2000 DODGE NEON boot
[x] Cancel search: bootPage 62 of 1285
DIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FRONT DRIVESHAFTS.....................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DRIVESHAFT DIAGNOSIS...................2
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
DRIVESHAFTS...........................3
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
DRIVESHAFT RECONDITION................7INNER TRIPOD JOINT SEAL BOOT...........7
OUTER C/V JOINT SEAL BOOT.............13
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE...............................17
SPECIAL TOOLS
DRIVESHAFT............................17
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FRONT DRIVESHAFTS
Vehicles equipped with either an automatic or
manual transmission use an unequal±length drive-
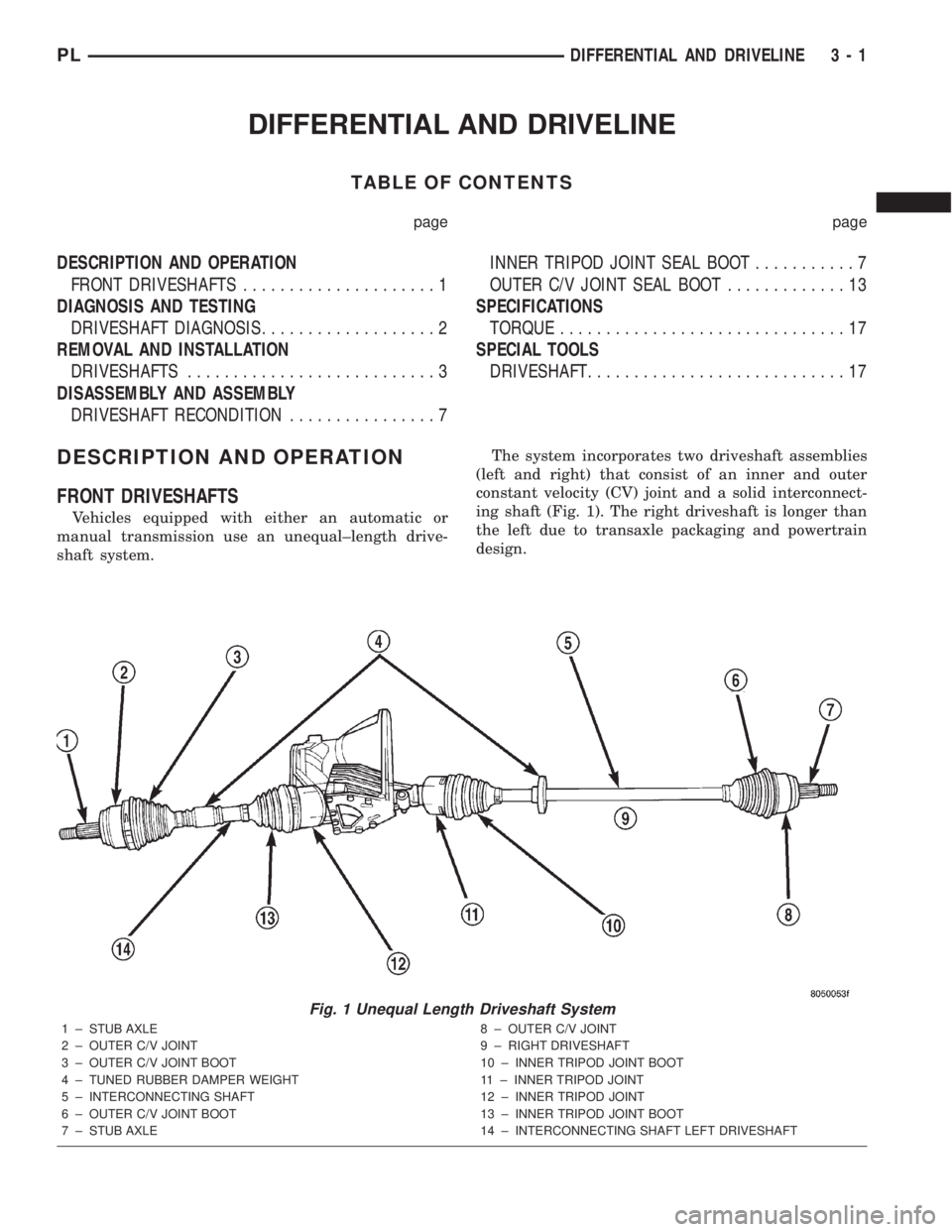
shaft system.The system incorporates two driveshaft assemblies
(left and right) that consist of an inner and outer
constant velocity (CV) joint and a solid interconnect-
ing shaft (Fig. 1). The right driveshaft is longer than
the left due to transaxle packaging and powertrain
design.
Fig. 1 Unequal Length Driveshaft System
1 ± STUB AXLE
2 ± OUTER C/V JOINT
3 ± OUTER C/V JOINT BOOT
4 ± TUNED RUBBER DAMPER WEIGHT
5 ± INTERCONNECTING SHAFT
6 ± OUTER C/V JOINT BOOT
7 ± STUB AXLE8 ± OUTER C/V JOINT
9 ± RIGHT DRIVESHAFT
10 ± INNER TRIPOD JOINT BOOT
11 ± INNER TRIPOD JOINT
12 ± INNER TRIPOD JOINT
13 ± INNER TRIPOD JOINT BOOT
14 ± INTERCONNECTING SHAFT LEFT DRIVESHAFT
PLDIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINE 3 - 1
Page 63 of 1285

Driveshafts used on both the right and left sides of
the vehicle use a tuned rubber damper weight
mounted to the interconnecting shaft (Fig. 1). The
damper weight applications vary by which side of the
vehicle the driveshaft is located on and the transmis-
sion application of the vehicle. When replacing a
driveshaft, be sure the replacement driveshaft has
the same damper weight as the original.
Both driveshaft assemblies use the same type of
inner and outer joints. The inner joint of both drive-
shaft assemblies is a tripod joint, and the outer joint
of both driveshaft assemblies is a Rzeppa joint. Both
tripod joints and Rzeppa joints are true constant
velocity (C/V) joint assemblies. The inner tripod joint
allows for the changes in driveshaft length through
the jounce and rebound travel of the front suspen-
sion.
On vehicles equipped with ABS brakes, the outer
C/V joint is equipped with a tone wheel used to
determine vehicle speed for ABS brake operation.
The inner tripod joint of both driveshafts is splined
into the transaxle side gears. The inner tripod joints
are retained in the side gears of the transaxle using
a snap ring located in the stub shaft of the tripod
joint. The outer C/V joint has a stub shaft that is
splined into the wheel hub and retained by a single
piece steel hub nut (Fig. 2). The hub nut is a locking
style; the nut lock, anti-rattle washer, and cotter pin
are not necessary.NOTE: This vehicle does not use a rubber±lip bear-
ing seal as on previous front±wheel±drive cars to
prevent contamination of the front wheel bearing.
On these vehicles, the face of the outer C/V joint
fits deeply into the steering knuckle, using a close
outer C/V joint±to±steering knuckle fit. This design
deters direct water splash on bearing seal while
allowing any water that gets in, to run out the bot-
tom of the steering knuckle bearing bore. It is
important to thoroughly clean the outer C/V joint
and the wheel bearing area in the steering knuckle
before it is assembled after servicing.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DRIVESHAFT DIAGNOSIS
VEHICLE INSPECTION
(1) Check for grease in the vicinity of the inboard
tripod joint and outboard C/V joint; this is a sign of
inner or outer joint seal boot or seal boot clamp dam-
age.
(2) A light film of grease may appear on the right
inner tripod joint seal boot; this is considered normal
and should not require replacement of the seal boot.
The right inner tripod joint seal boot is made of sili-
cone rubber; which will allow the weeping (sweating)
of the joint lubricant to pass through it while in oper-
ation.
NOISE AND/OR VIBRATION IN TURNS
A clicking noise and/or a vibration in turns could
be caused by one of the following conditions.
(1) Damaged outer C/V or inner tripod joint seal
boot or seal boot clamps. This will result in the loss
and/or contamination of the joint grease, resulting in
inadequate lubrication of the joint.
(2) Noise may also be caused by another compo-
nent of the vehicle coming in contact with the drive-
shafts.
CLUNKING NOISE DURING ACCELERATION
This noise may be a result of one of the following
conditions:
(1) A torn seal boot on the inner or outer joint of
the driveshaft assembly.
(2) A loose or missing clamp on the inner or outer
joint of the driveshaft assembly.
(3) A damaged or worn driveshaft C/V joint.
Fig. 2 Driveshaft Retaining Nut
1 ± DRIVESHAFT
2 ± HUB
3 ± HUB NUT
3 - 2 DIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 64 of 1285

SHUDDER OR VIBRATION DURING ACCELERATION
(1) A worn or damaged driveshaft inner tripod
joint.
(2) A sticking tripod joint spider assembly (inner
tripod joint only).
(3) Improper wheel alignment. See Wheel Align-
ment in this group for alignment checking and set-
ting procedures and specifications.
VIBRATION AT HIGHWAY SPEEDS
(1) Foreign material (mud, etc.) packed on the
backside of the wheel(s).
(2) Out of balance front tires or wheels. See Group
22, Wheels And Tires for the required balancing pro-
cedure.
(3) Improper tire and/or wheel runout. See Group
22, Wheels And Tires for the required runout check-
ing procedure.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
DRIVESHAFTS
CAUTION: Boot sealing is vital to retain special
lubricants and to prevent foreign contaminants
from entering the C/V joint. Mishandling, such as
allowing the assemblies to dangle unsupported, or
pulling or pushing the ends can cut boots or dam-
age C/V joints. During removal and installation pro-
cedures, always support both ends of the driveshaft
to prevent damage.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: The driveshaft, when installed, acts as a
bolt and secures the front hub/bearing assembly. If
vehicle is to be supported or moved on its wheels
with a driveshaft removed, install a PROPER±SIZED
BOLT AND NUT through front hub. Tighten bolt and
nut to 203 N´m (150 ft. lbs.). This will ensure that
the hub bearing cannot loosen.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Place transaxle in gated park.
(3) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(4) Remove wheel and tire assembly (Fig. 3).(5) Remove the driveshaft to hub and bearing
retaining nut (Fig. 4).
(6) If equipped with ABS, disconnect the front
wheel speed sensor and secure harness out of the
way.
Fig. 3 Wheel and Tire Removal
1 ± WHEEL/TIRE ASSY.
2 ± LUG NUT (5)
3 ± HUB
Fig. 4 Driveshaft Retaining Nut Removal
1 ± DRIVESHAFT
2 ± HUB
3 ± HUB NUT
PLDIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINE 3 - 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 68 of 1285

(8) Clean all foreign matter from threads of drive-
shaft outer stub axle. Install hub nut onto the
threads of the stub axle and tighten nut to 244 N´m
(180 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 15).
(9) Install front wheel and tire assembly. Install
front wheel lug nuts (Fig. 16) and tighten to 128 N´m
(95 ft. lbs.).(10) Check for correct fluid level in transaxle
assembly. Refer to Group 21 Transaxle, for the cor-
rect fluid level checking procedure for the type of
transaxle being checked.
(11) Lower vehicle.
(12) Connect battery negative cable.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
DRIVESHAFT RECONDITION
NOTE: The only service that is to be performed on
the driveshaft assemblies is the replacement of the
driveshaft seal boots.
If any failure of internal driveshaft components is
diagnosed during a vehicle road test or disassembly
of the driveshaft, the driveshaft will need to be
replaced as an assembly.
NOTE: Lubricant requirements and quantities are
different for inner joints than for outer joints. Use
only the recommended lubricants in the required
quantities when servicing driveshaft assemblies.
See (Fig. 17) for the exploded view of the front
driveshaft components.
INNER TRIPOD JOINT SEAL BOOT
REMOVAL
To remove sealing boot from driveshaft for replace-
ment, the driveshaft assembly must be removed from
the vehicle. See Driveshaft Removal and Installation
in this section for the required driveshaft removal
and replacement procedure.
The inner tripod joints use no internal retention in
the tripod housing to keep the spider assembly in the
housing. Therefore, do not pull on the interconnect-
ing shaft to disengage tripod housing from transmis-
sion stub shaft. Removal in this manner will cause
damage to the inboard joint sealing boots.
(1) Remove the driveshaft requiring boot replace-
ment from the vehicle. See Driveshaft Removal and
Installation in this section for the required driveshaft
removal procedure.
(2) Remove large boot clamp that retains inner tri-
pod joint sealing boot to tripod joint housing (Fig. 18)
and discard. Then remove small clamp that retains
inner tripod joint sealing boot to interconnecting
shaft and discard. Remove the sealing boot from the
tripod housing and slide it down the interconnecting
shaft.
Fig. 15 Driveshaft Retaining Nut Installation
1 ± DRIVESHAFT
2 ± HUB
3 ± HUB NUT
Fig. 16 Wheel and Tire Installation
1 ± WHEEL/TIRE ASSY.
2 ± LUG NUT (5)
3 ± HUB
PLDIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINE 3 - 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 70 of 1285
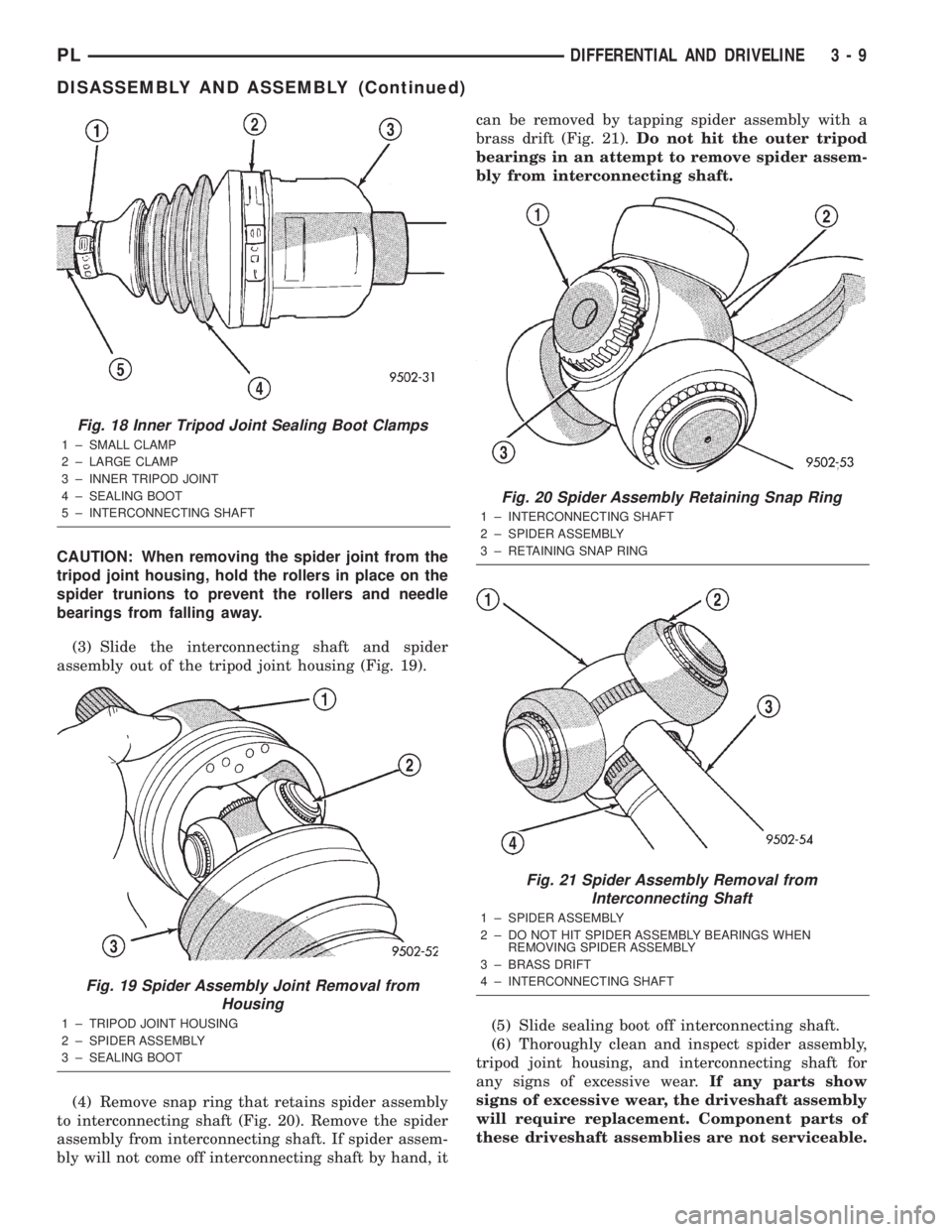
CAUTION: When removing the spider joint from the
tripod joint housing, hold the rollers in place on the
spider trunions to prevent the rollers and needle
bearings from falling away.
(3) Slide the interconnecting shaft and spider
assembly out of the tripod joint housing (Fig. 19).
(4) Remove snap ring that retains spider assembly
to interconnecting shaft (Fig. 20). Remove the spider
assembly from interconnecting shaft. If spider assem-
bly will not come off interconnecting shaft by hand, itcan be removed by tapping spider assembly with a
brass drift (Fig. 21).Do not hit the outer tripod
bearings in an attempt to remove spider assem-
bly from interconnecting shaft.
(5) Slide sealing boot off interconnecting shaft.
(6) Thoroughly clean and inspect spider assembly,
tripod joint housing, and interconnecting shaft for
any signs of excessive wear.If any parts show
signs of excessive wear, the driveshaft assembly
will require replacement. Component parts of
these driveshaft assemblies are not serviceable.
Fig. 18 Inner Tripod Joint Sealing Boot Clamps
1 ± SMALL CLAMP
2 ± LARGE CLAMP
3 ± INNER TRIPOD JOINT
4 ± SEALING BOOT
5 ± INTERCONNECTING SHAFT
Fig. 19 Spider Assembly Joint Removal from
Housing
1 ± TRIPOD JOINT HOUSING
2 ± SPIDER ASSEMBLY
3 ± SEALING BOOT
Fig. 20 Spider Assembly Retaining Snap Ring
1 ± INTERCONNECTING SHAFT
2 ± SPIDER ASSEMBLY
3 ± RETAINING SNAP RING
Fig. 21 Spider Assembly Removal from
Interconnecting Shaft
1 ± SPIDER ASSEMBLY
2 ± DO NOT HIT SPIDER ASSEMBLY BEARINGS WHEN
REMOVING SPIDER ASSEMBLY
3 ± BRASS DRIFT
4 ± INTERCONNECTING SHAFT
PLDIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINE 3 - 9
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 71 of 1285

INSTALLATION
NOTE: The inner tripod joint sealing boots are
made from two different types of material. High±
temperature applications use silicone rubber
whereas standard temperature applications use
Hytrel plastic. The silicone sealing boots are soft
and pliable. The Hytrel sealing boots are stiff and
rigid. The replacement sealing boot MUST BE the
same type of material as the sealing boot that was
removed.
(1) Slide inner tripod joint seal boot retaining
clamp, onto interconnecting shaft. Then slide the
replacement inner tripod joint sealing boot onto
interconnecting shaft.Inner tripod joint seal boot
MUST be positioned on interconnecting shaft,
so the raised bead on the inside of the seal boot
is in groove on interconnecting shaft (Fig. 22).
(2) Install spider assembly onto interconnecting
shaft with chamfer on spider assembly toward inter-
connecting shaft (Fig. 23). Spider assembly must be
installed on interconnecting shaft far enough to fully
install spider retaining snap ring. If spider assembly
will not fully install on interconnecting shaft by
hand, it can be installed by tapping the spider body
with a brass drift (Fig. 24).Do not hit the outer
tripod bearings in an attempt to install spider
assembly on interconnecting shaft.
(3) Install the spider assembly to interconnecting
shaft retaining snap ring into groove on end of inter-
connecting shaft (Fig. 25). Be sure the snap ring is
fully seated into groove on interconnecting shaft.(4) Distribute 1/2 the amount of grease provided in
the seal boot service package (DO NOT USE ANY
OTHER TYPE OF GREASE) into tripod housing. Put
the remaining amount into the sealing boot.
(5) Align tripod housing with spider assembly and
then slide tripod housing over spider assembly and
interconnecting shaft (Fig. 26).
(6) Install inner tripod joint seal boot to intercon-
necting shaft clamp evenly on sealing boot.
Fig. 22 Sealing Boot Installation on Interconnecting
Shaft
1 ± SEALING BOOT
2 ± RAISED BEAD IN THIS AREA OF SEALING BOOT
3 ± GROOVE
4 ± INTERCONNECTING SHAFT
Fig. 23 Spider Assembly Installation on
Interconnecting Shaft
1 ± SPIDER ASSEMBLY
2 ± INTERCONNECTING SHAFT
3 ± CHAMFER
Fig. 24 Installing Spider Assembly On
Interconnecting Shaft
1 ± DO NOT HIT BEARINGS WHEN INSTALLING THE SPIDER
ASSEMBLY
2 ± SPIDER ASSEMBLY
3 ± INTERCONNECTING SHAFT
4 ± BRASS DRIFT
3 - 10 DIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINEPL
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 72 of 1285

(7) Clamp sealing boot onto interconnecting shaft
using crimper, Special Tool C-4975-A and the follow-
ing procedure. Place crimping tool C-4975-A over
bridge of clamp (Fig. 27). Tighten nut on crimping
tool C-4975-A until jaws on tool are closed completely
together, face to face (Fig. 28).
CAUTION: Seal must not be dimpled, stretched, or
out±of±shape in any way. If seal is NOT shaped cor-
rectly, equalize pressure in seal and shape it by
hand.(8) Position sealing boot into the tripod housing
retaining groove. Install seal boot retaining clamp
evenly on sealing boot.
CAUTION: The following positioning procedure
determines the correct air pressure inside the inner
tripod joint assembly prior to clamping the sealing
boot to inner tripod joint housing. If this procedure
is not done prior to clamping sealing boot to tripod
joint housing, boot durability can be adversely
affected.
Fig. 25 Spider Assembly Retaining Snap Ring
Installed
1 ± INTERCONNECTING SHAFT
2 ± SPIDER ASSEMBLY
3 ± RETAINING SNAP RING
Fig. 26 Installing Tripod Housing on Spider
Assembly
1 ± TRIPOD JOINT HOUSING
2 ± SPIDER ASSEMBLY
3 ± SEALING BOOT
Fig. 27 Crimping Tool Installed on Sealing Boot
Clamp
1 ± SPECIAL TOOL C-4975A
2 ± INTERCONNECTING SHAFT
3 ± CLAMP
4 ± SEALING BOOT
Fig. 28 Sealing Boot Retaining Clamp Installed
1 ± CLAMP
2 ± JAWS OF SPECIAL TOOL C-4975A MUST BE CLOSED
COMPLETELY TOGETHER HERE
3 ± INTERCONNECTING SHAFT
4 ± SEALING BOOT
PLDIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINE 3 - 11
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 73 of 1285
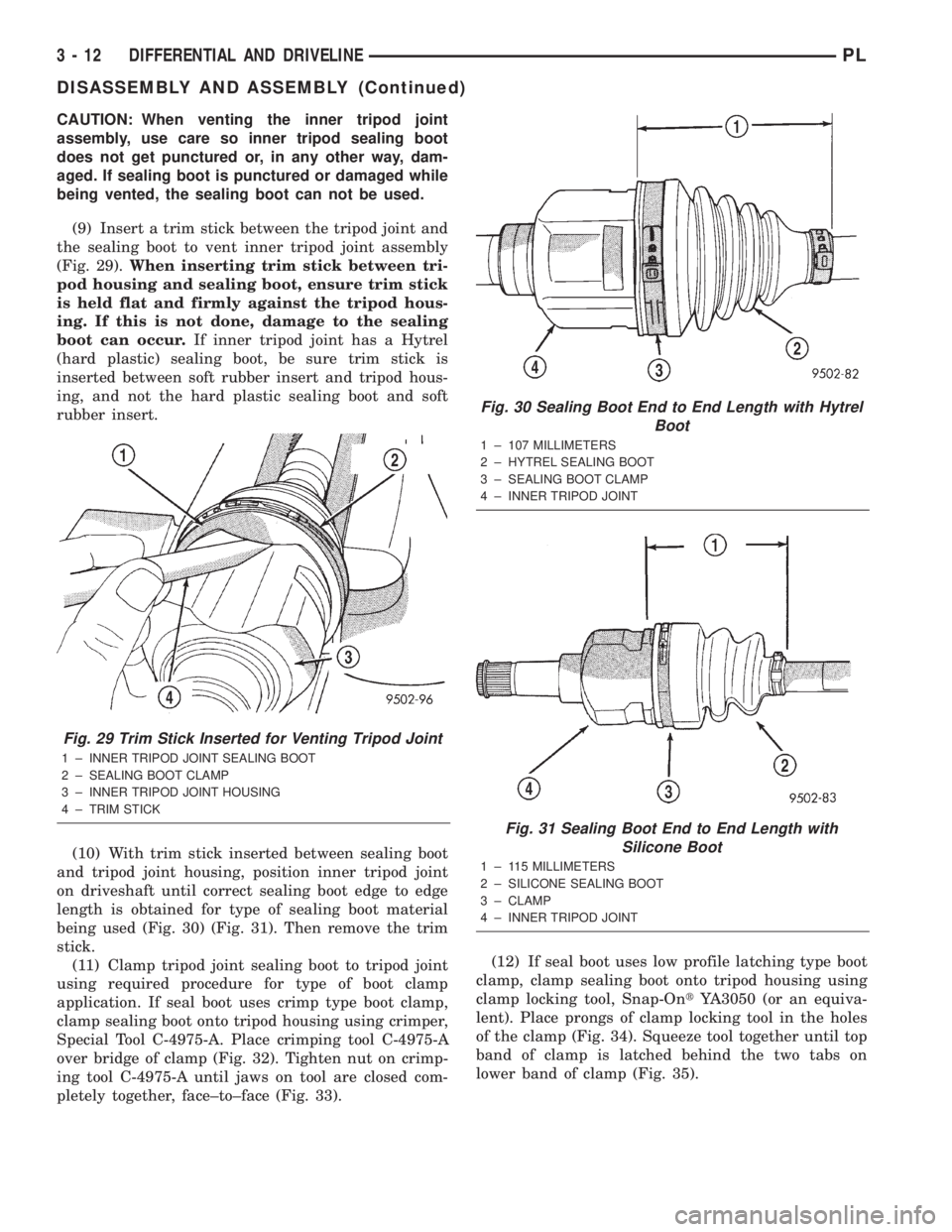
CAUTION: When venting the inner tripod joint
assembly, use care so inner tripod sealing boot
does not get punctured or, in any other way, dam-
aged. If sealing boot is punctured or damaged while
being vented, the sealing boot can not be used.
(9) Insert a trim stick between the tripod joint and
the sealing boot to vent inner tripod joint assembly
(Fig. 29).When inserting trim stick between tri-
pod housing and sealing boot, ensure trim stick
is held flat and firmly against the tripod hous-
ing. If this is not done, damage to the sealing
boot can occur.If inner tripod joint has a Hytrel
(hard plastic) sealing boot, be sure trim stick is
inserted between soft rubber insert and tripod hous-
ing, and not the hard plastic sealing boot and soft
rubber insert.
(10) With trim stick inserted between sealing boot
and tripod joint housing, position inner tripod joint
on driveshaft until correct sealing boot edge to edge
length is obtained for type of sealing boot material
being used (Fig. 30) (Fig. 31). Then remove the trim
stick.
(11) Clamp tripod joint sealing boot to tripod joint
using required procedure for type of boot clamp
application. If seal boot uses crimp type boot clamp,
clamp sealing boot onto tripod housing using crimper,
Special Tool C-4975-A. Place crimping tool C-4975-A
over bridge of clamp (Fig. 32). Tighten nut on crimp-
ing tool C-4975-A until jaws on tool are closed com-
pletely together, face±to±face (Fig. 33).(12) If seal boot uses low profile latching type boot
clamp, clamp sealing boot onto tripod housing using
clamp locking tool, Snap-OntYA3050 (or an equiva-
lent). Place prongs of clamp locking tool in the holes
of the clamp (Fig. 34). Squeeze tool together until top
band of clamp is latched behind the two tabs on
lower band of clamp (Fig. 35).
Fig. 29 Trim Stick Inserted for Venting Tripod Joint
1 ± INNER TRIPOD JOINT SEALING BOOT
2 ± SEALING BOOT CLAMP
3 ± INNER TRIPOD JOINT HOUSING
4 ± TRIM STICK
Fig. 30 Sealing Boot End to End Length with Hytrel
Boot
1 ± 107 MILLIMETERS
2 ± HYTREL SEALING BOOT
3 ± SEALING BOOT CLAMP
4 ± INNER TRIPOD JOINT
Fig. 31 Sealing Boot End to End Length with
Silicone Boot
1 ± 115 MILLIMETERS
2 ± SILICONE SEALING BOOT
3 ± CLAMP
4 ± INNER TRIPOD JOINT
3 - 12 DIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINEPL
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)