1993 DODGE TRUCK sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 355 of 1502

8D
- 4
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
•
Fig. 6 ignition Coil—3.9L/5.2L/5.9L
LDC-Gas
Engines Fig. 7 Ignition Coil—5.9L
HDC-Gas
Engine
• 5.9L HDC-Gas Engines: The coil is mounted to a
bracket that is bolted to the automatic belt tensioner mounting bracket (Fig. 7).
For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser
vice Procedures section of this group.
For removal and installation of this component, re
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
The sensor provides an input voltage to the power-
train control module (PCM) relating coolant temper ature. The PCM uses this input, along with inputs
from other sensors, to determine injector pulse width and ignition timing. As coolant temperature varies,
the coolant temperature sensor resistance will
change, resulting in a different input voltage to the
PCM. When the engine is cold, the PCM will operate in
the Open Loop Cycle. It will demand slightly richer air-fuel mixtures and higher idle speeds, until nor mal operating temperatures are reached. Refer to
Modes Of Operation in Group 14, Fuel System for a
description of Open and Closed Loop operation.
The sensor is installed in the intake manifold near
the thermostat housing (Fig. 8).
Fig. 8 Coolant Temperature Sensor—Typical
For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser
vice Procedures section of this group. For removal and installation of this component, re
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
INTAKE MANIFOLD CHARGE
AIR
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
The sensor element extends into the intake mani
fold air stream. It provides an input voltage to the
powertrain control module (PCM) indicating intake
manifold air temperature. The input from this sensor is used along with inputs from other sensors to de
termine injector pulse width. As the temperature of
the air-fuel stream in the manifold varies, the sensor
resistance will change. This will result in a different input voltage to the PCM. For more information, re
fer to Group 14, Fuel System. This sensor is installed in the intake manifold
(Figs.
9 or 10). For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser
vice Procedures section of this group. For removal and installation of this component, re
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE
(MAP)
SENSOR
The MAP sensor reacts to absolute pressure in the
intake manifold and provides an input voltage to the
powertrain control module (PCM). As engine load changes, manifold pressure varies, causing the MAP
sensor voltage to change. This change results in a
different input voltage to the PCM. The input volt age level supplies the PCM with information. This
relates to ambient barometric pressure during engine
Page 356 of 1502
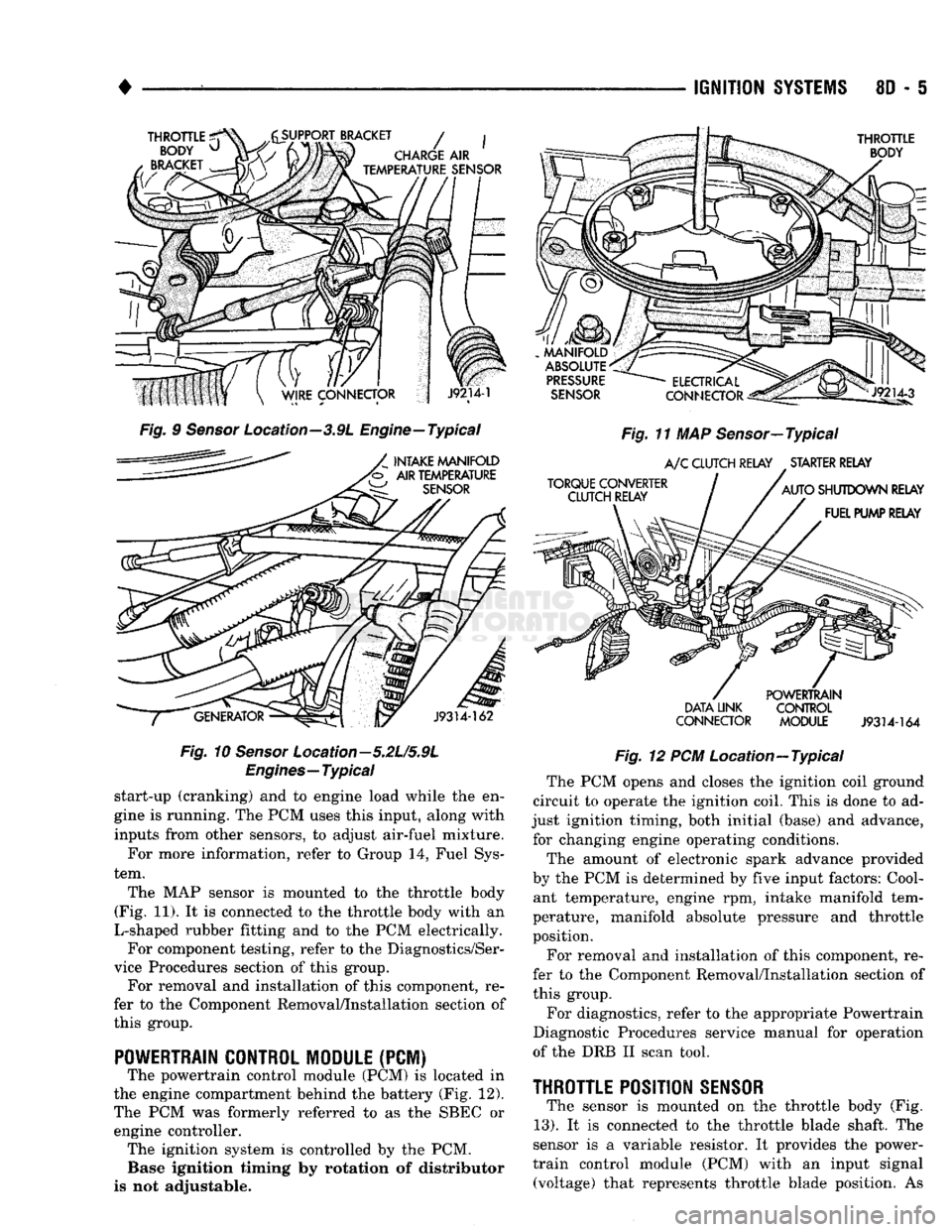
•
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
8D - 5
THROTTLE
^
BODY
u
BRACKET
y^SUPPORT
BRACKET
/ |
CHARGE
AIR
ijmmmmk
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
THROTTLE
BODY
Fig.
9
Sensor
Location—3.9L Engine—Typical
INTAKE MANIFOLD
'b AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
J9314-162
Fig.
10
Sensor
Location—5.2L/5.9L
Engines—Typical
start-up (cranking) and to engine load while the en
gine is running. The PCM uses this input, along with
inputs from other sensors, to adjust air-fuel mixture.
For more information, refer to Group 14, Fuel Sys
tem.
The MAP sensor is mounted to the throttle body
(Fig. 11). It is connected to the throttle body with an
L-shaped rubber fitting and to the PCM electrically. For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser
vice Procedures section of this group. For removal and installation of this component, re
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
(PCM) The powertrain control module (PCM) is located in
the engine compartment behind the battery (Fig. 12).
The PCM was formerly referred to as the SBEC or engine controller. The ignition system is controlled by the PCM. Base ignition timing by rotation of distributor
is not adjustable.
MANIFOLD
ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE
SENSOR
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH RELAY
ELECTRICAL
Jlp^
CONNECTOR
^gis!—
Fig.
11 MAP Sensor—Typical
A/C
CLUTCH RELAY STARTER RELAY
AUTO
SHUTDOWN RELAY FUEL PUMP RELAY
DATA LINK
CONNECTOR POWERTRAIN
CONTROL
MODULE
J9314-164
Fig.
12 PCM Location—Typical The PCM opens and closes the ignition coil ground
circuit to operate the ignition coil. This is done to ad
just ignition timing, both initial (base) and advance, for changing engine operating conditions.
The amount of electronic spark advance provided
by the PCM is determined by five input factors: Cool ant temperature, engine rpm, intake manifold tem
perature, manifold absolute pressure and throttle
position.
For removal and installation of this component, re
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
For diagnostics, refer to the appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures service manual for operation
of the DRB II scan tool.
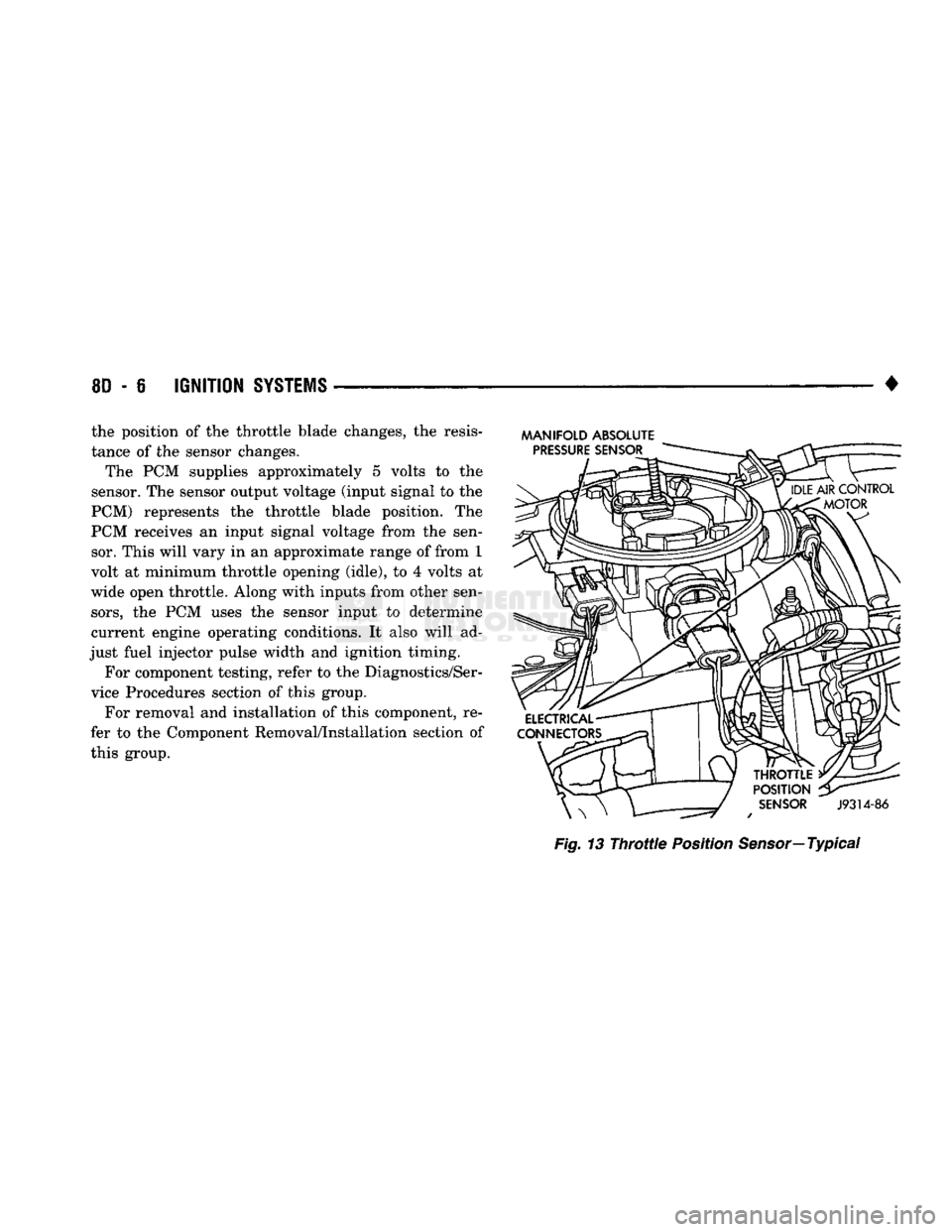
THROTTLE
POSITION
SENSOR
The sensor is mounted on the throttle body (Fig.
13).
It is connected to the throttle blade shaft. The
sensor is a variable resistor. It provides the power-
train control module (PCM) with an input signal (voltage) that represents throttle blade position. As
Page 357 of 1502
8D
- 6
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
• the position of the throttle blade changes, the resis
tance of the sensor changes.
The PCM supplies approximately 5 volts to the
sensor. The sensor output voltage (input signal to the
PCM) represents the throttle blade position. The
PCM receives an input signal voltage from the sen sor. This will vary in an approximate range of from 1
volt at minimum throttle opening (idle), to 4 volts at
wide open throttle. Along with inputs from other sen
sors,
the PCM uses the sensor input to determine
current engine operating conditions. It also will ad
just fuel injector pulse width and ignition timing.
For component testing, refer to the Diagnostics/Ser
vice Procedures section of this group.
For removal and installation of this component, re
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
Fig.
13
Throttle
Position
Sensor—
Typical
Page 358 of 1502

•
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
80 - 7
DIAGNOSTICS/SERW1CE
PROCEDURES
INDEX
page
Automatic Shut Down (ASD) Relay
7
Camshaft Position
Sensor
Test
...............
7
Crankshaft Position
Sensor
Test
8
Distributor
Cap
8
Distributor
Rotor
8
Engine
Coolant Temperature
Sensor
Test
10
General
Information
7
Ignition
Coil
8
Ignition
Secondary
Circuit
Diagnosis
10
GENERAL
INFORMATION
This section
of the
group, Diagnostics/Service Pro
cedures, will discuss basic ignition system diagnos
tics
and
service adjustments. For system operation
and
component identification,
refer
to the
Component Identification/System Opera
tion section
of
this group. For removal
or
installation
of
ignition system com
ponents, refer
to the
Component Removal/Installa
tion section
of
this group. For other useful information, refer
to
On-Board
Di
agnostics
in the
General Diagnosis sections
of
Group
14,
Fuel System
in
this manual. For operation
of the DRB II
Diagnostic Scan Tool,
refer
to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce
dures service manual.
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN
(ASD)
RELAY
Refer
to
Relays—Operation/Testing
in the
Group
14,
Fuel System section
of
this service manual.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR TEST
The camshaft position sensor
is
located
in the
dis
tributor
on all
engines. To perform
a
complete test
of
this sensor
and its
circuitry, refer
to the DRB II
diagnostic scan tool.
Also refer
to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics
Procedures manual.
To
test
the
sensor only, refer
to
the following: For this test,
an
analog (non-digital) voltmeter
is needed.
Do not
remove
the
distributor connector from
the
distributor. Using small paper clips, insert
them into
the
backside
of the
distributor wire har ness connector
to
make contact with
the
terminals.
Be sure that
the
connector
is not
damaged when
in
serting
the
paper clips. Attach voltmeter leads
to
these paper clips. (1) Connect
the
positive (
+
)
voltmeter lead into
the sensor output wire. This
is at
done
the
distribu tor wire harness connector.
For
wire identification,
refer
to
Group
8W,
Wiring Diagrams.
page
Ignition
Timing
12
Intake Manifold Charge
Air
Temperature
Sensor
Test
12
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
Sensor
Test
. 12
Oxygen
Sensor
Tests
17
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
............
14
Spark
Plug Secondary Cables
16
Spark
Plugs
............................
14
Throttle
Position
Sensor
Test
17
(2) Connect
the
negative
(-)
voltmeter lead into
the
ground wire.
For
wire identification, refer
to
Group
8W, Wiring Diagrams.
(3)
Set the
voltmeter
to the 15
Volt
DC
scale. (4) Remove distributor
cap
from distributor
(two
screws). Rotate (crank)
the
engine until
the
distribu
tor rotor
is
pointed towards
the
rear
of
vehicle.
The
movable pulse ring should
now be
within
the
sensor
pickup.
(5) Turn ignition
key to ON
position. Voltmeter
should read approximately
5.0
volts.
(6)
If
voltage
is not
present, check
the
voltmeter
leads
for a
good connection.
(7)
If
voltage
is
still
not
present, check
for
voltage
at
the
supply wire.
For
wire identification, refer
to
Group
8W,
Wiring Diagrams.
(8)
If
voltage
is not
present
at
supply wire, check
for voltage
at
pin-7
of
powertrain control module (PCM) 60-way connector. Leave
the PCM
connector
connected
for
this test. (9)
If
voltage
is
still
not
present, perform vehicle
test using
the DRB II
diagnostic scan tool. (10)
If
voltage
is
present
at
pin-7,
but not at the
supply wire: (a) Check continuity between
the
supply wire.
This
is
checked between
the
distributor connector and pin-7
at the PCM. If
continuity
is not
present,
repair
the
harness
as
necessary. (b) Check
for
continuity between
the
camshaft
position sensor output wire
and
pin-44
at the PCM.
If continuity
is not
present, repair
the
harness
as
necessary. (c) Check
for
continuity between
the
ground cir
cuit wire
at the
distributor connector
and
ground.
If continuity
is not
present, repair
the
harness
as
necessary. (11) While observing
the
voltmeter, crank
the en
gine with ignition switch.
The
voltmeter needle should fluctuate between
0 and 5
volts while
the en
gine
is
cranking. This verifies that
the
camshaft
po
sition sensor
in the
distributor
is
operating properly
and
a
sync pulse signal
is
being generated.
Page 359 of 1502
8D
- 8
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
• If sync pulse signal is not present, replacement of
the camshaft position sensor is necessary. For removal or installation of ignition system com
ponents, refer to the Component Removal/Installa
tion section of this group.
For system operation and component identification,
refer to the Component Identification/System Opera
tion section of this group.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
TEST
To perform a complete test of this sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the DRB II diagnostic scan tool.
Also refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics
Procedures manual. To test the sensor only, refer to
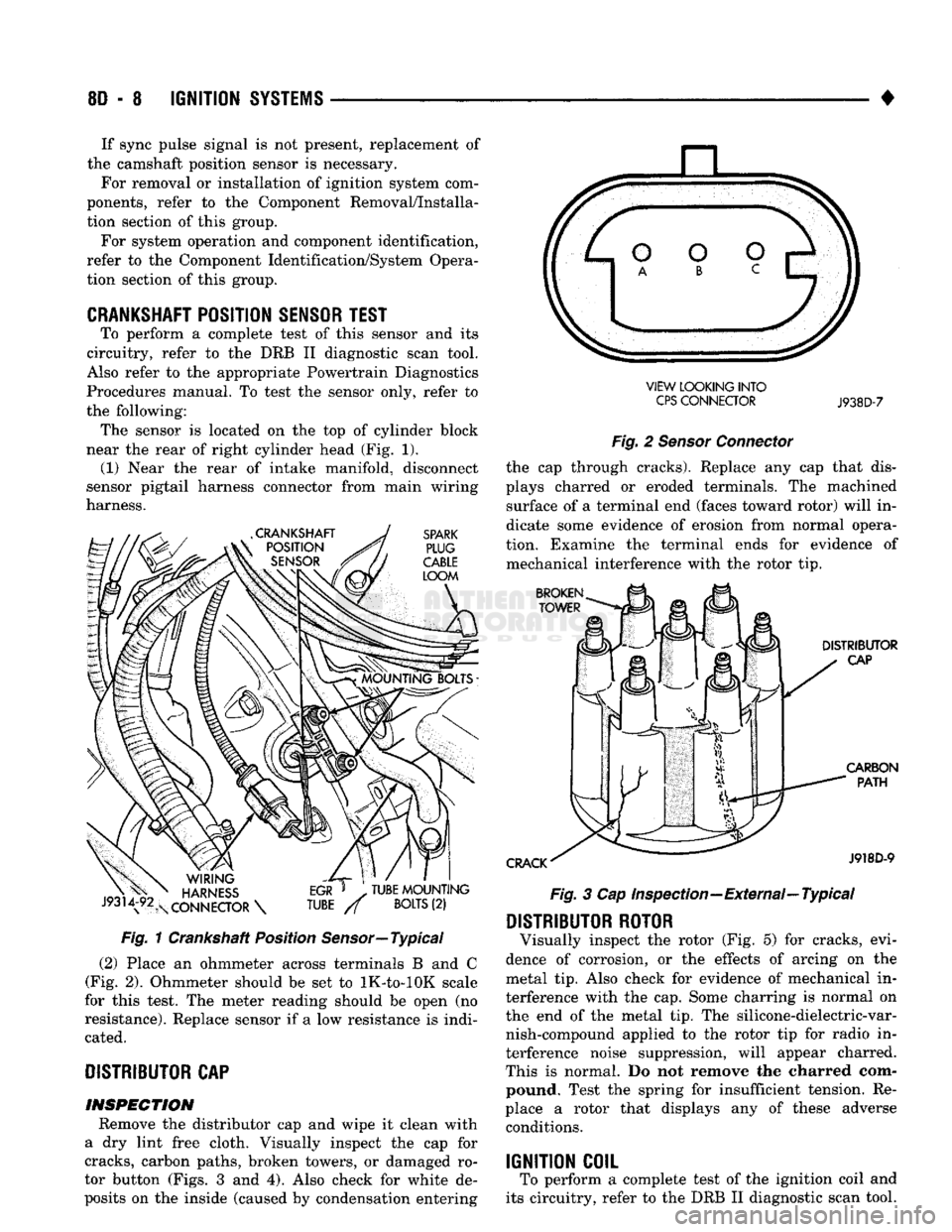
the following: The sensor is located on the top of cylinder block
near the rear of right cylinder head (Fig. 1). (1) Near the rear of intake manifold, disconnect
sensor pigtail harness connector from main wiring
harness. Fig. 1 Crankshaft Position Sensor—Typical
(2) Place an ohmmeter across terminals B and C
(Fig. 2). Ohmmeter should be set to lK-to-lOK scale
for this test. The meter reading should be open (no
resistance). Replace sensor if a low resistance is indi cated.
DISTRIBUTOR
CAP INSPECTION Remove the distributor cap and wipe it clean with
a dry lint free cloth. Visually inspect the cap for
cracks, carbon paths, broken towers, or damaged ro
tor button (Figs. 3 and 4). Also check for white de
posits on the inside (caused by condensation entering VIEW LOOKING INTO
CPS
CONNECTOR
J938D-7
Fig. 2 Sensor Connector the cap through cracks). Replace any cap that dis
plays charred or eroded terminals. The machined surface of a terminal end (faces toward rotor) will in
dicate some evidence of erosion from normal opera
tion. Examine the terminal ends for evidence of mechanical interference with the rotor tip. Fig. 3 Cap Inspection—External—Typical
DISTRIBUTOR ROTOR
Visually inspect the rotor (Fig. 5) for cracks, evi
dence of corrosion, or the effects of arcing on the
metal tip. Also check for evidence of mechanical in
terference with the cap. Some charring is normal on
the end of the metal tip. The silicone-dielectric-var nish-compound applied to the rotor tip for radio in
terference noise suppression, will appear charred.
This is normal. Do not remove the charred com pound. Test the spring for insufficient tension. Re
place a rotor that displays any of these adverse conditions.
IGNITION COIL
To perform a complete test of the ignition coil and
its circuitry, refer to the DRB II diagnostic scan tool.
Page 361 of 1502
8D
- 10
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
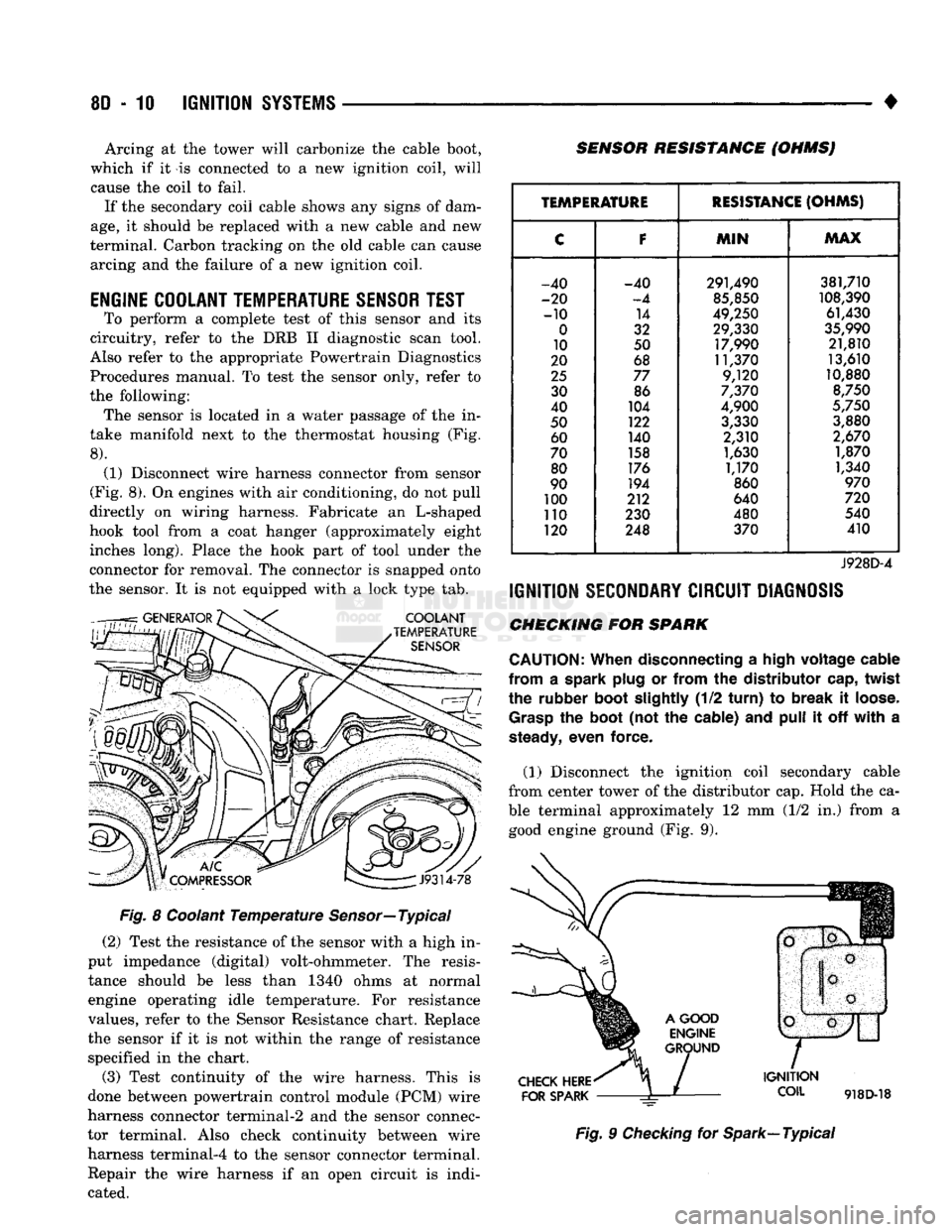
• Arcing at the tower will carbonize the cable boot,
which if it is connected to a new ignition coil, will cause the coil to fail. If the secondary coil cable shows any signs of dam
age,
it should be replaced with a new cable and new
terminal. Carbon tracking on the old cable can cause
arcing and the failure of a new ignition coil.
ENGINE
COOLANT
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
TEST
To perform a complete test of this sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the DRB II diagnostic scan tool.
Also refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics
Procedures manual. To test the sensor only, refer to
the following: The sensor is located in a water passage of the in
take manifold next to the thermostat housing (Fig.
8).
(1) Disconnect wire harness connector from sensor
(Fig. 8). On engines with air conditioning, do not pull
directly on wiring harness. Fabricate an L-shaped
hook tool from a coat hanger (approximately eight inches long). Place the hook part of tool under the
connector for removal. The connector is snapped onto
the sensor. It is not equipped with a lock type tab.
COOLANT
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
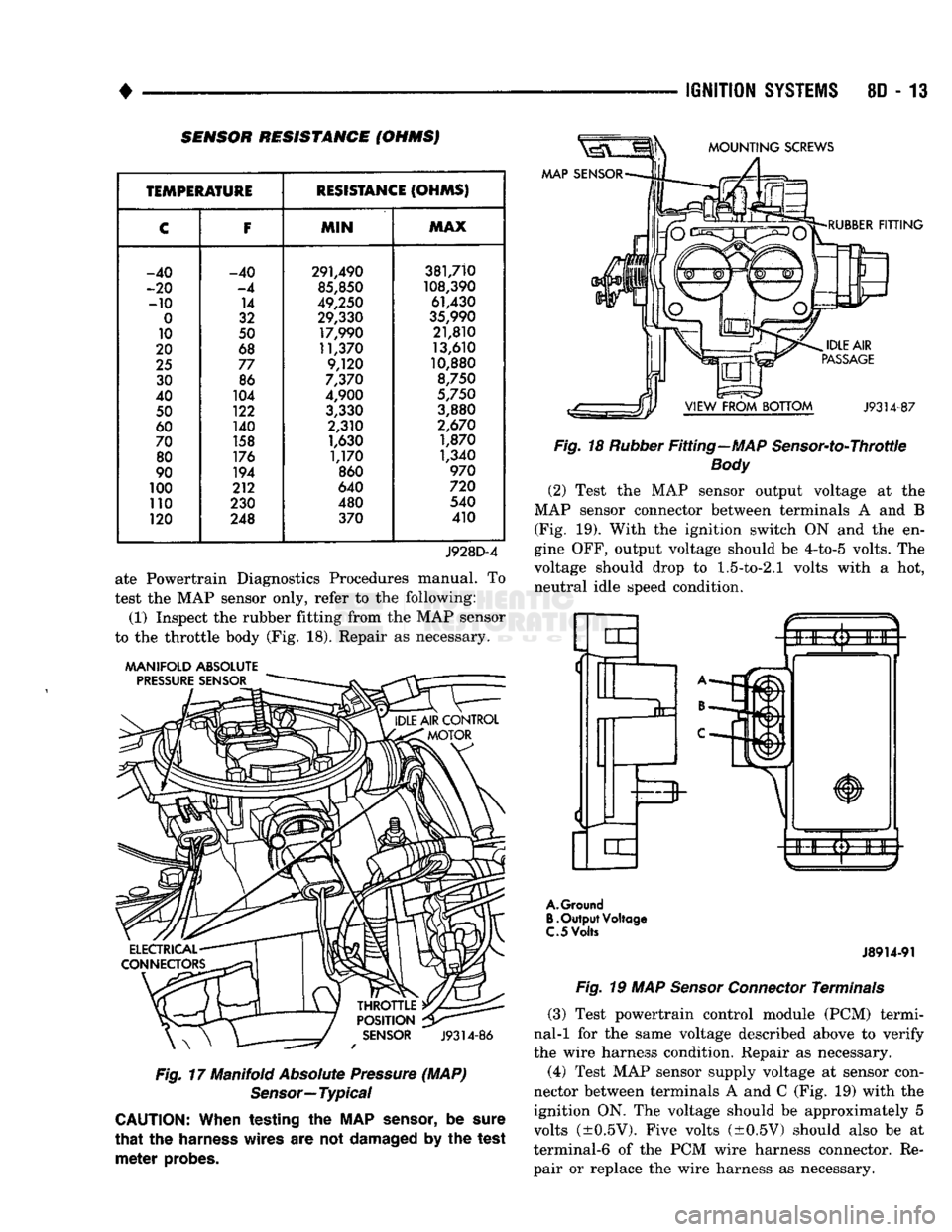
SENSOR RESISTANCE (OHMSJ
V
J9314-78
Fig. 8 Coolant Temperature Sensor—Typical (2) Test the resistance of the sensor with a high in
put impedance (digital) volt-ohmmeter. The resis tance should be less than 1340 ohms at normal
engine operating idle temperature. For resistance
values, refer to the Sensor Resistance chart. Replace
the sensor if it is not within the range of resistance specified in the chart.
(3) Test continuity of the wire harness. This is
done between powertrain control module (PCM) wire
harness connector terminal-2 and the sensor connec
tor terminal. Also check continuity between wire harness terminal-4 to the sensor connector terminal. Repair the wire harness if an open circuit is indi
cated.
TEMPERATURE
RESISTANCE
(OHMS)
C
F
MIN
MAX
-40 -40 291,490 381,710
-20
-4
85,850
108,390
-10 14
49,250 61,430
0
32 29,330
35,990
10 50 17,990 21,810
20 68 11,370 13,610
25
77 9,120 10,880
30 86
7,370
8,750
40 104
4,900
5,750
50 122
3,330 3,880
60 140 2,310
2,670
70 158
1,630 1,870
80 176
1,170 1,340
90 194
860
970
100 212 640
720
110 230 480 540
120 248 370 410
J928D-4
IGNITION
SECONDARY
CIRCUIT
DIAGNOSIS
CHECKING FOR SPARK
CAUTION:
When
disconnecting a
high
voltage
cable
from
a spark
plug
or
from
the
distributor
cap,
twist
the rubber
boot
slightly
(1/2
turn)
to
break
it
loose.
Grasp
the
boot
(not the cable) and
pull
it off
with
a
steady,
even force.
(1) Disconnect the ignition coil secondary cable
from center tower of the distributor cap. Hold the ca
ble terminal approximately 12 mm (1/2 in.) from a good engine ground (Fig. 9).
CHECK
HERE
FOR
SPARK
IGNITION
COIL
918D-18
Fig. 9 Checking for Spark—Typical
Page 363 of 1502
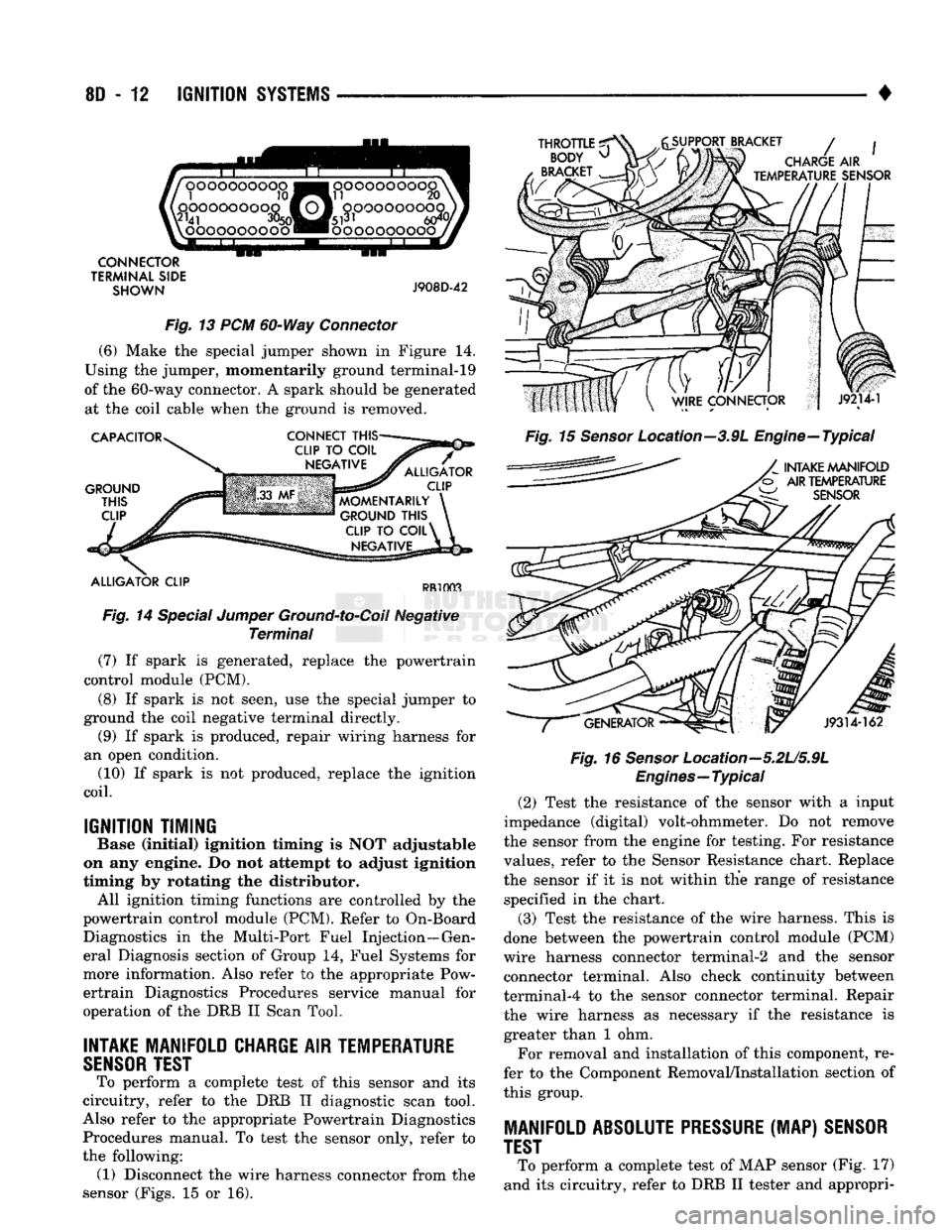
8D
- 12
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
•
XX
oooooooooo
,0000000000
\2141
3%
lOOOOOOOOOO
OOOOOOOOOO
si
20
fcji^OQOOOOOOJ
«r
~
• • -
•
- - #
•oooooooooo.
CONNECTOR
TERMINAL
SIDE
SHOWN
J908D-42
Fig. 13 PCM 60-Way Connector
(6) Make the special jumper shown in Figure 14.
Using the jumper, momentarily ground terminal-19
of the 60-way connector. A spark should be generated at the coil cable when the ground is removed.
CAPACITOR
GROUND
THIS
CLIP
CONNECT
THIS-
ALLIGATOR
CLIP
MOMENTARILY
GROUND
THIS
CLIP
TO
COIL^
NEGATIVE
ALLIGATOR
CLIP
PR1003
Fig. 14 Special Jumper Ground-to-Coil Negative Terminal (7) If spark is generated, replace the powertrain
control module (PCM).
(8) If spark is not seen, use the special jumper to
ground the coil negative terminal directly. (9) If spark is produced, repair wiring harness for
an open condition. (10) If spark is not produced, replace the ignition
coil.
IGNITION TIMING
Base (Initial) ignition timing Is NOT adjustable
on any engine. Do not attempt to adjust Ignition
timing by rotating the distributor. All ignition timing functions are controlled by the
powertrain control module (PCM). Refer to On-Board Diagnostics in the Multi-Port Fuel Injection—Gen
eral Diagnosis section of Group 14, Fuel Systems for
more information. Also refer to the appropriate Pow ertrain Diagnostics Procedures service manual for
operation of the DRB II Scan Tool.
INTAKE
MANIFOLD
CHARGE
AIR
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
TEST
To perform a complete test of this sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the DRB II diagnostic scan tool.
Also refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures manual. To test the sensor only, refer to
the following: (1) Disconnect the wire harness connector from the
sensor (Figs. 15 or 16).
THROTTLE
^
BODY
^
BRACKET
SUPPORT BRACKET
/
CHARGE
AIR
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
Fig. 15 Sensor Location--3.9L Engine—Typical
INTAKE
MANIFOLD
AIR
TEMPERATURE
W
SENSOR
J9314-162
Fig. 16
Sensor
Location—5.2U5.9L
Engines—Typical
(2) Test the resistance of the sensor with a input
impedance (digital) volt-ohmmeter. Do not remove
the sensor from the engine for testing. For resistance
values, refer to the Sensor Resistance chart. Replace
the sensor if it is not within the range of resistance specified in the chart.
(3) Test the resistance of the wire harness. This is
done between the powertrain control module (PCM)
wire harness connector terminal-2 and the sensor connector terminal. Also check continuity between
terminal-4 to the sensor connector terminal. Repair
the wire harness as necessary if the resistance is greater than 1 ohm.
For removal and installation of this component, re
fer to the Component Removal/Installation section of
this group.
MANIFOLD
ABSOLUTE PRESSURE
(MAP)
SENSOR
TEST
To perform a complete test of MAP sensor (Fig. 17)
and its circuitry, refer to DRB II tester and appropri-
Page 364 of 1502
IGNITION
SYSTEMS
8D - 13
SENSOR RESISTANCE (OHMS)
TEMPERATURE
RESISTANCE
(OHMS)
C
F
MIN
MAX
-40 -40 291,490 381,710
-20
-4
85,850 108,390
-10 14 49,250 61,430
0
32 29,330
35,990
10 50 17,990 21,810
20 68 11,370
13,610
25
77 9,120
10,880
30 86
7,370
8,750
40 104
4,900
5,750
50 122
3,330
3,880
60 140 2,310
2,670
70 158
1,630
1,870
80 176
1,170
1,340
90 194 860
970
100 212 640
720
110 230 480
540
120 248 370
410
J928D-4
ate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures manual. To
test the MAP sensor only, refer to the following:
(1) Inspect the rubber fitting from the MAP sensor
to the throttle body (Fig. 18). Repair as necessary.
MANIFOLD
ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE
SENSOR
J9314-86
Fig.
17 Manifold
Absolute
Pressure
(MAP)
Sensor—
Typical
CAUTION:
When
testing
the MAP
sensor,
be
sure
that
the
harness
wires
are not damaged by the
test
meter
probes.
AAAP
SENSOR
MOUNTING
SCREWS
RUBBER
FITTING
J9314-87
Fig.
18
Rubber
Fitting—MAP Sensor-to-Throttle
Body
(2) Test the MAP sensor output voltage at the
MAP sensor connector between terminals A and B (Fig. 19). With the ignition switch ON and the en
gine OFF, output voltage should be 4-to-5 volts. The
voltage should drop to
1.5-to-2.1
volts with a hot, neutral idle speed condition.
A.
Ground
B.
Output
Voltage
C.
5
Volts
J8914-91
Fig.
19 MAP
Sensor
Connector
Terminals
(3) Test powertrain control module (PCM) termi
nal-1 for the same voltage described above to verify
the wire harness condition. Repair as necessary.
(4) Test MAP sensor supply voltage at sensor con
nector between terminals A and C (Fig. 19) with the
ignition ON. The voltage should be approximately 5
volts (±0.5V). Five volts (±0.5V) should also be at
terminal-6 of the PCM wire harness connector. Re pair or replace the wire harness as necessary.