2006 DODGE RAM SRT-10 oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 3391 of 5267

49. Install the valve body. Verify that the pin on the
manual lever has properly engaged the TRS
selector plate. Tighten the valve body to transmis-
sion case bolts (1) to 12 Nꞏm (105 in.lbs.).
CAUTION: The primary oil filter seal MUST be fully
installed flush against the oil pump body. DO NOT
install the seal onto the filter neck and attempt to
install the filter and seal as an assembly. Damage
to the transmission will result.
50. Install a new primary oil filter seal in the oil pump
inlet bore. Seat the seal in the bore with the butt
end of a hammer, or other suitable tool.
51. Install the primary oil filter (1) and the oil cooler
return filter (2). Tighten the screw to hold the pri-
mary oil filter to the valve body to 4.5 Nꞏm (40
in.lbs.). Using Filter Wrench 8321, tighten the
cooler return oil filter to the transmission case to
9.5 Nꞏm (7 ft.lbs.).
52. Apply RTV silicone to theoil pan and install the
transmission oil pan. Tighten the bolts to 12 Nꞏm (105 in.lbs.).
53. Install the input (3), output (1), and line pressure
sensors (2). Tighten the bolts to 12 Nꞏm (105
in.lbs.).
Page 3392 of 5267

INSTALLATION
1. Check torque converter hub and hub drive flats for
sharp edges burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the
hub and flats with 320/400 grit paper and crocus
cloth if necessary. Verify that the converter hub
o-ring is properly installed and is free of any debris.
The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging pump
seal at installation.
2. If a replacement transmission is being installed,
transfer any components necessary, such as the
manual shift lever and shift cable bracket, from the
original transmission onto the replacement trans-
mission.
3. Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission fluid.
4. Align converter and oil pump.
5. Carefully insert converter in oil pump. Then rotate
converter back and forth until fully seated in pump
gears.
6. Check converter seating with steel scale (1) and
straightedge (2). Surface of converter lugs should
be at least 13mm (1/2 in.) to rear of straightedge when converter is fully seated.
7. Temporarily secure converter with C-clamp.
8. Position transmission on jack and secure it with
chains.
9. Check condition of converter driveplate. Replace
the plate if cracked, distorted or damaged.Also be
sure transmission dowel pins are seated in
engine block and protrude far enough to hold
transmission in alignment.
10. Apply a light coating of Mopar
High Temp
Grease to the torque converter hub pocket in the
rear pocket of the engine’s crankshaft.
11. Raise transmission (2) and align the torque con-
verter with the drive plate and transmission con-
verter housing with the engine block.
12. Move transmission forward. Then raise, lower or
tilt transmission to align the converter housing
with engine block dowels.
13. Carefully work transmission forward and over
engine block dowels until converter hub is seated
in crankshaft. Verify that no wires, or the transmis-
sion vent hose, have become trapped between
theengineblockandthetransmission.
14. Install two bolts to attach the transmission to the
engine.
15. Install remaining torque converter housing to
engine bolts. Tighten to 68 Nꞏm (50 ft.lbs.).
16. Install transfer case, if equipped. Tighten transfer
case nuts to 35 Nꞏm (26 ft.lbs.).
17. Install rear support to transmission. Tighten bolts
to 47 Nꞏm (35 ft.lbs.).
Page 3417 of 5267
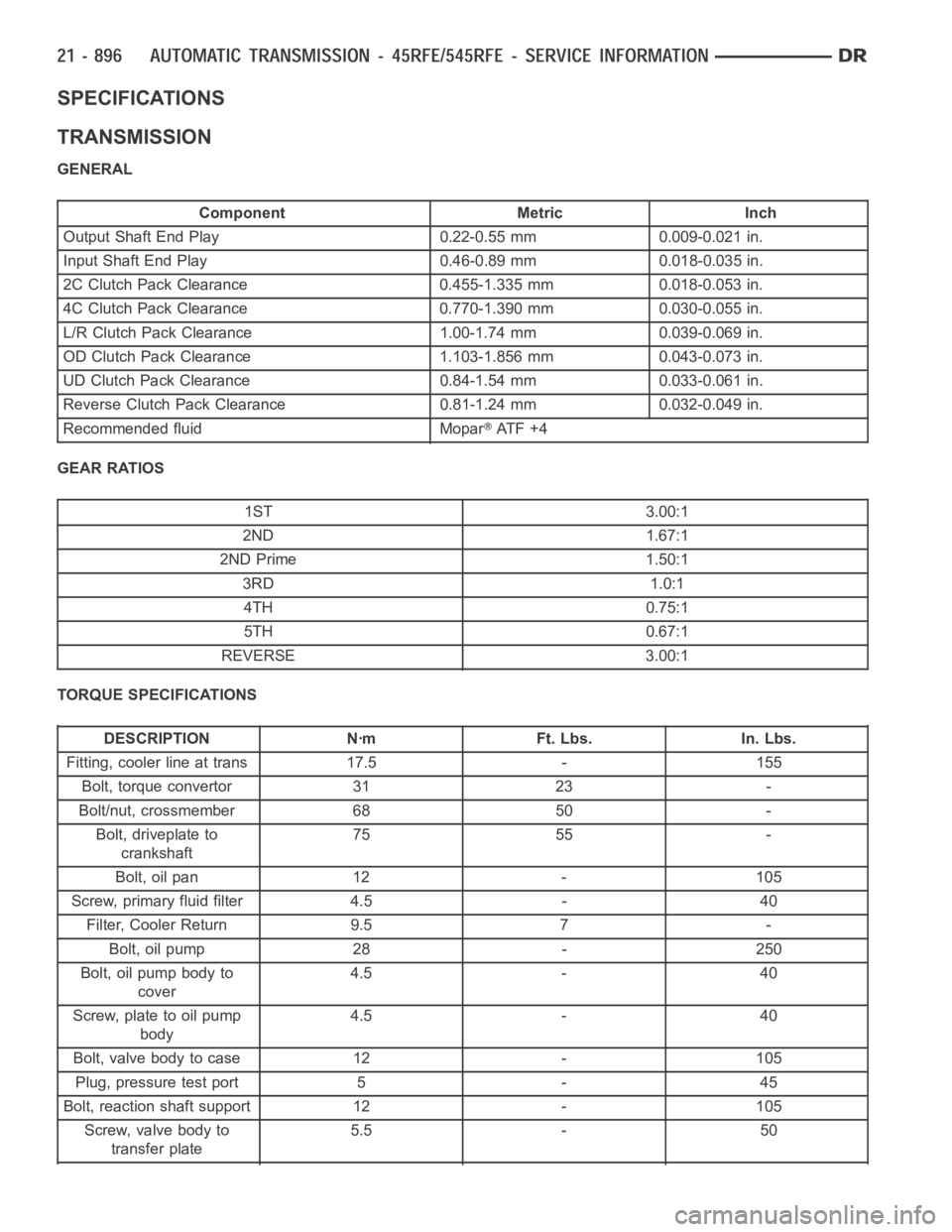
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION
GENERAL
Component Metric Inch
Output Shaft End Play 0.22-0.55 mm 0.009-0.021 in.
Input Shaft End Play 0.46-0.89 mm 0.018-0.035 in.
2C Clutch Pack Clearance 0.455-1.335 mm 0.018-0.053 in.
4C Clutch Pack Clearance 0.770-1.390 mm 0.030-0.055 in.
L/R Clutch Pack Clearance 1.00-1.74 mm 0.039-0.069 in.
OD Clutch Pack Clearance 1.103-1.856 mm 0.043-0.073 in.
UD Clutch Pack Clearance 0.84-1.54 mm 0.033-0.061 in.
Reverse Clutch Pack Clearance 0.81-1.24 mm 0.032-0.049 in.
Recommended fluid Mopar
AT F + 4
GEAR RATIOS
1ST 3.00:1
2ND 1.67:1
2ND Prime 1.50:1
3RD 1.0:1
4TH 0.75:1
5TH 0.67:1
REVERSE 3.00:1
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION Nꞏm Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fitting, cooler line at trans 17.5 - 155
Bolt, torque convertor 31 23 -
Bolt/nut, crossmember 68 50 -
Bolt, driveplate to
crankshaft75 55 -
Bolt, oil pan 12 - 105
Screw, primary fluid filter 4.5 - 40
Filter, Cooler Return 9.5 7 -
Bolt, oil pump 28 - 250
Bolt, oil pump body to
cover4.5 - 40
Screw, plate to oil pump
body4.5 - 40
Bolt, valve body to case 12 - 105
Plug, pressure test port 5 - 45
Bolt, reaction shaft support 12 - 105
Screw, valve body to
transfer plate5.5 - 50
Page 3419 of 5267

SPECIAL TOOLS
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - RFE
Gauge, Oil Pressure - C-3292
Gauge, Oil Pressure - C-3293SP
Dial Indicator - C-3339
Installer, Seal - C-3860-A
Compressor, Spring - 8249
Compressor, Spring - 8250
Compressor, Spring - 8251
Installer, Piston - 8252
Installer, Seal - 8253
Page 3427 of 5267

SEAL-ADAPTER HOUSING
REMOVAL
1. Remove the transfer case from the transmission.
2. Using a screw mounted on a slide hammer, remove the adapter housing seal.
INSTALLATION
1. Clean the adapter seal bore in the adapter housing
of any residue or particles remaining from the orig-
inal seal.
2. Install new oil seal in the adapter housing using
Seal Installer C-3860-A (1) . A properly installed
seal is flush to the face of the seal bore.
3. Install the transfer case onto the transmission.
Page 3430 of 5267

FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EFFECTS OF INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
Alowfluidlevelallowsthepumptotakeinairalongwiththefluid.Airinthe fluid will cause fluid pressures to be
low and develop slower than normal. If the transmission is overfilled, thegears churn the fluid into foam. This aer-
ates the fluid and causing the same conditions occurring with a low level. In either case, air bubbles cause fluid
overheating, oxidation, and varnish buildup which interferes with valveand clutch operation. Foaming also causes
fluid expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can easily be
mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
CAUSES OF BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating which has three primarycauses.
1. Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or clutch seal
failure.
2. A result of restricted fluid flow through the main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usually the result of a
faulty or improperly installed drainback valve, a damaged oil cooler, or severe restrictions in the coolers and lines
caused by debris or kinked lines.
3. Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not properly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer towing or similar high
load operation will overheat the transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly equipped. Such vehicles should
have an auxiliary transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling system,and the engine/axle ratio combination
needed to handle heavy loads.
FLUID CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a result of:
adding incorrect fluid
failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when checking level
engine coolant entering the fluid
internal failure that generates debris
overheat that generates sludge (fluid breakdown)
failure to replace contaminated converter after repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in transmission failure. Theusual results are erratic shifts, slippage,
abnormal wear and eventual failure due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid this condition by using rec-
ommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and other foreign mate-
rial on the cap and tube could fall into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the time to wipe the cap and tube
clean before withdrawing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is generally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy is to replace
the radiator as the cooler in the radiator is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated through the transmission,
an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should also be replaced whenever a failure generatessludge and debris. This is necessary
because normal converter flushing procedures will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions because it allows the pumpto take in air along with the fluid. As
in any hydraulic system, air bubbles make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the geartrain
churns up foam and cause the same conditions which occur with a low fluid level.
Page 3431 of 5267

In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating and/or fluid oxidation,and varnishing. This can interfere with nor-
mal valve, clutch, and accumulator operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping from the transmission vent
where it may be mistaken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level. It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure to wipe all
dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P(PARK) and N (NEUTRAL) positions. Place the selector lever in P (PARK)
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate.The engine should be running at idle speed for at least one
minute, with the vehicle on level ground.At normal operating temperature (approximately 82° C. or 180° F), the
fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT region (cross-hatched area) on theoil level indicator. The fluid level will be
approximately at the upper COLD hole of the dipstick at 21° C (70° F) fluid temperature.
NOTE: Engine and Transmission should be at normal operating temperature before performing this proce-
dure.
1. Start engine and apply parking brake.
2. Shift the transmission into DRIVE for approximately 2 seconds.
3. Shift the transmission into REVERSE for approximately 2 seconds.
4. Shift the transmission into PARK.
5. Hook up scan tool andselect transmission.
6. Select sensors.
7. Read the transmission temperature value.
8. Compare the fluid temperature value with the chart.
9. Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the dipstick according to the Transmission Fluid Temperature Chart.
NOTE: After adding any fluid to the transmission, wait a minimum of 2 minutes for the oil to fully drain from
the fill tube into the transmission before rechecking the fluid level.
10. Check transmission for leaks.
Page 3432 of 5267

FLUID AND FILTER REPLACEMENT
For proper service intervals (Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIP-
TION).
REMOVAL
1. Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
2. Place a large diameter shallow drain pan beneath the transmission pan.
3. Remove bolts holding front and sides of pan to transmission.
4. Loosen bolts holding rear of pan to transmission.
5. Slowly separate front of pan away from transmission allowing the fluid to drain into drain pan.
6. Hold up pan and remove remaining bolts holding pan to transmission.
7. While holding pan level, lower pan away from transmission.
8. Pour remaining fluid in pan into drain pan.
9. Remove the screw holding the primary oil filter (1)
to valve body.
10. Separate filter from valve body and oil pump and
pour fluid in filter into drain pan.
11. Inspect the oil filter seal in the bottom of the oil
pump. If the seal is not installed completely in the
oil pump, or is otherwise damaged, then remove
and discard the oil filter seal from the bottom of
the oil pump. If the seal is installed correctly and
is in good condition, it can be reused.
12. If replacing the cooler return filter (2), use Oil Fil-
ter Wrench 8321 to remove the filter from the
transmission.
13. Dispose of used trans fluid and filter(s) properly.
INSPECTION
Inspect bottom of pan and magnet for excessive amounts of metal. A light coating of clutch material on the bottom
of the pan does not indicate a problem unless accompanied by a slipping condition or shift lag. If fluid and pan are
contaminated with excessive amounts of debris, refer to the diagnosis section of this group.
CLEANING
1. Using a suitable solvent, clean pan and magnet.
2. Using a suitable gasket scraper, clean original sealing material from surface of transmission case and the trans-
mission pan.