1973 DATSUN B110 oil type
[x] Cancel search: oil typePage 6 of 513
CHASSIS
HYDRAULIC
CONTROL
SYSTEM
l
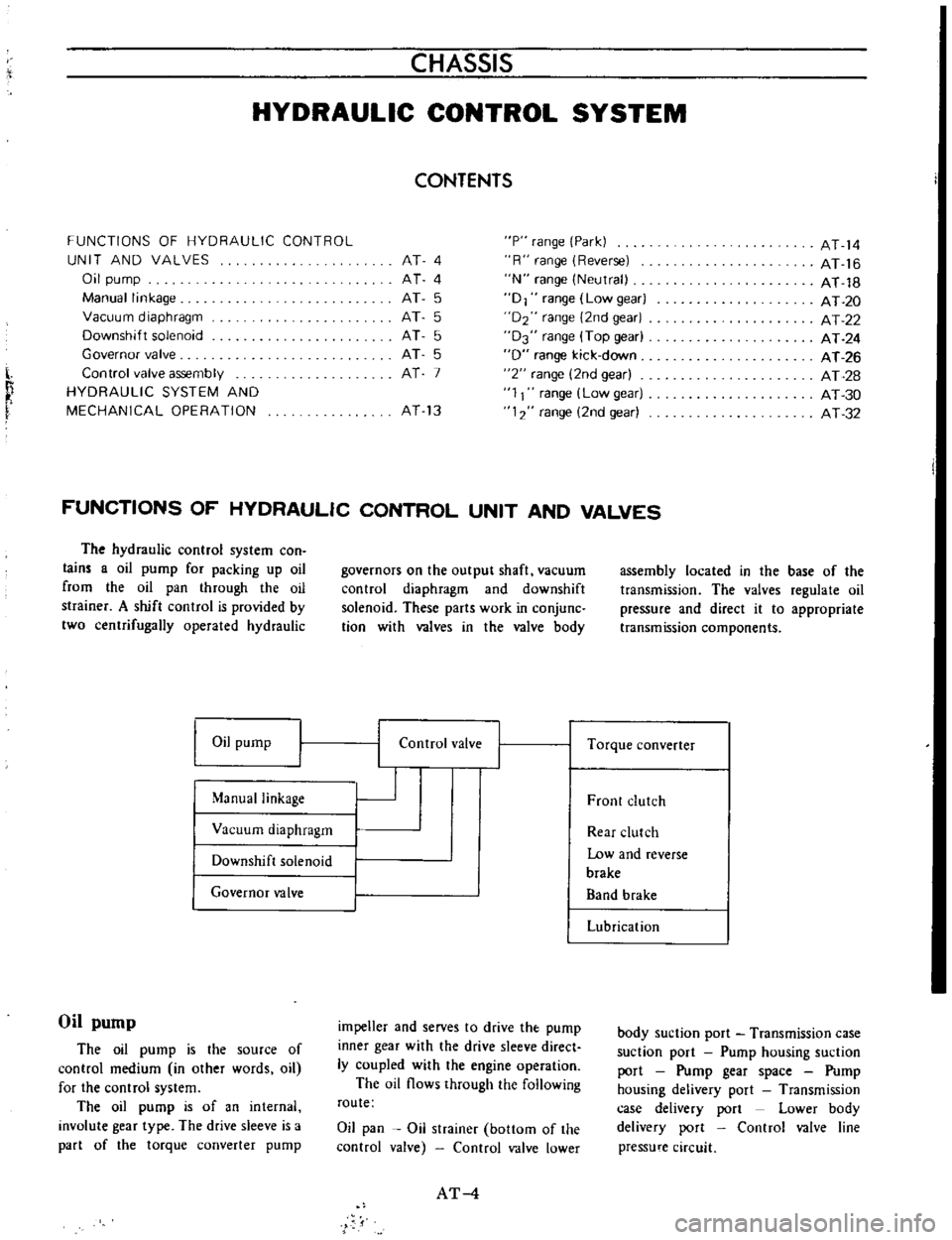
FUNCTIONS
OF
HYDRAULIC
CONTROL
UNIT
AND
VALVES
Oil
pump
Manual
linkage
Vacuum
diaphragm
Downshift
solenoid
Governor
valve
Control
valve
assembly
HYDRAULIC
SYSTEM
AND
MECHANICAL
OPERATION
CONTENTS
P
range
Park
R
range
Reverse
N
range
Neutral
D
range
Low
gear
D2
range
2nd
gear
D3
range
Top
gear
D
range
kick
down
2
range
2nd
gear
1
range
Low
gear
12
range
2nd
gear
AT
4
AT
4
AT
5
AT
5
AT
5
AT
5
AT
7
AT13
AT
14
AT
16
AT
18
AT
20
AT
22
AT
24
AT
26
AT
28
AT
30
AT
32
FUNCTIONS
OF
HYDRAULIC
CONTROL
UNIT
AND
VALVES
The
hydraulic
control
system
con
lain
a
oil
pump
for
packing
up
oil
from
the
oil
pan
through
the
oil
strainer
A
shift
control
is
provided
by
two
centrifugally
operated
hydraulic
Oil
pump
Manual
linkage
Vacuum
diaphragm
Downshift
solenoid
Governor
valve
Oil
pump
The
oil
pump
is
the
source
of
control
medium
in
other
words
oil
for
the
control
system
The
oil
pump
is
of
an
internal
involute
gear
type
The
drive
sleeve
is
a
part
of
the
torque
converter
pump
governors
on
the
output
shaft
vacuum
control
diaphragm
and
downshift
solenoid
These
parts
work
in
conjunc
tion
with
valves
in
the
valve
body
I
I
Control
valve
impeller
and
serves
to
drive
the
pump
inner
gear
with
the
drive
sleeve
direct
ly
coupled
with
the
engine
operation
The
oil
flows
through
the
following
route
Oil
pan
Oil
strainer
bottom
of
the
control
valve
Control
valve
lower
AT
4
assembly
located
in
the
base
of
the
transmission
The
valves
regulate
oil
pressure
and
direct
it
to
appropriate
transmission
components
I
Torque
converter
Front
clutch
Rear
clutch
Low
and
reverse
brake
Band
brake
Lubrication
body
suction
port
Transmission
case
suction
port
Pump
housing
suction
port
Pump
gear
space
Pump
housing
delivery
port
Transmission
case
delivery
port
Lower
body
delivery
port
Control
valve
line
pressure
circuit
Page 7 of 513
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
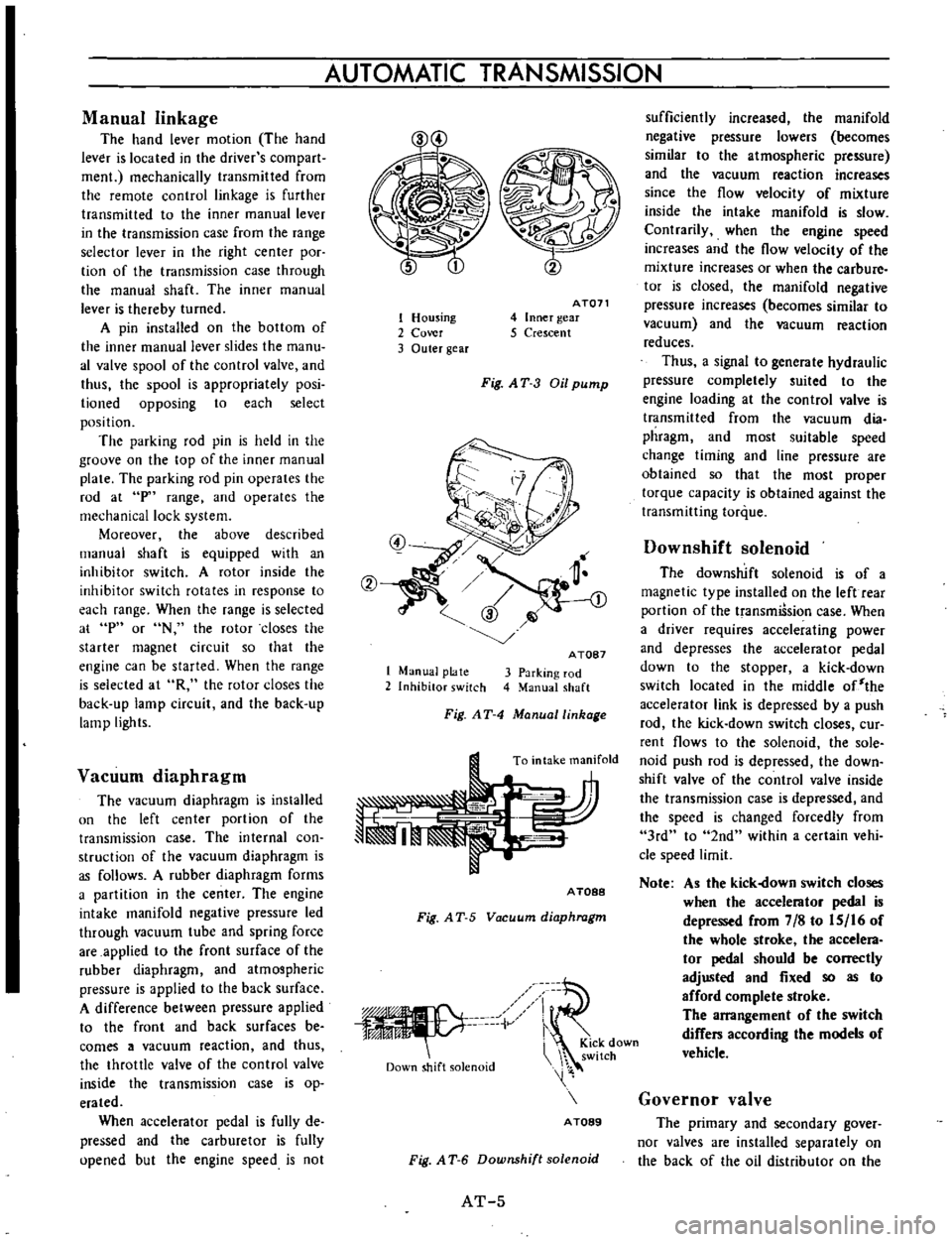
Manual
linkage
The
hand
lever
motion
The
hand
lever
is
located
in
the
driver
s
com
part
men
mechanically
transmitted
from
the
remote
control
linkage
is
further
transmitted
to
the
inner
manual
lever
in
the
transmission
case
from
the
range
selector
lever
in
the
right
center
poc
tion
of
the
transmission
case
through
the
manual
shaft
The
inner
manual
lever
is
thereby
turned
A
pin
installed
on
the
bottom
of
the
inner
manual
lever
slides
the
manu
al
valve
spool
of
the
control
valve
and
thus
the
spool
is
appropriately
posi
lioned
opposing
to
each
select
position
The
parking
rod
pin
is
held
in
the
groove
on
the
top
of
the
inner
manual
plate
The
parking
rod
pin
operates
the
rod
at
p
range
and
operates
the
mechanical
lock
system
Moreover
the
above
described
manual
shaft
is
equipped
with
an
inhibitor
switch
A
rotor
inside
the
inhibitor
switch
rotates
in
response
to
each
range
When
the
range
is
selected
at
p
or
N
the
rotor
closes
the
starter
magnet
circuit
so
that
the
engine
can
be
started
When
the
range
is
selected
at
R
the
rotor
closes
the
back
up
lamp
circuit
and
the
back
up
lamp
lights
Vacuum
diaphragm
The
vacuum
diaphragm
is
installed
un
the
left
center
portion
of
the
transmission
case
The
internal
con
struction
of
the
vacuum
diaphragm
is
as
follows
A
rubber
diaphragm
forms
a
partition
in
the
center
The
engine
intake
manifold
negative
pressure
led
through
vacuum
tube
and
spring
force
are
applied
to
the
front
surface
of
the
rubber
diaphragm
and
atmospheric
pressure
is
applied
to
the
back
surface
A
difference
between
pressure
applied
to
the
front
and
back
surfaces
be
comes
a
vacuum
reaction
and
thus
the
throttle
valve
of
the
control
valve
inside
the
transmission
case
is
op
erated
When
accelerator
pedal
is
fully
de
pressed
and
the
carburetor
is
fully
upened
but
the
engine
speed
is
not
1
Housing
2
Cover
3
Outer
gear
AT071
4
Inner
gear
5
Crescent
Fig
AT
3
Oil
pump
1
Manual
plate
2
Inhibitor
switch
A
TOB7
3
Parking
rod
4
Manual
shaft
Fig
AT
4
Manuallinhage
To
intake
manifold
A
TOBB
Fig
A
T
5
Vacuum
diaphragm
iV
Down
shift
solenoid
i
KiCk
down
switch
A
TOB9
Fig
A
T
6
Downshift
solenoid
AT
5
sufficiently
increased
the
manifold
negative
pressure
lowers
becomes
similar
to
the
atmospheric
pressure
and
the
vacuum
reaction
increases
since
the
flow
velocity
of
mixture
inside
the
intake
manifold
is
slow
Contrarily
when
the
engine
speed
increases
and
the
flow
velocity
of
the
mixture
increases
or
when
the
carbure
tor
is
closed
the
manifold
negative
pressure
increases
becomes
similar
to
vacuum
and
the
vacuum
reaction
reduces
Thus
a
signal
to
generate
hydraulic
pressure
completely
suited
to
the
engine
loading
at
the
control
valve
is
transmitted
from
the
vacuum
dia
phragm
and
most
suitable
speed
change
timing
and
line
pressure
are
obtained
so
that
the
most
proper
torque
capacity
is
obtained
against
the
transmitting
torque
Downshift
solenoid
The
downshift
solenoid
is
of
a
magnetic
type
installed
on
the
left
rear
portion
of
the
transmiSsion
case
When
a
driver
requires
accelerating
power
and
depresses
the
accelerator
pedal
down
to
the
stopper
a
kick
down
switch
located
in
the
middle
of
the
accelerator
link
is
depressed
by
a
push
rod
the
kick
down
switch
closes
cur
rent
flows
to
the
solenoid
the
sole
noid
push
rod
is
depressed
the
down
shift
valve
of
the
control
valve
inside
the
transmission
case
is
depressed
and
the
speed
is
changed
forcedly
from
3rd
to
2nd
within
a
certain
vehi
cle
speed
limit
Note
As
the
kick
own
switch
closes
when
the
accelerator
pedal
is
depressed
from
7
8
to
IS
16
of
the
whole
stroke
the
accelera
tor
pedal
should
be
correctly
adjusted
and
fixed
so
as
to
afford
complete
stroke
The
arrangement
of
the
switch
differs
according
the
models
of
vehicle
Governor
valve
The
primary
and
secondary
gover
nor
valves
are
installed
separately
on
the
back
of
the
oil
distributor
on
the
Page 46 of 513

L
J
i
C
E
Ee
1f
20mm
8
0
079
in
AT148
Cut
off
hatched
portion
Fig
A
T
80
Modifying
of
coil
spring
compres
or
3
Take
out
spring
retainer
j
and
spring@
See
Figure
AT
7
4
Blowout
piston
by
directing
a
iet
of
air
into
hole
in
clutch
drum
See
Figure
AT
I
Fig
AT
81
Blowing
out
pi3ton
Inspection
I
Check
for
sign
of
wear
or
damage
to
clutch
drive
plate
facing
If
found
worn
or
damaged
excessively
discard
See
Service
Data
for
limits
2
Check
for
wear
on
snap
ring
and
for
weakened
or
broken
coil
spring
If
necessary
replace
with
new
ones
Spring
retainer
should
also
be
in
spected
for
warpage
Assembly
I
Assembly
is
reverse
order
of
disas
sembly
Dip
aU
parts
in
clean
auto
matic
transmission
fluid
before
they
can
be
installed
2
Line
up
driven
plates
so
that
stripped
arcs
are
properly
aligned
pay
iog
particular
attention
to
the
location
of
oil
holes
in
clutch
drum
See
Figure
AT
82
Note
The
number
of
drive
and
driven
plates
varies
with
the
type
of
vehicles
For
detailed
informa
tion
also
see
Service
Data
Specifications
CHASSIS
AT150
Lubrication
hole
Fig
A
T
82
Inserting
clutch
plate
3
After
clutch
is
assembled
make
sure
that
clearance
between
snap
ring
CD
and
retaining
plate
@
is
held
within
specified
limits
If
necessary
try
with
other
plates
having
different
thickness
until
correct
clearance
is
obtained
See
Figure
AT
3
Specified
clearance
1
6
to
1
mm
0
063
to
0
071
in
Available
retaining
plate
No
Thickness
mm
in
I
10
6
0
417
2
10
0
425
3
11
0
0
433
4
11
2
0
441
5
II
4
0
449
6
11
6
0
457
AT151
Fig
A
T
83
MeOJluring
ring
to
plate
clearance
4
Testing
front
clutch
With
front
clutch
assembled
on
oil
pump
cover
direct
a
jet
of
air
into
hole
in
clutch
drum
See
Figure
AT
4
AT
42
Fig
A
T
84
Tesling
front
clutch
Rear
clutch
Disassembly
CD
ID
@
f
@
@
I
J
L
@
@
@
AT269
I
Rear
clutch
drum
6
Retaining
plate
2
Piston
7
Spring
retainer
3
Di
ed
plate
8
Drive
plate
4
Coil
spring
9
Driven
plate
5
Snap
ring
Fig
A
T
85
Sectional
view
of
Tear
clutch
I
Take
out
snap
ring
@
retaining
plate
@
drive
plate
l
driven
plate
@
and
dished
plate
j
Same
tech
nique
can
be
applied
as
in
disassem
bling
front
clutch
See
Figure
A
T
5
2
Remove
snap
ring
from
coil
spring
retainer
See
Figure
AT
6
ST25420000
ST2542000l
Ii
Removing
snap
ring
Page 47 of 513

3
Blowout
piston
by
directing
a
jet
of
air
into
hole
in
clutch
drum
See
Figure
AT
S
7
AT155
Fig
AT
87
Blowing
out
piston
Inspection
Refer
to
covering
topic
under
Front
Clutch
Assembly
Assembly
is
reverse
order
of
disas
sembly
Dip
all
parts
in
clean
auto
malic
transmission
fluid
before
as
sembling
Note
that
the
number
of
drive
and
driven
plates
varies
with
types
of
vehicles
For
details
refer
to
Service
Data
Specifications
I
After
rear
clutch
is
assembled
check
to
be
sure
that
clearance
be
tween
snap
ring
CD
and
retaining
plate
CV
is
held
within
prescribed
tolerances
See
Figure
A
T
S8
Specified
clearance
1
0
to
1
5
mm
0
039
to
0
059
in
AT1S6
Fig
A
T
88
Measuring
ring
to
plate
clearance
2
Testing
rear
clutch
Install
rear
clutch
on
oil
pump
cover
Blow
air
under
pressure
into
oil
hole
to
listen
for
definite
clutch
opera
tion
as
shown
in
Figure
AT
S9
AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
AT157
Fig
AT
89
Testing
rear
clutch
Low
reverse
brake
Disassembly
I
Follow
steps
as
per
instructed
on
page
AT
38
2
Blowout
piston
by
directing
a
jet
of
air
into
oil
hole
in
clutch
piston
Inspection
I
Check
drive
plate
facing
for
wear
or
damage
if
necessary
replace
Refer
to
Service
Data
Specifications
for
limits
2
Test
if
piston
return
spring
is
not
weakened
Discard
if
weakened
too
badly
beyond
use
3
Replace
any
defective
parts
with
new
ones
Assembly
1
After
low
reverse
piston
is
installed
assemble
thrust
spring
ring
return
spring
thrust
washer
and
one
way
clutch
inner
race
With
the
aid
of
Hex
head
Extension
ST25570000
tighten
hex
head
slotted
bolt
1
3
to
1
8
kg
m
9
4
to
13
ft
Ib
2
Enter
dished
plate
driven
plate
drive
plate
and
retaining
plate
into
transmission
case
in
this
written
order
Install
snap
ring
to
secure
the
instal
lation
Note
The
number
of
drive
and
driven
plates
varies
with
types
of
vehi
cles
For
detailed
information
refer
to
Service
Data
Specifi
cations
AT
43
3
Without
disturbing
the
above
setting
check
to
be
sure
that
clearance
between
snap
ring
and
retaining
plate
is
held
within
specified
limits
If
nec
essary
try
with
other
plates
having
different
thickness
until
correct
clear
ance
is
obtained
Specified
clearance
O
SO
to
1
05
mm
0
031
to
0
041
in
4
Blow
under
pressure
air
into
oil
hole
in
low
reverse
brake
to
listen
for
definite
brake
operation
as
shown
in
Figure
AT
90
0j
L
J
1
1
I
1
I
Y
1
If
lY
v
A
we
1
a
II
I
7
r
AT158
Fig
AT
90
Testing
low
reverse
brake
Servo
piston
Disassembly
1
Blowout
piston
by
directing
a
jet
of
air
into
hole
in
release
side
of
piston
2
Remove
servo
piston
return
spring
Inspection
Check
piston
for
wear
damage
or
any
other
defects
which
might
inter
fere
with
proper
brake
operation
AT159
Fig
A
T
91
Removing
piston
Page 50 of 513

I
Fig
AT
102
Removing
5
parote
plate
3
Pull
out
manual
valve
as
shown
in
Figure
AT
103
4
Remove
side
plate
Take
out
1st
2nd
shift
valve
2nd
3rd
shift
valve
pressure
modifier
valve
and
three
valve
springs
See
Figure
AT
I04
CHASSIS
AT170
Fig
AT
103
Removing
manual
valve
Note
Do
not
work
it
off
with
screw
drivers
to
avoid
damaging
machine
screws
5
Remove
side
plate
pull
out
pres
sure
regulator
valve
second
lock
valve
pressure
regulator
plug
and
two
valve
springs
sp
m
Pressure
regutlltor
sleeve
C
Prt
ssure
P
elato
piug
IZt
1
2iid3
d
h
1
alve
7
I
Solenoid
down
skutt
Throttle
back
up
alw
p
u
modif
Second
lock
alve
MllllU81
1st
2nd
shift
2nd
3rd
shift
Inspection
I
Check
valves
for
sign
of
burning
and
if
necessary
replace
2
Check
to
be
certain
that
oil
strainer
is
in
good
condition
If
found
damaged
in
any
ffi3nner
discard
3
Test
valve
springs
for
weakened
egulator
alve
3
1
ott
jj
r
of
U
d
4
t
i
i
J
j
r
r
lC
i
i
4
i
I
5
j
AT171
Fig
A
T
l
04
Removing
8ide
plate
6
Remove
side
plate
With
side
plate
removed
solenoid
downshift
valve
throttle
back
up
valve
vacuum
throttle
valve
2nd
3rd
timing
valve
and
three
valve
springs
are
free
for
removal
2nd
3rd
timing
3
ve
i
Vacuum
Ihrotlle
alve
aive
Fig
AT
L05
Components
parts
of
control
value
tension
if
necessary
replace
4
Examine
if
there
is
any
sign
of
damage
or
score
marks
on
separate
plate
If
left
unheeded
oil
will
bypass
correct
oil
passages
causing
many
types
of
abnormalities
in
the
system
AT
46
5
Check
oil
passages
in
valve
body
for
sign
of
damage
and
other
condi
tions
which
might
interfere
with
prop
er
valve
operation
6
Check
bolts
for
stripped
threads
Replace
as
required
Page 64 of 513

CHASSIS
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
General
specifications
Torque
converter
Type
Stall
torque
ratio
Transmission
Type
Control
elements
Gear
ratio
Selector
positions
Oil
pump
Type
Number
of
pump
Oil
Capacity
Hydraulic
control
system
Lubrication
system
Cooling
system
Multiple
disc
clutch
Band
brake
Multiple
disc
brake
One
way
clutch
1st
lnd
3rd
Reverse
P
Park
R
Reverse
N
Neutral
D
Drive
1
lnd
lock
I
Lock
up
AT
60
Symmetrical3
element
I
stage
l
phase
torque
converter
coupling
2
0
I
3
speed
forward
and
one
speed
reverse
with
planetary
gear
train
1
I
I
I
2
458
1
458
1
000
2
182
The
transmission
is
placed
in
neutral
The
output
shaft
is
fixed
The
engine
can
be
started
Backward
running
The
transmission
is
in
neutral
The
engine
can
be
started
Up
or
downshifts
automatically
to
and
from
1st
lnd
and
top
Fixed
at
2nd
Fixed
at
low
or
downshifts
from
2nd
Internally
intermeslting
involute
gear
pump
Automatic
transmission
fluid
Dexron
type
5
5
liters
57
8
U
S
qts
47
8
Imp
qts
Approximately
1
7
liters
27
8
U
S
qts
2
3
8
Imp
qts
in
torque
converter
Controlled
by
detecting
the
negative
pressure
of
intake
manifold
and
the
revolution
speed
of
output
shaft
Forced
lubrication
by
an
oil
pwnp
Air
cooled
Page 72 of 513

PROPELLER
SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
The
gear
carrier
is
made
of
light
and
strong
aluminum
alloy
metal
and
hypoid
bevel
gear
is
used
Adjust
drive
pinion
bearing
preload
with
non
adjusting
type
spacer
and
pinion
height
and
side
bearing
adjust
ment
with
spacer
shim
s
Millimeter
standardization
stilI
remains
for
all
the
screw
threads
of
this
unit
Therefore
adjustment
figures
stamped
on
screws
adjusting
shims
washers
differential
case
drive
pinion
and
carrier
are
in
millimeters
in
accordance
with
the
millimeter
standardization
of
parts
The
proper
lubrication
to
the
gear
housing
is
necessary
otherwise
it
would
shorten
the
durability
of
the
gear
and
cause
other
troubles
The
lubricant
should
be
checked
each
5
000
km
3
000
miles
and
replenished
each
50
000
km
30
000
miles
The
lubricant
should
be
drained
and
ref11led
at
the
end
of
the
first
1
000
km
600
miles
to
eliminate
any
loose
material
from
the
sump
which
results
from
breaking
Differential
lubricant
should
be
changed
at
least
every
50
000
km
30
000
miles
ConsIderations
should
be
given
to
the
following
matters
I
Nominated
hypoid
gear
oil
must
be
used
2
It
is
prohibited
to
use
any
gear
oil
of
different
viscosity
The
same
brand
must
always
be
selected
3
The
standard
oil
capacity
is
about
0
75
liter
0
198
US
gal
REMOVAL
Fig
PD
5
Removing
differential
gear
carrier
To
remove
the
gear
carrier
assembly
disconnect
the
drive
pinion
companion
flange
te
flange
yoke
connection
and
remove
two
rear
axle
shafts
Refer
to
REAR
AXLE
for
the
work
DISASSEMBLY
I
Install
the
gear
carrier
assembly
on
the
Gear
Carrier
Attachment
ST06320000
ST06320000
Fig
PD
6
Holding
differential
camer
2
Inspect
the
following
before
disassembling
I
Inspect
the
tooth
contact
pattern
with
a
lead
oxide
2
Measure
backlash
between
drive
gear
and
pinion
gear
using
a
dial
indicator
3
Put
match
mark
on
one
side
of
the
side
bearing
cap
by
the
use
of
a
punch
SIDCBEMING
c
e
Fig
PD
7
Putting
mark
PD
5
Page 84 of 513

PROPELLER
SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
Incorrect
adjustment
of
bearings
or
gears
Severe
service
due
to
an
excessive
loading
improper
use
of
clutch
Loosened
bolts
and
nuts
such
as
ring
gear
clamp
bolts
Oil
leakage
Worn
out
damaged
or
improperly
driven
front
oil
seal
or
bruised
dented
or
abnormally
worn
slide
face
of
companion
flange
Loosened
bolts
holding
gear
carrier
Defective
gasket
Loosen
filler
or
drain
plug
Clogged
or
damaged
breather
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
Type
of
differential
gear
carrier
assembly
Final
gear
type
Final
gear
ratio
number
of
teeth
Sedan
Coupe
Van
Drive
pinion
Preload
with
oil
seal
Preload
without
oil
seal
Thickness
of
drive
pinion
adjusting
shims
kg
cm
in
lb
kg
cm
in
lb
mm
in
Pinion
bearing
adjusting
spacer
Ring
gear
Backlash
between
ring
gear
and
pinion
Run
out
of
rear
side
of
ring
gear
mm
in
mm
in
Side
gear
and
pinion
mate
Thickness
of
side
gear
thrust
washers
mm
in
PD
17
Replace
defective
parts
Replace
defective
parts
Replace
defective
parts
Replace
the
defective
oil
seal
Ammend
the
affected
flange
with
sand
paper
or
replace
if
necessary
Tighten
the
bolts
to
specified
torque
Replace
defective
parts
with
new
ones
Tighten
the
plug
Repair
or
replace
H145A
Hypoid
3
900
39
10
7
to
9
6
1
to
7
8
6
to
8
5
2
to
6
9
From
2
74
to
3
25
0
1079
to
0
1280
Spacing
0
Q3
0
0012
Non
adjustable
collapsible
spacer
0
10
to
0
15
0
0039
to
0
0059
Less
than
0
05
0
0020
0
76
to
0
91
0
0299
to
0
0358