1987 SUZUKI GRAND VITARA light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 151 of 962
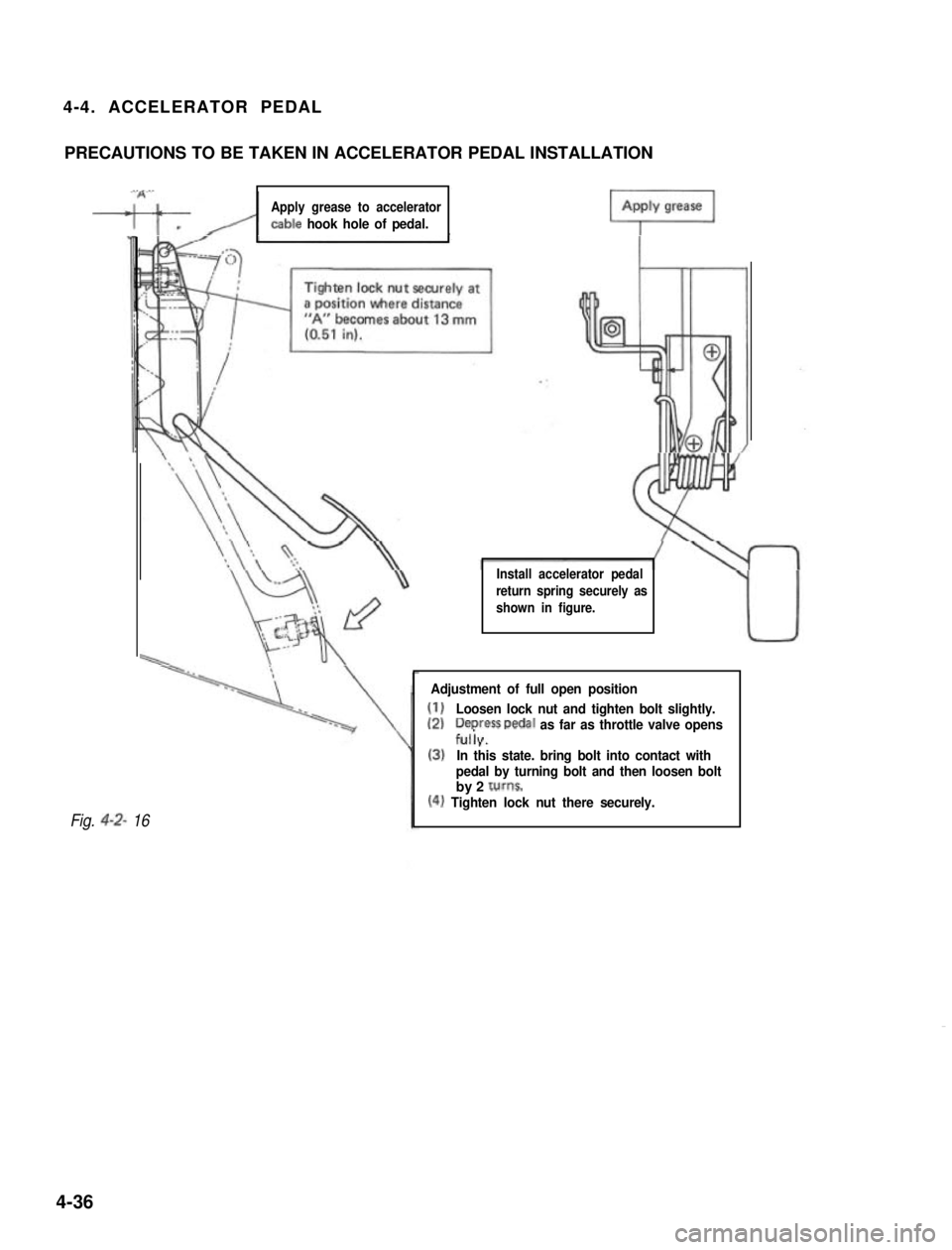
4-4. ACCELERATOR PEDAL
PRECAUTIONS TO BE TAKEN IN ACCELERATOR PEDAL INSTALLATION
“A’,
-w/i
Apply grease to accelerator
cable hook hole of pedal.
Install accelerator pedal
return spring securely as
shown in figure.
Fig. 4-2- 16
Adjustment of full open position
(1)Loosen lock nut and tighten bolt slightly.
(2)Depress Dedal as far as throttle valve opensf&
(3)In this state. bring bolt into contact with
pedal by turning bolt and then loosen boltby 2 tums.
(4) Tighten lock nut there securely.
4-36
Page 162 of 962
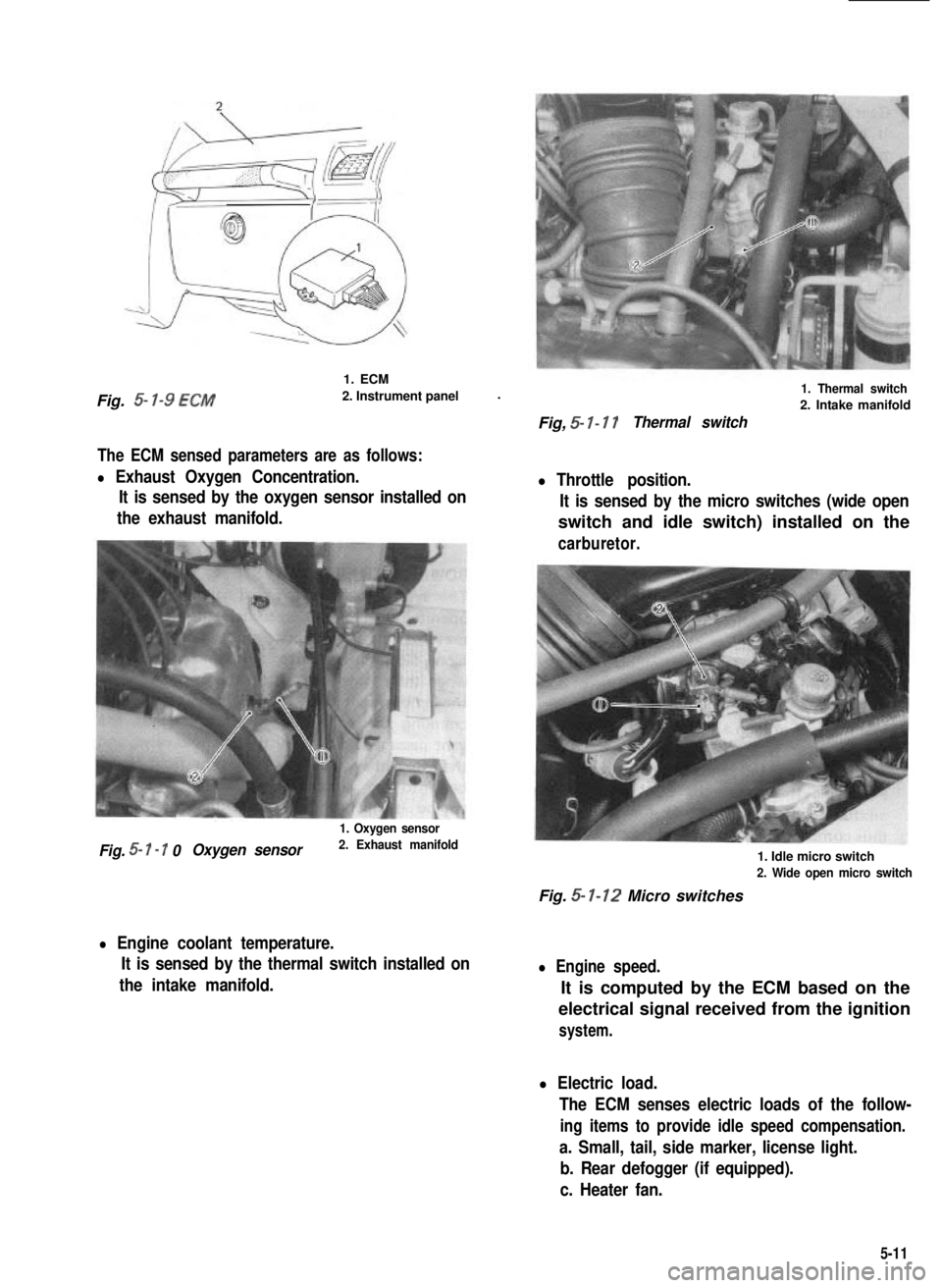
Fig. 5- l-9 ECM
1. ECM
2. Instrument panel.
The ECM sensed parameters are as follows:
l Exhaust Oxygen Concentration.
It is sensed by the oxygen sensor installed on
the exhaust manifold.
1. Oxygen sensor
Fig. 5- I - 7 0Oxygen sensor2. Exhaust manifold
l Engine coolant temperature.
It is sensed by the thermal switch installed on
the intake manifold.
1. Thermal switch
2. Intake manifold
Fig, 5- I- 17Thermal switch
l Throttle position.
It is sensed by the micro switches (wide open
switch and idle switch) installed on the
carburetor.
1. Idle micro switch
2. Wide open micro switch
Fig. 5- 1-12 Micro switches
l Engine speed.
It is computed by the ECM based on the
electrical signal received from the ignition
system.
l Electric load.
The ECM senses electric loads of the follow-
ing items to provide idle speed compensation.
a. Small, tail, side marker, license light.
b. Rear defogger (if equipped).
c. Heater fan.
5-11
Page 167 of 962

EGR DIAGNOSIS
Condition
Engine idles abnormally rough
and/or stalls.
Possible CauseCorrection
EGR valve vacuum hoses mis-Check EGR valve vacuum hose routing.
routed.Correct as required.
Leaking EGR valve.Check EGR valve for correct operation.
EGR valve gasket failed or looseCheck EGR attaching bolts for tightness.
EG R attaching bolts.If no loose, remove EGR valve and inspect
gasket.
Improper vacuum to EGR valveCheck vacuum from carburetor EGR port with
at idle.engine at stabilized operating temperature and
at idle speed.
Engine runs rough on light
throttle acceleration and has
poor part load performance.
Sticky EGR valve
EGR valve vacuum hose mis-
routed.
Loose EGR attaching bolts
Sticky or binding EGR valve.
Check EGR valve for correct operation,
Check EGR valve vacuum hose routing.
Correct as required.
Torque bolts.
Same as listing in “Engine idles Abnomrally
Rough and/or Stalls” condition.
Clean EGR passage deposits.
Perform EGR System Check.
EGR modulator valve blocked
or air flow restricted.
Check EGR modulator valve operation.
Engine stalls on decelerations.
Wrong or no EGR gasket.
EGR modulator valve blocked
of air flow restricted.
Install new gasket, torque attaching parts.
Check EGR modulator valve operation.
Restriction in EGR vacuum line.Check EGR vacuum lines for kinks, bends, etc.
Remove or replace hoses as required.
VSV filter plugged.
Sticking or binding EGR valve.
Check VSV for correct operation.
Check EGR valve for excessive deposits causing
sticky or binding operation.
Part throttle engine detonation.EGR modulator valve blockedCheck internal control valve operation.
of air flow restricted.
NOTE:
Non-functioning EGR valveInsufficient exhaust gas recircu-Check EGR valve hose routing. Check EGR
could contribute to partlation flow during part throttlevalve operation. Repair or replace as required.
throttle detonation. Detonationaccelerations.Replace valve as required. Check EGR passages
can be caused by several otherand valve for excessive deposit.
engine variables. Perform igni-Clean as required. Check VSV operation.
tion and carburetor related
diagnosis.
5-16
Page 171 of 962
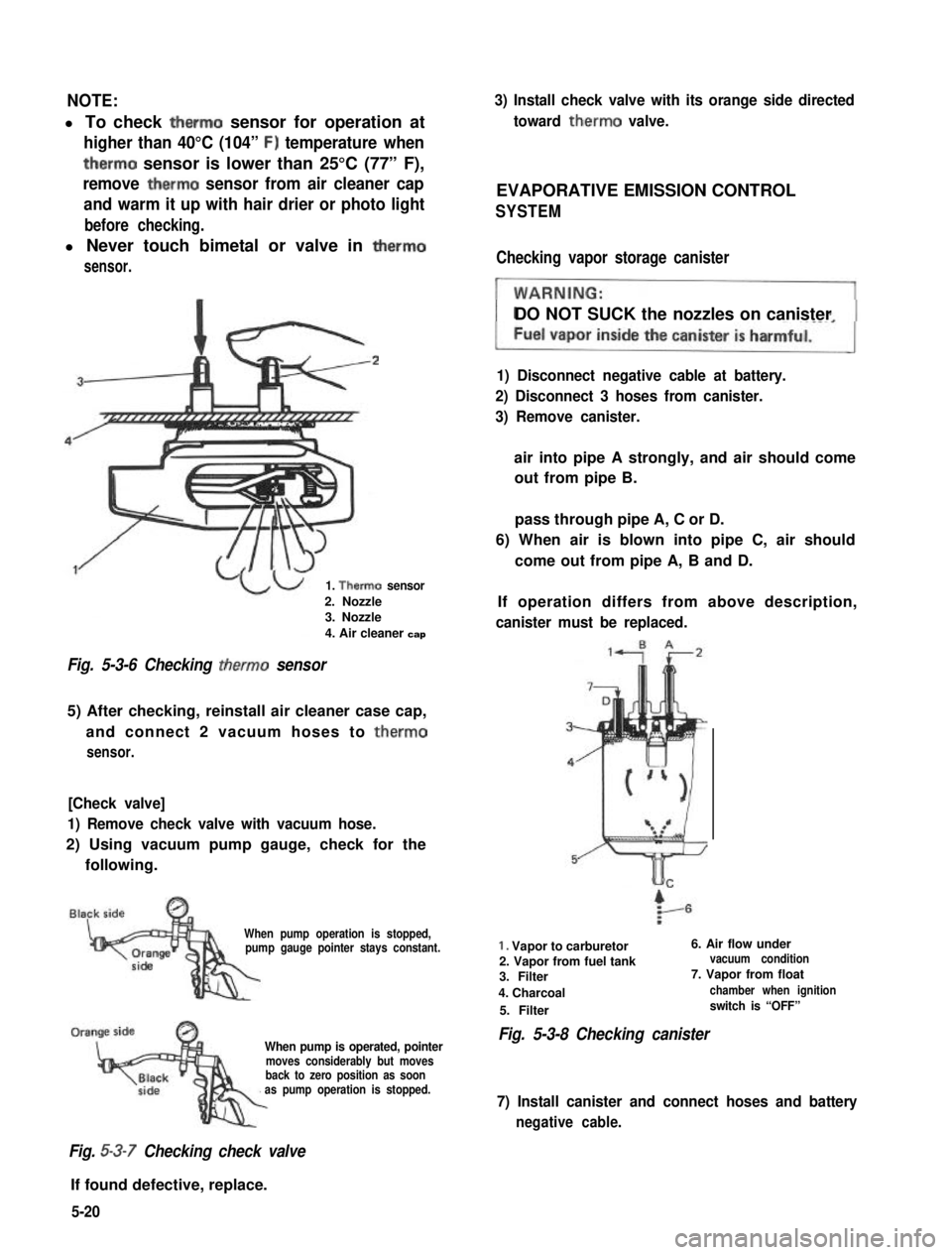
NOTE:
l To check therm0 sensor for operation at
higher than 40°C (104” F) temperature when
therm0 sensor is lower than 25°C (77” F),
remove therm0 sensor from air cleaner cap
and warm it up with hair drier or photo light
before checking.
l Never touch bimetal or valve in therm0
sensor.
1. Therm0 sensor
2. Nozzle3. Nozzle
4. Air cleaner cap
Fig. 5-3-6 Checking therm0 sensor
5) After checking, reinstall air cleaner case cap,
and connect 2 vacuum hoses to therm0
sensor.
[Check valve]
1) Remove check valve with vacuum hose.
2) Using vacuum pump gauge, check for the
following.
When pump operation is stopped,pump gauge pointer stays constant.
When pump is operated, pointermoves considerably but movesback to zero position as soonas pump operation is stopped.
Fig. 5-3-7 Checking check valve
If found defective, replace.
3) Install check valve with its orange side directed
toward therm0 valve.
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM
Checking vapor storage canister
DO NOT SUCK the nozzles on canister
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
2) Disconnect 3 hoses from canister.
3) Remove canister.
air into pipe A strongly, and air should come
out from pipe B.
pass through pipe A, C or D.
6) When air is blown into pipe C, air should
come out from pipe A, B and D.
If operation differs from above description,
canister must be replaced.
1. Vapor to carburetor6. Air flow under
2. Vapor from fuel tankvacuum condition
3. Filter7. Vapor from float
4. Charcoalchamber when ignition
5. Filterswitch is “OFF”
Fig. 5-3-8 Checking canister
7) Install canister and connect hoses and battery
negative cable.
5-20
Page 172 of 962
![SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 1987 Service Repair Manual [Hoses]
Visually inspect hoses and pipe for cracks,
damage, or excessive bends, and hose connec-
tion for tightness.
Fig. 5-3-9
HOT IDLE COMPENSATOR (HIC)
Checking Hot Idle Compensator
1) Remove air i SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 1987 Service Repair Manual [Hoses]
Visually inspect hoses and pipe for cracks,
damage, or excessive bends, and hose connec-
tion for tightness.
Fig. 5-3-9
HOT IDLE COMPENSATOR (HIC)
Checking Hot Idle Compensator
1) Remove air i](/manual-img/20/57437/w960_57437-171.png)
[Hoses]
Visually inspect hoses and pipe for cracks,
damage, or excessive bends, and hose connec-
tion for tightness.
Fig. 5-3-9
HOT IDLE COMPENSATOR (HIC)
Checking Hot Idle Compensator
1) Remove air intake case with hose.
2) Check temperature around HIC with thermo-
meter.
3) If temperature is below 45°C (113” F), air
should not come out of HIC when air is
blown into hose. If temperature is above
65°C (149” F), air comes out of HIC.
Replace H IC if defective.
4) After checking, install air intake case and
connect hose to intake manifold.
NOTE:
l To check HIC for operation at higher than
65°C (149°F) temperature when HIC (bi-
metal) temperature is lower than 45°C
(113”F), warm it up with hair drier or photo
light before checking.
l Never touch bimetal or valve in HIC.
1
Below 45°C (113’F)Above 65’C (149’F)
Fig.5-i- 10
DECELERATION MIXTURE CONTROL
SYSTEM
Checking
[Hoses]
Inspect each hose for pinholes, cracks or damage.
Also check to ensure that each joint is securely
connected. Any part found defective must be
corrected or replaced.
.
Fig. 5-3- 11
[Mixture control valve (MCV)]
1) Warm up the engine to normal operating
temperature.
2) Disconnect hose @ and reconnect it. At this
time, check that air is drawn into MCV.
NOTE:
At this time, the engine will idle rough or die,
but this is normal.
A piece of paper
If the above checks show anything wrong,
replace it.
5-21
Page 173 of 962
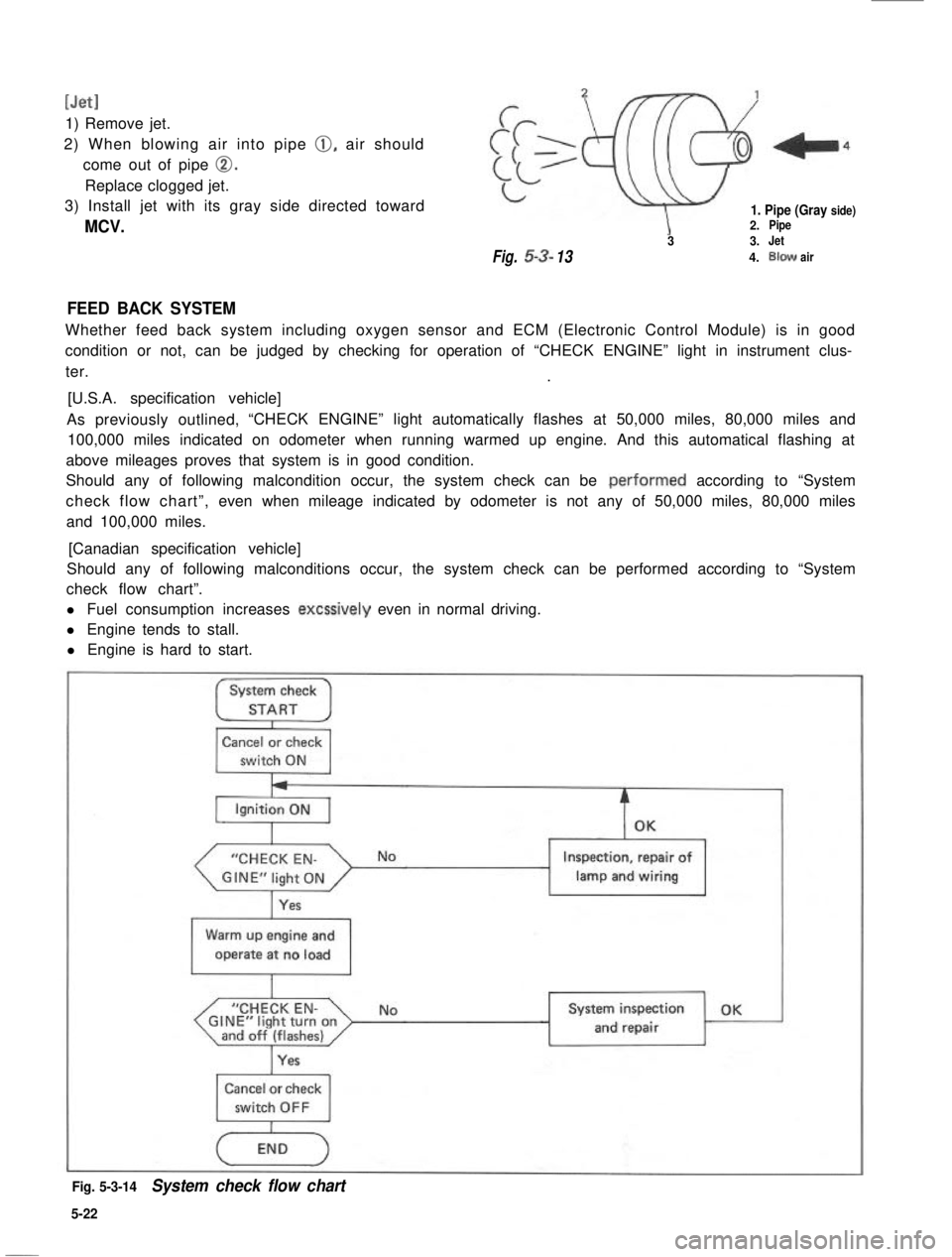
[Jet1
1) Remove jet.
2) When blowing air into pipe 0, air should
come out of pipe 0.
Replace clogged jet.
3) Install jet with its gray side directed toward
MCV.
1. Pipe (Gray side)2.Pipe
33.Jet
Fig.53-134.Blowair
FEED BACK SYSTEM
Whether feed back system including oxygen sensor and ECM (Electronic Control Module) is in good
condition or not, can be judged by checking for operation of “CHECK ENGINE” light in instrument clus-
ter..
[U.S.A. specification vehicle]
As previously outlined,“CHECK ENGINE” light automatically flashes at 50,000 miles, 80,000 miles and
100,000 miles indicated on odometer when running warmed up engine. And this automatical flashing at
above mileages proves that system is in good condition.
Should any of following malcondition occur, the system check can be .performed according to “System
check flow chart”,even when mileage indicated by odometer is not any of 50,000 miles, 80,000 miles
and 100,000 miles.
[Canadian specification vehicle]
Should any of following malconditions occur, the system check can be performed according to “System
check flow chart”.
l Fuel consumption increases excssively even in normal driving.
l Engine tends to stall.
l Engine is hard to start.
System check
STARTI
Cancel or check
switch ON
“CHECK EN-
Yes
Inspection, repair of
lamp and wiring1
Warm up engine and
operate at no load
I
“CHECK EN-GINE”light turnonand off (flashes)I
NoSystem inspection OK
and repair
Cancel or check
Fig. 5-3-14System check flow chart
5-22
Page 174 of 962
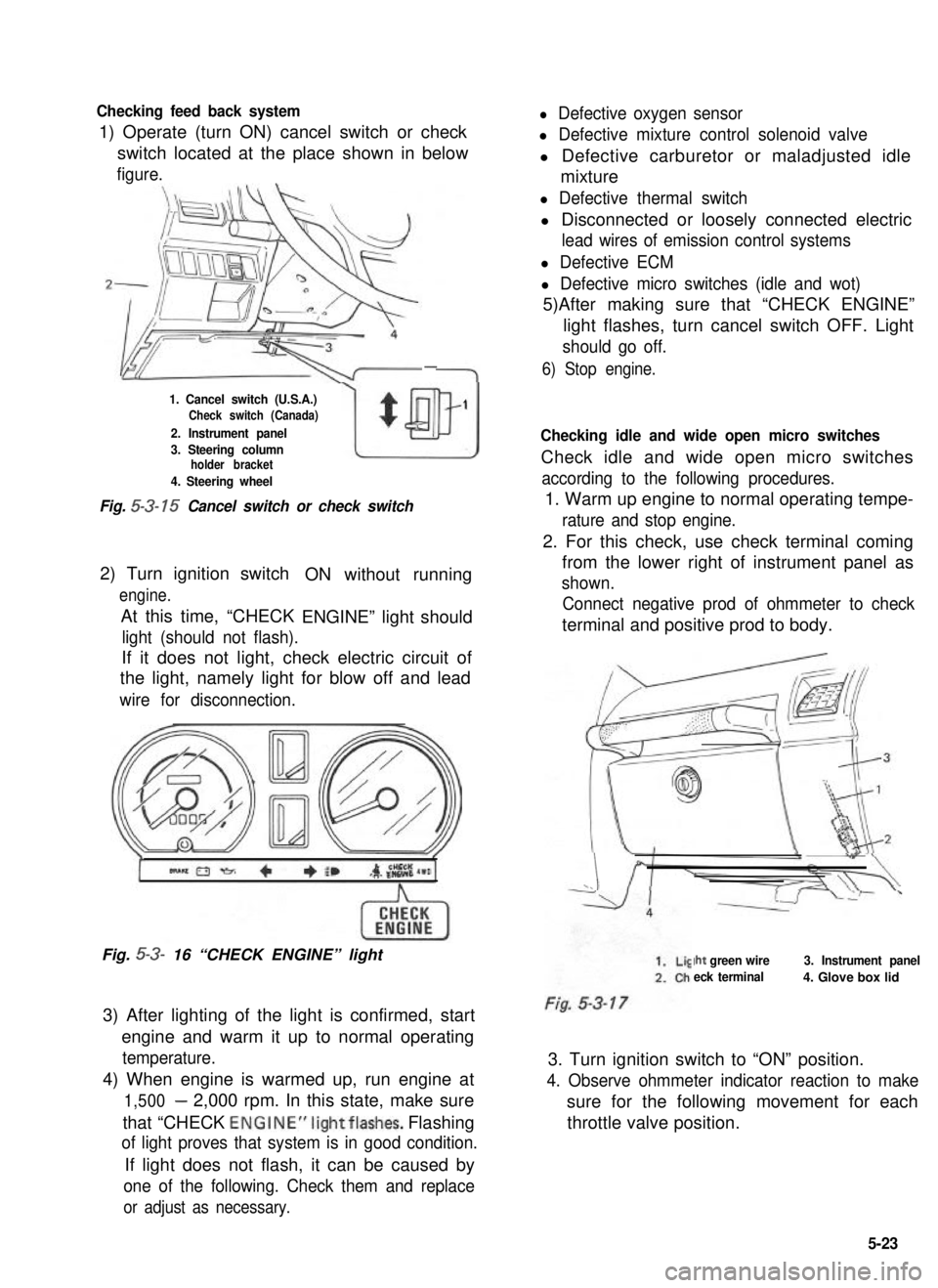
Checking feed back system
1) Operate (turn ON) cancel switch or check
l Defective oxygen sensor
l Defective mixture control solenoid valve
switch located at the place shown in belowl Defective carburetor or maladjusted idle
figure.mixture
-
1. Cancel switch (U.S.A.)Check switch (Canada)
2. Instrument panel
w
$
1
3. Steering columnholder bracket
4. Steering wheel
Fig. 5-3- 15 Cancel switch or check switch
2) Turn ignition switch
engine.
At this time, “CHECK
ON without running
ENGINE” light should
light (should not flash).
If it does not light, check electric circuit of
the light, namely light for blow off and lead
wire for disconnection.
Fig. 5-3- 16 “CHECK ENGINE” light
3) After lighting of the light is confirmed, start
engine and warm it up to normal operating
temperature.
4) When engine is warmed up, run engine at
1,500- 2,000 rpm. In this state, make sure
that “CHECK ENGINE”lightflashes. Flashing
of light proves that system is in good condition.
If light does not flash, it can be caused by
one of the following. Check them and replace
or adjust as necessary.
l Defective thermal switch
l Disconnected or loosely connected electric
lead wires of emission control systems
l Defective ECM
l Defective micro switches (idle and wot)
5)After making sure that “CHECK ENGINE”
light flashes, turn cancel switch OFF. Light
should go off.
6) Stop engine.
Checking idle and wide open micro switches
Check idle and wide open micro switches
according to the following procedures.
1. Warm up engine to normal operating tempe-
rature and stop engine.
2. For this check, use check terminal coming
from the lower right of instrument panel as
shown.
Connect negative prod of ohmmeter to check
terminal and positive prod to body.
Iht green wire
eck terminal
3. Instrument panel
4. Glove box lid
3. Turn ignition switch to “ON” position.
4. Observe ohmmeter indicator reaction to make
sure for the following movement for each
throttle valve position.
5-23
Page 183 of 962
![SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 1987 Service Repair Manual [Checking sensors and their lead wires]
The sensors constituting the feed back system are; wide open micro switch, idle micro switch, thermal
switch, high altitude compensator, thermal engine room swi SUZUKI GRAND VITARA 1987 Service Repair Manual [Checking sensors and their lead wires]
The sensors constituting the feed back system are; wide open micro switch, idle micro switch, thermal
switch, high altitude compensator, thermal engine room swi](/manual-img/20/57437/w960_57437-182.png)
[Checking sensors and their lead wires]
The sensors constituting the feed back system are; wide open micro switch, idle micro switch, thermal
switch, high altitude compensator, thermal engine room switch and fifth switch. If any of the above
sensors malfunctions or if the sensor circuit has some trouble, signals are not sent to the ECM and conse-
quently the feed back system will not function properly.
Therefore, check each sensor and its circuit according to the following procedure.
1) Turn OFF the ignition switch.
2) Disconnect the coupler from the ECM.
3) Connect the ohmmeter between the terminal @ of the disconnected coupler and the terminal @
(ground) as shown in below figure and measure the resistance. And then repeat the same with each of
the terminals 0, @I, @I, @ and @I.
1. Coupler (Viewed from wireharness side)
2. Wide open micro switch3. idle micro switch
4. Thermal switch
5. Thermal engine room switch6. Fifth switch
7. High altitude compensator
8. Gr/R (Gray/Red) lead wire9. Gr/Y (Gray/Yellow) lead wire10. 81 (Blue) lead wire
11. P/B (Pink/Black) lead wire
12. Gr/B (Gray/Black) lead wire
13. Lg/R (Light green/Red) lead wire
14. B/G (Black/Green) lead wire
Fig. 5-3-43 Checking sensors and their circuits
4) If each ohmmeter reading is as given below, the sensor and its circuit are in good condition. But if not,
the sensor itself may be defective or the lead wire disconnected or out of contact. After checking,
connect the coupler to ECM securely.
Idle micro switch
High altitude compensator
Thermal engine room switch
Wide open micro switch
1 Fifth switch
Ohmmeter
Terminal reading (S2)Condition
When coolant temp. is low.
When coolant temp. is above 46.5’C (I 16’F).
0 1
When engine is warm and accelerator pedal is not depressed.
When accelerator pedal is depressed a little.
00
@
When altitude is below 1,220 m (4,000 ft.).
0When altitude is above 1,220 m (4,000 ft.).
0
When temp. in engine room is low.
When temp. in engine room is above 19.5’C (67°F).
0When accelerator pedal is not depressed or depressed only a
0little.
CoWhen accelerator pedal is depressed all the way.
@ Oa
When gear shift lever is shifted to low, second, third, forth or
reverse gear position.
0When gear shift lever is shifted to fifth gear position.
5-32