1988 PONTIAC FIERO light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 865 of 1825

6E3-A-62 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8)
CODE 51
MEM-CAL ERROR
(FAULTY OR INCORRECT MEM-CAL)
IF OK, REPLACE MEMICAL, CLEAR MEMORY, AND RECHECK. IF CODE 51 REAPPEARS, REPLACE ECM.
CLEAR CODES AND CONFIRM "CLOSED LOOP" OPERATION AND NO "SERVICE ENGINE SOON" LIGHT.
CODE 52
CALPAK ERROR
(FAULTY OR INCORRECT CALPAK)
SOCKET. IF OK, REPLACE MEM-CAL, CLEAR MEMORY, AND RECHECK.
CLEAR CODES AND CONFIRM "CLOSED LOOP" OPERATION AND NO "SERVICE ENGINE SOON" LIGHT.
CODE 53
SYSTEM OVER VOLTAGE
CODE 53 WILL SET, IF VOLTAGE AT ECM IGNITION INPUT PIN IS GREATER THA
17.1 VOLTS FOR 2 SECONDS.
Page 866 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) 6E3-B-1
SYMPTOMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
............................................................. Before Starting Page B-I
lntermittents............................................................... PageB-2
...................................................... Hesitation, Sag, Stumble Page 8-3
....................................................... Surges and/or Chuggle Page B-3
.............................................. Lack of Power, Sluggish, or Spongy Page 8-4
Detonation/SparkKnock ...................................................... PageB-4
Cuts Out, Misses
............................................................ Page B-5
Backfire................................................................... PageB-5
.......................................................... Poor Fuel Economy Page 8-6
.......................................................... Dieseling, Run-on,. Page B-6
........................................ Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling Page B-6
............................................. Excessive
Exhaust Emissions or Odors Page B-7
Restricted Exhaust System Check (Chart
B-1) ....................................... Page 8-8
BEFORE STARTING
Before using this section you should have
performed the DIAGNOSTIC CIRCUIT CHECK
and found out that:
1. The ECM and "Service Engine Soon" light are
operating.
2. There are no trouble codes stored, or there is a
trouble code but no "Service Engine Soon" light.
Verify the customer complaint, and locate the
correct SYMPTOM below. Check the items
indicated under that symptom.
If the ENGINE CRANKS BUT WILL NOT
RUN, see CHART A-3.
Several of the symptom procedures below call
for a Careful Visual Check. This check should
include:
@ ECM grounds for being clean and tight
@ Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections, as shown on Emission Control
Information label.
@ Air leaks at throttle body mounting and intake
manifold.
@ Air leaks between MAF sensor and throttle
body.
@ Ignition wires for cracking, hardness, proper
routing, and carbon tracking.
@ Wiring for proper connections, pinches, and cuts.
The importance of this step cannot be stressed
too strongly
- it can lead to correcting a problem
without further checks and can save valuable time.
Page 867 of 1825

6E3-B-2 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Problem may or may not turn "ON" the "Service Engine Soon" light, or store a code.
DO NOT use the Trouble Code Charts in
An intermittent "Service Engine Soon" light
Section A for intermittent problems. The fault must
with no stored code may be caused by:
be present to locate the problem. If a fault is
@ Ignition coil shorted to ground and arcing at
intermittent, use of Trouble Code Charts
may result
spark plug wires or plugs.
in replacement of good parts.
"Service Engine Soon" light wire to
ECM
@ Most intermittent problems are caused by
shorted to ground. (CKT 419).
faulty electrical connections or wiring. Perform
Diagnostic "Test" Terminal wire to ECM,
careful check as described at start of Section
shorted to
ground.(CKT 451)
"B". Check for:
@ ECM power grounds. See ECSI wiring
@ Poor mating of the connector halves, or diagrams.
terminals not fully seated in the connector
@ Loss of trouble code memory. To check,
body (backed out). disconnect TPS and idle engine until "Service
@ Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
Engine Soon" light comes on. Code 22 should be
All connector terminals in problem circuit
stored, and kept in memory when ignition is
should be carefully reformed or replaced to turned "OFF". If not, the ECM is faulty.
insure proper contact tension.
@ Check for an electrical system interference
@ Poor terminal to wire connection. This caused by a defective relay, ECM driven
requires removing the terminal from the
solenoid, or switch. They can cause a sharp
connector body to check. See "Introduction"
electrical surge. Normally, the problem will
to Section
"6E". occur when the faulty component is operated.
@ If a visual check does not find the cause of the @ Check for improper installation of electrical
problem, the car can be driven with a voltmeter
options, such as lights,
%way radios, etc.
connected to
a suspected circuit. A "Scan" tool
EST wires should be kept away from spark plug
can also be used for monitoring input signals to wires, distributor wires, distributor housing,
the ECM to help detect intermittent conditions. coil, and generator. Wire from
ECM to
An abnormal voltage, or "Scan" reading, when distributor
(CKT 453) should be a good
the problem occurs, indicates the problem
may connection.
be in that circuit. If the wiring and connectors
@ Check for open diode across AIC compressor
check OK and a Trouble Code was stored for a
clutch, and for other open diodes (see wiring
circuit having a sensor, except for Codes
43, 44, diagrams).
and 45, substitute a known good sensor and
recheck.
HARD START
Definition: Engine cranks OK, but does not start for a long
time. Does eventually run, or may start but immediately dies.
Perform careful check as described at start of
Section
"B".
@ Make sure driver is using correct starting
procedure.
@ CHECK:
- TPS for sticking or binding or a high TPS
voltage with the throttle closed (should read
less than
.700 volts).
- High resistance in coolant sensor circuit or
sensor itself. See Code 15 chart or with
a
"Scan" tool compare coolant temperature with
ambient temperature on a cold engine.
- Fuel pressure CHART A-7.
- Water contaminated fuel.
- EGR operation. Be sure valve seats properly and
is not staying open. See CHART C-7.
- Both injector fuses (visually inspect).
- Ignition system - Check distributor for:
Proper Output with ST-125.
Worn shaft.
Bare and shorted wires.
Pickup coil resistance and connections.
Loose ignition coil ground.
Moisture in distributor cap.
@ If problem exists in cold weather, check cold start
valve. See CHART A-9.
Page 870 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS S.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) 6E3-B-5
Definition: Steady pulsation or jerking that follows engine
speed, usually more pronounced as engine load increases. The
exhaust has
a steady spitting sound at idle or low speed.
@ Perform careful visual check as described at blink
at any connector, it is a faulty injector drive
start of Section
"B". circuit harness, connector, or terminal.
@ Check for missing cylinder by: @ Perform the Injector Balance Test. See CHART
1. Disconnect IAC valve. Start engine. C-2A.
Remove one spark plug wire at a time
@ CHECK:
using insulated pliers. - Spark plug wires by connecting ohmmeter to
2. If there is an rpm drop on all cylinders ends
of each wire in question. If meter reads over
(equal to within
50 rpm), go to "ROUGH, 30,000
ohms, replace wire(s).
UNSTABLE, OR INCORRECT IDLE, - Fuel System - Plugged fuel filter, water, low
STALLING" symptom. Reconnect IAC pressure. See CHART A-7.
valve.
- Valve timing.
3. If there is no rpm drop on one or more - Secondary voltage using a shop ocilliscope or a
cylinders, or excessive variation in drop, spark tester 5-26792 (ST-125)
or equivalent.
check for spark on the suspected
@ Visually inspect distributor cap and rotor for
cylinder(s) with J 26792 (ST-125) Spark moisture, dust, cracks, burns, etc. Spray cap and
Gap Tool or equivalent. If no spark, see plug wires with fine water mist to check for
Section 6D for Intermittent Operation or shorts.
Miss. If there is spark, remove spark
@ A miss condition can be caused by EM1
plug(s) in these cylinders and check for: (Electromagnetic Interference) on the reference
- Cracks circuit. EM1 can usually be detected by
- Wear monitoring engine rpm with a "Scan" tool. A
- Improper Gap sudden
increase in rpm with little change in
- Burned Electrodes actual engine rpm change, indicates EM1 is
- Heavy Deposits present.
@ Perform compression check on questionable If
the problem exists, check routing of secondary
cylinder(s) found above. If compression is low, wires, check
all distributor ground circuits.
repair as necessary. See Section
"6". @ Remove rocker covers. Check for bent pushrods,
@ Disconnect all injector harness connectors. worn
rocker arms, broken valve springs, worn
Connect
5-34730-2 Injector Test Light or camshaft
lobes. Repair as necessary. See Section
equivalent 6 volt test light between the
"6A".
harness terms, of each injector connector and
note light while cranking. If test light fails to
BACKFIRE
Definition: Fuel ignites in intake manifold, or
in exhaust system, making a loud popping noise.
@ CHECK: - Spark plugs for crossfire also inspect (distributor
- Loose wiring connector or air duct at MAF
cap, spark plug wires, and proper routing of plug
sensor. wires).
- Compression - Look for sticking or leaking - Ignition system for intermittent condition. (See
valves. Section
"6D").
- EGR operation for being open all the time. See - Engine timing - see emission control information
CHART C-7. label.
- EGR gasket for faulty or loose fit. - Perform fuel system diagnosis check, CHART A-
- Valve timing. 7A.
- Output voltage of ignition coil using a shop - Perform injector balance test CI-IART C-2A.
ocilliscope or spark tester 5-26792 (ST-125) or
- A.I.R. system check valves - See Section "C-6".
equivalent.
Page 875 of 1825

6E3-C-1 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
COMPONENT SYSTEMS
Section "C" provides information on the following:
@ General description of components and systems .
@ On-vehicle service .
@ Part names and group numbers .
@ Diagnostic charts . These include a functional check of the system as well as diagnosis of any problem
found in the functional check
.
For locations of components, wiring diagrams, and ECM Terminal End View. refer to the front on the "A"
section of the engine being diagnosed
.
Following are the sub-section identification and the system covered:
............................. @ C1 Electronic Control Module (ECM) and Sensors Page C1-I
@ C2 Fuel Control System ................................................. Page C2-I
.............................. @ C3 Evaporative Emission Control System (EECS) Page C3-1
@ C4 Ignition SystemIEST ................................................ Page C4-1
@ C5 Electronic Spark Control ............................................. Page C5-1
..................................... @ C6 Air Injection Reaction (AIR) System Page C6-1
.................................. @ C7 Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System Page C7-1
.................................... C8 Transmission Converter Clutch (TCC) Page C8-1
................................................. @ C12 Electric Cooling Fan Page C12-1
................................... @ C13 Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) Page C13-1
DIAGNOSTIC CHARTS
The Diagnostic Charts for each system are found after the on-car service and parts information at the back of
each section
. Following are the charts found in this section .
@ Chart C-1A Park Neutral Switch ........................................... Page C1-10
@ Chart C-2A Injector Balance Test .......................................... Page C2-18
@ Chart C-2C Idle Air Control (IAC) System Check ............................... Page C2-20
@ Chart C-3 Canister Purge Valve Check ..................................... Page C3-4
@ Chart C-4 Ignition System Check ......................................... Page C4-4
@ Chart C-5 Electronic Spark Control System Check ............................ Page C5-4
@ Chart C-6 AIR Management Check ....................................... Page C6-6
@ Chart C-7 Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Check ............................. Page C7-4
@ Chart C-8A Automatic
Transmission Converter Clutch (TCC) ...................... Page C8-6
......................... @ Chart C-8B Manual Transmission Shift Light Diagnosis Page C8-10
@ Chart C-12 Cooling Fan Control Circuit Diagnosis ............................. Page C12-2
Page 876 of 1825
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.0L (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) 6E3-C1-1
SECTION C1
ELECTRONlC CONTROL MODULE (ECM) AND SENSORS
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION ................ C1-I
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULE ....... C1-I
PJIEM-CAL......................... C1-I
ECM Function.. .................. C1-I
INFORMATION SENSORS ............. Cl-2
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor . . C1-2
MAF Sensor ..................... C1-2
MAT Sensor .................... C1-2
Oxygen (02) Sensor. ............... C1-3
Throttle Position Sensor ............ C1-3
Knocksensor .................... C1-3
Vehicle Speed Sensor .............. C1-3
...... ParkINeutral Switch (Auto Only) C1-3
NC "ON" Signal .................. C1-4
Distributor Reference Signal ......... C1-4
DIAGNOSIS
......................... C1-4
ECM............................. C1-4
MEM-CAL......................... C1-4
ECMINPUTS....................... C1-4
........ Coolant Temperature Sensor C1-5
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
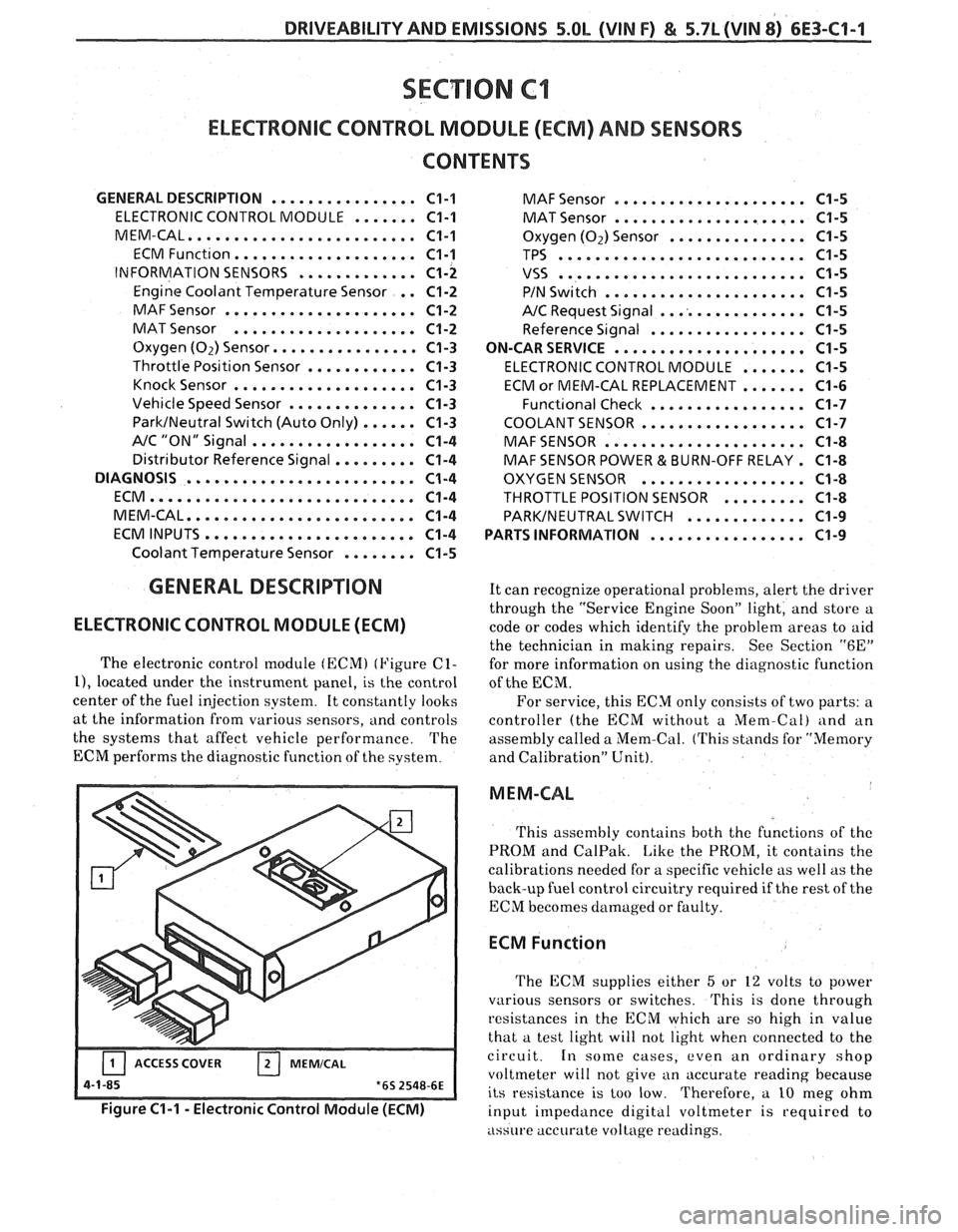
The electronic control [nodule (ECM) (Figure C1-
11, located under the instrument panel, is the control
center of the fuel injection system. It constantly looks
at the information from various sensors,
and controls
the systems that affect vehicle performance. The
ECM performs the diagnostic function of the system.
-- Figure C1-1 - Electronic Control Module (ECM)
MAF Sensor ..................... C1-5
MAT Sensor ..................... C1-5
Oxygen (02) Sensor ............... C1-5
TPS ........................... C1-5
VSS ........................... C1-5
PIN Switch ...................... C1-5
NC Request Signal ................ C1-5
Reference Signal ................. C1-5
ON-CAR SERVICE
..................... C1-5
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULE ....... C1-5
ECM or MEM-CAL REPLACEMENT ....... C1-6
Funct~onal Check ................. C1-7
COOLANT SENSOR .................. C1-7
MAFSENSOR ...................... C1-8
MAF SENSOR POWER & BURN-OFF RELAY . C1-8
OXYGEN SENSOR .................. C1-8
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR ......... C1-8
PARKINEUTRAL SWITCH ............. C1-9
PARTS INFORMATION
................. C1-9
It can recognize operational problems, alert the driver
through the "Service Engine Soon" light, and store a
code or codes which identify the problem areas to aid
the technician in making repairs. See Section
"6E"
for more information on using the diagnostic function
of the
ECM.
For service, this ECM only consists of two parts: a
controller (the ECM without a
Mem-Cal) and an
assembly called a Mem-Cal. (This stands for "Memory
and Calibration" Unit).
M EM-CAL
This assembly contains both thc functions of thc
PROM and CalPak. Like the PROM, it contains the
calibrations needed for a specific vehicle as well as the
back-up fuel control circuitry required if the rest of the
ECM becomes damaged or faulty.
ECM Function
The ECM supplies either 5 or 12 volts to power
various sensors or switches.
This is done through
resistances in the ECM which are so high in value
that a test light will not light when connected to the
circuit.
In some cases, even an ordinary shop
voltmeter will not give an accurate reading because
its resistance is too low. Therefore, a
10 nleg ohm
input impedance digital voltmeter is
requircd to
assure accurate voltage readings.
Page 877 of 1825
6E3-61-2 S.OL (VIM F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
The ECM controls output circuits such as the
injector, IAC, cooling fan relay, etc. by controlling the
ground circuit through transistors in the ECM.
INFORMATION SENSORS
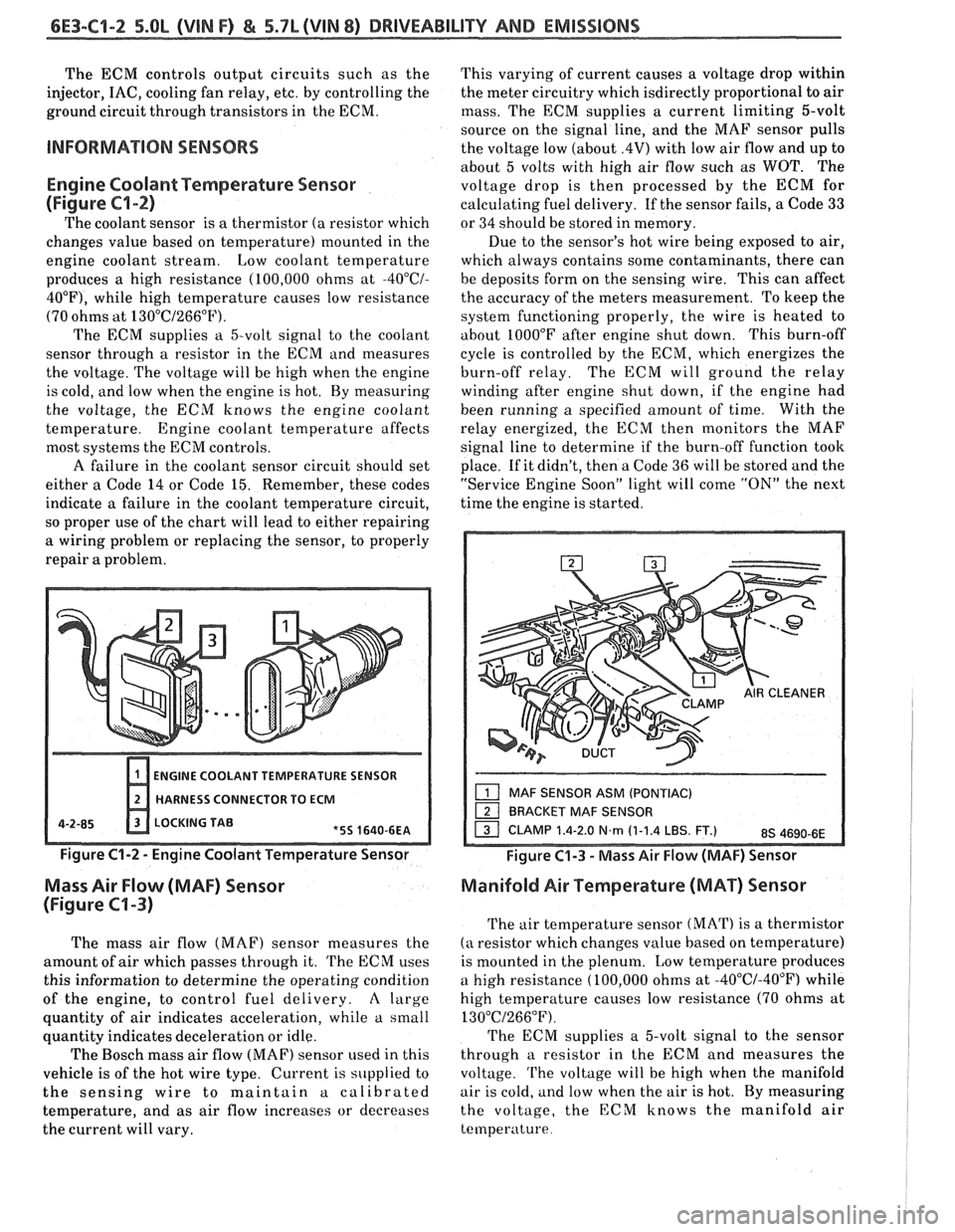
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
(Figure
Cl-2)
The coolant sensor is a thermistor (a resistor which
changes value based on temperature) mounted in the
engine coolant stream. Low coolant temperature
produces a high resistance (100,000 ohms at
-4O0C/-
40°F), while high temperature causes low resistance
(70 ohms at
130°C/266"F).
The ECM supplies a 5-volt signal to the coolant
sensor through
a resistor in the ECM and measures
the voltage. The voltage will be high when the engine
is cold, and low when the engine is hot. By measuring
the voltage, the ECM knows the engine coolant
temperature. Engine coolant temperature affects
most systems the
ECM controls.
A failure in the coolant sensor circuit should set
either a Code 14 or Code
15. Remember, these codes
indicate
a failure in the coolant temperature circuit,
so proper use of the chart will lead to either repairing
a wiring problem or replacing the sensor, to properly
repair
a problem.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
HARNESS CONNECTOR TO
ECM
4-2-85 LOCKING TAE
Figure C1-2 - Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
(Figure
C1-3)
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor measures the
amount of air which passes through it.
'l'he ECM uses
this information to determine the operating condition
of the engine, to control fuel delivery.
A large
quantity of air indicates acceleration, while a small
quantity indicates deceleration or idle.
The Bosch mass air flow
(MAF) sensor used in this
vehicle is of the hot wire type. Current is supplied to
the sensing wire to maintain a calibrated
temperature, and as air flow increases or decreases
the current will vary. This varying
of current causes a voltage drop within
the meter circuitry which isdirectly proportional to air
mass. The ECM supplies a current limiting 5-volt
source on the signal line, and the MAF sensor pulls
the voltage low (about
.4V) with low air flow and up to
about 5 volts with high air flow such as
WOT. The
voltage drop is then processed by the ECM for
calculating fuel delivery. If the sensor fails, a Code 33
or 34 should be stored in memory.
Due to the sensor's hot wire being exposed to air,
which always contains some contaminants, there can
be deposits form on the sensing wire. This can affect
the accuracy of the meters measurement. To keep the
system functioning properly, the wire is heated to
about
1000°F after engine shut down. This burn-off
cycle is controlled by the ECM, which energizes the
burn-off relay. The ECM will ground the relay
winding after engine shut down, if the engine had
been running a specified amount of time. With the
relay energized, the ECM then monitors the MAF
signal line to determine if the burn-off function took
place. If it didn't, then a Code 36 will be stored and the
"Service Engine Soon" light will come
"ON" the next
time the engine is started.
Figure C1-3 - Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
Manifold Air Temperature (MAT) Sensor
The air temperature sensor (MAT) is a thermistor
(a resistor which changes value based on temperature)
is mounted in the plenum.
Low temperature produces
a high resistance (100,000 ohms at
-40°C/-40°F) while
high temperature causes low resistance (70 ohms at
130°C/266"F).
The ECM supplies a 5-volt signal to the sensor
through a resistor in the ECM and measures the
voltage. 'l'he voltage will be high when the manifold
air is cold, and low when the air is hot. By measuring
the voltage, the ECM knows the manifold air
temperature
Page 879 of 1825

6E3-C1-4 5.0L (VIN F) & 5.7L(VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
See Section "8A" for more information on the PIN
switch, which is part of the neutrallstart and backup
light switch assembly.
NC "ON" Signal
This signal tells the ECM that the NC selector
switch is turned "ON", and that the pressure cycling
switch is closed. The
ECM uses this to adjust the idle
speed when the air conditioning is working.
[f this signal is not available to the ECM, idle may
be rough, especially when the NC compressor cycles.
The voltage at ECM terminal "B8" should equal
battery voltage on a
C60 system and about 5 volts on a
C68 option, when
NC is requested and the pressure
cycling switch is closed.
Distributor Reference Signal
The distributor sends a signal to the ECM to tell it
both engine rpm and crankshaft position. See ignition
system Section
"C4" for further information.
DIAGNOSIS
To read the codes, use a "Scan" tool or ground the
diagnostic terminal with the engine not running and
the ignition "ON". The "Service Engine Soon" light
will flash Code 12 three times and then flash each code
stored in memory three times. All codes stored in
memory would have been read when Code 12 was
flashed again. No new codes can be stored when in the
diagnostics mode (diagnostics lead grounded). This
eliminates confusion while the system is being worked
on.
To clear the codes from memory:
@ Ignition "OFF".
@ Disconnect battery pigtail, located near the
battery, for 30 seconds.
Since the ECM can have a failure which may
affect only one circuit, following the diagnostic
procedures in this section will determine which circuit
has a problem and where it is.
If a diagnostic chart indicates that the
ECM
connections or ECM is the cause of a problem,and the
ECM is replaced, but does not correct the problem, one
of the following may be the reason:
-
@ There is a problem with the ECM terminal
connections.
- The diagnostic chart will say ECM
connections or ECM. The terminals may have to
be removed from the connector in order to check
them properly.
@ The ECM, or Mem-Cal is not correct for the
application.
- The incorrect components may cause
a malfunction and
may or may not set u code.
@ The problem is intermittent. - 'l'his means that the
problem is not present at the time the system is
being checked. In
this case, refer to the "Symptoms" portion
of the
manual and make a careful physical inspection
of
all portions of the system involved.
@ Shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness. - Solenoids
and relays are turned
"ON" and "OFF" by the
ECM, using internal electronic switches called
"Drivers".
A shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness in a
GMP4 computer will not damage the ECM,
but will cause the circuit and controlled
component to be inoperative. When the
circuit fault is not present or has been
repaired, the
"Quad-Driver" will again
operate in a normal manner due to it's fault
protected design.
If a fault has been repaired
in a circuit controlled by a "Quad-Driver",
the original ECM should be reinstalled and
the circuit checked for proper operation.
ECM replacement will
not be necessary if the
repaired circuit or component now operates
correctly.
534636 or BT 8405 testers or equivalent provide a
fast, accurate means of checking for a shorted coil
or a short to battery voltage.
@ The Mem-Cal may be faulty. - Although these
rarely fail, it operates as part of the ECM.
Therefore, it could be the cause
of the problem.
Substitute a known good Mem-Cal.
@ The replacement ECM may be faulty - After the
ECM is replaced, the system should be rechecked
for proper operation. If the diagnostic chart again
indicates the ECM is the problem, substitute a
known good ECM. Although this is a rare
condition, it could happen.
ECM
A faulty ECM will be determined in the diagnostic
charts.
MEM-CAL
An incorrect or faulty Mem-Cal, which is part of
the ECM, may set a Code 41 or 52. Also, be sure Mem-
Cal is fully seated and latched in the socket.
ECM INPUTS
A11 of the sensors and input switches can be
diagnosed by the use of
a "Scan" tool. Following is a
short clescription of how the sensors and switches can
he diagnosed
by the use of a "Scan" tool. The "Scan"
can also be used to compare the values for a normal
running engine with the engine you're diagnosing.