2000 DODGE NEON electrical
[x] Cancel search: electricalPage 201 of 1285

(10) Radiator can now be lifted free from engine
compartment.Care should be taken not to dam-
age radiator cooling fins or water tubes during
removal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Slide radiator down into position behind radia-
tor support (yoke).
(2) Attach air conditioning condenser to radiator, if
equipped (Fig. 25), with four mounting screws.
Tighten screws to 5.4 N´m (50 in. lbs.). Then seat the
radiator assembly lower rubber isolators into the
mounting holes provided in the lower crossmember.
(3) Install and tighten radiator isolator mounting
bracket screws to 10 N´m (90 in. lbs.) (Fig. 24). The
radiator should have clearance to move up, approxi-
mately 5±8 mm (0.20±0.31 in.) after assembled.
(4) Install lower radiator hose. Align the hose and
position the clamp so it will not interfere with engine
components.
(5) Connect automatic transmission hoses, if
equipped. Tighten hose clamps to 2 N´m (18 in. lbs.).
(6) Slide fan module down into clip(s) on lower
radiator flange (Fig. 23). Install retaining screws and
tighten to 7.5 N´m (65 in. lbs.).
(7) Connect the cooling fan motor electrical connec-
tor.
(8) Install upper radiator hose. Align the hose and
position the clamp so they will not interfere with the
engine or the hood.
(9) Connect negative cable to battery.
(10) Fill cooling system with coolant. Refer to pro-
cedure in this section.
(11) Operate engine until it reaches normal operat-
ing temperature. Check cooling system and auto-
matic transmission for correct fluid levels.
RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
REMOVAL
(1) Turn the drain cock stem counterclockwise to
unscrew the stem. When the stem is unscrewed to
the end of the threads, pull the stem (Fig. 26) from
the radiator tank.
INSTALLATION
(1) Push the draincock assembly body into the
tank opening.
(2) Tighten the draincock stem by turning clock-
wise to 2.0-2.7 N´m (18-25 in. lbs.).
COOLING FAN MODULE
All models use a single speed electric motor driven
cooling system fan. The fan module includes a motor,
fan blade, and support shroud. The module is fas-
tened to the radiator by screws.
REMOVAL
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK PLUG OR THE RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Drain cooling system below upper radiator hose
level. Refer to procedure in this section.
(3) Remove upper radiator hose from radiator (Fig.
27).
(4) Disconnect fan module electrical connector.
(5) Remove fan module screws from radiator (Fig.
28).
(6) Lift fan shroud up and out of lower shroud
attachment clips.
(7) Refer to Disassembly and Assembly in this sec-
tion for fan module sub-component service proce-
dures.
Fig. 25 A/C Condenser to Radiator Mounting Screws
1 ± AIR CONDITIONING CONDENSER TO RADIATOR
MOUNTING SCREWS
2 ± LOWER ISOLATOR MOUNTS
Fig. 26 Draincock
1 ± DRAIN COCK BODY
2 ± DRAIN COCK HOUSING
7 - 22 COOLING SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 202 of 1285
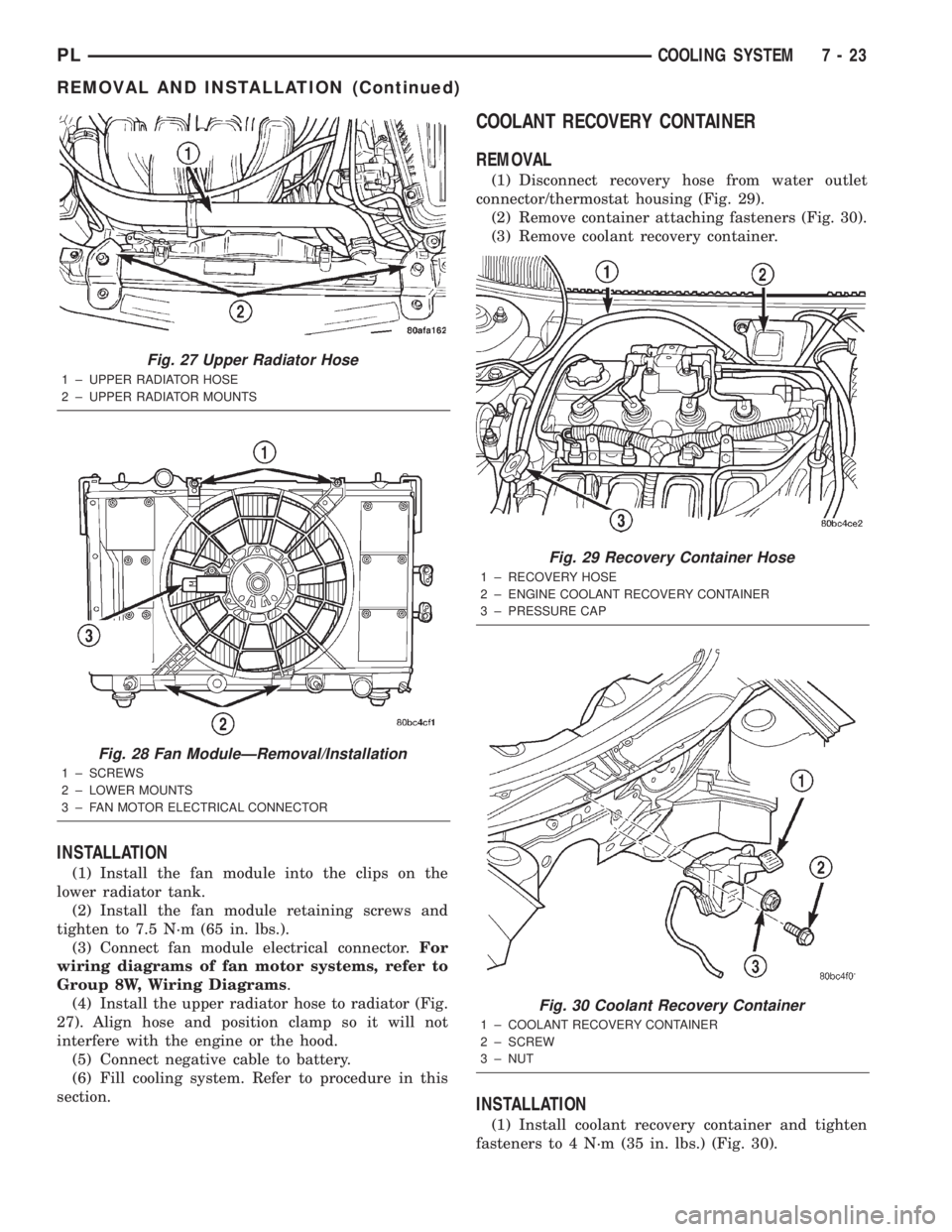
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the fan module into the clips on the
lower radiator tank.
(2) Install the fan module retaining screws and
tighten to 7.5 N´m (65 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect fan module electrical connector.For
wiring diagrams of fan motor systems, refer to
Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
(4) Install the upper radiator hose to radiator (Fig.
27). Align hose and position clamp so it will not
interfere with the engine or the hood.
(5) Connect negative cable to battery.
(6) Fill cooling system. Refer to procedure in this
section.
COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect recovery hose from water outlet
connector/thermostat housing (Fig. 29).
(2) Remove container attaching fasteners (Fig. 30).
(3) Remove coolant recovery container.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install coolant recovery container and tighten
fasteners to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) (Fig. 30).
Fig. 27 Upper Radiator Hose
1 ± UPPER RADIATOR HOSE
2 ± UPPER RADIATOR MOUNTS
Fig. 28 Fan ModuleÐRemoval/Installation
1 ± SCREWS
2 ± LOWER MOUNTS
3 ± FAN MOTOR ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
Fig. 29 Recovery Container Hose
1 ± RECOVERY HOSE
2 ± ENGINE COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
3 ± PRESSURE CAP
Fig. 30 Coolant Recovery Container
1 ± COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
2 ± SCREW
3 ± NUT
PLCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 23
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 210 of 1285

BATTERY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION..........................1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
BATTERY IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD).........2
CHARGING TIME REQUIRED................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BATTERY BUILT-IN TEST INDICATOR.........3
BATTERY IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD).........4
BATTERY LOAD TEST......................6
BATTERY OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE...........7
SERVICE PROCEDURES
BATTERY CHARGING......................7CHARGING COMPLETELY DISCHARGED
BATTERY..............................8
VISUAL INSPECTION......................9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
BATTERY...............................10
BATTERY THERMOWRAP..................10
BATTERY TRAY..........................11
SPECIFICATIONS
BATTERY SPECIFICATIONS................11
TORQUE...............................11
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
The battery (Fig. 1) stores, stabilizes, and delivers
electrical current to operate various electrical sys-
tems in the vehicle. The determination of whether a
battery is good or bad is made by its ability to accept
a charge. It also must supply high-amperage current
for a long enough period to be able to start the vehi-
cle. The capability of the battery to store electrical
current comes from a chemical reaction. This reac-
tion takes place between the sulfuric acid solution
(electrolyte) and the lead +/- plates in each cell of the
battery. As the battery discharges, the plates react
with the acid from the electrolyte. When the charging
system charges the battery, the water is converted to
sulfuric acid in the battery. The concentration of acid
in the electrolyte is measured as specific gravity
using a hydrometer. The original equipment (OE)
battery is equipped with a hydrometer (test indica-
tor) built into the battery cover. The specific gravity
indicates the battery's state-of-charge. The OE bat-
tery is sealed and water cannot be added.
The battery is vented to release gases that are cre-
ated when the battery is being charged and discharged.
The battery top, posts, and terminals should be cleaned
when other under hood maintenance is performed.
When the electrolyte level is below the top of the
plates, Yellow/Clear in the test Indicator, the battery
must be replaced. The battery must be completely
charged, and the battery top, posts, and cable clamps
must be cleaned before diagnostic procedures are per-
formed.
Fig. 1 Battery Location
1 ± BATTERY
2 ± LEFT STRUT TOWER
3 ± PDC
4 ± THROTTLE BODY
5 ± AIR CLEANER HOUSING
PLBATTERY 8A - 1
Page 211 of 1285

DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
BATTERY IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD)
A completely normal vehicle will have a small
amount of current drain on the battery with the key
out of the ignition. It can range from 4 to 10 milli-
amperes after all the modules time out. If a vehicle
will not be operated for approximately a 20 days, the
IOD fuse should be disconnected to minimize the
vehicle electrical drain on the battery. The IOD fuse
is located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
Refer to the PDC cover to locate the proper fuse.
CHARGING TIME REQUIRED
WARNING: NEVER EXCEED 20 AMPS WHEN
CHARGING A COLD -1ÉC (30ÉF) BATTERY. PER-
SONAL INJURY MAY RESULT.
The time required to charge a battery will vary
depending upon the following factors.
SIZE OF BATTERY
A completely discharged large heavy-duty battery
may require more recharging time than a completely
discharged small capacity battery, refer to Battery
Charging Timetable for charging times.
TEMPERATURE
A longer time will be needed to charge a battery at
-18ÉC (0ÉF) than at 27ÉC (80ÉF). When a fast charger
is connected to a cold battery, current accepted by
battery will be very low at first. In time, the battery
will accept a higher rate as battery temperature
warms.
CHARGER CAPACITY
A charger which can supply only five amperes will
require a much longer period of charging than a
charger that can supply 20 amperes or more.
STATE OF CHARGE
A completely discharged battery requires more
charging time than a partially charged battery.
NOTE: Do not attempt to recharge a battery with a
yellow/clear test indicator.
Electrolyte is nearly pure water in a completely
discharged battery. At first, the charging current
amperage will be low. As water is converted back to
sulfuric acid inside the battery, the current amp rate
will rise. Also, the specific gravity of the electrolyte
will rise, bringing the green ball (Fig. 2) into view at
approximately 75 percent state-of-charge.
BATTERY CHARGING TIMETABLE
CHARGING
AMPERAGE5
AMPERES10
AMPERES20
AMPERES
OPEN
CIRCUIT
VOLTAGEHOURS CHARGING AT 21É C (70É F)
12.25 TO
12.496 HOURS 3 HOURS 1.5 HOURS
12.00 TO
12.2410 HOURS 5 HOURS 2.5 HOURS
10.00 TO
11.9914 HOURS 7 HOURS 3.5 HOURS
*BELOW
10.0018 HOURS 9 HOURS 4.5 HOURS
*REFER TO CHARGING A COMPLETELY DISCHARGED
BATTERY
Fig. 2 Reading Test Indicator
1 ± TEST INDICATOR/STATE OF CHARGE
2 ± REPLACE BATTERY
3 ± CLEAR
4 ± BLACK
5 ± GREEN
8A - 2 BATTERYPL
Page 212 of 1285

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BATTERY BUILT-IN TEST INDICATOR
USING TEST INDICATOR
The Test Indicator (Fig. 2), (Fig. 3) and (Fig. 4)
measures the specific gravity of the electrolyte. Spe-
cific Gravity (SG) of the electrolyte will show state-
of-charge (voltage). The test indicator WILL NOT
show cranking capacity of the battery. Refer to Bat-
tery Load Test for more information. Look into the
sight glass (Fig. 2), (Fig. 4) and note the color of the
indicator. Refer to the following description of colors:
NOTE: GREEN = 75 to 100% state-of-charge
The battery is adequately charged for further test-
ing and may be returned to use. If the vehicle will
not crank for a maximum 15 seconds, refer to BAT-
TERY LOAD TEST in this Group for more informa-
tion.
NOTE: BLACK OR DARK=0to75%state-of-chargeThe battery is INADEQUATELY charged and must
be charged until green dot is visible, (12.4 open cir-
cuit volts or greater) before the battery is tested or
returned to use. Refer to Causes of Battery Discharg-
ing in this group for more information.
NOTE: CLEAR COLOR = Replace Battery
WARNING: DO NOT CHARGE, ASSIST BOOST,
LOAD TEST, OR ADD WATER TO THE BATTERY
WHEN CLEAR COLOR DOT IS VISIBLE. PERSONAL
INJURY MAY OCCUR.
A clear color dot shows electrolyte level in battery
is below the test indicator (Fig. 2). Water cannot be
added to a maintenance free battery. The battery
must be replaced. A low electrolyte level may be
caused by an over charging condition. Refer to Gen-
erator Test Procedures on Vehicle.
CAUSES OF BATTERY DISCHARGING
It is normal to have a small 5 to 25 milliamperes
continuous electrical draw from the battery. This
draw will take place with the ignition in the OFF
position, and the courtesy, dome, storage compart-
ments, and engine compartment lights OFF. The con-
tinuous draw is due to various electronic features or
accessories that require electrical current with the
ignition OFF to function properly. When a vehicle is
not used over an extended period of approximately 20
days the IOD fuse should be pulled. The fuse is
located in the power distribution center. Disconnec-
tion of this fuse will reduce the level of battery dis-
charge. Refer to the Battery Diagnosis and Testing
table, and to the proper procedures.
Fig. 3 Battery Construction and Test Indicator -
Typical
1 ± POSITIVE POST
2 ± VENT
3 ± TEST INDICATOR
4 ± VENT
5 ± NEGATIVE POST
6 ± PLATE GROUPS
7 ± ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
8 ± GREEN BALL
9 ± MAINTENANCE FREE BATTERY
Fig. 4 Test Indicator - Typical
1 ± SIGHT GLASS
2 ± PLASTIC TUBE
3 ± GREEN BALL
4 ± BATTERY TOP
PLBATTERY 8A - 3
Page 213 of 1285

BATTERY DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
STEPS POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
VISUAL INSPECTION
CHECK FOR POSSIBLE
DAMAGE TO BATTERY AND
CLEAN BATTERY.(1) LOOSE BATTERY POST,
CRACKED BATTERY COVER
OR CASE, LEAKS OR ANY
OTHER PHYSICAL
(2) BATTERY OK.(1) REPLACE BATTERY
(2) CHECK STATE OF CHARGE.
REFER TO TEST INDICATOR.
TEST INDICATOR
CHECK CHARGE EYE COLOR(1) GREEN
(2) BLACK
(3) CLEAR(1) BATTERY IS CHARGED.
PERFORM BATTERY 0PEN
CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TEST
(2) PERFORM BATTERY
CHARGING PROCEDURE.
(3) REPLACE BATTERY.
BATTERY OPEN CIRCUIT
VOLTAGE TEST(1) BATTERY IS ABOVE 12.40
VOLTS
(2) BATTERY IS BELOW 12.40
VOLTS.(1) PERFORM THE BATTERY LOAD
TEST.
(2) PERFORM BATTERY
CHARGING PROCEDURE.
BATTERY CHARGING (1) BATTERY ACCEPTED
CHARGE.
(2) BATTERY WILL NOT
ACCEPT CHARGE(1) ENSURE THAT THE INDICATOR
EYE IS GREEN AND PERFORM
BATTERY 0PEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE
TEST
(2) PERFORM CHARGING A
COMPLETELY DISCHARGED
BATTERY.
BATTERY LOAD TEST (1) ACCEPTABLE MINIMUM
VOLTAGE.
(2) UNACCEPTABLE MINIMUM
VOLTAGE(1) BATTERY IS OK TO PUT IN
USE, PERFORM BATTERY
IGNITION OFF DRAW TEST.
(2) REPLACE BATTERY AND
PERFORM BATTERY IGNITION OFF
DRAW TEST.
CHARGING A COMPLETELY
DISCHARGED BATTERY(1) BATTERY ACCEPTED
CHARGE.
(2)BATTERY WILL NOT
ACCEPT CHARGE.(1) ENSURE THAT THE INDICATOR
EYE IS GREEN AND PERFORM
BATTERY 0PEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE
TEST.
(2) REPLACE BATTERY.
IGNITION OFF DRAW TEST (1) IOD IS 5-25
MILLIAMPERES.
(2) IOD EXCEEDS 25
MILLIAMPERES.(1) VEHICLE IS NORMAL.
(2) ELIMINATE EXCESS IOD DRAW.
ABNORMAL BATTERY DISCHARGING
²Corroded battery posts, cables or terminals.
²Loose or worn generator drive belt.
²Electrical loads that exceed the output of the
charging system due to equipment or accessories
installed after delivery.
²Slow driving speeds in heavy traffic conditions
or prolonged idling with high-amperage electrical
systems in use.²Defective electrical circuit or component causing
excess Ignition Off Draw (IOD). Refer to Battery
Ignition Off Draw (IOD).
²Defective charging system.
²Defective battery.
BATTERY IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD)
High current draw on the battery with the ignition
OFF will discharge a battery. After a dead battery is
recharged, the vehicle ignition off draw (IOD) should
8A - 4 BATTERYPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 214 of 1285

be checked. To determine if a high current draw con-
dition exists first check the vehicle with a test lamp.
(1) Verify that all electrical accessories are OFF.
²Remove key from ignition switch
²Turn off all lights
²Trunk lid is closed
²Engine compartment hood lamp is disconnected
or lamp removed
²Map lamp on rear view mirror
²Glove box door is closed
²Sun visor vanity lights are OFF
²All doors are closed
²Allow the ignition key lamp system to time out
in approximately 30 seconds, if equipped.
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable (Fig. 5).
(3) Connect a 12 Volt test lamp, with a cold resis-
tance of 5-7 ohms, between the battery negative cable
clamp and the negative post (Fig. 6). If test lamp
goes out system is OK. If test lamp lights and stays
ON, go to Test Lamp Stays ON procedure.
TEST LAMP STAYS ON
There is either a short circuit or a fault in an elec-
tronic module. Two fuses in the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) feed the modules with ignition off
draw.
²Interior lamps fuse (10 Amp) (IOD) PDC
²Fuel pump fuse (20 Amp) in PDC.
(1) Remove interior lamp and fuel pump fuses. By
removing these fuses all ignition off draw from thevehicle electronics will be disconnected. The test
lamp should go out. If test lamp goes out go to Step
2. If test lamp does not go out there is a current
draw or short circuit. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Dia-
grams.
(2) Install the fuel pump fuse. If test lamp lights,
there is a current draw or short circuit in the A14
wiring circuit feed.
(a) Disconnect Powertrain Control Module.
(b) If test lamp goes out, replace Powertrain
Control Module.
(c) If test lamp does not go out, there is a cur-
rent draw or short circuit in the A14 circuit feed.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
(3) Install the interior lamp fuse. If test lamp
lights, there is a current draw or short circuit in the
M01 circuit. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams. If
test lamp stays out, go to Step 4.
(4) Use a multi-meter that has at least a range of
200 milliamperes. Install meter between the battery
negative cable and battery negative post (Fig. 7).
Carefully remove the test lamp without disconnecting
the meter. After all modules time-out the total vehi-
cle IOD should be less than 10 milliamperes. If igni-
tion off draw is more than 10 milliamperes go to Step
5.
(5) Remove both fuses from the Power Distribution
Center:
²Fuel pump fuse (20 Amp)
²Interior lamps fuse (10 Amp)
(6) If there is any reading with fuses removed
there is a current draw or short circuit in the wiring.
Fig. 5 Disconnect and Isolate Battery Negative
Cable
1 ± NEGATIVE CABLE
2 ± NEGATIVE BATTERY POST
Fig. 6 Ignition OFF (IOD) Test
1 ± NEGATIVE TERMINAL
2 ± 12 VOLT TEST LIGHT
3 ± PDC
4 ± AIR CLEANER HOUSING
5 ± NEGATIVE BATTERY POST
PLBATTERY 8A - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 217 of 1285

²It passes the 15 second load test. Refer to Bat-
tery Load Test.
²The built in test indicator dot is GREEN (Fig.
2).
NOTE: The battery cannot be refilled with water, it
must be replaced.
WARNING: DO NOT CHARGE A BATTERY THAT
HAS EXCESSIVELY LOW ELECTROLYTE LEVEL.
BATTERY MAY SPARK INTERNALLY AND
EXPLODE. EXPLOSIVE GASES FORM OVER THE
BATTERY. DO NOT SMOKE, USE FLAME, OR CRE-
ATE SPARKS NEAR BATTERY. DO NOT ASSIST
BOOST OR CHARGE A FROZEN BATTERY. BAT-
TERY CASING MAY FRACTURE. BATTERY ACID IS
POISON, AND MAY CAUSE SEVERE BURNS. BAT-
TERIES CONTAIN SULFURIC ACID. AVOID CON-
TACT WITH SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING. IN THE
EVENT OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER AND
CALL PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT OF
REACH OF CHILDREN.
CAUTION: Disconnect the battery NEGATIVE cable
first, before charging battery to avoid damage to
electrical systems. Lift the red battery boot cover
from the positive cable clamp. Do not exceed 16.0
volts while charging battery. Refer to the instruc-
tions supplied with charging equipment
Battery electrolyte may bubble inside of battery
case while being charged properly. If the electrolyte
boils violently, or is discharged from the vent holes
while charging, immediately reduce charging rate or
turn off charger. Evaluate battery condition. Battery
damage may occur if charging is excessive.
Some battery chargers are equipped with polarity
sensing devices to protect the charger or battery from
being damaged if improperly connected. If the bat-
tery state of charge is too low for the polarity sensor
to detect, the sensor must be bypassed for charger to
operate. Refer to operating instructions provided
with battery charger being used.
CAUTION: Charge battery until test indicator
appears green. Do not overcharge.
It may be necessary to jiggle the battery or vehicle
to bring the green dot in the test indicator into view.
After the battery has been charged to 12.4 volts or
greater, perform a load test to determine cranking
capacity. Refer to Battery Load Test in this Group. If
the battery passes the load test, the battery is OK to
use. If battery will not pass the load test, it must be
replaced. Properly clean and inspect battery holddowns, tray, terminals, cables, posts, and top before
completing service.
CHARGING COMPLETELY DISCHARGED
BATTERY
The following procedure should be used to recharge
a completely discharged battery. Unless procedure is
properly followed, a good battery may be needlessly
replaced. Refer to Battery Charging Rate Table for
proper charging time.
(1) Measure the voltage at battery posts with a
voltmeter accurate to 1/10 volt (Fig. 12). If below 10
volts, charge current will be low, and it could take
some time before it accepts a current in excess of a
few milliamperes. Such low current may not be
detectable on amp meters built into many chargers.
(2) Connect charger leads. Some chargers feature
polarity protection circuitry that prevents operation
unless charger is connected to battery posts correctly.
A completely discharged battery may not have
enough voltage to activate this circuitry. This may
happen even though the leads are connected properly.
(3) Battery chargers vary in the amount of voltage
and current they provide. For the time required for
the battery to accept measurable charger current at
various voltages, refer to the Battery Charging Rate
table. If charge current is still not measurable after
charging times, the battery should be replaced. If
charge current is measurable during charging time,
the battery may be good, and charging should be
completed in the normal manner.
BATTERY CHARGING RATE
Voltage Hours
16.0 volts maximum up to 4 hours
14.0 to 15.9 volts up to 8 hours
13.9 volts or less up to 16 hours
Fig. 12 Voltmeter Accurate to 1/10 Volt (Connected)
8A - 8 BATTERYPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)