
224 225
225 226
226 227
227 228
228 229
229 230
230 231
231 232
232 233
233 234
234 235
235 236
236 237
237 238
238 239
239 240
240 241
241 242
242 243
243 244
244 245
245 246
246 247
247 248
248 249
249 250
250 251
251 252
252 253
253 254
254






