1988 PONTIAC FIERO light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 936 of 1825
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.0L (VIN F) €4 5.7L (VIN 8) 6E3-C7-1
SECTION C7
EXHAUST GAS REClRCULATlON (EGR) SYSTEM
CONTENTS
................ GENERAL DESCRIPTIlDN C7-1 DIAGNOSIS ........................ C7-2
PURPOSE
......................... C7-1 EGR VALVE ...................... C7-3
....................... OPERATION C7-1 EGR Manifold Passage ............... C7-3
.................... EGR CONTROL C7-1
EGR CONTROL SOLENOID ............ C7-3
NEGATIVE BACKPRESSURE EGR VALVE
. . C7-2 PARTS INFORMATION ................. C7-3
......... EGR VALVE IDENTIFICATION.. C7-2
... RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION C7-2
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
PURPOSE
The EGR system is used to lower NO, (oxides of
nitrogen) emission levels caused by high combustion
temperature. It does this by decreasing combustion
temperature. The main element of the system is the EGR valve
operated by vacuum and mounted on the intake
manifold.
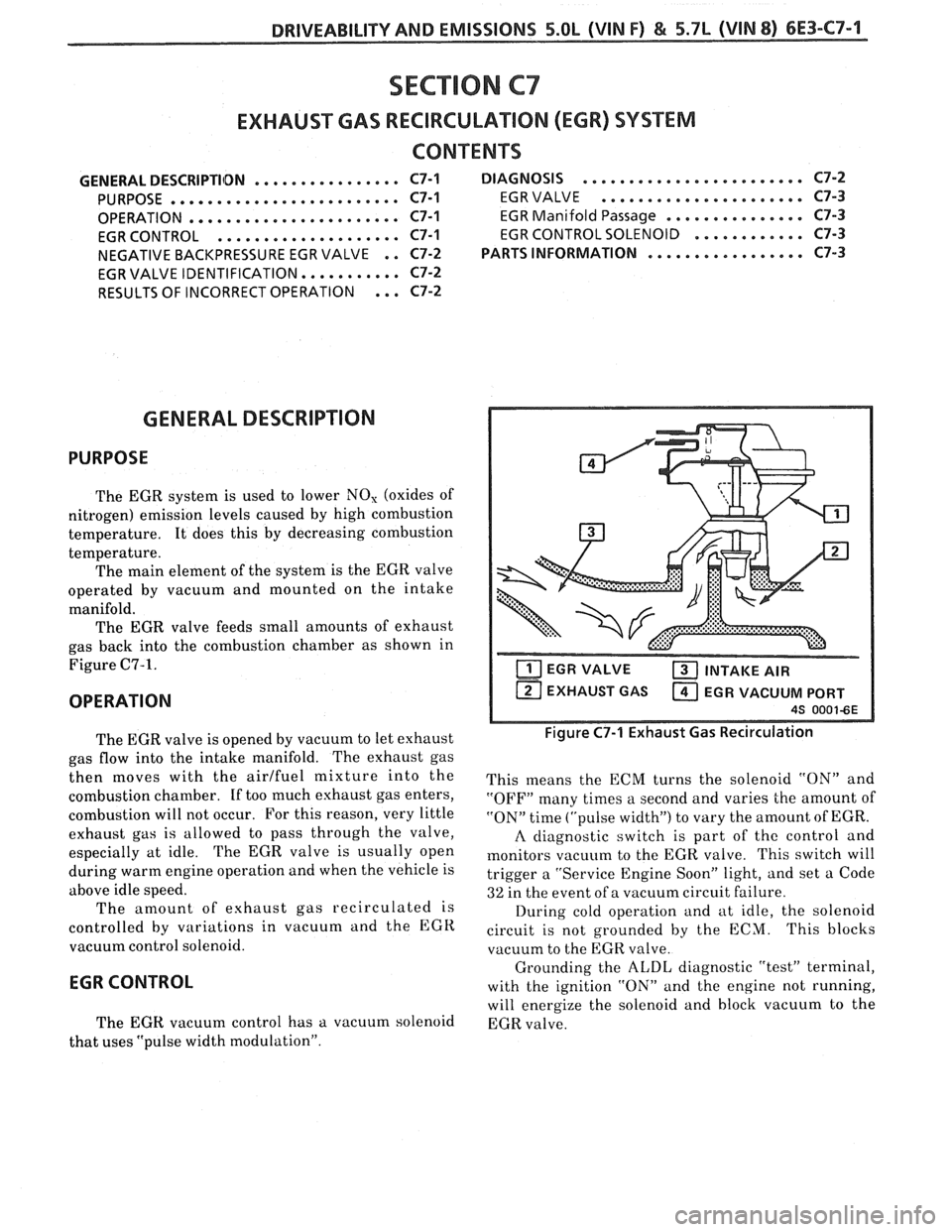
The EGR valve feeds small amounts of exhaust
gas back into the combustion chamber as shown in
Figure
C7-1.
OPERATION
The EGR valve is opened by vacuum to let exhaust
gas flow into the intake manifold. The exhaust gas
then moves with the
airlfuel mixture into the
combustion chamber.
If too much exhaust gas enters,
combustion will not occur. For this reason, very little
exhaust gas is allowed to pass through the valve,
especially at idle. The EGR valve is usually open
during warm engine operation and when the vehicle is
above idle speed. The amount of exhaust gas recirculated is
controlled by variations in vacuum and the
EGR
vacuum control solenoid.
EGR CONTROL
The EGR vacuum control has a vacuum solenoid
that uses "pulse width modulation".
EGR VALVE INTAKE AIR
EXHAUST GAS EGR VACUUM PORT
Figure C7-1 Exhaust Gas Recirculation
This means the ECM turns the solenoid "ON" and
"OFF" many times a second and varies the amount of
"ON" time ("pulse width") to vary the amount of EGR.
A diagnostic switch is part of the control and
monitors vacuum to the EGR valve. This switch will
trigger a "Service Engine Soon" light, and set a Code
32 in the event of a vacuum circuit failure.
During cold operation and at idle, the solenoid
circuit is not grounded by the ECM. This blocks
vacuum to the EGR valve.
Grounding the
ALDL diagnostic "test" terminal,
with the ignition "ON" and the engine not running,
will energize the solenoid and block vacuum to the
EGR valve.
Page 942 of 1825

DWlVEABlLlTV AND EMISSIONS 5.01, QVIN F) & 5.71 (VIN 8) 6E3-C8-1
TRANSMISSION CONVERTER CLUTCH (KC) SYSTEM
AND MANUAL "TRANSMISSION SHlFT LBGH"O"=Ob ONLY
CONTENTS
................ GENERAL DESCRIPTION C8-1 DIAGNOSIS ....................... .. C8-1
........ PURPOSE ......................... CS-1 SHIFT LIGHT (MIT) DESCRIPTION C8-1
....................... OPERATION C8-1 DIAGNOSIS ......................... CS-1
OM-CAR SERVICE ..................... C8-1
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
PURPOSE
The transmission converter clutch (TCC) system
uses
a solenoid operated valve in the automatic
transmission to couple the engine flywheel to the
output shaft of the transmission thru the torque
converter. This reduces the slippage losses in the
converter, which increases fuel economy.
OPERATION
For the converter clutch to apply, two conditions
must be met:
e Internal transmission fluid pressure must be
correct. For information on internal transmission
operation, see Section
"7A". This section will
cover only the electrical operation of the TCC
system.
@ The ECM grounds a switch internally to turn
"ON" a solenoid in the transmission. This moves a
check ball, which will allow the converter clutch
to apply, if the hydraulic pressure is correct, as
described above.
The ECM controls the TCC apply solenoid by
looking at several sensors:
@ Speedo Buffer Sensor (also called Vehicle Speed
Sensor
(VSS) Speed must be above a certain value
before the clutch can apply.
@ Coolant Temperature Sensor Engine must be
warmed
LIP before clutch can apply about 65" C
(149°F).
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) After the
converter clutch applies, the ECM uses the
information
from the TPS to release the clutch
when the car is accelerating or decelerating at
a
certain rate.
The brake switch
is also part of the 'I'CC circuit as
it will remove battery voltage to the
'FCC solenoid
when the brake pedal is depressed.
@ Gear Select Switch The 4th gear switch is used to
send a signal to the ECM telling it when the
transmission is in 4th
gear
The ECM uses this information to vary the conditions
under which the clutch applies or releases. However,
the transmission does not have to be in fourth gear in
order for the ECM to turn the clutch "ON".
If the converter clutch is applied at all times, the
engine will stall immediately, just as in a manual
transmission with the clutch applied.
If the converter
clutch does not apply, fuel
ecomony may be lower than expected. If the vehicle
speed sensor fails, the TCC will not apply. If the 4th
gear switch does not operate, the TCC may not apply
at the right time.
DIAGNOSIS
The diagnosis of the TCC system is covered in
CHART C-$A. If the ECM detects a problem in the
system, a Code 24 should set. In this case, see Code 24
CHART.
SHIFT LIGHT (MR) DESCRIPTION
The purpose of the shift light is to provide a
display which indicates the optimum fuel economy
point for up shifting the manual transmission based
on engine speed and load. The display is
a lamp on the
instrument panel. Activation
of the ECM driver turns
the lamp "ON".
DIAGNOSIS
The shift light circuit can be checked using
CEIAR'I' C-8B.
ON-CAR SERVICE
See Section "8B" if the shift light bulb needs
replacement.
See Section
"GE" to repair wiring problem.
@ See Section "C- 1" if ECM is to be replaced.
Page 943 of 1825
6E3-C8-2 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
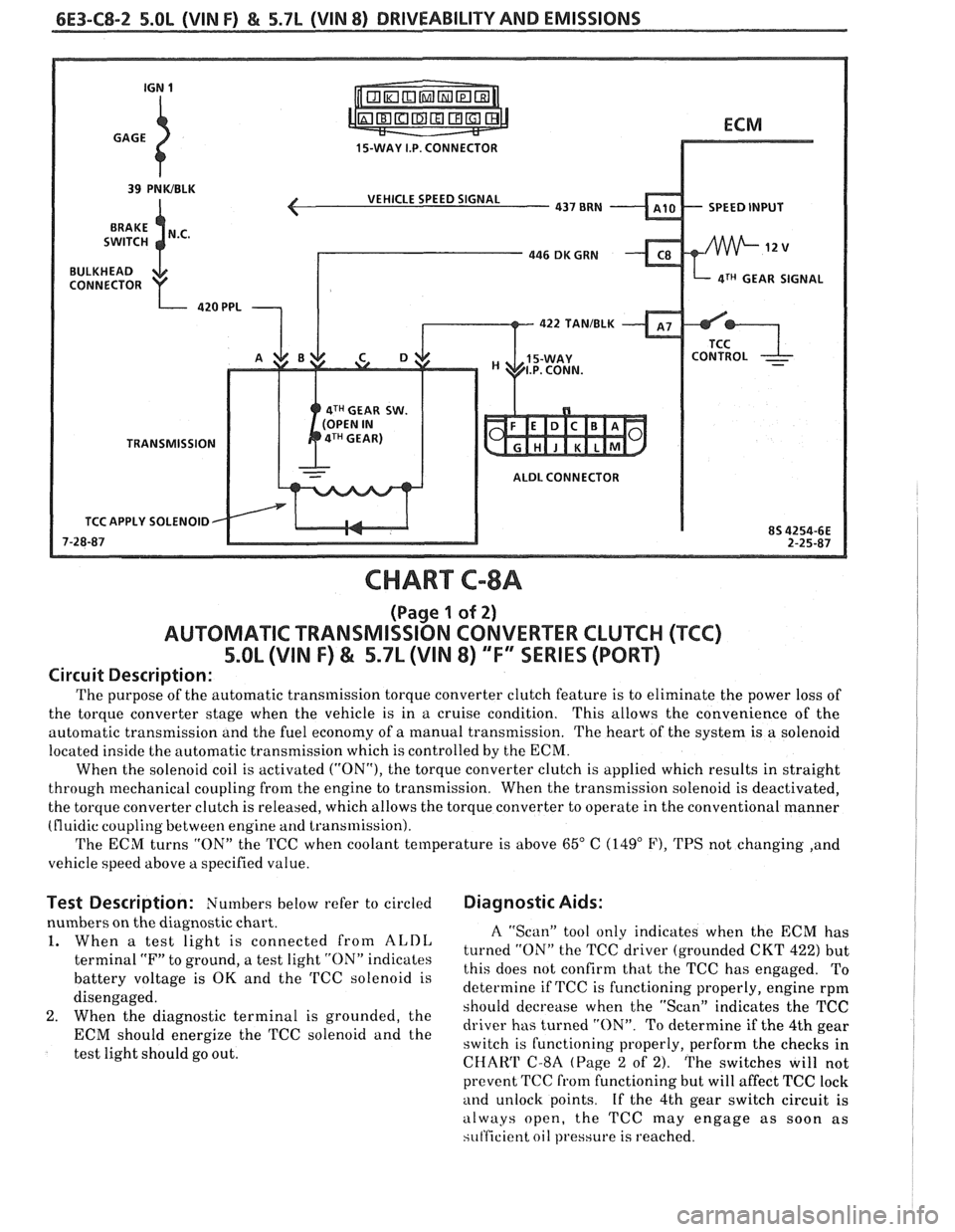
15-WAY I.P. CONNECTOR
VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL
SPEED INPUT
4TH GEAR SIGNAL
422
TANIBLK
4TH GEAR SW.
TRANSMISSION ALDL CONNECTOR
TCC APPLY SOLENOID
CHART C-8A
(Page 1 of 2)
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) "F'" SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The purpose of the automatic transmission torque converter clutch feature is to eliminate the power loss of
the torque converter stage when the vehicle is in a cruise condition. This allows the convenience
of the
automatic transmission and the fuel economy of
a manual transmission. The heart of the system is a solenoid
located inside the automatic transmission which is controlled by the ECM.
When the solenoid coil is activated
("ON"), the torque converter clutch is applied which results in straight
through mechanical coupling from the engine to transmission. When the transmission solenoid is deactivated,
the torque converter clutch is released, which allows the torque converter to operate in the conventional manner
(fluidic coupling between engine
and transmission).
The ECM turns "ON" the TCC when coolant temperature is above
65" C (149" F), TPS not changing ,and
vehicle speed above
a specified value.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled Diagnostic Aids:
nbers on the diagnostic chart.
When
a test light is connected from ALDL
terminal "F" to ground, a test light "ON" indicates
battery voltage is
OK and the TCC solenoid is
disengaged.
When the diagnostic terminal is grounded, the
ECM should energize the TCC solenoid and the
test light should go out.
A "Scan" tool only indicates when the ECM has
turned "ON" the TCC driver (grounded CKT
422) but
this does not confirm that the TCC has engaged. To
determine if TCC is functioning properly, engine rpm
should decrease when the "Scan" indicates the TCC
driver has turned "ON". To determine if the 4th gear
switch is functioning properly, perform the checks in
CHAW C-8A (Page 2 of 2). The switches will not
prevent TCC
from functioning but will affect TCC lock
and unlock points. If the 4th gear switch circuit is
always open, the TCC may engage as soon as
si~t'ficient oil pressure is reached.
Page 947 of 1825
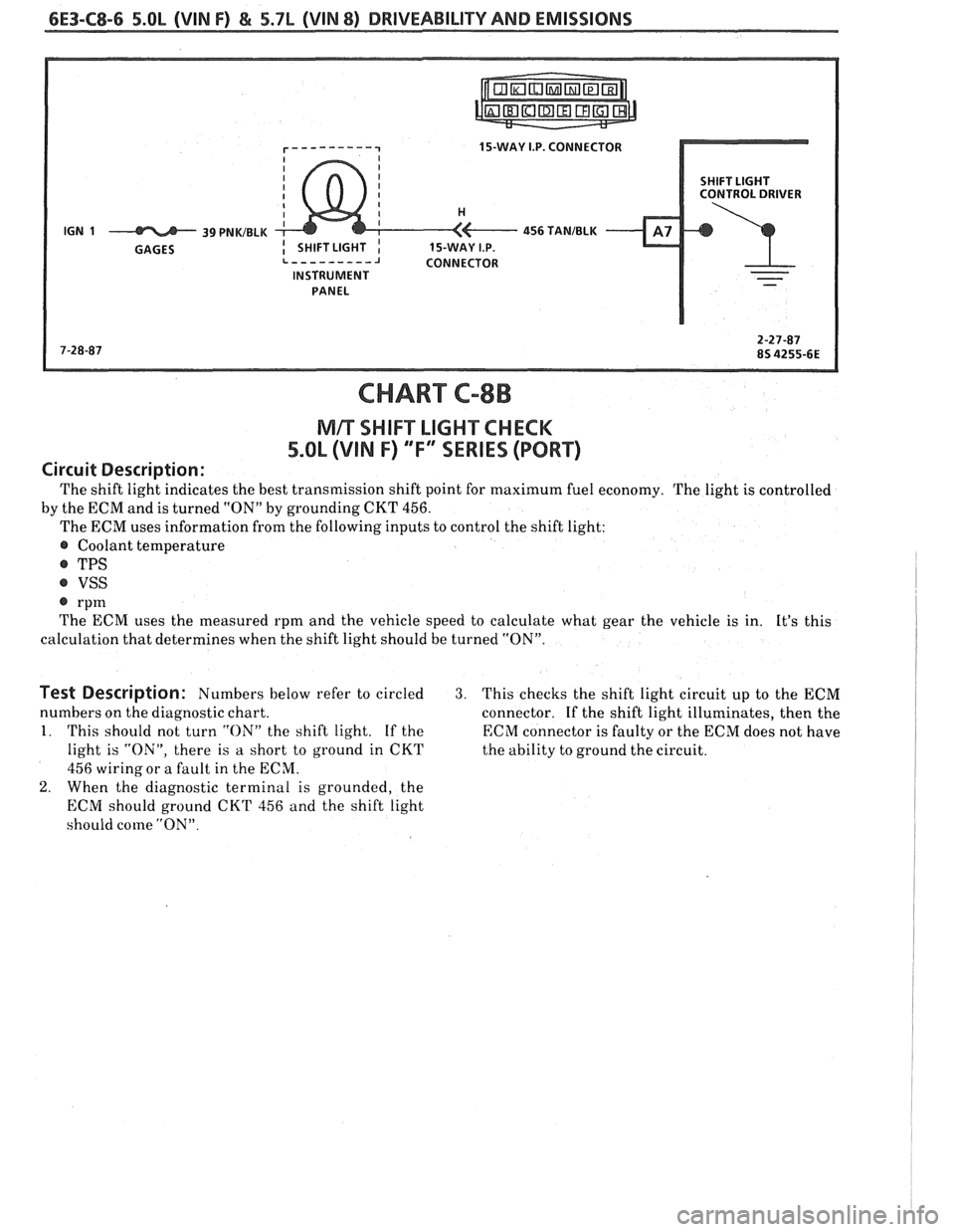
6E3-C8-6 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (WIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
15-WAY I.P. CONNECTOR
SHIFT LIGHT
CONTROL DRIVER
INSTRUMENT PANEL
CHART C-8B
NlR SI-IIFT LIGHT CHECK
5.OL (VIN F) "F" "SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The shift light indicates the best transmission shift point for maximum fuel economy. The light is controlled
by the ECM and is turned
"ON" by grounding CKT 456.
The ECM uses information from the following inputs to control the shift light:
@ Coolant temperature
@ TPS
@ VSS
@ rpm
The ECM uses the measured rpm and the vehicle speed to calculate what gear the vehicle is in. It's this
calculation that determines when the shift light should be turned "ON".
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled 3. This checks the shift light circuit up to the ECM
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
connector.
If the shift light illuminates, then the
1. This should not turn "ON" the shift light. If the ECM connector is faulty or the ECM does not have
light is "ON", there is a short to ground in CKT
the ability to ground the circuit.
456 wiring or a fault in the ECM.
2. When the diagnostic terminal is grounded, the
ECM should ground
CKT 456 and the shift light
should come
"ON".
Page 951 of 1825
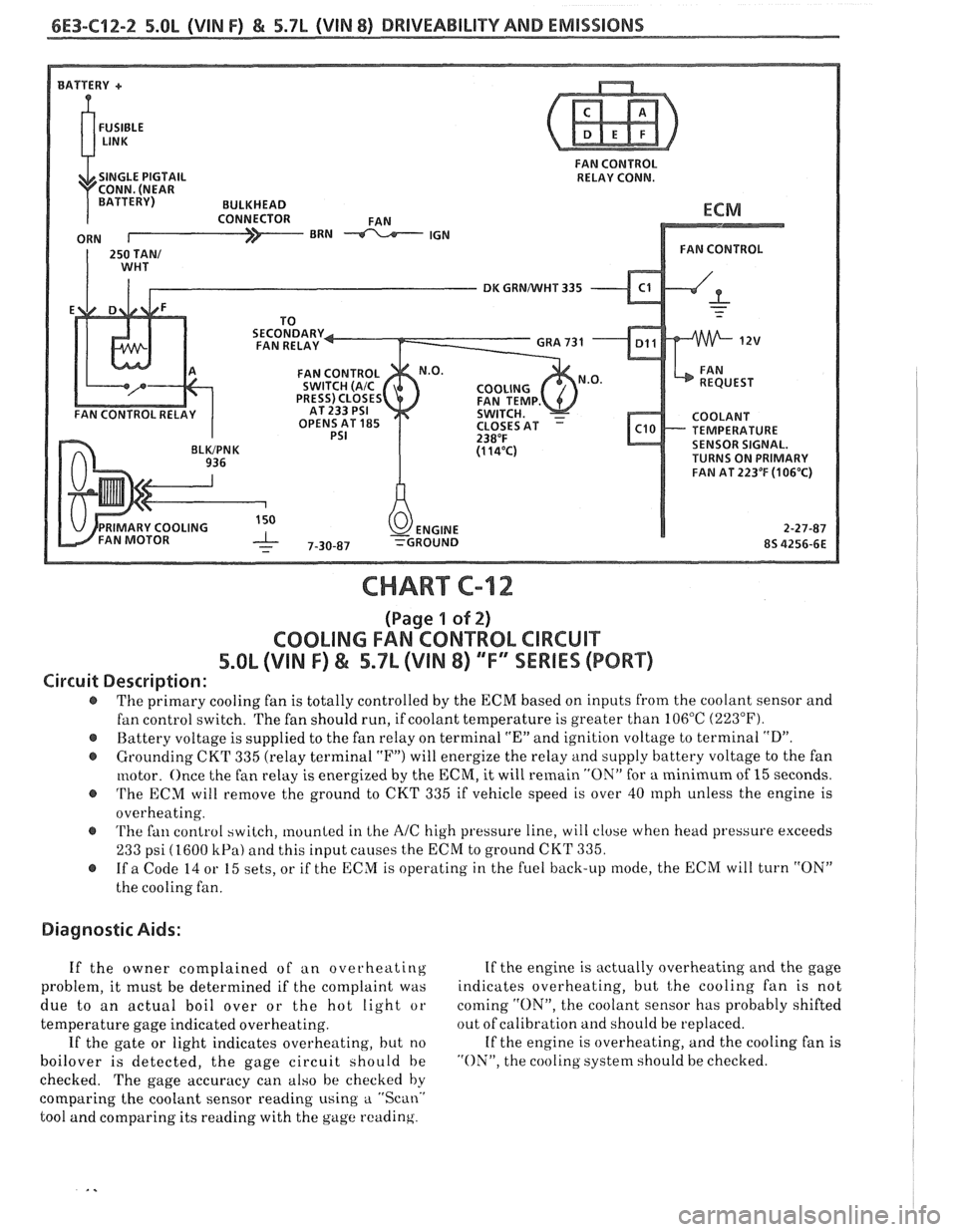
6E3-C12-2 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7b (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
FAN CONTROL
RELAY CONN.
DK GRNNVHT 335
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR SIGNAL.
TURNS ON PRIMARY
FAN AT
223OF (1 06'C)
CHART C-12
(Page 1 of 2)
COOLING FAN CONTROL CIRCUIT
5.8L (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) "F" SSERlES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The primary cooling fan is totally controlled by the ECM based on inputs from the coolant sensor and
fan control switch. The fan should run, if coolant temperature is greater than 106°C
(223°F).
@ Battery voltage is supplied to the fan relay on terminal "En and ignition voltage to terminal "D".
@ Grounding CKT 335 (relay terminal "F") will energize the relay and supply battery voltage to the fan
motor. Once the fan relay is energized by the
ECM, it will remain "ON" for a minimum of 15 seconds.
@ 'I'he ECM will remove the ground to CKT 335 if vehicle speed is over 40 rnph unless the engine is
overheating.
@ 'I'he fan control switch, mounted in Lhe AIC high pressure line, will close when head pressure exceeds
233 psi (1600 kPa) and this input causes the ECM to ground CKT 335.
@ If a Code 14 or 15 sets, or if the ECM is operating in the fuel back-up mode, the ECM will turn "ON"
the cooling fan.
Diagnostic Aids:
If the owner complained of an overheating If
the engine is actually overheating and the gage
problem, it must be determined if the complaint was indicates
overheating, but
t,he cooling fan is not
due to an actual boil over or the hot light or coming
"ON", the
coolant sensor has probably shifted
temperature gage indicated overheating. out
of calibration and should be replaced.
If the gate or light indicates overheating, but no If
the engine is overheating, and the cooling fan is
boilover is detected, the gage circuit should be "ON", the cooling system should be checked.
checked. The gage accuracy can also be checked by
comparing the coolant sensor reading using
a "Scan.'
tool and comparing its reading with the gage reading.
Page 953 of 1825
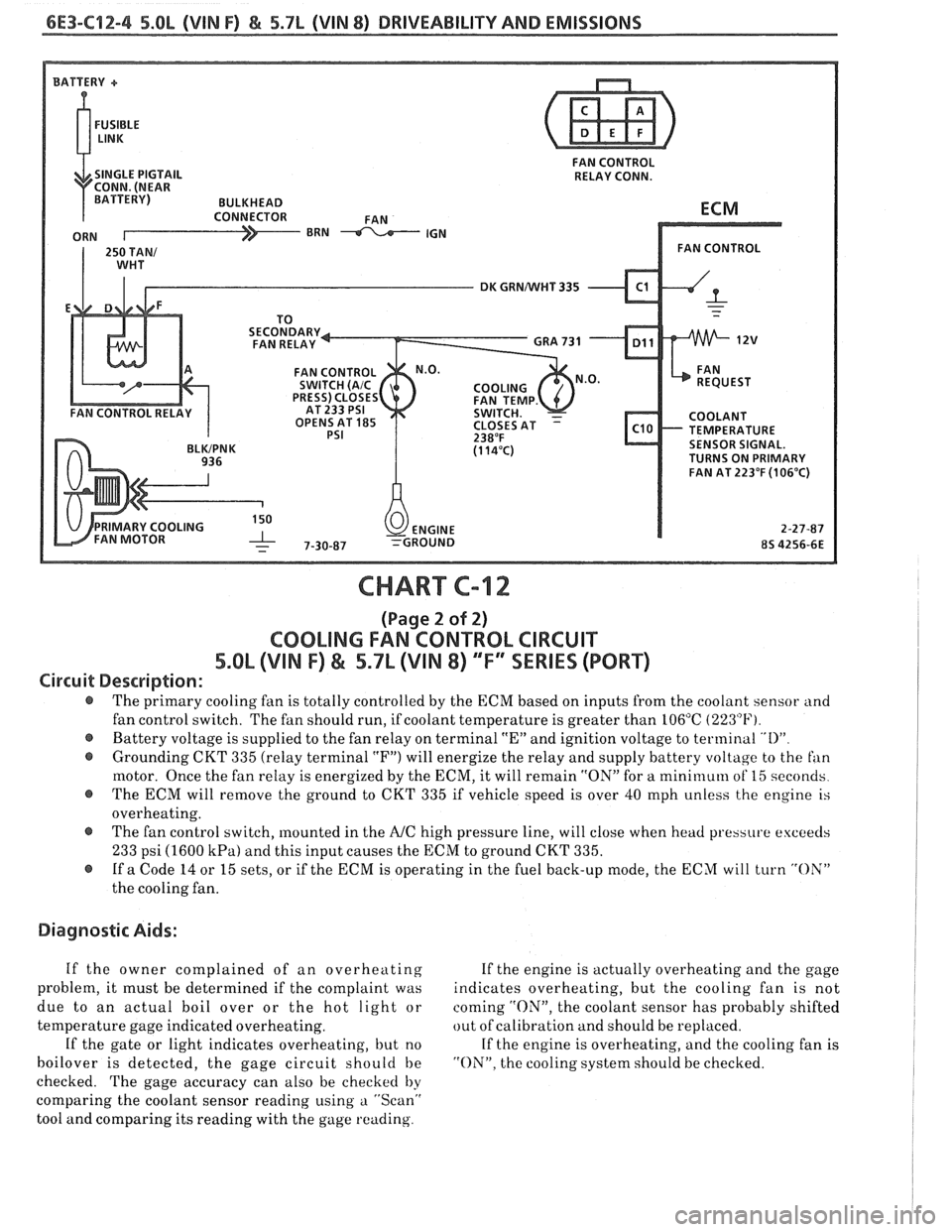
6E3-C12-4 5.8L (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
FAN CONTROL
SINGLE PIGTAIL RELAY CONN.
DK GRNNVHT 335
OPENS AT
185 TEMPERATURE SENSOR SIGNAL.
TURNS ON PRIMARY
FAN AT 223°F
(106°C)
CHART C-12
(Page 2 of 2)
COOLING FAN CONTROL CIRCUIT
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) ""FYSERlES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
@ The primary cooling fan is totally controlled by the ECM based on inputs from the coolant sensor and
fan control switch. The fan should run, if coolant temperature is greater than 106°C
(223°F).
@ Battery voltage is supplied to the fan relay on terminal "En and ignition voltage to terminal "I)"
@ Grounding CKT 335 (relay terminal "F") will energize the relay and supply battery voltage to the fan
motor. Once the fan relay is energized by the ECM, it will remain "ON" for a mini~nuln of 15 seconds
@ The ECM will remove the ground to CKT 335 if vehicle speed is over 40 mph unless the engine is
overheating.
@ The fan control switch, mounted in the A/C high pressure line, will close when head pressure exceeds
233 psi (1600 kPa) and this input causes the ECM to ground CKT 335.
@ If a Code 14 or 15 sets, or if the ECM is operating in the fuel back-up mode, the ECM will turn "OX"
the cooling fan.
Diagnostic Aids:
If the owner complained of an overheating If the engine is actually overheating and the gage
problem, it must be determined if the complaint was indicates overheating, but the cooling fan is not
due to an actual boil over or the hot light or coming
"ON", the coolant sensor has probably shifted
temperature gage indicated overheating. out
of calibration and should be replaced.
If the gate or light indicates overheating, but no If the engine is overheating, and the cooling fan is
boilover is detected, the gage circuit should be "ON". the cooling system should be checked.
checked. The gage accuracy can also be checked
by
comparing the coolant sensor reading using a "Scan"
tool and comparing its reading with the gage reading.
Page 958 of 1825

INDEX
SECTION PAGE
.................... Acceleration Mode C2-2
A/C On Signal
General Description
................. C1-4
......................... Diagnosis C1-5
Air Injection Check Valve
............... C6-4
Air Injection Control (Pedes) Valve
........ C6-1
Air Injection Reaction (A.I.R.) System
General Description
................. C6-1
......................... Diagnosis C6-2
Air Management Check (Pedes)
.......... C6-6
AirPump ........................... C6-2
........................... Service C6-3
...................... ALDL Connector A- 12
Automatic Transmission
Overdrive Switch Adjustment
.......... C8-3
Automatic Transmission Converter Clutch
(TCC) Electrical Diagnosis
.............. C8-6
Backfire
............................ B-5
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
......... C2-3
....................... Before Starting B-I
........................ Burnoff Relay C1-8
......................... Calpac Error 8-60
........................ Canister Hose C3-3
Canister Purge Solenoid
................ C3-3
Chart
A-1 :
.......... No Service Engine Soon Light A-1
0
Chart
A-2:
No ALDL Data. Or Won't Flash Code 12.
Or Service Engine Soon Light On Steady
. . A-1 2
Chart A-3:
Engine Cranks But Won't Run
.......... A-14
Chart A-7:
................ Fuel System Diagnosis A- 18
Chart A-9:
........... Cold Start Valve Circuit Test A-22
Chart
B-1:
Restricted Exhaust System Check ........ B-8
Chart
C-1A:
......... ParkINeutral Switch Diagnosis C1-10
Chart C-2A:
................. Injector Balance Test C2-18
Chart C-2C:
Idle Air Control (IAC) System Check ...... C2-20
SECTION PACE
Chart C-3:
........... Canister Purge Valve Check C3-4
Chart C-4:
................ Ignition System Check C4-4
Chart
6-5:
.......... Electronic Spark Control (ESC) C5-4
Chart C-6:
.............. Air Management Check C6-6
Chart C-7:
Exhaust Gas Recirculation
............. C7-4
Chart
C-8A:
Automatic Transmission Converter Clutch
............................. (TCC) C8-6
Chart C-8B:
Manual Transmission With Overdrive
.... C8-10
Chart C- 12
:
................. Cooling Fan Control C12-2
............................ Chuggle B-3
................... Clear Flood Mode.. C2-2
......................... Closed Loop C2-1
Code12
............................ C4-1
Code13
............................ A-24
Code14
............................ A-26
Code15
............................ A-28
Code21
............................ A-30
Code22
............................ A-32
Code23
............................ A-34
Code24
............................ A-36
Code25
............................ A-38
Code32
............................ A-40
Code33
............................ A-42
Code34
............................ A-44
Code36
............................ A-46
Code41
............................ A-48
Code42
............................ A-50 C4-2
Code43
............................ A-52
Code44
............................ A-54
Code45
............................ A-56
Code46
............................ A-58
Code54
............................ A-60
...................... Codes 51.52. 53 A-62
Cold Start Tube And Valve Assembly
...... C2-7
Cold Start Fuel
lnjection Sw~tch
.................. General Description C2-11
......................... Diagnosis A-22
.................. Component Location A-2
Coolant Temperature Sensor
.................. General Description C1-2
.......................... Diagnosis C1-4
A-26
........................... Service C1-7
Page 959 of 1825

INDEX
SECTION PAGE
Cooling Fan Control
................. General Description C12-1
........................ Diagnosis C12-2
........................... Cuts Out B-5
................... Cylinder Select Error A-48
.................... Deceleration Mode C2-3
......................... Detonation B-4
..................... Dieseling. Run On B-6
............. Distributor Reference Signal C1-4
...................... ECM Terminals A-7
.................. ECM Wiring Diagram A3-A6
EGR Control Valve
................. General Description C7-1
................. Valve Identification C7-2
................... Diagnosis. Service C7-2
A-40
.................. EGR Control Solenoid C7-3
......................... EGR Check C7-4
Electronic Control Module
................. General Description C1-1
......................... Diagnosis C1-4
............................ Service C1-5
..................... Function Check C1-7
Electronic Spark Control (ESC) System
................. General Description C5-1
................... Diagnosis. Service C5-4
Electronic Spark Timing EST
............. A-50
A-52
Engine Cranks But Won't Run
............ A-14
........................ Engine Knock C5-4
.......................... ESC Module C5-2
.......................... ESC Sensor C5-1
.................... ESC System Check C5-4
................... ESTllgnition System C4-1
Evaporative Emission Control System
................. General Description C3-1
.......................... Diagnosis C3-2
Exhaust Emissions Excessive (Odors)
....... B-7
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System
.... C7-1
Exhaust System Check Restricted
......... B-8
Fuel Control System
................. General Description C2- 1
......................... Diagnosis C2-5
..................... Fuel Cutoff Mode C2-3
SECTION PAGE
Fuel Injectors ........................
Fuel Pressure Connection Assy ............
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure ...........
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit .............
Fuel Pump Relay ......................
Fuel Rail
General Description
.................
........................... Service
Fuel System Diagnosis
..................
Fuel System Pressure Test ...............
Fuel Tank Pressure Control Valve .........
.......................... Hard Start B-2
.......... HE1 High Energy Ignition System C4-1
.......................... Hesitation
B-3
............ Idle Air Control System Check C2-20
.................. Idle Air
Control Valve C2-4
......................... Diagnosis C2-5
.................... Ignition System EST C4-1
........ Ignition System Check Integral Coil C4-4
........................ Incorrect Idle B-6
.................. Information Sensors C1.2. 9
.................. Injector
Balance Test C2-18
........................ lntermittents B-2
........................ Knock Sensor C1-3
........................ Lack Of Power B-4
......... Light. Manual Transmission Shift C8-6
.............. Light. Service Engine Soon A-10
MAF Sensor
.................. General Description C1-2
.......................... Diagnosis C1-5
A.42.44. 46
............................ Service C1-8
... Manual Transmission Electrical Diagnosis C8-10
MAT Sensor
.................. General Description C1-2
......................... Diagnosis C1-5
A.34. 38