1985 FORD GRANADA oil viscosity
[x] Cancel search: oil viscosityPage 3 of 255

1•2
Every 12 000 miles (20 000 km) or
12 months – whichever comes sooner
m mCheck operation of latches, check straps and locks; lubricate if
necessary (Section 19)
m mCheck condition and tension of auxiliary drivebelt(s); adjust or
renew as necessary (Section 21)
m mCheck tightness of battery terminals, clean and neutralise
corrosion if necessary (Section 22)
m mCheck engine valve clearances (Section 23) m
mCheck tightness of inlet manifold bolts (V6 only) (Section 24) m
mRenew spark plugs (Section 20) m
mClean air conditioning condenser fins (when applicable)
(Section 25)
m mCheck air conditioning refrigerant charge (when applicable)
(Section 26)
m mCheck manual gearbox oil level (Section 18) m
mCheck final drive oil level (Section 27) m
mLubricate automatic transmission selector/kickdown linkage
(Section 28)
m mCheck security and condition of steering and suspension
components, gaiters and boots (Section 29)
m mCheck condition and security of driveshaft joints (Section 30) m
mInspect underbody and panels for corrosion or other damage
(Section 31)
m mInspect brake pipes and hoses (Section 32) m
mClean idle speed control linkage at throttle (when applicable)
(Section 33)
m mRoad test and check operation of ABS (Section 34)m
mCheck automatic transmission fluid level (engine hot)
(Section 17)
m mCheck engine for satisfactory hot starting (Section 37)m
mCheck that automatic choke is fully off with engine hot (not fuel-
injection models) (Section 36)
m mCheck power steering fluid level (when applicable) (Section 35)
Every 24 000 miles (40 000 km) or
2 years - whichever comes sooner
m
mRenew air cleaner element (Section 38) m
mClean and inspect distributor cap, rotor arm, HT leads and coil
tower (Section 39)
m mAdjust automatic transmission brake bands (Section 40)m
mRenew fuel filter (fuel-injection models only) (Section 41) m
mRenew crankcase ventilation vent valve (carburettor models)
(Section 42)
Every 36 000 miles (60 000 km) or
3 years - whichever comes sooner
m
mRenew brake hydraulic system seals and hoses if necessary
(Section 43)
m mRenew brake hydraulic fluid (Section 44) m
mRenew camshaft drivebelt on SOHC models - recommended as
a precautionary measure (Section 45)
Every 2 years - regardless of mileage
m
mRenew coolant (Section 46)
Lubricants and fluidsComponent or systemLubricant type/specification
1 EngineMultigrade engine oil, viscosity range
SAE 10W/30 to 20W/50 to API SG/CD
or better
2 Cooling systemSoft water/antifreeze to Ford spec.
SSM 97B9103-A or SDM-M97B49-A
3 Manual transmission:
N9Semi-synthetic gear oil to Ford
spec. ESD M2C175-A (80 EP)
MT75Gear oil to Ford spec. ESD-
M2C186-A
4 Automatic transmissionATF to Ford spec. SQM-2C9010-A
(TQ Dexron II)
5 Final driveGear oil SAE 90EP to APIGL5
6 Brake hydraulic systemHydraulic fluid to Ford spec.
SAM- 6C9103-A
7 Power steeringATFto Ford spec. SQM-2C9010-A
(TQDexron II)
Maintenance Schedule
procarmanuals.com
Page 85 of 255
Cooling system
The cooling system is of pressurised type
and includes a front mounted crossflow
radiator, belt-driven water pump, temperature-
sensitive thermo-viscous fan (on DOHC
models, an electrically-operated cooling fan is
fitted, operated by a switch in the thermostat
housing), wax type thermostat, and an
expansion and degas tank.
The radiator matrix is of copper and brass
construction and the end tanks are of plastic.
On automatic transmission models the right-
hand side end tank incorporates the
transmission oil cooler.
The thermostat is located behind the water
outlet elbow at the front of the cylinder head
on OHCmodels, and on the front of the water
pump on V6 models. Its purpose is to ensure
rapid engine warm-up by restricting the flow of
coolant in the engine when cold, and also to
assist in regulating the normal operating
temperature of the engine.
The expansion tank incorporates a pressure
cap which effectively pressurises the cooling
system as the coolant temperature rises,
thereby increasing the boiling point of the
coolant. The tank also has a further degas
function. Any accumulation of air bubbles in
the coolant, in particular in the thermostat
housing and the radiator, is returned to the
tank and released in the air space thus
maintaining the efficiency of the coolant.
On models fitted with the auxiliary warning
system, the expansion tank contains a level
sensor which operates a warning light if the
coolant level falls significantly.
When the engine is started from cold, the
water pump circulates coolant around the
cylinder block, cylinder head(s) and inlet
manifold. The warm coolant passes through
the automatic choke housing (when
applicable) and through the heater matrix
before returning to the engine. As the coolant
expands, the level in the expansion tank rises.
Circulation of coolant through the radiator is
prevented while the thermostat is shut. When
the coolant reaches the predeterminedtemperature the thermostat opens and hot
water passes through the top hose to the top
of the radiator. As the water circulates down
through the radiator, it is cooled by the
passage of air past the radiator when the car is
in forward motion, supplemented by the action
of the thermo-viscous fan when necessary.
Having reached the bottom of the radiator, the
water is now cool and the cycle is repeated.
Circulation of water continues through the
expansion tank, inlet manifold and heater at all
times; the heater temperature control being by
an air flap.
The thermo-viscous fan is controlled by the
temperature of air behind the radiator. When
the air temperature reaches a predetermined
level, a bi-metallic coil commences to open a
valve within the unit and silicon fluid is fed
through a system of vanes. Half of the vanes
are driven directly by the water pump and the
remaining half are connected to the fan blades.
The vanes are arranged so that drive is
transmitted to the fan blades in relation to the
drag or viscosity of the fluid, and this in turn
depends on ambient temperature and engine
speed. The fan is therefore only operated when
required, and compared with direct drive type
fan represents a considerable improvement in
fuel economy, drivebelt wear and fan noise.
Air conditioning
Air conditioning is fitted as standard on
Scorpio models and is optionally available on
some other models. In conjunction with the
heater, the system enables any reasonable air
temperature to be achieved inside the car, it
also reduces the humidity of the incoming air,
aiding demisting even when cooling is not
required.
The refrigeration side of the air conditioning
system functions in a similar way to a
domestic refrigerator. A compressor, belt-
driven from the crankshaft pulley, draws
refrigerant in its gaseous phase from an
evaporator. The compressed refrigerant
passes through a condenser where it loses
heat and enters its liquid phase. After
dehydration the refrigerant returns to the
evaporator where it absorbs heat from air
passing over the evaporator fins. The
refrigerant becomes a gas again and the cycle
is repeated.Various subsidiary controls and sensors
protect the system against excessive
temperature and pressures. Additionally,
engine idle speed is increased when the
system is in use to compensate for the
additional load imposed by the compressor.
Precautions
Antifreeze mixture
Antifreeze mixture is poisonous. Keep it out
of reach of children and pets. Wash splashes
off skin and clothing with plenty of water.
Wash splashes off vehicle paintwork to avoid
discolouration.
Antifreeze/water mixture must be renewed
every two years to preserve its anti-corrosive
properties. In climates where antifreeze
protection is unnecessary, a corrosion
inhibitor may be used instead - consult a Ford
dealer. Never run the engine for long periods
with plain water as coolant. Only use the
specified antifreeze, as inferior brands may not
contain the necessary corrosion inhibitors, or
may break down at high temperatures.
Antifreeze containing methanol is particularly
to be avoided, as the methanol evaporates.
The specified mixture is 45 to 50%
antifreeze and 50 to 55% clean soft water (by
volume). Mix the required quantity in a clean
container.
Air conditioning refrigerant
Although the refrigerant is not itself toxic, in
the presence of a naked flame (or a lighted
cigarette) it forms a highly toxic gas. Liquid
refrigerant spilled on the skin will cause
frostbite. If refrigerant enters the eyes, rinse
them with a dilute solution of boric acid and
seek medical advice immediately.
In view of the above points, and of the need
for specialised equipment for evacuating and
recharging the system, any work which
requires the disconnection of a refrigerant line
must be left to a specialist.
Do not allow refrigerant lines to be exposed
to temperatures above 110°C (230°F) - eg
during welding or paint drying operations and
do not operate the air conditioning system if it
is known to be short of refrigerant, or further
damage may result.
1General information and
precautions
3•2Cooling, heating and ventilation systems
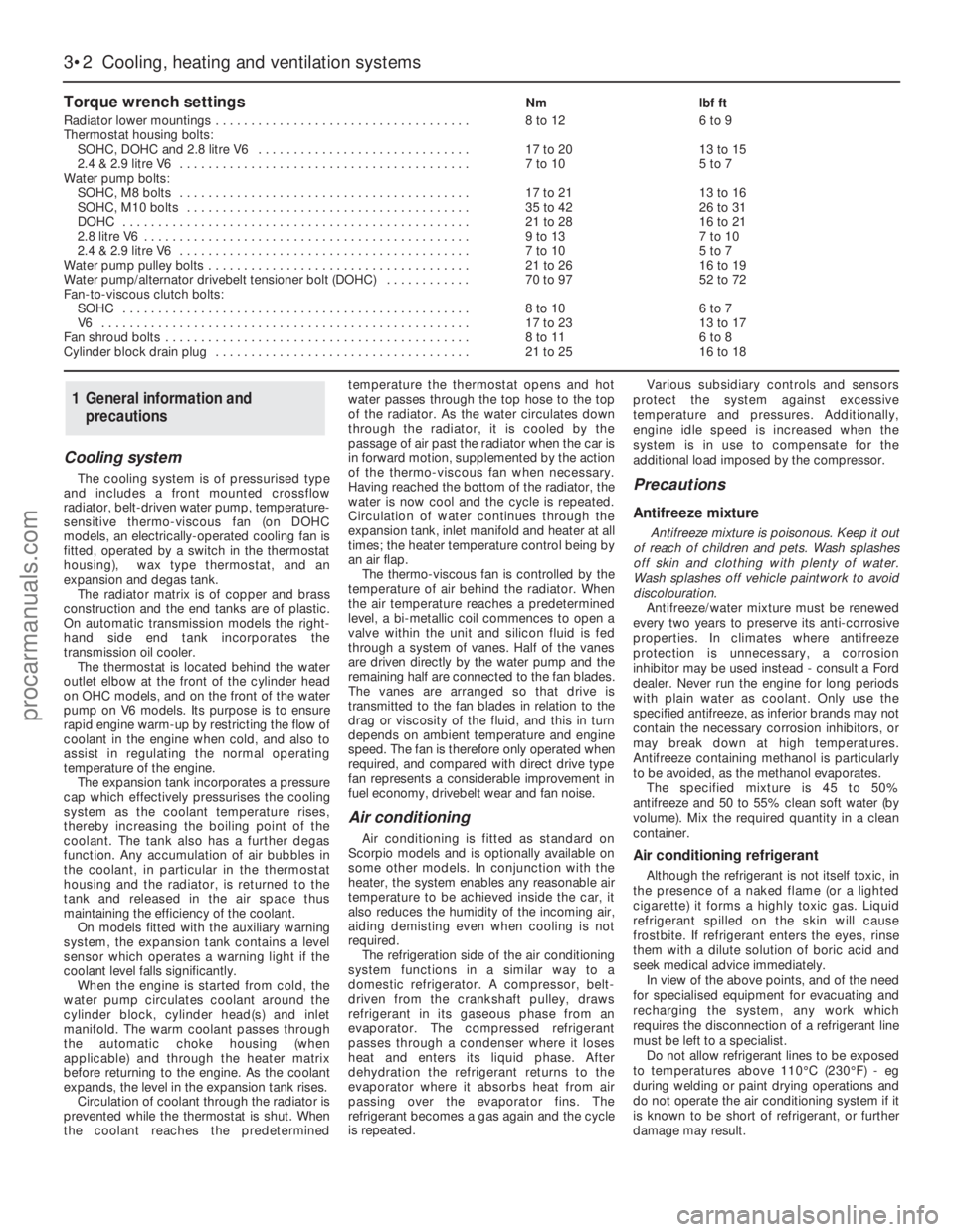
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Radiator lower mountings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 126 to 9
Thermostat housing bolts:
SOHC, DOHC and 2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2013 to 15
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 105 to 7
Water pump bolts:
SOHC, M8 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2113 to 16
SOHC, M10 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4226 to 31
DOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2816 to 21
2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 to 137 to 10
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 105 to 7
Water pump pulley bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2616 to 19
Water pump/alternator drivebelt tensioner bolt (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 9752 to 72
Fan-to-viscous clutch bolts:
SOHC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 106 to 7
V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2313 to 17
Fan shroud bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Cylinder block drain plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2516 to 18
procarmanuals.com
Page 250 of 255

REF•15Glossary of Technical Terms
RotorIn a distributor, the rotating device
inside the cap that connects the centre
electrode and the outer terminals as it turns,
distributing the high voltage from the coil
secondary winding to the proper spark plug.
Also, that part of an alternator which rotates
inside the stator. Also, the rotating assembly
of a turbocharger, including the compressor
wheel, shaft and turbine wheel.
RunoutThe amount of wobble (in-and-out
movement) of a gear or wheel as it’s rotated.
The amount a shaft rotates “out-of-true.” The
out-of-round condition of a rotating part.
SSealantA liquid or paste used to prevent
leakage at a joint. Sometimes used in
conjunction with a gasket.
Sealed beam lampAn older headlight design
which integrates the reflector, lens and
filaments into a hermetically-sealed one-piece
unit. When a filament burns out or the lens
cracks, the entire unit is simply replaced.
Serpentine drivebeltA single, long, wide
accessory drivebelt that’s used on some
newer vehicles to drive all the accessories,
instead of a series of smaller, shorter belts.
Serpentine drivebelts are usually tensioned by
an automatic tensioner.
ShimThin spacer, commonly used to adjust
the clearance or relative positions between
two parts. For example, shims inserted into or
under bucket tappets control valve
clearances. Clearance is adjusted by
changing the thickness of the shim.
Slide hammerA special puller that screws
into or hooks onto a component such as a
shaft or bearing; a heavy sliding handle on the
shaft bottoms against the end of the shaft to
knock the component free.SprocketA tooth or projection on the
periphery of a wheel, shaped to engage with a
chain or drivebelt. Commonly used to refer to
the sprocket wheel itself.
Starter inhibitor switchOn vehicles with an
automatic transmission, a switch that
prevents starting if the vehicle is not in Neutral
or Park.
StrutSee MacPherson strut.
TTappetA cylindrical component which
transmits motion from the cam to the valve
stem, either directly or via a pushrod and
rocker arm. Also called a cam follower.
ThermostatA heat-controlled valve that
regulates the flow of coolant between the
cylinder block and the radiator, so maintaining
optimum engine operating temperature. A
thermostat is also used in some air cleaners in
which the temperature is regulated.
Thrust bearingThe bearing in the clutch
assembly that is moved in to the release
levers by clutch pedal action to disengage the
clutch. Also referred to as a release bearing.
Timing beltA toothed belt which drives the
camshaft. Serious engine damage may result
if it breaks in service.
Timing chainA chain which drives the
camshaft.
Toe-inThe amount the front wheels are
closer together at the front than at the rear. On
rear wheel drive vehicles, a slight amount of
toe-in is usually specified to keep the front
wheels running parallel on the road by
offsetting other forces that tend to spread the
wheels apart.
Toe-outThe amount the front wheels are
closer together at the rear than at the front. On
front wheel drive vehicles, a slight amount of
toe-out is usually specified.
ToolsFor full information on choosing and
using tools, refer to the Haynes Automotive
Tools Manual.
TracerA stripe of a second colour applied to
a wire insulator to distinguish that wire from
another one with the same colour insulator.
Tune-upA process of accurate and careful
adjustments and parts replacement to obtain
the best possible engine performance.TurbochargerA centrifugal device, driven by
exhaust gases, that pressurises the intake air.
Normally used to increase the power output
from a given engine displacement, but can
also be used primarily to reduce exhaust
emissions (as on VW’s “Umwelt” Diesel
engine).
UUniversal joint or U-jointA double-pivoted
connection for transmitting power from a
driving to a driven shaft through an angle. A
U-joint consists of two Y-shaped yokes and a
cross-shaped member called the spider.
VValveA device through which the flow of
liquid, gas, vacuum, or loose material in bulk
may be started, stopped, or regulated by a
movable part that opens, shuts, or partially
obstructs one or more ports or passageways.
A valve is also the movable part of such a
device.
Valve clearanceThe clearance between the
valve tip (the end of the valve stem) and the
rocker arm or tappet. The valve clearance is
measured when the valve is closed.
Vernier caliperA precision measuring
instrument that measures inside and outside
dimensions. Not quite as accurate as a
micrometer, but more convenient.
ViscosityThe thickness of a liquid or its
resistance to flow.
VoltA unit for expressing electrical
“pressure” in a circuit. One volt that will
produce a current of one ampere through a
resistance of one ohm.
WWeldingVarious processes used to join metal
items by heating the areas to be joined to a
molten state and fusing them together. For
more information refer to the Haynes
Automotive Welding Manual.
Wiring diagramA drawing portraying the
components and wires in a vehicle’s electrical
system, using standardised symbols. For
more information refer to the Haynes
Automotive Electrical and Electronic Systems
Manual.
Serpentine drivebelt
procarmanuals.com