1988 PONTIAC FIERO ESP inoperative
[x] Cancel search: ESP inoperativePage 135 of 1825

3-10 STEERING, SUSPENSION, TIRES AND WHEELS DIAGNOSIS
Reminder Keeps Operating With Key In Lock
Cylinder, Driver's Door Open Or Closed; Ceases
When Key Is Removed
Inspect
s Door jamb switch on driver's side misadjusted or
inoperative.
e Wire from signal switch to door jamb switch
shorted.
A. This condition indicates the lock cylinder or
the reminder switch is at fault. To verify,
check for continuity at the
"E" and "F"
male column connector contacts, with the
key removed from the lock cylinder. If
continuity exists, the fault is in the column.
B. Insert the key into the lock, then turn the
lock toward the "Start" position. If the
reminder stops when the key is in the
"Run" position or when it is turned past
"Run" toward "Start," the problem is a
sticky lock cylinder actuator.
COLUMN-MOUNTED DIMMER SWITCH
No "Low" or "High" Beam
Inspect
e Loose connector at dimmer switch
e Improper adjustment
e Internally damaged or worn switch. Check the
continuity on the switch at the It. green and at the
tan switch terminals by pushing in the plunger all
the way.
A click should be heard. If there is no
continuity, replace the dimmer switch. If there is
continuity, refer
to'section 8A for electricaldiag-
nosis.
PIVOT AND SWITCH ASSEMBLY
Switch Inoperative: No "Low," "High" and/or
"Wash"
e Loose body-to-switch connector
a Broken or damaged switch
Internally damaged or worn switch. Connect a
new switch without removing the old one. If the
system functions, replace the switch. If the
system doesn't function, refer to Section
8A for
electrical diagnosis.
STEERING GEAR AND PUMP LEAKS
General Procedure
Inspect
s Overfilled reservoir
s Fluid aeration and overflow
e , Hose connections
Verify exact point of leakage Example:
Torsion bar, stub shaft and
adjuster seals are close together; the exact
spot where the system is leaking may not be
clear.
Example: The point from which the fluid is
dripping is not necessarily the point where
the system is leaking; fluid overflowing from
the reservoir, for instance.
e When service is required:
A. Clean leakage area upon disassembly.
B. Replace leaking seal.
C. Check component sealing surfaces for
damage.
D. Reset bolt torque to specifications, where
required.
Some complaints about the power steering system
may be reported as:
A. Fluid leakage on garage floor
B. Fluid leaks visible on steering gear or pump
C. Growling noise, especially when parking or
when engine is cold
D. Loss of power steering when parking
E. Heavy steering effort
When troubleshooting these kinds of complaints,
check for an external leak in the power steering system.
For further diagnosis of leaks, refer to External
Leakage Check in this section.
External Leakage Check
Fig. 12
The purpose of this procedure is to pinpoint the
location of the leak.
In some cases, the leak can easily be located. But,
seepage-type leaks may be more difficult to isolate. To
locate seepage leaks, use the following method.
1. With the engine off, wipe dry the complete power
steering system.
2. Check the fluid level in the pump's reservoir. Add
fluid if necessary.
3. Start the engine, then turn the steering wheel
from stop to stop several times. Do not hold it at
a stop for any length of time, as this can damage
the power steering pump. It is easier if someone
else operates the steering wheel while you search
for the seepage.
4. Find the exact area of the leak and repair leak.
SEAL REPLACEMENT
RECOMMENDATIONS
Lip seals, which seal rotating shafts, require
special treatment. This type of seal is used on the
steering gear and on the drive shaft of the pump. When
there is a leak in one of these areas, always replace the
seal(s), after inspecting and thoroughly cleaning the
sealing surfaces. Replace the shaft only if very severe
pitting is found. If the corrosion in the lip seal contact
zone is slight, clean the surface of the shaft with crocus
cloth. Replace the shaft only if the leakage cannot be
stopped by first smoothing with crocus cloth.
Page 580 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - 5.OL (\/IN El 6EZ-CZ-5
sent to the ECM. The ECM then increases the injector
base pulse width, permitting increased fuel flow.
As the throttle valve rotates in response to
movement of the accelerator pedal, the throttle shaft
transfers this rotational movement to the
'I'PS. A
potentiometer (variable resistor) within the TPS
assembly changes its resistance (and voltage drop) in
proportion to throttle movement.
By applying a reference voltage (5.0 volts) to the
TPS input, a varying voltage (reflecting throttle
position) is available at the TPS output. For example,
approximately 2.5 volts results from a 50% throttle
valve opening (depending on TPS calibration). The
voltage output from the TPS assembly is routed to the
ECM for use in determining throttle position.
FUEL PUMP
The fuel pump is a turbine type, low pressure
electric pump, mounted in the fuel tank. Fuel
is
pumped at a positive pressure (above 62
kPa or 9 psi)
from the fuel pump through the in-line filter to the
pressure regulator in the TBI assembly Excess
fuel is
returned to the fuel tank through the fuel return line.
The fuel pump is attached to the fuel gage sender
assembly. A fuel strainer is attached to the fuel pump
inlet line and prevents dirt particles from entering the
fuel line and tends to separate
water from the fuel
Vapor lock problems are reduced when using an
electric
pump because the fuel is pushed from the tank
under pressure rather than being pulled
under
vacuum, a condition that produces vapor.
An inoperative fuel pump would cause
a. no start
condition. A fuel pump which does not provide enough
pressure can result in poor performance. (See "Fuel
System Pressure Test" procedure).
FUEL PUMP ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT
When the key is first turned "ON" without the
engine running, the ECM turns the
Fuel pump relay
"ON" for two seconds. This builds
up the fuel pressure
quickly. If the engine is not started within two
seconds, the
ECM shuts the fuel pump "OFF" and
waits until the engine starts. As soon as the engine is
cranked, the ECM turns the relay
"ON" and runs the
fuel pump.
As a backup system to the fuel pump relay, the
fuel pump can also be turned on
by the oil pressure
switch. The oil pressure sender has two circuits
internally. One operates the oil pressure indicator or
gage in the instrument cluster,
itnd the other is
anormally open switch which closes when oil pressure
reaches about 28
kPa (4 psi). If the fuel pump relay
fails, the oil pressure switch will run the fuel pump. An
inoperative fuel pump relay can result in long
cranking times, particularly if the engine is cold. The
oil pressure switch will turn on the fuel pump as soon
as oil pressure
reaches about 28 kPa (4 psi).
FUEL CONTROL
Always start with the "Diagnostic Circuit Check"
in Section
"6E2-A". This will reduce diagnosis time
and prevents unnecessary replacement of parts. The
information in this check will direct diagnosis
concerning "Engine
Crunlis But Won't Run" and the
"Fuel Control System," Section
"6E2-C2", including
diagnosis of an injector, pressure regulator,
fuel pump,
fuel
pump relay, and oil pressure switch.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
A "Scan" tool reads IAC position in steps, calletl
"Counts." "0" steps indicates the ECM is commanding
the
IAC to be driven in, to a fully seiltetl position
(minimum idle air).
The higher the number steps, the
more idle air being allowed to pass
by the IAC valve.
cnose Refer to CHART C-2C for information to cliil,
the function of the IAC valve.
Driva bility
Refer to Section "B" for driveability symptoms
related to the fuel control.
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
GENERAL SEWVICE INFORMATION
CAUTION:
e To prevent personal injury or damage to the
vehicle
as the result sf an accidental start,
disconnect and reconnect the negative
battery cable before and after service is
performed.
@ Also, catch any fuel that leaks out when
disconnecting the fuel lines, by covering the
fittings with
a shop cloth. Place the cloth in
an approved container when work is
complete.
The 'FBI unit repair procedures cover component
replacement with the unit on the vehicle,
tIowever,
throttle body replacement requires that the complete
unit
be removed from the enginc.
Page 723 of 1825

6E3-Cl-4 2.8L (VIN S) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
BarWNeutral Switch (Auto Only)
The ParWNeutral (PIN) switch indicates to the
ECM when the transmission is in Park or Neutral.
This information is used for the TCC and the IAC
valve operation.
Important
Vehicle should not be driven with ParWNeutral
switch disconnected as idle quality will be affected
and a possible false Code
24 (VSS).
See Section "$A" for more information on the PIN
switch, which is part of the neutrallstart and backup
light switch assembly.
NC '"n" Signal
This signal tells the ECM that the A/C selector
Switch is turned on, and that the pressure cycling
switch is closed. The ECM uses this to adjust the idle
Speed when the air conditioning is working.
If this signal is not available to the ECM, idle may
be rough, especially when the
A/C compressor cycles.
The voltage at ECM terminal "B8" should equal
battery voltage when
AIC is requested and the
pressure cycling switch is closed.
The signal at
B8 will cause the ECM to turn on the
A/C clutch by energizing the A/C relay.
Distributor Reference Signal
The distributor sends a signal to the ECM to tell it
both engine RPM and crankshaft position. See EST
System for further information.
To read the codes, use a "Scan" tool or ground the
diagnostic terminal with the engine not running and
the ignition on. The "Service Engine Soon" light will
flash Code 12 three times and
then flash each code
stored in memory three times. All codes stored in
memory would have been read when Code 12 was
flashed again. No new codes can be stored when in the
Diagnostics Mode (diagnostics lead grounded).
This
eliminates confusion while the system is being worked
on. To clear the codes from memory:
@ Ignition off
@ Remove fuse located in a weather proof holder
located near the battery for 30 seconds.
Since the ECM can have
a failure which may
effect only one circuit, following the Diagnostic
Procedures in this section will determine which circuit
has a problem and where it is. If
a diagnostic chart indicates that the ECM
connections or ECM is the cause of
a problem and the
ECM is replaced, but does not correct the problem, one
of the following may be the reason:
€9
connections. - The diagnostic chart will say "ECM
connections or ECM. The terminals may have to be
removed from the connector in order to check them
properly.
@ The ECM or PROM is not correct for the
application.
- The incorrect components may cause a
malfunction and may or may not set a code.
@ The problem is intermittent. - This means that
the problem is not present at the time the system is
being checked. In this case, refer to the "Symptoms"
portion of the manual and make a careful physical
inspection of all portions of the system involved.
@ Shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness. -
Solenoids and relays are turned "ON" and "OFF" by
the
ECM,using internal electronic switches called
"Drivers". Each driver is part of
a group of four called
"Quad-drivers". Failure of one driver can damage any
other driver in the set.
Solelloid and relay coil
resistance must measure more than 20 ohms. Less
resistance will cause early failure of the ECM
"driver". A shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness,
with a GMP4 computer, will not damage the ECM, but
will cause the component to be inoperative.
Before replacing an ECM, be sure to check the coil
resistance of all solenoids and relays controlled by the
ECM. See ECM wiring diagram for the
solenoid(s)
and relay(s) and the coil terminal identification.
534636 or BT 8405 testers or equivalent provide
a fast, accurate means of checking for a shorted coil or
a short to battery voltage.
@ The PROM may be faulty. - Although these
rarely fail, it operates as part of the ECM. Therefore,
it could be the cause of the problem. Substitute a
known good PROM.
@ The replacement ECM may be faulty. - After the
ECM is replaced, the system should be rechecked for
proper operation. If the diagnostic chart again
indicates the ECM is the problem, substitute
a known
good ECM. Although this is a rare condition, it could
happen.
ECM
A faulty ECM will be determined in the diagnostic
charts or
by a Code 55.
PROM
A faulty PROM may result in a Code 51.
Page 729 of 1825
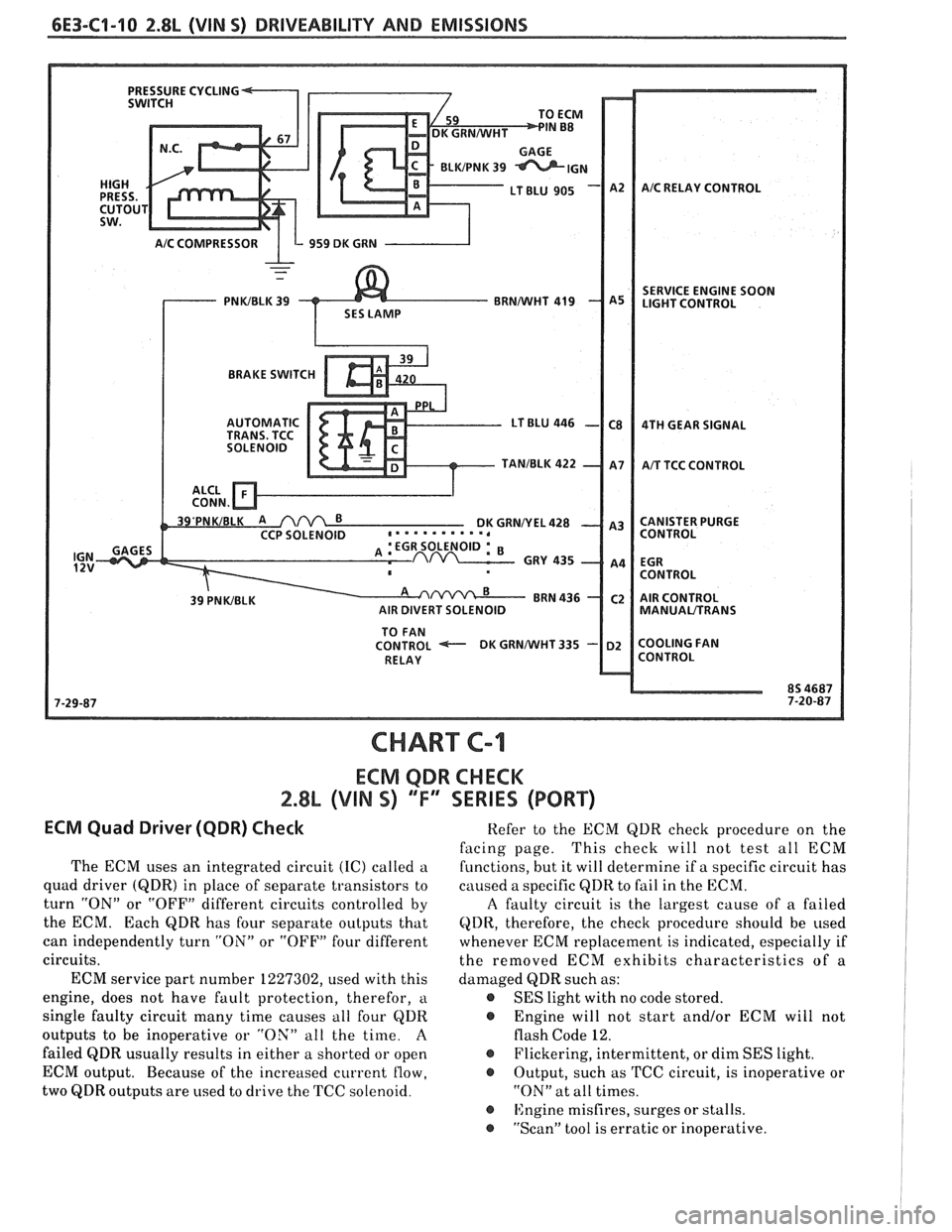
6E3-C1-10 2.8L (VIN 5) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
- 959 DK GRN
BRAKE SWITCH
MANUALTRANS
TO FAN
CONTROL +-- DK GRNMIHT335 - COOLING FAN
RELAY
CHART C-I
ECM QDR CHECK
2.8% (VIN S) 'TI' SERIES (PORT)
ECM Quad Driwer (QDR) Check
The ECM uses an integrated circuit (IC) called a
quad driver
(QDR) in place of separate transistors to
turn "ON" or "OFF" different circuits controlled by
the ECM. Each
QDR has four separate outputs that
can independently turn "ON" or "OFF" four different
circuits.
ECM service part number 1227302, used with this
engine, does not have fault protection, therefor,
a
single faulty circuit many time causes all four QDR
outputs to be inoperative or "OX" all the time.
A
failed QDR usually results in either a shorted or open
ECM output. Because of the increased current
flow,
two QDR outputs are used to drive the TCC solenoid. Refer
to the ECM QDR check procedure on the
facing page. This
check will not test all ECM
functions, but it will determine if a specific circuit has
caused a specific
QDR to fail in the ECM.
A faulty circuit is the largest cause of a failed
QDR, therefore, the check procedure should be used
whenever ECM replacement is indicated, especially if
the removed ECM exhibits characteristics of a
damaged QDR such as:
@ SES light with no code stored.
@ Engine will not start and/or ECM will not
flash Code 12.
@ Flickering, intermittent, or dim SES light.
@ Output, such as TCC circuit, is inoperative or
"ON" at all times.
@ ISngine misfires, surges or stalls.
@ "Scan" tool is erratic or inoperative.
Page 879 of 1825

6E3-C1-4 5.0L (VIN F) & 5.7L(VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
See Section "8A" for more information on the PIN
switch, which is part of the neutrallstart and backup
light switch assembly.
NC "ON" Signal
This signal tells the ECM that the NC selector
switch is turned "ON", and that the pressure cycling
switch is closed. The
ECM uses this to adjust the idle
speed when the air conditioning is working.
[f this signal is not available to the ECM, idle may
be rough, especially when the NC compressor cycles.
The voltage at ECM terminal "B8" should equal
battery voltage on a
C60 system and about 5 volts on a
C68 option, when
NC is requested and the pressure
cycling switch is closed.
Distributor Reference Signal
The distributor sends a signal to the ECM to tell it
both engine rpm and crankshaft position. See ignition
system Section
"C4" for further information.
DIAGNOSIS
To read the codes, use a "Scan" tool or ground the
diagnostic terminal with the engine not running and
the ignition "ON". The "Service Engine Soon" light
will flash Code 12 three times and then flash each code
stored in memory three times. All codes stored in
memory would have been read when Code 12 was
flashed again. No new codes can be stored when in the
diagnostics mode (diagnostics lead grounded). This
eliminates confusion while the system is being worked
on.
To clear the codes from memory:
@ Ignition "OFF".
@ Disconnect battery pigtail, located near the
battery, for 30 seconds.
Since the ECM can have a failure which may
affect only one circuit, following the diagnostic
procedures in this section will determine which circuit
has a problem and where it is.
If a diagnostic chart indicates that the
ECM
connections or ECM is the cause of a problem,and the
ECM is replaced, but does not correct the problem, one
of the following may be the reason:
-
@ There is a problem with the ECM terminal
connections.
- The diagnostic chart will say ECM
connections or ECM. The terminals may have to
be removed from the connector in order to check
them properly.
@ The ECM, or Mem-Cal is not correct for the
application.
- The incorrect components may cause
a malfunction and
may or may not set u code.
@ The problem is intermittent. - 'l'his means that the
problem is not present at the time the system is
being checked. In
this case, refer to the "Symptoms" portion
of the
manual and make a careful physical inspection
of
all portions of the system involved.
@ Shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness. - Solenoids
and relays are turned
"ON" and "OFF" by the
ECM, using internal electronic switches called
"Drivers".
A shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness in a
GMP4 computer will not damage the ECM,
but will cause the circuit and controlled
component to be inoperative. When the
circuit fault is not present or has been
repaired, the
"Quad-Driver" will again
operate in a normal manner due to it's fault
protected design.
If a fault has been repaired
in a circuit controlled by a "Quad-Driver",
the original ECM should be reinstalled and
the circuit checked for proper operation.
ECM replacement will
not be necessary if the
repaired circuit or component now operates
correctly.
534636 or BT 8405 testers or equivalent provide a
fast, accurate means of checking for a shorted coil
or a short to battery voltage.
@ The Mem-Cal may be faulty. - Although these
rarely fail, it operates as part of the ECM.
Therefore, it could be the cause
of the problem.
Substitute a known good Mem-Cal.
@ The replacement ECM may be faulty - After the
ECM is replaced, the system should be rechecked
for proper operation. If the diagnostic chart again
indicates the ECM is the problem, substitute a
known good ECM. Although this is a rare
condition, it could happen.
ECM
A faulty ECM will be determined in the diagnostic
charts.
MEM-CAL
An incorrect or faulty Mem-Cal, which is part of
the ECM, may set a Code 41 or 52. Also, be sure Mem-
Cal is fully seated and latched in the socket.
ECM INPUTS
A11 of the sensors and input switches can be
diagnosed by the use of
a "Scan" tool. Following is a
short clescription of how the sensors and switches can
he diagnosed
by the use of a "Scan" tool. The "Scan"
can also be used to compare the values for a normal
running engine with the engine you're diagnosing.