1988 PONTIAC FIERO air conditioning
[x] Cancel search: air conditioningPage 2 of 1825

1988
SER
This manual applies to the 1988 Pontiac Firebird Models.
It contains the latest product information available at the
time of publication approval. lnformation pertaining to
the operation of the vehicle is contained in the Owner's
Manual which accompanies each vehicle. The right is
reserved to make changes at any time without notice.
Any references to brand names in this manual is intended
merely as an example of the types of
lubricant% tools,
materials, etc, recommended for use in servicing 1988
Pontiac Models. In all cases, an equivalent may be used.
PONTIAC DIVISION
GENERAL
MOTORS CORPORATION
PONTIAC, MICHIGAN 48053
1987 General Motors Corp. All Rights Reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in any
retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means,
including but not limited to electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written
permission of General Motors Corp. This includes all text,
illustrations, tables and charts.
S-881 OF 9-87 Printed in Canada
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION NAME
GENERAL INFORMATION
OA. General lnformation
OB. Maintenance & Lubrication
1 SECT.
HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
1A. Heating and Ventilation
1 B. Air Conditioning
1D1. R-4 AIC Com~ressor Overhaul
FRAME AND BUMPERS
2B. Bumpers 2C. Chassis Sheet Metal
STEERING, SUSPENSION, WHEELS
AND TIRES
3. Diagnosis
3A. Wheel Alignment
3B5. Steering Wheels and Columns 3B6. Steering Linkage 3B7. Power Steering Gear and Pump
3C. Front Suspension
3D. Rear Suspension
3E. Tires and Wheels
FINAL DRIVE
4A. Propeller Shaft
4B. Rear Axle
4B1. Bora-Warner Axle
BRAKES 5. Brakes 5A3. Comoosite Master Cvlinder 5B1. Disc r rake Caliper ~ssembly - 300013100 Series 5B6. Disc Brake Caliper Assembly - 3548
Series
5C3. Direct Torque Drum Brake Assembly 5D2. Power Head Assembly - Tandem Diaohraam 5F. ~~ecifications and Special Tools
ENGINE 6. Engine General lnformation 6A2. 2.8L 6A3. 5.OL & 5.7L 6B. Engine Cooling
6C. En~ine Fuel
6D. ~ngine Electrical 6D1. Battery 6D2. Cranking System 6D3. Charging System 6D4. Ignition System 6D5. Engine Wiring
6E. Driveabilitv and Emissions
6E2. ~missions' 6E3. Emissions - PFI
6F. Engine Exhaust
TRANSMISSION 7A. Automatic Transmission - General
lnformation
7A1. Automatic Transmission - On-Car
Service
700R4. Automatic Transmission Hydraulic Diagnosis
700R4. Automatic Transmission Unit Repair
76. 5-Speed Manual Transmission
7C. Clutch
CHASSIS ELECTRICAL 8A. Electrical Diagnosis
8B. Lighting and Horns
8C. Instrument
Panel, Gages
& Console
8E. Windshield Wiper &Washer System
ACCESSORIES 9A. Radio Systems and Antennas 9B. Cruise Control 9G. Miscellaneous Accessories
I BODY SERVICE MANUAL END
OF
MANUAL
Page 16 of 1825

- -
GENERAL INFORMATION OA-13
LIST OF AUTOMOTIVE ABBREVIATIONS
WHICH MAY
BE USED IN THIS MANUAL
A-6 - Axial 6 Cyl. A C Compressor AIC - Air Conditioning
ACC - Auto'matic Climate Control
EMF
- Electromotive Force PAIR - Pulse Air Injection Reaction System
EMR - Electronic Module Retard
P B - Power Brakes
EOS - Exhaust Oxygen Sensor
PCV - Positive Crankcase Ventilation
ESC - Electronic Spark Control
PECV - Power Enrichment Control Valve
APT
- Adjustable Part Throttle
AT - Automatic Transmission
ATC - Automatic Temperature Control
ATDC
- After Top Dead Center
FMVSS
- Federal Motor Vehicle Safety BAR0 - Barometric Absolute Pressure Sensor
Ft. Lb. - Foot Pounds (Torque)
Bat. + - Positive Terminal FWD - Front Wheel Drive
- Four Wheel Drive
BHP - Brake Horsepower 4 x 4 - Four Wheel Drive
BP - Back Pressure
BTDC - Before Top Dead Center
HD - Heavy Duty HE1 - High Energy Ignition
Cat. Conv. - Catalytic Converter
CC - Catalytic Converter
- Cubic Centimeter - Converter Clutch
CCC - Computer Command Control
HVM
- Heater-Vent-Module
IAC
- ldle Air Control CCOT - Cycling Clutch (Orifice) Tube IC - Integrated Circuit CCP - Controlled Canister Purge
ID - Identification
C.E. - Check Engine - Inside Diameter
CEAB - Cold Engine Airbleed ILC - Idle Load Compensator
CEMF - Counter Electromotive Force I/P - Instrument Panel
CID - Cubic Inch Displacement ISC - Idle Speed Control CLOOp - Closed Loop
CLCC - Closed Loop Carburetor Control km - Kilometers
CP
- Canister Purge kmiL - Kilometers Liter (mpg) Cu. In. - Cubic Inch kPa - Kilopascals
CV - Constant Velocity
Cyl.
- Cylinder(s)
L-4 - Four Cylinder In-Line (Engine)
DBB - Dual Bed Bead L-6 - Six Cylinder In-Line (Engine)
DBM - Dual Bed Monolith
LF - Left Front DEFl - Digital Electronic Fuel Injection LR - Left Rear DFI - Digital Fuel Injection
Diff. - Differential Man. Vac. - Manifold Vacuum Distr. - Distributor MAP - Manifold Absolute Pressure
EAC
- Electric Air Control Valve
EAS - Electric Air Switching Valve MPG - Miles Per Gallon
ECC - Electronic Comfort Control
MPH - Miles Per Hour
ECM - Electronic Control Module MT - Manual Transmission
N.m - Newton Metres (Torque)
Emission Control
Fig. 014-15 -- Common Abbreviations
Page 21 of 1825

OB-4 MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION
Tire and wheel operation - Be alert to a vibra-
tion of the steering wheel or seat at normal highway
speeds. This may mean a wheel balance is needed. Also, a
pull right or left on a straight, level road may show the
need for
a tire pressure adjustment or wheel alignment.
Steering system operation - Be alert to
changes in steering action. An inspection is needed when
the steering wheel is harder to turn or has too much free
play or if unusual sounds are noted when turning or
parking.
Headlight aim operation - Take note of light
pattern occasionally. If beam aim doesn't look right,
headlights should be adjusted.
AT EACH FUEL FILL
Engine oil level check - Check engine oil level
and add if necessary. See your Owner's
Manual for further
details.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Engine coolant level and condition - Check
engine coolant level in coolant reservoir tank and add if
necessary. Replace if dirty or rusty. See your Owner's
Manual for further details.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Windshield washer fluid level check -- Check
washer fluid level in container and add if necessary.
Hood latch operation - When opening hood on
cars equipped with hoods that open from the front, note
the operation of secondary latch. It should keep hood from
opening all the way when primary latch is released. Make
sure that hood closes firmly.
AT LEAST MONTI-ILY
Tire and wheel inspection and pressure
check--
Check tires for abnormal wear or damage. Also,
check for damaged wheels. Keep pressures as shown on
Tire Placard on the driver's door (include spare unless it is
a stowaway). Pressure should b\: checked when tires are
"cold". See "Tires" in Owner's Manual for further
infomation.
Light operation check - Check operation of
license plate light, side-marker lights, headlights includ-
ing high beams, parking lights, taillights, brake lights.
turn signals, backup lights, instrument panel and interior
lights and hazard warning flashers.
Fluid leak check - After the car has been parked
for a while, inspect the surface beneath the car for water,
oil, fuel or other fluids. Water dripping from the air
conditioning system after use is normal. If you notice fuel
leaks or fumes, the cause should be found and corrected at
once.
AT LEAST TWICE A YEAR (FOR EXAMPLE,
EVERY SPRING AND FALL)
Power steering pump fluid level check --
Check power steering pump fluid level in accordance with
Owner's Manual instructions and keep at proper level.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Brake master cylinder reservoir fluid level
check ---- Check fluid and keep at proper level. Note: It is
normal for the brake fluid level to go down slightly as the
brake pads wear
- so be sure to keep reservoir filled.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have
it inspected and repaired at once.
Clutch system service --- manual transmis-
sionltransaxle --- For cars equipped with hydraulic
clutch system, check the reservoir fluid level and add fluid
as required. All others, check clutch pedal free travel and
adjust as necessary. See your Owner's Manual for further
details.
~
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Weatherstrip Lubrication - Clean surface and
then apply a thin film of silicone grease with a clean cloth.
EACH TIME OIL IS CHANGED
Automatic and manual transmissionltrans-
axle fluid level check - Check transmission/transaxle
fluid level and add as required. (Corvette only) if equipped
with manual transmission
- check fluid in the overdrive
unit and add as required.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have
it inspected and repaired at once.
Brake systems inspection - For convenience,
the following should be done when wheels are removed
for rotation: Inspect lines and hoses for proper hookup,
binding, leaks, cracks, chafing, etc. Inspect disc brake
pads for wear and rotors for surface condition. Also in-
spect drum brake linings for wear and cracks. Inspect
other brake parts, including drums, wheel cylinders, park-
ing brake, etc. at the same time. Check parking brake
adjustment.
INSPECT BRAKES MORE OFTEN IF DRIVING
HABITS OR CONDITIONS RESULT IN FREQUENT
BRAKING.
Steering, suspension and front drive axle
boot and seal inspection
- Inspect front and rear
suspension and steering system for damaged, loose or
missing parts, signs of wear or lack of lubrication. Inspect
power steering lines and hoses for proper hookup, bind-
ing, leaks, cracks, chafing, etc. (On cars equipped with
manual steering gear, check for seal leakage.) On
front-
wheel-drive cars, clean then inspect drive axle boot seals
for damage, tears or leakage. Replace seals if necessary.
Exhaust system inspection - Inspect complete
system. Inspect body near the exhaust system. Look for
broken, damaged, missing or out-of-position parts as well
as open seams, holes, loose connections or other condi-
tions which could cause a heat buildup in the tloor pan or
could let exhaust fumes seep into the trunk or passenger
compartment.
Page 22 of 1825

MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION OB-5
Throttle linkage inspection -- Inspect for inter-
ference, binding, damaged or missing parts.
Engine drive belts inspection - Inspect all
belts for cracks, fraying and wear. Adjust or replace as
needed.
Rear axle service (if equipped) - Check gear
lubricant level and add if needed. For cars equipped with a
limited slip rear axle, fluid does not require changing
(except Caprice and Corvette
- change fluid and required
additive at first
7,500 miles (12 500 km). See your
Owner's Manual or "Recommended Fluids
& Lubricants
Chart" in this section.
IF YOU USE YOUR GAR TO PULL A TRAILER,
CHANGE GEAR LUBRICANT EVERY 7,500 MILES
(12 500 KM).
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Power antenna - Clean and then lubricate power
antenna mast. The proper lubricant as shown in Figure
OB-2 should be used.
AT LEAST ONCE A YEAR
Lap and shoulder belts condition and opera-
tion
- Inspect belt system, including webbing, buckles,
latch plates, retractors, guide loops and anchors.
Moveable head restraint operation - On cars
with moveable restraints, make sure restraints stay in the
desired position. (See adjustment instructions in your
Owner's Manual.)
Seatback latch and recliner operation on
cars equipped
with recliner seat --- Be sure seat-
backs latch on those cars with folding seats using mechan-
ical latches. Make sure the recliner is holding by pushing
and pulling on the top of the
seatback while it is reclined.
See your Owner's Manual for seat operating information.
Spare tire and jack storage- Be alert to rattles
in rear of car. Make sure the space tire, all jacking equip-
ment, any tire inflator and any covers or doors are securely
stowed at all times. Oil jack ratchet or screw mechanism
after each use.
Key lock service - Lubricate key lock cylinder at
least annually.
Body lubrication service - Lubricate all body
door hinges including the tailgate or hatchback lid (if
equipped). Also lubricate the body hood, fuel door and
rear compartment hinges and latches including interior
glove box and counsel doors, and any folding seat
hardware.
"Fansmissionltransaxle neutral or clutch
starl switch operation
CAUnON: Before pedorming the follow-
ing safety switch check, be sure to have
enough room around the car. Then, firmly
apply both the parking brake (see your
Owner's Manual for procedure) and the
regular brakes. Do not use the accelerator pedal.
If the engine
starls, be ready to turn
off the ignition promptly. Take these pre-
cautions because the car could move
without warning and possibly cause per-
sonal injury or properly damage. On auto-
matic transmissionltransaxle cars, try to
starl the engine in each gear. The starler
should crank only in "Park" or "Neutral."
On manual transmissionltransaxle cars,
place the
shiR lever in "Neutral," push the
clutch halfway and try to starl. The starler
should crank only when the clutch is fully
depressed.
Steering column lock operation
- While
parked, try to turn key to "Lock" in each gear range. The
key should turn to "Lock" only when gear is in "Park" on
automatic or "Reverse" on manual
transmissionltransax-
le. On cars with key release lever, try to turn key toULock"
without depressing the lever. The key should turn to
"Lock" only with the key lever depressed. On all vehicles,
the key should come out only in "Lock."
Parking brake and transmissionltransaxle
"Park" mechanism operation
CAUT1ON:Before checking the holding
ability of the parking brake and automatic
transmissionltransaxle "Park" mecha-
nism, park on a fairly steep hill with
enough room for movement in the down-
hill direction. To reduce the risk of person-
al injury or property damage, be prepared
to apply the regular brakes promptly if the
car begins to move.
To check the parking brake, with the engine running and
transmission/transaxle in "Neutral." slowly remove foot
pressure from the regular brake pedal (until the car is held
by only the parking brake).
To check the automatic transmissionltransaxle "Park"
mechanism holding ability, release all brakes after shift-
ing the transmissionltransaxle to "Park."
ljnderbody flushing - At least every spring,
tlush from the underbody with plain water any corrosive
materials used for ice and snow removal and dust control.
Take care to thoroughly clean any areas where mud and
other debris can collect.
Sediment packed in closed areas
of the vehicle should be loosened before being flushed.
Engine cooling system service - Inspect
coolant and freeze protection. If dirty or rusty, drain, flush
and refill with new coolant. Keep coolant
at the proper
mixture as specified in your Owner's Manual. This pro-
vides proper freeze protection. corrosion inhibitor level
and engine operating temperature. Inspect hoses and re-
place if cracked. swollen or deteriorated. Tighten hose
clamps. Clean outside of radiator and air conditioning
condensor. Wash radiator filler cap and neck.
To help
ensure proper operation. a pressure test of both the cooling
system and cap is also recommended. (See maintenance
schedule charts in Figure
OB-l for the recommended
coolant change interval.)
Page 44 of 1825

AIR CONDITIONING 1B-1
SECTION 1B
R COND
When performing air conditioning diagnosis on vehicles equipped with a catalytic converter, it will be necessary to
WARM the engine to a NORMAL operating temperature BEFORE attempting to idle the engine for periods greater
than five
(5) minutes. Once the engine attains normal idle, diagnosis and adjustments can be made.
CONTENTS
.................. General Description .................................. 1B-1 Accumulator Assembly Service .1B-19
.......................... C.C.O.T. A!C System ................................ 1B-1 On-Vehicle Sewice ..... 1B-20
....................................... System Components - Functional ................. 1B-2 Blower Motor .1B-20
..................................... System Components - Control ..................... 1B-3 Hi-Blower Relay 1B-20
...................................... Relays and Switches ................................... 1B-3 Blower Resistor 1B-20
Diagnosis ................................................. 1B-5 Controller, Blower Switch or Vacuum
................................................ Testing the Refrigerant System ...................... 1B-5 Valve .lB-20
Insufficient Cooling "Quick-Check Temperature Control Cable ....................... .1B-20
.................................... Procedure.. ............................................. 1B-5 Vacuum
Harness .lB-20
C.C.O.T. A/C System Diagnostic Control Wiring Harness ........................... .1B-20
..... ................................. Procedure.. ............................................. 1B-8 Heater
Core .. .lB-21
................................ Leak Testing ........................................... 1B-12 Lower Heater Outlet 1B-21
............................... Service Procedures ................................. .1B-12 Heater Module Case .lB-21
.......................... O-Ring Replacement ................................ .1B- 12 Pressure Cycling Switch .1B-21
....................................... Handling Refrigerant- 12 ............................ .1B- 13 Vacuum Tank .lB-21
Discharging, Adding Oil, Evacuating Liquid Line .......................................... .1B-23
and
Charging Procedures - AIC Accumulator ......................................... .1B-23
.................................... Systems .............................................. .1B-14 Evaporator Core .1B-24
In-Line Air Conditioning Evaporator Case .................................... .1B-24
.......................................... Filter
Installation.. .................................. .1B- 18 Compressor .lB-24
.............................................
................ Expansion Tube (Orifice) Service .1 B- 19 Condenser IB-24
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
All engines are equipped with a fixed displace- evaporator temperature. The pressure cycling switch
ment (R-4) air conditioning compressor. This
com- is the freeze protection device in the system and
pressor may cycle on and off under normal air
senses refrigerant pressure on the suction side of the
conditioning demand. system. This switch is located on a standard
Schrader- -
All air conditioning systems that use the fixed
displacement R-4 compressor are referred to as
C. C.O.T. (Cycling Clutch, Orifice Tube) type sys-
tems. This is the same system that has been used on
all General Motors vehicles in the past several years.
The C.C.O.T. NG System
The Cycling Clutch Orifice Tube (C.C.O.T.)
refrigeration system is designed to cycle a compressor
on and off to maintain desired cooling and to prevent
evaporator freeze. Passenger compartment comfort is
maintained by the temperature lever on the controller.
Control of the refrigeration cycle (on and off
operation of the compressor) is done with a switch
which senses low-side pressure as an indicator of type
valve low-side fitting. During air temperatures
over 10°C
(50°F), the equalized pressures within the
charged
A/C system will close the contacts of the
pressure switch. When an air conditioning mode
(max, norm, bi-level, defrost) is selected, electrical
energy is supplied to the compressor clutch coil. AS
the compressor reduces the evaporator pressure
to
approximately 175 kPa (25 psi), the pressure switch
will open, de-energizing the compressor clutch.
As
the system equalizes and the pressure reaches approxl-
mately 315 kPa (46 psi), the pressure switch contacts
close, re-energizing the clutch coil. This cycling
coy
tinues and maintains average evaporator discharge air
temperature at approximately 1°C (33°F). Because of
this cycling, some slight increases and decreases of
engine speedlpower may be noticed under certain con-
ditions. This is normal as the system is designed
to
cycle to maintain desired cooling, thus preventing
evaporator freeze-up.
Page 45 of 1825
18-2 AIR CONDITIONING
SYSTEM GONIPONENE - FFUNCnIONAL
Compressor
All compressors are belt driven from the engine
crankshaft through the compressor clutch pulley. The
compressor pulley rotates without driving the com-
pressor shaft until an electromagnetic clutch coil is
energized. When voltage is applied to energize the
clutch coil, the clutch plate and hub assembly is
drawn rearward toward the pulley. The magnetic
force locks the clutch plate and pulley together as one
unit to drive the compressor shaft.
As the compressor shaft is driven, it compresses
the low-pressure refrigerant vapor from the evaporator
into a high-pressure, high-temperature vapor. Carried
with the refrigerant is the refrigerant oil which is used
to lubricate the compressor. Complete compressor
overhaul procedures can be found in Section
ID of the
General Service Manual.
Pressure Relief Valve
The compressor is equipped with a pressure
relief valve which is placed in the system as a safety
factor. Under certain conditions, the refrigerant on the
discharge side may exceed the designed operating
pressure. To prevent system damage, the valve is
designed to open automatically at approximately
3036
kPa (440 psi). Conditions that might cause this valve
to open (defective high pressure cut-off switch, inop-
erative electric cooling fan, etc.) should be corrected,
and the refrigerant oil and refrigerant should be
replaced as necessary.
A muffler is used on some refrigerant systems to
reduce compressor noises from high or low pressure
vibrations.
Condenser Gore
The condenser assembly in front of the radiator
is made up of coils which carry the refrigerant TO
cooling fins to provide rapid transfer of heat. The air
passing through the condenser cools the high-pressure
refrigerant vapor causing it to condense to a liquid.
Expansion (Orifice) Tube
The plastic expansion tube, with its mesh screen
and orifice, is located in the evaporator inlet pipe at
the liquid line connection. It provides a restriction to
the high-pressure liquid refrigerant in the liquid line,
metering the flow of refrigerant to the evaporator as a
low-pressure liquid. The expansion tube and orifice
are protected from contamination by filter screens on
both inlet and outlet sides. The tube is serviced only
as a replacement assembly.
When the engine is turned "OFF" with the
A/C
system operating, the refrigerant in the system will
flow from the high-pressure side of the expansion tube (orifice) to the low-pressure side until the pressure
is
equalized. This may be detected as a faint sound of
liquid flowing (hissing) for 30 to
60 seconds and is a
normal condition.
Evaporator Gore
The evaporator is a device which cools and
dehumidifies the air before it enters the car. High-
pressure liquid refrigerant flows through the expan-
sion tube (orifice) into the low-pressure area of the
evaporator. The heat in the air passing through the
evaporator core is transferred to the cooler surface of
the core, thereby cooling the air. As the process of
heat transfer from the air to the evaporator core sur-
face is taking place, any moisture (humidity) in the air
condenses on the outside surface of the evaporator
core and is drained off as water.
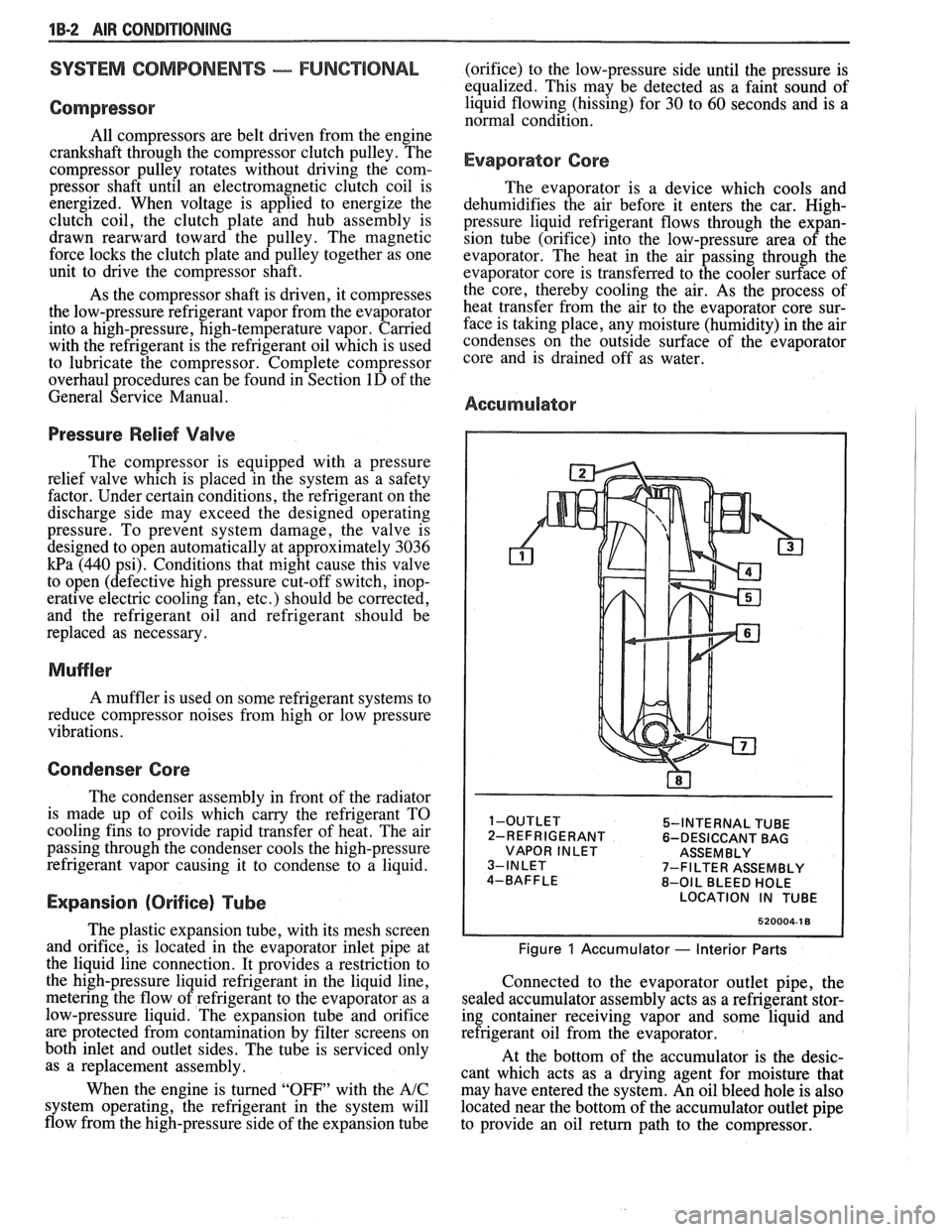
Accumulator
5-INTERNAL TUBE
2-REFRIGERANT 6-DESICCANT BAG
VAPOR INLET ASSEMBLY
7-FILTER ASSEMBLY
8-OIL BLEED HOLE
LOCATION IN TUBE
520004-1 8
Figure 1 Accumulator - Interior Parts
Connected to the evaporator outlet pipe, the
sealed accumulator assembly acts as a refrigerant stor-
ing container receiving vapor and some liquid and
refrigerant oil from the evaporator.
At the bottom of the accumulator is the desic-
cant which acts as a drying agent for moisture that
may have entered the system. An oil bleed hole is also
located near the bottom of the accumulator outlet pipe
to provide an oil return path to the compressor.
Page 46 of 1825

AIR CONDITIONING 1 B-3
A low-side pressure Schrader valve service fit-
ting is located near the top of the accumulator. A
similar Schrader fitting may be provided for mounting
the pressure cycling switch. It is not necessary to dis-
charge the system to replace the switch. The accumu-
lator is serviced only as a replacement assembly.
Heater Core
The heater core heats the air before it enters the
car. Engine coolant is circulated through the core to
heat the outside air passing over the fins of the core.
The core is functional at all times (no water valve) and
may be used to temper conditioned air in
A/C mode,
as well as heat or vent mode.
SYSTEM COMPONENTS --- CON"FOL
Controller
The operation of the A/C system is controlled by
the switches and the lever on the control head. The
compressor clutch and blower are connected electri-
cally to the control head by a wiring harness. The
blower circuit is open in the off mode and air flow is
provided by the four blower speeds available in the
remaining modes. Cooled and dehumidified air is
available in the max, normal, bi-level and defrost
modes.
Temperature is controlled by the position of the
temperature lever on the control head. A cable con-
nects this lever to the temperature door which controls
air flow through the heater core. As the temperature
lever is moved through its range of travel, a sliding
clip on the cable at the temperature valve connection
should assume a position assuring that the temperature
door will seat in both extreme positions. Temperature
door position is independent of mode selection. The
temperature cable attaches to the right side of the air
conditioning module. The temperature door on some
models is controlled electrically, thereby eliminating
the need for the temperature cable.
The electric engine cooling fan on some cars is
not part of the
A/C system; however, the fan is
operational any time the
A/C control is in Max.,
Norm, or Bi-Level modes. Some models provide for
engine cooling fan operation when the controller is in
the defrost mode. This added feature is part of the
A/C
controller function and is aimed at preventing exces-
sive compressor head temperatures. It also allows the
A/C system to function more efficiently. On some
models during road speed (above
35 mph) conditions
when air flow through the condenser coil is adequate
for efficient cooling, the engine cooling fan will be
turned off. The operation of the cooling fan is con-
trolled by the ECM through the cooling fan relay.
Complete wiring diagrams and diagnosis for the
AIC Electrical System are in Section 8A. Section 8A
also contains additional diagnostic information
regarding air flows and vacuum logic.
Vacuum Lines
Vacuum lines are molded to a connector which
is attached to a vacuum control switch on the control
head assembly.
In case of leakage or hose collapse, it will not be
necessary to replace the entire harness assembly.
Replacement can be made by cutting the hose and
inserting a plastic connector. If an entire hose must be
replaced, cut all hoses off at the connector and then
attach hoses directly to the control head vacuum
switch. (NOTE: The Fiero uses an electric motor to
control mode selection. Therefore, it will not have a
vacuum harness.
)
Vacuum Tank
During heavy acceleration, the vacuum supply
from the carburetor drops. A check valve in the vac-
uum tank maintains vacuum so that, under load condi-
tions, vacuum will be available for continuous use.
REWVS AND SWITCHES
High-Pressure Compresssr Gut-OFF Switch
The high-side, high-pressure cut-off switch in
the rear head of the compressor is a protective device
intended to prevent excessive compressor head pres-
sures and reduce the chance of refrigerant escape
through a safety relief valve. Normally closed, this
switch will open the circuit at a high-side pressure of
approximately 2700
kPa (430 psi 9 20 psi) and
reclose the circuit at approximately 1379 kPa (200 psi
9 50 psi).
Lsw-Pressure Cut-On Switch
Compressor protection is provided on some cars
by a low-pressure cut-off switch which will open in
the event of a low-charge condition. This switch can
be located in the liquid line or in the rear head of the
compressor. This switch will also keep the compres-
sor from running during cold weather.
Pressure eyesing Switch
The refrigeration cycle (on and off operation of
the compressor) is controlled by a switch which
senses the low-side pressure as an indicator of evapo-
rator temperature. The pressure cycling switch is the
freeze protection device in the system and senses
refrigerant pressure on the suction side of the system.
This switch is located on a standard Schrader-type
valve low-side fitting. This switch also provides com-
pressor cut-off during cold weather.
Additional compressor protection results from
the operating characteristics of the low-side pressure
cycling system. If a massive discharge occurs or the
orifice tube becomes plugged, low-side pressures
could be insufficient to close the contacts of the pres-
sure switch. In the event of a low charge, insufficient
cooling accompanied by rapid compressor clutch
cycling will be noticed at high air temperatures.
Page 47 of 1825

18-4 AIR CONDITIONING
If replacement of the pressure cycling switch is
necessary, it is important to note that this may be done
without removing the refrigerant charge.
A Schrader-
type valve is located in the pressure switch fitting.
During replacement of the pressure switch, a new
oiled O-ring must be installed and the switch assem-
bled to the specified torque of
6- 13 N*m (5- 10 lb. ft.).
Power Steering Gut-OH, or Anticipate
Switch
Engine idle quality on some cars is maintained
by cutting off the compressor (switch normally
closed) when high power steering loads are imposed.
On other cars the switch (normally open) provides a
signal to the ECM to allow engine control systems to
compensate for high-power steering loads.
Wide-Open Tkroale (WOT) Compressor
Cut-Out
Switch
A switch located on the throttle corltrols of some
carburetor equipped cars opens the circuit to the com-
pressor clutch during full throttle acceleration. The
switch activates a relay that controls the compressor
clutch. During full throttle acceleration
on cars
equipped with TBI or
Em, the TPS sends a signal to
the ECM, thereby controlling the compressor clutch.
Air Conditioning Time Delay Relay
This relay on some cars controls the current to
the entire air conditioning system and provides a short
delay of air conditioning operation upon start-up.
Constant Run Relay
Engine idle quality on some cars is maintained
by a "constant run" system (constant run relay) that
eliminates compressor cycling during engine idle for a
predetermined time after the vehicle has come to rest
from road speed.
If the idle period continues for an
extended time, the
A/C system may return to a con-
ventional C.C.O.T. mode for a short time to prevent
system freeze-up. The
A/C control relay and constant
run relays are both controlled by the Electronic Con-
trol Module (ECM) which determines operating con-
ditions by evaluating input from the distributor
(engine speed), vehicle speed sensor, air sensor and
A/C compressor "on" signal.
5-PRESSURE CYCLING 8-EXPANSION TUBE
SWITCH (ORIFICE)
6-DESSICANT BAG O-LIQUID LINE
7-OIL BLEED HOLE
10-PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
@ ee LOW PRESSURE LIQUID HIGH PRESSURE LIQUID LOW PRESURE VAPOR HIGH PRESSURE VAPOR
Figure 2 A/C System - Typical