1993 DODGE TRUCK tire pressure
[x] Cancel search: tire pressurePage 6 of 1502

INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION
DESIGNATIONS,
LABELS/PLATES/DECALS,
CODES
AND DIMENSIONS/WEIGHTS .
CONTENTS
page
MEASUREMENT
AND TORQUE
... 1 SPECIFICATIONS
page
. 11
DESIGNATIONS, LABELS/PLATES/DECALS, CODES
AND
DIMENSIONS/WEIGHTS
INDEX
page
Engine
and
Transmission/Transfer
Case
Identification
2
Engine/Transmission/GVWR
4
Equipment
Identification
Plate
3
International
Vehicle Control
and
Display
Symbols
10
Major Component
Identification 3
VEHICLE DESIGNATIONS The Vehicle Code chart lists description and code
for Ram Truck and Sport Utility vehicles. The codes are used to identify vehicle types in charts, captions
and in service procedures. The vehicle codes are
dif
ferent than the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) or the wheelbase/model code.
VEHICLE SAFETY CERTIFICATION
LABEL
A certification label is attached to the left side
B-pillar. The label certifies that the vehicle conforms
to Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS).
The label also lists the: • Month and year of vehicle manufacture
• Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR). The gross
front and rear axle weight ratings (GAWR's) are
based on a minimum rim size and maximum cold tire inflation pressure Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
Type of vehicle
Type of rear wheels (single or dual) Bar code
Month, Day and Hour (MDH) of final assembly
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) PLATE The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) plate is
attached to the top left side of the instrument panel.
The VIN contains 17 characters that provide data
concerning the vehicle. Refer to the decoding chart to
determine the identification of a vehicle.
page
Trailer
Towing Specifications
4
Vehicle Code Plate
2
Vehicle Designations
1
Vehicle Dimension
4
Vehicle
Identification
Number (VIN) Plate
1
Vehicle Safety
Certification
Label
............. 1
Vehicle Weights
4
VEHICLE CODE
DESIGNATIONS
VEHICLE CODE
= AD
(DODGE
RAM
PICKUP
&
CHASSIS
CAB)
VEHICLE
FAMILY LINE DESCRIPTION
AD1
D150
AD2
D250
AD3
D350
PICKUP
4x2
AD5
W150
AD6
W250
AD7
W350
PICKUP
4x4
AD2
D250
AD3
D350
CHASSIS
CAB
4x2
AD6
W250
AD7
W350
CHASSIS
CAB
4x4
AD4
AD100
AD4
AD150
SPORT
UTILITY
4x2
AD8
AD100
AD8 AD
150
SPORT
UTILITY
4x4
J90IN-32
Page 21 of 1502

0 - 2
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
• Commercial service
When a vehicle is continuously subjected to severe
driving conditions, lubricate:
• Body components
• All the driveline coupling joints
• Steering linkage More often than normal driving conditions
DUSTY
AREAS
With this type of severe driving condition, special
care should be given to the:
• Engine air cleaner filter
• PCV filter
• Crankcase ventilation system
• Brake booster control valve air filter. Verify that the filters and the associated compo
nents are clean. Also verify that they are functioning
effectively. This will minimize the amount of abra sive particles that enter the engine.
OFF-ROAD
(4WD)
OPERATION
After off-road (4WD) operation, inspect the under
side of the vehicle. Inspect the:
• Tires
• Body structure
• Steering components
• Suspension components • Exhaust system
• Threaded fasteners
HARSH
SURFACE ENVIRONMENTS
After extended operation in harsh environments,
the brake drums, brake linings, and rear wheel bear ings should be inspected and cleaned. This will pre
vent wear and erratic brake action.
ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
The following routine maintenance is recommended
on a monthly basis: TIRES—Inspect the tires for unusual wear/damage.
Determine if the inflation pressure is adequate for
the vehicle load. BATTERY—Inspect and clean the terminals.
Tighten the terminals if necessary. FLUIDS—Determine if the component fluid levels
are acceptable. Add fluid, if necessary. LIGHTS/ELECTRICAL—Test all the electrical sys
tems in the vehicle for proper operation. It is also recommended that the engine oil and the
washer fluid level be determined at each fuel fill-up.
VEHICLE
NOISE CONTROL
Vehicles with a GVWR of 4 535 kg (10,000 lbs), or
more, are required to comply with Federal Exterior Noise Regulations (Fig. 2).
VEHICLE
NOISE
EMISSION
CONTROL INFORMATION
DATE
OF
VEHICLE
MANUFACTURE
THIS
VEHICLE CONFORMS
TO
U.S. EPA REGULATIONS FOR NOISE EMISSION
APPLICABLE
TO
MEDIUM
AND HEAVY
DUTY
TRUCKS. THE
FOLLOWING
ACTS OR THE CAUSING THEREOF BY ANY PERSON ARE PROHIBITED BY THE NOISE CONTROL ACT
OF 1972. (A) THE
REMOVAL
OR
RENDERING
INOPERATIVE, OTHER
THAN
FOR
PURPOSES
OF
MAINTENANCE,
REPAIR.
OR REPLACEMENT, OF ANY NOISE CONTROL DEVICE OR ELEMENT OF
DESIGN
(LISTED
IN
THE
OWNERS
MANUAL)
INCORPORATED
INTO
THIS
VEHICLE
IN COMPLIANCE
WITH
THE NOISE CONTROL
ACT:
(B) THE
USE
OF
THIS
VEHICLE
AFTER SUCH DEVICE
OR
ELEMENT
OF
DESIGN HAS BEEN REMOVED
OR
RENDERED
INOPERATIVE.
PU626D
Fig.
2 Vehicle
Noise
Emission
Control Information
Label
UNAUTHORIZED
DEFEAT
OF
NOISE
CONTROL COMPONENTS
Federal law prohibits removal, altering or other
wise defeating any noise control component. This in
cludes before or after the vehicle is in use. Federal
law also prohibits the use of a vehicle after a noise
control component is defeated.
REQUIRED MAINTENANCE/SERVICE
FOR
NOISE
CONTROL
The following maintenance is required after each
6-month or 9 600 km (6,000 miles) interval. This will
ensure that the vehicle noise control components are
operating properly.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
Inspect exhaust system for exhaust leaks and dam
aged components. The exhaust hangers, clamps and
U-bolts should be attached and in good condition.
Burned or ruptured mufflers, damaged exhaust pipes should be replaced. Refer to Group 11—Exhaust Sys
tem/Intake Manifold for service information.
AIR
FILTER
HOUSING/CANISTER
Inspect the air filter assembly for proper fit. Verify
the cover is securely attached to the housing/canis
ter. Inspect all the air filter housing hoses for con nections. The gasket between the air filter housing and throttle body must be in good condition. The air
filter element should be clean and serviced according
to the maintenance schedule.
FUEL
REQUIREMENTS
GASOLINE
ENGINES
All engines require the use of unleaded gasoline to
reduce the effects of lead to the environment. Also unleaded fuel is necessary to prevent damage to the
catalytic converter/02 sensor. The fuel must have a
minimum octane rating of 87 based on the (R + M)/2
calculation method.
Page 35 of 1502

0-18
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
•
COOLANT FREEZE PROTECTION
Cooling systems contain a 50/50 mixture of anti
freeze (ethylene glycol) and distilled water. This is
the recommended coolant mixture.
It is recommended that the degree of coolant pro
tection be tested every 12 months. If the coolant is
contaminated or rusty, the cooling system should be
drained, flushed. Refill with a 50/50 mixture of fresh
coolant. Refer to Group 7—Cooling Systems for addi
tional information.
SYSTEM
INSPECTION
WARNING:
IF THE
ENGINE
HAS
BEEN RECENTLY
OPERATED,
DO NOT
REMOVE
THE
RADIATOR
CAP.
THIS WILL AVOID
YOU
BEING SCALDED
WITH
HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT.
(1) Test the radiator cap for proper sealing and op
eration. Use caution when removing the radiator cap
to avoid contact with hot coolant. Place a heavy rag
or towel over the cap and turn to the first stop. Do
not press down. Pause to allow the pressure to re
lease through the overflow tube. Then press down
and turn counterclockwise to remove the cap.
(2) Inspect the coolant overflow tubing and the
connections at the coolant reserve tank and at the
radiator.
(3) Inspect the entire cooling system for leaks. A
black-light detector can be used as an aid in detect ing the source of coolant leaks.
(4) Inspect the radiator and air conditioner con
denser fins for debris, etc. (5) If necessary, refer to Group 7—Cooling Systems
for additional information and service procedures.
RADIATOR CAP
The radiator cap must be completely tightened to
provide proper pressure. Inspect and test radiator cap
when cooling system service is performed.
MAIN,
FLUSH
AND
FILL
WARNING: ANTI-FREEZE (ETHYLENE GLYCOL)
IS
POISONOUS.
KEEP
OUT OF THE
REACH
OF
CHIL
DREN.
Drain, flush, and fill the cooling system at the in
terval specified in maintenance schedule. For proper service instructions see Group 7, Cooling System.
HOSES AND
FITTINGS
It is recommended that rubber hoses be periodi
cally inspected. Inspect all hose fittings for looseness and corrosion.
ENGINE
AIR
CLEANER
FILTER
ELEMENT
MAINTENANCE
SCHEDULE
With normal driving conditions, the engine air
cleaner filter element should be replaced:
• Light-Duty Cycle-after each 48 000 km (30,000
miles) interval has elapsed
• Heavy-Duty Cycle-after
each
38 000 km (24,000
miles) interval has elapsed
When the vehicle is operated in dusty areas, the
filter element should be replaced more often.
For Diesel engines, the air filter canister should be
cleaned at the same time the filter is replaced.
SERVICE/REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove the air cleaner cover.
(2) Remove the air cleaner filter (Fig. 4).
CAUTION:
Do not tap the filter or immerse the filter medium in liquid to remove trapped debris.
(3) Clean filter by blowing the trapped debris from
the filter with compressed air (Fig. 5). Direct the air in the opposite direction of normal intake air flow.
Keep the air nozzle at least two inches away from
the filter.
(4) If the filter has become partially saturated with
oil,
replace the filter. Inspect the crankcase ventilat
ing system for proper operation.
(5) Wash the air cleaner cover and body with
cleaning solvent. Wipe it dry.
(6) Install the air cleaner filter element. Attach
the cover to the body (Fig. 4).
Fig,
4
Engine
Air Oeaner—
Typical
Page 51 of 1502

0
- 32
LUBRICATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
•
Fig.
5 Parking Brake Ratio Lever Lubrication (2) Note any indication of brake overheating,
wheel dragging or the vehicle pulling to one side.
(3) Evaluate any performance complaints received
from the owner/operator. (4) Repair the brake system as necessary (refer to
Group 5—Brakes for additional information and ser
vice procedures).
BODY
COMPONENT
MECHANISMS
LUBRICATION REQUIREMENTS
All operating mechanisms and linkages should be
lubricated when necessary. This will maintain ease of operation and provide protection against rust and
excessive wear. The door weatherstrip seals should
be lubricated to prolong their life as well as to im prove door sealing.
LUBRICANT SPECIFICATIONS
All applicable exterior and interior vehicle operat
ing mechanisms should be:
• Inspected • Cleaned
• All the pivoting/sliding contact areas on the mech anisms should then be lubricated.
MOPAR®Multi-Mileage Lubricant or an equiva
lent, should be used to lubricate the mechanisms.
The door weatherstrip seals should be lubricated
with silicone lubricant spray. Refer to the Body Lu
bricant Specifications chart below for additional lu
bricant applications.
LUBRICATION
(1) When necessary, lubricate the cab and cargo
box operating mechanisms with the specified lubri
cants.
(2) Apply silicone lubricant to a cloth and wipe it
on door seals to avoid over-spray that can soil pas
senger clothing. (3) Before applying lubricant, the component
should be wiped clean. After lubrication, any excess
lubricant should be removed.
(4) The hood latch, latch release mechanism, latch
striker and safety latch should be lubricated periodi
cally.
(5) The door lock cylinders should be lubricated 2
times each year (preferably autumn and spring): • Spray a small amount of lock cylinder lubricant di
rectly into the lock cylinder
• Apply a small amount to the key and insert it into
the lock cylinder • Rotate it to the locked position and then back to
the unlocked position several times
• Remove the key. Wipe the lubricant from it with a
clean cloth to avoid soiling of clothing.
TIRES
RECOMMENDED MAINTENANCE
The condition of the tires should be inspected. The
inflation pressures tested/corrected at the same time as the engine oil is changed and the oil filter is re
placed.
The tires/wheels should be rotated periodically to
ensure even tread wear. The tires/wheels should be
rotated at the first 12 000 km (7,500-miles) interval.
Thereafter, at each 24 000 km (15,000-miles) inter
val.
INSPECTION
Inspect the tires for excessive wear, damage. Test
the tires for the recommended inflation pressure and adjust the pressure accordingly. Refer to the tire in
flation pressure decal located on the left door face. Also to Group 22—Tires And Wheels for tire pressure charts, tire replacement, and treadwear indica
tors.
ROTATION
Tires/wheels should be rotated according to the rec
ommended interval. The first tire/wheel rotation is
the most important for establishing the prevention of uneven tread wear. After rotation, adjust the tire in
flation pressure to the air pressure recommended on
the decal located on the left door face.
Refer to Group 22—Tires And Wheels for the rec
ommended method of tire/wheel rotation.
HEADLAMPS
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
Every six months check the headlamp beams to en
sure that the headlamp beams are correctly posi
tioned.
AIM
ADJUSTMENT
Refer to Group 8L—Lamps for headlamp aim ad
justment procedures.
Page 56 of 1502
FRONT SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 3
FRONT
WHEEL
ALIGNMENT
GENERAL
INFORMATION
Front wheel alignment involves
the
correct posi
tioning
of the
tire contact patch
in
relation
to the
pavement.
The
positioning
is
accomplished through
the suspension
and
steering linkage adjustments.
An
alignment
is
essential
for
efficient steering
and
direc
tional stability.
The
most important factors
of
front
end alignment
are
camber, caster
and toe
position. Routine inspection
of
the front
suspension
and
steering components
is a
good
preventative
maintenance practice.
Inspection
also
helps
to
ensure
safe operation
of the
vehicle.
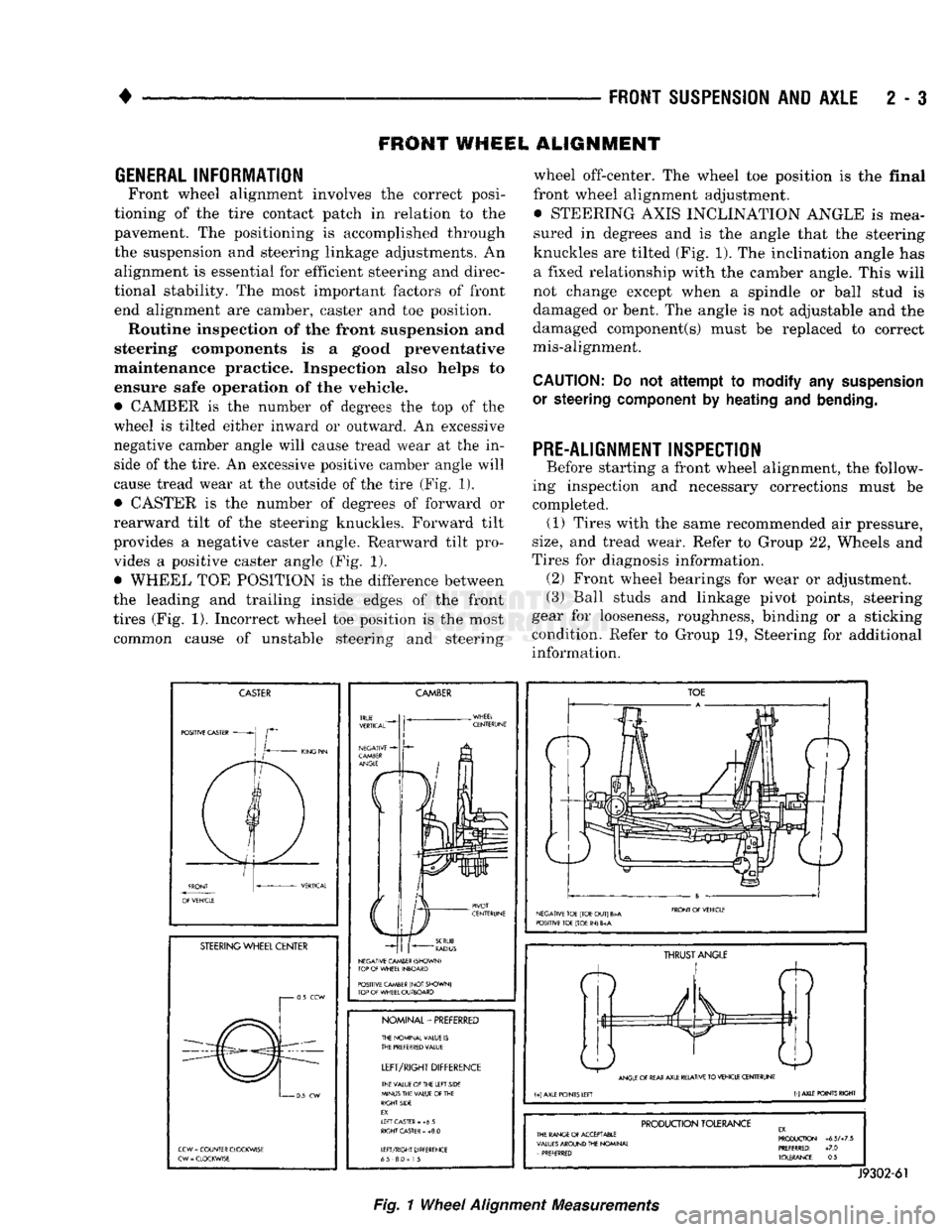
• CAMBER
is the
number
of
degrees
the top of the
wheel
is
tilted either inward
or
outward.
An
excessive
negative camber angle will cause tread wear
at the in
side
of
the tire.
An
excessive positive camber angle will
cause tread wear
at the
outside
of
the tire (Fig.
1),
• CASTER
is the
number
of
degrees
of
forward
or
rearward tilt
of the
steering knuckles. Forward tilt
provides
a
negative caster angle. Rearward tilt pro vides
a
positive caster angle
(Fig. 1).
• WHEEL
TOE
POSITION
is the
difference between
the leading
and
trailing inside edges
of the
front
tires (Fig.
1).
Incorrect wheel
toe
position
is the
most common cause
of
unstable steering
and
steering wheel off-center.
The
wheel
toe
position
is the
final
front wheel alignment adjustment. • STEERING AXIS INCLINATION ANGLE
is
mea
sured
in
degrees
and is the
angle that
the
steering
knuckles
are
tilted (Fig. 1).
The
inclination angle
has
a fixed relationship with
the
camber angle. This will
not change except when
a
spindle
or
ball stud
is
damaged
or
bent.
The
angle
is not
adjustable
and the
damaged component(s) must
be
replaced
to
correct
mis-alignment.
CAUTION:
Do not
attempt to modify
any
suspension
or steering
component
by
heating
and
bending.
PRE-ALIGNMENT INSPECTION
Before starting
a
front wheel alignment,
the
follow
ing inspection
and
necessary corrections must
be
completed.
(1)
Tires with
the
same recommended
air
pressure,
size,
and
tread wear. Refer
to
Group
22,
Wheels
and
Tires
for
diagnosis information. (2) Front wheel bearings
for
wear
or
adjustment.
(3) Ball studs
and
linkage pivot points, steering
gear
for
looseness, roughness, binding
or a
sticking
condition. Refer
to
Group
19,
Steering
for
additional information.
CASTER
POSITIVE CASTER
STEERING
WHEEL CENTER
i 0.5
CCW
0
5
CW
CCW
=
COUNTER CLOCKWISE
CW
-
CLOCKWISE
CAMBER
NEGATIVE CAMBER (SHOWN)
TOP
OF
WHEEL INBOARD
POSITIVE CAMBER
(NOT
SHOWN)
TOP
OF
WHEEL OUTBOARD
NOMINAL-PREFERRED
THE NOMINAL VALUE
IS
THE
PREFERRED
VALUE
LEFT/RIGHT
DIFFERENCE
THE VALUE
Of
THE LEFT SIDE
MINUS THE VALUE
OF
THE
RIGHT SIDE
EX.
If
FT CASTER
- +6 5
RIGHT
CASTER
»
+8.0
LEFT/RIGHT DIFFERENCE
65 8.0
=
1
5
TOE
NEGATIVE TOE (TOE
OUT)
B>A
POSITIVE TOE (TOE
IN) 6
FRONT
Of
VEHICLE
ft
THRUST
ANGLE
ANGLE
OF
REAR
AXLE RELATIVE
TO
VEHICLE CENTERUNE
(+)
AXLE POINTS LEFT
(-)
AXLE POINTS RIGHT
PRODUCTION
TOLERANCE
THE RANGE
Of
ACCEPTABLE
VALUES
AROUND THE NOMINAL
-
PREFERRED PRODUCTION
+6.5A7.5
PREFERRED:
+7.0
TOLERANCE:
0.5
J9302-61
Fig.
1
Wheel
Alignment
Measurements
Page 57 of 1502
2 - 4 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE
•
I
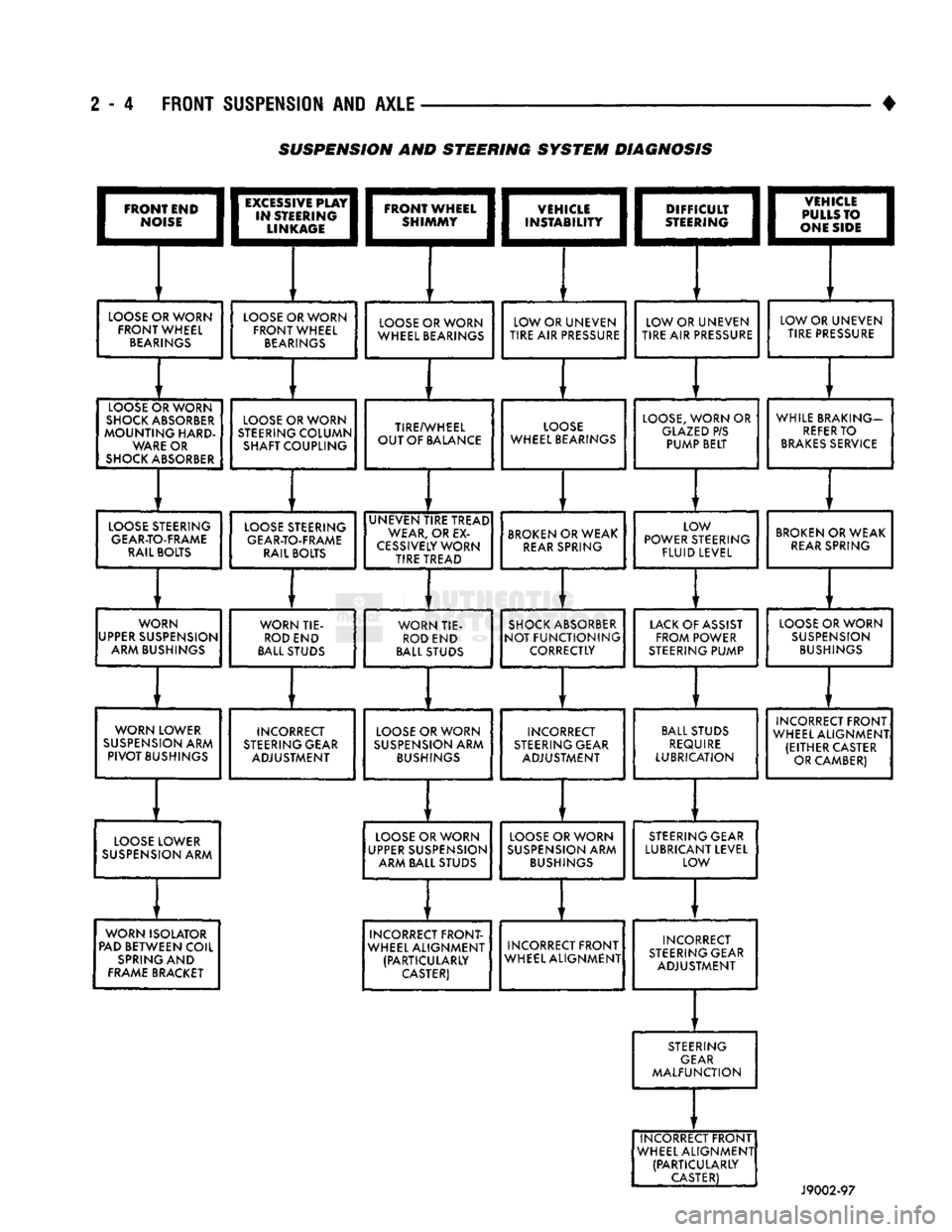
FRONT END
|
|*?£E;
LOOSE
OR WORN
FRONT WHEEL
BEARINGS
LOOSE
C
SHOCKS
MOUNTir
WAR
SHOCK
A )RWORN
JSORBER
nIG
HARD-
E
OR
BSORBER
EXCiSSIVE
PLAY
STEERING
LINKAGE
LOOSE
OR WORN
FRONT WHEEL
BEARINGS
LOOSE
C
STEERINC
SHAFT
C
)RWORN
7
COLUMN
OUPLING
DIFFICULT
STEERING
LOOSE
OR WORN
WHEEL BEARINGS
TIRE/V
OUT OF
f
VHEEL
JA
LANCE
LOW OR UNEVEN
TIRE
AIR
PRESSURE
LO(
WHEEL B
DSE
EARINGS
LOW OR UNEVEN
TIRE AIR
PRESSURE
1vsnciEi
I
1
PULLS
TO I
I
|
ONE SIDE
j
LOOSE,
WORN
OR
GLAZED
P/S PUMP BELT LOW OR UNEVEN
TIRE PRESSURE
WHILE BR
REFE
BRAKES
AKING—
R
TO
SERVICE
LOOSE
STEERING
GEAR-TO-FRAME
RAIL BOLTS
LOOSE
STEERING
GEAR-TO-FRAME
RAIL BOLTS UNEVEN TIRE TREAD
WEAR,
OR
EX
CESSIVELY
WORN TIRE TREAD
BROKEN
OR WEAK
REAR
SPRING LOW
POWER STEERING
FLUID
LEVEL
BROKEN
OR WEAK
REAR
SPRING
WORN
UPPER
SUSPENSION ARM BUSHINGS WORN TIE-
ROD
END
BALL
STUDS WORN TIE-
ROD
END
BALL
STUDS
SHOCK
ABSORBER
NOT FUNCTIONING
CORRECTLY
LACK
OF ASSIST
FROM POWER
STEERING
PUMP
LOOSE
OR WORN
SUSPENSION
BUSHINGS
WORN LOWER
SUSPENSION
ARM
PIVOT
BUSHINGS INCORRECT
STEERING
GEAR ADJUSTMENT
LOOSE
OR WORN
SUSPENSION
ARM
BUSHINGS
INCORRECT
STEERING
GEAR ADJUSTMENT
BALL
STUDS
REQUIRE
LUBRICATION INCORRECT FRONT
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (EITHER CASTER OR CAMBER)
LOOSE
LOWER
SUSPENSION
ARM
LOOSE
OR WORN
UPPER
SUSPENSION ARM BALL STUDS
LOOSE
OR WORN
SUSPENSION
ARM
BUSHINGS
STEERING
GEAR
LUBRICANT LEVEL LOW
WORN ISOLATOR
PAD
BETWEEN COIL
SPRING
AND
FRAME
BRACKET INCORRECT FRONT-
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (PARTICULARLY
CASTER)
INCORRECT FRONT
WHEEL ALIGNMENT INCORRECT
STEERING
GEAR ADJUSTMENT
STEERING
GEAR
MALFUNCTION
INCORRECT FRONT
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (PARTICULARLY
CASTER)
J9002-97
SUSPENSION AND STEERING
SYSTEM
DIAGNOSIS
Page 58 of 1502

•
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 5 (4) Front wheels for excessive radial, lateral
runout and unbalance. Refer to Group 22, Wheels and Tires for diagnosis information.
(5) Suspension components for wear and noise. Check
components for correct torque. Refer to Groups 2 and 3, Suspension and Axle for additional information.
WHEEL
ALIGNMENT
MEASUREMENTS/ADJUSTMENTS
The front wheel alignment positions must be set to
the specified limits. This will prevent abnormal tire
tread wear. The equipment manufacturer's recommenda
tions for use of their
equipment
should always
be followed. All
damaged
front suspension sys
tem components
should
be replaced. Do not at tempt to straighten any
bent
component.
CAMBER AND CASTER-2WD VEHICLES Camber and caster angle adjustments involve repo
sitioning the upper suspension arm cam adjustment
bolts (Fig. 2). Alignment adjustments are accom
plished by loosening the nuts and changing the posi
tion of the cam bolt.
(1) Remove all foreign material from the adjust
ment bolt threads.
(2) Record the camber and caster measurements
before loosening the adjustment bolt nuts.
(3) The camber angle should be adjusted as near as
possible to the preferred angle. The caster should be
the same at both sides of the vehicle. Refer to the Specifications chart.
CAMBER AND CASTER—4WD VEHICLES For 4WD vehicles, the correct wheel camber (verti
cal tilt) angle is factory preset at zero degree (0°).
Camber cannot be altered by adjustment.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to
adjust
the
camber
an
gle by
heating
or bending the axle or any
suspen
sion
component. If camber angle is
incorrect,
the
component(s)
causing
an
incorrect
angle must be replaced.
(1) It is important that the camber (vertical tilt)
angle be the same for both front wheels.
(2) The camber angle should be measured with ac
curate wheel alignment equipment. The acceptable
range is -1° to +1°. Refer to the Specifications chart.
Road test the vehicle and observe the steering
wheel return-to-center position. Before road testing,
check
and
correct
the tire
inflation pressures. Inflate
both
of the front tires
with exactly the
same
pressure.
During the road test, make vehicle turns to both
the left and right. If the steering wheel returns to
ward the center position unassisted, the caster angle is correct. However, if the steering wheel does not re turn toward the center position unassisted, an incor
rect caster angle is probable.
(1) The caster angle is factory preset at positive
two degrees
(
+
2°).
The acceptable range is +1/2° to +
3
1/2°.
(2) The caster angle should be measured with ac
curate wheel alignment equipment.
(3) Caster angle can be adjusted by installing ta
pered shims between the front axle pads and the spring brackets. The caster angle should be adjusted
as near as possible to the preferred angle.
(4) Record the caster measurement before remov
ing the original shims from the spring pads.
(5) The caster should be the same at both sides of
the vehicle. Refer to the Specifications chart.
RN1030
Fig.
2 Caster &
Camber
Adjustment Location—2WD
Vehicles
WHEEL TOE POSITION The wheel toe position adjustment should be the fi
nal front wheel alignment adjustment. In all in stances, follow the equipment manufacturer's
recommended procedure.
(1) Secure the steering wheel with the front wheels
in the straight-ahead position. For vehicles equipped
with power steering, start the engine before straight ening the wheels.
With power steering, the engine should be op
erating during the wheel toe position adjust
ment.
(2) Loosen the tie rod adjustment sleeve clamp
bolts (Fig. 3).
(3) Adjust the wheel toe position by rotating the
tie rod adjustment sleeve (Fig. 3). Rotate each tie-rod end in the direction of
sleeve rotation during the adjustment (Fig. 3).
This will ensure that both tie-rod ends are at the center of their travel.
(4) If applicable, turn the ignition switch off.
Page 68 of 1502

•
FRONT
SUSPENSION
AND
AXLE
2 - 15 Ensure the shock absorber is positioned on the
stud with retainers correctly located (Fig. 2).
(2)
Position the inner retainers on the mounting
studs.
(3) Install the shock on the upper and lower stud
and install the outer retainers.
(4) Install the nuts on the frame bracket and axle
(Fig. 2). (5) Tighten the shock absorber upper and lower
nuts;
• Standard shock upper and lower nut to 75 Nnn (55
ft. lbs.) torque
• Air-adjustable shock upper nut to 75 N»m (55 ft. lbs.) torque, lower nut to 271 Nnn (200 ft. lbs.)
torque
CAUTION:
Vehicles
with
air
shocks MUST
maintain
a
minimum
pressure
of 10 to 15 psi (70 to 105 kPa). Operation below the specified minimum
pressures
may cause damage.
(6) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
LEAF
SPRINGS
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the frame until all weight is
removed from the front springs. (2) With the front tires in contact with the surface,
position support stands under the frame side rails. (3) Remove the nuts, lockwashers, U-bolts that at
tach the spring to the axle shaft tubes (Fig. 3).
SPRING
BRACKET SPRING
BRACKET SPRING
SHACKLE
PLATE
FRONT
SPRING
AXLE
TUBE U-BOLT LEFT
SIDE
J9017-33
Fig.
3 Front
Suspension
(4) Remove the spring front eye pivot nut and bolt,
rear spring shackle nuts, shackle plates. Remove the spring from the vehicle (Fig. 3).
INSTALLATION
(1) Align the spring front eye with the bolt hole in
the frame bracket and install the pivot bolt and nut (Fig. 3). (2) Position the shackle plates at the spring rear
eye and frame rail bracket. Install the nuts (Fig. 3). (3) Tighten the shackle plate nuts and front pivot
bolt nut until all slack is taken up. (4) Position the spring on the axle tube with the
spring center bolt seated in locating hole in axle tube
pad (Fig. 3).
(5) Install the U-bolts, new lockwashers and nuts.
(6) Tighten the nuts snug against the spring
bracket.
(7) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle
with the weight being supported by the tires. (8) Tighten the spring nuts according to the follow
ing specifications:
• Model 44 Axle: U-bolt/Stud nuts - 115 Nnn (85 ft. lbs.) torque
Front pivot bolt/nut — 135 Nnn (100 ft. lbs.) torque
Rear shackle bolt/nut — 81 Nnn (60 ft. lbs.) torque
• Model 60 Axle: U-bolt nuts - 129 Nnn (95 ft. lbs.) torque Front pivot bolt/nut - 135 Nnn (100 ft. lbs.) torque
Rear shackle bolt/nut - 108 Nnn (80 ft. lbs.)
torque
SPRING LEAF-REPLACEMENT
If a spring has acquired a set (lost significant
height), it should be replaced. (1) Remove the spring from the vehicle. If neces
sary, refer to the removal procedure. (2) Remove the spring leaf alignment clips.
(3) Clamp the spring in a vise. Remove the nut
and center bolt (Fig. 4).
SPRING
CENTER
RATCHET
AND
SOCKET
WRENCH
Fig.
4 Leaf
Spring
Disassembly
(4) Insert a long drift or punch into the center bolt
hole and slowly release the vise jaws.