1973 DATSUN B110 ECU
[x] Cancel search: ECUPage 49 of 513
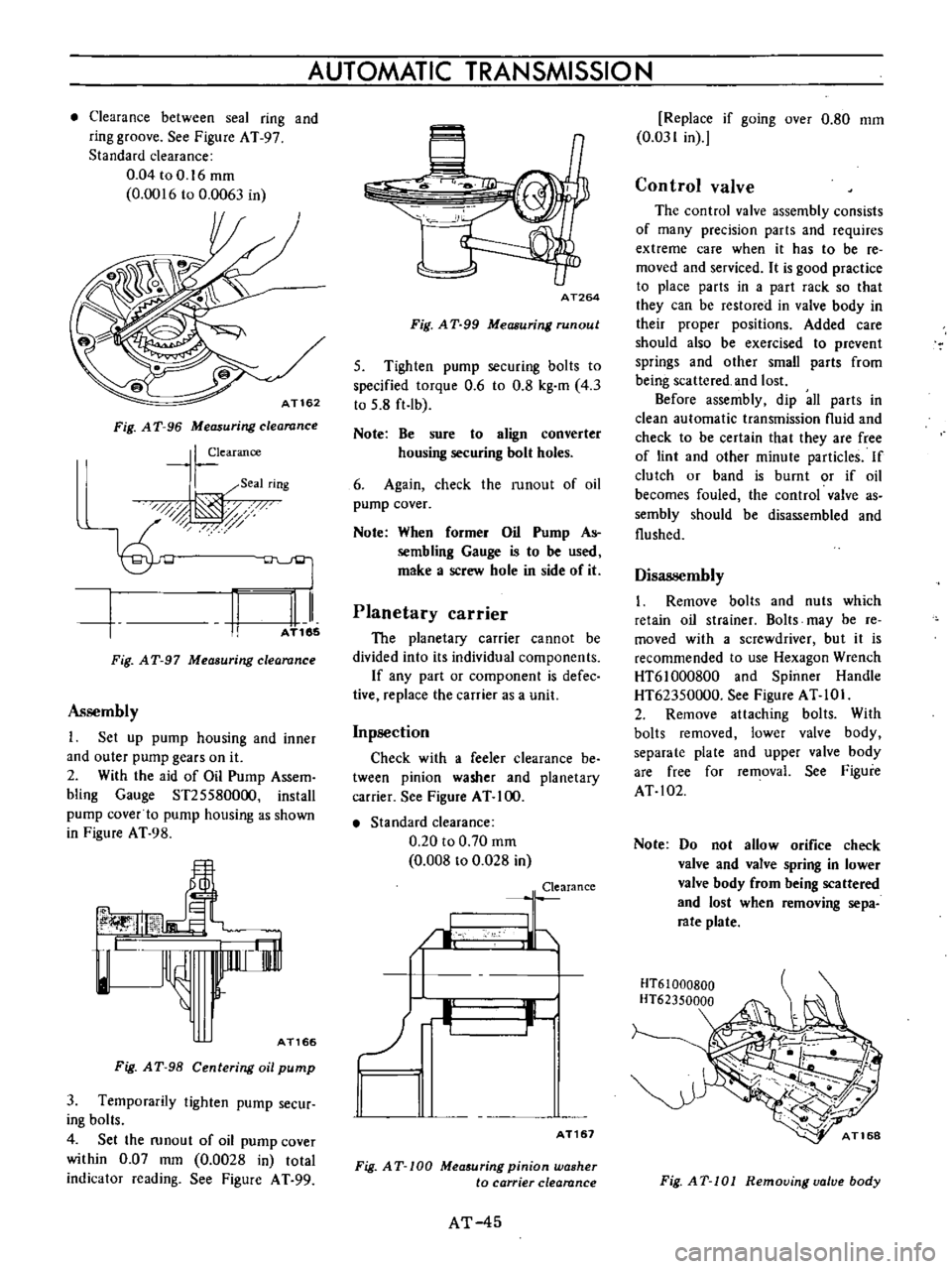
Clearance
between
seal
ring
and
ring
groove
See
Figure
AT
97
Standard
clearance
0
04toO
16mm
0
0016
to
0
0063
in
AT162
Fig
A
T
96
Measuring
clearance
I
earance
I
Seal
rIng
0d
t
AT185
II
Fig
AT
97
Measuring
clearance
Assembly
1
Set
up
pump
housing
and
inner
and
outer
pump
gears
on
it
2
With
the
aid
of
Oil
Pump
Assem
bling
Gauge
ST255800oo
install
pump
cover
to
pump
housing
as
shown
in
Figure
AT
98
lnnrr
i
rnl
l
AT166
Fig
A
T
98
Centering
oil
pump
3
Temporarily
tighten
pump
secur
ing
bolts
4
Set
the
runout
of
oil
pump
cover
within
0
07
mm
0
0028
in
total
indicator
reading
See
Figure
A
T
99
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
AT264
Fig
A
T
99
Measuring
run
out
5
Tighten
pump
securing
bolts
to
specified
torque
0
6
to
0
8
kg
m
4
3
to
5
8
ft
Ib
Note
Be
sure
to
align
converter
housing
securing
bolt
holes
6
Again
check
the
runout
of
oil
pump
cover
Note
When
former
Oil
Pump
As
sembling
Gauge
is
to
be
used
make
a
screw
hole
in
side
of
it
Planetary
carrier
The
planetary
carrier
cannot
be
divided
into
its
individual
components
If
any
part
or
component
is
defec
tive
replace
the
carrier
as
a
unit
Inpsection
Check
with
a
feeler
clearance
be
tween
pinion
washer
and
planetary
carrier
See
Figure
AT
100
Standard
clearance
0
20
to
0
70
mm
0
008
to
0
028
in
Clearance
I
LJ
b
II
I
AT161
Fig
AT
100
Mea
uring
pinion
washer
to
carrier
clearance
AT
45
Replace
if
going
over
0
80
mm
0
031
in
Control
valve
The
control
valve
assembly
consists
of
many
precision
parts
and
requires
extreme
care
when
it
has
to
be
re
moved
and
serviced
It
is
good
practice
to
place
parts
in
a
part
rack
so
that
they
can
be
restored
in
valve
body
in
their
proper
positions
Added
care
should
also
be
exercised
to
prevent
springs
and
other
small
parts
from
being
scattered
and
lost
Before
assembly
dip
all
parts
in
clean
automatic
transmission
nuid
and
check
to
be
certain
that
they
are
free
of
lint
and
other
minute
particles
If
clutch
or
band
is
burnt
or
if
oil
becomes
fouled
the
control
valve
as
sembly
should
be
disassembled
and
flushed
Disassembly
1
Remove
bolts
and
nuts
which
retain
oil
strainer
Bolts
may
be
re
moved
with
a
screwdriver
but
it
is
recommended
to
use
Hexagon
Wrench
HT61000800
and
Spinner
Handle
HT62350000
See
Figure
AT
10
I
2
Remove
attaching
bolts
With
bolts
removed
lower
valve
body
separate
plate
and
upper
valve
body
are
free
for
removal
See
Figure
AT
102
Note
Do
not
allow
orifice
check
valve
and
valve
spring
in
lower
valve
body
from
being
scattered
and
lost
when
removing
sepa
rate
plate
HT61000BOO
HT62350000
Fig
AT
101
Removing
valve
body
Page 55 of 513

c
Inspection
and
adJu
Stmenf
trouble
first
check
the
linhge
f
no
1
i
jI
fect
is
found
in
the
lin1
age
check
of
manu
a
l
liiiJ
i
the
inhibitor
switch
Th
d
1F
aI
S
t
th
I
I
f
e
a
JU
i
J
u
epara
e
e
range
se
eet
ever
rom
Iy
important
ii
s3
ns
etion
of
oil
the
lower
shift
rod
and
turn
the
range
1
level
for
the
automatiC
tran
smission
select
lever
to
N
Therefore
great
care
should
be
exer
Note
In
the
position
N
the
slot
of
cised
because
defective
adjustment
will
the
manual
shaft
is
vertical
result
in
the
breakdown
of
the
trans
By
the
use
of
the
tester
check
the
two
bIack
yellow
BY
wires
from
the
inhibitor
switch
in
the
ranges
N
and
P
and
the
two
red
bIack
RB
wires
in
the
range
R
for
continuity
Turn
range
select
lever
to
both
directions
from
each
lever
set
position
and
check
each
continuity
range
It
is
normal
if
the
electricity
is
on
while
the
lever
is
within
an
angle
of
about
3
0
on
both
sides
from
each
lever
set
line
How
ever
if
its
continuity
range
is
obvi
ously
unequal
on
both
sides
the
adjustment
is
required
f
any
malfunction
is
found
un
screw
the
fastening
nut
of
the
range
selector
lever
and
two
fastening
bolts
of
the
switch
body
and
then
remove
the
machine
screw
under
the
switch
body
Adjust
the
manual
shaft
correct
ly
to
the
position
N
by
means
of
the
selector
lever
When
the
slot
of
the
shaft
becomes
vertical
the
detent
works
to
position
the
shaft
correctly
with
a
click
sound
Move
the
switch
slightly
aside
so
that
the
screw
hole
will
be
aligned
with
the
pin
hole
of
the
internal
rotor
combined
with
the
manual
shaft
and
check
their
alignment
by
inserting
a
1
5
0101
0
0591
in
diameter
pin
into
the
holes
If
the
alignment
is
made
correct
1
5ten
the
switch
body
with
the
bolts
pull
out
the
pin
and
tighten
up
the
screw
again
into
the
hole
and
fasten
the
selector
lever
as
before
Check
over
again
the
continuity
with
the
tester
If
the
malfunction
still
remains
replace
the
inhibitor
switch
mission
Inspection
Pull
the
selector
lever
toward
you
and
turn
it
so
far
as
p
to
1
range
where
clicks
will
be
felt
by
hand
This
is
the
detent
of
manual
valve
in
the
body
and
indicates
the
correct
posi
tion
of
the
lever
Inspect
whether
the
pointer
of
selector
dial
corresponds
to
this
point
and
also
whether
the
lever
comes
in
alignment
with
the
stepping
of
posi
tion
plate
when
it
is
released
Adjustment
This
procedure
can
be
accom
plished
by
referring
to
Removal
and
nstallation
Checking
and
adjusting
inhibitor
switch
The
inhibitor
switch
serves
to
light
the
reverse
lamp
in
the
range
R
of
the
transmission
operation
and
also
to
rotate
the
starter
motor
in
the
ranges
N
and
P
j
r@
I
If
r
f
B
@
I
Jt
@
@
c
v@
i
r
fji
AT109
1
Inhibitor
switch
2
Manual
shaft
3
Washer
4
Nut
5
Manual
plate
Fig
AT
II
0
Con
truction
of
inhibitor
witch
6
Washer
7
Nut
8
Inhibitor
switch
9
Range
select
lever
Check
whether
the
reverse
lamp
and
the
starter
motor
operate
normal
ly
in
these
ranges
If
there
is
any
t
ki
A
mm
ATIC
TRANSMISSION
STALL
TEST
The
purpose
of
this
test
is
to
check
the
transmission
and
engine
for
trou
ble
by
measuring
the
maximwn
num
bers
of
revolutions
of
the
engine
while
vehicle
is
held
in
a
stalled
condition
and
the
carburetor
is
in
full
throttle
operation
with
the
selector
lever
in
AT
51
rang
s
D
2
and
I
respectively
and
by
com
pairing
the
measured
re
sults
with
the
standard
values
Standard
stall
revolution
1
750
to
2
000
rpm
Components
to
be
tested
and
test
items
1
Clutches
brake
and
band
in
trans
mission
for
slipping
2
Torque
converter
for
function
3
Engine
for
overall
property
Stall
test
procedures
Before
testing
check
the
enigne
oil
and
torque
converter
oil
warm
up
the
engine
cooling
water
to
the
suitable
temperature
by
warming
up
ope
ration
at
1
200
rpm
with
the
selector
lever
in
the
range
P
for
several
minutes
and
warm
up
the
torque
converter
oil
to
the
suitable
temperature
60
to
IOOoC
140
to
2120F
1
Mount
the
engine
tachometer
at
a
location
that
allows
good
visibility
from
the
driver
s
seat
and
put
a
mark
on
specified
revolutions
on
the
meter
2
Secure
the
front
and
rear
wheels
completely
with
chocks
and
apply
the
hand
brake
Be
sure
to
depress
the
brake
pedal
firmly
with
the
left
foot
before
depressing
down
the
accelerator
pedal
3
Throw
the
selector
lever
into
the
range
D
4
Slowly
depress
the
accelerator
pedal
down
till
the
throttle
valve
is
fully
opened
Quickly
read
and
record
the
engine
revolution
when
the
engine
begins
to
rotate
steadily
and
then
release
the
accelerator
pedal
5
Turn
the
selector
lever
into
N
and
operate
the
enigne
at
approxi
mately
1
200
rpm
for
more
than
one
minute
to
cool
down
the
torque
con
verter
oil
and
coolant
6
Make
similar
stall
tests
in
the
ranges
2
I
and
R
Note
The
stall
test
operation
as
spec
ified
in
the
item
4
should
be
made
within
five
seconds
If
it
takes
too
long
the
oil
deterio
rates
and
the
clutches
brake
Page 69 of 513
CHASSIS
Mureover
excessive
sleeve
yoke
spline
ta
transmission
main
spline
lash
and
wear
of
both
front
and
rear
universal
joints
will
cause
vibrations
affecting
riding
comfort
REMOVAL
Disconnect
the
flange
yoke
and
the
pinion
flange
by
removing
bolts
at
the
rear
end
of
the
propeller
shaft
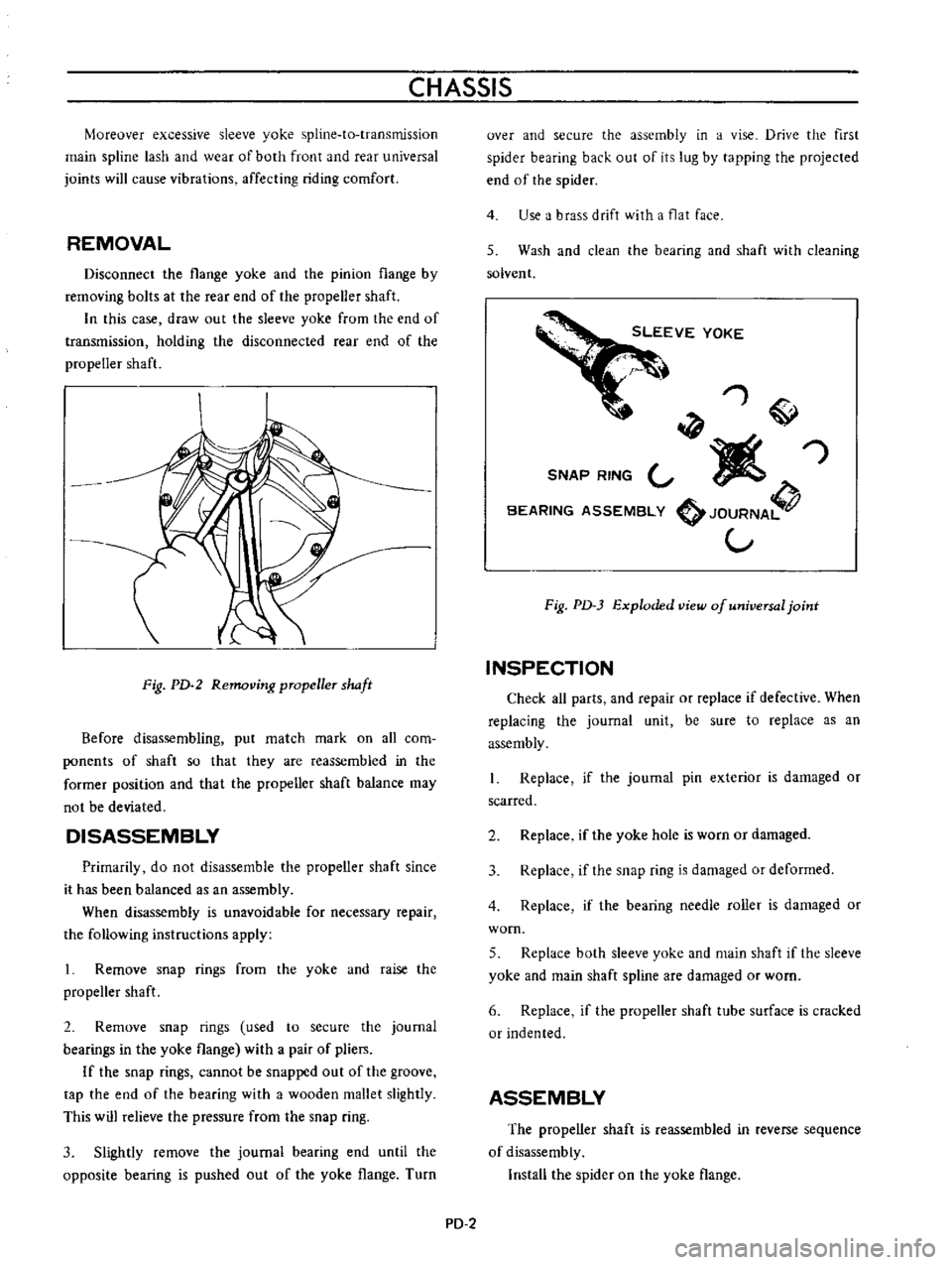
In
this
case
draw
out
the
sleeve
yoke
from
the
end
of
transmission
holding
the
disconnected
rear
end
of
the
propeller
shaft
Fig
PD
2
Removing
pmpeller
shaft
Before
disassembling
put
match
mark
on
all
com
ponents
of
shaft
so
that
they
are
reassembled
in
the
former
position
and
that
the
propeller
shaft
balance
may
not
be
deviated
DISASSEMBLY
Primarily
do
not
disassemble
the
propeller
shaft
since
it
has
been
balanced
as
an
assembly
When
disassembly
is
unavoidable
for
necessary
repair
the
following
instructions
apply
1
Remove
snap
rings
from
the
yoke
and
raise
the
propeller
shaft
2
Remove
snap
rings
used
to
secure
the
journal
bearings
in
the
yoke
flange
with
a
pair
of
pliers
If
the
snap
rings
cannot
be
snapped
out
of
the
groove
tap
the
end
of
the
bearing
with
a
wooden
mallet
slightly
This
will
relieve
the
pressure
from
the
snap
ring
3
Slightly
remove
the
journal
bearing
end
until
the
opposite
bearing
is
pushed
out
of
the
yoke
flange
Turn
over
and
secure
the
assembly
in
a
vise
Drive
the
first
spider
bearing
back
out
of
its
lug
by
tapping
the
projected
end
of
the
spider
4
Use
a
brass
drift
with
a
flat
face
5
Wash
and
clean
the
bearing
and
shaft
with
cleaning
solvent
1
W
SNAP
RING
V
I
1Iiff
BEARING
ASSEMBLY
JOURNA
V
Fig
PD
3
Exploded
view
of
universal
joint
INSPECTION
Check
all
parts
and
repair
or
replace
if
defective
When
replacing
the
journal
unit
be
sure
to
replace
as
an
assembly
Replace
if
the
journal
pin
exterior
is
damaged
or
scarred
2
Replace
if
the
yoke
hole
is
worn
or
damaged
3
Replace
if
the
snap
ring
is
damaged
or
deformed
4
Replace
if
the
bearing
needle
roller
is
damaged
or
worn
5
Replace
both
sleeve
yoke
and
main
shaft
if
the
sleeve
yoke
and
main
shaft
spline
are
damaged
or
worn
6
Replace
if
the
propeller
shaft
tube
surface
is
cracked
or
Indented
ASSEMBLY
The
propeller
shaft
is
reassembled
in
reverse
sequence
of
disassembly
Install
the
spider
on
the
yoke
flange
PD
2
Page 70 of 513
PROPELLER
SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
Insert
the
journal
into
the
yoke
flange
Tap
the
journal
bearing
into
the
yoke
flange
using
a
brass
drift
smaller
than
the
hole
in
the
yoke
Tap
the
other
bearing
into
the
opposite
end
of
the
yoke
flange
until
the
bearing
is
in
line
with
the
snap
ring
grooves
With
a
pair
of
pliers
install
the
snap
rings
on
both
ends
of
the
yoke
flange
Insert
the
flange
assembly
in
the
sleeve
yoke
Place
the
other
yoke
bearing
into
the
opposite
end
of
the
yoke
and
tap
this
bearing
into
the
yoke
until
the
bearing
is
in
line
with
the
snap
ring
grooves
Install
the
snap
rings
on
both
ends
of
the
yoke
When
all
parts
are
assembled
check
the
spider
and
surroundings
for
tightness
When
the
clearance
is
excessive
adjust
with
over
size
snap
rings
as
follows
Snap
ring
over
size
Thickness
Color
mrn
in
identification
I
46
0
0575
White
I
48
0
0583
Yellow
1
50
0
0591
Red
1
52
0
0598
Green
1
54
0
0606
Blue
1
56
0
0614
1
58
0
0622
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
Distance
between
joints
mm
in
Tube
outer
diameter
x
thickness
mm
in
Sleeve
yoke
specification
Outer
dia
x
inner
dia
x
pitch
mm
in
Brown
No
mark
I
189
46
8
68
9
x
1
6
2
713
x
0
0630
Involute
spline
20
x
80
x
I
0
787
x
3
150
x
0
0394
Permissible
unbalance
gr
cm
in
oz
rpm
15
0
2
4
000
Allowable
max
swinging
torque
of
spider
journal
10
9
kg
cm
in
lb
Propeller
shaft
run
out
mm
in
Tightening
torque
of
companion
flange
nuts
kg
m
ft
Ib
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
Condition
Probable
cause
Noise
and
vibration
Distorted
propeller
shaft
Unbalanced
propeller
shaft
Corrective
action
less
than
0
6
0
024
2
0
to
2
7
I4
to
20
Using
exclusively
an
arbor
press
restraighten
If
distortion
is
excessive
replace
propeller
shaft
Check
for
balance
If
unbalance
exceeds
the
limit
replace
it
Recorrect
Replace
the
sleeve
yoke
Replace
the
journal
Replace
with
correct
snap
ring
Retighten
nuts
to
the
specified
torque
Incorrectly
positioned
flange
yoke
Excessive
spline
lash
Worn
or
damaged
journal
Inconect
snap
rings
Loose
nuts
securing
the
flange
yoke
to
the
companion
flange
PD
3
Page 89 of 513
FRONT
AXLE
FRONT
SUSPENSION
FRONT
AXLE
AND
SUSPENSION
ASSEMBLY
Removal
1
Jack
up
the
vehicle
and
support
the
vehicle
with
stands
See
the
Section
GL
2
Remove
the
hub
nuts
and
remOve
the
wheel
3
Remove
the
splash
board
4
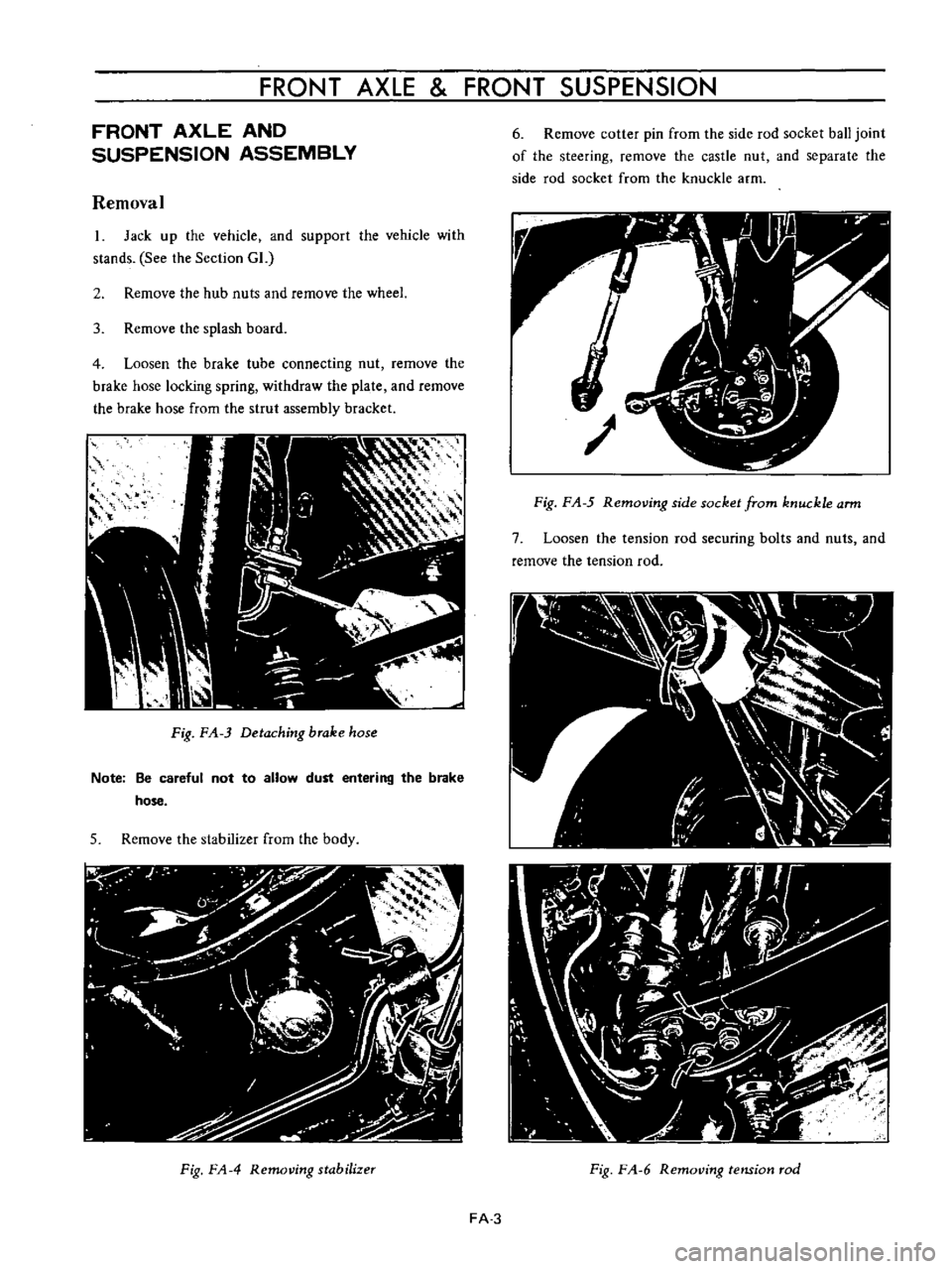
Loosen
the
brake
tube
connecting
nut
remove
the
brake
hose
locking
spring
withdraw
the
plate
and
remOve
the
brake
hose
from
the
strul
assembly
bracket
Fig
FA
3
Detaching
brake
hose
Note
Be
careful
not
to
allow
dust
entering
the
brake
hose
5
Remove
the
stabilizer
from
the
body
Fig
FA
4
Removing
stabilizer
6
Remove
cotter
pin
from
the
side
rod
socket
ball
joint
of
the
steering
remove
the
castle
nut
and
separate
the
side
rod
socket
from
the
knuckle
arm
Fig
F
A
5
Removing
side
socket
from
knuckle
arm
7
Loosen
the
tension
rod
securing
bolts
and
nuts
and
remove
the
tension
rod
Fig
F
A
6
RemotJing
tension
rod
FA
3
Page 91 of 513
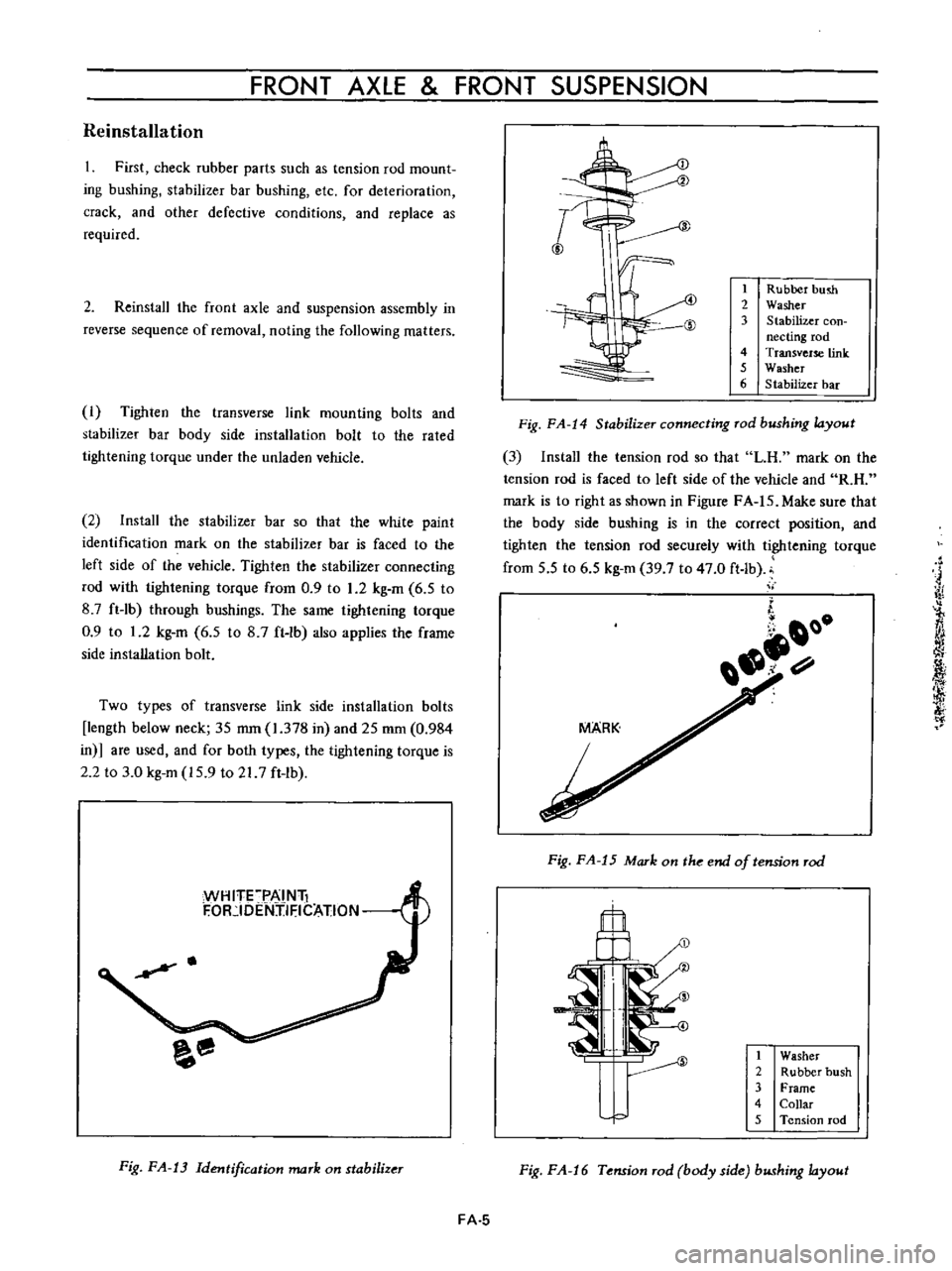
FRONT
AXLE
FRONT
SUSPENSION
Reinstalla
tion
First
check
rubber
parts
such
as
tension
rod
mount
ing
bushing
stabilizer
bar
bushing
etc
for
deterioration
crack
and
other
defective
conditions
and
replace
as
required
2
Reinstall
the
front
axle
and
suspension
assembly
in
reverse
sequence
of
removal
noting
the
following
matters
1
Tighten
the
transverse
link
mounting
bolts
and
stabilizer
bar
body
side
installation
bolt
to
the
raled
tightening
torque
under
the
unladen
vehicle
2
Install
the
stabilizer
bar
so
that
the
white
paint
identification
mark
on
the
stabilizer
bar
is
faced
to
the
left
side
of
the
vehicle
Tighten
the
stabilizer
connecting
rod
with
tightening
torque
from
0
9
to
1
2
kg
m
6
5
to
8
7
ft
lb
through
bushings
The
same
tightening
torque
0
9
to
1
2
kg
m
6
5
to
8
7
ft
Ib
also
applies
the
frame
side
installation
bolt
Two
types
of
transverse
link
side
installation
bolts
length
below
neck
35
mm
1
378
in
and
25
mm
0
984
in
are
used
and
for
both
types
the
tightening
torque
is
2
2
to
3
0
kg
m
15
9
to
217
ft
lb
WH
ITFPAI
Nli
F
OR
IDENjIFICATION
H
Fig
FA
13
Identification
mark
on
stabilizer
I
J
1
Rubber
hush
2
Washer
3
Stabilizer
con
necting
rod
4
Transverse
link
5
Washer
6
Stabilizer
bar
Fig
FA
14
Stabilizer
connecting
rod
bushing
layout
3
Install
the
tension
rod
so
that
LH
mark
on
the
tension
rod
is
faced
to
left
side
of
the
vehicle
and
R
H
mark
is
to
right
as
shown
in
Figure
FA
IS
Make
sure
that
the
body
side
bushing
is
in
the
correct
position
and
tighten
the
tension
rod
securely
with
tightening
torque
from
5
5
to
6
5
kg
m
39
7
to
47
0
ft
lb
ii
j
iY
l
fj
i
f
i
Of
1
0
Fig
FA
15
Mark
on
the
end
of
tension
rod
il
1
Washer
2
Rubber
bush
3
Frame
4
Collar
5
Tension
rod
Fig
FA
16
Tension
rod
body
side
bushing
layout
FA
5
Page 92 of 513

CHASSIS
Tightening
torque
of
front
suspension
cross
member
and
body
is
3
2
to
4
0
kg
m
23
1
to
28
9
ft
Ib
5
Tightening
torque
of
bolt
used
to
secure
the
upper
portion
of
the
strut
assembly
on
the
body
is
1
6
to
2
1
kg
m
11
6
to
15
2ft
lb
FRONT
AXLE
Removal
I
Jack
up
the
vehicle
remove
the
wheel
and
discon
nect
the
brake
hose
at
the
strut
outer
casing
bracket
unit
For
details
see
Removal
of
front
axle
and
suspension
assembly
2
Remove
the
brake
caliper
installation
bolts
and
remove
the
caliper
assembly
Disc
type
brake
3
Remove
the
brake
druOL
Drum
type
brake
4
Remove
the
hub
cap
with
a
flal
headed
screwdriver
or
other
proper
tool
and
hammer
Be
sure
to
tap
lightly
5
Remove
cotter
pin
from
the
wheel
bearing
lock
nut
and
remove
the
lock
nut
6
With
the
wheel
bearing
washer
and
wheel
bearing
installed
on
the
wheel
hub
remove
the
wheel
hub
from
the
spindle
In
the
case
of
a
disc
type
brake
the
wheel
hub
may
be
removed
with
the
disc
rotor
installed
on
the
wheel
hub
Fig
FA
17
Removing
wheel
hub
7
Remove
the
return
spring
and
brake
shoes
remove
brake
disc
assembly
installation
bolts
and
remove
the
brake
disc
assembly
from
the
spindle
Drum
type
brake
Fig
FA
IS
Removing
brake
disc
a
ssembly
8
Remove
baffle
plate
set
screws
and
remove
the
baffle
plate
Disc
type
brake
Fig
FA
19
Removingbaffleplate
9
Utilizing
two
grooves
inside
the
wheel
hub
tap
and
remove
the
wheel
bearing
outer
race
from
the
hub
Fig
FA
20
Removing
wheel
bearing
outer
race
FA
6
Page 97 of 513
FRONT
AXLE
FRONT
SUSPENSION
t
t
Fig
FA
26
Returning
wheel
bearing
lock
nut
4
Turn
the
wheel
hub
a
few
turns
both
clockwise
and
counterclockwise
again
to
allow
the
bearing
breaking
in
measure
bearing
rotation
starting
torque
apply
a
cotter
pin
to
secure
the
nut
if
the
measured
starting
torque
is
within
the
rated
value
and
install
the
hub
cap
hub
cap
Wheel
bearing
rotation
starting
torque
9
0
kg
cm
7
8
in
1b
4
0
kg
cm
3
4
7
in
1b
At
the
hub
bolt
1
57
kg
3
461b
New
bearing
0
7
kg
1
54lb
Used
bearing
No
slackness
should
exist
toward
the
axis
direction
New
bearing
Used
bearing
J
o
i
@
j
Be
sure
to
remove
the
brake
pad
Disc
type
brake
Correctly
measure
starting
force
toward
tangential
direction
against
the
hub
bolt
Fig
FA
27
Measuring
wheel
bearing
ro
ation
starting
torque
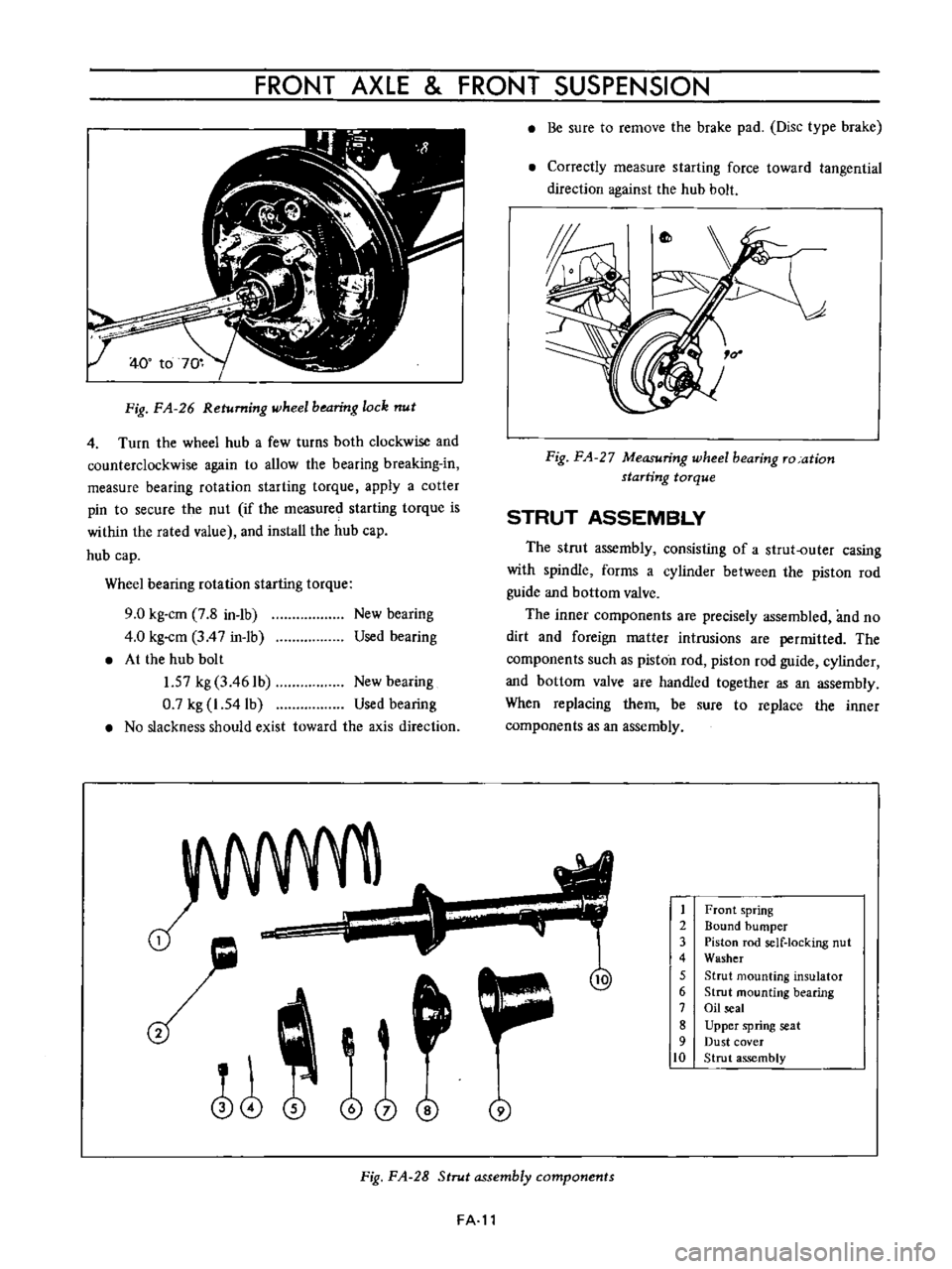
STRUT
ASSEMBLY
The
strut
assembly
consisting
of
a
strut
outer
casing
with
spindle
forms
a
cylinder
between
the
piston
rod
guide
and
bottom
valve
The
inner
components
are
precisely
assembled
and
no
dirt
and
foreign
matter
intrusions
are
permitted
The
components
such
as
piston
rod
piston
rod
guide
cylinder
and
bottom
valve
are
handled
together
as
an
assembly
When
replacing
them
be
sure
to
replace
the
inner
components
as
an
assembly
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Front
spring
Bound
bumper
Piston
rod
self
locking
nut
Washer
Strut
mounting
insulator
Strut
mounting
bearing
Oil
seal
Upper
spring
seat
Dust
cover
Strut
assembly
Fig
FA
28
Strut
assembly
components
FA
l1