1995 ACURA TL lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 936 of 1771

Description
The automatic transmission is a combination of a 3-element torque converter and a dual-shaft electronically controlled
automatic transmission which provides 4 speeds forward and 1 reverse. The entire unit is positioned in line with the engine.
Torque Converter, Gears and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine and stator, assembled in a single unit.
They are connected to the engine crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns.
Around the outside of the drive plate is a ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being started.
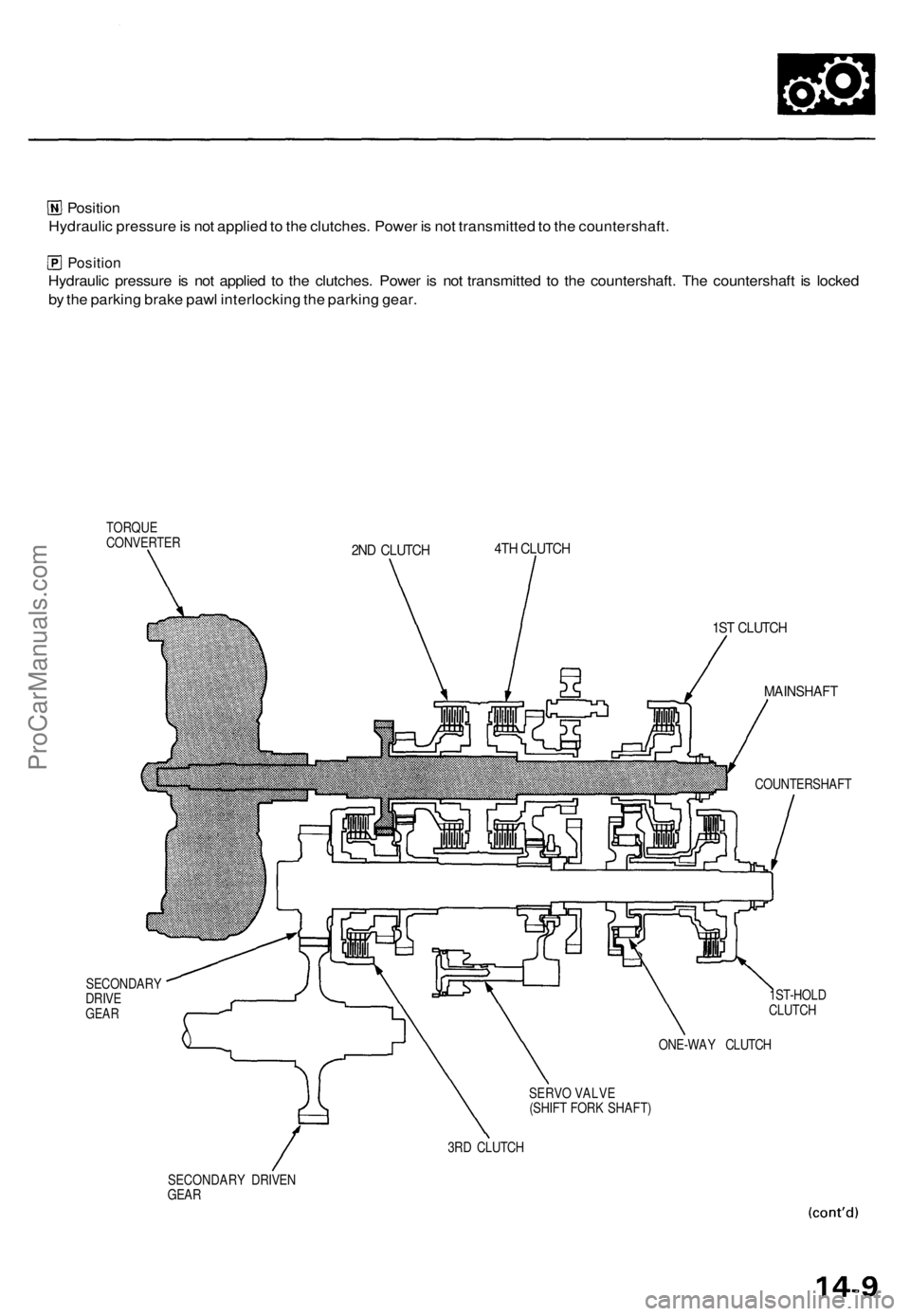
The entire torque converter assembly serves as a flywheel while transmitting power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has two parallel shafts: the mainshaft and the countershaft. The mainshaft is in line with the engine
crankshaft.
The mainshaft includes the 1st, 2nd and 4th clutches, and gears for 4th, 2nd, 1st and reverse (3rd gear is integral with the
mainshaft, while the reverse gear is integral with 4th gear).
The countershaft includes the 3rd, and 1st-hold clutches, and gears for 3rd, 4th, 1st, 2nd, reverse, and parking. The sec-
ondary drive gear is integrated with the countershaft.
The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the countershaft.
When certain combinations of gears in the transmission are engaged by clutches, power is transmitted from the mainshaft
to the countershaft to provide and positions.
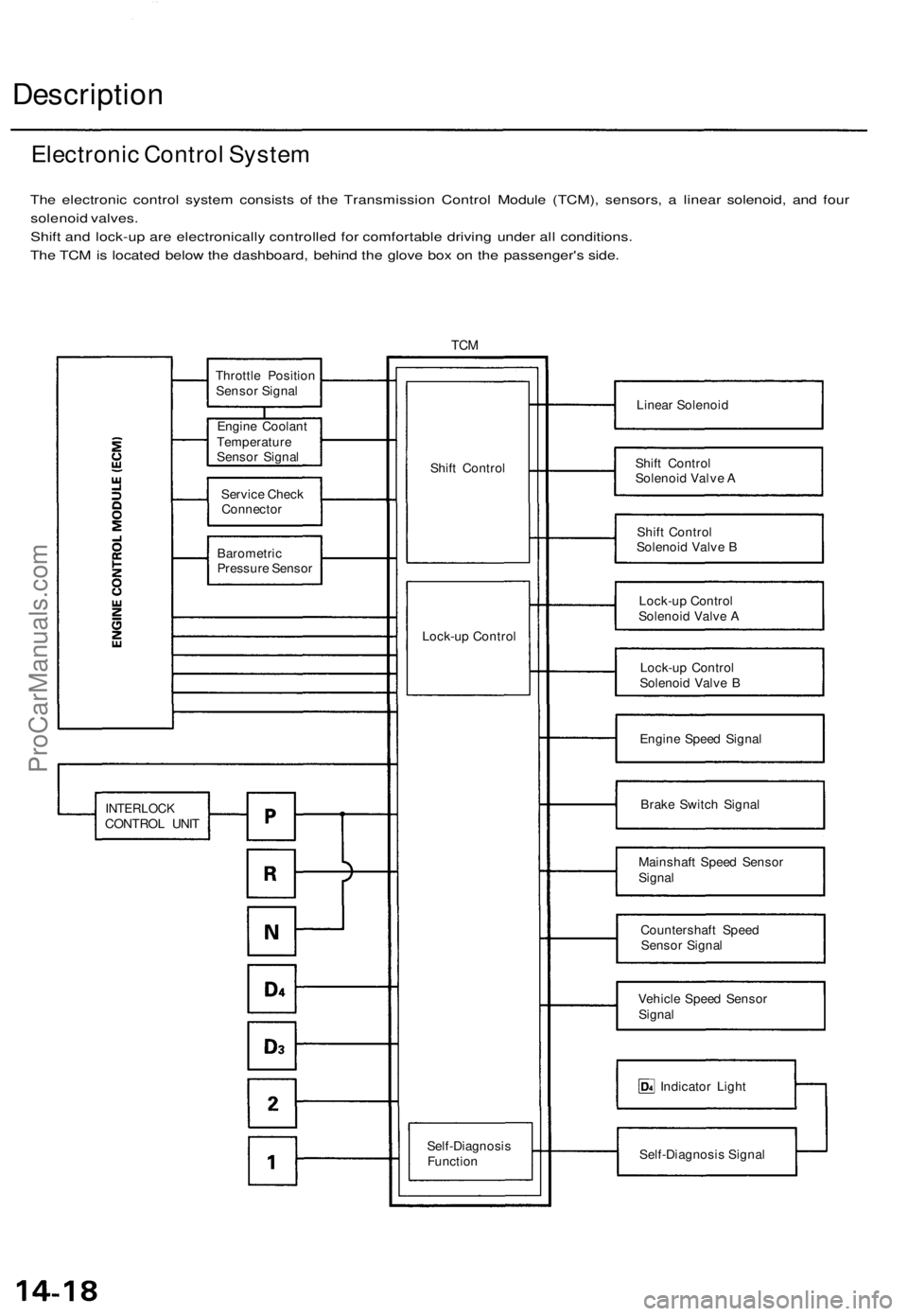
Electronic Control
The electronic control system consists of the Transmission Control Module (TCM), sensors, a linear solenoid and four
solenoid valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions.
The TCM is located below the dashboard, behind the glove box on the passenger's side.
Hydraulic Control
The lower valve body assembly includes the main valve body, the servo body and the shift control solenoid valves. They
are bolted on the lower part of the transmission housing.
Other valve bodies, the regulator valve body, the ATF pump body, the 2nd accumulator body, and the throttle valve body,
are bolted to the torque converter housing.
The main valve body contains the manual valve, the 1 - 2 shift valve, the 2 - 3 shift valve, the 3 - 4 shift valve, the 4th kick-
down valve, the 2 - 3 orifice control valve, the 3 - 4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve, the servo control valve,
and the main orifice control valve.
The servo body contains the servo valve, 3rd and 4th accumulator pistons.
The regulator valve body contains the regulator valve, the lock-up shift valve, and the cooler relief valve.
Fluid from the regulator passes through the manual valve to the various control valves.
The throttle valve body includes the throttle valve which is bolted onto the 2nd accumulator body. The 2nd accumulator
piston is assembled in the 2nd accumulator body.
The linear solenoid is joined with the throttle valve body.
The ATF pump body contains the modulator valve, the lock-up control valve, the lock-up timing valve, and the relief valve.
The torque converter check valve is located in the torque converter housing under the ATF pump body.
The 1st and 1st-hold accumulator pistons are assembled in the rear cover.
The clutches receive fluid from their respective feed pipes or internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the vehicle determines which shift control solenoid valve the TCM will acti-
vate. Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes
a line to one of the clutches, engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear.
Lock-up Mechanism
In position, in 2nd, 3rd and 4th, and in position in 3rd, pressurized fluid is drained from the back of the torque con-
verter through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this takes place,
the mainshaft rotates at the same speed as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the TCM optimizes the
timing of the lock-up mechanism. The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid
valves A and B, and throttle valve. When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, the modulator pressure changes.
The lock-up control solenoid valves A and B are mounted on the torque converter housing, and are controlled by the TCM.ProCarManuals.com
Page 937 of 1771
Description
(cont'd)
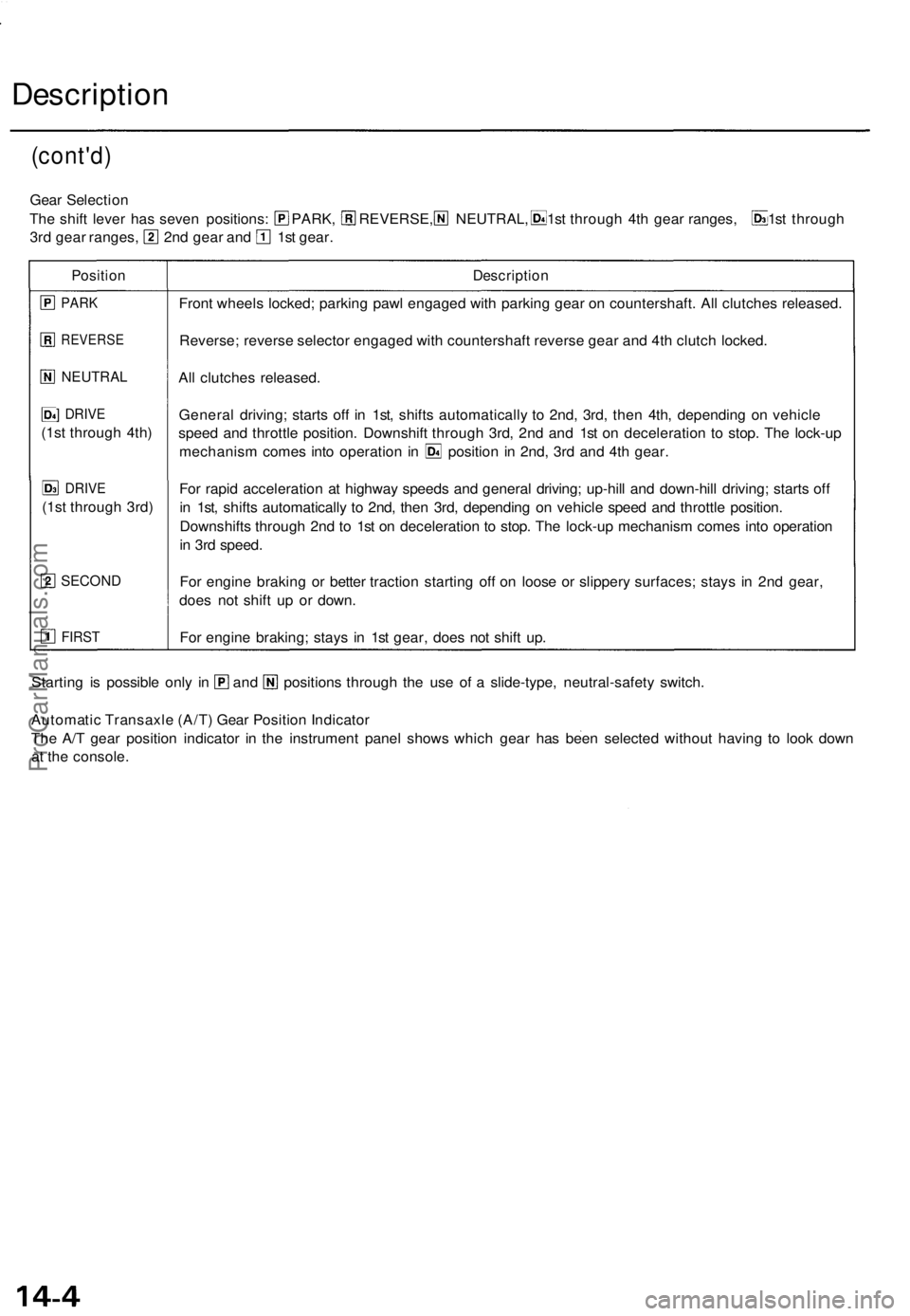
Gear Selectio n
The shif t leve r ha s seve n positions : PARK , REVERSE, NEUTRAL , 1st throug h 4t h gea r ranges , 1s t throug h
3rd gea r ranges , 2n d gea r an d 1s t gear .
Positio nDescriptio n
PARK
REVERS E
NEUTRAL
] DRIV E
(1st throug h 4th )
DRIV E
(1st throug h 3rd )
SECON D
FIRST
Front wheel s locked ; parkin g paw l engage d wit h parkin g gea r o n countershaft . Al l clutche s released .
Reverse ; revers e selecto r engage d wit h countershaf t revers e gea r an d 4t h clutc h locked .
Al l clutche s released .
Genera l driving ; start s of f i n 1st , shift s automaticall y t o 2nd , 3rd , the n 4th , dependin g o n vehicl e
spee d an d throttl e position . Downshif t throug h 3rd , 2n d an d 1s t o n deceleratio n t o stop . Th e lock-u p
mechanis m come s int o operatio n i n positio n i n 2nd , 3r d an d 4t h gear .
Fo r rapi d acceleratio n a t highwa y speed s an d genera l driving ; up-hil l an d down-hil l driving ; start s of f
i n 1st , shift s automaticall y t o 2nd , the n 3rd , dependin g o n vehicl e spee d an d throttl e position .
Downshift s throug h 2n d t o 1s t o n deceleratio n t o stop . Th e lock-u p mechanis m come s int o operatio n
i n 3r d speed .
Fo r engin e brakin g o r bette r tractio n startin g of f o n loos e o r slipper y surfaces ; stay s i n 2n d gear ,
doe s no t shif t u p o r down .
Fo r engin e braking ; stay s i n 1s t gear , doe s no t shif t up .
Startin g i s possibl e onl y i n an d position s throug h th e us e o f a slide-type , neutral-safet y switch .
Automati c Transaxl e (A/T ) Gea r Positio n Indicato r
Th e A/ T gea r positio n indicato r i n th e instrumen t pane l show s whic h gea r ha s bee n selecte d withou t havin g t o loo k dow n
a t th e console .
ProCarManuals.com
Page 939 of 1771

Description
Clutches
The four-spee d automati c transmissio n use s hydraulically-actuate d clutche s t o engag e o r disengag e th e transmissio n gears .
Whe n hydrauli c pressur e i s introduce d int o th e clutc h drum , th e clutc h pisto n moves . Thi s presse s th e frictio n disc s an d
stee l plate s together , lockin g the m s o the y don' t slip . Powe r i s the n transmitte d throug h th e engage d clutc h pac k t o it s
hub-mounte d gear .
Likewise , whe n th e hydrauli c pressur e is ble d fro m th e clutc h pack , th e pisto n release s th e frictio n disc s an d th e stee l plates ,
an d the y ar e fre e t o slid e pas t each . Thi s allow s th e gea r t o spi n independentl y o n it s shaft , transmittin g n o power .
1s t Clutc h
Th e 1s t clutc h engages/disengage s 1s t gear , an d is locate d a t th e en d o f th e mainshaft , jus t behin d th e rea r cover .
Th e 1s t clutc h i s supplie d hydrauli c pressur e b y it s AT F fee d pip e withi n th e mainshaft .
1st-hol d Clutc h
The 1st-hol d clutc h engages/disengages 1st-hold o r position , an d i s locate d a t th e en d o f th e countershaft , jus t behin d
th e rea r cover . Th e 1st-hol d clutc h is supplie d hydrauli c pressur e b y it s AT F fee d pip e withi n th e countershaft .
2n d Clutc h
Th e 2n d clutc h engages/disengage s 2n d gear , an d i s locate d a t th e cente r o f th e mainshaft . Th e 2n d clutc h i s joine d back -
to-bac k t o th e 4t h clutch . Th e 2n d clutc h i s supplie d hydrauli c pressur e throug h th e mainshaf t b y a circui t connecte d t o th e
interna l hydrauli c circuit .
3r d Clutc h
Th e 3r d clutc h engages/disengage s 3r d gear , an d i s locate d a t th e en d o f th e countershaft .
Th e 3r d clutc h i s supplie d hydrauli c pressur e b y it s AT F fee d pip e withi n th e countershaft .
4t h Clutc h
Th e 4t h clutc h engages/disengage s 4t h gear , a s wel l a s revers e gear , an d i s locate d a t th e cente r o f th e mainshaft . Th e 4t h
clutc h i s joine d back-to-bac k t o th e 2n d clutch . Th e 4t h clutc h i s supplie d hydrauli c pressur e b y it s AT F fee d pip e withi n th e
mainshaft .
One-wa y Clutc h
Th e one-wa y clutc h i s positione d betwee n th e countershaf t 1s t gea r an d th e parkin g gear , wit h th e parkin g gea r spline d t o th e
countershaft . Th e 1s t gea r provide s th e oute r rac e surface , an d th e parkin g gea r provide s th e inne r rac e surface . Th e one -
wa y clutc h lock s u p whe n powe r i s transmitte d fro m th e mainshaf t 1s t gea r t o th e countershaf t 1s t gear .
The 1s t clutc h an d gear s remai n engage d in th e 1st , 2nd , 3rd , an d 4t h gea r range s i n th e o r position .
However, th e one-wa y clutc h disengage s whe n th e 2nd , 3rd , o r 4t h clutches/gear s ar e applie d in th e o r position .
Thi s i s becaus e th e increase d rotational speed o f th e gear s o n th e countershaf t override s th e lockin g "spee d range " o f th e
one-wa y clutch . Thereafter , th e one-wa y clutc h free-wheel s wit h th e 1s t clutc h stil l engaged .
COUNTERSHAF T 1S T GEA R
LOCK S
SPRA G
LOCKSFREE
PARKIN G GEA RNOTE : Vie w fro m rea r cove r side .
ProCarManuals.com
Page 942 of 1771
Position
Hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches. Power is not transmitted to the countershaft.
Position
Hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches. Power is not transmitted to the countershaft. The countershaft is locked
by the parking brake pawl interlocking the parking gear.
TORQUE
CONVERTER
SECONDARY
DRIVE
GEAR
2ND CLUTCH
4TH CLUTCH
1ST CLUTCH
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
1ST-HOLD
CLUTCH
ONE-WAY CLUTCH
SERVO VALVE
(SHIFT FORK SHAFT)
3RD CLUTCH
SECONDARY DRIVEN
GEARProCarManuals.com
Page 951 of 1771
Description
The electronic control system consists of the Transmission Control Module (TCM), sensors, a linear solenoid, and four
solenoid valves.
Shift and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions.
The TCM is located below the dashboard, behind the glove box on the passenger's side.
TCM
Linear Solenoid
Shift Control
Solenoid Valve A
Shift Control
Solenoid Valve B
Lock-up Control
Solenoid Valve A
Lock-up Control
Solenoid Valve B
Engine Speed Signal
Brake Switch Signal
Mainshaft Speed Sensor
Signal
Countershaft Speed
Sensor Signal
Vehicle Speed Sensor
Signal
Indicator Light
Self-Diagnosis Signal
Electronic Control System
Shift Control
Lock-up Control
Throttle Position
Sensor Signal
Engine Coolant
Temperature
Sensor Signal
Service Check
Connector
Barometric
Pressure Sensor
INTERLOCK
CONTROL UNIT
Self-Diagnosis
FunctionProCarManuals.com
Page 952 of 1771
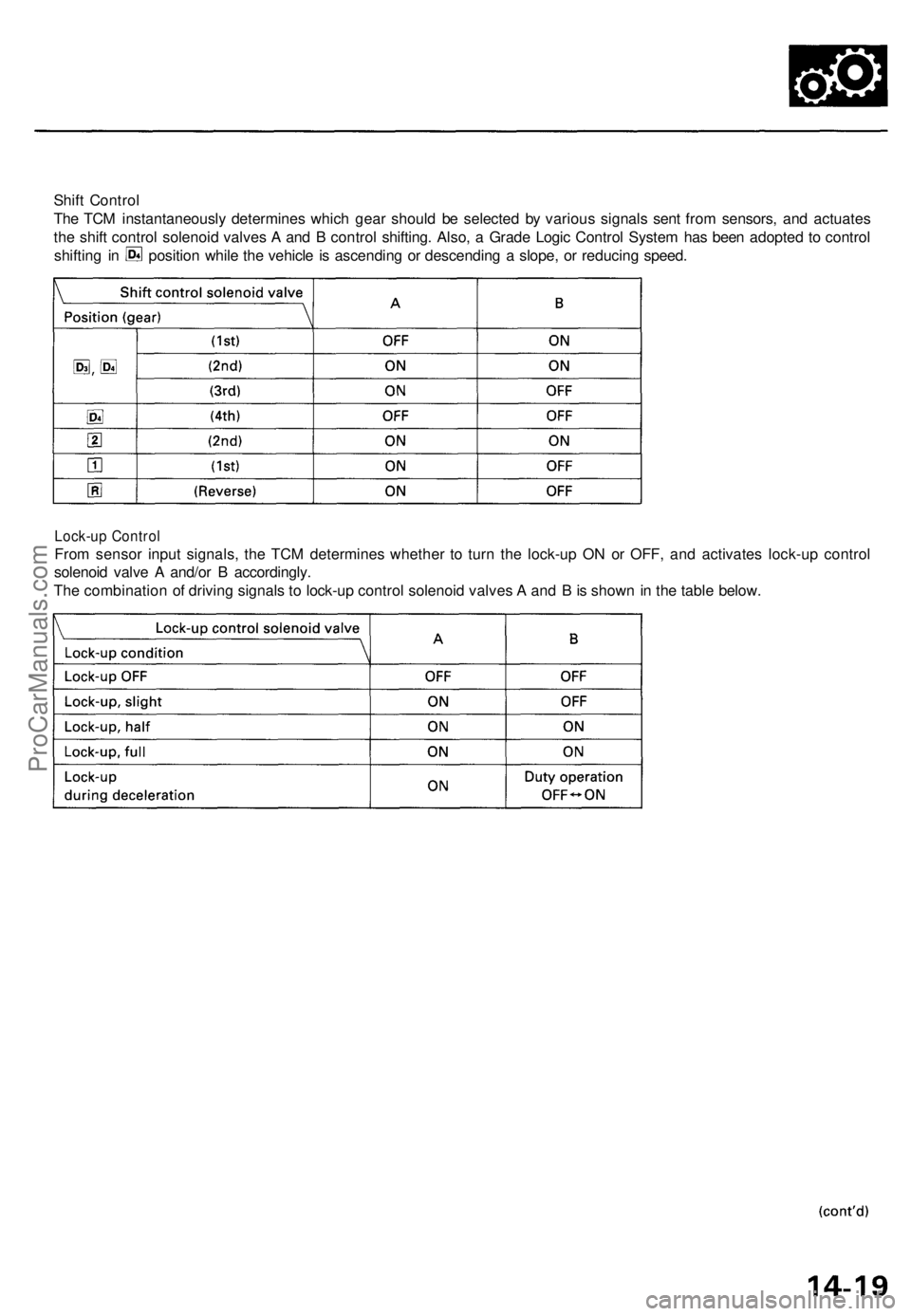
Shift Control
The TCM instantaneously determines which gear should be selected by various signals sent from sensors, and actuates
the shift control solenoid valves A and B control shifting. Also, a Grade Logic Control System has been adopted to control
shifting in position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope, or reducing speed.
Lock-up Control
From sensor input signals, the TCM determines whether to turn the lock-up ON or OFF, and activates lock-up control
solenoid valve A and/or B accordingly.
The combination of driving signals to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B is shown in the table below.ProCarManuals.com
Page 954 of 1771
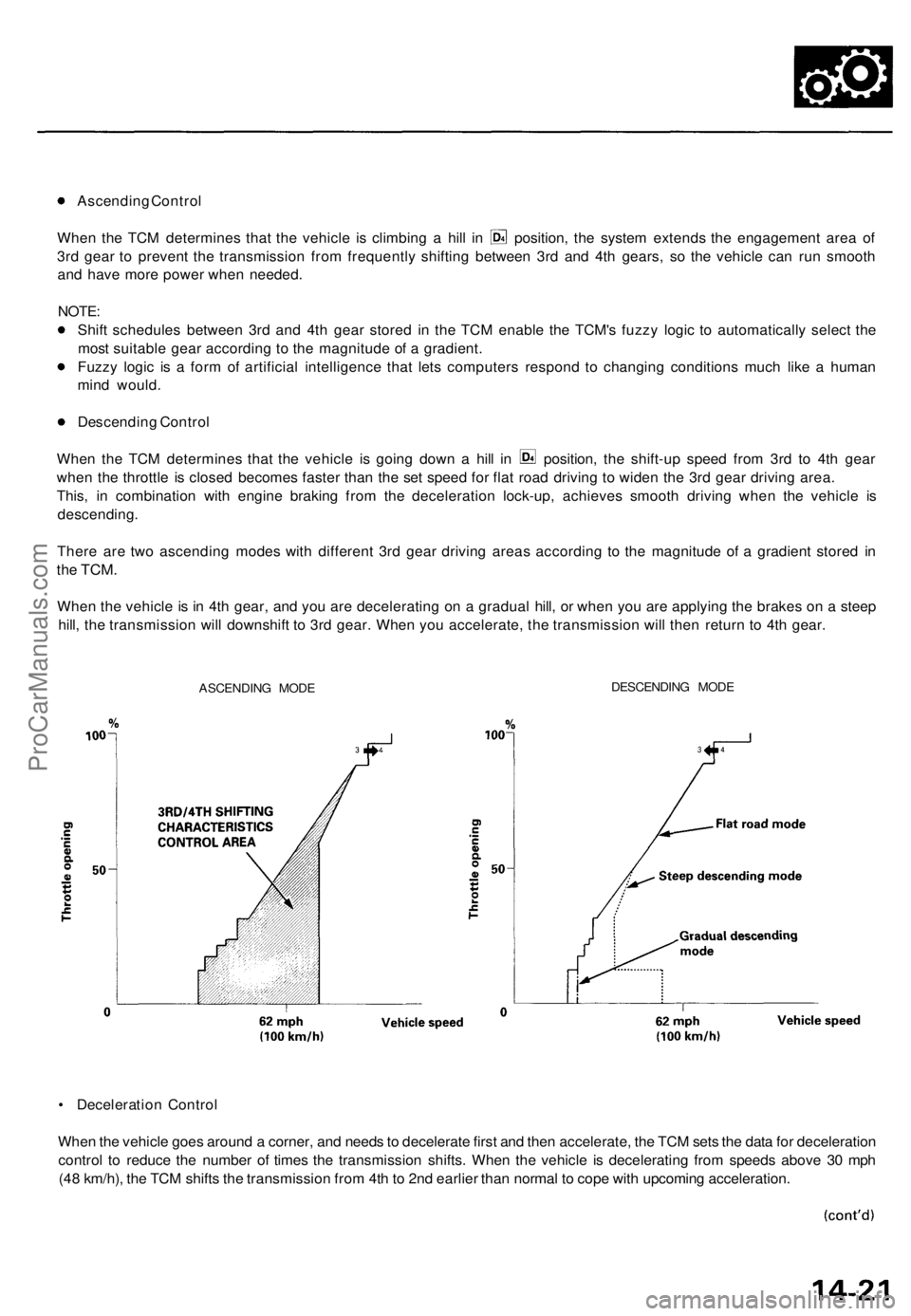
Ascending Control
When the TCM determines that the vehicle is climbing a hill in position, the system extends the engagement area of
3rd gear to prevent the transmission from frequently shifting between 3rd and 4th gears, so the vehicle can run smooth
and have more power when needed.
NOTE:
Shift schedules between 3rd and 4th gear stored in the TCM enable the TCM's fuzzy logic to automatically select the
most suitable gear according to the magnitude of a gradient.
Fuzzy logic is a form of artificial intelligence that lets computers respond to changing conditions much like a human
mind would.
Descending Control
When the TCM determines that the vehicle is going down a hill in position, the shift-up speed from 3rd to 4th gear
when the throttle is closed becomes faster than the set speed for flat road driving to widen the 3rd gear driving area.
This, in combination with engine braking from the deceleration lock-up, achieves smooth driving when the vehicle is
descending.
There are two ascending modes with different 3rd gear driving areas according to the magnitude of a gradient stored in
the
TCM.
When the vehicle is in 4th gear, and you are decelerating on a gradual hill, or when you are applying the brakes on a steep
hill, the transmission will downshift to 3rd gear. When you accelerate, the transmission will then return to 4th gear.
ASCENDING MODE
DESCENDING MODE
• Deceleration Control
When the vehicle goes around a corner, and needs to decelerate first and then accelerate, the TCM sets the data for deceleration
control to reduce the number of times the transmission shifts. When the vehicle is decelerating from speeds above 30 mph
(48 km/h), the TCM shifts the transmission from 4th to 2nd earlier than normal to cope with upcoming acceleration.ProCarManuals.com
Page 955 of 1771
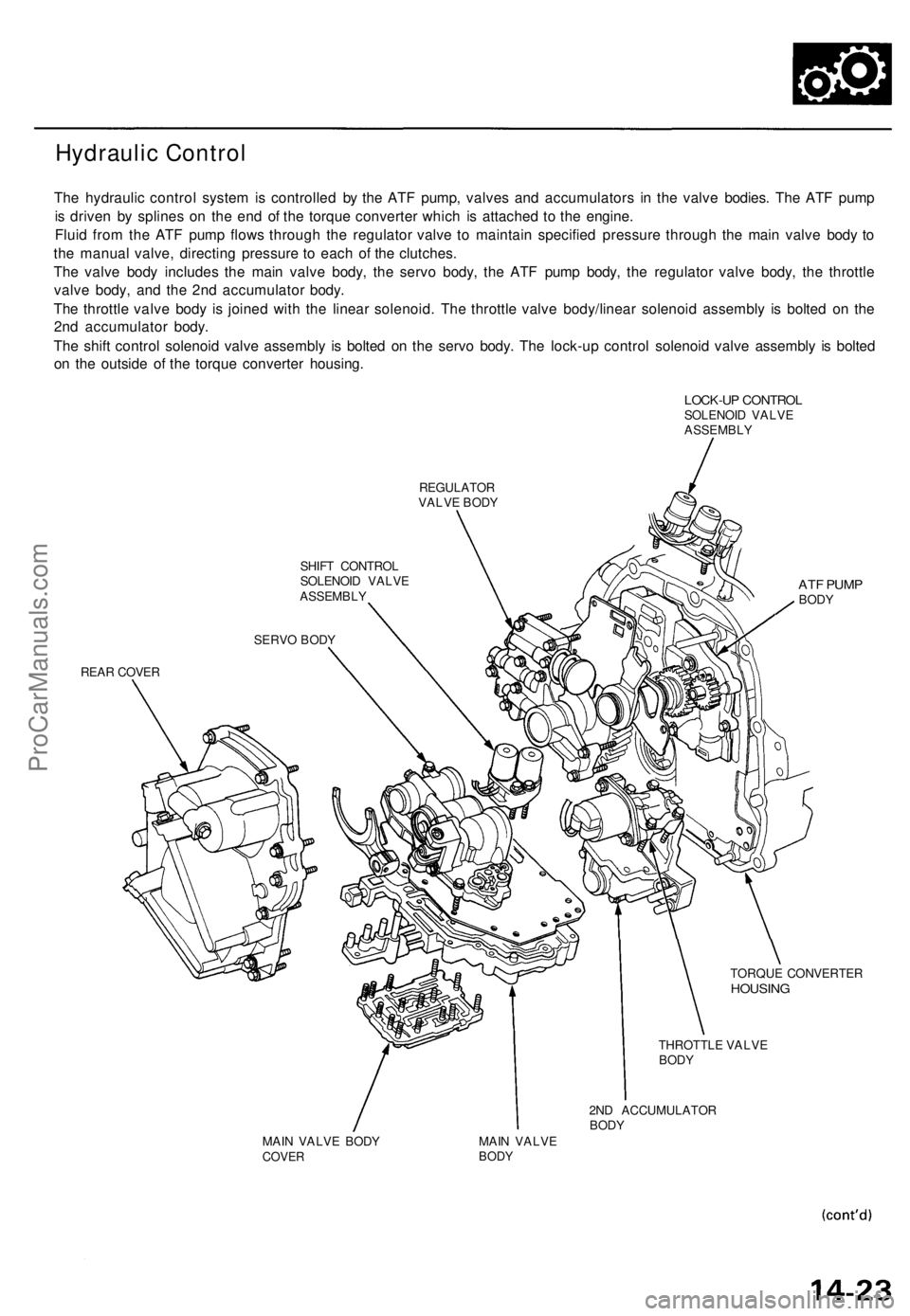
Hydraulic Control
The hydrauli c contro l syste m is controlle d b y th e AT F pump , valve s an d accumulator s i n th e valv e bodies . Th e AT F pum p
i s drive n b y spline s o n th e en d o f th e torqu e converte r whic h i s attache d t o th e engine .
Flui d fro m th e AT F pum p flow s throug h th e regulato r valv e t o maintai n specifie d pressur e throug h th e mai n valv e bod y t o
th e manua l valve , directin g pressur e t o eac h o f th e clutches .
Th e valv e bod y include s th e mai n valv e body , th e serv o body , th e AT F pum p body , th e regulato r valv e body , th e throttl e
valv e body , an d th e 2n d accumulato r body .
Th e throttl e valv e bod y i s joine d wit h th e linea r solenoid . Th e throttl e valv e body/linea r solenoi d assembl y i s bolte d o n th e
2n d accumulato r body .
Th e shif t contro l solenoi d valv e assembl y i s bolte d o n th e serv o body . Th e lock-u p contro l solenoi d valv e assembl y i s bolte d
o n th e outsid e o f th e torqu e converte r housing .
LOCK-UP CONTRO LSOLENOI D VALV E
ASSEMBL Y
REGULATO RVALVE BOD Y
SHIF T CONTRO L
SOLENOI D VALV E
ASSEMBL Y
REA R COVE R
ATF PUM PBODY
TORQU E CONVERTE RHOUSING
THROTTL E VALV EBODY
2ND ACCUMULATO RBODYMAIN VALV E BOD YCOVE RMAIN VALV EBODY
SERV O BOD Y
ProCarManuals.com