Page 1004 of 1897
- DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI-125
281 Author�: Date�:
2001 AVALON (RM808U)
OK
2 Check for open and short in harness and connector between ECM and VVT sen-
sor (See page IN-30).
NG Repair or replace harness or connector.
OK
3 Inspect sensor installation and signal plate teeth of camshaft timing gear.
NG Tighten sensor. Replace camshaft timing gear.
OK
Check and replace ECM (See page IN-30).
Page 1005 of 1897
DI-126
- DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
282 Author�: Date�:
2001 AVALON (RM808U)
DTC P1346 VVT Sensor/Camshaft Position Sensor Cir-
cuit Range/Performance Problem (Bank 1)
DTC P1351 VVT Sensor/Camshaft Position Sensor Cir-
cuit Range/Performance Problem (Bank 2)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P1345, P1350 on page DI-124.
DTC No.DTC Detection ConditionTrouble Area
P1346Deviation in crankshaft position sensor signal and VVT sensor
(bank 1) signal (2 trip detection logic)�Mechanical system malfunction (Jumping teeth of timing belt,
blt t thd)
P1351Deviation in crankshaft position sensor signal and VVT sensor
(bank 2) signal (2 trip detection logic)belt stretched)
�ECM
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P1345, P1350 on page DI-124.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using TOYOTA hand-held tester or OBD II scan tool. Because freeze frame records
the engine conditions when the malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, it is useful for determining
whether the vehicle was running or stopped, the engine was warmed up or not, the air-fuel ratio was lean
or rich, etc. at the time of the malfunction.
1 Check valve timing (Check for loose and jumping teeth of timing belt) (See page
EM-15).
NG Adjust valve timing (Repair or replace timing
belt).
OK
Check and replace ECM (See page IN-30).
DI6TA-01
Page 1013 of 1897
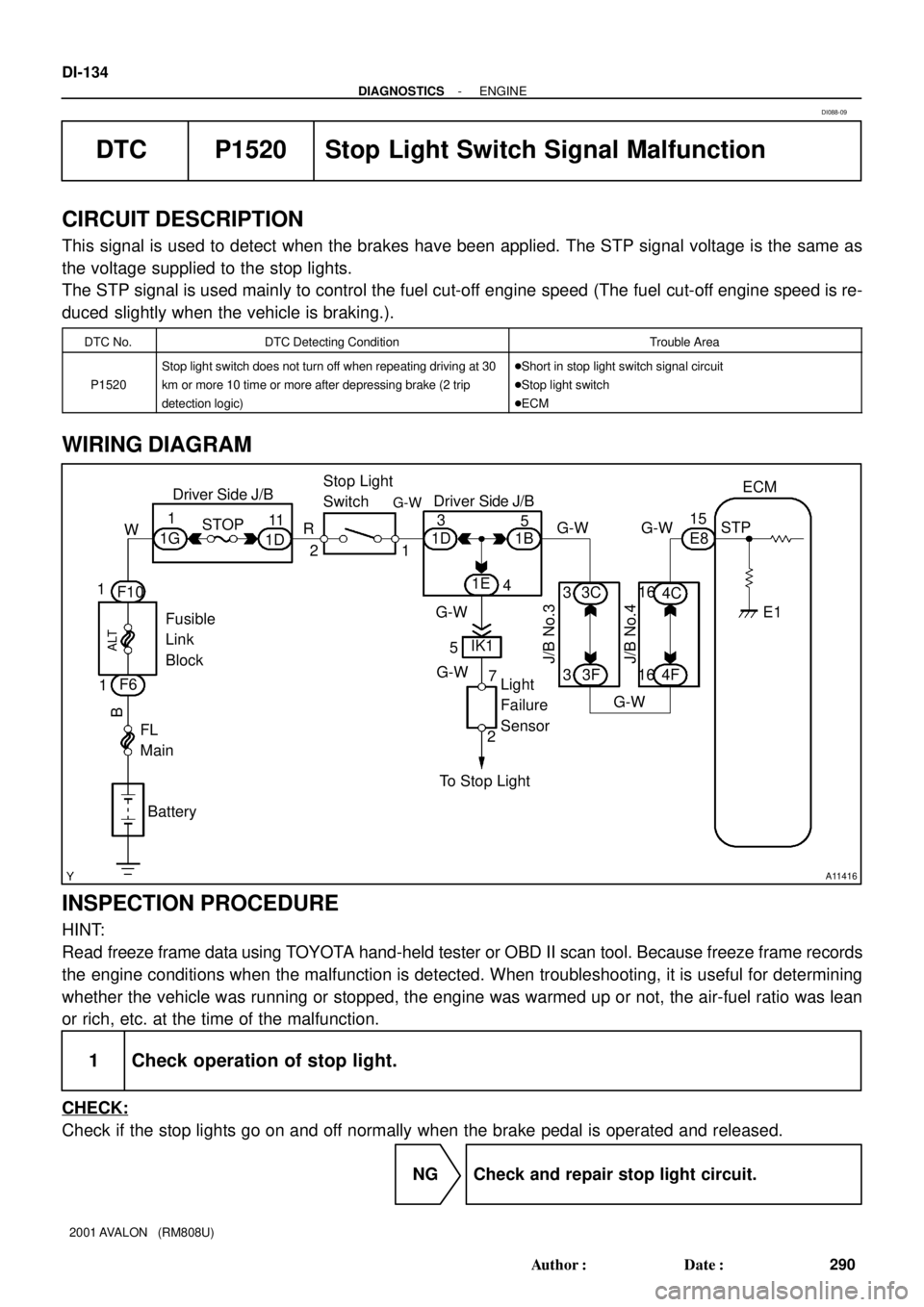
A11416
Fusible
Link
Block
FL
Main
BatteryStop Light
Switch
ALT
B
F10
F6STOP
R
211D 1B
1E
45
Light
Failure
Sensor 7
2
To Stop LightE8 15ECM
STP
E1 Driver Side J/B
3 11
W
1 1
16
4C 3C
3164F3F 3
5IK1 1D 1
1GG-W
G-WDriver Side J/B
J/B No.3
J/B No.4
G-W
G-W G-W G-W
DI-134
- DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
290 Author�: Date�:
2001 AVALON (RM808U)
DTC P1520 Stop Light Switch Signal Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
This signal is used to detect when the brakes have been applied. The STP signal voltage is the same as
the voltage supplied to the stop lights.
The STP signal is used mainly to control the fuel cut-off engine speed (The fuel cut-off engine speed is re-
duced slightly when the vehicle is braking.).
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P1520
Stop light switch does not turn off when repeating driving at 30
km or more 10 time or more after depressing brake (2 trip
detection logic)�Short in stop light switch signal circuit
�Stop light switch
�ECM
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using TOYOTA hand-held tester or OBD II scan tool. Because freeze frame records
the engine conditions when the malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, it is useful for determining
whether the vehicle was running or stopped, the engine was warmed up or not, the air-fuel ratio was lean
or rich, etc. at the time of the malfunction.
1 Check operation of stop light.
CHECK:
Check if the stop lights go on and off normally when the brake pedal is operated and released.
NG Check and repair stop light circuit.
DI088-09
Page 1021 of 1897
- DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI-53
209 Author�: Date�:
DTC P0171 System too Lean (Fuel Trim)
DTC P0172 System too Rich (Fuel Trim)
DTC P0174 System too Lean (A/F Lean Malfunction,
Bank2)
DTC P0175 System too Rich (Bank2)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Fuel trim refers to the feedback compensation value compared to the basic injection time. Fuel trim includes
short-term fuel trim and long-term fuel trim.
Short-term fuel trim is the short-term fuel compensation used to maintain the air-fuel ratio at its ideal
theoretical value.
The signal from the A/F sensor is approximately proportional to the existing air-fuel ratio, and ECM compar-
ing it with the ideal theoretical value, the ECM reduces fuel volume immediately if the air-fuel ratio is rich
and increases fuel volume if it is lean.
Long-term fuel trim compensates the deviation from the central value of the short-term fuel trim stored up
by each engine tolerance, and the deviation from the central value due to the passage of time and changes
of using environment.
If both the short-term fuel trim and long-term fuel trim exceed a certain value, it is detected as a malfunction
and the MIL lights up.
DTC No.DTC Detecting ConditionTrouble Area
P0171
P0174When air-fuel ratio feedback is stable after engine warming up,
fuel trim is considerably in error on rich side (2 trip detection
logic)
�Air induction system
�Injector blockage
�Mass air flow meter
�Engine coolant temp. sensor
�Fuel pressure
�Gas leakage on exhaust system
�Open or short in A/F sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1) circuit
�A/F sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
�ECM
P0172
P0175When air-fuel ratio feedback is stable after engine warming up,
fuel trim is considerably in error on lean side (2 trip detection
logic)
�Injector leak, blockage
�Mass air flow meter
�Engine coolant temp. sensor
�Ignition system
�Fuel pressure
�Gas leakage on exhaust system
�Open or short in A/F sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1) circuit
�A/F sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1)
�ECM
DI6T4-03
Page 1022 of 1897

DI-54
- DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
210 Author�: Date�:
HINT:
�When the DTC P0171 or P0174 is recorded, the actual air-fuel ratio is on the lean side. When DTC
P0172 or P0175 is recorded, the actual air-fuel ratio is on the rich side.
�If the vehicle runs out of fuel, the air-fuel ratio is lean and DTC P0171 or P0174 is recorded. The MIL
then comes on.
�If the total of the short-term fuel trim value and the long-term fuel trim value is within + 35 % (80°C
(176°F) or more), the system is functioning normally.
�The A/F sensors (bank 1, 2 sensor 1) output voltage and the short-term fuel trim value can be read
using the OBD II scan tool or hand-held tester.
�The ECM controls the voltage of AFR+, AFL+, AFR- and AFL- terminals of ECM to the fixed voltage.
Therefore, it is impossible to confirm the A/F sensor output voltage without OBD II scan tool or hand-
held tester.
�OBD II scan tool (excluding hand-held tester) displays the one fifth of the A/F sensors (bank 1, 2 sen-
sor 1) output voltage which is displayed on the hand-held tester.
WIRING DIAGRAM
Refer to DTC P0125 on page DI-43.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using TOYOTA hand-held tester or OBD II scan tool. Because freeze frame records
the engine conditions when the malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, it is useful for determining
whether the vehicle was running or stopped, the engine was warmed up or not, the air-fuel ratio was lean
or rich, etc. at the time of the malfunction.
1 Check air induction system (See page SF-1).
NG Repair or replace.
OK
2 Check injector injection (See page SF-23).
NG Replace injector.
OK
Page 1023 of 1897
- DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI-55
211 Author�: Date�:
3 Check mass air flow meter (See page SF-31) and engine coolant temperature
sensor (See page SF-73).
NG Repair or replace.
OK
4 Check for spark and ignition (See page IG-1).
NG Repair or replace.
OK
5 Check fuel pressure (See page SF-6).
NG Check and repair fuel pump, pressure regulator,
fuel pipe line and filter.
OK
6 Check gas leakage on exhaust system.
NG Repair or replace.
OK
Page 1024 of 1897

DI-56
- DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
212 Author�: Date�:
7 Check output voltage A/F sensor (bank 1, 2 sensor 1).
PREPARATION:
(a) Connect the OBDII scan tool or TOYOTA hand-held tester to the DLC3.
(b) Warm up the A/F sensor with the engine speed at 2,500 rpm for approx. 90 sec.
CHECK:
Read the voltage value of the A/F sensor on the screen of OBDII scan tool or TOYOTA hand-held tester
when you perform all the following conditions.
HINT:
The voltage of the AFR+ or AFL+ terminal of the ECM is 3.3 fixed the AFR- or AFL- terminal is 3.0 V fixed.
Therefore, it is impossible to check the A/F sensor output voltage at the terminals (AFR+, AFL+/AFR-, AFL-)
of the ECM.
OK:
ConditionA/F Sensor Voltage value
Engine idling
Engine racing�Not remains at 3.30 V (0.660 V*)
�Not remains at38V(076V*) or moreDriving at engine speed 1,500 rpm or more and vehicle
speed 40 km/h (25mph) or more, and operate throttle valve
open and close�Not remains at 3.8 V (0.76 V*) or more
�Not remains at 2.8 V (0.56 V*) or less
*: When you use OBDII scan tool (excluding TOYOTA hand-held tester)
HINT:
�During fuel enrichment, there is a case that the output voltage of the A/F sensor is below 2.8 V (0.56
V*), it is normal.
�During fuel cut, there is a case that the output voltage of the A/F sensor is above 3.8 V (0.76 V*), it
is normal.
�If the output voltage of the A/F sensor remains at 3.30 V (0.660 V*) even after performing all the above
conditions, the A/F sensor circuit may be open.
�If the output voltage of the A/F sensor remains at 3.8 V (0.76 V*) or more, or 2.8 V (0.56 V*) or less
even after performing all the above conditions, the A/F sensor circuit may be short.
*: When you use the OBDII scan tool (excluding TOYOTA hand-held tester).
OK Go to step 9.
NG
Page 1025 of 1897
- DIAGNOSTICSENGINE
DI-57
213 Author�: Date�:
8 Check for open and short in harness and connector between ECM and A/F sen-
sors (bank 1, 2 sensor 1) (See page IN-30).
NG Repair or replace harness or connector.
OK
Replace A/F sensor.
9 Perform confirmation driving pattern (See page DI-106).
Go
10 Is there DTC P0171, P0172, P0174 or P0175 being output again?
YES Check and replace ECM (See page IN-30).
NO
11 Did vehicle runs out of fuel in past?
NO Check for intermittent problems
(See page DI-3).
YES
DTC P0171, P0172, P0174 or P0175 is caused
by running out of fuel.