2005 NISSAN NAVARA fuse
[x] Cancel search: fusePage 1650 of 3171
GI-28
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits please refer to the previous schematic.
In any powered circuit, an open can be found by methodically checking the system for the presence of voltage.
This is done by switching the DMM to the voltage function.
lConnect one probe of the DMM to a known good ground.
lBegin probing at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end.
lWith SW1 open, probe at SW1 to check for voltage.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than SW1.
no voltage; open is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
lClose SW1 and probe at relay.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the relay.
no voltage; open is between SW1 and relay (point B).
lClose the relay and probe at the solenoid.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the solenoid.
no voltage; open is between relay and solenoid (point C).
Any powered circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
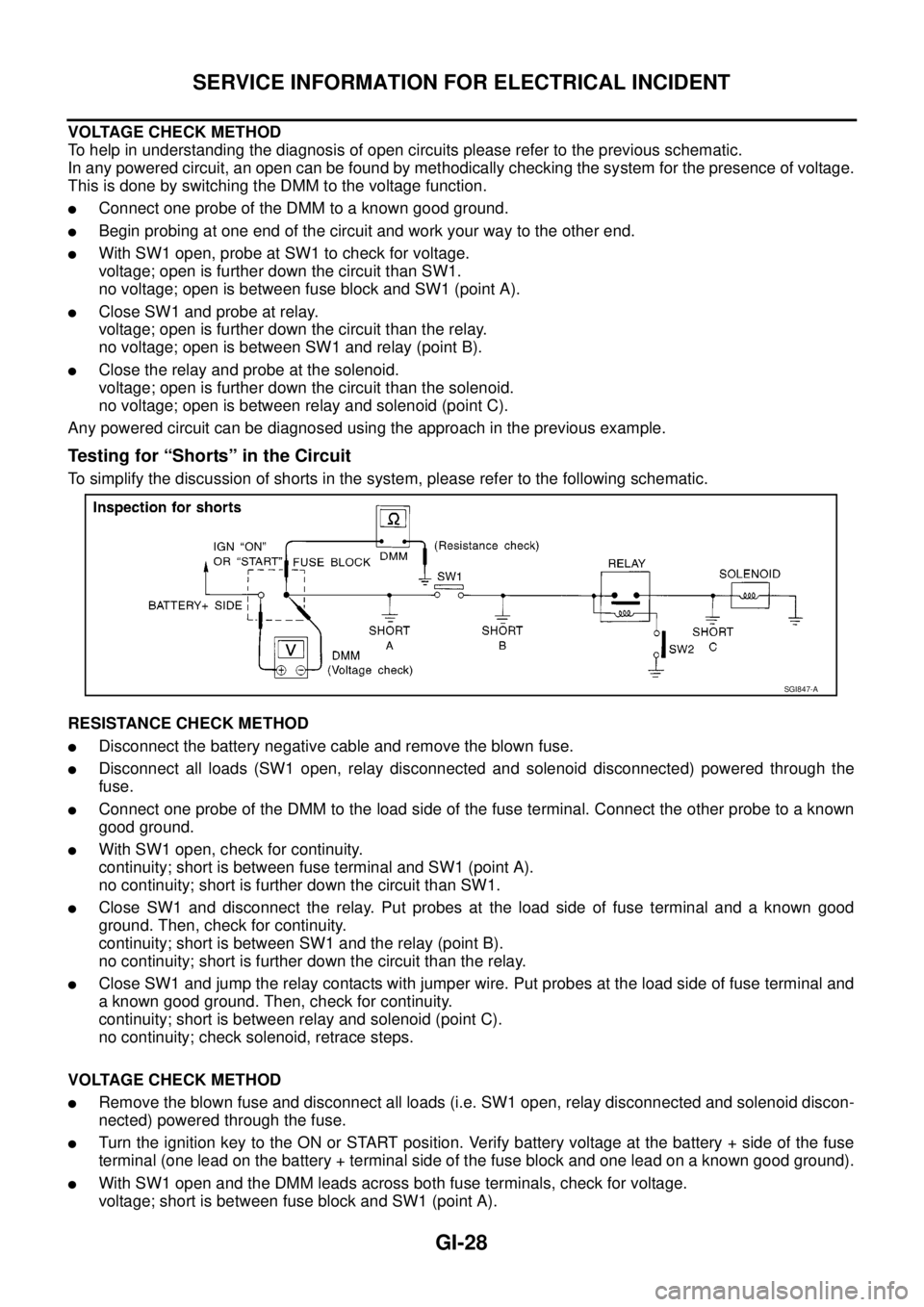
Testing for “Shorts” in the Circuit
To simplify the discussion of shorts in the system, please refer to the following schematic.
RESISTANCE CHECK METHOD
lDisconnect the battery negative cable and remove the blown fuse.
lDisconnect all loads (SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid disconnected) powered through the
fuse.
lConnect one probe of the DMM to the load side of the fuse terminal. Connect the other probe to a known
good ground.
lWith SW1 open, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between fuse terminal and SW1 (point A).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
lClose SW1 and disconnect the relay. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a known good
ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
lClose SW1 and jump the relay contacts with jumper wire. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and
a known good ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between relay and solenoid (point C).
no continuity; check solenoid, retrace steps.
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
lRemove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i.e. SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid discon-
nected) powered through the fuse.
lTurn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Verify battery voltage at the battery + side of the fuse
terminal (one lead on the battery + terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known good ground).
lWith SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
SGI847-A
Page 1651 of 3171
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-29
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
lWith SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check
for voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
lWith SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the relay and the disconnected solenoid (point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
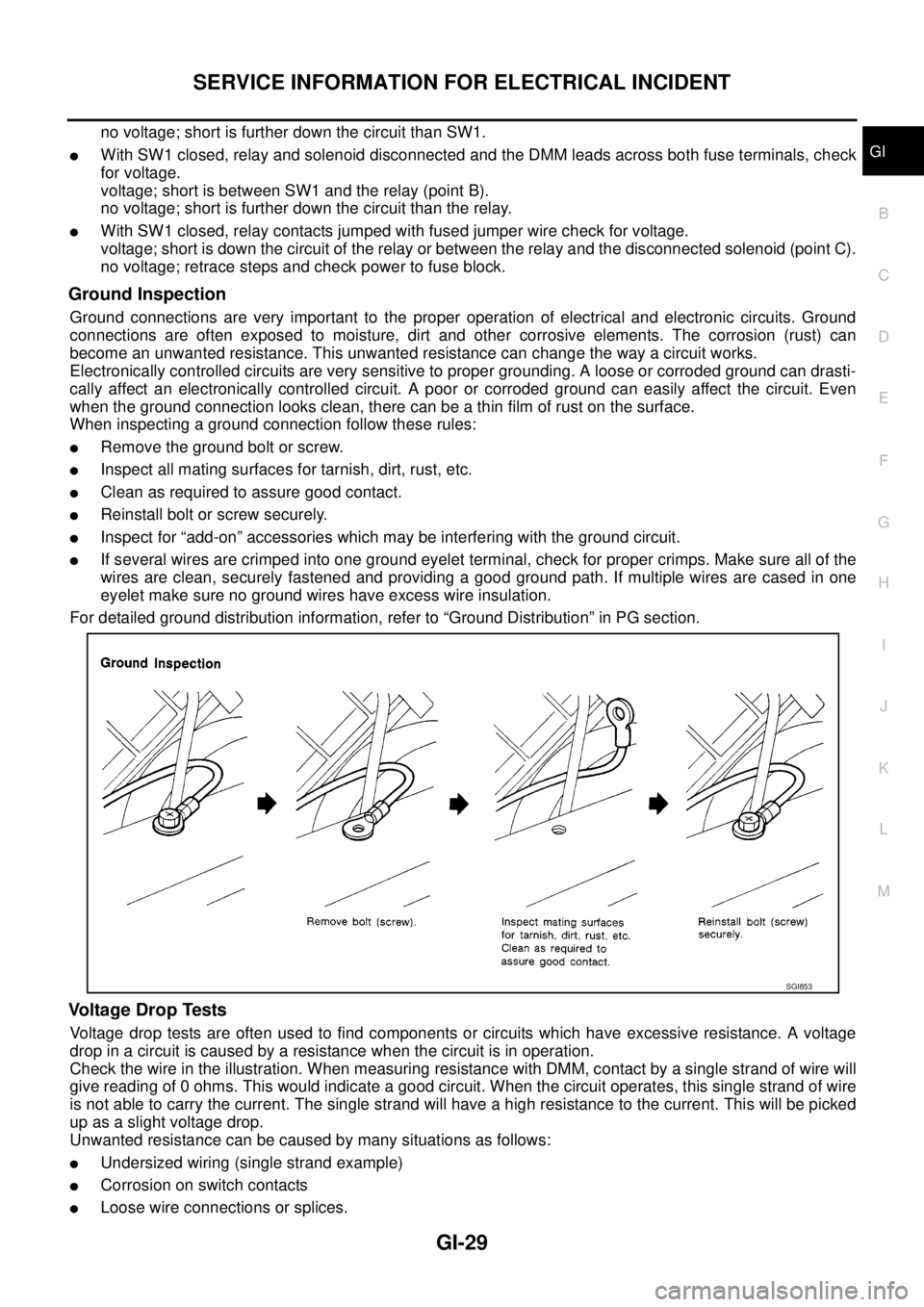
Ground Inspection
Ground connections are very important to the proper operation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground
connections are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can
become an unwanted resistance. This unwanted resistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can drasti-
cally affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can easily affect the circuit. Even
when the ground connection looks clean, there can be a thin film of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
lRemove the ground bolt or screw.
lInspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
lClean as required to assure good contact.
lReinstall bolt or screw securely.
lInspect for “add-on” accessories which may be interfering with the ground circuit.
lIf several wires are crimped into one ground eyelet terminal, check for proper crimps. Make sure all of the
wires are clean, securely fastened and providing a good ground path. If multiple wires are cased in one
eyelet make sure no ground wires have excess wire insulation.
For detailed ground distribution information, refer to “Ground Distribution” in PG section.
Voltage Drop Tests
Voltage drop tests are often used to find components or circuits which have excessive resistance. A voltage
drop in a circuit is caused by a resistance when the circuit is in operation.
Check the wire in the illustration. When measuring resistance with DMM, contact by a single strand of wire will
give reading of 0 ohms. This would indicate a good circuit. When the circuit operates, this single strand of wire
is not able to carry the current. The single strand will have a high resistance to the current. This will be picked
up as a slight voltage drop.
Unwanted resistance can be caused by many situations as follows:
lUndersized wiring (single strand example)
lCorrosion on switch contacts
lLoose wire connections or splices.
SGI853
Page 1701 of 3171
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
GW-15
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
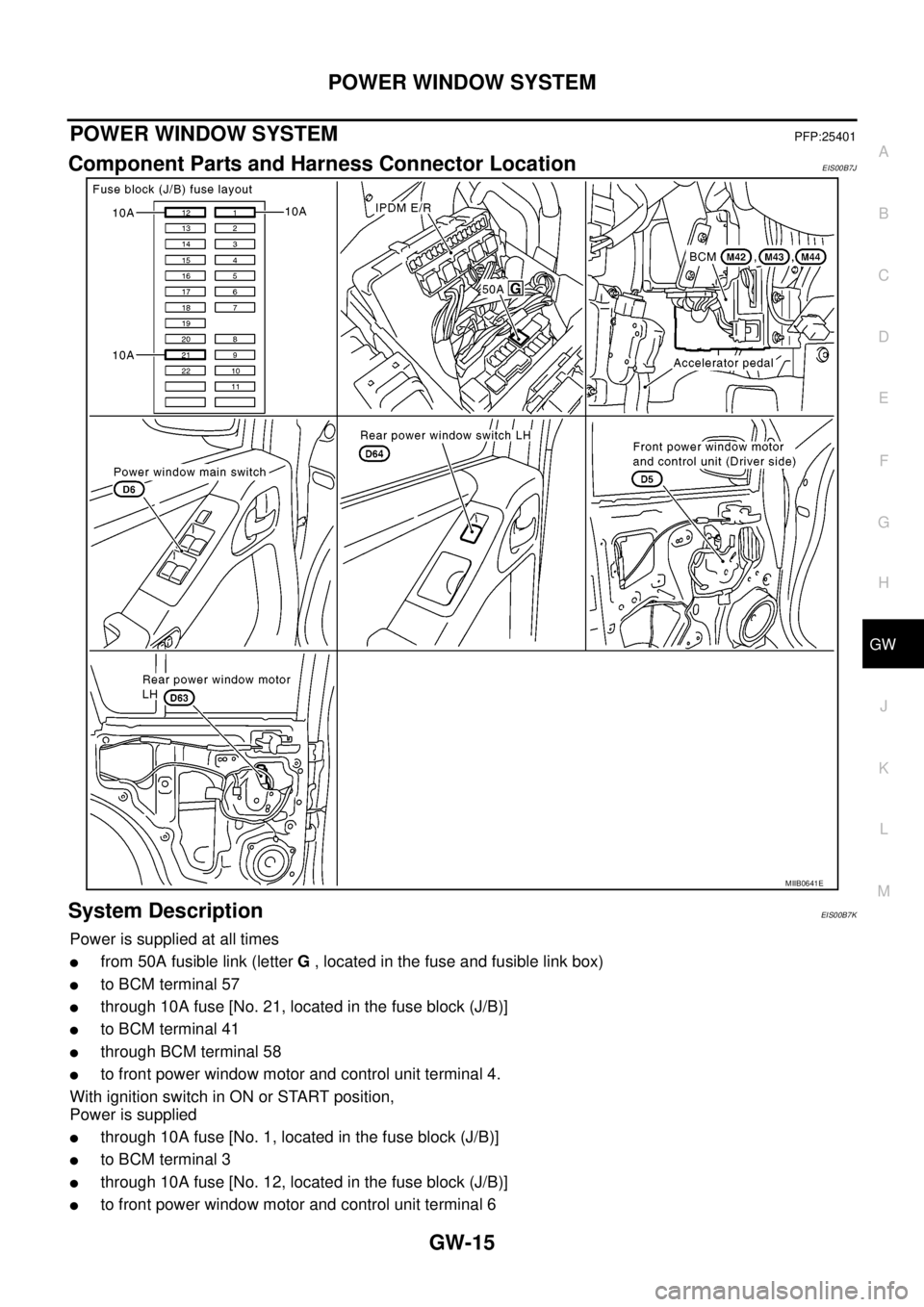
POWER WINDOW SYSTEMPFP:25401
Component Parts and Harness Connector LocationEIS00B7J
System DescriptionEIS00B7K
Power is supplied at all times
lfrom 50A fusible link (letterG, located in the fuse and fusible link box)
lto BCM terminal 57
lthrough 10A fuse [No. 21, located in the fuse block (J/B)]
lto BCM terminal 41
lthrough BCM terminal 58
lto front power window motor and control unit terminal 4.
With ignition switch in ON or START position,
Power is supplied
lthrough 10A fuse [No. 1, located in the fuse block (J/B)]
lto BCM terminal 3
lthrough 10A fuse [No. 12, located in the fuse block (J/B)]
lto front power window motor and control unit terminal 6
MIIB0641E
Page 1711 of 3171

POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
GW-25
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
Terminal and Reference Value for BCMEIS00B7P
Work FlowEIS00B7Q
1. Check the symptom and customer's requests.
2. Understand the outline of system. Refer toGW-15, "
System Description".
3. According to the trouble diagnosis chart, repair or replace the cause of the malfunction.
Refer toGW-25, "
Trouble Diagnosis Symptom Chart".
4. Does power window system operate normally? Yes, GO TO 5, If No, GO TO 3.
5. Inspection end.
Trouble Diagnosis Symptom ChartEIS00C0A
Terminal Wire color Item ConditionVoltage (V)
(Approx.)
3 Y Ignition switch (ON or START)Ignition switch
(ON or START position)Battery voltage
41 Y Battery power supply (Fuse) — Battery voltage
53 W Power window pow er supply (IGN)When ignition switch ON Battery voltage
When ignition switch OFF 0
55 B Ground — 0
57 W Battery power supply (Fusible link) — Battery voltage
58 P Power window power supply (BAT) — Battery voltage
Symptom Diagnosis / service procedure Refer to page
None of the power window can be operated using any
switch1. BCM power supply and ground circuit check.GW-26
2. Power window main switch power supply and
ground circuit check.GW-27
Driver side power window cannot be operated 1. Driver side power window motor check.GW-28
Passenger side power window cannot be operated1. Passenger side power window motor circuit checkGW-292. Power window switch check 1GW-33
3. passenger side power window circuit checkGW-31
Rear LH side power window cannot be operated1. Rear LH power window motor circuit checkGW-302. Power window switch check 1GW-33
3. Rear LH power window circuit checkGW-32
Rear RH side power window cannot be operated1. Rear RH power window motor circuit checkGW-312. Power window switch check 1GW-33
3. Rear RH power window circuit checkGW-33
Power window does not operate using power window
switch. (Power window can be operated using power win-
dow main switch)1. Power window switch check 2GW-34
Anti-pinch system does not operate normal
Replace front power window motor and control unit
(driver side)—
Power window timer does not operated
Page 1712 of 3171
![NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Workshop Manual GW-26
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
BCM Power Supply and Ground Circuit Check
EIS00B7T
1.CHECK FUSE
lCheck 10A fuse [No. 1, located in the fuse block (J/B)].
lCheck 10A fuse [No. 21, located in the fuse block ( NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Workshop Manual GW-26
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
BCM Power Supply and Ground Circuit Check
EIS00B7T
1.CHECK FUSE
lCheck 10A fuse [No. 1, located in the fuse block (J/B)].
lCheck 10A fuse [No. 21, located in the fuse block (](/manual-img/5/57362/w960_57362-1711.png)
GW-26
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
BCM Power Supply and Ground Circuit Check
EIS00B7T
1.CHECK FUSE
lCheck 10A fuse [No. 1, located in the fuse block (J/B)].
lCheck 10A fuse [No. 21, located in the fuse block (J/B)].
lCheck 50A fusible link (letterGlocated in the fuse and fusible link box).
NOTE:
Refer toGW-15, "
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location".
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 2.
NG >> If fuse is blown, be sure to eliminate cause of malfunction before installing new fuse.
2.CHECK POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect BCM connector.
3. Turn ignition switch ON.
4. Check voltage between BCM connector M42, 43, 44 terminal 3,
41, 57 and ground.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 3.
NG >> Repair or replace harness.
3.CHECK GROUND CIRCUIT
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect BCM.
3. Check continuity between BCM connector M44 terminal 55 and
ground.
OK or NG
OK >> Power supply and ground circuit is OK.
NG >> Repair or replace harness.3 - Ground : Battery voltage
41 - Ground : Battery voltage
57 - Ground : Battery voltage
MIIB0733E
55 - Ground : Continuity should exist.
MIIB0594E
Page 1714 of 3171
GW-28
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
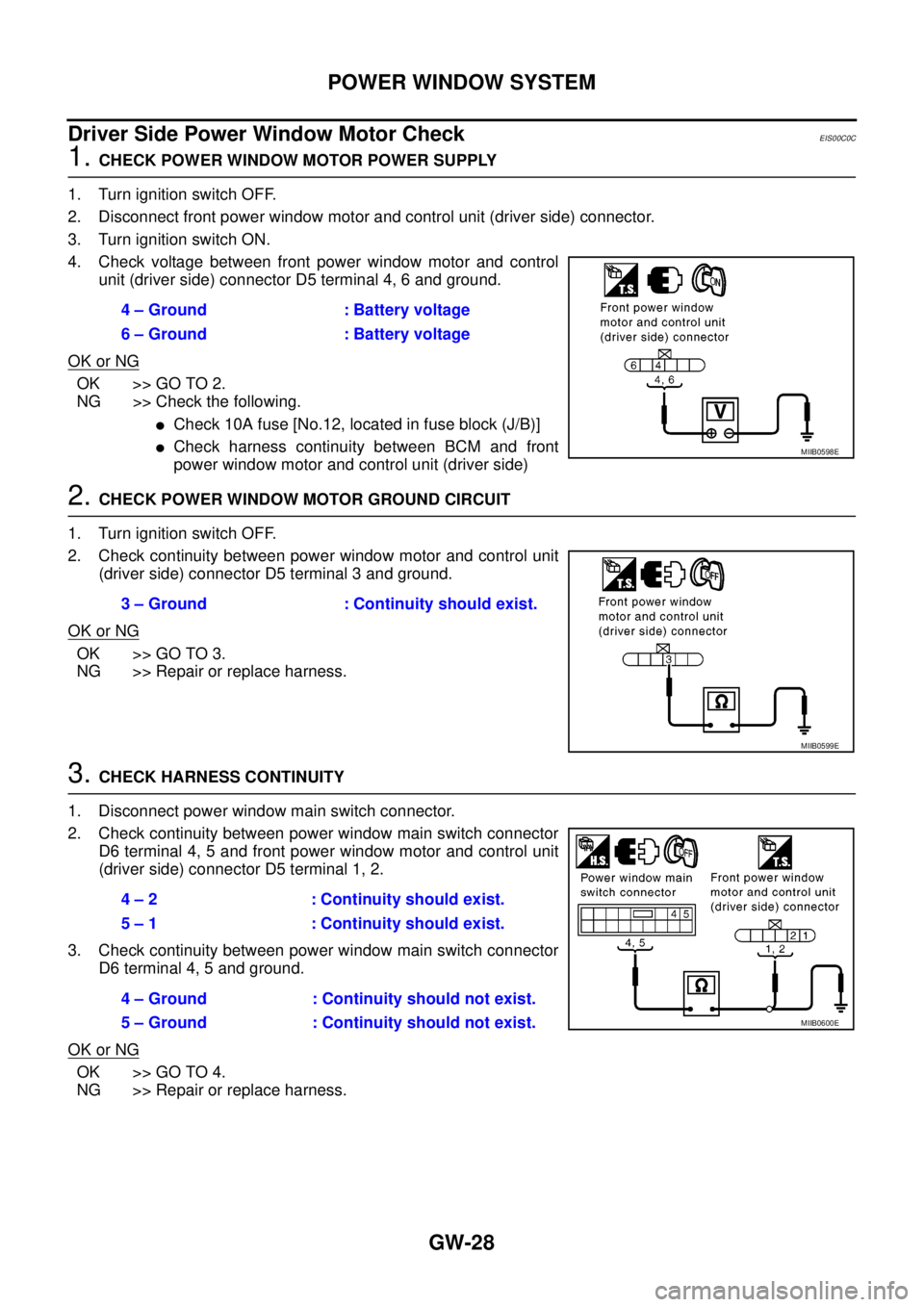
Driver Side Power Window Motor Check
EIS00C0C
1.CHECK POWER WINDOW MOTOR POWER SUPPLY
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect front power window motor and control unit (driver side) connector.
3. Turn ignition switch ON.
4. Check voltage between front power window motor and control
unit (driver side) connector D5 terminal 4, 6 and ground.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 2.
NG >> Check the following.
lCheck 10A fuse [No.12, located in fuse block (J/B)]
lCheck harness continuity between BCM and front
power window motor and control unit (driver side)
2.CHECK POWER WINDOW MOTOR GROUND CIRCUIT
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Check continuity between power window motor and control unit
(driver side) connector D5 terminal 3 and ground.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 3.
NG >> Repair or replace harness.
3.CHECK HARNESS CONTINUITY
1. Disconnect power window main switch connector.
2. Check continuity between power window main switch connector
D6 terminal 4, 5 and front power window motor and control unit
(driver side) connector D5 terminal 1, 2.
3. Check continuity between power window main switch connector
D6 terminal 4, 5 and ground.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 4.
NG >> Repair or replace harness.4 – Ground : Battery voltage
6 – Ground : Battery voltage
MIIB0598E
3 – Ground : Continuity should exist.
MIIB0599E
4 – 2 : Continuity should exist.
5 – 1 : Continuity should exist.
4 – Ground : Continuity should not exist.
5 – Ground : Continuity should not exist.
MIIB0600E
Page 1733 of 3171
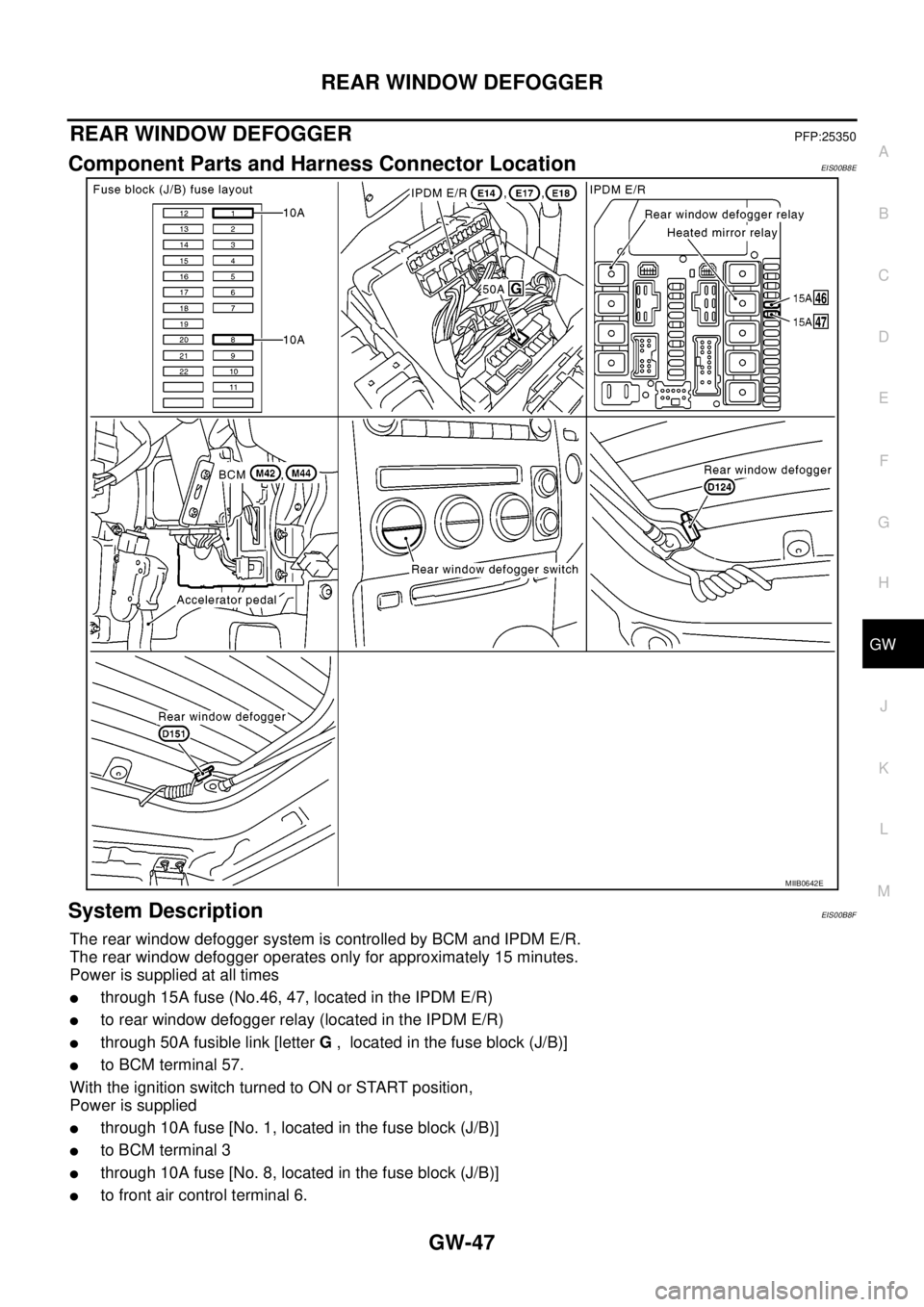
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
GW-47
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGERPFP:25350
Component Parts and Harness Connector LocationEIS00B8E
System DescriptionEIS00B8F
The rear window defogger system is controlled by BCM and IPDM E/R.
The rear window defogger operates only for approximately 15 minutes.
Power is supplied at all times
lthrough 15A fuse (No.46, 47, located in the IPDM E/R)
lto rear window defogger relay (located in the IPDM E/R)
lthrough 50A fusible link [letterG, located in the fuse block (J/B)]
lto BCM terminal 57.
WiththeignitionswitchturnedtoONorSTARTposition,
Power is supplied
lthrough 10A fuse [No. 1, located in the fuse block (J/B)]
lto BCM terminal 3
lthrough 10A fuse [No. 8, located in the fuse block (J/B)]
lto front air control terminal 6.
MIIB0642E
Page 1742 of 3171
GW-56
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
Trouble Diagnoses Symptom Chart
EIS00B8N
lMake sure other systems using the signal of the following systems operate normally.
BCM Power Supply and Ground Circuit CheckEIS00B8O
First perform the “SELF-DIAG RESULTS” in “BCM” with CONSULT-II, when perform the each trouble
diagnosis. Refer toBCS-16, "
CAN Communication Inspection Using CONSULT-II (Self-Diagnosis)".
1.CHECK FUSE
lCheck 10A fuse [No. 1, located in the fuse block (J/B)]
lCheck 50A fusible link (letterGlocated in the fuse and fusible link box)
NOTE:
Refer toGW-47, "
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location".
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 2.
NG >> If fuse is blown, be sure to eliminate cause of malfunction before installing new fuse. Refer toPG-
4, "POWER SUPPLY ROUTING CIRCUIT".
2.CHECK POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect BCM connector.
3. Turn ignition switch ON.
4. Check voltage between BCM connector M42, M44 terminal 3,
57 and ground.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 3.
NG >> Repair or replace harness.
Symptom Diagnoses / Service procedure Refer to page
Rear window defogger and door mirror defoggers do not
operate.1. BCM power supply and ground circuit checkGW-56
2. IPDM E/R auto active test checkPG-19
3. Rear window defogger power supply circuit checkGW-59
4. Rear window defogger switch circuit checkGW-57
5. Rear window defogger circuit checkGW-59
6. Replace IPDM E/RPG-26
Rear window defogger switch does not light, and rear win-
dow defogger is not displayed on the display, but rear win-
dow defogger operates.1. Rear window defogger signal checkGW-60
3 - Ground : Battery voltage
57 - Ground : Battery voltage
MIIB0730E