2006 DODGE RAM SRT-10 check oil
[x] Cancel search: check oilPage 1492 of 5267
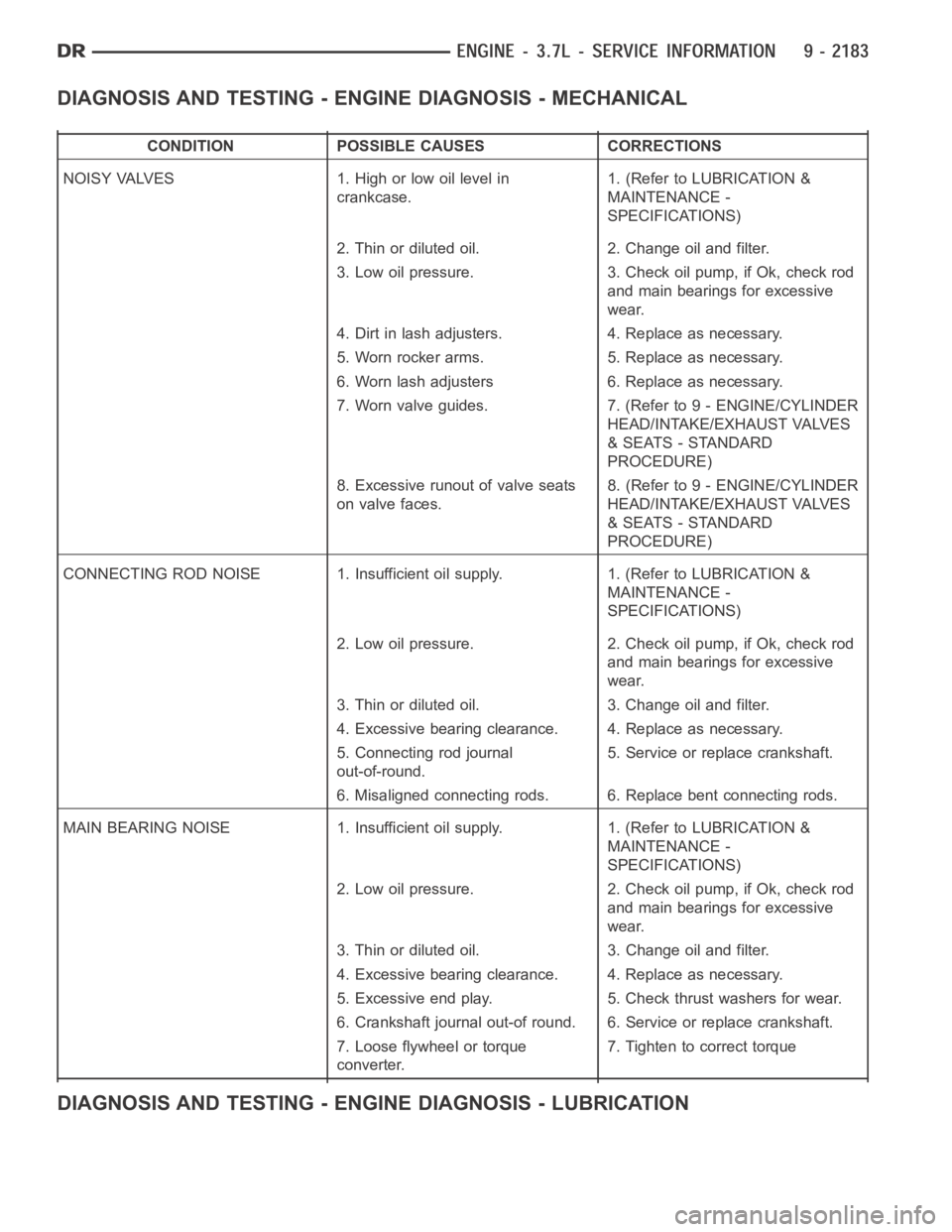
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil and filter.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
4. Dirt in lash adjusters. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Worn rocker arms. 5. Replace as necessary.
6. Worn lash adjusters 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Worn valve guides. 7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
8. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.8. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION&
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.5. Service or replace crankshaft.
6. Misaligned connecting rods. 6. Replace bent connecting rods.
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE -
SPECIFICATIONS)
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Excessive end play. 5. Check thrust washers for wear.
6. Crankshaft journal out-of round. 6. Service or replace crankshaft.
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.7. Tighten to correct torque
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - LUBRICATION
Page 1493 of 5267

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL LEAKS 1. Gaskets and O-Rings. Misaligned
or damaged.1. Replace as necessary.
(a) Loose fasteners, broken or
porous metal parts.(a) Tighten fasteners, Repair or
replace metal parts.
2. Crankshaft rear seal 2. Replace as necessary (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR -
REMOVAL).
3. Crankshaft seal flange.
Scratched, nicked or grooved.3. Polish or replace crankshaft.
4. Oil pan flange cracked. 4. Replace oil pan (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN -
REMOVAL).
5. Timing chain cover seal,
damaged or misaligned.5. Replace seal (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - FRONT
- REMOVAL).
6. Scratched or damaged vibration
damper hub.6. Polish or replace damper.
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check and correct oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit. 2. Replace sending unit (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL
PRESSURE SENSOR/SWITCH -
REMOVAL).
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump and bearing
clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Replace oil filter (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL FILTER
- REMOVAL).
5. Worn oil pump. 5. Replace oil pump (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP
- REMOVAL).
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil and filter.
7. Excessive bearing clearance. 7. Replace as necessary.
8. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 8. Replace oil pump (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP
- REMOVAL).
9. Oil pick up tube loose, damaged
or clogged.9. Replace as necessary.
Page 1494 of 5267

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL PUMPING AT RINGS; SPARK
PLUGS FOULING1. Worn or damaged rings. 1. Hone cylinder bores and replace
rings.
2. Carbon in oil ring slots. 2. Replace rings (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON
RINGS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
3. Incorrect ring size installed. 3. Replace rings (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON
RINGS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
4. Worn valve guides. 4. Ream guides and replace valves
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
5. Leaking valve guide seals. 5. Replace valve guide seals.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compressionpressure test can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunctions.
Ensurethebatteryiscompletelychargedandtheenginestartermotorisingood operating condition. Otherwise the
indicated compression pressures may not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
1. Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed air.
2. Remove the spark plugs.
3. Disable the fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DESCRIPTION).
4. Remove the ASD relay (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/AUTO SHUTDOWNRELAY-
REMOVAL).
5. Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate the engine with the engine starter motor for three revolutions.
6. Record the compression pressure on the 3rd revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylinders.
7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for the correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDERCOMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seating).
Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water jacket.
Any causes for combustion/compression pressure loss.
1. Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO NOT install the radiatorcap.
2. Start and operate the engine until it attains normal operating temperature, then turn the engine OFF.
3. Remove the spark plugs.
4. Remove the oil filler cap.
5. Remove the air cleaner hose.
6. Calibrate the tester according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The shop air source for testing should maintain
483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379 kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recommended.
7. Perform the test procedures on each cylinder according to the tester manufacturer’s instructions. Set piston of
cylinder to be tested at TDC compression,While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping through the throttle
body, tailpipe and oil filler cap opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal, with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pressure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be maintained in the
cylinder.
Page 1498 of 5267

17. Disconnect the engine wiring harness at the fol-
lowing points :
Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor (4)
Fuel Injectors
Throttle Position (TPS) Switch (2)
Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor (3)
Engine Oil Pressure Switch
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Manifold Absolute Pressure MAP) Sensor
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
Coil Over Plugs
Crankshaft Position Sensor
18. Remove coil over plugs.
19. Release fuel rail pressure.
20. Remove fuel rail and secure away from engine.
NOTE: It is not necessary to release the quick
connect fitting from the fuel supply line for engine
removal.
21. Remove the PCV hose.
22. Remove the breather hoses.
23. Remove the vacuum hose for the power brake
booster.
24. Disconnect knock sensors.
25. Remove engine oil dipstick tube.
26. Remove intake manifold.
27. Install engine lifting fixture,special tool#8247, using original fasteners from the removed intake manifold, and
fuel rail. Torque to factory specifications.
NOTE: Recheck bolt torque for engine lift plate before removing engine.
28. Secure the left and right engine wiring harnesses away from engine.
29. Raise vehicle.
30. Disconnect oxygen sensor wiring.
Page 1504 of 5267

34. Install the A/C compressor (2).
35. Install the drive belt.
36. Install the fan shroud with the viscous fan assem-
bly.
37. Install the radiator core support bracket.
38. Install the air cleaner assembly.
39. Refill the engine cooling system.
40. Recharge the air conditioning.
41. Check and fill engine oil.
42. Connect the battery negative cable.
43. Start the engine and check for leaks.
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - 3.7L ENGINE
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Type 90°SOHCV612Valve
Number of Cylinders 6
Firing Order 1-6-5-4-3-2
Lead Cylinder No. 1 Left Bank
Compression Ratio 9.6:1
Max. Variation Between Cylinders 25%
Metric Standard
Displacement 3.7 Liters 226 Cubic Inches
Bore 93.0 mm 3.66 in.
Stroke 90.8 mm 3.40 in.
Horsepower 211 @ 5200 RPM
Torque 236ft. lbs.@4000 PRM
Compression Pressure 1172-1551 kPa 170-225 psi
CYLINDER BLOCK
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Bore Diameter 93.013 ± .0075 mm 3.6619 ± 0.0003 in.
Out of Round (MAX) 0.076 mm 0.003 in.
Taper (MAX) 0.051 mm 0.002 in.
PISTONS
Page 1536 of 5267

HEAD-CYLINDER-RIGHT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTER
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several items. Check the followingitems.
1. Engine oil level too high or too low. This may cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause them to be
spongy.
2. Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylinder head. Low speed runningupto1hourmayberequired.
3. Turn engine off and let set for a few minutes before restarting. Repeat this several times after engine has
reached normal operating temperature.
4. Low oil pressure.
5. The oil restrictor in cylinder head gasket or the oil passage to the cylinder head is plugged with debris.
6. Airingestedintooilduetobrokenorcrackedoilpumppickup.
7. Worn valve guides.
8. Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring retainer.
9. Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maximum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
10. Oil leak or excessive cam bore wear in cylinder head.
11. Faulty lash adjuster.
a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while installed in cylinder head and cam on camshaft at base circle.
Depress part of rocker arm over adjuster. Normal adjusters should feel firm when pressed quickly. When pressed
very slowly, lash adjusters should collapse.
b. Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace.
c. Before installation, make sure adjusters are full of oil. This can be verified by little plunger travel when lash
adjuster is depressed quickly.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL RIGHT CYLINDER HEAD
1. Disconnect battery negative cable.
2. Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
3. Disconnect the exhaust pipe at the right side
exhaust manifold.
4. Drain the engine coolant (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
5. Lower the vehicle.
6. Remove the intake manifold (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - REMOVAL).
7. Remove the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
8. Remove the fan shroud (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
9. Remove oil fill housing from cylinder head.
10. Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
11. Rotate the crankshaft until the damper timing
mark is aligned with TDC indicator mark (2).
Page 1542 of 5267

12. Remove Special Tool 8429 (1).
13. Install the timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
14. Install the crankshaft damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
INSTALLATION). Tighten damper bolt 175 Nꞏm
(130 Ft. Lbs.).
15. Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
16. Install the fan shroud (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION).
17. Install the cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
18. Install the intake manifold (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - INSTALLA-
TION).
19. Install oil fill housing onto cylinder head.
20. Refill the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
21. Raise the vehicle.
22. Install the exhaust pipe onto the right exhaust manifold.
23. Lower the vehicle.
24. Reconnect battery negative cable.
25. Start the engine and check for leaks.
Page 1553 of 5267

BLOCK-ENGINE
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder block is made of cast iron.The block is a closed deck design with the left bank forward. To provide
high rigidity and improved NVH an enhanced compacted graphite bedplate isbolted to the block. The block design
allows coolant flow between the cylinders bores, and an internal coolant bypass to a single poppet inlet thermostat
is included in the cast aluminum front cover.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE HONING
Before honing, stuff plenty of clean shop towels under
the bores and over the crankshaft to keep abrasive
materials from entering the crankshaft area.
1. Used carefully, the Cylinder Bore Sizing Hone
C-823, equipped with 220 grit stones, is the best
tool for this job. In addition to deglazing, it will
reduce taper and out-of-round, as well as removing
light scuffing, scoring and scratches. Usually, a few
strokes will clean up a bore and maintain the
required limits.
CAUTION: DO NOT use rigid type hones to remove
cylinder wall glaze.
2. Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done if the
cylinder bore is straight and round. Use a cylinder
surfacing hone, Honing Tool C-3501, equipped with
280 grit stones (C-3501-3810). about 20-60
strokes, depending on the bore condition, will be
sufficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Using
honing oil C-3501-3880, or a light honing oil, avail-
able from major oil distributors.
CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil, mineral spirits, or kerosene.
3. Honing should be done by moving the hone up and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern (1). The hone
marks should INTERSECT at 50° to 60° for proper seating of rings (2).
4. A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and 300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper crosshatch angle.
The number of up and down strokes per minute can be regulated to get the desired 50° to 60° angle. Faster up
and down strokes increase the crosshatch angle.
5. After honing, it is necessary that the block be cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush to wash
parts with a solution of hot water and detergent. Dry parts thoroughly. Usea clean, white, lint-free cloth to check
that the bore is clean. Oil the bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
CLEANING
Thoroughly clean the oil pan and engine block gasket surfaces.
Use compressed air to clean out:
The galley at the oil filter adaptor hole.
The front and rear oil galley holes.
The feed holes for the crankshaft main bearings.
Once the block has been completely cleaned, apply Loctite PST pipe sealantwith Teflon 592 to the threads of the
front and rear oil galley plugs. Tighten the 1/4 inch NPT plugs to 20 Nꞏm (177in. lbs.) torque. Tighten the 3/8 inch
NPT plugs to 27 Nꞏm (240 in. lbs.) torque.