2006 DODGE RAM SRT-10 oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: oil pressurePage 2029 of 5267

CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or equivalent.
Perform test following the procedures supplied with the tool kit.
HYDRAULIC TAPPET NOISE DIAGNOSIS
PRELIMINARY STEP TO CHECKING THE HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
Before disassembling any part of the engine to correct tappet noise, checkengine oil level and oil pressure.
1. Check the engine oil level.
Oil Level Check: stop engine after reaching normal operating temperature
The oil level should never be above the FULL mark on dipstick, or below the ADD mark. Either of
these two conditions could be responsible for noisy tappets. Allow 5 minutes to stabilize oil level,
check dipstick.
2. Remove oil pressure sensor.
3. Install a reliable oil pressure gauge at oil pressure sensor location.
The oil pressure should be 206.8 - 551.6 kPa (30 - 80 psi) at 2000 rpm.
OIL LEVEL TOO HIGH
If oil level is above the FULL mark on dipstick, it is possible for the connecting rods to dip into the oil while engine
is running and create foam. Foam in oil pan would be fed to the hydraulic tappets by the oil pump causing them to
become soft and allow valves to seat noisily.
OIL LEVEL TOO LOW
Low oil level may allow pump to take in air which when fed to the tappets, causes them to become soft and allows
valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake side of pump through which air canbedrawnwillcreatethesametappet
action. Check the lubrication system from the intake strainer to the pump cover, including the relief valve retainer
cap. When tappet noise is due to aeration, it may be intermittent or constant, and usually more than one tappet will
be noisy. When oil level and leaks have been corrected, engine should be operated at fast idle to allow all of the air
inside of the tappets to be bled out.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE DIAGNOSIS
To determine source of valve train noise, operate engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed and listen for
source of the noise.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are sometimes mistaken for noisytappets. If such is the case,
noise may be dampened by applying side thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not appreciably reduced, it
can be assumed the noise is in the tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets and push rod ends for
wear.
Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a heavy click. A light noise isusually caused by excessive leak-down
around the unit plunger which will necessitate replacing the tappet, or bythe plunger partially sticking in the tappet
body cylinder. A heavy click is caused either by a tappet check valve not seating, or by foreign particles becoming
wedged between the plunger and the tappet body causing the plunger to stickin the down position. This heavy click
will be accompanied by excessive clearance between the valve stem and rocker arm as valve closes. In either case,
tappet assembly should be removed and replaced.
ENGINE OIL LEAK INSPECTION
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the engine, particularly at thearea of the suspected leak. If an oil leak
source is not readily identifiable, thefollowingstepsshouldbefollowed:
1. Do not clean or degrease the engine at this time because some solvents maycause rubber to swell, temporarily
stopping the leak.
2. Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for approximately 15
minutes. Check the oil dipstick to make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated with a bright yellow color
under a black light.
Page 2030 of 5267

3. Using a black light, inspect the entire engine for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area of oil leak. If
the oil leak is found and identified, repair as necessary.
4. If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at various speeds for approximately 24 km (15 miles), and repeat inspec-
tion.
5.If the oil leak source is not positively identified at this time, proceed with the air leak detection test method
as follows:
1. Disconnect the PCV hoses at the cylinder head covers and plug or cap the outlet on the covers.
2. Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
3. Gradually apply air pressure from 6.89 kPa (1 psi) to 17.23 kPa (2.5 psi) maximum while applying soapy water
at the suspected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable test pressure that provides the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is detected and identified, repair per service manual procedures.
4. If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal area, refer to the section, Inspection for Rear Seal Area
Leak.
6. If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply. Remove the air hose, allplugs, and caps. Connect the PCV
hoses. Proceed to next step.
7. Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various speeds approx-
imately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the engine for signs of an oil leak by usinga black light.
NOTE: If oil leakage is observed at the dipstick tube to oil pan location; remove the tube, clean and reseal
using Mopar
Stud & Bearing Mount (press fit tube applications only), and for O-ring style tubes, remove
tube and replace the O-ring seal.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the source of an oil leak in therear seal area of the engine, a more
involved inspection is necessary. The following steps should be followedto help pinpoint the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal area:
1. Disconnect the battery.
2. Raise the vehicle.
3. Remove clutch housing inspection cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil. Use a black light to check
for the oil leak. If a leak is present in this area, remove transmission for further inspection.
a. Circular spray pattern generally indicates seal leakage or crankshaftdamage.
b. Where leakage tends to run straight down, possible causes are a porous block, oil gallery cup plug or rear
crankshaft seal retainer gasket leak. See proper repair procedures for these items.
4. If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crankcase as previously described.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
5. If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the crankshaft and watch forleakage. If a leak is detected between
the crankshaft and seal while slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the crankshaft seal surface is damaged.
The seal area on the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches that canbe polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially machined to complement the function of the rear oil seal.
6. For bubbles that remain steady with shaft rotation, no further inspection can be done until disassembled.
7. After the oil leak root cause and appropriate corrective action have been identified, replace component(s) as
necessary.
Page 2033 of 5267

5. Identify the fluid in the cylinder(s) (i.e., coolant, fuel, oil or other).
6. Make sure all fluid has been removed from the cylinders. Inspect engine for damage (i.e., connecting rods, pis-
tons, valves, etc.)
7. Repair engine or components as necessary to prevent this problem from re-occurring.
CAUTION: Squirt approximately one teaspoon of oil into the cylinders, rotateenginetolubricatethecylin-
der walls to prevent damage on restart.
8. Install new spark plugs.
9. Drain engine oil and remove oil filter.
10. Fill engine with specified amount of approved oil and install new oil filter.
11. Connect negative battery cable.
12. Start engine and check for any leaks.
REMOVAL - ENGINE ASSEMBLY
1. Perform fuel pressure release procedure (Refer to
14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
2. Disconnect negative battery cable.
3. Disconnect throttle body air inlet duct, remove air
cleaner cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR INTAKE
SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER ELEMENT - REMOVAL).
4. Raise and support the vehicle.
5. Remove the lower engine shield.
6. Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING
COOLING SYSTEM).
7. Paint mark and remove the driveshaft (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - REMOVAL).
8.Removethetransmission(Referto21-TRANS-
MISSION/TRANSAXLE/MANUAL - REMOVAL).
9. Remove the starter (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - REMOVAL).
10. Disconnect the front exhaust pipe flange to
exhaust manifold fasteners (1 and 2).
11. Disconnect the hydraulic cooling fan lines and capture any spillage (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR
FA N - R E M O VA L ) .
12. Drain engine oil and remove the oil filter.
13. Separate the air conditioning hose from the fan shroud.
14. Disconnect the lower radiator hose.
15. Disconnect the power steering line support bracket at the lower left ofthe radiator.
16. Loosen both engine mount through bolts.
Page 2040 of 5267

30. Connect oil cooler lines (4) and connect the oil
pressure sensor (1) and oil temperature sensor
(5).
31. Install the power steering line support bracket at
the radiator.
32. Install lower radiator hose.
33. Connect the cooling fan hydraulic lines (Refer to 7
- COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTAL-
LATION).
34. Connect the A/C line to the fan shroud.
35. Install under body shield.
36. Lower vehicle.
37. Fill engine crankcase with the proper oil to the
correct level (Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTE-
NANCE/FLUID TYPES - SPECIFICATIONS).
38. Evacuate and recharge the air conditioning (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMB-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
39. Fill the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
40. Fill power steering to proper leveland purge the system (Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
41. Connect the negative battery cable.
42. Start the engine and run until operating temperature is obtained.
43. Turn engine off and inspect for leaks.
44. Recheck all fluid levels, fill as required.
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Ty pe 9 0° V-1 0
Number of Cylinders 10
Firing Order 1-10-9-4-3-6-5-8-7-2
Compression Ratio 9.6:1
Brake Horsepower 501@5600 RPM
Torque 525 ft. lbs. @4100 RPM
Crankshaft Forged Steel
Cylinder Block Aluminum Alloy with Interference Fit Cast Iron Liners
Connecting Rods Cracked Cap Powdered Metal
Pistons Cast Aluminum Alloy
Metric Standard
Displacement 8.3L 505 cu. in.
Bore 102.4 mm 4.03 in.
Stroke 100.6 mm 3.96 in.
Compression Pressure 1069-1172 kPa 155-170 psi
Engine Weight (Approx.) 284 Kilograms 625 Lbs.
Page 2044 of 5267
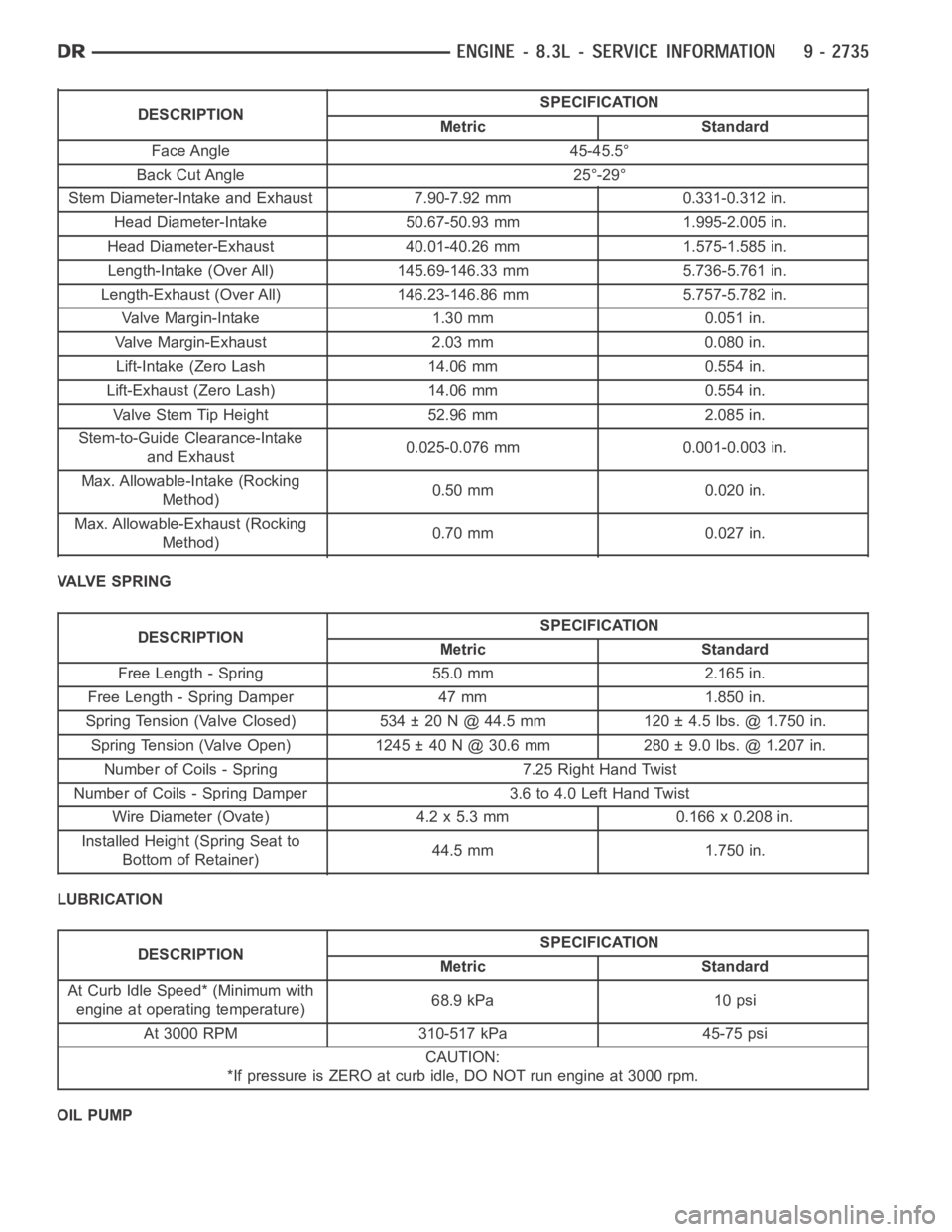
DESCRIPTIONSPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Face Angle 45-45.5°
Back Cut Angle 25°-29°
Stem Diameter-Intake and Exhaust 7.90-7.92 mm 0.331-0.312 in.
Head Diameter-Intake 50.67-50.93 mm 1.995-2.005 in.
Head Diameter-Exhaust 40.01-40.26 mm 1.575-1.585 in.
Length-Intake (Over All) 145.69-146.33 mm 5.736-5.761 in.
Length-Exhaust (Over All) 146.23-146.86 mm 5.757-5.782 in.
Valve Margin-Intake 1.30 mm 0.051 in.
Valve Margin-Exhaust 2.03 mm 0.080 in.
Lift-Intake (Zero Lash 14.06 mm 0.554 in.
Lift-Exhaust (Zero Lash) 14.06 mm 0.554 in.
Valve Stem Tip Height 52.96 mm 2.085 in.
Stem-to-Guide Clearance-Intake
and Exhaust0.025-0.076 mm 0.001-0.003 in.
Max. Allowable-Intake (Rocking
Method)0.50 mm 0.020 in.
Max. Allowable-Exhaust (Rocking
Method)0.70 mm 0.027 in.
VALVE SPRING
DESCRIPTIONSPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Free Length - Spring 55.0 mm 2.165 in.
Free Length - Spring Damper 47 mm 1.850 in.
Spring Tension (Valve Closed) 534 ± 20 N @ 44.5 mm 120 ± 4.5 lbs. @ 1.750 in.
Spring Tension (Valve Open) 1245 ± 40 N @ 30.6 mm 280 ± 9.0 lbs. @ 1.207 in.
Number of Coils - Spring 7.25 Right Hand Twist
Number of Coils - Spring Damper 3.6 to 4.0 Left Hand Twist
Wire Diameter (Ovate) 4.2 x 5.3 mm 0.166 x 0.208 in.
Installed Height (Spring Seat to
Bottom of Retainer)44.5 mm 1.750 in.
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTIONSPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
At Curb Idle Speed* (Minimum with
engine at operating temperature)68.9 kPa 10 psi
At 3000 RPM 310-517 kPa 45-75 psi
CAUTION:
*If pressure is ZERO at curb idle, DO NOT run engine at 3000 rpm.
OIL PUMP
Page 2045 of 5267
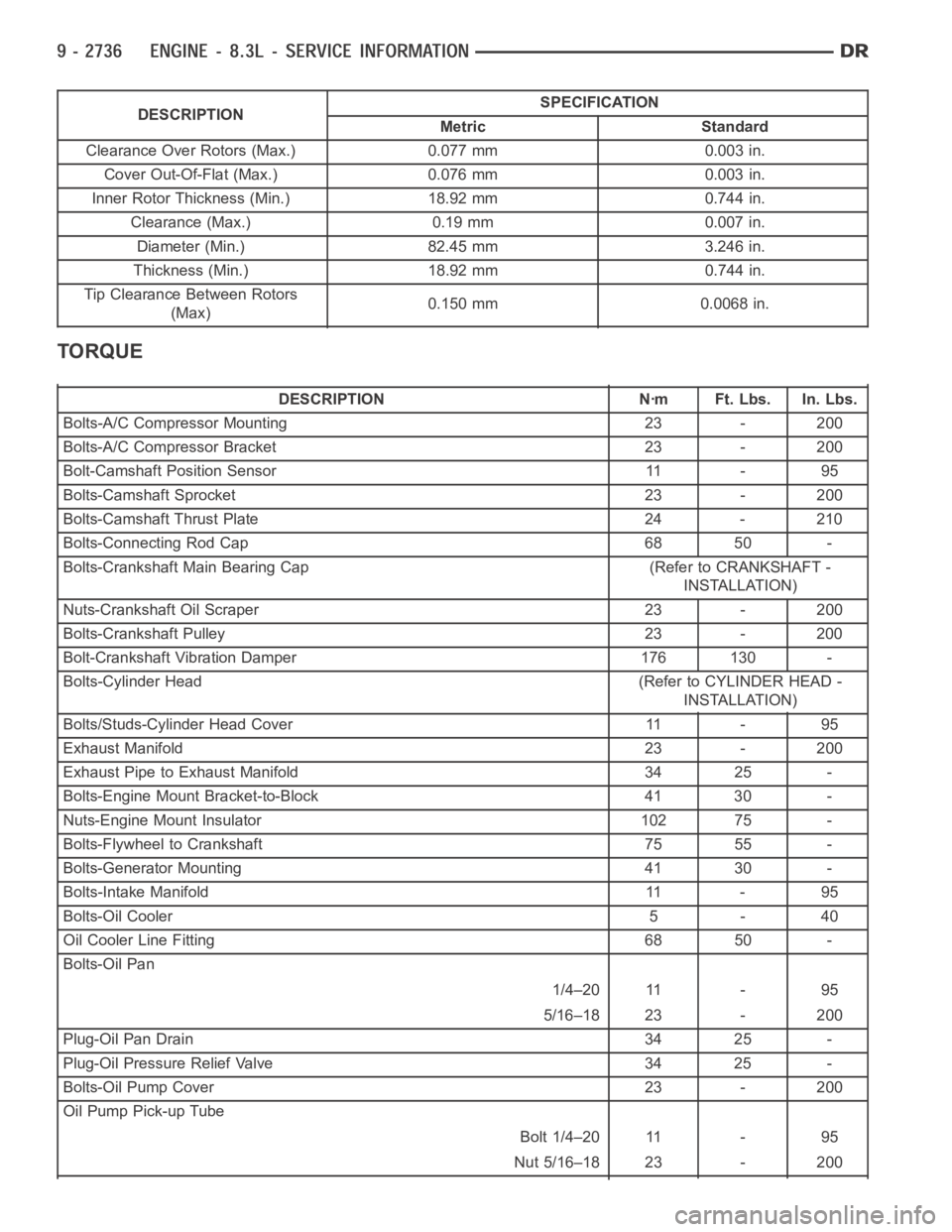
DESCRIPTIONSPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Clearance Over Rotors (Max.) 0.077 mm 0.003 in.
Cover Out-Of-Flat (Max.) 0.076 mm 0.003 in.
Inner Rotor Thickness (Min.) 18.92 mm 0.744 in.
Clearance (Max.) 0.19 mm 0.007 in.
Diameter (Min.) 82.45 mm 3.246 in.
Thickness (Min.) 18.92 mm 0.744 in.
Tip Clearance Between Rotors
(Max)0.150 mm 0.0068 in.
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION Nꞏm Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Bolts-A/C Compressor Mounting 23 - 200
Bolts-A/C Compressor Bracket 23 - 200
Bolt-Camshaft Position Sensor 11 - 95
Bolts-Camshaft Sprocket 23 - 200
Bolts-Camshaft Thrust Plate 24 - 210
Bolts-Connecting Rod Cap 68 50 -
Bolts-Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap (Refer to CRANKSHAFT -
INSTALLATION)
Nuts-Crankshaft Oil Scraper 23 - 200
Bolts-Crankshaft Pulley 23 - 200
Bolt-Crankshaft Vibration Damper 176 130 -
Bolts-Cylinder Head (Refer to CYLINDER HEAD -
INSTALLATION)
Bolts/Studs-Cylinder Head Cover 11 - 95
Exhaust Manifold 23 - 200
Exhaust Pipe to Exhaust Manifold 34 25 -
Bolts-Engine Mount Bracket-to-Block 41 30 -
Nuts-Engine Mount Insulator 102 75 -
Bolts-Flywheel to Crankshaft 75 55 -
Bolts-Generator Mounting 41 30 -
Bolts-Intake Manifold 11 - 95
Bolts-Oil Cooler 5 - 40
Oil Cooler Line Fitting 68 50 -
Bolts-Oil Pan
1/4–20 11 - 95
5/16–18 23 - 200
Plug-Oil Pan Drain 34 25 -
Plug-Oil Pressure Relief Valve 34 25 -
Bolts-Oil Pump Cover 23 - 200
Oil Pump Pick-up Tube
Bolt 1/4–20 11 - 95
Nut 5/16–18 23 - 200
Page 2046 of 5267
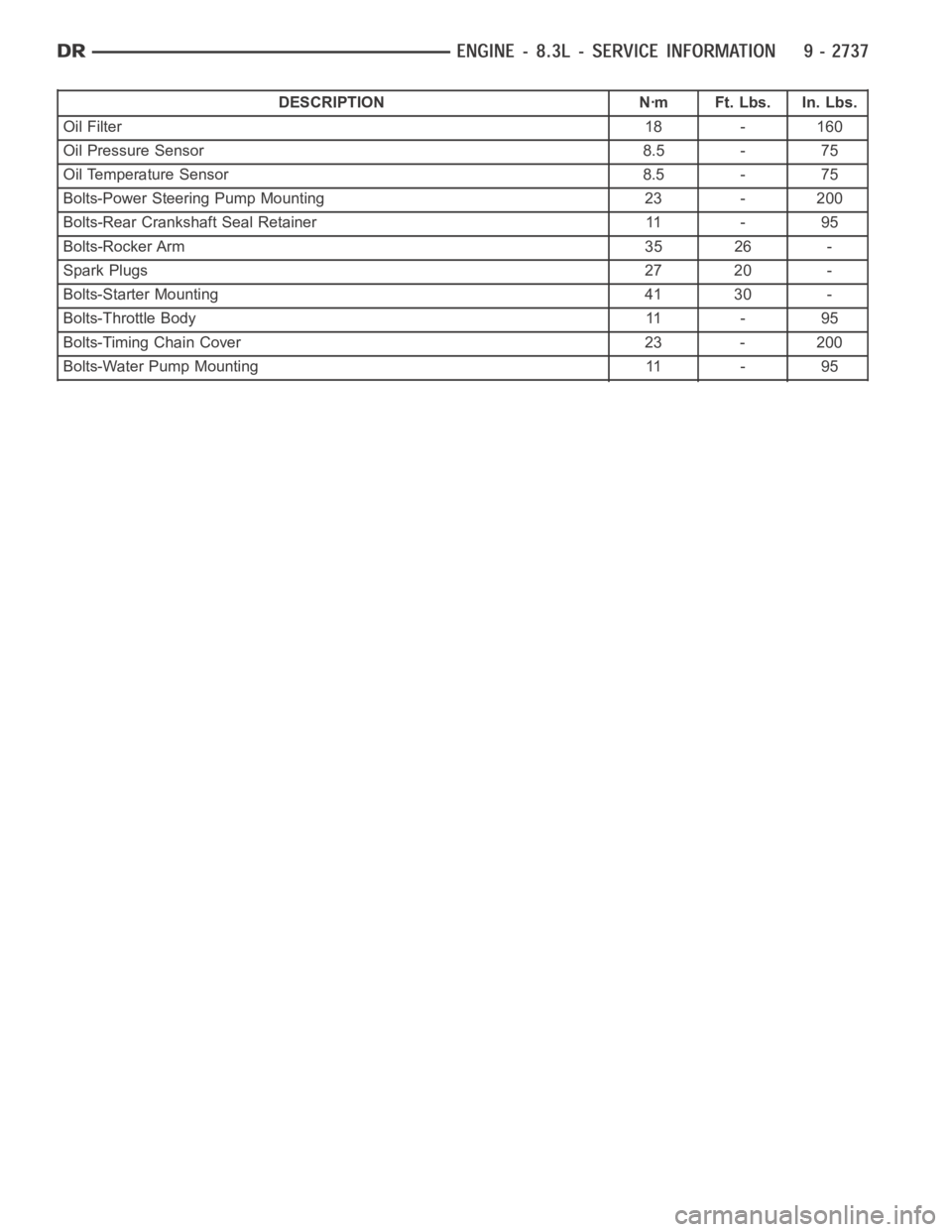
DESCRIPTION Nꞏm Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Oil Filter18 - 160
Oil Pressure Sensor 8.5 - 75
Oil Temperature Sensor 8.5 - 75
Bolts-Power Steering Pump Mounting 23 - 200
Bolts-Rear Crankshaft Seal Retainer 11 - 95
Bolts-Rocker Arm 35 26 -
Spark Plugs27 20 -
Bolts-Starter Mounting 41 30 -
Bolts-Throttle Body 11 - 95
Bolts-Timing Chain Cover 23 - 200
Bolts-Water Pump Mounting 11 - 95
Page 2066 of 5267

HEAD(S)-CYLINDER
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD(S)
NOTE: Care must be taken to protect the intake
manifold and cylinder head covers powder coating
from scrapes and abrasions. This procedure cov-
ers either the left or right cylinder head.
The aluminum alloy cylinder head shown in is held in
place by 12,
1⁄2inch bolts (5) and 8,1⁄4inch bolts (4).
1. Release the fuel pressure (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
2. Disconnect negative battery cable.
3. Disconnect the throttle body air inlet duct, IAT sen-
sor, CCV hose and remove the air cleaner cover
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR
CLEANER HOUSING - REMOVAL).
4. Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING
COOLING SYSTEM).
5. Raise and support the vehicle.
6. Disconnect the front exhaust pipe to exhaust man-
ifold connection.
7. Lower the vehicle.
8. Remove intake manifold (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD-REMOVAL).
9. Disconnect the spark plug wires by pulling on the boot straight out in line with the spark plug. Dislodge spark
plug retainers from the cylinder head cover studs and position the spark plug wires aside.
10. Disconnect the oil level indicator tube and set aside.
11. Disconnect CCV hoses from cylinder head covers.
12. Remove the cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS - REMOVAL).
13. Remove exhaust manifold heat shields.
14. Remove exhaust manifold(s) and gasket(s) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL).
NOTE: If rocker arms and push rods are to be reused, identify each componentto ensure installation in
original locations.
15. Remove the rocker arm and pedestal assemblies (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS -
REMOVAL).
16. Remove push rods.
17. Remove the 12 head bolts and 8 cylinder head tappet gallery bolts from cylinder head(s).
18. Remove cylinder head(s) and gasket(s).