1988 PONTIAC FIERO wiring
[x] Cancel search: wiringPage 406 of 1825

V-8 ENGINE 6A3-27
3. When finish honing
a cylinder bore to fit a piston,
the hone should be moved up and down at a
sufficient speed to obtain very fine uniform
surface finish marks in a cross-hatch pattern of
approximately
45" to 65" included angle. The
finish marks should be clean but not sharp, free
from imbedded particles and torn or folded
metal.
4. Permanently mark
the piston for the cylinder to
which it has been fitted and proceed to hone
cylinders and fit the remaining pistons.
NOTICE: Handle the pistons with care and do not
attempt to force them through the cylinder until
the cylinder has been honed to correct size as this
type piston can be distorted through careless
handling.
5. Thoroughly
clean the bores with hot water and
detergent. Scrub well with a stiff bristle brush and
rinse thoroughly with hot water. It is extremely
essential that a good cleaning operation be
performed. If any of the abrasive material is
allowed to remain in the cylinder bores, it will
rapidly wear the new rings and cylinder bores in
addition to the bearings lubricated by the
contaminated oil, the bores should be swabbed
and then wiped with a clean dry cloth. Cylinder
should not be cleaned with kerosene or gasoline.
Clean the remainder of the cylinder block to
remove the excess material spread during the
honing operation.
Piston Selection
1. Check USED piston to cylinder bore clearance as
follows:
a. Measure
the "Cylinder Bore Diameter"
with a telescope gage
"2-1/2" (64mm) from
top of cylinder bore").
b. Measure
the
"Piston Diameter" (at skirt
across center line of piston pin).
c. Subtract
piston diameter from cylinder bore
diameter to determine "Piston to Bore
Clearance".
d. Determine if piston to bore clearance is in
the acceptable range.
2. If
used piston is not acceptable, check Piston Size
Chart and determine if a new piston can be
selected to fit cylinder bore within the acceptable
range.
3. If
cylinder bore must be reconditioned, measure
new piston diameter (across center line of piston
pin) then hone cylinder bore to correct clearance
(preferable range).
4. Mark the piston to identify the cylinder for which
it was fitted.
OIL FILTER BYPASS VALVE
Inspection and Replacement
With the oil filter removed, check the spring and
fibre valve for operation. Inspect for a cracked or
broken valve. If replacement is necessary, the oil filter
adapter and bypass valve assembly must be replaced as an
assembly. Clean valve chamber in cylinder block
thoroughly. Torque retaining screws to specifications.
ENGINE ASSEMBLY
Removal
1. Disconnect battery.
2. Remove air cleaner.
3. Remove hood.
4. Drain radiator.
5. Remove lower radiator hose.
6. Remove upper fan shroud.
7. Remove upper radiator hose and coolant
recovery hose.
8. Remove transmission cooler lines.
9. Remove radiator.
10. Remove fan assembly.
1 1. Remove heater hoses.
12. Disconnect
carburetor linkage, includes cruise
control detent cable.
13. Remove vacuum brake booster line.
14. Remove
distributor cap and lay wiring aside.
15. Disconnect necessary wires and hoses.
16. Remove power steering
pump and lay aside.
17. Raise vehicle.
18. Remove exhaust
pipes at exhaust manifold.
19. Remove dust cover.
20. Remove converter bolts.
2 1. Disconnect starter wires.
22. Remove bell housing bolts.
23. Remove
motor mount through bolts.
24. Disconnect fuel lines
at fuel pump.
25. Lower vehicle.
26. Support transmission.
27. Remove
A.I.R./Converter pipe bracket.
28. Remove engine, include removing wire
from
bracket at rear left of engine.
Installation
1. Position engine
assembly in vehicle.
2. Attach
motor mount to engine brackets and
lower engine in place.
3. Remove engine lifting device.
4. Remove transmission floor jack.
5. Raise vehicle on hoist.
6. Install mount "through" bolts. Torque to
specifications.
7. Install bell housing bolts. Torque to
specifications.
8. On vehicles with automatic transmissions, install
I
converter to flywheel attaching bolts. Torque to
specifications.
9. Install flywheel splash shield of converter
housing cover as applicable. Torque attaching
bolts to specifications.
I
10. Install starter wires.
1 1. Connect fuel lines.
12. Connect exhaust pipe at manifold.
13. Lower vehicle on hoist.
14. Reinstall power steering pump, if so equipped.
15. Connect necessary wires and hoses.
Page 444 of 1825

BATTERY 6D1.1
SECTION 6Dl
BATTERY
CONTENTS
.......................... .. General Description ................................ 6D1- 1 Battery Charging ...... 6D 1-2
Battery .......................... ... ....................... 6D 1 - 1 Charging Completely Discharged
.................................................... ............................. Ratings .................... ... 6D 1 - 1 Battery 6D 1-3
........................................... Reserve Capacity ..................................... 6D 1 - 1 Jump Starting 6D
1-4
Cranking ............a*............ 6D1-1 On-Gar Service ...................................... 6Dl-5 .................................. Built-In Hydrometer 6D 1-2 Battery Cable Routing ............................... 6D 1-5 Diagnosis ................................................... 6Dl-2
Specifications .............................................. 6D 1-7 ............................. Service Procedures ..... 6D 1-2
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The engine electrical system includes the battery,
ignition (primary and secondary), starter (and related
wiring) and the generator (and related wiring).
Diagnostic charts (see Section 6D) will aid in
trouble-shooting system faults. When a fault is traced
to a particular component, refer to that components'
section of the service manual.
BATTERY
The sealed battery (see Fig. 1) is standard on all
cars. (See Specifications for specific applications.)
There are no vent plugs in the cover. The battery is
completely sealed, except for two small vent holes in
the sides. These vent holes allow the small amount of
gas produced in the battery to escape. The battery has
the following advantages over conventional batteries:
1. No water addition for the life of the battery.
2. Overcharge protection. If too much voltage is
applied to the battery, it will not accept as much
current as a conventional battery. In a
conventional battery, the excess voltage will still
try to charge the battery, leading to gassing which
causes liquid loss.
3. Not as liable to self-discharge as compared to a
conventional battery. This is particularly
important when a battery is left standing for long
periods of time.
4. More power available in a lighter and smaller
case.
The battery has three major functions in the
electrical system: First, it provides a source of energy
for cranking the engine; Second, it acts as a voltage
stabilizer for the electrical system; And third, it can, for
a limited time, provide energy when the electrical load
used exceeds the output of the generator.
Ratings
A battery has two ratings: (1) a reserve capacity
rating at 27°C (80°F) which is the time a fully charged
battery will provide 25 amperes current flow at or
above 10.5 volts; and (2) a cold rating at -18°C (0°F)
which indicates the cranking load capacity (see
Diagnosis Section for specific battery ratings).
BUILT-IN
HYDROMETER
Fig. 1 Sealed Battery
Reserve Capacity
The "Reserve Capacity" is the maximum length
of time it is possible to travel at night with minimum
electrical load and no generator output.
Expressed in minutes it is the time required for
a fully charged battery, at a temperature of 80°F being
discharged at a constant current of 25-amperes, to
reach a terminal voltage of 10.5 volts.
Cold Cranking Amperage
The "Cold Cranking Amperage" test is expressed
at a battery temperature of
0°F. The current rating is
the minimum amperage, which must be maintained by
the battery for 30 seconds at the specified temperature,
while meeting a minimum voltage requirement of 7.2
volts. This rating is a measure of cold cranking
capacity.
The battery is not designed to last indefinitely;
however, with proper care, it will provide many years
of service.
If the battery tests good, but fails to perform
satisfactorily in service for no apparent reason, the
following are some of the more important factors that
may point to the cause of trouble:
1. Vehicle
accessories left on overnight.
2. Slow
average driving speeds for short periods.
Page 452 of 1825

CRANKING SYSTEM CD2-1
CRANK NG SYSTEM
General Description ................................. 6D2-1 Service Procedures .................................. 6D2-3
Cranking System ......................... ... ........ 6D2- 1 Cranking
System ..................... .. ............. 6D2-3
Starter Motor ............................................. 6D2-1 On-Car Service ....................................... 6D2-4 Solenoid .................................................. 6D2- 1
Starter ........................... ... ...................... 6D2-4 Diagnosis ..................................................... 6D2-1 Specifications ............................................. 6D2- I I Cranking System ......................... ... ...... 6D2- 1
Unit Repair ............................................ 6D2-6- 1 1
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The engine electrical system includes the battery, Battery: To determine the condition of the
ignition (primary and secondary), starter (and related battery,
follow the testing procedure outlined in the
wiring) and the generator (and related wiring). Battery section
(6D1).
Diagnostic charts (see Section 6D) will aid in Wiring: Inspect the wiring for damage. Inspect trouble-shooting system faults. When a fault is traced all connections to the cranking motor, solenoid, to a articular component, refer to that components' ignition switch and battery, including all ground
section of the service manual.
connections. Clean and tighten all connections, as
CRANKING SYSTEM
The cranking circuit consists of the battery,
starting motor, ignition switch, and related electrical
wiring. These components are connected electrically as
shown in Fig. 1.
Starter Motor
Wound field starter motors have pole pieces,
arranged around the armature, that are energized by
wound field coils.
Solenoid
Enclosed shift lever cranking motors have the
shift lever mechanism and the solenoid plunger
enclosed in the drive housing, protecting them from
exposure to dirt, icing conditions and splash.
In the basic circuit shown in Fig. 1, solenoid
windings are energized when the switch is closed. The
resulting plunger and shift lever movement causes the
pinion to engage the engine flywheel ring gear and the
solenoid main contacts to close, and cranking takes
place. When the engine starts, pinion overrun protects
the armature from excessive speed until the switch is
opened, at which time the return spring causes the
pinion to disengage. To prevent excessive overrun, the
switch should open immediately when the engine
starts.
DIAGNOSIS
CRANKING SYSTEM
Before removing any unit in a cranking circuit for
repair, the following checks should be made:
Electrical System General Diagnosis:
Follow the procedures shown in Section 6D to isolate
problem. required.
Solenoid
and Ignition Switch: Inspect all
switches to determine their condition.
Starter Motor Noise: To correct starter motor
noise during starting, use the following procedure:
1. Refer to Fig. 2 to determine the problem.
2. If the complaint is noise, correction can be
achieved by proper "shimming" as follows:
a. Check
flywheel for damage
- bent flywheel,
unusual wear, etc.
b. Start
engine and carefully touch outside
diameter of rotating flywheel ring gear with
chalk or crayon to show high point of tooth
runout. Turn engine off and rotate flywheel
so that the marked teeth are in the area of
the starter pinion gear.
c. Disconnect negative battery cable to
prevent cranking of engine.
d. Check pinion to flywheel clearance, as
shown in Fig. 3, by using a wire gage of
.5mm (.02OU) minimum thickness (or
diameter). Center a pinion tooth between
two flywheel teeth and gage, as shown in
Fig. 3. Do not gage in the corners, where a
misleading larger dimension may be
observed. If the clearance is under this
minimum, shimming the starter away from
the flywheel is required.
e. If
the clearance is grossly over
.5mm (.02OU)
in the vicinity of 1.5mm (.06OU) or more,
shimming the starter toward the flywheel is
required. (This is generally the problem
causing broken flywheel teeth or starter
housings.) Shimming the starter toward the
flywheel can be accomplished by shimming
only the outboard starter mounting pad.
A
shim of .4mm (.015") thickness, at this
Page 453 of 1825
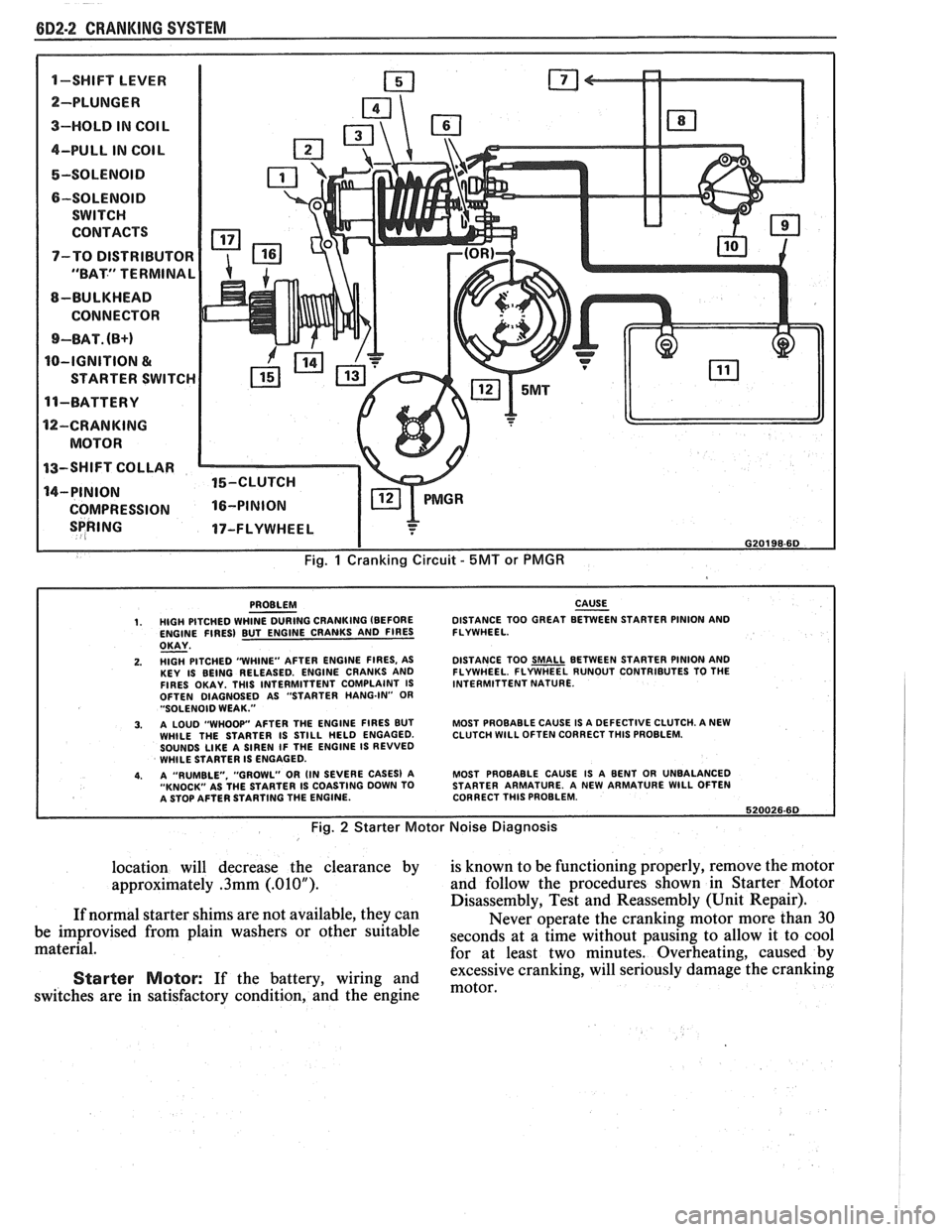
6D2-2 CRANKING SYSTEM
1-SWIFT LEVER m
SPRING 17-FLYWHEEL I
I G20198-6D
Fig. 1 Cranking Circuit - 5MT or PMGR
PROBLEM CAUSE - 1. HIGH PITCHED WHINE DURING CRANKING (BEFORE DISTANCE
TOO GREAT BETWEEN STARTER PINION AND
ENGINE FIRES) BUT ENGINE CRANKS AND FIRES FLYWHEEL.
OKAY - 2. HlGH PITCHED "WHINE"
AFTER ENGINE FIRES, AS
KEY IS BEING RELEASED. ENGINE CRANKS AND
FIRES OKAY. THlS INTERMITTENT COMPLAINT IS
OFTEN DIAGNOSED AS "STARTER HANG-IN"
OR "SOLENOID WEAK."
3. A LOUD "WHOOP" AFTER THE ENGINE FIRES BUT
WHILE THE STARTER IS STILL HELD ENGAGED.
SOUNDS
LIKE A SIREN IF THE ENGINE IS REVVED
WHILE STARTER IS ENGAGED.
4. A "RUMBLE. "GROWL" OR (IN SEVERE CASES) A
"KNOCK" AS THE STARTER IS COASTING DOWN TO
A STOP AFTER STARTING THE ENGINE. DISTANCE
TOO
SMALL BETWEEN STARTER PINION AND
FLYWHEEL. FLYWHEEL RUNOUT CONTRIBUTES TO THE
INTERMITTENT NATURE.
MOST PROBABLE CAUSE IS A DEFECTIVE CLUTCH. A NEW
CLUTCH
WlLL OFTEN CORRECT THlS PROBLEM.
MOST PROBABLE CAUSE IS A BENT OR UNBALANCED
STARTER ARMATURE. A NEW ARMATURE
WlLL OFTEN
CORRECT THlS PROBLEM.
620026.60
Fig. 2 Starter Motor Noise Diagnosis
location will decrease the clearance by is known to be functioning properly, remove the motor
approximately
.3mm (.01OU). and follow the procedures shown in Starter Motor
Disassembly, Test and Reassembly (Unit Repair).
If normal starter shims are not available, they can
Never operate the cranking motor more than 30
be improvised from plain washers or other suitable
seconds at a time without pausing to allow it to cool material.
for at least two minutes. Overheating, caused by
excessive cranking, will seriously
damage the cranking Starter Motor: If the battery, wiring and motor, switches are in satisfactory condition, and the engine
Page 464 of 1825

CHARGING SYSTEM 6D3-1
SECTION 6D3
CHARG NG SYSTEM
CONTENTS
General Description ................................. 6D3- 1 Charging System ........................................ 6D3- 1
.......................................... Charging System - CS ............................... 6D3- 1 On-Car Service 6D3-2
................................................... Diagnosis .. 6D3- 1 Generator 6D3-3 ...................... ......................... ............................................. 6D3- 1 Specifications 6D3-3 Service Procedures .................................. Unit Repair .. 6D3-4-6 ............................... ............
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The engine electrical system includes the battery,
ignition (primary and secondary), starter (and related
wiring) and the generator (and related wiring).
Diagnostic charts (see Section 6D) will aid in
trouble-shooting system faults. When a fault is traced
to a particular component, refer to that components'
section of the service manual.
CHARGING SYSTEM-CS
The CS Charging System has several sizes
available, including the CS-130 and CS-144. The
number (130 or 144) denotes the
OD in mm of the
stator laminations.
CS generators use a new type regulator and a
diode trio is not used. A delta stator, rectifier bridge,
and rotor with slip rings and brushes are electrically
similar to earlier generators. A conventional pulley and
fan is used and, on the CS-130, an internal fan cools the
slip ring end frame, rectifier bridge and regulator.
Unlike three-wire generators, the CS-130 and
CS-144 may be used with only two connections
-
battery positive and an "L" terminal to the charge
indicator bulb. Use of "P",
"F", and "S" terminals is
optional. The "P" terminal is connected to the stator,
and may be connected externally to
a tachometer or other
device. The
"F" terminal is connected internally
to field positive, and may be used as a fault indicator.
The "S" terminal may be connected externally to a
voltage, such as battery voltage, to sense voltage to be
controlled.
As on other charging systems, the charge
indicator lights when the switch is closed, and goes out
when the engine is running. If the charge indicator is
on with the engine running, a charging system defect
is indicated. For all kinds of defects, the indicator will
glow at full brilliance, not "half lit". Also, the charge
indicator will be on with the engine running if system
voltage is too high or too low. The regulator voltage
setting varies with temperature, and limits system
voltage by controlling rotor field current.
This regulator switches rotor field current on and
off at a fixed frequency of about 400 cycles per second.
By varying the on-off time, correct average field
current for proper system voltage control is obtained.
At high speeds, the on-time may be 10% and the
off-time 90%. At low speeds, with high electrical loads,
on-off time may be 90% and
lo%, respectively.
No periodic maintenance on the generator is
required.
DIAGNOSIS
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CHARGING SYSTEM
The generator does not require periodic
lubrication. The rotor shaft is mounted on ball bearings
at the drive end and roller bearings at the slip ring end.
Each contains a permanent grease supply. At periodic
intervals, check mounting bolts for tightness and adjust
belt tension (see Section
6B), if applicable.
e When adjusting belt tension, apply pressure at
center of generator, never against either end
frame.
GENERATOR BENCH CHECK-CS
To check generator in a test stand, remove as
specified in On-Car Service and proceed as follows: 1.
Make connections as shown in Figure
lH, except
leave the carbon pile disconnected. The ground
polarity of generator and battery must be the
same. The battery must be fully charged. Use a
30-500
OHM resistor between battery and "L"
terminal.
2. Slowly increase generator speed and observe
voltage.
3. If the voltage is uncontrolled and increases above
16.0 volts, the rotor field is shorted, the regulator
is defective, or both.
A shorted rotor field coil can
cause the regulator to become defective. NOTE:
The battery must be fully charged when making
this test.
Page 465 of 1825
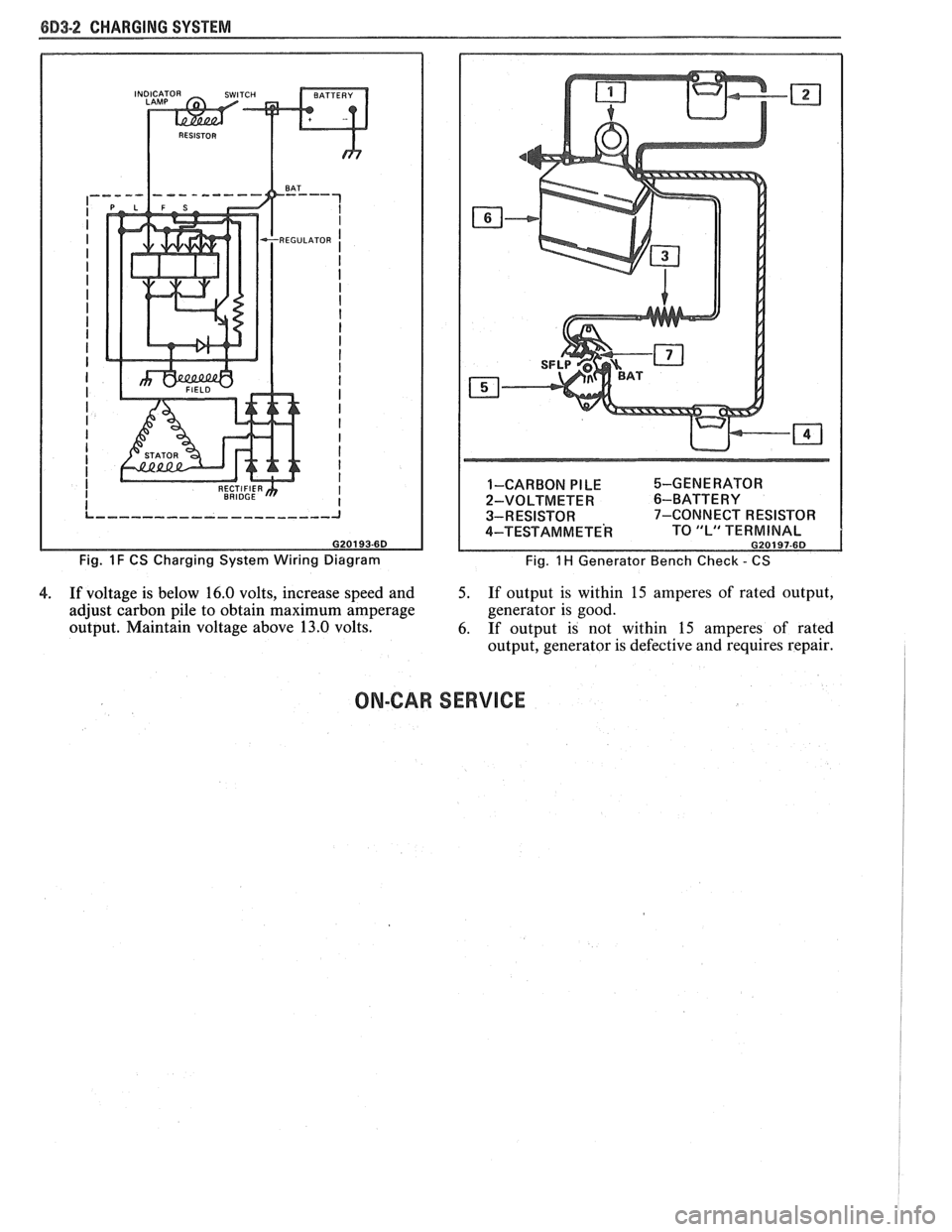
8D3-2 CHARGING SYSTEM
Fig. 1 F CS Charging System Wiring Diagram 1-CARBON
PILE %-GENERATOR
2-VOLTMETER
6-BATTERY
3-RESISTOR 7-CONNECT RESISTOR
4-TEST AM METE^ TO "L" TERMINAL G20197-6D
Fig. 1 H Generator Bench Check - CS
4. If voltage is below 16.0 volts, increase speed and 5. If output is within 15 amperes of rated output,
adjust carbon pile to obtain maximum amperage generator
is good.
output. Maintain voltage above 13.0 volts.
6. If output is not within
15 amperes of rated
output, generator is defective and requires repair.
ON-CAR SERVICE
Page 470 of 1825

IGNITION SYSTEM 6D4-1
ON SYSTEM
CONTENTS
General Description ............................... 6D4-1 Service Procedures ............................. 6D4-3
Ignition System .......................................... 6D4-1
Ignition System .......................................... 6D4-3
Distributor Ignition ................................ 6D4-1
Distributor Ignition ................................ 6D4 -3
Diannosis .................................................... 6D4-3 On-Car Service ......................................... 6D4-5 -
Ignition System .......................................... (334-3 Ignition System ........................... .. .............. 6D4-5
Distributor ................................................. 6D4 -7 HE1 Distributor .................................... 6D4-3
GENERAL DESCRIPION
The engine electrical system includes the battery,
ignition (primary and secondary), starter (and related
wiring) and the generator (and related wiring).
Diagnostic charts (see Section 6D) will aid in
trouble-shooting system faults. When a fault is traced
to a particular component, refer to that components'
section of the service manual.
IGNITION SYSTEM
Distributor Ignition
The ignition circuit consists of the battery,
distributor, ignition switch, spark plugs and primary
and secondary wiring. Refer to the Battery portion of
this section for battery information.
PIE1 Distributor
The Nigh Energy Ignition (HEI) distributor with
Electronic Spark Timing (EST), used on most engines,
combines all ignition components in one unit. The
ignition coil is in the distributor cap and connects
through a resistance brush to the rotor.
The distributor has an internal magnetic pick-up
assembly which contains a permanent magnet, a pole
piece with internal teeth and a pick-up coil. When the
teeth of the timer core, rotating inside the pole piece,
line up with the teeth of the pole piece, an induced
voltage in the pick-up coil signals the electronic module
to trigger the coil primary circuit. The primary current
decreases and a high voltage is induced in the ignition
coil secondary winding. This voltage is directed
through the rotor and secondary leads to fire the spark
plugs. The capacitor in the distributor is for radio noise
suppression,
All spark timing changes in the
HE1 (EST)
distributor are done electronically by an Electronic
Control Module (ECM), which monitors information
from various engine sensors, computes the desired
spark timing and signals the distributor to change the
timing accordingly.
A back-up spark advance system
is incorporated to signal the ignition module in case of
(ECM) failure. No vacuum or mechanical advance is
used. Further (EST) information is found in sections 6E
Emissions Control, and
8A Electrical
Troubleshooting.
Ignition Timing
Timing specifications for each engine are listed in
Section
6E. When using a timing light, connect an
adapter between the No. 1 spark plug and the No. 1
spark plug wire, or use an inductive type pick-up.
Do
not pierce the plug lead.
Once the insulation of the
spark plug cable has been broken, voltage will jump to
the nearest ground, and the spark plug will not fire
properly.
Always follow the tune-up label
procedures when adjusting timing.
Some engines will incorporate a magnetic timing
probe hole for use with special electronic timing
equipment. Fig.
1A shows a typical magnetic probe
hole. Consult manufacturer's instructions for use of
this equipment.
Secondary Wiring
The spark plug wiring used with ignition systems
is a carbon impregnated cord conductor, encased in an
8MM (5/16") diameter silicone rubber jacket. The
silicone jacket withstands very high temperatures and
also provides an excellent insulator for the higher
voltage of the
HE1 system. Silicone spark plug boots
form a tight seal on the plug.
The boot should be
twisted 1/2 turn before removing. Care should
also be exercised when connecting a timing light or
other pick-up equipment. Do not force anything
between the boot and wiring, or through the silicone
jacket. Connections should be made in parallel using
an adapter. DO NOT pull on the wire to remove. Pull
on the boot, or use a tool designed for this purpose.
Spark Plugs
Resistor type, tapered seat spark plugs are used
on all engines (except aluminum heads). No gasket is
used on these tapered seat plugs. See Figs.
1B and 1C
for an explanation of coding on spark plugs.
Normal service is assumed to be a mixture of
idling, slow speed, and high speed driving. Occasional
or intermittent high-speed driving is needed for good
Page 473 of 1825

684.4 IGNITION SYSTEM
a spark plug wire from a spark plug, twist the 4. Do not wipe grease from module, or distributor
boot on the spark plug and pull
on the boot to base,
if same module is to be replaced.
remove the wire, or use a special tool designed to
remove spark plug boots.
Install or Connect
Remove or Disconnect
1. Ignition switch battery feed wire and tachometer
lead (if equipped) from distributor cap. Also
release the coil connectors from the cap. (DO
NOT use a screwdriver or tool to release the
locking tabs.)
2. Distributor cap by turning four screws
counterclockwise. Move cap out of the way.
3. Four-terminal ECM harness from distributor.
4. If necessary, remove secondary wires from cap,
release wiring harness latches and remove wiring
harness retainer. The spark plug wire numbers
are indicated on the retainer.
5. Distributor clamp screw and hold-down clamp.
6. Note position of rotor, then pull distributor up
until rotor just stops turning counterclockwise
and again note position of rotor.
To insure correct timing of the distributor,
the distributor must be INSTALLED with
the rotor correctly positioned as noted.
If the engine was accidentally cranked after the
distributor was removed, the following procedure can
be used for installing:
1. Remove No. 1 spark plug.
2. Place finger over No. 1 spark plug hole and crank
engine slowly until compression is felt.
3. Align timing mark on pulley to "0" on engine
timing indicator.
4. Turn rotor to point between No. 1 and No. 8
spark plug towers on distributor cap on V8
engines, between No. 1 and No. 6 on V6 engines,
and No.
1 and No. 4 on 4 cylinder engines.
5. Install distributor and connect ignition feed wire.
6. Install distributor cap and spark plug wires.
7. Check engine timing (see Set Ignition Timing).
Install or Connect
1. Insert distributor, positioning rotor as removed.
2. Distributor hold-down clamp and screw.
3. Wiring harness retainer and secondary wires, if
removed.
4. ECM harness connector.
5. Distributor cap.
6. Coil connectors.
7. Battery wire and tachometer lead, if equipped.
Module
It is not necessary to remove the distributor from
car.
Remove or Disconnect
1. Distributor cap and rotor.
2. Two module attaching screws, and lift module
UP. 3. Leads from module. (Observe color code on leads
as these cannot be interchanged.)
NOTICE: If a new module is to be installed, a
package of silicone grease will be included with it.
Spread the grease on the metal face of the module
and on the distributor base where the module
seats. This grease is necessary for module cooling.
1. Module.
2. Module leads (observe color code).
3. Attaching screws to module.
4. Rotor.
5. Cap.
Pick-Up Coil
1. Remove distributor from car and follow
instructions in Unit Repair, as applicable.
Rotor
Fig. 1
1. Remove distributor cap.
2. The rotor is retained by two screws and is
provided with a slot which fits over a square lug,
,
so that the rotor can be installed in only one
position.
Integral Ignition Coil
Fig. I
Remove or Disconnect
1. Distributor cap.
2. Three coil cover attaching screws, and lift off
cover.
3. Coil attaching screws and lift ignition coil and
leads from cap.
Install or Connect I
1. Coil and attaching screws.
2. Coil leads.
3. Coil cover and attaching screws.
Capacitor
Fig. 1
The capacitor is part of the coil wire harness
assembly. Since the capacitor is used only for radio
noise suppression, it will seldom need replacement.
Remove or Disconnect I
1. Distributor cap and rotor.
2. Capacitor attaching screw and unplug connector
from module. It may help to loosen the module.
Install or Connect I
1. Plug into module.
2. Capacitor and hold-down screw (be sure ground
lead is under screw).