1993 DODGE TRUCK air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 242 of 1502

•
BRAKES
5 - 55 Inspect the cylinder bore. Light discoloration and
dark stains in the bore are normal and will not im
pair cylinder operation. If desired, the bore can be lightly polished but only with crocus cloth. Replace
the cylinder if the bore is scored, pitted or heavily corroded. Honing the bore to restore the surface is not recommended.
Inspect the cylinder pistons. The piston surfaces
should be smooth and free of scratches, scoring and
corrosion. Replace the pistons if worn, scored, or cor
roded. Do attempt to restore the surface by sanding or polishing.
Discard the old piston cups and the spring and ex
pander. These parts are not reusable. The original
dust boots may be reused but only if they are in good condition.
ASSEMBLING
WHEEL CYLINDER
(1) Lubricate wheel cylinder bore, pistons, piston
cups and spring and expander with ^clean brake fluid. (2) Install first piston in cylinder bore. Then in
stall cup in bore and against piston. Be sure lip of
piston cup is facing inward (toward spring and
expander) and flat side is against piston.
(3) Install spring and expanders followed by re
maining piston cup and piston.
(4) Install boots on each end of cylinder and insert
push rods in boots.
(5)
Install cylinder bleed screw.
WHEEL
CYLINDER INSTALLATION
(1) Start brakeline into cylinder.
(2) Position cylinder on support plate and install
cylinder attaching bolts. (3) Tighten brakeline fitting and cylinder attach
ing bolts. (4) Install anchor pin bushing, cam plate, adjuster
cable, parking brake lever, spring washer and anchor
bolt and nut.
(5) Install brakeshoes and brake drum as described
in this section. (6) Install axle shaft.
(7) Install wheel and tire.
(8) Remove supports and lower vehicle.
SUPPORT
PLATE REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove wheel and tire.
(3) Remove axle shaft.
(4) Remove brake drum, brake shoes and wheel
cylinder as described in this section. (5) Remove bolts/nuts attaching support plate to
axle and remove support plate.
SUPPORT PLATE INSTALLATION
(1) Transfer wheel cylinder and parking brake le
ver components to replacement support plate. (2) Position support plate on axle and install at
taching bolts/nuts. (3) Lubricate shoe contact surfaces of support plate
with Mopar multi-purpose, or high temperature bear ing grease. (4) Install brakeshoes. Adjust shoes to drum with
brake gauge. (5) Install brake drum.
(6) Install axle shaft.
(7) Install wheel and tire.
(8) Remove supports and lower vehicle.
Page 270 of 1502

•
CLUTCH
6-17
CLUTCH PEDAL INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate pedal shaft, pedal shaft bore and all
bushings with Mopar Multi Mileage grease. (2) Insert pedal pin into cylinder push rod. Then
position clutch pedal in support. (3) Slide pedal shaft through clutch pedal bore and
bushings. (4) Install bolt that retains pedal shaft in support.
(5) Secure push rod to pedal pin with wave washer,
flat washer and retaining ring.
FLYWHEEL SERVICE
Inspect the flywheel whenever the clutch disc,
cover and housing are removed for service. Check
condition of the flywheel face, hub, ring gear teeth,
and flywheel bolts. Minor scratches, burrs, or glazing on the flywheel
face can be scuff sanded with 180 grit emery cloth. However, the flywheel should be replaced if the disc
contact surface is severely scored, heat checked,
cracked, or obviously worn. Cleanup of minor flywheel scoring should be per
formed with surface grinding equipment. Remove
only enough material to reduce scoring (approximate
ly 0.001 - 0.003 in.). Heavy stock removal is not rec
ommended. Replace the flywheel if scoring is severe
and deeper than 0.076 mm (0.003 in.). Excessive
stock removal can result in flywheel cracking or
warpage after installation; it can also weaken the flywheel and interfere with proper clutch release. Check flywheel runout if misalignment is sus
pected. Runout should not exceed 0.08 mm (0.003
in.).
Measure runout at the outer edge of the fly
wheel face with a dial indicator. Mount the dial in
dicator on a stud installed in place of one of the
flywheel attaching bolts. Clean the crankshaft flange before mounting the
flywheel. Dirt and grease on the flange surface may cock the flywheel causing excessive runout. Check condition of the flywheel hub and attaching
bolts.
Replace the flywheel if the hub exhibits cracks in the area of the attaching bolt holes. Install new attaching bolts whenever the flywheel
is replaced and use Mopar Lock N' Seal, or Loctite
242 on replacement bolt threads.
Recommended flywheel bolt torques are:
• 75 N»m (55 ft. lbs.) for gas engine flywheels
• 137 N*m (101 ft. lbs.) for diesel flywheels Inspect the teeth on the starter ring gear. If the
teeth are worn or damaged, the flywheel should
be replaced as an assembly. This is the recom mended and preferred method of repair.
In cases where a new flywheel is not readily avail
able,
a replacement ring gear can be installed. How
ever, the following precautions must be observed to
avoid damaging the flywheel and replacement gear.
(a) Mark position of the old gear for alignment
reference on the flywheel. Use a scriber for this
purpose.
(b) Wear protective goggles or approved safety
glasses. Also wear heat resistent gloves when han
dling a heated ring gear. (c) Remove the old gear by cutting most of the
way through it (at one point) with an abrasive cut off wheel. Then complete removal with a cold chisel
or punch. (d) The ring gear is a shrink fit on the flywheel.
This means the gear must be expanded by heating in order to install it. The method of heating and expanding the gear is extremely important. Ev
ery surface of the gear must be heated at the same
time to produce uniform expansion. An oven or
similar enclosed heating device must be used. Tem
perature required for uniform expansion is 325-350° F.
CAUTION:
Never
use an
oxy/acetylene torch
to re
move
the old
gear,
or to
heat
and
expand
a new
gear.
The
high temperature
of the
torch flame
will
cause
localized heating
and
damage
the
flywheel.
In
addition,
using
the
torch
to
heat
a
replacement gear
will
cause uneven heating
and
expansion.
The
torch
flame
will
also
anneal
the
gear
teeth
resulting
in
rapid wear
and
damage
after
installation.
(e) The heated gear must be installed evenly to
avoid misalignment or distortion. A shop press and
suitable press plates should be used to install the
gear if at all possible.
(f) Be sure to wear eye and hand protection.
Heat resistent gloves and safety goggles are needed
for personal safety. Also use metal tongs, vise
grips,
or similar tools to position the gear as necessary for installation.
(g) Allow the flywheel and ring gear to cool
down before installation. Set the assembly on a
workbench and let it cool in normal shop air.
CAUTION:
Do not
use water,
or
compressed
air to
cool
the
flywheel.
The
rapid cooling produced
by
water
or
compressed
air can
distort,
or
crack
the
gear
and
flywheel.
Page 275 of 1502

DIAGNOSIS
PRELIMINARY
CHECKS
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM OVERHEATING Establish what driving conditions caused the com
plaint. Abnormal loads on the cooling system such as
the following may be the cause:
1.
PROLONGED IDLE, VERY HIGH AMBI
ENT TEMPERATURE, SLIGHT TAIL WIND AT
IDLE, SLOW TRAFFIC, TRAFFIC JAMS, HIGH SPEED OR STEEP GRADES.
Driving techniques that avoid overheating are:
• Idle with A/C off when temperature gauge is at
end of normal range. * Increasing engine speed for more air flow is recom
mended.
2.
TRAILER TOWING: Consult Trailer Towing section of owners manual.
Do not exceed limits.
3.
AIR CONDITIONING; ADD-ON OR AFTER
MARKET: A maximum cooling package should have been or
dered with vehicle if add-on or after market A/C is
SYMPTOM AND ACTION
SYMPTOM
installed. If not, maximum cooling system compo
nents should be installed for model involved per
manufacturer's specifications.
4.
RECENT SERVICE OR ACCIDENT RE
PAIR:
Determine if any recent service has been performed
on vehicle that may effect cooling system. This may
be:
• Engine adjustments (incorrect timing)
• Slipping engine accessory drive belt(s) • Brakes (possibly dragging)
• Changed parts. Incorrect water pump or pump ro
tating in wrong direction due to belt not correctly
routed
• Reconditioned radiator or cooling system refilling (possibly under filled or air trapped in system).
If investigation reveals none of the above as a
cause for an engine overheating complaint, refer to
the following Symptom and Action chart:
PRELIMINARY FIRST) ACTION
Blinking Engine Temperature
Warning Light or High Gauge indication - Without Coolant Loss
Normal during temporary operation
with
heavy load, towing
a
trailer,
high
outdoor temperatures, and/or on
a
steep
Loss
grade.
Coolant Loss
Hot Vehicle (Not Engine) Heat Damage,
Hot Carpet, Seat,
Hot
Catalytic
Converter,
Smoke, Burnt Odor
Hot Engine Crackling Noise Hot Smell
Severe Local Hot Spots
Coolant Color
Coolant Reserve Bottle Level Changes
Coolant Not Returning To Radiator
Improper refilling procedures
can
result
in
trapped air
in
the
system.
Subsequent
operation
of the
pressure cap and coolant reserve system
will
deaereate
the
cooling
system.
A low
coolant
level
will
then result
in the
Coolant Reserve
Tank. Add coolant.
If
condition persists,
refer
to
System
Diagnosis.
Check
heat shielding, exhaust
system,
engine emission controls, ignition
timing, engine misfiring.
A
moderate amount
of
sound from heating
metal
can
be
expected
with
any
vehicle. However,
a
crackling sound from
trie
thermostat
housing,
a hot
smell and/or severe local
hot
spots on
an
engine can indicate blocked coolant
passages,
bad castina, core sand deposits and subsequent blockage,
cracked cylinder block
or
head,
or
blown cylinder head gasket. Usually
accompanied
with
coolant
loss.
Coolant
color is
not
necessarily
an
indication
of
adequate
temperature
or
corrosion
protection.
Level changes
are to be
expected as coolant volume fluctuates
with
engine
temperature.
If the
level
in the
bottle
is
between
the
Maximum and Minimum
marks
at
normal engine operating temperature,
the
level
should
return
to
within
that
range
after
operation
at
elevated temperatures.
Coolant
will
not
return
to the
radiator
if the
radiator cap vent valve does
not
function,
if
an
air
leak destroys vacuum,
or if the
overflow
passage
is
blocked
or
restricted. Inspect
all
portions
of the
overflow
passage,
pressure
cap,
filler
neck nipple, hose, and
passages
within
the
bottle
for
vacuum leak
only. Coolant
return
failure
will
be
evident
by a low
level
in the
radiator.
Reserve
bottle
level
should increase during heat-up.
J9207-31
Page 276 of 1502
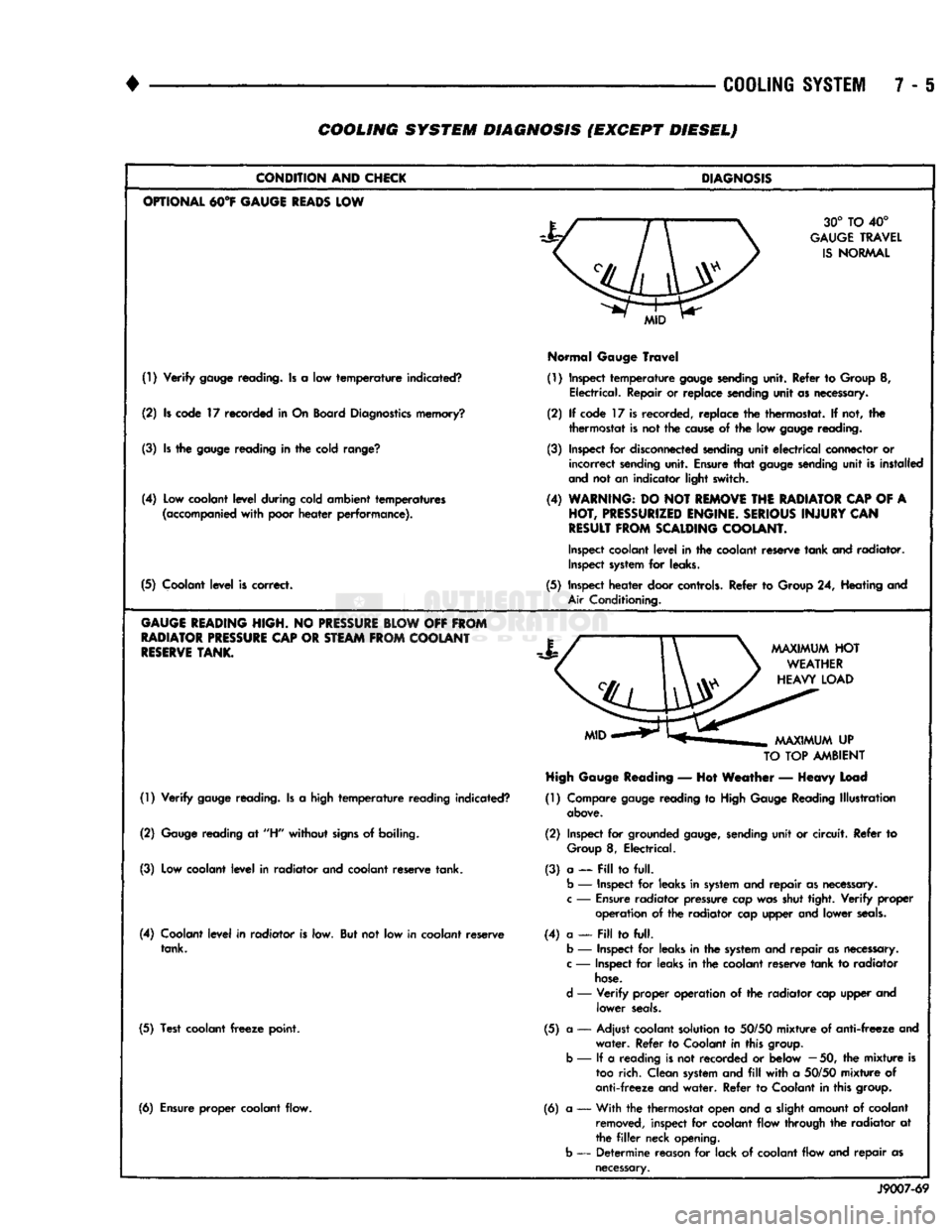
•
COOLING
SYSTEM
7 - 6 COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS (EXCEPT DIESEL)
CONDITION
AND
CHICK
OPTIONAL
M°¥
GAUGE
READS
LOW
(!) Verify
gauge
reading. Is a low temperature indicated?
(2) Is code 17 recorded in On Board
Diagnostics
memory?
(3) Is the
gauge
reading in the cold
range?
(4) Low coolant level during cold ambient temperatures
(accompanied
with poor heater performance).
(5) Coolant level is correct.
GAUGE
HEADING
HIGH.
NO
PRESSURE
BLOW
OFF
FROM
RADIATOR
PRESSURE
CAP
OR
STEAM
FROM
COOLANT
RESERVE
TANK.
(1) Verify
gauge
reading. Is a high temperature reading indicated?
(2)
Gauge
reading at
"H"
without
signs
of boiling.
(3) Low coolant level in radiator and coolant reserve tank.
(4) Coolant level in radiator is low. But not low in coolant reserve tank.
(5) Test coolant
freeze
point.
(6) Ensure proper coolant flow.
DIAGNOSIS
30° TO 40°
GAUGE
TRAVEL
IS
NORMAL
Normal
Gauge
Travel
(1) Inspect temperature
gauge
sending
unit. Refer to Group 8, Electrical. Repair or replace sending unit as necessary.
(2) If code 17 is recorded, replace the thermostat. If not, the thermostat is not the
cause
of the low
gauge
reading.
(3) Inspect for
disconnected
sending
unit electrical connector or incorrect
sending
unit. Ensure that
gauge
sending
unit is installed
and
not an indicator light switch.
(4)
WARNING:
DO NOT
REMOVE
THE
RADIATOR
CAP
OF A
HOT,
PRESSURIZED
ENGINE.
SERIOUS
INJURY
CAN
RESULT
FROM
SCALDING
COOLANT.
Inspect
coolant level in the coolant reserve tank and radiator.
Inspect
system
for leaks.
(5) Inspect heater door
controls.
Refer to Group 24, Heating and
Air
Conditioning.
TO
TOP
AMBIENT
High
Gauge
Reading
— Hot Weather — Heavy Load
(1) Compare
gauge
reading to
High
Gauge
Reading Illustration
above.
(2) Inspect for grounded
gauge,
sending
unit or circuit. Refer to
Group
8, Electrical.
(3) a — Pill to full.
b
— Inspect for leaks in
system
and repair as
necessary,
c
—
Ensure
radiator pressure cap was shut tight. Verify
proper
operation of the radiator cap upper and lower
seals.
(4) a —
Fill
to full,
b
— Inspect for leaks in the
system
and repair as
necessary,
c
— Inspect for leaks in the coolant reserve tank to radiator
hose.
d
— Verify proper operation of the radiator cap upper and lower
seals.
(5) a — Adjust coolant solution to
50/50
mixture of anti-freeze and water. Refer to Coolant in this
group,
b
— If a reading is not recorded or below
—
50, the mixture is
too
rich. Clean
system
and
fill
with a
50/50
mixture of
anti-freeze and water. Refer to Coolant in this
group.
(6) a •— With the thermostat open and a slight amount of coolant
removed,
inspect for coolant flow through the radiator at
the
filler
neck opening,
b
— Determine reason for lack of coolant flow and repair as
necessary.
J9007-69
Page 277 of 1502

7 - 6
COOLING
SYSTEM
• COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS (EXCEPT DIESEL)—CONTINUED
Condition and Checks
Diagnosis
(7) Other possible
causes.
(7) a — If
symptom
occurs
during high speed operation inspect for
plugged
air
inlet
side of the radiator or condenser,
plugged
radiator core tubes, add on A/C package
without
proper radiator, engine not operating
within
specifications,
dragging
brakes,
trailer
towing or
hill
climbing, or an insect screen.
b — If
symptom
occurs
during high or low
speed
operation inspect for: thermostat being stuck
partially
open if ambient
temperature
is
below
70°F
and
the vehicle
has
high
mileage,
plugged
air
inlet
side of the radiator or
condenser, add on
A/C
with
incorrect radiator.
c
— If
symptom
occurs
during low
speed
operation only, inspect the radiator fan drive. Repair as necessary.
TEMPERATURE
GAUGE
READS
HOT.
PRESSURE
CAP
VENTS
RESULTING
IN
STEAM
AND
COOLANT
TRANSFER
TO
COOLANT
RESERVE
TANK.
(1) Coolant
level
low in radiator and coolant reserve tank. (1) a —
Fill
cooling
system
and vent trapped air.
b — Inspect for leaks. Repair as necessary.
c
—
Ensure
that
pressure cap
is
completely shut and
seals.
d
— If
level
is low in radiator but normal in the coolant reserve tank, check the
filler
cap to coolant reserve
bottle
connection and pressure cap seal.
(2) Test coolant
freeze
point. (2) Adjust coolant to
50/50
mix of
anti-freeze
and
water.
Refer to
Coolant
section in this group.
(3)
Ensure
coolant
is
flowing through system. (3) a — With the coolant
level
low and the thermostat open, check
for coolant flow through the radiator at the
filler
neck.
b — If a
metal
cracking
sound
is heard, inspect for core sand restricting coolant flow through the
water
jacket
and/or a
faulty
cylinder head casting.
(4) Thermostat stuck in the
closed
position
(prevalent
in cold ambient temperatures). (4) Replace thermostat if found to be stuck in
closed
position.
Refer
to the Thermostat Testing section in this group.
(5) Cylinder head gasket leak. (5) Inspect for leaking cylinder head gasket
with
a commercially
available Block Leak Tester.
J9007-57
Page 278 of 1502
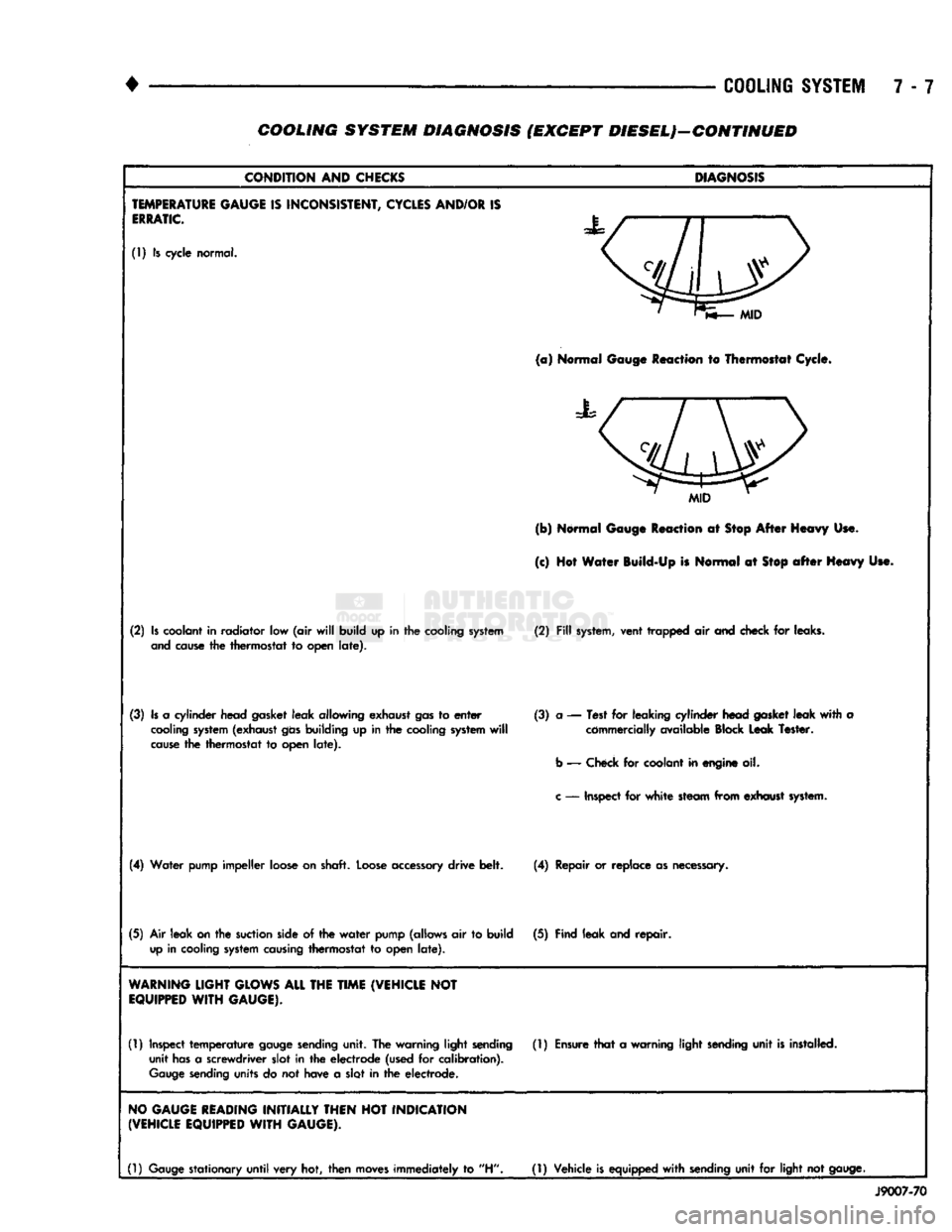
•
COOLING
SYSTEM
7 - 7 COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS (EXCEPT DIESELJ-GONTINUED
CONDITION
AND
CHECKS
DIAGNOSIS
TEMPERATURE
GAUGE
IS
INCONSISTENT,
CYCLES
AND/OR
IS
ERRATIC.
(1) Is cycle normal.
MID
(a)
Normal Gauge Reaction to Thermostat Cycle.
MID
(b) Normal Gauge Reaction at Stop After Heavy Use.
(c) Hot Water Build-Up is Normal at
Stop
after
Heavy Use.
(2)
Is
coolant in radiator low (air
will
build up in the cooling
system
(2)
Fill
system,
vent trapped air and check for leaks,
and
cause
the thermostat to open
late).
(3)
Is
a cylinder head gasket leak allowing exhaust
gas
to
enter
(3) a — Test for leaking cylinder head
gasket
leak
with
a
cooling
system
(exhaust
gas
building up in the cooling
system
will
commercially available Block Leak Tester,
cause
the thermostat to open
late).
b
— Check for coolant in engine oil.
c
— Inspect for
white
steam from exhaust
system.
(4)
Water pump impeller loose on shaft.
Loose
accessory
drive belt. (4) Repair or replace as necessary.
(5)
Air leak
on
the
suction
side of the
water
pump (allows air to build (5) Find leak and repair,
up
in cooling
system
causing
thermostat to open
late).
WARNING
LIGHT
GLOWS
ALL
THE
TIME
(VEHICLE
NOT
EQUIPPED
WITH
GAUGE).
(1) Inspect
temperature
gauge
sending
unit. The warning light
sending
(1)
Ensure
that
a warning light
sending
unit
is
installed, unit
has
a screwdriver slot in the electrode (used for calibration).
Gauge
sending
units do not have a slot in the electrode.
NO
GAUGE
READING
INITIALLY
THEN
HOT
INDICATION
(VEHICLE
EQUIPPED
WITH
GAUGE).
(1)
Gauge
stationary
until
very hot, then
moves
immediately to "H"
(1)
Vehicle
is
equipped
with
sending
unit for light not
gauge.
J9007-70
Page 279 of 1502

7 - 8
COOLING
SYSTEM
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS (EXCEPT DIESEL)—CONTINUED
Condition and Check
Diagnosis
PRESSURE
CAP
VENTS
TO
ATMOSPHERE
AND COOLANT
RESERVE
TANK.
TEMPERATURE
GAUGE
READING
ABOVE
NORMAL
BUT NOT HIGH.
(1) Test radiator pressure cap
relief
pressure. Refer to Radiator Pressure cap section in this group. (1) Replace cap if
relief
pressure is lower than 14 psi.
COOLANT
LOSS
VISIBLE
ON
GROUND
BELOW
VEHICLE,
BUT
NO
PRESSURE
CAP
BLOW
OFF.
(1) Inspect
system
for leaks. (1) Repair as necessary.
COOLANT
LOSS
PAST
PRESSURE
CAP
TOP
SEAL,
VISIBLE
ON
RADIATOR
FILLER
NECK.
(1) With normal gauge reading. (1) a — Pressure cap not installed tightly.
b — Pressure cap top seal leaks.
c
— Pressure cap diaphragm bowed.
d — Damaged radiator
filler
neck.
e — Pressure cap top seal out of position.
(2) With high or low gauge reading on new vehicle. (2) a — Kinked coolant reserve
system
hose.
b — Coolant reserve
system
tank
plastic
tube
plugged,
c
— Pressure cap seal out of position.
DETONATION
OR
PREIGNITION.
NOT
CAUSED
BY IGNITION
OR
ENGINE
CONDITIONS.
(1) Check engine coolant
freeze
point. If the
tester
does
not register a reading or if
the
reading
is
below
50°F,
inspect
ethylene-
glycol/water
ratio.
A 100
percent
solution of ethylene-glycol in
the
system
causes
the engine to run
hotter
and
possibly
overheat. (1) a — Adjust coolant solution to
50/50
water
ethylene-glycol
mixture.
b — If 100
percent
ethylene-glycol solution
is
found in system, clean and flush
system
before
replacing
with
50/50
mixture
of ethylene-glycol and
water.
COOLING
SYSTEM
HOSES
COLLAPSE
ON
COOLDOWN.
(1) Inspect pressure cap
vent
valve. (1) a — Gasket swell can
prevent
valve from opening,
b — Replace pressure cap.
(2) Coolant reserve
tank
hose plugged or kinked. (2) Repair as necessary.
(3) Inside of pressure cap plugged. (3) Clean cap or replace if necessary.
COOLING
SYSTEM
SUSPECTED
AS
CAUSE
OF
INADEQUATE
AIR
CONDITIONING
SYSTEM
PERFORMANCE.
(1) Inspect for plugged radiator and/or condenser. (1) Clean
with
low pressure
water
from fan side.
(2) Inspect for
missing
air
seals
in the recirculating air path. (2) Repair as necessary.
EXCESSIVE
FAN
NOISE
(1) Inspect for loose or
bent
fan blades. (1) Replace fan.
(2) Inspect clearance
between
fan and adjacent
part.
(2) Repair or replace as necessary.
(3) Inspect radiator and condenser for incoming air obstructions. (3) Clean air path
with
low pressure
water
from fan side.
(4) Inspect
viscous
fan drive. (4) Replace if
viscous
drive
does not
operate
properly.
HEAT
ODOR
(1) Was
temperature
gauge reading
high?
(1) If
YES,
refer
to
GAUGE
READING
HIGH. If NO,
refer
to steps
2, 3, and 4.
(2) Are all
heat
shields in place? (2) If
YES,
refer
to
steps
3 and 4. If NO,
repair
as required.
(3) If the air side of the
heat
exchanger
plugged?
(3) Clean as necessary.
(4) Engine running rich
causing
catalytic converter to overheat. (4) Repair as necessary.
POOR
DRIVEABIUTY.
SUSPECT
THERMOSTAT
FAILED
IN
OPEN
POSITION.
(1) Check On-Board
Diagnostics.
Is code 17 set in memory? (1) If
YES,
replace thermostat. If NO,
refer
to the appropriate
Driveability Manual.
J9007-59
Page 280 of 1502

•
COOLING
SYSTEM
7 - 9 COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS (EXCEPT DIESEL)—CONTINUED
Condition
and Chock
Diagnosis
POOR
HEATER
PERFORMANCE.
SUSPECT
THERMOSTAT
FAILED
IN
OPEN
POSITION.
(1)
Does gauge
read
low?
(1) If YES, replace thermostat. If NO, inspect the
auxiliary
heater
vacuum
water valve. The
valve
should
be open except when the
climate
controls are
OFF
or in the
MAX
A/C mode.
(2) Is coolant level
low?
(2)
Fill
cooling system and
inspect for leaks. Repair as
necessary.
(3) Check
On-Board
Diagnostics.
Is
code
17 set in memory? (3) If
YES,
replace thermostat. If NO, inspect the auxiliary heater
vacuum
water valve. The valve
should
be open except when the climate controls are OFF or in the MAX A/C mode.
J9007-61