2006 DODGE RAM SRT-10 Fuel injector removal
[x] Cancel search: Fuel injector removalPage 1498 of 5267

17. Disconnect the engine wiring harness at the fol-
lowing points :
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor (4)
Fuel Injectors
Throttle Position (TPS) Switch (2)
Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor (3)
Engine Oil Pressure Switch
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Manifold Absolute Pressure MAP) Sensor
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
Coil Over Plugs
Crankshaft Position Sensor
18. Remove coil over plugs.
19. Release fuel rail pressure.
20. Remove fuel rail and secure away from engine.
NOTE: It is not necessary to release the quick
connect fitting from the fuel supply line for engine
removal.
21. Remove the PCV hose.
22. Remove the breather hoses.
23. Remove the vacuum hose for the power brake
booster.
24. Disconnect knock sensors.
25. Remove engine oil dipstick tube.
26. Remove intake manifold.
27. Install engine lifting fixture,special tool#8247, using original fasteners from the removed intake manifold, and
fuel rail. Torque to factory specifications.
NOTE: Recheck bolt torque for engine lift plate before removing engine.
28. Secure the left and right engine wiring harnesses away from engine.
29. Raise vehicle.
30. Disconnect oxygen sensor wiring.
Page 1601 of 5267

5. Disconnect vapor purge hose, brake booster hose, speed control servo hose, positive crankcase ventilation
(PCV) hose.
6. Disconnect generator electrical connections.
7. Disconnect air conditioning compressor electrical connections.
8. Disconnect left and right radio suppressor straps.
9. Disconnect and remove ignition coil towers.
10. Remove top oil dipstick tube retaining bolt and ground strap.
11. Bleed fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
12. Remove fuel rail.
13. Remove throttle body assembly and mounting bracket.
14. Drain cooling system below coolant temperature level (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
15. Remove the heater hoses from the engine front cover and the heater core.
16. Unclip and remove heater hoses and tubes from intake manifold.
17. Remove coolant temperature sensor (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR -
REMOVAL).
18. Remove intake manifold retaining fasteners in reverse order of tightening sequence.
19. Remove intake manifold.
INSTALLATION
1. Install intake manifold gaskets.
2. Install intake manifold.
3. Install intake manifold retaining bolts and tighten in
sequence shown in to 12 Nꞏm (105 in. lbs.).
4. Install left and right radio suppressor straps.
5. Install throttle body assembly.
6. Connect throttle cable and speed control cable to
throttle body.
7. Install fuel rail.
8. Install ignition coil towers.
9. Position and install heater hoses and tubes onto intake manifold.
10. Install the heater hoses to the heater core and engine front cover.
11. Connect electrical connectors for the following components:
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
Coolant Temperature (CTS) Sensor
Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
Ignition coil towers
Fuel injectors
Page 1634 of 5267

30. Disconnect engine harness at the following points
:
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor (4)
Fuel Injectors
Throttle Position (TPS) Switch (2)
Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor (3)
Engine Oil Pressure Switch
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) Sensor
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
Coil Over Plugs
31. Disconnect the vacuum lines at the throttle body
and intake manifold.
32. Remove power steering pump and position out of
the way.
33. Install Special Tools 8400 Lifting Studs, into the
cylinder heads.
34. Install Engine Lifting Fixture Special Tool 8347 (3)
following these steps.
Holding the lifting fixture at a slight angle, slide
the large bore in the front plate over the hex por-
tion of the lifting stud.
Position the two remaining fixture arms onto the
two Special Tools 8400 Lifting Studs, in the cyl-
inder heads.
Pull foward and upward on the lifting fixture so
that the lifting stud rest in the slotted area below
the large bore.
Secure the lifting fixture to the three studs using
three 7/16 – 14 N/C locknuts.
Make sure the lifting loop in the lifting fixture is in
the last hole (closest to the throttle body) to min-
imize the angle of engine during removal.
Page 1909 of 5267
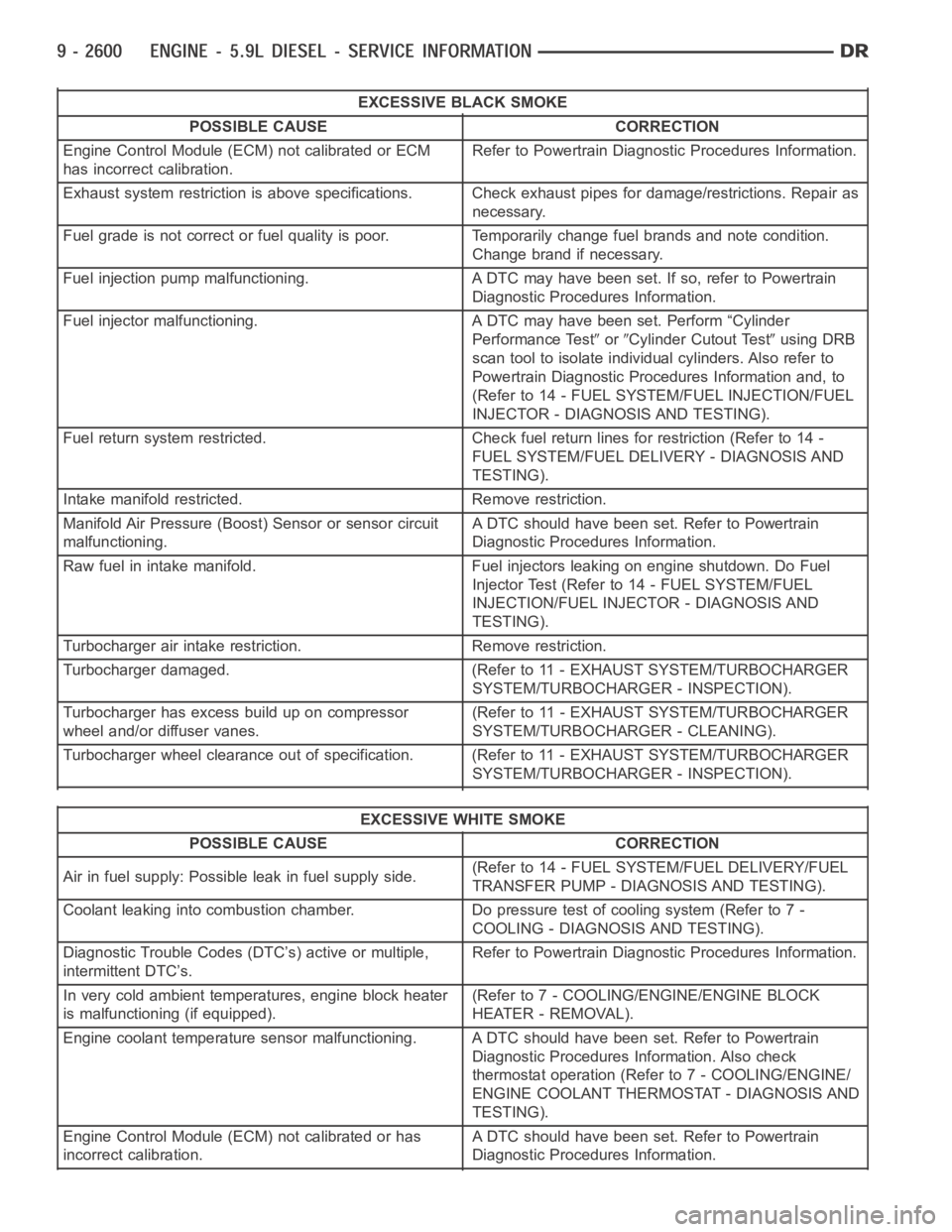
EXCESSIVE BLACK SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Engine Control Module (ECM) not calibrated or ECM
has incorrect calibration.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Exhaust system restriction is above specifications. Check exhaust pipesfor damage/restrictions. Repair as
necessary.
Fuel grade is not correct or fuel quality is poor. Temporarily change fuel brands and note condition.
Change brand if necessary.
Fuel injection pump malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. If so, refer toPowertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Fuel injector malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. Perform “Cylinder
Performance Test
orCylinder Cutout Testusing DRB
scan tool to isolate individual cylinders. Also refer to
Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information and, to
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL
INJECTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel return system restricted. Check fuel return lines for restriction (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Intake manifold restricted. Remove restriction.
Manifold Air Pressure (Boost) Sensor or sensor circuit
malfunctioning.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Raw fuel in intake manifold. Fuel injectors leaking on engine shutdown. DoFuel
Injector Test (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Turbocharger air intake restriction. Remove restriction.
Turbocharger damaged. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - INSPECTION).
Turbocharger has excess build up on compressor
wheel and/or diffuser vanes.(Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - CLEANING).
Turbocharger wheel clearance out of specification. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUSTSYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - INSPECTION).
EXCESSIVE WHITE SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Air in fuel supply: Possible leak in fuel supply side.(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL
TRANSFER PUMP - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Coolant leaking into combustion chamber. Do pressure test of cooling system (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC’s) active or multiple,
intermittent DTC’s.Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information.
In very cold ambient temperatures, engine block heater
is malfunctioning (if equipped).(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK
HEATER - REMOVAL).
Engine coolant temperature sensor malfunctioning. A DTC should have beenset. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information. Also check
thermostat operation (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Engine Control Module (ECM) not calibrated or has
incorrect calibration.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Page 1910 of 5267

EXCESSIVE WHITE SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Fuel filter plugged. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system
testing.
Fuel grade not correct or fuel quality is poor. Temporarily change fuel brands and note condition.
Change brand if necessary.
Fuel heater element or fuel heater temperature sensor
malfunctioning. This will cause wax type build-up in fuel
filter.Refer to Fuel Heater Testing (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL HEATER -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel injector malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Perform “Cylinder
Performance Test
orCylinder cutout Testusing DRB
scan tool to isolate individual cylinders. Also refer to
Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures Information and,
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL
INJECTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Fuel injector hold-downs loose. Torque to specifications.
Fuel injector protrusion not correct. Check washer (shim) at bottom of fuel injector for
correct thickness. (Referto 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR - INSTALLATION)
Fuel injection pump malfunctioning. A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Fuel supply side restriction. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system
testing.
Fuel transfer (lift) pump malfunctioning. A DTC may have been set. Refer toPowertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Intake/Exhaust valve adjustments not correct (too tight). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/INTAKE/
EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
Intake manifold air temperature sensor malfunctioning. A DTC should havebeen set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information.
Intake manifold heater circuit not functioning correctly in
cold weather.A DTC should have been set. Refer to Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures Information. Also check heater
elements for correct operation.
Intake manifold heater elements not functioning
correctly in cold weather.A DTC should have been set if heater elements are
malfunctioning. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Information.
Internal engine damage (scuffed cylinder). Analyze engine oil and inspect oil filter to locate area of
probable damage.
Restriction in fuel supply side of fuel system. Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Manual for fuel system
testing.
EXCESSIVE BLUE SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Dirty air cleaner or restricted turbocharger intake duct. Check Filter Minder
at air filter housing. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER
ELEMENT - REMOVAL).
Air leak in boost system between turbocharger
compressor outlet and intake manifold.Service air charge system..
Obstruction in exhaust manifold. Remove exhaust manifold and inspect forblockage
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST
MANIFOLD - REMOVAL).
Page 1911 of 5267

EXCESSIVE BLUE SMOKE
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Restricted turbocharger drain tube. Remove turbocharger drain tube and remove
obstruction.
Crankcase ventilation system plugged. Inspect crankcase ventilation system for function
Valve seals are worn, brittle, or improperly installed. Replace valve stemoilseals(Referto9-ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS - REMOVAL).
Valve stems and/or guides are worn. Remove valves and inspect valves and guides. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST
VALVES & SEATS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Broken or Improperly installed piston rings. Tear down engine and inspectpiston rings.
Excessive piston ring end gap. Remove pistons and measure piston ring end gap
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON RINGS
- STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Excessive cylinder bore wear and taper. Remove pistons and measure cylinder bore wear and
taper (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Cylinder damage. Remove pistons and inspect cylinder bore for cracks or
porosity. Repair with cylinder liner if necessary. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
Piston damage. Remove pistons and inspect for cracks, holes. Measure
piston for out-of-round and taper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON & CONNECTING
ROD - INSPECTION).
Turbocharger failure. (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER - INSPECTION).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER COMPRESSION/LEAKAGE TESTS
CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compressionpressure test can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunctions.
Ensure batteries are completely charged and the engine starter motor is ingood operating condition. Otherwise, the
indicated compression pressures may not be valid for diagnostic purposes.
1. Disconnect the fuel inlet line to the fuel filter housing. Plug the fuel line from the fuel tank.
NOTE: Failure to plug fuel line will result in fuel leak.
2. Remove fuel transfer pump relay from PDC.
3. Start the engine and idle until the engine stalls (runs out of fuel).
4. Remove the cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) -
REMOVAL)
5. Remove the cylinder head cover carrier gasket. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
6. Remove the high pressure fuel line between the cylinder head and fuel rail for the cylinder to be tested. Use
tool# 9011 to cap this fuel rail on the cylinder being tested.
7. Remove the fuel connector tube nut and fuel connector tube.
8. Remove the exhaust rocker lever.
9. Use Tool 9010 to remove the injector and copper sealing washer.
10. Install the exhaust rocker lever and torque to 36 Nꞏm (27 ft. lbs.).
11. Cover the remaining rocker levers with clean shop towels to prevent anyoil splatter under the hood.
Page 1912 of 5267

12. Place a rag over the compression test tool fitting. Crank the engine for2–3 seconds to purge any fuel that may
have drained into the cylinder when the injector was removed.
13. Connect the compression test gauge.
14. Crank the engine for 5 seconds and record the pressure reading. Repeat this step three times and calculate the
average of the three readings.
NOTE: The minimum cylinder pressure is 350 psi. Cylinder pressure should be within 20% from cylinder to
cylinder.
15. Combustion pressure leakage can be checked if cylinder pressure is below the specification. Perform the leak-
age test procedure on each cylinder according to the tester manufacturer instructions.
16. Upon completion of the test check and erase any engine related fault codes.
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seating).
Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water jacket.
Any causes for combustion/compression pressure loss
1. Start and operate the engine until it attains normal operating temperature.
2. Disconnect injector harness connectors.
3. Disconnect breather tube and breather drain tube from valve cover.
4. Remove the cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) -
REMOVAL)
5. Disconnect harness from injectors.
6. Remove the cylinder head cover carrier gasket. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
7. BringthecylindertobetestedtoTDC.
8. Remove the high pressure fuel line between the cylinder head and the fuelrail for the cylinder to be tested.
9. Install capping Tool 9011 onto the rail.
10. Remove the high pressure connector nut and high pressure connector with Tool 9015.
11. Remove the exhaust and intake rocker lever.
12. Use Tool # 9010 to remove the injector and copper sealing washer.
13. Install compression test Tool # 9007 into the injector bore.
14. Connect the leakage tester and perform the leakage test procedure on each cylinder according to the tester
manufacturer’s instructions.
15. Upon completion of the test check and erase any engine related fault codes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken when apply-
ing form-in-place gaskets to assure obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-place gasket material
unless specified.Bead size, continuity, and location are of great importance. Too thin a bead can result in leakage
while too much can result in spill-overwhich can break off and obstruct fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the
proper width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket materials that are used in the engine area. Mopar
Engine RTV
GEN II, Mopar
ATF-RTV, and MoparGasket Maker gasket materials, each have different properties and can not
be used in place of the other.
MOPAR
ENGINE RTV GEN II
Page 1914 of 5267

3. Place a shop towel around the fuel injectors to catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure in the cyl-
inder head. Remove the fuel injectors (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR -
REMOVAL).
4. With all injectors removed, rotatethe crankshaft using the crankshaftbarring tool (PN 7471–B).
5. Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel, oil, etc.).
6. Be sure all fluid has been removed from the cylinders.
7. Repair engine or components as necessary to prevent this problem from occurring again.
8. Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent damage on restart.
9. Install fuel injectors (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/FUEL INJECTOR - INSTALLATION).
10. Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL FILTER -
REMOVAL).
11. Installthedrainplug.Tightentheplugto50Nꞏm(37ft.lbs.)torque.
12. Install a new oil filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL FILTER - INSTALLATION).
13. Fill engine crankcase with the specified amount and grade of oil (Referto LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/
FLUID TYPES - SPECIFICATIONS).
14. Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
15. Start the engine and check for any leaks.
REMOVAL - ENGINE
1. Disconnect both battery negative cables.
2. Disconnect engine grid heater harness at grid
heater relays.
3. Disconnect electrical connections from rear of alter-
nator.
4. Recover A/C refrigerant. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
5. Raise vehicle on a hoist.
6. Drain engine coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
7. Remove engine oil drain plug and drain engine oil.
8. Reinstall drain plug. Tighten to 50 Nꞏm (37 ft. lbs.)
torque.
9. Lower the vehicle.
10. Remove fan (3) and fan drive (2). Refer to (Refer
to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
REMOVAL).