1999 SUBARU LEGACY light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 113 of 1456
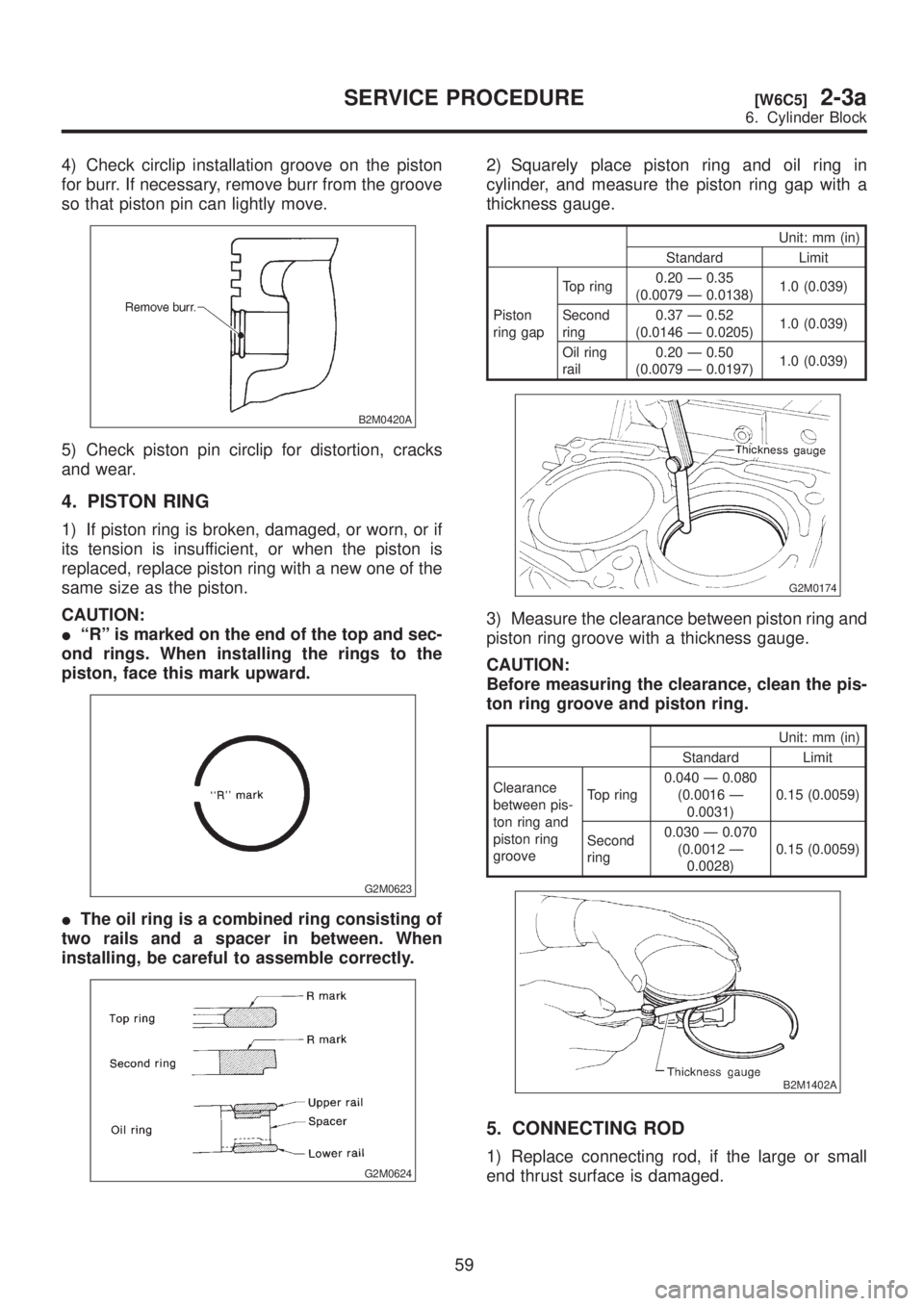
4) Check circlip installation groove on the piston
for burr. If necessary, remove burr from the groove
so that piston pin can lightly move.
B2M0420A
5) Check piston pin circlip for distortion, cracks
and wear.
4. PISTON RING
1) If piston ring is broken, damaged, or worn, or if
its tension is insufficient, or when the piston is
replaced, replace piston ring with a new one of the
same size as the piston.
CAUTION:
IªRº is marked on the end of the top and sec-
ond rings. When installing the rings to the
piston, face this mark upward.
G2M0623
IThe oil ring is a combined ring consisting of
two rails and a spacer in between. When
installing, be careful to assemble correctly.
G2M0624
2) Squarely place piston ring and oil ring in
cylinder, and measure the piston ring gap with a
thickness gauge.
Unit: mm (in)
Standard Limit
Piston
ring gapTop ring0.20 Ð 0.35
(0.0079 Ð 0.0138)1.0 (0.039)
Second
ring0.37 Ð 0.52
(0.0146 Ð 0.0205)1.0 (0.039)
Oil ring
rail0.20 Ð 0.50
(0.0079 Ð 0.0197)1.0 (0.039)
G2M0174
3) Measure the clearance between piston ring and
piston ring groove with a thickness gauge.
CAUTION:
Before measuring the clearance, clean the pis-
ton ring groove and piston ring.
Unit: mm (in)
Standard Limit
Clearance
between pis-
ton ring and
piston ring
grooveTop ring0.040 Ð 0.080
(0.0016 Ð
0.0031)0.15 (0.0059)
Second
ring0.030 Ð 0.070
(0.0012 Ð
0.0028)0.15 (0.0059)
B2M1402A
5. CONNECTING ROD
1) Replace connecting rod, if the large or small
end thrust surface is damaged.
59
[W6C5]2-3aSERVICE PROCEDURE
6. Cylinder Block
Page 132 of 1456

2. Engine Noise
Type of sound Condition Possible cause
Regular clicking soundSound increases as engine
speed increases.IValve mechanism is defective.
IIncorrect valve clearance
IWorn valve rocker
IWorn camshaft
IBroken valve spring
Heavy and dull clankOil pressure is low.IWorn crankshaft main bearing
IWorn connecting rod bearing (big end)
Oil pressure is normal.ILoose flywheel mounting bolts
IDamaged engine mounting
High-pitched clank
(Spark knock)Sound is noticeable when
accelerating with an overload.IIgnition timing advanced
IAccumulation of carbon inside combustion chamber
IWrong spark plug
IImproper gasoline
Clank when engine speed is
medium (1,000 to 2,000 rpm)Sound is reduced when fuel
injector connector of noisy cyl-
inder is disconnected.
(NOTE*)IWorn crankshaft main bearing
IWorn bearing at crankshaft end of connecting rod
Knocking sound when engine
is operating under idling speed
and engine is warmSound is reduced when fuel
injector connector of noisy cyl-
inder is disconnected.
(NOTE*)IWorn cylinder liner and piston ring
IBroken or stuck piston ring
IWorn piston pin and hole at piston end of connecting rod
Sound is not reduced if each
fuel injector connector is dis-
connected in turn. (NOTE*)IUnusually worn valve lifter
IWorn cam gear
IWorn camshaft journal bore in crankcase
Squeaky sound ÐIInsufficient generator lubrication
Rubbing sound ÐIDefective generator brush and rotor contact
Gear scream when starting
engineÐIDefective ignition starter switch
IWorn gear and starter pinion
Sound like polishing glass with
a dry clothÐILoose drive belt
IDefective engine coolant pump shaft
Hissing sound ÐILoss of compression
IAir leakage in air intake system, hoses, connections or
manifolds
Timing belt noise ÐILoose timing belt
IBelt contacting case/adjacent part
Valve tappet noise ÐIIncorrect valve clearance
NOTE*:
When disconnecting fuel injector connector, Malfunction Indicator Light (CHECK ENGINE light) illuminates and trouble code is
stored in ECM memory.
Therefore, carry out the CLEAR MEMORY MODE
necting fuel injector connector.
78
2-3a[K200]DIAGNOSTICS
2. Engine Noise
Page 150 of 1456

1) Remove left-hand intake camshaft sprocket.
2) Remove left-hand exhaust camshaft sprocket.
3) Remove right-hand intake camshaft sprocket.
4) Remove right-hand exhaust camshaft sprocket.
ST 499207300 CAMSHAFT SPROCKET
WRENCH
S2M0413A
5) Remove crankshaft sprocket.
S2M0414
6) Remove tensioner bracket.
H2M2407
7) Remove left-hand belt cover No. 2.
S2M0415
8) Remove right-hand belt cover No. 2.
B2M0738
B: INSPECTION
1. TIMING BELT
1) Check timing belt teeth for breaks, cracks and
wear. If any fault is found, replace belt.
2) Check the condition of back side of belt; if any
crack is found, replace belt.
CAUTION:
IBe careful not to let oil, grease or coolant
contact the belt. Remove quickly and thor-
oughly if this happens.
IDo not bend the belt sharply.
Bending radius: h
60 mm (2.36 in) or more
G2M0115
2. AUTOMATIC BELT TENSION
ADJUSTER
1) Visually check oil seals for leaks, and rod ends
for abnormal wear or scratches. If necessary,
replace automatic belt tension adjuster assembly.
CAUTION:
Slight traces of oil at rod's oil seal does not
indicate a problem.
2) Check that the adjuster rod does not move
when a pressure of 294 N (30 kg, 66 lb) is applied
to it. This is to check adjuster rod stiffness.
3) If the adjuster rod is not stiff and moves freely
when applying 294 N (30 kg, 66 lb), check it using
the following procedures:
19
[W2B2]2-3bSERVICE PROCEDURE
2. Timing Belt
Page 165 of 1456

1) Camshaft installation
Apply engine oil to cylinder head at camshaft bear-
ing location before installing camshaft. Install cam-
shaft so that rocker arm is close to or in contact
with ªbase circleº of cam lobe.
CAUTION:
IWhen camshafts are positioned as shown in
figure, camshafts need to be rotated at a mini-
mum to align with timing belt during installa-
tion.
IRight-hand camshaft need not be rotated
when set at position shown in figure.
Left-hand intake camshaft: Rotate 80É clock-
wise.
Left-hand exhaust camshaft: Rotate 45É
counter-clockwise.
B2M1200A
2) Camshaft cap installation
(1) Apply fluid packing sparingly to cap mating
surface.
CAUTION:
Do not apply fluid packing excessively. Failure
to do so may cause excess packing to come
out and flow toward oil seal, resulting in oil
leaks.
Fluid packing:
THREE BOND 1215 or equivalent
G2M0752
(2) Apply engine oil to cap bearing surface and
install cap on camshaft as shown by identifica-
tion mark.
(3) Gradually tighten cap in at least two stages
in alphabetical sequence shown in figure, and
then tighten to specified torque.
B2M1395B
(4) Similarly, tighten cap on exhaust side.
After tightening cap, ensure camshaft rotates
only slightly while holding it at ªbaseº circle.
34
2-3b[W3C1]SERVICE PROCEDURE
3. Camshaft
Page 171 of 1456

(5) Put new valve guide, coated with sufficient
oil, in cylinder, and insert ST1 into valve guide.
Press in until the valve guide upper end is flush
with the upper surface of ST2.
ST1 499767200 VALVE GUIDE REMOVER
ST2 498267700 VALVE GUIDE ADJUSTER
B2M1398A
(6) Check the valve guide protrusion.
Valve guide protrusion: L
12.0 Ð 12.4 mm (0.472 Ð 0.488 in)
(7) Ream the inside of valve guide with ST.
Gently rotate the reamer clockwise while press-
ing it lightly into valve guide, and return it also
rotating clockwise. After reaming, clean valve
guide to remove chips.
ST 499767400 VALVE GUIDE REAMER
CAUTION:
IApply engine oil to the reamer when ream-
ing.
IIf the inner surface of the valve guide is torn,
the edge of the reamer should be slightly
ground with an oil stone.
IIf the inner surface of the valve guide
becomes lustrous and the reamer does not
chips, use a new reamer or remedy the reamer.
(8) Recheck the contact condition between
valve and valve seat after replacing valve guide.
4. INTAKE AND EXHAUST VALVE
1) Inspect the flange and stem of valve, and
replace if damaged, worn, or deformed, or if ªHº is
less than the specified limit.
H:
Intake
Standard
1.2 mm (0.047 in)
Limit
0.8 mm (0.031 in)
Exhaust
Standard
1.5 mm (0.059 in)
Limit
0.8 mm (0.031 in))
Valve overall length:
Intake
105.9 mm (4.169 in)
Exhaust
106.2 mm (4.181 in)
G2M0153
2) Put a small amount of grinding compound on
the seat surface and lap the valve and seat sur-
face. Install a new intake valve oil seal after lap-
ping.
40
2-3b[W4C4]SERVICE PROCEDURE
4. Cylinder Head
Page 174 of 1456

1) Installation of valve spring and valve
(1) Coat stem of each valve with engine oil and
insert valve into valve guide.
CAUTION:
When inserting valve into valve guide, use spe-
cial care not to damage the oil seal lip.
(2) Set cylinder head on ST1.
(3) Install valve spring and retainer using ST2.
ST1 498267600 CYLINDER HEAD TABLE
ST2 499718000 VALVE SPRING REMOVER
CAUTION:
Be sure to install the valve springs with their
close-coiled end facing the seat on the cylinder
head.
B2M1221A
(4) Compress valve spring and fit valve spring
retainer key.
(5) After installing, tap valve spring retainers
lightly with wooden hammer for better seating.
2) Install valve lifter and valve shim.
43
[W4D0]2-3bSERVICE PROCEDURE
4. Cylinder Head
Page 189 of 1456
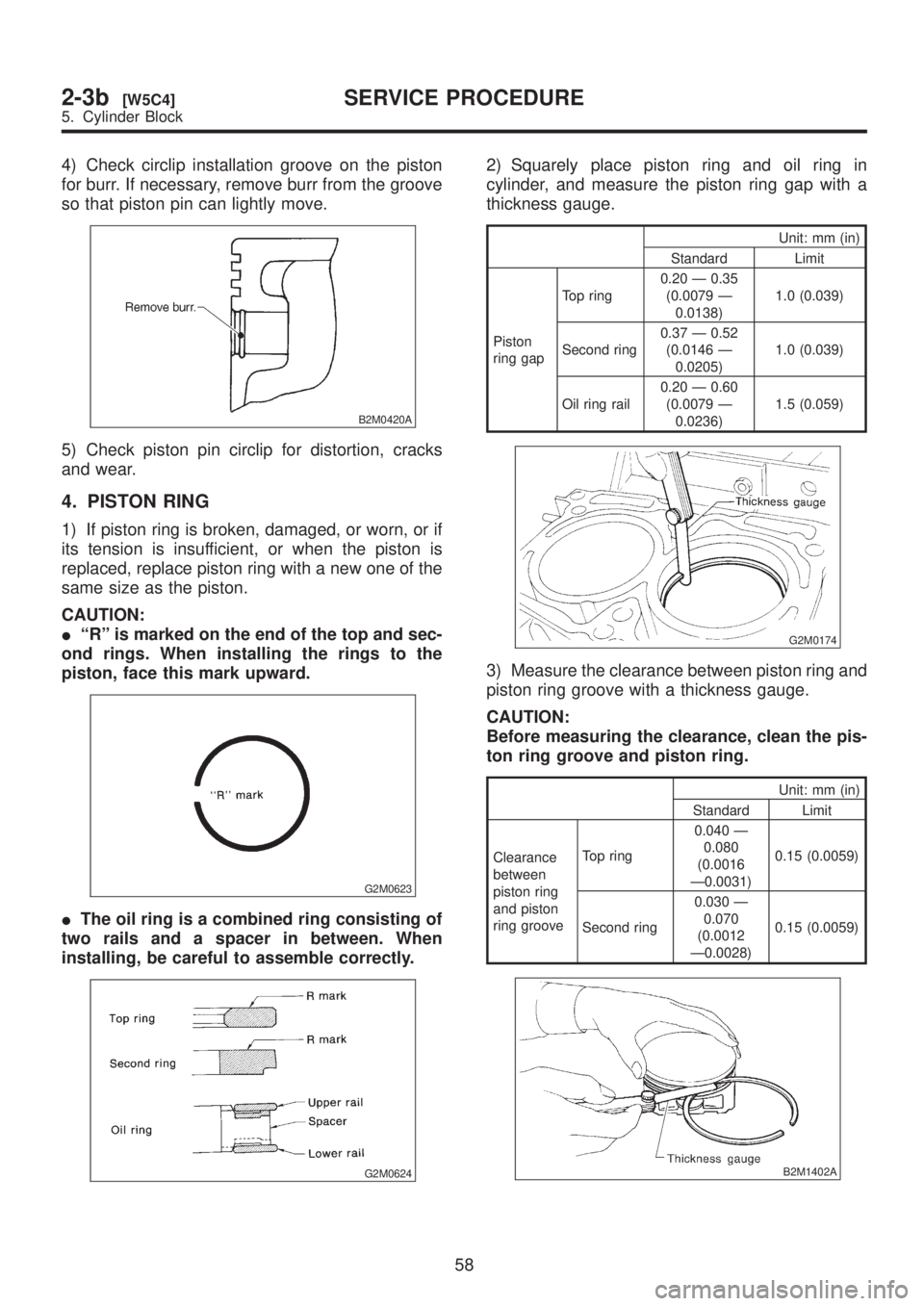
4) Check circlip installation groove on the piston
for burr. If necessary, remove burr from the groove
so that piston pin can lightly move.
B2M0420A
5) Check piston pin circlip for distortion, cracks
and wear.
4. PISTON RING
1) If piston ring is broken, damaged, or worn, or if
its tension is insufficient, or when the piston is
replaced, replace piston ring with a new one of the
same size as the piston.
CAUTION:
IªRº is marked on the end of the top and sec-
ond rings. When installing the rings to the
piston, face this mark upward.
G2M0623
IThe oil ring is a combined ring consisting of
two rails and a spacer in between. When
installing, be careful to assemble correctly.
G2M0624
2) Squarely place piston ring and oil ring in
cylinder, and measure the piston ring gap with a
thickness gauge.
Unit: mm (in)
Standard Limit
Piston
ring gapTop ring0.20 Ð 0.35
(0.0079 Ð
0.0138)1.0 (0.039)
Second ring0.37 Ð 0.52
(0.0146 Ð
0.0205)1.0 (0.039)
Oil ring rail0.20 Ð 0.60
(0.0079 Ð
0.0236)1.5 (0.059)
G2M0174
3) Measure the clearance between piston ring and
piston ring groove with a thickness gauge.
CAUTION:
Before measuring the clearance, clean the pis-
ton ring groove and piston ring.
Unit: mm (in)
Standard Limit
Clearance
between
piston ring
and piston
ring grooveTop ring0.040 Ð
0.080
(0.0016
Ð0.0031)0.15 (0.0059)
Second ring0.030 Ð
0.070
(0.0012
Ð0.0028)0.15 (0.0059)
B2M1402A
58
2-3b[W5C4]SERVICE PROCEDURE
5. Cylinder Block
Page 207 of 1456
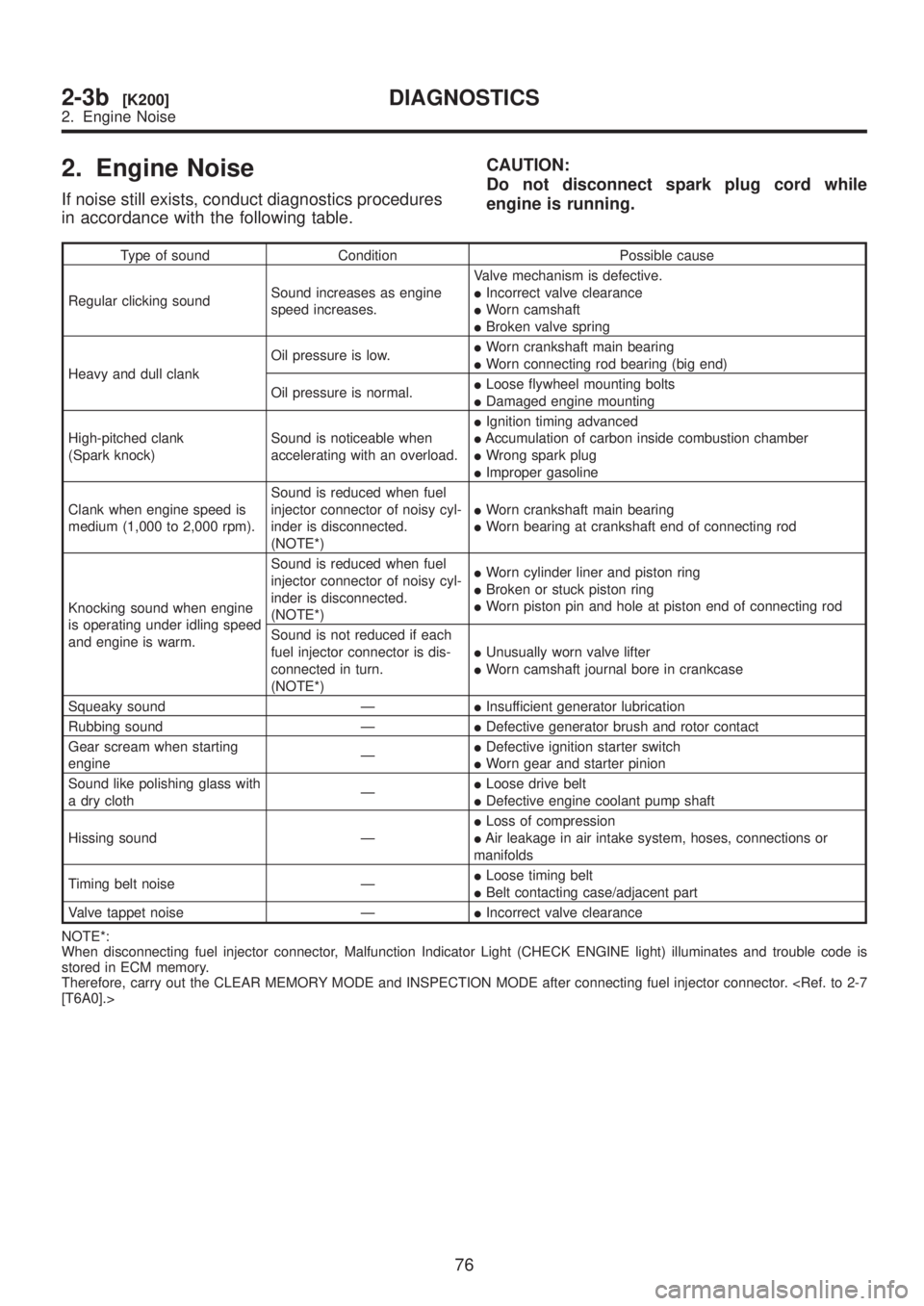
2. Engine Noise
If noise still exists, conduct diagnostics procedures
in accordance with the following table.CAUTION:
Do not disconnect spark plug cord while
engine is running.
Type of sound Condition Possible cause
Regular clicking soundSound increases as engine
speed increases.Valve mechanism is defective.
IIncorrect valve clearance
IWorn camshaft
IBroken valve spring
Heavy and dull clankOil pressure is low.IWorn crankshaft main bearing
IWorn connecting rod bearing (big end)
Oil pressure is normal.ILoose flywheel mounting bolts
IDamaged engine mounting
High-pitched clank
(Spark knock)Sound is noticeable when
accelerating with an overload.IIgnition timing advanced
IAccumulation of carbon inside combustion chamber
IWrong spark plug
IImproper gasoline
Clank when engine speed is
medium (1,000 to 2,000 rpm).Sound is reduced when fuel
injector connector of noisy cyl-
inder is disconnected.
(NOTE*)IWorn crankshaft main bearing
IWorn bearing at crankshaft end of connecting rod
Knocking sound when engine
is operating under idling speed
and engine is warm.Sound is reduced when fuel
injector connector of noisy cyl-
inder is disconnected.
(NOTE*)IWorn cylinder liner and piston ring
IBroken or stuck piston ring
IWorn piston pin and hole at piston end of connecting rod
Sound is not reduced if each
fuel injector connector is dis-
connected in turn.
(NOTE*)IUnusually worn valve lifter
IWorn camshaft journal bore in crankcase
Squeaky sound ÐIInsufficient generator lubrication
Rubbing sound ÐIDefective generator brush and rotor contact
Gear scream when starting
engineÐIDefective ignition starter switch
IWorn gear and starter pinion
Sound like polishing glass with
a dry clothÐILoose drive belt
IDefective engine coolant pump shaft
Hissing sound ÐILoss of compression
IAir leakage in air intake system, hoses, connections or
manifolds
Timing belt noise ÐILoose timing belt
IBelt contacting case/adjacent part
Valve tappet noise ÐIIncorrect valve clearance
NOTE*:
When disconnecting fuel injector connector, Malfunction Indicator Light (CHECK ENGINE light) illuminates and trouble code is
stored in ECM memory.
Therefore, carry out the CLEAR MEMORY MODE and INSPECTION MODE after connecting fuel injector connector.
76
2-3b[K200]DIAGNOSTICS
2. Engine Noise