1993 DODGE TRUCK sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 365 of 1502

8D
- 14
IGNITION SYSTEMS
• (5) Test the MAP sensor ground circuit at sensor
connector terminal-A (Fig. 19) and PCM connector
terminal-4. Repair the wire harness if necessary.
(6) Test the MAP sensor ground circuit at the
PCM connector between terminal-4 and terminal-11
with an ohmmeter. If the ohmmeter indicates an
open circuit, inspect for a defective sensor ground
connection. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring for location of
this connection. If the ground connection is good, re
place the PCM. If terminal-4 has a short circuit to 12 volts +, correct this condition before replacing the
PCM.
POWERTRAIN
CONTROL MODULE {PCM)
The PCM (formerly called the SBEC or engine -con
troller) is located in the engine compartment (Fig.
20). DATA UNK CONTROL
CONNECTOR MODULE
J9314-164
Fig.
20 PCM Location The ignition system is controlled by the PCM.
For removal and installation of this component, re
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
For diagnostics, refer to the appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures service manual for operation
of the DRB II scan tool.
SPARK
PLUGS
For spark plug removal, cleaning, gap adjustment
and installation, refer to the Component Removal/In
stallation section of this group. Spark plug cable boot heat shields are pressed into
the cylinder head to surround each cable boot and
spark plug (Fig. 21). These shields protect the spark
plug boots from damage (due to intense engine heat
generated by the exhaust manifolds) and should not
be removed. After the spark plug cable has been in stalled, the lip of the cable boot should have a small
air gap to the top of the heat shield (Fig. 21). Faulty carbon and/or gas fouled plugs generally
cause hard starting, but they will clean up at higher
engine speeds. Faulty plugs can be identified in a
Fig.
21 Heat
Shields
number of ways: poor fuel economy, power loss, de
crease in engine speed, hard starting and, in general,
poor engine performance.
Remove the spark plugs and examine them for
burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken por celain insulators. Keep plugs arranged in the order
in which they were removed from the engine. An iso
lated plug displaying an abnormal condition indi
cates that a problem exists in the corresponding
cylinder. Replace spark plugs at the intervals recom
mended in the maintenance chart in Group 0, Lubri
cation and Maintenance.
Spark plugs that have low mileage may be cleaned
and reused if not otherwise defective. Refer to the
following Spark Plug Condition section of this group.
CONDITION
NORMAL OPERATING
The few deposits present on the spark plug will
probably be light tan or slightly gray in color. This is evident with most grades of commercial gasoline (Fig. 22). There will not be evidence of electrode
burning. Gap growth will not average more than ap proximately 0.025 mm (.001 in) per 1600 km (1000
miles) of operation. Spark plugs that have normal
wear can usually be cleaned, have the electrodes filed, have the gap set and then be installed.
Some fuel refiners in several areas of the United
States have introduced a manganese additive (MMT)
for unleaded fuel. During combustion, fuel with
MMT causes the entire tip of the spark plug to be coated with a rust colored deposit. This rust color can
be misdiagnosed as being caused by coolant in the combustion chamber. Spark plug performance is not affected by MMT deposits.
COLD
FOULING/CARBON FOULING
Cold fouling is sometimes referred to as carbon
fouling. The deposits that cause cold fouling are ba-
Page 368 of 1502
•
IGNITION SYSTEMS
80-17
or punctured, there will
be a
noticeable spark jump
from
the
damaged area
to the
test probe.
The
cable
running from
the
ignition coil
to the
distributor
cap
can
be
checked
in the
same manner. Cracked, dam aged
or
faulty cables should
be
replaced with resis
tance type cable. This
can be
identified
by the
words ELECTRONIC SUPPRESSION printed
on the
cable
jacket.
Use
an
ohmmeter
to
test
for
open circuits, exces
sive resistance
or
loose terminals. Remove
the
dis
tributor
cap
from
the
distributor.
Do not
remove cables from
cap.
Remove cable from spark plug.
Connect ohmmeter
to
spark plug terminal
end of ca
ble
and to
corresponding electrode
in
distributor
cap.
Resistance should
be 250 to 1000
Ohms
per
inch
of
cable.
If not,
remove cable from distributor
cap
tower and connect ohmmeter
to the
terminal ends
of
cable.
If resistance
is not
within specifications
as
found
in
the Spark Plug Cable Resistance chart, replace
the
cable. Test
all
spark plug cables
in
this manner.
SPARK
PLUG CABLE RESISTANCE
MINIMUM
MAXIMUM
250
Ohms
Per
Inch
1000
Ohms
Per
Inch
3000
Ohms
Per
Foot
12,000
Ohms
Per
Foot
J908D-43 To test ignition coil-to-distributor
cap
cable,
do not
remove
the
cable from
the cap.
Connect ohmmeter
to
rotor button (center contact)
of
distributor
cap and
terminal
at
ignition coil
end of
cable.
If
resistance
is
not within specifications
as
found
in the
Spark Plug
Cable Resistance chart, remove
the
cable from
the
distributor
cap.
Connect
the
ohmmeter
to the
termi
nal ends
of the
cable.
If
resistance
is not
within spec
ifications
as
found
in the
Spark Plug Cable
Resistance chart, replace
the
cable. Inspect
the
igni
tion coil tower
for
cracks, burns
or
corrosion.
For removal
and
installation
of
spark plug cables,
refer
to
Spark Plug Secondary Cables
in the
Compo nent Removal/Installation section.
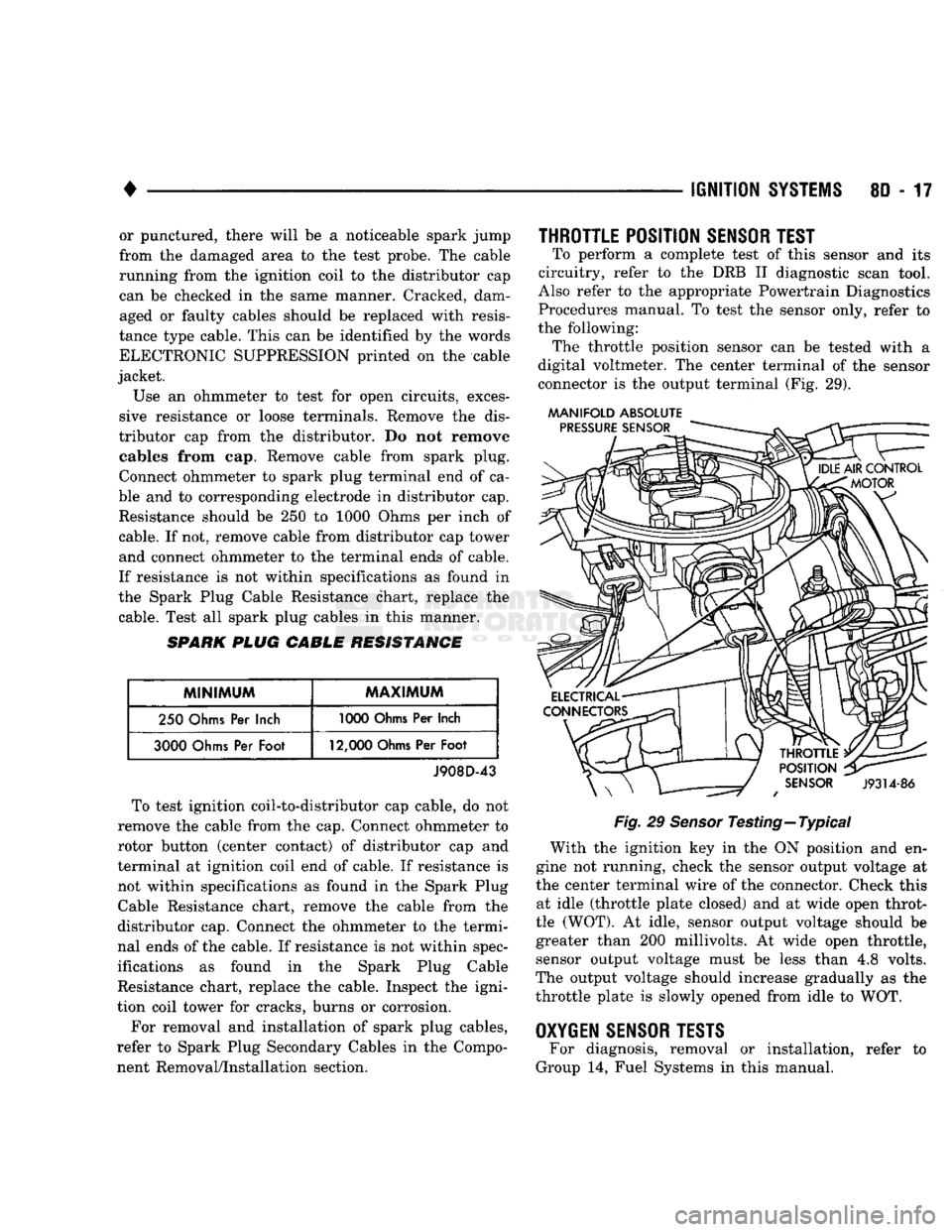
THROTTLE POSITION
SENSOR
TEST
To perform
a
complete test
of
this sensor
and its
circuitry, refer
to the DRB II
diagnostic scan tool.
Also refer
to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics
Procedures manual.
To
test
the
sensor only, refer
to
the following: The throttle position sensor
can be
tested with
a
digital voltmeter.
The
center terminal
of the
sensor
connector
is the
output terminal
(Fig. 29).
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
Fig.
29
Sensor
Testing—Typical With
the
ignition
key in the ON
position
and en
gine
not
running, check
the
sensor output voltage
at
the center terminal wire
of the
connector. Check this at idle (throttle plate closed)
and at
wide open throt
tle (WOT).
At
idle, sensor output voltage should
be
greater than
200
millivolts.
At
wide open throttle, sensor output voltage must
be
less than
4,8
volts.
The output voltage should increase gradually
as the
throttle plate
is
slowly opened from idle
to WOT.
OXYGEN
SENSOR
TESTS
For diagnosis, removal
or
installation, refer
to
Group
14,
Fuel Systems
in
this manual.
Page 369 of 1502
8D
- 18
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
•
COMPONENT REMGWAL/INSTALLATION
INDEX
page
Automatic
Shut Down (ASD) Relay
18
Camshaft
Position
Sensor
, 18
Crankshaft Position
Sensor
18
Distributor
Service
20
Engine
Coolant Temperature
Sensor
20
General
Information
18
Ignition
Coil
21
page
Intake
Manifold Charge
Air
Temperature
Sensor
. 22
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
Sensor
..... 22
Oxygen
(02)
Sensor
22
Powertrain
Control
Module (PCM)
22
Spark
Plug Secondary Cables
24
Spark
Plugs
23
Throttle
Position
Sensor
(TPS)
24
GENERAL
INFORMATION
This section
of the
group, Component Removal/In
stallation, will discuss
the
removal
and
installation
of ignition system components. For basic ignition system diagnostics
and
service
adjustments, refer
to the
Diagnostics/Service Proce
dures section
of
this group. For system operation
and
component identification,
refer
to the
Component Identification/System Opera
tion section
of
this group.
AUTOMATIC
SHUT DOWN
(ASb)
RELAY
The automatic shut down
(ASD)
relay
is
located
in
the engine compartment
(Fig. 1).
TORQUE CONVERTER
CLUTCH RELAY
A/C
CLUTCH RELAY STARTER RELAY
AUTO
SHUTDOWN RELAY FUEL PUMP RELAY DATA UNK
CONNECTOR POWERTRAIN
CONTROL
MODULE
J9314-164
Fig.
1
Auto
Shut Down
Relay
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable
at
battery.
(2)
Remove
the
relay
by
pulling from connector.
INSTALLATION
(1) Check
the
terminals
in the
relay connector
for
corrosion
or
damage before installation.
(2)
Push
the
relay into
the
connector.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The camshaft position sensor
is
located
in the
dis
tributor
(Fig. 2).
REMOVAL
Distributor removal
is not
necessary
to
remove
camshaft position sensor.
CAMSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
SYNC
SIGNAL
GENERATOR
DISTRIBUTOR
ASSEMBLY
J9314-82
Fig.
2
Camshaft Position Sensor—Typical
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable
at
battery.
(2)
Remove distributor
cap
from distributor
(two
screws).
(3) Disconnect camshaft position sensor wiring
harness from main engine wiring harness.
(4) Remove distributor rotor from distributor shaft.
(5)
Lift
the
camshaft position sensor assembly from
the distributor housing
(Fig. 2).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install camshaft position sensor
to
distributor.
Align sensor into notch
on
distributor housing.
(2)
Connect wiring harness.
(3) Install rotor.
(4) Install distributor
cap.
Tighten mounting
screws.
CRANKSHAFT
POSITION SENSOR
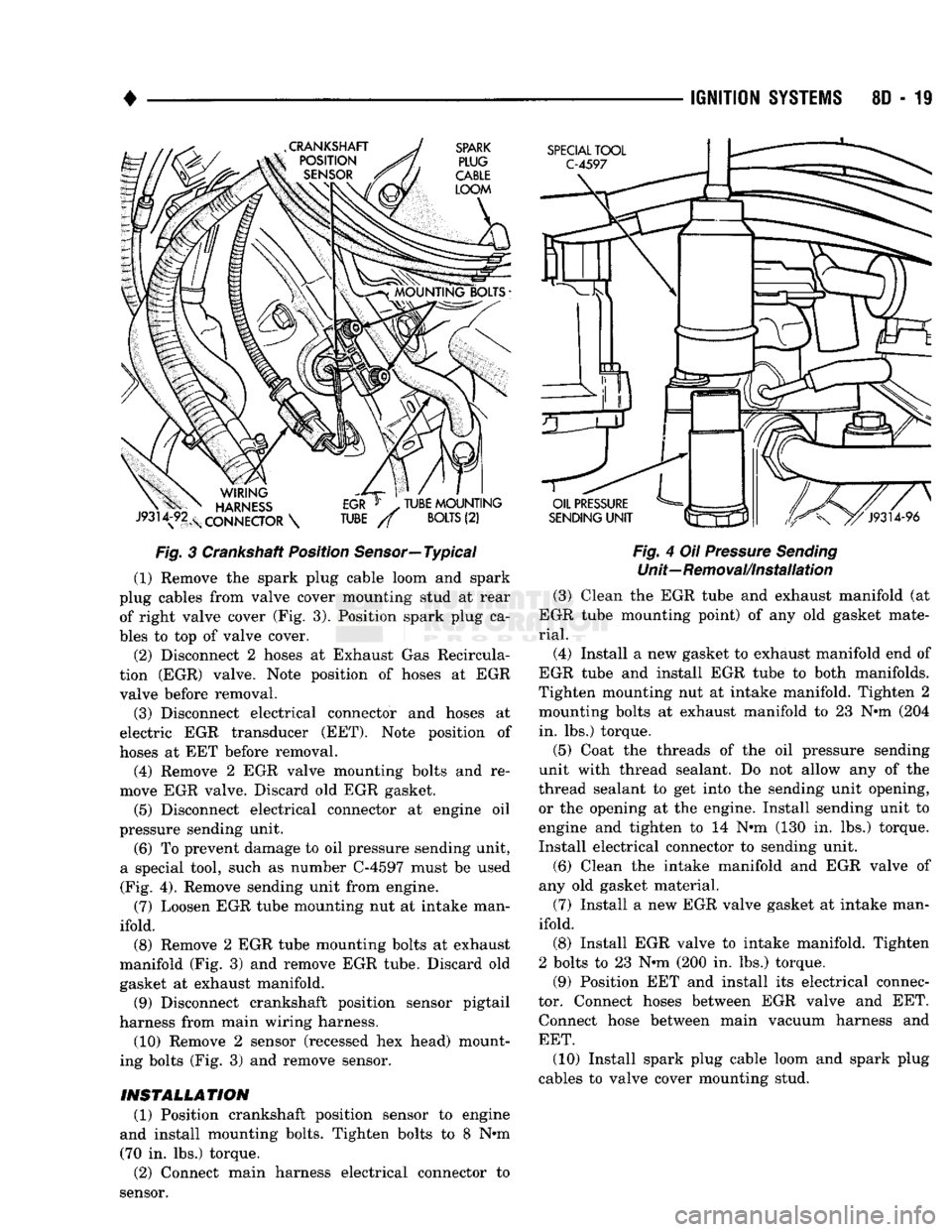
REMOVAL The sensor
is
bolted
to the top of the
cylinder block
near
the
rear
of
right cylinder head
(Fig. 3).
Page 370 of 1502
•
Fig.
3 Crankshaft Position Sensor—Typical (1) Remove the spark plug cable loom and spark
plug cables from valve cover mounting stud at rear of right valve cover (Fig. 3). Position spark plug ca
bles to top of valve cover.
(2) Disconnect 2 hoses at Exhaust Gas Recircula
tion (EGR) valve. Note position of hoses at EGR valve before removal.
(3) Disconnect electrical connector and hoses at
electric EGR transducer (EET). Note position of
hoses at EET before removal.
(4) Remove 2 EGR valve mounting bolts and re
move EGR valve. Discard old EGR gasket.
(5) Disconnect electrical connector at engine oil
pressure sending unit.
(6) To prevent damage to oil pressure sending unit,
a special tool, such as number C-4597 must be used (Fig. 4). Remove sending unit from engine.
(7) Loosen EGR tube mounting nut at intake man
ifold.
(8) Remove 2 EGR tube mounting bolts at exhaust
manifold (Fig. 3) and remove EGR tube. Discard old
gasket at exhaust manifold.
(9) Disconnect crankshaft position sensor pigtail
harness from main wiring harness.
(10) Remove 2 sensor (recessed hex head) mount
ing bolts (Fig. 3) and remove sensor.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position crankshaft position sensor to engine
and install mounting bolts. Tighten bolts to 8 N#m (70 in. lbs.) torque. (2) Connect main harness electrical connector to
sensor.
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
80-19
Fig.
4 Oil
Pressure
Sending
Unit—Removal/Installation (3) Clean the EGR tube and exhaust manifold (at
EGR tube mounting point) of any old gasket mate
rial.
(4) Install a new gasket to exhaust manifold end of
EGR tube and install EGR tube to both manifolds.
Tighten mounting nut at intake manifold. Tighten 2 mounting bolts at exhaust manifold to 23 N#m (204 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Coat the threads of the oil pressure sending
unit with thread sealant. Do not allow any of the
thread sealant to get into the sending unit opening, or the opening at the engine. Install sending unit to
engine and tighten to 14 N»m (130 in. lbs.) torque.
Install electrical connector to sending unit.
(6) Clean the intake manifold and EGR valve of
any old gasket material.
(7) Install a new EGR valve gasket at intake man
ifold. (8) Install EGR valve to intake manifold. Tighten
2 bolts to 23 N«m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(9) Position EET and install its electrical connec
tor. Connect hoses between EGR valve and EET. Connect hose between main vacuum harness and
EET.
(10) Install spark plug cable loom and spark plug
cables to valve cover mounting stud.
Page 371 of 1502
8D
- 20
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
•
ENGINE
COOLANT
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING. COOLING SYSTEM MUST BE PARTIALLY DRAINED BEFORE REMOV
ING THE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR. RE
FER TO GROUP 7, COOLING.
REMOVAL
(1) Partially drain cooling system. Refer to Group
7, Cooling.
(2)
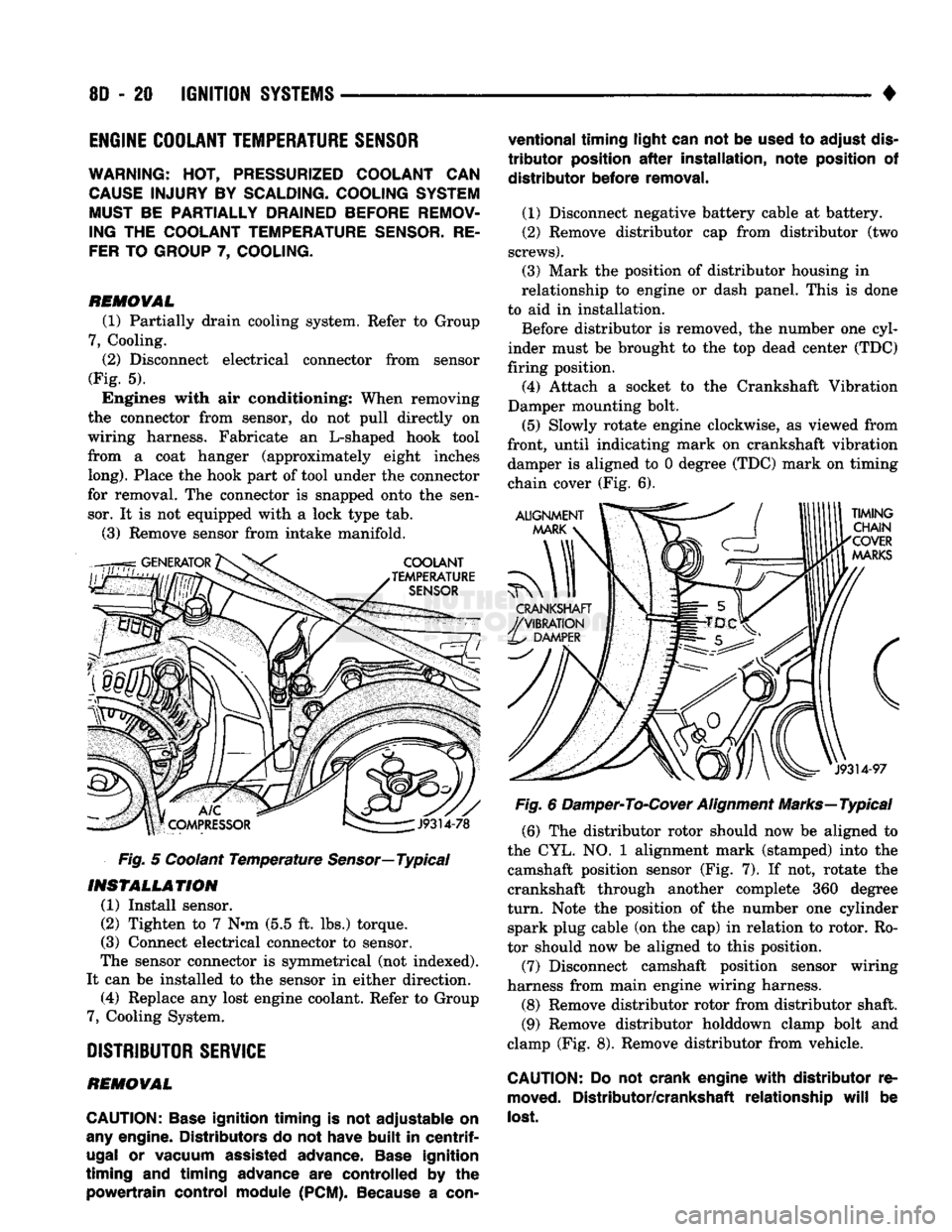
Disconnect electrical connector from sensor
(Fig. 5). Engines with air conditioning: When removing
the connector from sensor, do not pull directly on
wiring harness. Fabricate an L-shaped hook tool
from a coat hanger (approximately eight inches
long).
Place the hook part of tool under the connector
for removal. The connector is snapped onto the sen sor. It is not equipped with a lock type tab.
(3) Remove sensor from intake manifold.
Fig. 5 Coolant Temperature
Sensor—
Typical
INSTALLATION
(1) Install sensor.
(2) Tighten to 7 Nnn (5.5 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
The sensor connector is symmetrical (not indexed).
It can be installed to the sensor in either direction. (4) Replace any lost engine coolant. Refer to Group
7, Cooling System.
DISTRIBUTOR
SERVICE
REMOVAL
CAUTION:
Base
ignition timing
is not
adjustable
on
any
engine. Distributors
do not
have
built
in
centrif
ugal
or
vacuum assisted advance.
Base
ignition
timing
and
timing advance
are
controlled
by the
powertrain control module
(PCM).
Because
a
con
ventional timing light can
not be
used
to
adjust
dis
tributor
position
after
installation, note position
of
distributor before removal.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Remove distributor cap from distributor (two
screws).
(3) Mark the position of distributor housing in
relationship to engine or dash panel. This is done
to aid in installation. Before distributor is removed, the number one cyl
inder must be brought to the top dead center (TDC)
firing position. (4) Attach a socket to the Crankshaft Vibration
Damper mounting bolt.
(5) Slowly rotate engine clockwise, as viewed from
front, until indicating mark on crankshaft vibration damper is aligned to 0 degree (TDC) mark on timing
chain cover (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6 Damper-To-Cover Alignment Marks—Typical (6) The distributor rotor should now be aligned to
the CYL. NO. 1 alignment mark (stamped) into the camshaft position sensor (Fig. 7). If not, rotate the
crankshaft through another complete 360 degree
turn.
Note the position of the number one cylinder spark plug cable (on the cap) in relation to rotor. Ro
tor should now be aligned to this position.
(7) Disconnect camshaft position sensor wiring
harness from main engine wiring harness.
(8) Remove distributor rotor from distributor shaft. (9) Remove distributor holddown clamp bolt and
clamp (Fig. 8). Remove distributor from vehicle.
CAUTION: Do not
crank engine
with
distributor
re
moved.
Distributor/crankshaft relationship
will
be
lost.
Page 372 of 1502
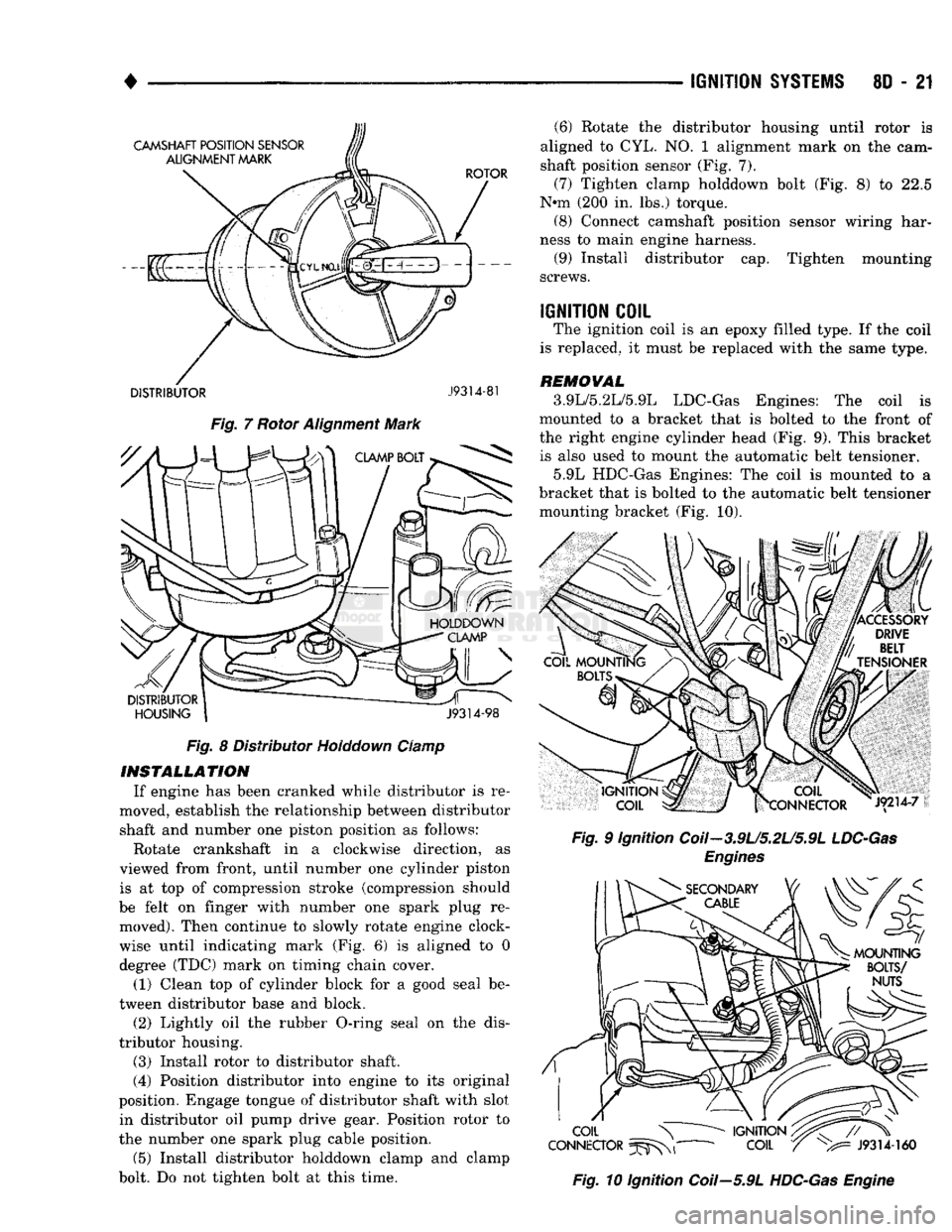
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
80 - 21
DISTRIBUTOR
J9314-81
Fig.
7 Rotor Alignment Mark Fig. 8 Distributor Holddown Clamp
INSTALLATION
If engine has been cranked while distributor is re
moved, establish the relationship between distributor shaft and number one piston position as follows:
Rotate crankshaft in a clockwise direction, as
viewed from front, until number one cylinder piston is at top of compression stroke (compression should
be felt on finger with number one spark plug re moved). Then continue to slowly rotate engine clock
wise until indicating mark (Fig. 6) is aligned to 0
degree (TDC) mark on timing chain cover.
(1) Clean top of cylinder block for a good seal be
tween distributor base and block.
(2) Lightly oil the rubber O-ring seal on the dis
tributor housing.
(3) Install rotor to distributor shaft.
(4) Position distributor into engine to its original
position. Engage tongue of distributor shaft with slot in distributor oil pump drive gear. Position rotor to
the number one spark plug cable position.
(5) Install distributor holddown clamp and clamp
bolt. Do not tighten bolt at this time. (6) Rotate the distributor housing until rotor is
aligned to CYL. NO. 1 alignment mark on the cam
shaft position sensor (Fig. 7).
(7) Tighten clamp holddown bolt (Fig. 8) to 22.5
N*m (200 in. lbs.) torque. (8) Connect camshaft position sensor wiring har
ness to main engine harness. (9) Install distributor cap. Tighten mounting
screws.
IGNITION
COIL
The ignition coil is an epoxy filled type. If the coil
is replaced, it must be replaced with the same type.
REMOVAL
3.9L/5.2L/5.9L LDC-Gas Engines: The coil is
mounted to a bracket that is bolted to the front of
the right engine cylinder head (Fig. 9). This bracket is also used to mount the automatic belt tensioner.
5.9L HDC-Gas Engines: The coil is mounted to a
bracket that is bolted to the automatic belt tensioner mounting bracket (Fig. 10).
Fig.
9 Ignition Coil-3.9U5.2U5.9L
LDC-Gas
Engines
Fig.
10 Ignition Coil—5.9L
HDC-Gas
Engine
Page 373 of 1502
8D
- 22
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
• (1) Disconnect the wiring and secondary cable from
the ignition coil (Figs. 9 or 10).
WARNING:
(3.9L/5.2L/5.9L
LDC-GAS ENGINES)
DO
NOT REMOVE
THE
COIL MOUNTING BRACKET-TO-
CYLINDER HEAD MOUNTING BOLTS.
THE
COIL MOUNTING BRACKET
IS
UNDER ACCESSORY
DRIVE BELT TENSION.
IF
THIS BRACKET
IS TO BE
REMOVED
FOR ANY
REASON,
ALL
BELT TENSION
MUST FIRST
BE
RELIEVED. REFER
TO THE
BELT
SECTION
OF
GROUP
7,
COOLING SYSTEM.
(2) Remove ignition coil from coil mounting
bracket (two bolts).
INSTALLATION (1) Install the ignition coil to coil bracket. If nuts
and bolts are used to secure coil to coil bracket,
tighten to 11 N«m (100 in. lbs.) torque. If the coil mounting bracket has been tapped for coil mounting
bolts,
tighten bolts to 5 N«m (50 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect all wiring to ignition coil.
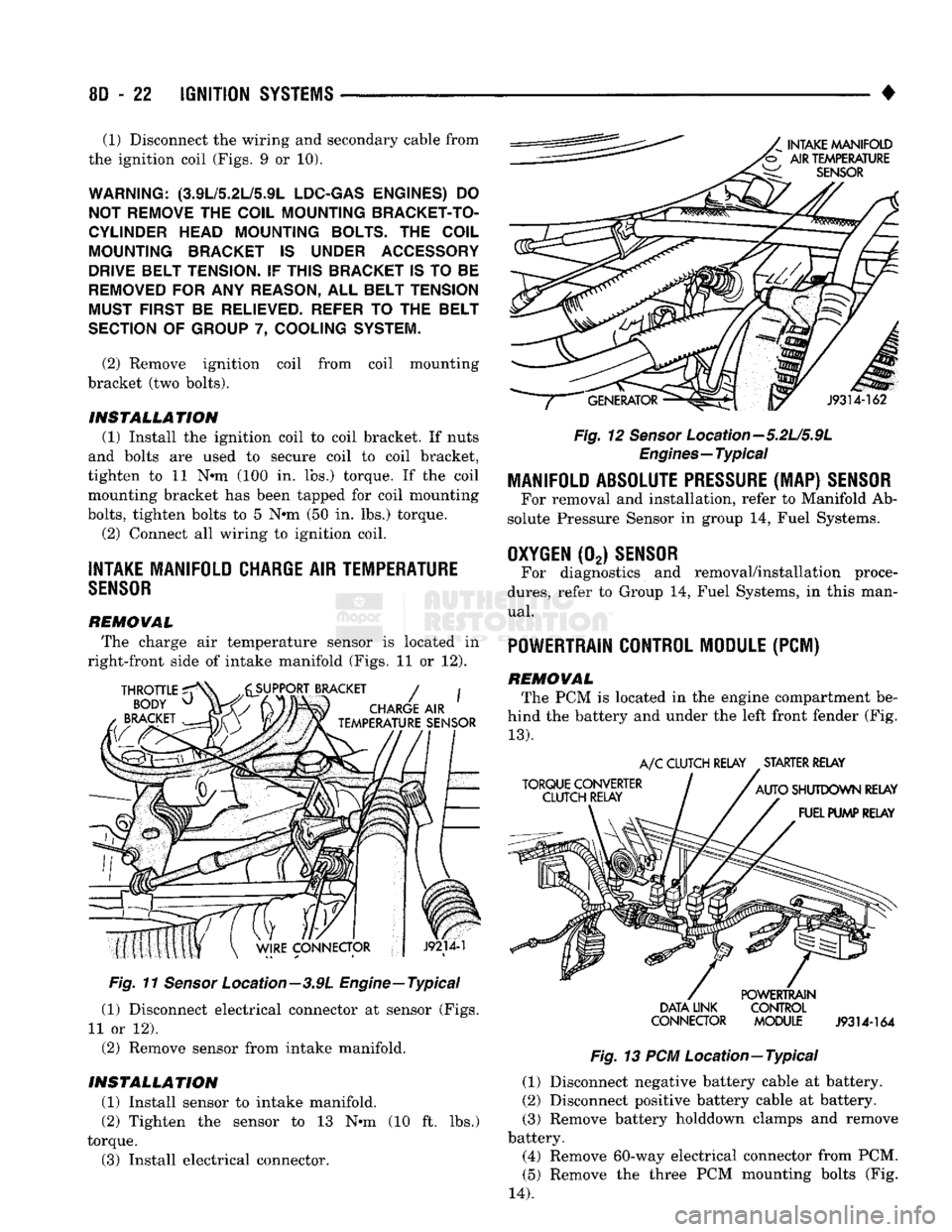
INTAKE MANIFOLD CHARGE
AIR
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
REMOVAL The charge air temperature sensor is located in
right-front side of intake manifold (Figs. 11 or 12).
Fig.
11
Sensor
Location—3.9L Engine—Typical
(1) Disconnect electrical connector at sensor (Figs.
11 or 12).
(2) Remove sensor from intake manifold.
INSTALLATION (1) Install sensor to intake manifold. (2) Tighten the sensor to 13 N-m (10 ft. lbs.)
torque. (3) Install electrical connector.
Fig.
12
Sensor
Location—5.2L/5.9L
Engines—Typical
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE
(MAP)
SENSOR
For removal and installation, refer to Manifold Ab
solute Pressure Sensor in group 14, Fuel Systems.
OXYGEN
(02)
SENSOR
For diagnostics and removal/installation proce
dures,
refer to Group 14, Fuel Systems, in this man
ual.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
(PCM)
REMOVAL The PCM is located in the engine compartment be
hind the battery and under the left front fender (Fig.
13).
DATA
UNK CONTROL
CONNECTOR MODULE
J9314-164
Fig.
13 PCM Location—Typical (1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Disconnect positive battery cable at battery.
(3) Remove battery holddown clamps and remove
battery.
(4) Remove 60-way electrical connector from PCM.
(5) Remove the three PCM mounting bolts (Fig.
14).
Page 375 of 1502
8D
- 24
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
•
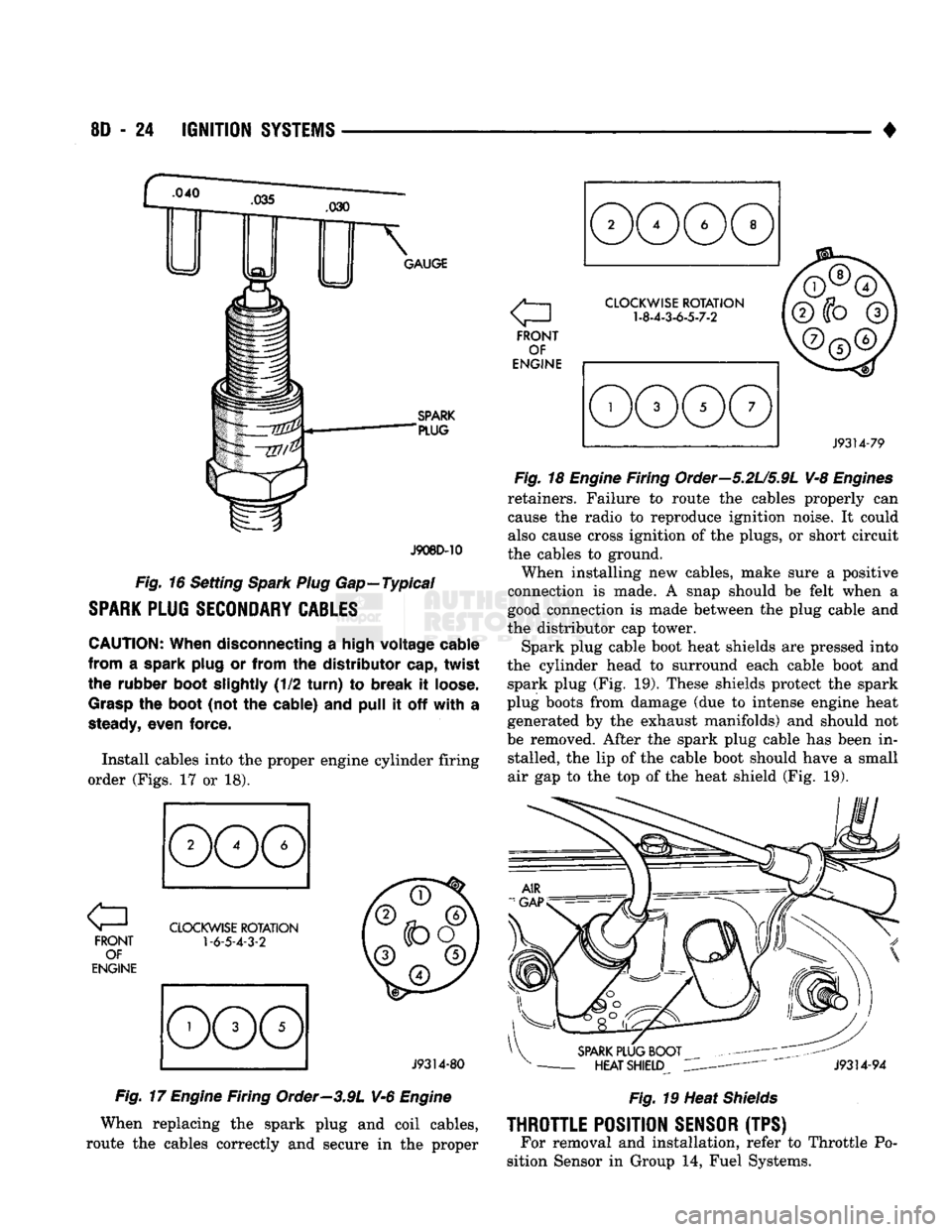
.040
GAUGE
SPARK
"PLUG
J908D-10
Fig.
16 Setting
Spark Plug
Gap—Typical
SPARK
PLUG
SECONDARY
CABLES
CAUTION:
When disconnecting
a
high voltage cable
from
a
spark plug
or
from
the
distributor cap, twist
the rubber boot slightly
(1/2
turn)
to
break
it
loose.
Grasp
the
boot
(not
the
cable)
and
pull
it off
with
a
steady,
even force.
Install cables into
the
proper engine cylinder firing
order (Figs.
17 or 18).
FRONT OF
ENGINE
CLOCKWISE
ROTATION
1-6-5-4-3-2
J9314-80
Fig.
17
Engine
Firing Order—3.9L V-6
Engine
When replacing
the
spark plug
and
coil cables,
route
the
cables correctly
and
secure
in the
proper a
FRONT OF
ENGINE
CLOCKWISE
ROTATION
1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2
J9314-79
Fig.
18
Engine
Firing Order—5.2U5.9L V-8
Engines
retainers. Failure
to
route
the
cables properly
can
cause
the
radio
to
reproduce ignition noise.
It
could
also cause cross ignition
of the
plugs,
or
short circuit
the cables
to
ground.
When installing
new
cables, make sure
a
positive
connection
is
made.
A
snap should
be
felt when
a
good connection
is
made between
the
plug cable
and
the distributor
cap
tower.
Spark plug cable boot heat shields
are
pressed into
the cylinder head
to
surround each cable boot
and
spark plug
(Fig. 19).
These shields protect
the
spark
plug boots from damage
(due to
intense engine heat generated
by the
exhaust manifolds)
and
should
not
be removed. After
the
spark plug cable
has
been
in
stalled,
the lip of the
cable boot should have
a
small
air
gap to the top of the
heat shield
(Fig. 19).
SPARK
PLUG BOOT
-
HEAT SHIELD
J9314-94
Fig.
19 Heat
Shields
THROTTLE
POSITION
SENSOR
(TPS) For removal
and
installation, refer
to
Throttle
Po
sition Sensor
in
Group
14,
Fuel Systems.