2007 ISUZU KB P190 brake
[x] Cancel search: brakePage 3257 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–15
W hen the cruise control ON-OFF switch, located on the right hand side of the dash panel, is pressed, the PIM, on
receiving the input from the switch, turns on the cruise ON-OFF switch warning lamp to inform the user that the cruise
control has been engaged.
W hen the cruise control switch assembly is pressed to SET/COAST, the PIM on receiving the input, sends a signal via
the serial data bus to the ECM. Providing the pre-conditions for cruise control operation have been met, the ECM
activates cruise control and commands the PIM to turn on the instrument cluster cruise set warning lamp, to inform the
user that cruise control is active. The ECM receives all the various inputs required to maintain the correct speed and then
controls the throttle plate depending on the load on the engine (ascending or descending hills, etc).
The cruise control is deactivated by either pressing the brake pedal, clutch pedal, cruise CANCEL or by the cruise control
ON-OFF button. In each of these instances, the ECM receives an input when any of these switches are activated. For
further information on the cruise control system, refer to 8C Cruise Control – HFV6.
3.7 Brake Torque Management
Brake torque management places limits on engine torque when the brakes are applied, regardless of the accelerator
pedal position (APP). The conditions under which brake torque management occur are as follows:
• The accelerator has been depressed before the brakes are applied,
• The brakes are applied and the ECM receives an input from the stop lamp switch,
• Vehicle speed is greater than 5 km/h,
• Engine speed is greater than 1200 rpm and
• Conditions exist for greater than 2.5 seconds.
W hen brake torque management has been implemented, the torque is reduced by altering the throttle plate opening by
25%. The ECM will monitor the rate at which the vehicle is slowing and adjust the throttle plate opening accordingly.
3.8 Emission Control Systems
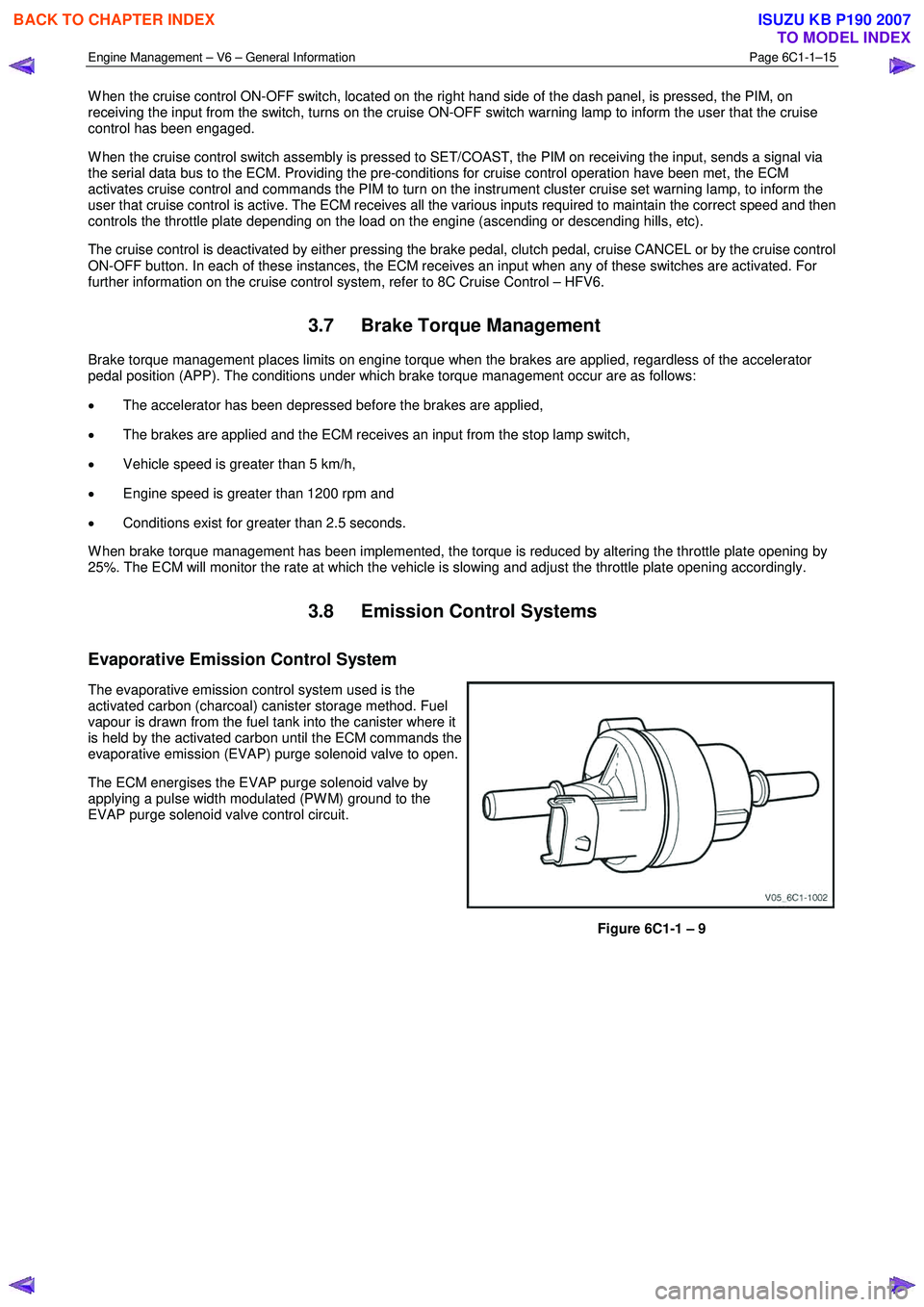
Evaporative Emission Control System
The evaporative emission control system used is the
activated carbon (charcoal) canister storage method. Fuel
vapour is drawn from the fuel tank into the canister where it
is held by the activated carbon until the ECM commands the
evaporative emission (EVAP) purge solenoid valve to open.
The ECM energises the EVAP purge solenoid valve by
applying a pulse width modulated (PW M) ground to the
EVAP purge solenoid valve control circuit.
Figure 6C1-1 – 9
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3261 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–19
4 Component Description and
Operation
4.1 A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor
The engine control module (ECM) applies a positive 5 V reference voltage and ground to the air-conditioner (A/C)
refrigerant pressure sensor. The A/C refrigerant pressure sensor provides signal voltage to the ECM that is proportional
to the A/C refrigerant pressure. The ECM monitors the A/C refrigerant pressure sensor signal voltage to determine the
refrigerant pressure.
• The A/C refrigerant pressure sensor voltage increases as the refrigerant pressure increases.
• W hen the ECM detects the refrigerant pressure exceeds a predetermined value, the ECM activates the cooling
fans to reduce the refrigerant pressure.
• W hen the ECM detects the refrigerant pressure is too high or too low, the ECM disables the A/C clutch to protect
the A/C compressor from damage.
4.2 Brake Pedal Switch Assembly
Stop Lamp and Initial Brake Apply Switch
The stop lamp and initial brake apply switch assembly (1) is
located on the brake pedal support.
The engine control module (ECM) uses the brake pedal
switch inputs to determine when the brake pedal is
depressed.
The ECM uses the two break pedal switch inputs for:-
• Enabling cruise control,
• Brake torque management,
• Cross referencing the stop lamp switch against the
initial brake apply switch for correct operation.
For further information on brake torque management,
refer to 3.7 Brake Torque
Management.
For further information on the cruise control system, refer to
3.6 Cruise Control System.
Figure 6C1-1 – 13
Stop Lamp Switch
The stop lamp switch contacts are normally open with the brake pedal at rest and closed when the brake pedal is
depressed.
Initial Brake Apply Switch
The initial brake apply switch contacts are normally closed with the brake pedal at rest and open when the brake pedal is
depressed.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3293 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–15
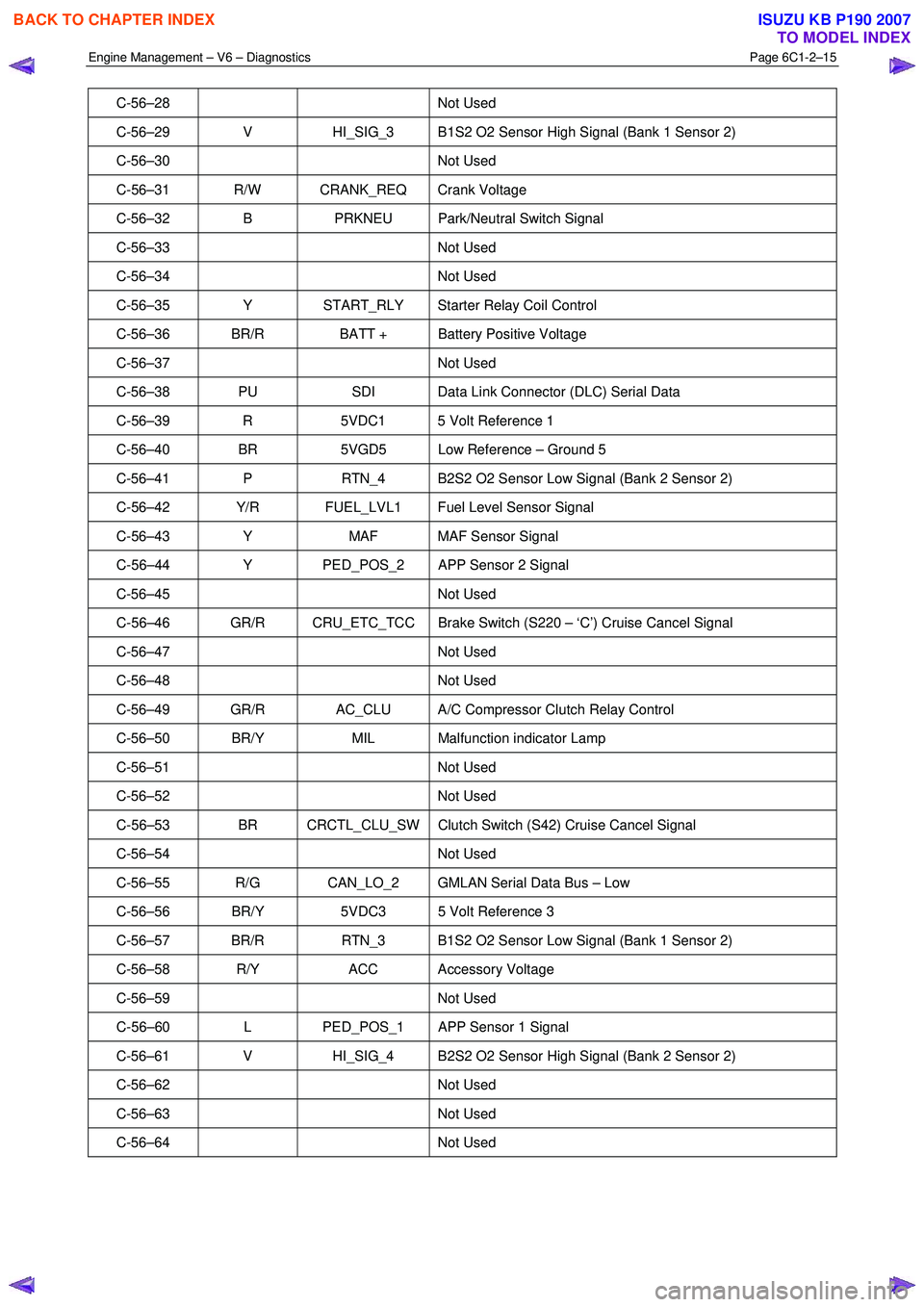
C-56–28 Not Used
C-56–29 V HI_SIG_3 B1S2 O2 Sensor High Signal (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
C-56–30 Not Used
C-56–31 R/W CRANK_REQ Crank Voltage
C-56–32 B PRKNEU Park/Neutral Switch Signal
C-56–33 Not Used
C-56–34 Not Used
C-56–35 Y START_RLY Starter Relay Coil Control
C-56–36 BR/R BATT + Battery Positive Voltage
C-56–37 Not Used
C-56–38 PU SDI Data Link Connector (DLC) Serial Data
C-56–39 R 5VDC1 5 Volt Reference 1
C-56–40 BR 5VGD5 Low Reference – Ground 5
C-56–41 P RTN_4 B2S2 O2 Sensor Low Signal (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
C-56–42 Y/R FUEL_LVL1 Fuel Level Sensor Signal
C-56–43 Y MAF MAF Sensor Signal
C-56–44 Y PED_POS_2 APP Sensor 2 Signal
C-56–45 Not Used
C-56–46 GR/R CRU_ETC_TCC Brake Switch (S220 – ‘C’) Cruise Cancel Signal
C-56–47 Not Used
C-56–48 Not Used
C-56–49 GR/R AC_CLU A/C Compressor Clutch Relay Control
C-56–50 BR/Y MIL Malfunction indicator Lamp
C-56–51 Not Used
C-56–52 Not Used
C-56–53 BR CRCTL_CLU_SW Clutch Switch (S42) Cruise Cancel Signal
C-56–54 Not Used
C-56–55 R/G CAN_LO_2 GMLAN Serial Data Bus – Low
C-56–56 BR/Y 5VDC3 5 Volt Reference 3
C-56–57 BR/R RTN_3 B1S2 O2 Sensor Low Signal (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
C-56–58 R/Y ACC Accessory Voltage
C-56–59 Not Used
C-56–60 L PED_POS_1 APP Sensor 1 Signal
C-56–61 V HI_SIG_4 B2S2 O2 Sensor High Signal (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
C-56–62 Not Used
C-56–63 Not Used
C-56–64 Not Used
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3312 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–34
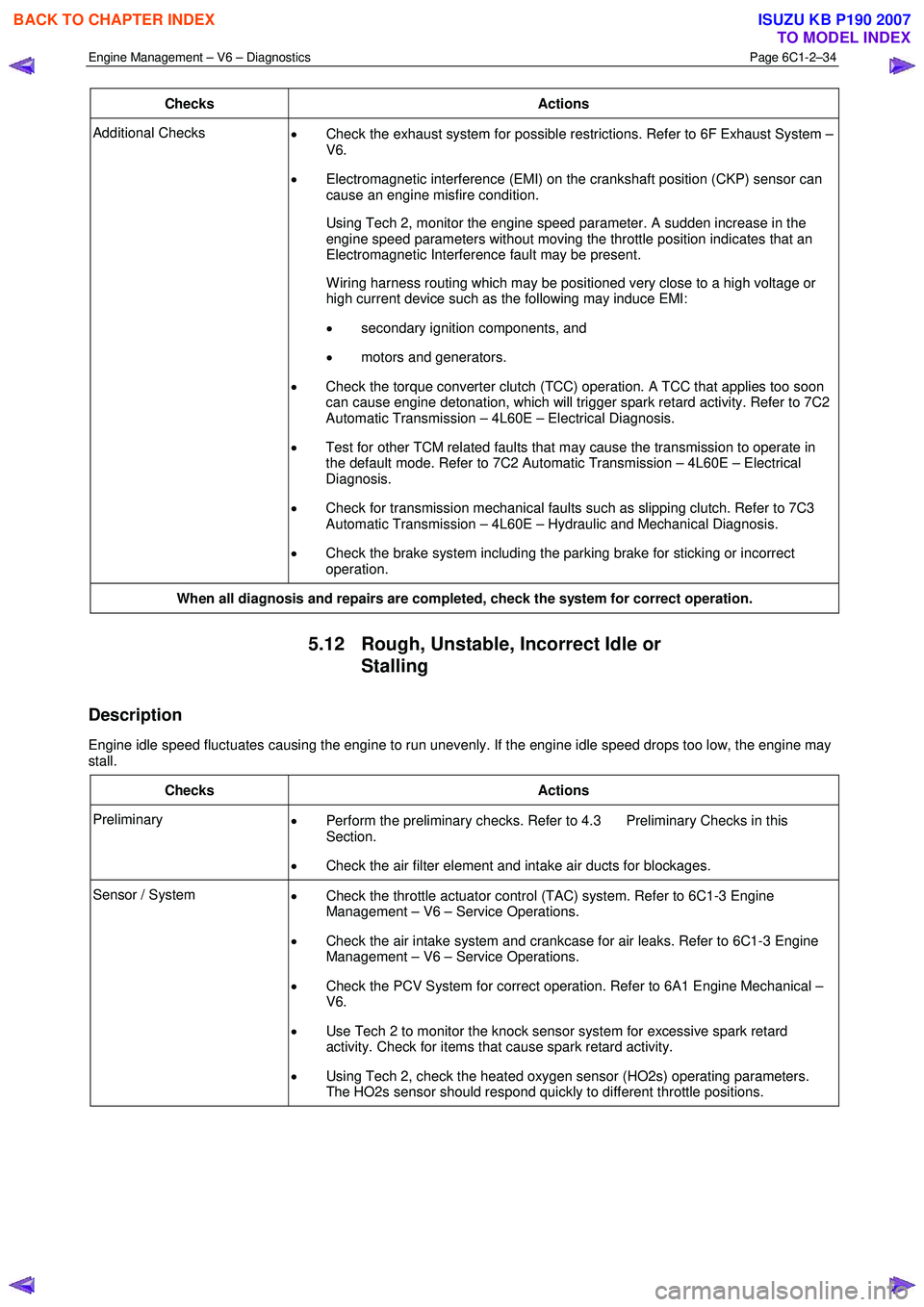
Checks Actions
Additional Checks
• Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to 6F Exhaust System –
V6.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor can
cause an engine misfire condition.
Using Tech 2, monitor the engine speed parameter. A sudden increase in the engine speed parameters without moving the throttle position indicates that an
Electromagnetic Interference fault may be present.
W iring harness routing which may be positioned very close to a high voltage or high current device such as the following may induce EMI:
• secondary ignition components, and
• motors and generators.
• Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. A TCC that applies too soon
can cause engine detonation, which will trigger spark retard activity. Refer to 7C2
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis.
• Test for other TCM related faults that may cause the transmission to operate in
the default mode. Refer to 7C2 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical
Diagnosis.
• Check for transmission mechanical faults such as slipping clutch. Refer to 7C3
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Hydraulic and Mechanical Diagnosis.
• Check the brake system including the parking brake for sticking or incorrect
operation.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.12 Rough, Unstable, Incorrect Idle or
Stalling
Description
Engine idle speed fluctuates causing the engine to run unevenly. If the engine idle speed drops too low, the engine may
stall.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Check the air filter element and intake air ducts for blockages.
Sensor / System
• Check the throttle actuator control (TAC) system. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Check the air intake system and crankcase for air leaks. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Check the PCV System for correct operation. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
• Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard
activity. Check for items that cause spark retard activity.
• Using Tech 2, check the heated oxygen sensor (HO2s) operating parameters.
The HO2s sensor should respond quickly to different throttle positions.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3333 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–55
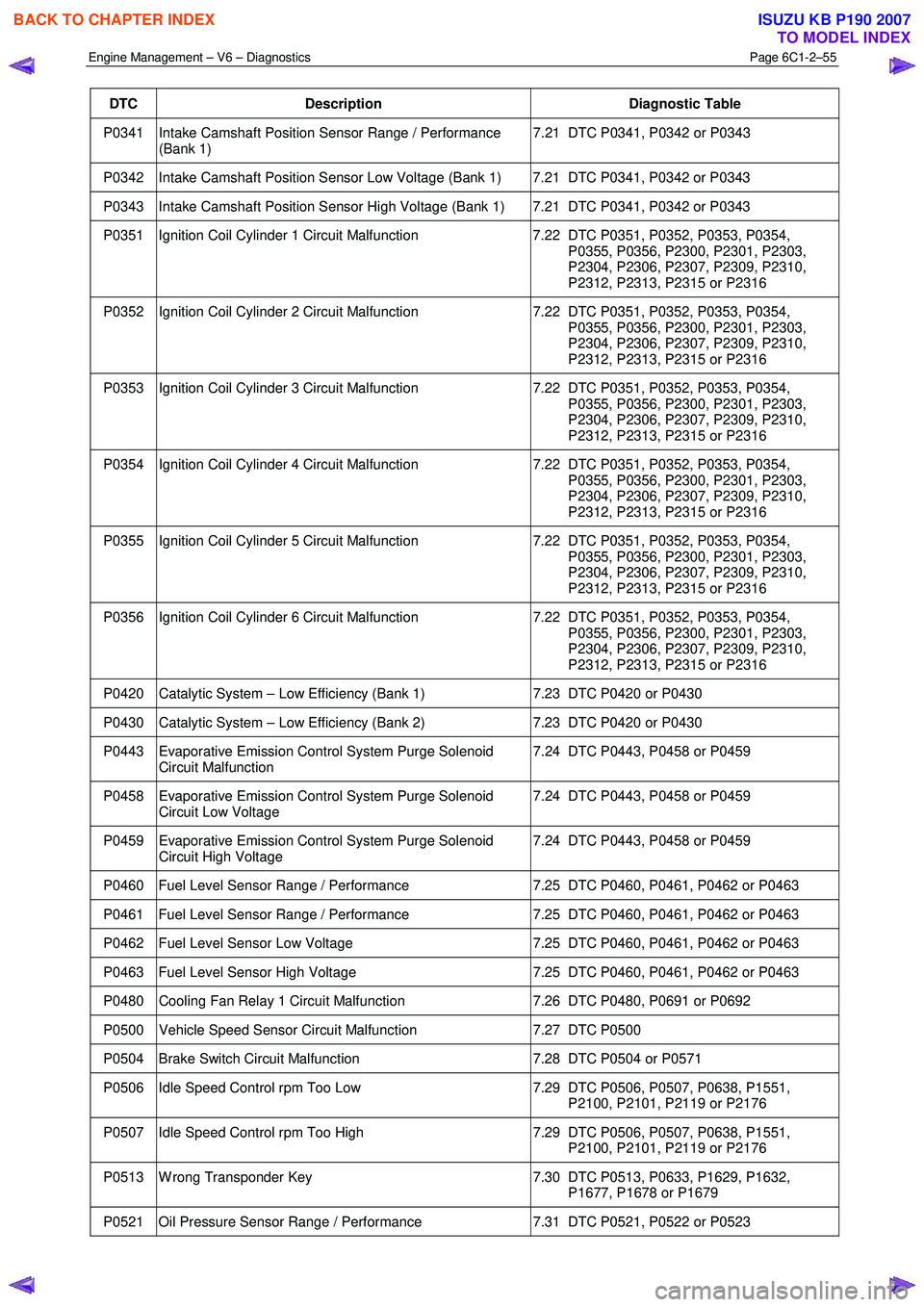
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
P0341 Intake Camshaft Position Sensor Range / Performance
(Bank 1) 7.21 DTC P0341, P0342 or P0343
P0342 Intake Camshaft Position Sensor Low Voltage (Bank 1) 7.21 DTC P0341, P0342 or P0343
P0343 Intake Camshaft Position Sensor High Voltage (Bank 1) 7.21 DTC P0341, P0342 or P0343
P0351 Ignition Coil Cylinder 1 Circuit Malfunction
7.22 DTC P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354,
P0355, P0356, P2300, P2301, P2303,
P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309, P2310,
P2312, P2313, P2315 or P2316
P0352 Ignition Coil Cylinder 2 Circuit Malfunction 7.22 DTC P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354,
P0355, P0356, P2300, P2301, P2303,
P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309, P2310,
P2312, P2313, P2315 or P2316
P0353 Ignition Coil Cylinder 3 Circuit Malfunction 7.22 DTC P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354,
P0355, P0356, P2300, P2301, P2303,
P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309, P2310,
P2312, P2313, P2315 or P2316
P0354 Ignition Coil Cylinder 4 Circuit Malfunction 7.22 DTC P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354,
P0355, P0356, P2300, P2301, P2303,
P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309, P2310,
P2312, P2313, P2315 or P2316
P0355 Ignition Coil Cylinder 5 Circuit Malfunction 7.22 DTC P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354,
P0355, P0356, P2300, P2301, P2303,
P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309, P2310,
P2312, P2313, P2315 or P2316
P0356 Ignition Coil Cylinder 6 Circuit Malfunction 7.22 DTC P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354,
P0355, P0356, P2300, P2301, P2303,
P2304, P2306, P2307, P2309, P2310,
P2312, P2313, P2315 or P2316
P0420 Catalytic System – Low Efficiency (Bank 1) 7.23 DTC P0420 or P0430
P0430 Catalytic System – Low Efficiency (Bank 2) 7.23 DTC P0420 or P0430
P0443 Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Solenoid
Circuit Malfunction 7.24 DTC P0443, P0458 or P0459
P0458 Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Solenoid
Circuit Low Voltage 7.24 DTC P0443, P0458 or P0459
P0459 Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Solenoid
Circuit High Voltage 7.24 DTC P0443, P0458 or P0459
P0460 Fuel Level Sensor Range / Performance
7.25 DTC P0460, P0461, P0462 or P0463
P0461 Fuel Level Sensor Range / Performance 7.25 DTC P0460, P0461, P0462 or P0463
P0462 Fuel Level Sensor Low Voltage 7.25 DTC P0460, P0461, P0462 or P0463
P0463 Fuel Level Sensor High Voltage 7.25 DTC P0460, P0461, P0462 or P0463
P0480 Cooling Fan Relay 1 Circuit Malfunction 7.26 DTC P0480, P0691 or P0692
P0500 Vehicle Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction 7.27 DTC P0500
P0504 Brake Switch Circuit Malfunction 7.28 DTC P0504 or P0571
P0506 Idle Speed Control rpm Too Low 7.29 DTC P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551,
P2100, P2101, P2119 or P2176
P0507 Idle Speed Control rpm Too High 7.29 DTC P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551,
P2100, P2101, P2119 or P2176
P0513 W rong Transponder Key 7.30 DTC P0513, P0633, P1629, P1632,
P1677, P1678 or P1679
P0521 Oil Pressure Sensor Range / Performance 7.31 DTC P0521, P0522 or P0523
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3334 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–56
DTC Description Diagnostic Table
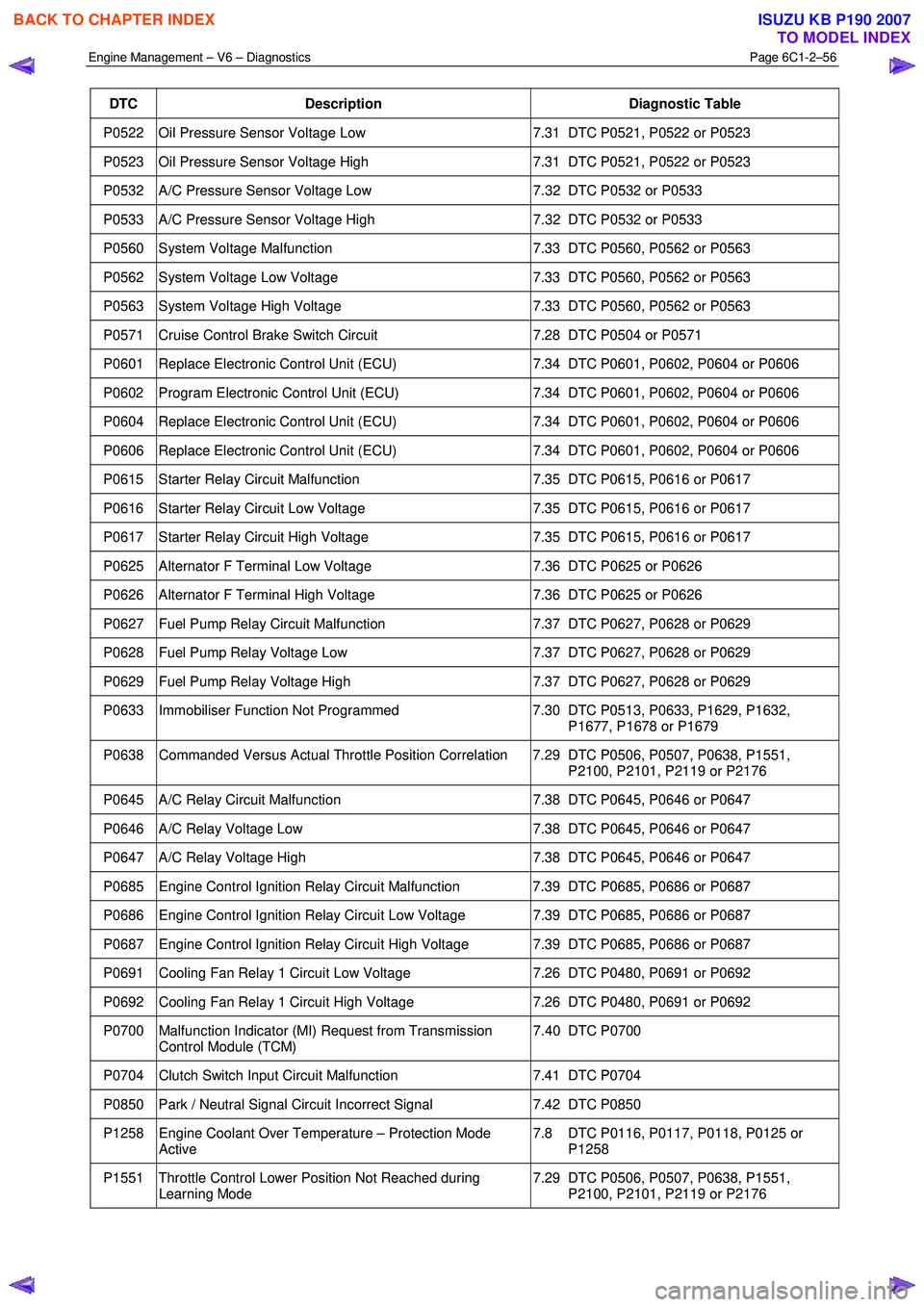
P0522 Oil Pressure Sensor Voltage Low 7.31 DTC P0521, P0522 or P0523
P0523 Oil Pressure Sensor Voltage High 7.31 DTC P0521, P0522 or P0523
P0532 A/C Pressure Sensor Voltage Low 7.32 DTC P0532 or P0533
P0533 A/C Pressure Sensor Voltage High 7.32 DTC P0532 or P0533
P0560 System Voltage Malfunction 7.33 DTC P0560, P0562 or P0563
P0562 System Voltage Low Voltage 7.33 DTC P0560, P0562 or P0563
P0563 System Voltage High Voltage 7.33 DTC P0560, P0562 or P0563
P0571 Cruise Control Brake Switch Circuit 7.28 DTC P0504 or P0571
P0601 Replace Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 7.34 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 or P0606
P0602 Program Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 7.34 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 or P0606
P0604 Replace Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 7.34 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 or P0606
P0606 Replace Electronic Control Unit (ECU) 7.34 DTC P0601, P0602, P0604 or P0606
P0615 Starter Relay Circuit Malfunction 7.35 DTC P0615, P0616 or P0617
P0616 Starter Relay Circuit Low Voltage 7.35 DTC P0615, P0616 or P0617
P0617 Starter Relay Circuit High Voltage 7.35 DTC P0615, P0616 or P0617
P0625 Alternator F Terminal Low Voltage 7.36 DTC P0625 or P0626
P0626 Alternator F Terminal High Voltage 7.36 DTC P0625 or P0626
P0627 Fuel Pump Relay Circuit Malfunction 7.37 DTC P0627, P0628 or P0629
P0628 Fuel Pump Relay Voltage Low 7.37 DTC P0627, P0628 or P0629
P0629 Fuel Pump Relay Voltage High 7.37 DTC P0627, P0628 or P0629
P0633 Immobiliser Function Not Programmed 7.30 DTC P0513, P0633, P1629, P1632,
P1677, P1678 or P1679
P0638 Commanded Versus Actual Throttle Position Correlation 7.29 DTC P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551, P2100, P2101, P2119 or P2176
P0645 A/C Relay Circuit Malfunction 7.38 DTC P0645, P0646 or P0647
P0646 A/C Relay Voltage Low 7.38 DTC P0645, P0646 or P0647
P0647 A/C Relay Voltage High 7.38 DTC P0645, P0646 or P0647
P0685 Engine Control Ignition Relay Circuit Malfunction 7.39 DTC P0685, P0686 or P0687
P0686 Engine Control Ignition Relay Circuit Low Voltage 7.39 DTC P0685, P0686 or P0687
P0687 Engine Control Ignition Relay Circuit High Voltage 7.39 DTC P0685, P0686 or P0687
P0691 Cooling Fan Relay 1 Circuit Low Voltage 7.26 DTC P0480, P0691 or P0692
P0692 Cooling Fan Relay 1 Circuit High Voltage 7.26 DTC P0480, P0691 or P0692
P0700 Malfunction Indicator (MI) Request from Transmission
Control Module (TCM) 7.40 DTC P0700
P0704 Clutch Switch Input Circuit Malfunction
7.41 DTC P0704
P0850 Park / Neutral Signal Circuit Incorrect Signal 7.42 DTC P0850
P1258 Engine Coolant Over Temperature – Protection Mode
Active 7.8 DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 or
P1258
P1551 Throttle Control Lower Position Not Reached during Learning Mode 7.29 DTC P0506, P0507, P0638, P1551,
P2100, P2101, P2119 or P2176
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3348 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–70
Additional Information
• The MAF sensor circuit DTCs is a Type B DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action
taken when a Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTC.
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the MAF sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Inspect the MAF sensor for an incorrectly routed harness or if the harness is too close to the following:
− ignition coil,
− solenoids,
− relays, and
− motors.
• A low minimum air rate may cause this DTC to set during deceleration. Inspect for the following conditions:
− a plugged or a collapsed intake air duct, or a dirty air filter element,
− objects that block the MAF sensor air inlet screen, and
− sticking or dirty throttle plate or throttle bore.
• Any un-metered air that enters the engine may cause this DTC to set. Inspect for vacuum leaks in the following:
− intake manifold,
− throttle body,
− barometric pressure (BARO) sensor seal,
− EVAP canister purge valve seal,
− brake booster system,
− air induction system, and
− crankcase ventilation system.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
DTC P0101, P0102 or P0103 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0101, P0102 or P0103 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3380 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–102
3-way catalytic converter damage. The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will flash ON and OFF when the conditions for
catalytic converter damage are present. DTCs P0301 through P0306 correspond to cylinders 1 through 6. If the ECM is
able to determine that a specific cylinder is misfiring, the DTC for that cylinder will set. If the misfire rate is sufficient to
cause emission levels to exceed a predetermined value, this DTC sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• DTCs P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0335, P0336, or P0338 are not set.
• The engine speed is between 400 – 7,000 rpm and steady.
• The delivered torque signal is more than 10 percent at idle.
• The delivered torque signal is between 9 – 30 percent with the transmission in drive.
• The intake air temperature (IAT) is more than –30° C.
• The fuel level is more than 12 percent.
• The torque management is not active.
• DTC P0300 runs continuously when the above conditions exist for at least 1,000 engine revolutions.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
• The ECM detects a crankshaft rotation speed variation indicating a misfire rate sufficient to cause emissions levels
to exceed mandated standards.
• The condition above exists for more than 4 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The control module activates the MIL on the second ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails.
• The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic
fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the
second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure.
The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The ECM turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after four consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic
runs and does not fail.
• A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission
related diagnostic.
• Use Tech 2 to clear the MIL and the DTC.
Additional Information
• A misfire DTC could be caused by an excessive vibration from sources other than the engine. Inspect for the
following possible sources:
− A tyre or wheel that is out of round or out of balance
− Variable thickness brake rotors
− An unbalanced drive shaft
− Certain rough road conditions
− A damaged accessory drive component or belt
• A misfire DTC could be caused by a camshaft actuator stuck in the full advance or retard position.
• For an intermittent condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007