2006 DODGE RAM SRT-10 ignition
[x] Cancel search: ignitionPage 1625 of 5267
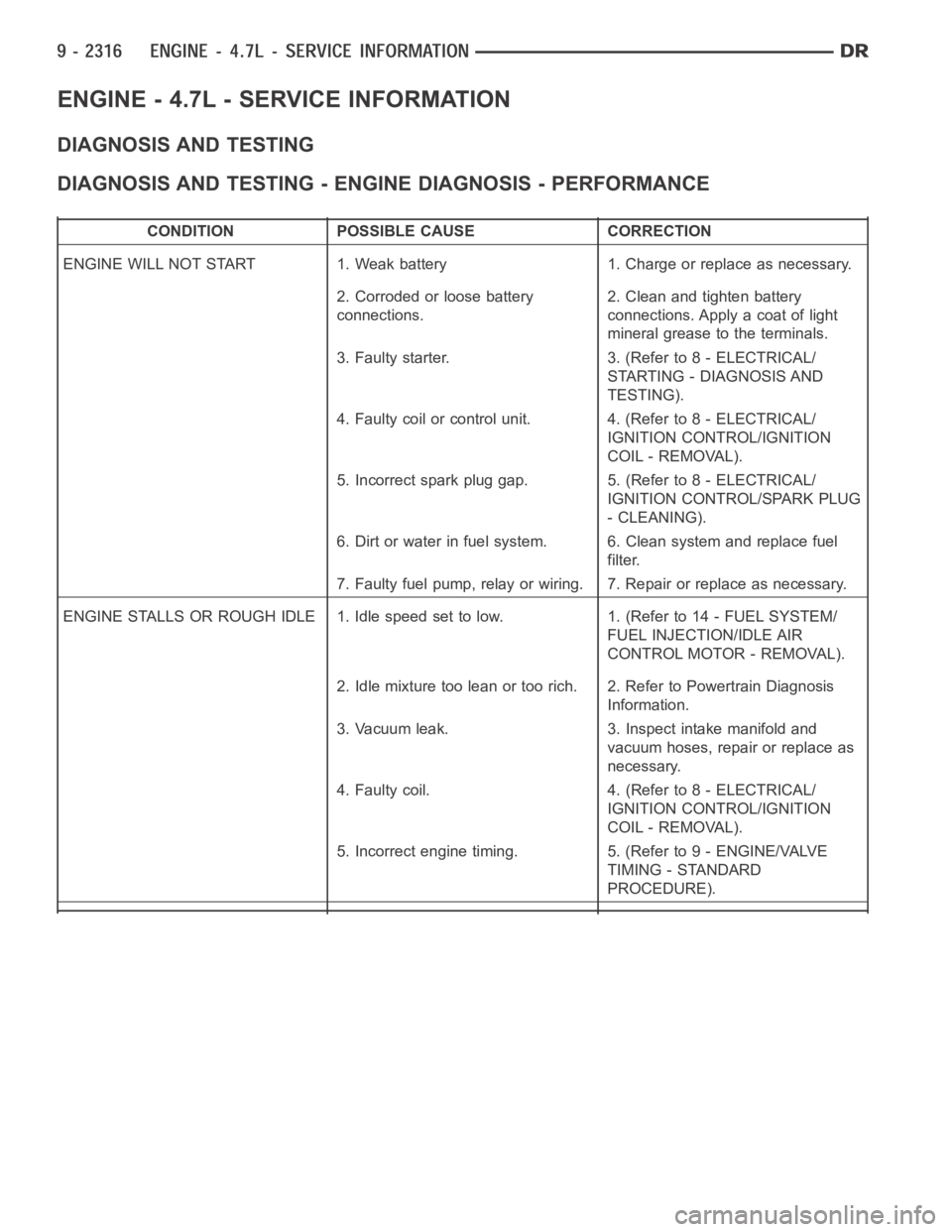
ENGINE - 4.7L - SERVICE INFORMATION
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
4. Faulty coil or control unit. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
6. Dirt or water in fuel system. 6. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
7. Faulty fuel pump, relay or wiring. 7. Repair or replace as necessary.
ENGINE STALLS OR ROUGH IDLE 1. Idle speed set to low. 1. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL INJECTION/IDLE AIR
CONTROL MOTOR - REMOVAL).
2. Idle mixture too lean or too rich. 2. Refer to Powertrain Diagnosis
Information.
3. Vacuum leak. 3. Inspect intake manifold and
vacuum hoses, repair or replace as
necessary.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect engine timing. 5. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE
TIMING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
Page 1626 of 5267

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE LOSS OF POWER 1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Dirt or water in fuel system. 2. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump. 3. Refer to the Appropriate
Diagnostic Information
4. Blown cylinder head gasket. 4. Replace cylinder head gasket.
5. Low compression. 5. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
6. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system.7. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
8. Faulty coil. 8. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Dirt in fuel system. 2. Clean fuel system.
3. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 3. Replcae as necessary.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
ENGINE MISSES AT HIGH SPEED 1. Spark plugs dirty or incorrectly
gapped.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
2. Faulty coil. 2. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
3. Dirt or water in fuel system. 3. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
Page 1628 of 5267

Ensurethebatteryiscompletelychargedandtheenginestartermotorisingood operating condition. Otherwise the
indicated compression pressures may not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
1. Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed air.
2. Remove the spark plugs.
3. Disable the fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DESCRIPTION).
4. Remove the ASD relay (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/AUTO SHUTDOWNRELAY-
REMOVAL).
5. Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate the engine with the engine starter motor for three revolutions.
6. Record the compression pressure on the 3rd revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylinders.
7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for the correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDERCOMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seating).
Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water jacket.
Any causes for combustion/compression pressure loss.
1. Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO NOT install the radiatorcap.
2. Start and operate the engine until it attains normal operating temperature, then turn the engine OFF.
3. Remove the spark plugs.
4. Remove the oil filler cap.
5. Remove the air cleaner hose.
6. Calibrate the tester according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The shop air source for testing should maintain
483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379 kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recommended.
7. Perform the test procedures on each cylinder according to the tester manufacturer’s instructions. Set piston of
cylinder to be tested at TDC compression,While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping through the throttle
body, tailpipe and oil filler cap opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal, with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pressure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be maintained in the
cylinder.
Refer to CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART .
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
THROTTLE BODYIntake valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary.
Inspect valve springs. Replace as
necessary.
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
TAILPIPEExhaust valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary.
Inspect valve springs. Replace as
necessary.
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
RADIATORHead gasket leaking or cracked
cylinder head or blockRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace defective part
MORE THAN 50% LEAKAGE
FROM ADJACENT CYLINDERSHead gasket leaking or crack in
cylinder head or block between
adjacent cylindersRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace gasket, head, or block as
necessary
Page 1678 of 5267

COVER - CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head covers are made of injection molded thermo-set plastic,and are not interchangeable from side-
to-side. It is imperativethat nothing rest on the cylinder head covers. Prolonged contact with other items may wear
a hole in the cylinder head cover.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - RIGHT SIDE
1. Disconnect battery negative cable.
2. Remove air cleaner assembly, resonator assembly and air inlet hose.
3. Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
4. Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - REMOVAL).
5. Remove air conditioning compressor retaining bolts and move compressortotheleft.
6. Remove heater hoses.
7. Disconnect injector and ignition coil connectors.
8. Disconnect and remove positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) hose.
9. Remove oil fill tube.
10. Un-clip injector and ignition coil harness and move away from cylinderhead cover.
11. Remove right rear breather tube and filter assembly.
12. Remove cylinder head cover retaining bolts.
13. Remove cylinder head cover.
NOTE: The gasket may be used again, provided no cuts, tears, or deformationhas occurred.
REMOVAL - LEFT SIDE
1. Disconnect negative cable from battery.
2. Remove the resonator assemble and air inlet hose.
3. Disconnect injector connectors and un-clip the injector harness.
4. Route injector harness in front of cylinder head cover.
5. Disconnect the left side breather tube and remove the breather tube.
6. Remove the cylinder head cover mounting bolts.
7. Remove cylinder head cover and gasket.
NOTE: The gasket may be used again, provided no cuts, tears, or deformationhas occurred.
CLEANING
Clean cylinder head cover gasket surface.
Clean head rail, if necessary.
Page 1679 of 5267

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - RIGHT SIDE
CAUTION: Do not use harsh cleaners to clean the
cylinder head covers. Severe damage to covers
may occur.
1. Clean cylinder head cover and both sealing sur-
faces. Inspect and replace gasket as necessary.
2. Install cylinder head cover and hand start all fas-
teners (1). Verify that all double ended studs are in
the correct location shown in.
3. Tighten cylinder head cover bolts and double
ended studs to 12 Nꞏm (105 in. lbs).
4. Install right rear breather tube and filter assembly.
5. Connect injector, ignition coil electrical connectors and harness retaining clips.
6. Install the oil fill tube.
7. Install PCV hose.
8. Install heater hoses.
9. Install air conditioning compressor retaining bolts.
10. Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLATION).
11. Fill Cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
12. Install air cleaner assembly, resonator assembly and air inlet hose.
13. Connect battery negative cable.
INSTALLATION - LEFT SIDE
CAUTION: Do not use harsh cleaners to clean the
cylinder head covers. Severe damage to covers
may occur.
1. Clean cylinder head cover and both sealing sur-
faces. Inspect and replace gasket as necessary.
2. Install cylinder head cover and hand start all fas-
teners. Verify that all studs are in the correct loca-
tion shown in.
3. Tighten cylinder head cover bolts (1) and double
ended studs to 12 Nꞏm (105 in. lbs.).
4. Install left side breather and connect breather tube.
5. Connect injector electrical connectors and injector
harness retaining clips.
6. Install the resonator and air inlet hose.
7. Connect negative cable to battery.
Page 1732 of 5267

MANIFOLD - INTAKE
DESCRIPTION
The intake manifold is made of a composite material and features long runners which maximizes low end torque.
The intake manifold uses single plane sealing which consist of eight individual press in place port gaskets to prevent
leaks. Eight studs and two bolts are used to fasten the intake to the head.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by lower than normal manifoldvacuum. Also, one or more cylinders may
not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN ADIRECT LINE
WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN. DO NOT WEAR
LOOSE CLOTHING.
1. Start the engine.
2. Spray a small stream of water at the suspected leak area.
3. If a change in RPM is observed the area of the suspected leak has been found.
4. Repair as required.
REMOVAL
1. Disconnect negative cable from battery.
2. Remove resonator assembly and air inlet hose.
3. Disconnect throttle and speed control cables.
4. Disconnect electrical connectors for the following components:
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
Coolant Temperature (CTS) Sensor
Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
5. Disconnect brake booster hose and positive crankcase ventilation (PCV)hose.
6. Disconnect generator electrical connections.
7. Disconnect air conditioning compressor electrical connections.
8. Disconnect left and right radio suppressor straps.
9. Disconnect and remove ignition coil towers (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL -
REMOVAL).
10. Remove top oil dipstick tube retaining bolt and ground strap.
11. Bleed fuel system (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
12. Remove fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - REMOVAL).
13. Remove throttle body assembly and mounting bracket.
14. Drain cooling system below coolant temperature level (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Page 1734 of 5267

INSTALLATION
1. Install intake manifold gaskets.
2. Position intake manifold.
3. Install intake manifold retaining bolts and tighten in
sequence shown in to 12 Nꞏm (105 in. lbs.).
4. Install left and right radio suppressor straps.
5. Install throttle body assembly.
6. Install throttle cable bracket.
7. Connect throttle cable and speed control cable to
throttle body.
8. Install fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - INSTALLATION).
9. Install ignition coil towers (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL -
INSTALLATION).
10. Position and install heater hoses and tubes onto intake manifold.
11. Install the heater hoses to the heater core and engine front cover.
12. Connect electrical connectors for the following components:
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
Coolant Temperature (CTS) Sensor
Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
Ignition coil towers
Fuel injectors
13. Install top oil dipstick tube retaining bolt and ground strap.
14. Connect generator electrical connections.
15. Connect Brake booster hose and Positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) hose.
16. Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
17. Install resonator assembly and air inlet hose.
18. Connect negative cable to battery.
Page 1758 of 5267

ENGINE - 5.7L - SERVICE INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION
The 5.7L engine (345 CID) eight-cylinder engine is a 90° V-Type lightweight, deep skirt cast iron block, aluminum
heads, single cam, overhead valve engine with hydraulic roller tappets. The heads incorporate splayed valves with
a hemispherical style combustion chamber and dual spark plugs. The cylinders are numbered from front to rear; 1,
3, 5, 7 on the left bank and 2, 4, 6, 8 on the right bank. The firing order is 1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the causes of malfunctions notdetected and remedied by routine main-
tenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either performance (e.g., engineidles rough and stalls) or mechanical
(e.g., a strange noise).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) - PERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING)—MECHANICAL for possible causes and corrections of malfunctions. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be necessary for specificengine malfunctions that can not be iso-
lated with the Service Diagnosis charts. Information concerning additional tests and diagnosis is provided within the
following diagnosis:
Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
Cylinder Combustion Pressure LeakageTest (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSISAND TESTING).
Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKEMANIFOLD - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
4. Faulty coil or control unit. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
6. Dirt or water in fuel system. 6. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
7. Faulty fuel pump, relay or wiring. 7. Repair or replace as necessary.