2006 DODGE RAM SRT-10 engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 5048 of 5267

4.ACTUATOR DTC DETECTION TEST
NOTE: The Actuator DTC Detection Test clears all door actuator related DTCs when the test is actuated.
If not done so previously, start the engine.
With the scan tool, select System Tests and then select Actuator DTC Detection. When the test is complete, select
View DTCs.
Does the scan tool display any DTCs?
Yes, Dual-Zone
Diagnose and repair the DTC(s). If multiple DTCs are present, beginning with the passenger blend door,
diagnose and repair all short high DTCs and then all short low DTCs. Refer tothe Table of Contents in
this Section for a complete list of HVAC related symptoms.
Yes, Single-Zone
Diagnose and repair the DTC(s). If multiple DTCs are present, beginning with the common circuit, diag-
nose and repair all short high DTCs and then all short low DTCs. Refer to the Table of Contents in this
Section for a complete list of HVAC related symptoms.
No>>
If you are here due to a stored DTC, it is possible that a technician may not have erased the DTC
following a repair. If possible, verify if the vehicle was recently in for this type of service. Otherwise,
either Go To 5 or visually inspect the related wiring harness for chafed, pierced, pinched, and partially
broken wires and the wiring harness connectors for broken, bent, pushed out, and corroded terminals,
and repair as necessary.
Perform BODY VERIFICATION TEST - VER 1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
5.ACTUATOR CALIBRATION TEST
NOTE: For vehicles equipped with EBL, running the HVAC Door Recalibrationwill cause the EBL status
indicator to flash.
NOTE: The Actuator Calibration Test clears all door actuator related DTCswhen the test is actuated.
If not done so previously, start the engine.
With the scan tool, select System Tests and then select Actuator Calibration Test. When the test is complete, select
View DTCs.
Does the scan tool display any DTCs?
Ye s>>
Diagnose and repair the DTC(s). Refer to the Table of Contents in this Section for a complete list of
HVAC related symptoms.
No>>
No problem found. However, if you are here due to a stored DTC, it is possiblethat a technician may
not have erased the DTC following a repair. If possible, verify if the vehicle was recently in for this type
of service. Otherwise, visually inspect the related wiring harness for chafed, pierced, pinched, and par-
tially broken wires and the wiring harness connectors for broken, bent, pushed out, and corroded ter-
minals, and repair as necessary.
Perform BODY VERIFICATION TEST - VER 1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Page 5050 of 5267

HVAC - SERVICE INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION
A manually controlled single zone type heating-air conditioning system or a manually controlleddualzonetypeheat-
ing-air conditioning system is available on this model.
To maintain the performance level of the heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) system, the engine cooling
system must be properly maintained. The use of a bug screen is not recommended. Any obstructions in front of the
radiator or A/C condenser will reduce the performance of the A/C and enginecooling systems.
The engine cooling system includes the radiator, thermostat, radiator hoses and the engine coolant pump. Refer to
7 - Cooling for more information before opening or attempting any service to the engine cooling system.
All vehicles are equipped with a common heater, ven-
tilation and air conditioning (HVAC) housing (1). The
system combines air conditioning, heating, and venti-
lating capabilities in a single unit housing mounted
within the passenger compartment under the instru-
ment panel. The HVAC housing includes:
Blend-air door(s) and actuator(s) (2)
Recirculation-air door and actuator (3)
A/C evaporator (4)
Blower motor (5)
Blower motor resistor (6)
Evaporator temperature sensor (7)
Heater core (8)
Mode-air doors and actuators (9)
Based upon the system and mode selected, conditioned air can exit the HVAC housing through one or a combi-
nation of the three main housing outlets: defrost, panel or floor. The defrost and the panel outlets are located on the
top of the housing and, the floor outlet is located on the bottom of the housing. Once the conditioned air exits the
HVAC housing, it is further directed through molded plastic ducts to the various outlets within the vehicle interior.
These outlets and their locations are as follows:
Defroster Outlet- A single large defroster outlet is located in the center of the instrumentpanel top cover,
near the base of the windshield.
Side Window Demister Outlets- There are two side window demister outlets, one is located at each out-
board end of the instrument panel top cover, near the belt line at the A-pillars.
Panel Outlets- There are four panel outlets in the instrument panel, one located near each outboard end of
the instrument panel facing the rear of the vehicle and two located near thetop of the instrument panel center
bezel.
Front Floor Outlets- There are two front floor outlets, one located above each side of the floorpanel center
tunnel near the dash panel.
Rear Outlets- On Mega Cab models there are two outlets located at the rear of the center front seat.
OPERATION
Both the manual temperature control (MTC) single zone and dual zone heating-A/C system are blend-air type sys-
tems. In a blend-air heating-A/C, a blend-air door controls the amount of conditioned air that is allowed to flow
through, or around, the heater core.In the available dual zone system, twoblend-air doors are used to provide
completely independent side-to-side temperature control of the discharge air. The temperature control(s) determines
the discharge air temperature(s) by operating the blend door actuator(s), which move the blend-air door(s). This
design allows almost immediate control of output air temperature(s).
Page 5054 of 5267

NOTE: When connecting the service equipment coupling to the line fitting,verify that the valve of the cou-
pling is fully closed. This will reduce the amount of effort required to make the connection.
NOTE: The work area ambient temperature must be above 21° C (70° F) and the evaporator temperature
must be above 13° C (55° F) prior to conducting the A/C Performance Test.
1. Conduct the A/C System Performance Test (Cooldown Test) found within the HVAC System Test (refer to 24 -
HVAC Electrical Diagnostics). If no diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are found in the A/C-heater control, power-
train control module (PCM) or engine control module (ECM) (depending on engine application), gateway module
or the totally integrated power module (TIPM), go to Step 2. If any DTCs are found, repair as required, then
proceedtoStep2.
2. Connect a tachometer and a manifold gauge set or an A/C recycling/charging station.
3. Operate the heating-A/C system under the following conditions.
Engine at 1,000 rpm at operating temperature
Door or windows open
Transmission in Park or Neutral with parking brake set (depending on application)
A/C-heater controls set to Recirculation mode (max-A/C), full cool, panel mode, high blower and with A/C com-
pressor engaged. If the A/C compressor does not engage, see the A/C System Diagnosis chart.
4. Insert a thermometer in the driver side center panel air outlet and operate the A/C system until the thermometer
temperature stabilizes.
5. With the A/C compressor clutch engaged, compare the air temperature at the center panel outlet and the A/C
compressor discharge pressure (high side) to the A/C Performance Temperature and Pressure chart. The com-
pressor clutch may cycle, depending upon the ambient temperature and humidity. If the clutch cycles, use the
readings obtained before the clutch disengaged.
A/C PERFORMANCE TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE
Ambient Air
Temperature21° C
(70° F)27° C
(80° F)32° C
(90° F)38° C
(100° F)43° C
(110° F)
Air Temperature at
Center Panel Outlet7° C
(45° F)7° C
(45° F)13° C
(55° F)13° C
(55° F)18° C
(64° F)
Compressor Inlet
Pressure at Service
Port (low Side)138 to 207 kPa
(20to30psi)172to241kPa
(25to35psi)207 to 276
kPa
(30to40psi)241 to 310
kPa
(35to45psi)276to345kPa
(40to50psi)
Compressor
Discharge Pressure at
Service Port (High
Side)1034 to 1724
kPa
(150 to 250
psi)1379to2068
kPa
(200 to 300
psi)1724to2413
kPa
(250 to 350
psi)1999 to 2689
kPa
(290 to 390
psi)2413to2965
kPa
(350 to 430 psi)
6. If the air outlet temperature fails to meet the specifications in the A/CPerformance Temperature and Pressure
chart, or if the A/C compressor discharge pressure is high, refer to the A/CSystem Diagnosis chart.
A/C SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Constant compressor
engagement and warm air
from passenger vents.1. Low refrigerant system
charge.1. See Refrigerant System Leaks in this group.
Test the refrigerant system for leaks. Repair,
evacuate and charge the refrigerant system, if
required.
Equal pressures, but the
compressor clutch does not
engage.1. No refrigerant in the
refrigerant system.1. See Refrigerant System Leaks in this group.
Test the refrigerant system for leaks. Repair,
evacuate and charge the refrigerant system, if
required.
Page 5056 of 5267

Condition Possible Causes Correction
5. Engine overheating.5. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the
cooling system and repair, if required.
The low side pressure is too
high, and the high side
pressure is too low.1. Accessory drive belt
slipping.1. Refer to Cooling for more information. Inspect
the accessory drive belt condition and tension.
Tighten or replace the accessory drive belt, if
required.
2. Fixed orifice tube not
installed.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace the
liquid line, if required.
3. Faulty A/C compressor.3. See A/C Compressor in this group. Replace the
compressor, if required.
The low side pressure is too
low, and the high side
pressure is too high.1. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the refrigerant lines.1. See Liquid, Suction, and Discharge Line in this
group. Inspect the refrigerant lines for kinks, tight
bends or improper routing. Correct the routing or
replace the refrigerant line, if required.
2. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the fixed orifice
tube.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace the
liquid line, if required.
3. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the condenser.3. See A/C Condenser in this group. Replace the
restricted condenser, if required.
HEATER PERFORMANCE
Before performing the following tests, refer to Group 7 - Cooling for the procedures to check the engine coolant
level and flow, engine coolant reserve/recovery system operation, accessory drive belt condition and tension, radi-
ator air flow and the fan drive operation. Perform the HVAC System Test (refer to 24 - HVAC Electrical Diagnostics).
If any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are found in the A/C-heater control, powertrain control module (PCM) or
engine control module (ECM) (depending on engine application), gateway module or totally integrated power module
(TIPM), repair as necessary.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT: TEST AND ACTION
Engine coolant is provided to the heater system through two heater hoses. With the engine idling at normal oper-
ating temperature, set the temperature control to maximum heat position,the mode control to the floor position, and
the blower motor control to the highest speed position. Using a test thermometer, check the temperature of the air
being discharged from the floor outlets. Compare the test thermometer reading to the Heater Temperature Refer-
ence chart.
HEATER TEMPERATURE REFERENCE
Ambient Air Temperature16° C
(60° F)21° C
(70° F)26° C
(80° F)32° C
(90° F)
Minimum Air Temperature at
Floor Outlet62° C
(144° F)64° C
(147° F)65° C
(150° F)67° C
(153° F)
If the heater outlet air temperature is below the minimum specification, refer to Group 7 - Cooling. Both of the heater
hoses should be hot to the touch. The coolant return heater hose should be slightly cooler than the coolant supply
heater hose. If the return hose is much cooler than the supply hose, locate and repair the engine coolant flow
obstruction in the cooling system. RefertoGroup7-Coolingformoreinformation.
OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW
Possible locations or causes of obstructed coolant flow are as follows:
Faulty water pump.
Faulty thermostat.
Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
Page 5057 of 5267

Improper heater hose routing.
Plugged heater hoses or supply and return ports at the cooling system connections.
Plugged heater core.
If proper coolant flow through the cooling system is verified, and heater outlet air temperature is low, a mechanical
problem may exist.
MECHANICAL PROBLEMS
Possible locations or causes of insufficient heat due to mechanical problems are as follows:
Obstructed cowl air intake.
Obstructed heater system outlets.
Blend-air door(s) or actuator(s) not functioning properly.
Faulty blower motor system
Faulty A/C-heater control
TEMPERATURE CONTROL
If the heater outlet air temperature cannot be adjusted with the temperature control on the A/C-heater control, the
following could require service:
Faulty A/C-heater control.
Faulty blend door actuator(s).
Faulty, obstructed or improperly installed blend-air door.
Faulty related wiring harness or connectors.
Improper engine coolant temperature.
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C SYSTEM
Item Description Notes
A/C Compressor Denso 10S17 (3.7L/4.7L/5.7L/8.3L
engines)ND-8 PAG oil
Visteon HS-18 (5.9L engine) VC-46 PAG oil
Freeze–up Control Evaporator Temperature Sensor A/C evaporator mounted
High psi Control A/C pressure transducer A/C discharge line mounted
Refrigerant Charge Capacity Refer to the A/C Underhood
Specification Label located in the
engine compartment.R134a refrigerant
A/C Clutch Field Coil Draw 3.2 - 3.3 amps @ 12V ± 0.5V @
21° C (70° F)3.7L/4.7L/5.7L/8.3L engines
3.1 - 4 amps @ 12V ± 0.5V @ 21°
C(70°F)5.9L engine
A/C Clutch Air Gap 0.35 - 0.60 mm (0.014 - 0.024 in.) 3.7L/4.7L/5.7L/8.3L engines
0.35 - 0.75 mm (0.014 - 0.030 in.) 5.9L engine
TORQUE
Page 5058 of 5267
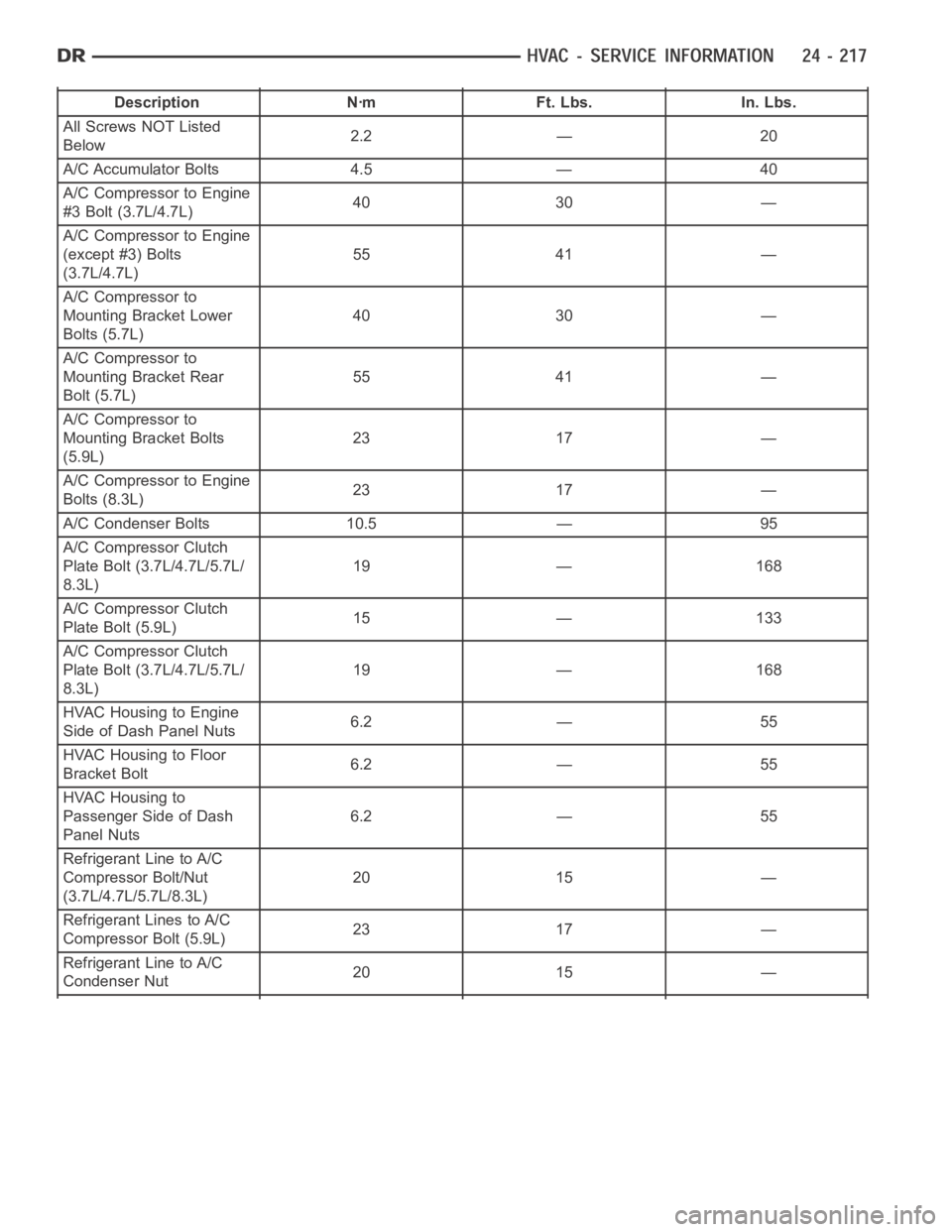
Description Nꞏm Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
All Screws NOT Listed
Below2.2 — 20
A/C Accumulator Bolts 4.5 — 40
A/C Compressor to Engine
#3 Bolt (3.7L/4.7L)40 30 —
A/C Compressor to Engine
(except #3) Bolts
(3.7L/4.7L)55 41 —
A/C Compressor to
Mounting Bracket Lower
Bolts (5.7L)40 30 —
A/C Compressor to
Mounting Bracket Rear
Bolt (5.7L)55 41 —
A/C Compressor to
Mounting Bracket Bolts
(5.9L)23 17 —
A/C Compressor to Engine
Bolts (8.3L)23 17 —
A/C Condenser Bolts 10.5 — 95
A/C Compressor Clutch
Plate Bolt (3.7L/4.7L/5.7L/
8.3L)19 — 168
A/C Compressor Clutch
Plate Bolt (5.9L)15 — 133
A/C Compressor Clutch
Plate Bolt (3.7L/4.7L/5.7L/
8.3L)19 — 168
HVAC Housing to Engine
Side of Dash Panel Nuts6.2 — 55
HVAC Housing to Floor
Bracket Bolt6.2 — 55
HVAC Housing to
Passenger Side of Dash
Panel Nuts6.2 — 55
Refrigerant Line to A/C
Compressor Bolt/Nut
(3.7L/4.7L/5.7L/8.3L)20 15 —
Refrigerant Lines to A/C
Compressor Bolt (5.9L)23 17 —
Refrigerant Line to A/C
Condenser Nut20 15 —
Page 5073 of 5267

CLUTCH-A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION
NOTE: Denso 10S17 A/C clutch assembly shown.
Visteon HS-18 compressor similar.
The A/C compressor clutch assembly consists of a
stationary electromagnetic field coil (4), bearing and
pulley assembly (3), shims (7) and a clutch plate (2)
that is splined to the compressor shaft and secured by
a bolt (1). These components provide the means to
engage and disengage the A/C compressor from the
engine accessory drive belt.
The A/C clutch bearing and pulley assembly on both
A/C compressors are retained to the front of the com-
pressor with a snap ring (6). The A/C clutch field coil
on the Denso 10S17 A/C compressor is also retained
to the front of the compressor using a snap ring (5).
The field coil on the Visteon HS-!8 compressor is
pressed onto the front of the compressor.
OPERATION
The A/C compressor clutch components provide the means to engage and disengage the A/C compressor from the
engine accessory drive belt. When the electromagnetic A/C clutch field coil is energized, it magnetically draws the
clutch plate into contact with the clutch pulley and drives the compressorshaft. When the coil is not energized, the
pulley freewheels on the clutch hub bearing, which is part of the pulley assembly.
A/C compressor clutch engagement is controlled by the powertrain controlmodule (PCM) or the engine control mod-
ule (ECM), depending on engine application. When the A/C-heater control is set to any A/C position, it sends a
request signal on the CAN-B bus to the totally integrated power module (TIPM), which then transfers the request on
the CAN-C Bus to the PCM/ECM, which determines if operating conditions arecorrect for A/C clutch engagement.
When all operating conditions have been met, the PCM/ECM sends a signal on adedicated hard-wired circuit back
to the totally integrated power module (TIPM) to energize the internal A/Cclutch high side driver. When energized,
the A/C clutch high side driver provides battery current to the A/C clutch field coil.
The A/C clutch control system is diagnosed using a scan tool (Refer to 24 - HVAC Electrical Diagnostics and to 9
- Engine Electrical Diagnostics for more information).
The A/C compressor clutch components cannot be repaired and, if faulty or damaged, they must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
A/CCOMPRESSORCLUTCHCOIL
The A/C compressor clutch coil electrical circuit is controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM) or the engine
control module (ECM) (depending on engine application) through the totally integrated power module (TIPM) (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/COIL-A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH -OPERATION for more
information). Begin testing of a suspected compressor clutch coil problem by performing the preliminary checks.
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
1. Using a scan tool, check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) in the A/C-heater control, TIPM, PCM/ECM and if
equipped with the 8.3L engine, the gateway module. If no DTCs are found, go to Step 2. If any DTCs are found,
repair as required.
2. If the A/C compressor clutch still will not engage, verify the refrigerant charge level (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM LEAKS). If the refrig-
erant charge level is OK, go to TESTS . If the refrigerant charge level is notOK, adjust the refrigerant charge as
required.
Page 5074 of 5267

TESTS
1. Verify the battery state of charge (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
2. Connect an ammeter (0 to 10 ampere scale selected) in series with the clutch coil feed terminal. Connect a
voltmeter (0 to 20 volt scale selected) to measure voltage across the battery and the clutch coil.
3. With the A/C-heater control in the A/C mode and the blower motor at low speed, start the engine and allow it to
run at a normal idle speed.
4. The A/C compressor clutch should engage immediately, and the clutch coil supply voltage should be within two
volts of the battery voltage. If the coil supply voltage is OK, go to Step 5. If the coil supply voltage is not within
two volts of battery voltage, test the clutch coil feed circuit for excessive voltage drop and repair as necessary.
5. For the acceptable A/C clutch coil current draw specifications refer to24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING -
SPECIFICATIONS. Specifications apply for a work area temperature of 21° C(70° F). If voltage is more than
12.5 volts, add electrical loads by turning on electrical accessories until voltage reads below 12.5 volts.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
A/C CLUTCH PLATE INSPECTION
NOTE: The A/C clutch can be serviced inthe vehicle. The refrigerant systemcan remain fully-charged dur-
ing compressor clutch, pulley and bearing assembly, or coil replacement.
Examine the friction surfaces of the pulley and the
clutch plate (2) for wear. The pulley and clutch plate
should be replaced if there is excessive wear or scor-
ing.
If the friction surfaces are oily, inspect the shaft and
nose area of the A/C compressor (1) for refrigerant oil.
If refrigerant oil is found, the compressor shaft seal is
leaking and the A/C compressor must be replaced.
Check the pulley bearing for roughness or excessive
leakage of grease. Replace the pulley and bearing
assembly, if required.
A/C CLUTCH BREAK-IN
After a new A/C compressor clutch hasbeen installed, cycle the compressorclutch approximately 20 times (5 sec-
onds on, then 5 seconds off). During this procedure, set the A/C-heater controls to the A/C Recirculation Mode, the
blower motor in the highest speed position, and the engine speed at 1500 to 2000 rpm. This procedure (burnishing)
will seat the opposing friction surfaces and provide a higher compressor clutch torque capability.