2000 DODGE NEON fuel cap
[x] Cancel search: fuel capPage 3 of 1285

LUBRICANTS AND GREASES
Lubricating grease is rated for quality and usage
by the NLGI. All approved products have the NLGI
symbol (Fig. 2) on the label. At the bottom NLGI
symbol is the usage and quality identification letters.
Wheel bearing lubricant is identified by the letter
ªGº. Chassis lubricant is identified by the latter ªLº.
The letter following the usage letter indicates the
quality of the lubricant. The following symbols indi-
cate the highest quality.
INTERNATIONAL SYMBOLS
DaimlerChrysler Corporation uses international
symbols to identify engine compartment lubricant
and fluid check and fill locations (Fig. 3).
FLUID CHECK/FILL POINTS AND LUBRICATION
LOCATIONS
The fluid check/fill points and lubrication locations
are located in each applicable Sections.
LUBRICATION POINT LOCATIONS
Lubrication point locations are located in each
applicable Sections.
SPECIFICATIONS
FLUID CAPACITIES
Fuel Tank (approximate)....47.5 Liter (12.5 gal.)
Engine Oil ± With Filter....... 4.3Liter (4.5 qts.)
Engine Oil ± Without Filter.... 3.8Liter (4.0 qts.)
Cooling System ± Includes Heater & Coolant
Recovery Bottle*........... 6.2Liter (6.5 qts.)
Automatic Transaxle ± Estimated Service
Fill........................ 3.8L(4.0 qts.)
Automatic Transaxle ± 31 TH ± Overhaul Fill
Capacity with Torque Converter Empty . . . 8.4 L
(8.9. qts.)
Manual Transaxle ± NV T350........ 1.9to2.2L
(4.0 to 4.6 pts.)
*Capacities include 1 qt. for coolant reserve tank.
Fig. 2 NLGI Symbol
1 ± WHEEL BEARINGS
2 ± CHASSIS LUBRICATION
3 ± CHASSIS AND WHEEL BEARINGS
Fig. 3 International Symbols
0 - 2 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 187 of 1285

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
HIGH OR ENGINE COOLANT
WARNING LAMP ILLUMINATES.
COOLANT MAY OR MAY NOT BE
LOST FROM SYSTEM. (CONT.)6. Poor seals at radiator cap. 6. (a) Check condition of cap and
cap seals. Refer to Radiator cap
Inspection. Replace cap if
necessary.
(b) Check condition of filler neck. If
neck is bent or damaged, replace
neck.
7. Coolant level low in radiator, but
not in coolant recovery/reserve
container. This indicates the
radiator is not drawing coolant from
the coolant recovery/reserve
container as the engine cools. As
the engine cools, a vacuum is
formed inside the cooling system. If
the radiator cap seals are defective,
or the cooling system has a leak, a
vacuum cannot be formed.7. (a) Check condition of radiator
cap and cap seals. Replace cap if
necessary.
(b) Check condition of filler neck.
Replace if damaged.
(c) Check condition of hose from
filler neck to coolant container. It
should be tight at both ends without
any kinks or tears. Replace hose as
necessary.
(d) Check coolant recovery/reserve
container and hose for blockage.
Repair as necessary.
8. Freeze point of coolant not
correct. Mixture ratio may be too
rich.8. Check coolant concentration.
Refer to Coolant Concentration
Testing in this section. Adjust
glycol-to-water ration as required.
9. Coolant not flowing through
system.9. Check for coolant flow at filler
neck with some coolant removed,
engine warm, and thermostat open.
Coolant should be observed flowing
through filler neck. If flow is not
observed, determine reason for lack
of flow and repair as necessary.
10. Radiator or A/C condenser fins
are dirty or clogged.10. Clean obstruction from fins.
11. Radiator core is plugged or
corroded.11. Replace or re-core radiator.
12. Fuel or ignition system
problems.12. Refer to Fuel and Ignition
System groups for diagnosis. Also
refer to the appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedure manual.
13. Dragging Brakes. 13. Inspect brake system and repair
as necessary. Refer to Group 5,
Brakes for diagnosis.
14 Bug screen or other aftermarket
accessory is being used causing
reduced air flow.14. Remove bug screen or
accessory.
15. Thermostat partially or
completely closed. This is more
prevalent on high mileage vehicles.15. Check thermostat operation and
replace as necessary. Refer to
thermostat in this section for
procedure.
7 - 8 COOLING SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 215 of 1285

Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams. If OK go to
Step 7.
(7) Install interior lamp fuse. After installing fuse,
the current can reach 250 milliamperes. After time-
out the reading should not exceed 8 milliamperes. If
NOT OK go to Step 8. If OK go to Step 9.
²Ignition key lamp system
²Radio
²Remote keyless entry module, if equipped
(8) Disconnect radio and ignition switch key lamp
one component at time, to see if any component is at
fault. If the high reading is not eliminated there is a
short circuit in the wiring. Refer to Group 8W, Wir-
ing Diagrams.
CAUTION: Always disconnect the meter before
opening a door.
(9) Remove interior lamps fuse and install the fuel
pump fuse. The reading should be between 1-3 milli-
amperes. If reading is higher than 3 milliamperes:
(a) Disconnect Powertrain Control Module.
(b) If reading drops to zero, replace Powertrain
Control Module.
(c) If reading remains the same there is a cur-
rent draw or short circuit in the A14 circuit. Refer
to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
BATTERY LOAD TEST
A fully charged battery must have cranking capac-
ity, to provide the starter motor and ignition system
enough power to start the engine over a broad range
of ambient temperatures. A battery load test will ver-
ify the actual cranking capability of the battery.WARNING: IF BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF FREEZ-
ING, LEAKING, LOOSE POSTS, OR EXCESSIVELY
LOW ELECTROLYTE LEVEL, DO NOT TEST. ACID
BURNS OR AN EXPLOSIVE CONDITION MAY
RESULT.
(1) Remove both battery cables, negative cable
first. The battery top, cables and posts should be
clean. If green dot is not visible in indicator, charge
the battery. Refer to Battery Charging Procedures in
this group.
(2) Connect a Volt/Ammeter/Load tester to the bat-
tery posts (Fig. 8). Rotate the load control knob of the
Carbon pile rheostat to apply a 300 amp load. Apply
this load for 15 seconds to remove the surface charge
from the battery, and return the control knob to off
(Fig. 9).
(3) Allow the battery to stabilize for 2 minutes,
and then verify open circuit voltage.
Fig. 7 Milliampere Meter Connection
1 ± NEGATIVE TERMINAL
2 ± MILLIAMPERE METER
3 ± PDC
4 ± AIR CLEANER HOUSING
5 ± NEGATIVE BATTERY POST
Fig. 8 Volt-Ammeter Load Tester Connections -
Typical
1 ± INDUCTION AMPMETER CLAMP
2 ± NEGATIVE CLAMP
3 ± POSITIVE CLAMP
Fig. 9 Remove Surface Charge From Battery
8A - 6 BATTERYPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 729 of 1285

any fluid that may possibly be in the cylinder under
pressure.
(4) With all spark plugs removed, rotate engine
crankshaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(5) Identify the fluid in the cylinder(s) (i.e., cool-
ant, fuel, oil or other).
(6) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders. Inspect engine for damage (i.e., connecting
rods, pistons, valves, etc.).
(7) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from re-occurring.
CAUTION: Squirt approximately one teaspoon of oil
into the cylinders, rotate engine to lubricate the cyl-
inder walls to prevent damage on restart.
(8) Install new spark plugs.
(9) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter.
(10) Fill engine with specified amount of approved
oil and install new oil filter.
(11) Connect negative battery cable.
(12) Start engine and check for any leaks.
CHECKING ENGINE OIL LEVEL
The best time to check engine oil level is after it
has sat overnight, or if the engine has been running,allow the engine to be shut off for at least 5 minutes
before checking oil level.
Checking the oil while the vehicle is on level
ground will improve the accuracy of the oil level
reading. Remove dipstick (Fig. 7) and observe oil
level. Add oil only when the level is at or below the
ADD mark (Fig. 8).
Fig. 7 Dipstick and Engine Oil Fill Locations
1 ± ENGINE OIL FILL
2 ± ENGINE COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER3 ± ENGINE OIL DIPSTICK
4 ± COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE CAP
Fig. 8 Oil Level
1 ± ENGINE OIL LEVEL DIPSTICK
9 - 6 ENGINEPL
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 730 of 1285

ENGINE OIL SERVICE
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOVERN-
MENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLECTION
CENTER IN YOUR AREA.
ENGINE OIL SPECIFICATION
CAUTION: Do not use non-detergent or straight
mineral oil when adding or changing crankcase
lubricant. Engine failure can result.
API SERVICE GRADE CERTIFIED
Use an engine oil that is API Service Grade Certi-
fied. MOPARtprovides engine oils that conforms to
this service grade.
SAE VISCOSITY
An SAE viscosity grade is used to specify the vis-
cosity of engine oil. Use only, engine oils with multi-
ple viscosities such as 5W-30 or 10W-30. These are
specified with a dual SAE viscosity grade which indi-
cates the cold-to-hot temperature viscosity range.
SAE 5W-30 engine oil is preferred. Select an engine
oil that is best suited to your particular temperature
range and variation (Fig. 9).
ENERGY CONSERVING OIL
An Energy Conserving type oil is recommended for
gasoline engines. The designation of ENERGY CON-
SERVING is located on the label of the engine oil
container.
CONTAINER IDENTIFICATION
Standard engine oil identification notations have
been adopted to aid in the proper selection of engine
oil. The identifying notations are located on the label
of engine oil plastic bottles and the top of engine oil
cans (Fig. 10).
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Group 0, Lubrication and Mainte-
nance.TO CHANGE ENGINE OIL
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
Hoisting and Jacking Recommendations.
(3) Remove oil fill cap.
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug and
gasket if damaged.
(6) Install drain plug in crankcase.
(7) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type and amount of engine oil described in this sec-
tion.
(8) Install oil fill cap.
(9) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(10) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
Fig. 9 Temperature/Engine Oil Viscosity
Fig. 10 Engine Oil Container Standard Notations
PLENGINE 9 - 7
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 732 of 1285

should not be disassembled to determine the
cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
(11) Clean or replace spark plugs as necessary and
adjust gap as specified in Group 8, Electrical.
Tighten to specifications.
(12) Test resistance of spark plug cables. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System Secondary Cir-
cuit Inspection.
(13) Test coil output voltage, primary and second-
ary resistance. Replace parts as necessary. Refer to
Group 8, Electrical Ignition System.
(14) Check fuel pump pressure at idle and differ-
ent RPM ranges. Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for
Specifications.
(15) The air filter elements should be replaced as
specified in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance.
(16) Inspect crankcase ventilation system as out
lined in Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance. For
emission controls see Group 25, Emission Controls
for service procedures.
(17) Inspect and adjust accessory belt drives refer-
ring to Group 7, Cooling System, Accessory Drive
Belts for proper adjustments.
(18) Road test vehicle as a final test.
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379kPa (200 psi) maximum, with 552 kPa (80 psi) rec-
ommended.
Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage per cylinder.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
LASH ADJUSTER (TAPPET) NOISE DIAGNOSIS
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) During this time, turn engine off and let set for
a few minutes before restarting. Repeat this several
times after engine has reached normal operating
temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor pressed into the vertical oil
passage to the cylinder head is plugged with debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Faulty lash adjuster.
a. Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head. Depress part of rocker
arm over adjuster. Normal adjusters should feel very
firm. Spongy adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
b. Remove suspected rocker arms (sohc) or lash
adjuster (dohc) and replace.
ENGINE OIL LEAK INSPECTION
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
PLENGINE 9 - 9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 799 of 1285
exhaust manifold, the other is a unique under-floor
catalytic converter (Fig. 3).
The three-way catalytic converter simultaneously
converts three exhaust emissions into harmless
gases. Specifically, HC and CO emissions are con-
verted into water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) are converted into elemen-
tal Nitrogen (N) and water. The three-way catalyst is
most efficient in converting HC, CO and NOx at the
stoichiometric air fuel ratio of 14.7:1.
The oxygen content in a catalyst is important for
efficient conversion of exhaust gases. When a high
oxygen content (lean) air/fuel ratio is present for an
extended period, oxygen content in a catalyst can
reach a maximum. When a rich air/fuel ratio is
present for an extended period, the oxygen content in
the catalyst can become totally depleted. When this
occurs, the catalyst fails to convert the gases. This is
known as catalyst ªpunch through.9
Catalyst operation is dependent on its ability to
store and release the oxygen needed to complete the
emissions-reducing chemical reactions. As a catalyst
deteriorates, its ability to store oxygen is reduced.
Since the catalyst's ability to store oxygen is some-
what related to proper operation, oxygen storage can
be used as an indicator of catalyst performance.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Pro-
cedure for diagnosis of a catalyst related Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC).
The combustion reaction caused by the catalyst
releases additional heat in the exhaust system, caus-ing temperature increases in the area of the reactor
under severe operating conditions. Such conditions
can exist when the engine misfires or otherwise does
not operate at peak efficiency.Do notremove spark
plug wires from plugs or by any other means short
out cylinders, if exhaust system is equipped with a
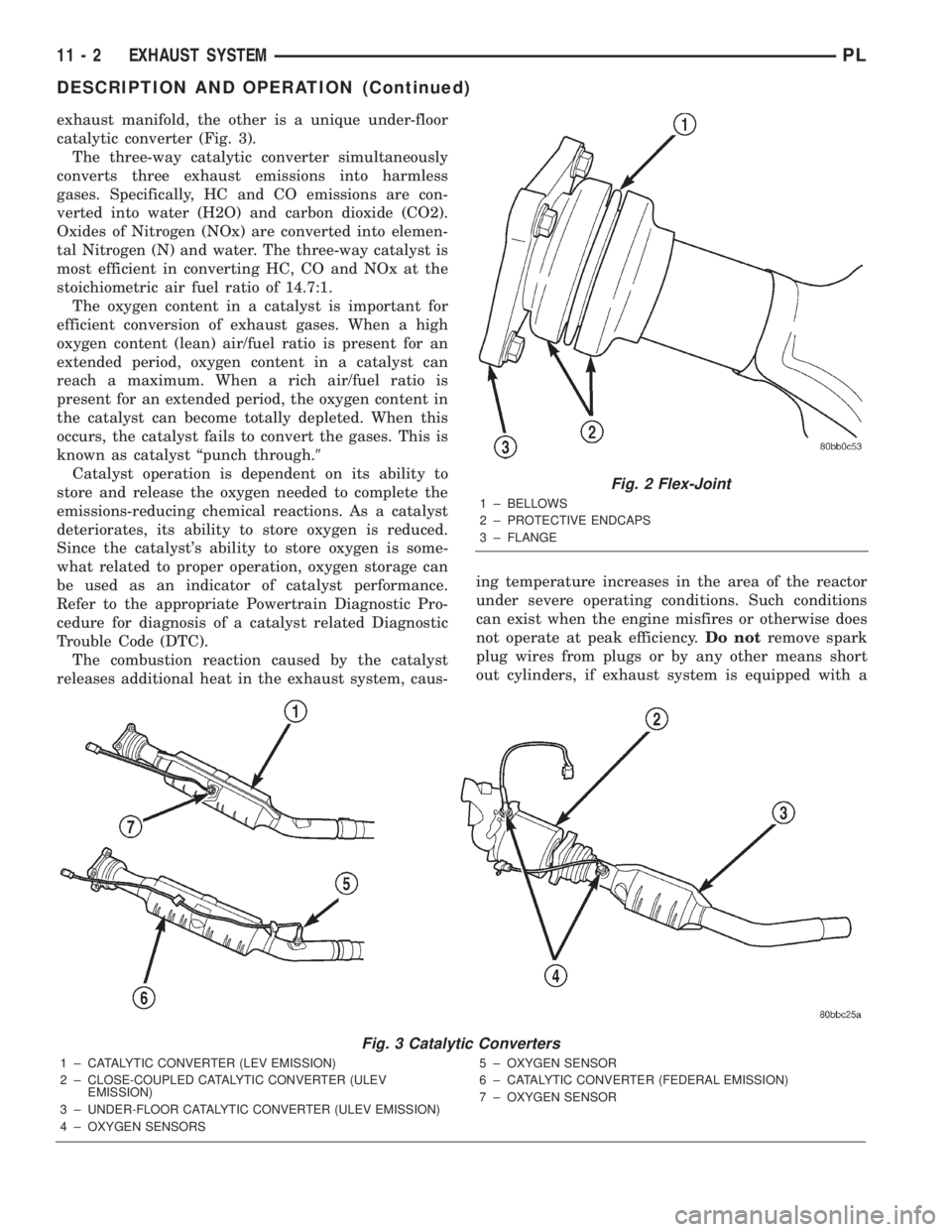
Fig. 2 Flex-Joint
1 ± BELLOWS
2 ± PROTECTIVE ENDCAPS
3 ± FLANGE
Fig. 3 Catalytic Converters
1 ± CATALYTIC CONVERTER (LEV EMISSION)
2 ± CLOSE-COUPLED CATALYTIC CONVERTER (ULEV
EMISSION)
3 ± UNDER-FLOOR CATALYTIC CONVERTER (ULEV EMISSION)
4 ± OXYGEN SENSORS5 ± OXYGEN SENSOR
6 ± CATALYTIC CONVERTER (FEDERAL EMISSION)
7 ± OXYGEN SENSOR
11 - 2 EXHAUST SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 822 of 1285

FUEL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM.................... 1FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM.................. 21
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FUEL REQUIREMENTS.....................1
GASOLINE/OXYGENATE BLENDS.............2
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM...................3
FUEL PUMP MODULE......................3
ELECTRIC FUEL PUMP.....................4
FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT................4
FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR....4
FUEL TANK..............................4
FUEL RAIL...............................4
FUEL INJECTORS.........................5
PRESSURE-VACUUM FILLER CAP............5
ONBOARD REFUELING VAPOR RECOVERY....6
CONTROL VALVE/PRESSURE RELIEF.........6
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS.................6
ROLLOVER VALVES.......................7
FUEL TUBES/LINES/HOSES AND CLAMPS......8
SERVICE PROCEDURES
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE...........................8INJECTOR CONNECTOR....................8
DRAINING FUEL TANK.....................9
HOSES AND CLAMPS......................9
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS.................9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAY............12
FUEL PUMP RELAY.......................12
FUEL PUMP MODULE.....................12
FUEL FILTER / PRESSURE REGULATOR......13
FUEL PUMP INLET STRAINER..............14
FUEL LEVEL SENSOR.....................14
FUEL INJECTORS........................15
FUEL TANK.............................16
FUEL FILLER NECK.......................17
ACCELERATOR PEDAL....................18
THROTTLE CABLE.......................19
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE...............................20
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FUEL REQUIREMENTS
OPERATION
Your engine is designed to meet all emissions reg-
ulations and provide excellent fuel economy and per-
formance when using high quality unleaded gasoline
having an octane rating of 87. The use of premium
gasoline is not recommended. The use of premium
gasoline will provide no benefit over high quality reg-
ular gasoline, and in some circumstances may result
in poorer performance.
Light spark knock at low engine speeds is not
harmful to your engine. However, continued heavyspark knock at high speeds can cause damage and
immediate service is required. Engine damage result-
ing from operation with a heavy spark knock may
not be covered by the new vehicle warranty.
Poor quality gasoline can cause problems such as
hard starting, stalling and hesitations. If you experi-
ence these symptoms, try another brand of gasoline
before considering service for the vehicle.
The American Automobile Manufacturers Associa-
tion, AAMA, has issued gasoline specifications to
define the minimum fuel properties necessary to
deliver enhanced performance and durability for your
vehicle. DaimlerChrysler Corporation recommends
the use of gasoline that meet the AAMA specifica-
tions if they are available.
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 1