2006 DODGE RAM SRT-10 lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 4312 of 5267

MOTOR-SHIFT
DESCRIPTION
The shift motor (1) consists of a permanent magnet
D.C. motor with gear reduction to convert a high
speed-low torque device into a low speed-high torque
device. The output of the device is coupled to a shaft
which internally moves the mode and range forks that
change the transfer case operating ranges. The motor
is rated at 25 amps maximum at (23° C (72° F) with
10 volts at the motor leads.
OPERATION
The transfer case shift motor responds to the Transfer
Case Control Module (TCCM) commands to move the transfer case shift sectorbi-directionally, as required, to
obtain the transfer case operating mode indicated by the instrument panelmounted selector switch.
REMOVAL
NOTE: New shift motor assemblies are shipped in the 2WD/AWD position. If a new shift motor assembly will
be installed, it will be necessary to shift the transfer case to the 2WD/AWDposition prior to motor removal.
1. Raise the vehicle on a suitable hoist.
2. Disengage the wiring connectors from the shift motor and mode sensor.
3. Remove the bolts holding the shift motor and mode sensor assembly onto the transfer case.
4. Separate the shift motor and mode sensor assembly from the transfer case.
INSTALLATION
1. Verify that the shift sector o-ring is clean and properly positioned over the shift sector and against the transfer
case.
NOTE: Verify that the shift motor position and sector shaft orientation are aligned. It may be necessary to
manually shift the transfer case if the shift motor and sector shaft are notaligned.
2. Position the shift motor and mode sensor assembly onto the transfer case.
3. Install the bolts to hold the assembly onto the transfer case. Tighten the bolts to 16-24 Nꞏm (12-18 ft.lbs.).
CAUTION: If the original shift motor and mode sensor assembly bolts are reused, be sure to use Mopar
Lock & Seal or Loctite™ 242 to replenish the lock patch material originallyfound on the bolts
4. Engage the wiring connectors to the shift motor and mode sensor.
5. Refill the transfer case as necessary.
6. Lower vehicle and verify transfer case operation.
Page 4322 of 5267

Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capacity as other types of tires of the same size. They also use the
same recommended inflation pressures.
The use of oversized tires, either in the front or rear of the vehicle, can cause vehicle drive train failure. This could
also cause inaccurate wheel speed signals when the vehicle is equipped with Anti-Lock Brakes.
The use of tires from different manufactures on the same vehicle is NOT recommended. The proper tire pressure
should be maintained on all four tires.
TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH SPEEDS
For proper tire pressure specification refer to the Owners Manual.
REPLACEMENT TIRES
The original equipment tires provide a proper balance of many characteristics such as:
Ride
Noise
Handling
Durability
Tread life
Traction
Rolling resistance
Speed capability
It is recommended that tires equivalent to the original equipment tires beused when replacement is needed.
Failure to use equivalent replacement tires may adversely affect the safety and handling of the vehicle.
The use of oversize tires may cause interference with vehicle components.Under extremes of suspension and
steering travel, interference with vehicle components may cause tire damage.
WARNING: Failure to equip the vehicle with tires having adequate speed capability can result in sudden tire
failure.
TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES
WARNING: Over or under inflated tires can affect
vehicle handling and tread wear. This may cause
the tire to fail suddenly, resulting in loss of vehicle
control.
Under inflation will cause rapid shoulder wear (1), tire
flexing, and possible tire failure.
Page 4339 of 5267

BODY
WARNING
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: Use an OSHA approved breathing filter when spraying paint or solvents in a confined area. Per-
sonal injury can result.
Avoidprolongedskincontactwithpetroleumoralcohol–basedcleaningsolvents. Personal injury can
result.
Do not stand under a hoisted vehicle that is not properly supported on safety stands. Personal injury can
result.
CAUTION: When holes must be drilled or punched in an inner body panel, verify depth of space to the outer
body panel, electrical wiring, or other components. Damage to vehicle canresult.
Do not weld exterior panels unless combustible material on the interior ofvehicle is removed from the
repair area. Fire or hazardous conditions, can result.
Always have a fire extinguisher ready for use when welding.
Disconnect the negative (-) cable clamp from the battery when servicing electrical components that are
live when the ignition is OFF. Damage to electrical system can result.
Do not use abrasive chemicals or compounds on painted surfaces. Damage to finish can result.
Do not use harsh alkaline based cleaning solvents on painted or upholstered surfaces. Damage to finish
or color can result.
Do not hammer or pound on plastic trim panel when servicing interior trim. Plastic panels can break.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WAT E R L E A K S
Water leaks can be caused by poor sealing, improper body component alignment, body seam porosity, missing
plugs, or blocked drain holes. Centrifugal and gravitational force can cause water to drip from a location away from
the actual leak point, making leak detection difficult. All body sealing points should be water tight in normal wet-
driving conditions. Water flowing downward from the front of the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not always seal water tight under all conditions. At times, side glass or
door seals will allow water to enter the passenger compartment during highpressure washing or hard driving rain
(severe) conditions. Overcompensating on door or glass adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under severe
conditions can cause premature sealwear and excessive closing or latching effort. After completing a repair, water
test vehicle to verify leak has stopped before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE WATER LEAK TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place, body drains are clear, and body components are properly aligned and
sealed. If component alignment or sealing is necessary, refer to the appropriate section of this group for proper
procedures.
WATER LEAK TESTS
WARNING: Do not use electric shop lights or tools in water test area. Personal injury can result.
When the conditions causing a water leak have been determined, simulate the conditions as closely as possible.
Ifaleakoccurswiththevehicleparkedinasteadylightrain,floodtheleak area with an open-ended garden
hose.
If a leak occurs while driving at highway speeds in a steady rain, test the leak area with a reasonable velocity
stream or fan spray of water. Direct the spray in a direction comparable to actual conditions.
If a leak occurs when the vehicle is parked on an incline, hoist the end or sideofthevehicletosimulatethis
condition. This method can be used when the leak occurs when the vehicle accelerates, stops or turns. If the
leak occurs on acceleration, hoist the front of the vehicle. If the leak occurs when braking, hoist the back of the
Page 4341 of 5267

POSSIBLE CAUSE OF WIND NOISE
Moldings standing away from body surface can catch wind and whistle.
Gaps in sealed areas behind overhanging body flanges can cause wind-rushing sounds.
Misaligned movable components.
Missing or improperly installed plugs in pillars.
Weld burn through holes.
Improperly installed roof rack cross bars.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
BODY LUBRICATION
All mechanisms and linkages should be lubricated when necessary. This will maintain ease of operation and provide
protection against rust and excessive wear. The weatherstrip seals should be lubricated to prolong their life as well
as to improve door sealing.
All applicable exterior and interior vehicle operating mechanisms should be inspected and cleaned. Pivot/sliding con-
tact areas on the mechanisms should then be lubricated.
1. When necessary, lubricate the operating mechanisms with the specifiedlubricants.
2. Apply silicone lubricant to a clothand wipe it on door seals to avoid over-spray that can soil passenger’s cloth-
ing.
3. Before applying lubricant, the component should be wiped clean. After lubrication, any excess lubricant should be
removed.
4. The hood latch, latch release mechanism, latch striker, and safety latch should be lubricated periodically.
5. The door lock cylinders should be lubricated twice each year (preferably autumn and spring).
Spray a small amount of lock cylinder lubricant directly into the lock cylinder.
Apply a small amount to the key and insert it into the lock cylinder.
Rotate it to the locked position and then back to the unlocked position several times.
Remove the key. Wipe the lubricant from it with a clean cloth to avoid soiling of clothing.
HEAT STAKING
1. Remove trim panel.
2. Bend or move the trim panel components at the heat staked joints. Observethe heat staked locations and/or
component seams for looseness.
3. Heat stake the components.
a. If the heat staked or component seam location is loose, hold the two components tightly together and using
a soldering gun with a flat tip, melt the material securing the components together. Do not over heat the
affected area, damage to the exterior of the trim panel may occur.
b. Iftheheatstakedmaterialisbrokenormissing,useahotglueguntoapplynewmaterialtotheareatobe
repaired. The panels that are being heat staked must be held together whiletheapplyingtheglue.Oncethe
new material is in place, it may be necessary to use a soldering gun to melt the newly applied material. Do
not over heat the affected area, damage to the exterior of the trim panel mayoccur.
4. Allow the repaired area to cool and verify the repair.
5. Install trim panel.
BUZZ, SQUEAK & RATTLE
Buzz, Squeak & Rattles (BSR) may be caused by any one or more of the followingand may be corrected as indi-
cated:
Loose fasteners should be tightened to specifications.
Damaged or missing clips should be replaced.
Damaged trim panels should be replaced.
Incorrectly installed trim panels should be reinstalled properly.
Page 4342 of 5267
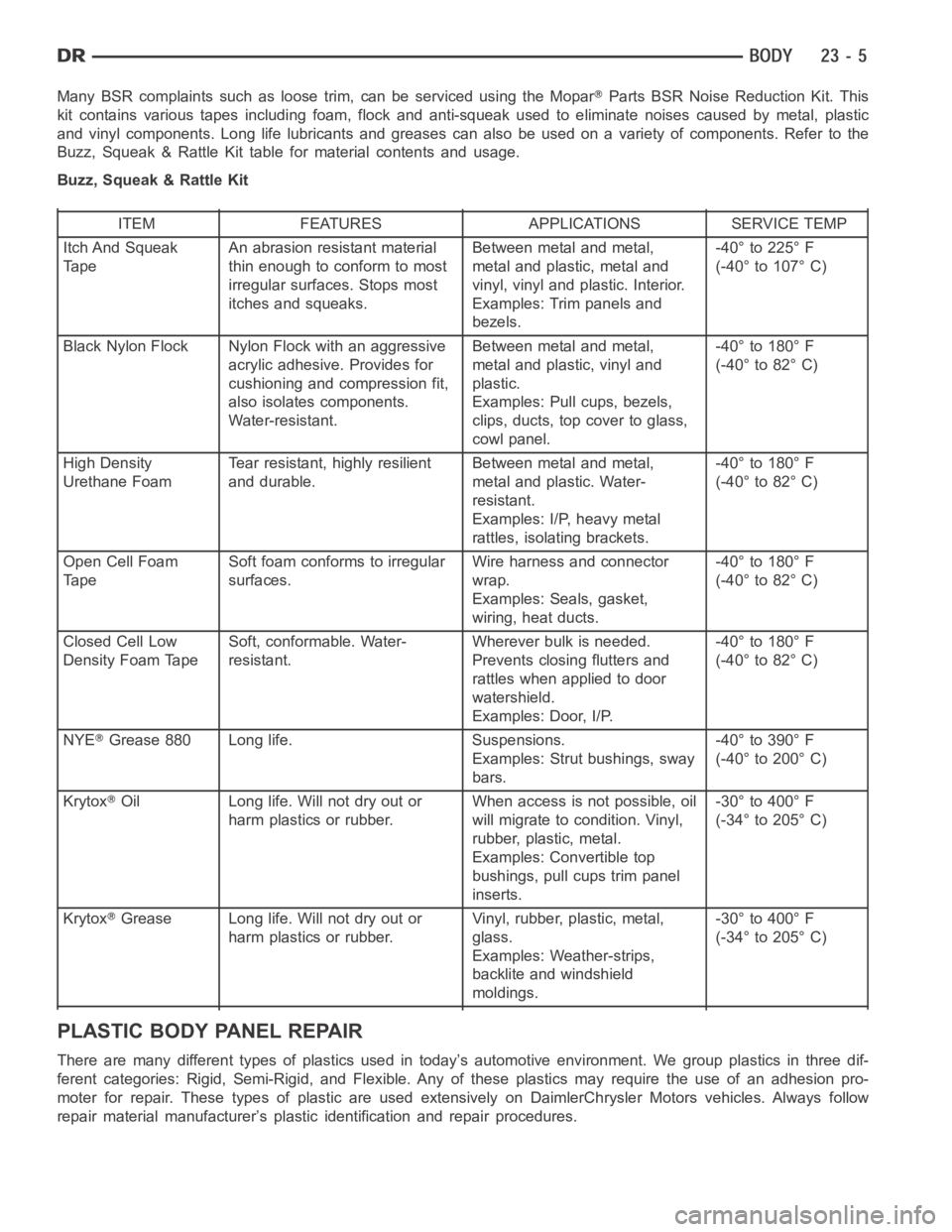
Many BSR complaints such as loose trim, can be serviced using the MoparParts BSR Noise Reduction Kit. This
kit contains various tapes including foam, flock and anti-squeak used to eliminate noises caused by metal, plastic
and vinyl components. Long life lubricants and greases can also be used on avariety of components. Refer to the
Buzz, Squeak & Rattle Kit table for material contents and usage.
Buzz, Squeak & Rattle Kit
ITEM FEATURES APPLICATIONS SERVICE TEMP
Itch And Squeak
TapeAn abrasion resistant material
thin enough to conform to most
irregular surfaces. Stops most
itches and squeaks.Between metal and metal,
metal and plastic, metal and
vinyl, vinyl and plastic. Interior.
Examples: Trim panels and
bezels.-40° to 225° F
(-40° to 107° C)
Black Nylon Flock Nylon Flock with an aggressive
acrylic adhesive. Provides for
cushioning and compression fit,
also isolates components.
Water-resistant.Between metal and metal,
metal and plastic, vinyl and
plastic.
Examples: Pull cups, bezels,
clips, ducts, top cover to glass,
cowl panel.-40° to 180° F
(-40° to 82° C)
High Density
Urethane FoamTear resistant, highly resilient
and durable.Between metal and metal,
metal and plastic. Water-
resistant.
Examples: I/P, heavy metal
rattles, isolating brackets.-40° to 180° F
(-40° to 82° C)
Open Cell Foam
TapeSoft foam conforms to irregular
surfaces.Wire harness and connector
wrap.
Examples: Seals, gasket,
wiring, heat ducts.-40° to 180° F
(-40° to 82° C)
Closed Cell Low
Density Foam TapeSoft, conformable. Water-
resistant.Wherever bulk is needed.
Prevents closing flutters and
rattles when applied to door
watershield.
Examples: Door, I/P.-40° to 180° F
(-40° to 82° C)
NYE
Grease 880 Long life. Suspensions.
Examples: Strut bushings, sway
bars.-40° to 390° F
(-40° to 200° C)
Krytox
Oil Long life. Will not dry out or
harm plastics or rubber.When access is not possible, oil
will migrate to condition. Vinyl,
rubber, plastic, metal.
Examples: Convertible top
bushings, pull cups trim panel
inserts.-30° to 400° F
(-34° to 205° C)
Krytox
Grease Long life. Will not dry out or
harm plastics or rubber.Vinyl, rubber, plastic, metal,
glass.
Examples: Weather-strips,
backlite and windshield
moldings.-30° to 400° F
(-34° to 205° C)
PLASTIC BODY PANEL REPAIR
There are many different types of plastics used in today’s automotive environment. We group plastics in three dif-
ferent categories: Rigid, Semi-Rigid, and Flexible. Any of these plastics may require the use of an adhesion pro-
moter for repair. These types of plastic are used extensively on DaimlerChrysler Motors vehicles. Always follow
repair material manufacturer’s plastic identification and repair procedures.
Page 4344 of 5267
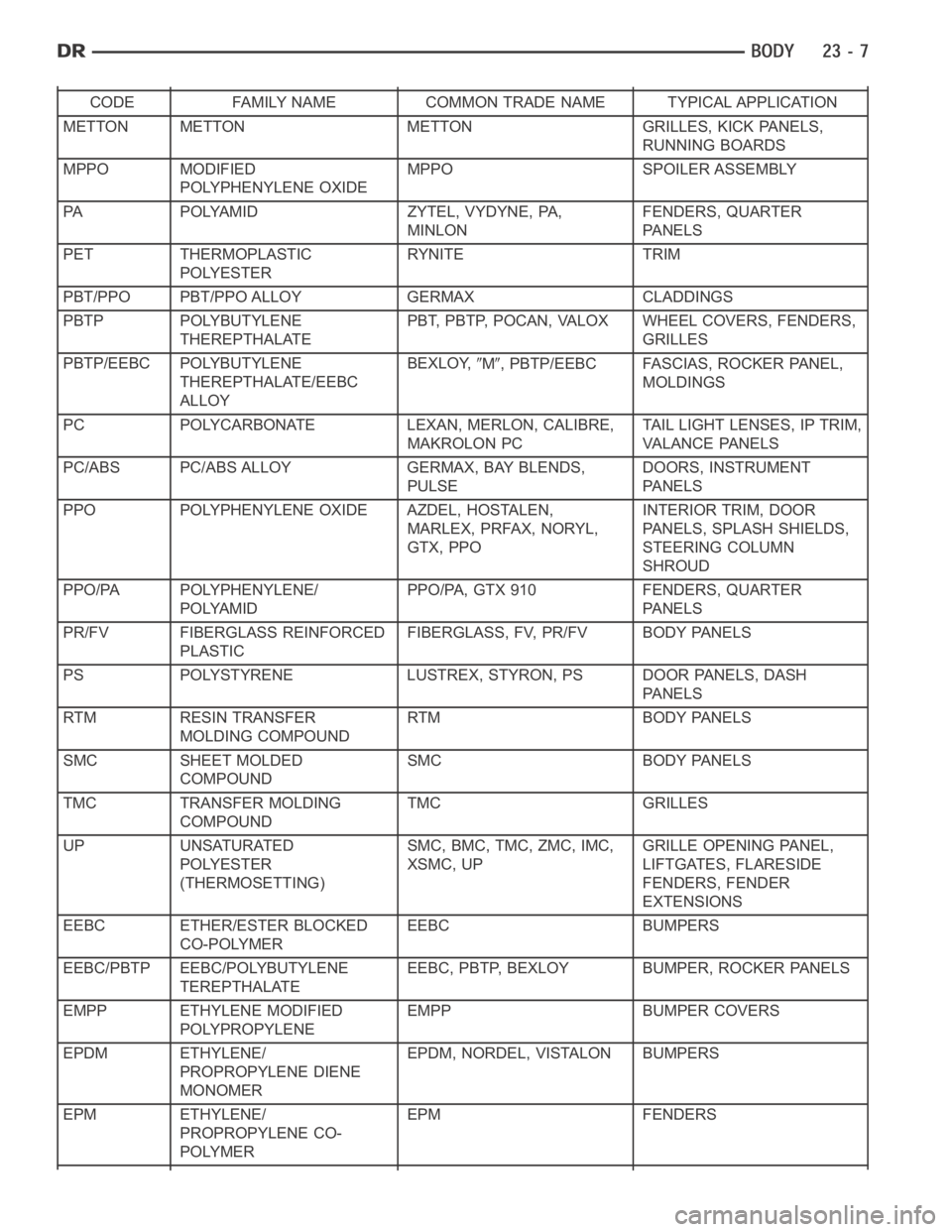
CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
METTON METTON METTON GRILLES, KICK PANELS,
RUNNING BOARDS
MPPO MODIFIED
POLYPHENYLENE OXIDEMPPO SPOILER ASSEMBLY
PA POLYAMID ZYTEL, VYDYNE, PA,
MINLONFENDERS, QUARTER
PA N E L S
PET THERMOPLASTIC
POLYESTERRYNITE TRIM
PBT/PPO PBT/PPO ALLOY GERMAX CLADDINGS
PBTP POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATEPBT, PBTP, POCAN, VALOX WHEEL COVERS, FENDERS,
GRILLES
PBTP/EEBC POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATE/EEBC
ALLOYBEXLOY,
M, PBTP/EEBC FASCIAS, ROCKER PANEL,
MOLDINGS
PC POLYCARBONATE LEXAN, MERLON, CALIBRE,
MAKROLON PCTAIL LIGHT LENSES, IP TRIM,
VA L A N C E PA N E L S
PC/ABS PC/ABS ALLOY GERMAX, BAY BLENDS,
PULSEDOORS, INSTRUMENT
PA N E L S
PPO POLYPHENYLENE OXIDE AZDEL, HOSTALEN,
MARLEX, PRFAX, NORYL,
GTX, PPOINTERIOR TRIM, DOOR
PANELS, SPLASH SHIELDS,
STEERING COLUMN
SHROUD
PPO/PA POLYPHENYLENE/
POLYAMIDPPO/PA, GTX 910 FENDERS, QUARTER
PA N E L S
PR/FV FIBERGLASS REINFORCED
PLASTICFIBERGLASS, FV, PR/FV BODY PANELS
PS POLYSTYRENE LUSTREX, STYRON, PS DOOR PANELS, DASH
PA N E L S
RTM RESIN TRANSFER
MOLDING COMPOUNDRTM BODY PANELS
SMC SHEET MOLDED
COMPOUNDSMC BODY PANELS
TMC TRANSFER MOLDING
COMPOUNDTMC GRILLES
UP UNSATURATED
POLYESTER
(THERMOSETTING)SMC, BMC, TMC, ZMC, IMC,
XSMC, UPGRILLE OPENING PANEL,
LIFTGATES, FLARESIDE
FENDERS, FENDER
EXTENSIONS
EEBC ETHER/ESTER BLOCKED
CO-POLYMEREEBC BUMPERS
EEBC/PBTP EEBC/POLYBUTYLENE
TEREPTHALATEEEBC, PBTP, BEXLOY BUMPER, ROCKER PANELS
EMPP ETHYLENE MODIFIED
POLYPROPYLENEEMPP BUMPER COVERS
EPDM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE DIENE
MONOMEREPDM, NORDEL, VISTALON BUMPERS
EPM ETHYLENE/
PROPROPYLENE CO-
POLYMEREPM FENDERS
Page 4350 of 5267

17. Using a 125 mm (5 in.) 24 grit disc grinder, grind
a50mm(2in.)to75mm(3in.)wideand2mm
(0.080 in.) deep path across the gaps around the
patch. With compressed air, blow dust from
around patch.
18. Apply adhesive backed nylon mesh (dry wall tape)
over gaps around patch.
19. Mix enough adhesive to cover the entire patch
area.
20. Apply adhesive over the mesh around patch, and
smooth epoxy with a wide spreader to reduce fin-
ish grinding. Use two to three layers of mesh and
adhesive to create a stronger repair.
PATCHED PANEL SURFACING
After patch panel is installed, the patch area can be finished using the same methods as finishing other types of
body panels. If mesh material is exposed in the patched area, grind surfacedown, and apply a coat of high quality
rigid plastic body filler. Prime, block sand, and paint as required.
Page 4355 of 5267

CABLE-CHECK
REMOVAL
1. Open the tailgate and locate the tailgate check
cable (3) on the left and right of the cargo box
below the tailgate striker (1) as necessary.
2. Pry the cable lock tab(s) (4) outward using a
screwdriver or flat bladed tool (2) and remove the
tailgate check cable(s) from the cargo box.
3. Remove the bolt (1) that secures the tailgate check
cable (2) to the left and right side of the tailgate (3)
as necessary.
4. Remove the tailgate check cable(s) from the
tailgate.