1990 MITSUBISHI SPYDER check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 136 of 2103
ENGINE OVERHAUL Rocker, Arms
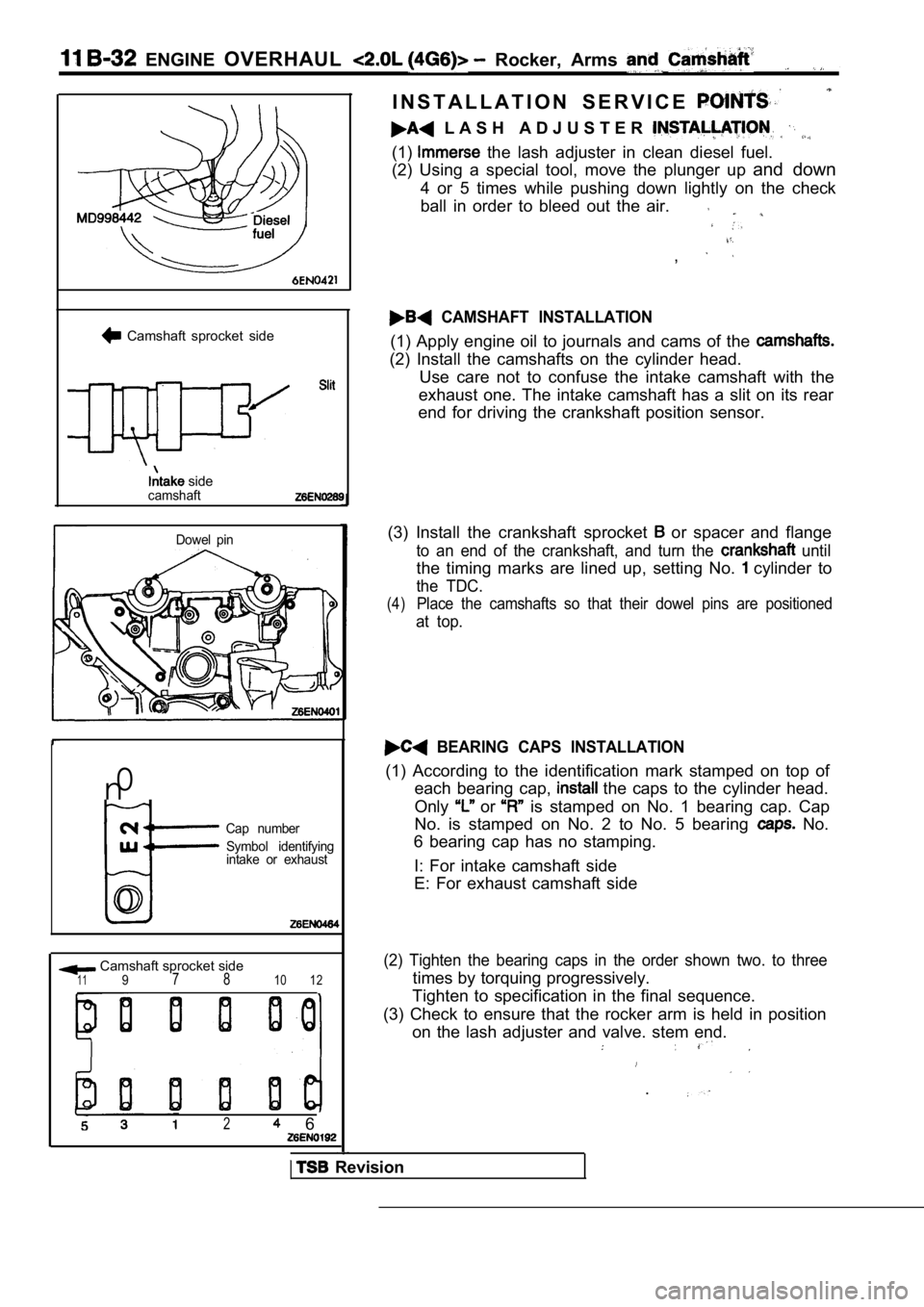
Camshaft sprocket side
sidecamshaft
Dowel pin
n0
Cap number
Symbol identifying
intake or exhaust
0
Camshaft sprocket side1197 810 12
2 6
I N S T A L L A T I O N S E R V I C E
L A S H A D J U S T E R
(1) the lash adjuster in clean diesel fuel.
(2) Using a special tool, move the plunger up and down
4 or 5 times while pushing down lightly on the chec k
ball in order to bleed out the air.
,
CAMSHAFT INSTALLATION
(1) Apply engine oil to journals and cams of the
(2) Install the camshafts on the cylinder head. Use care not to confuse the intake camshaft with th e
exhaust one. The intake camshaft has a slit on its rear
end for driving the crankshaft position sensor.
(3) Install the crankshaft sprocket
or spacer and flange
to an end of the crankshaft, and turn the until
the timing marks are lined up, setting No. cylinder to
the TDC.
(4)Place the camshafts so that their dowel pins are po sitioned
at top.
BEARING CAPS INSTALLATION
(1) According to the identification mark stamped on top of
each bearing cap,
the caps to the cylinder head.
Only
or is stamped on No. 1 bearing cap. Cap
No. is stamped on No. 2 to No. 5 bearing
No.
6 bearing cap has no stamping.
I: For intake camshaft side
E: For exhaust camshaft side
(2) Tighten the bearing caps in the order shown two . to three
times by torquing progressively.
Tighten to specification in the final sequence.
(3) Check to ensure that the rocker arm is held in position
on the lash adjuster and valve. stem end.
.
Revision
Page 138 of 2103
11 ENGINE OVERHAUL Rocker
.
INSPECTION
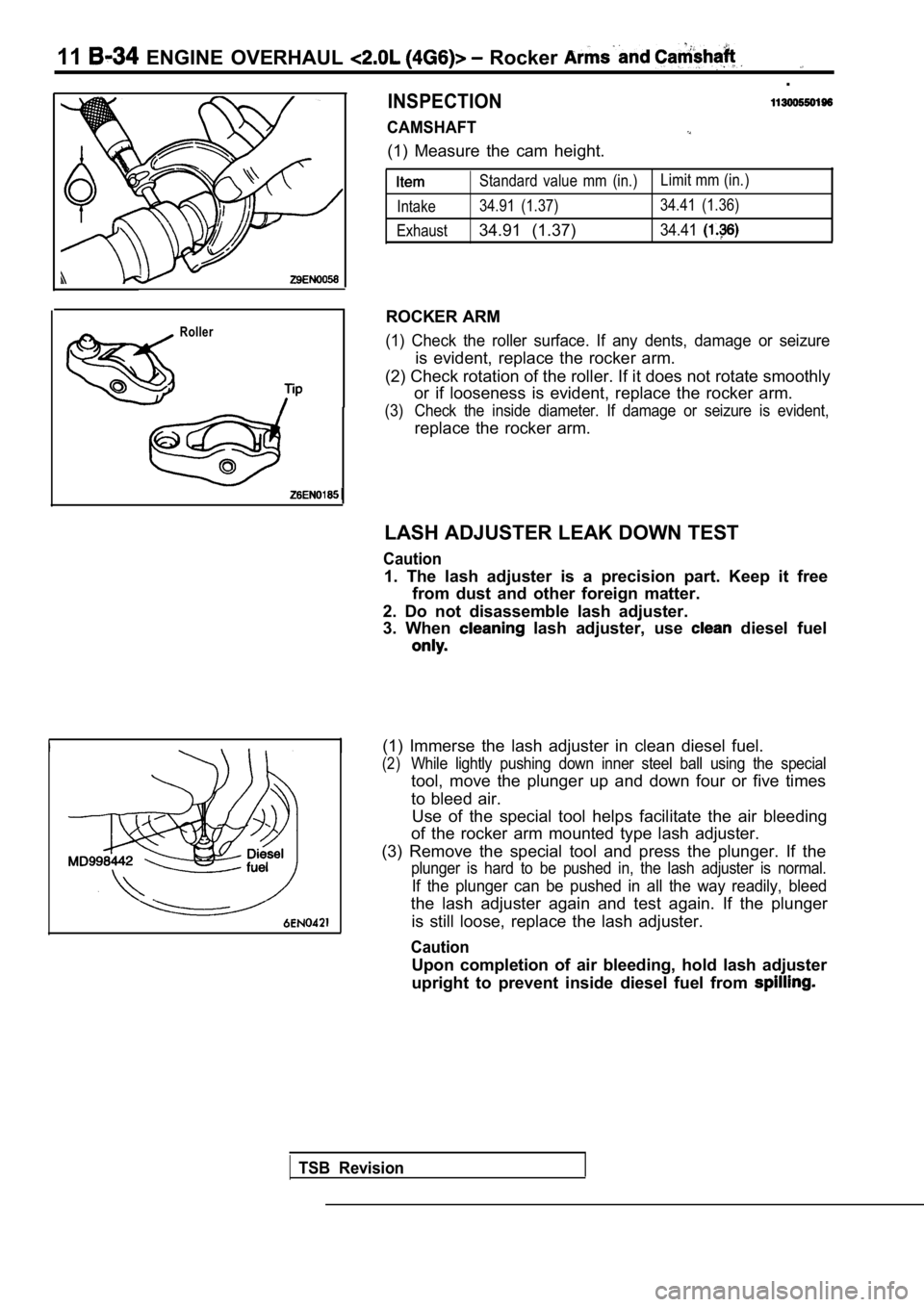
CAMSHAFT
(1) Measure the cam height.
Roller
Standard value mm (in.)Limit mm (in.)
Intake 34.91 (1.37) 34.41 (1.36)
Exhaust
34.91 (1.37)34.41
ROCKER ARM
(1) Check the roller surface. If any dents, damage or seizure
is evident, replace the rocker arm.
(2) Check rotation of the roller. If it does not ro tate smoothly
or if looseness is evident, replace the rocker arm.
(3) Check the inside diameter. If damage or seizure is evident,
replace the rocker arm.
LASH ADJUSTER LEAK DOWN TEST
Caution
1. The lash adjuster is a precision part. Keep it f ree
from dust and other foreign matter.
2. Do not disassemble lash adjuster.
3. When
lash adjuster, use diesel fuel
(1) Immerse the lash adjuster in clean diesel fuel.
(2)While lightly pushing down inner steel ball using t he special
tool, move the plunger up and down four or five tim es
to bleed air. Use of the special tool helps facilitate the air bl eeding
of the rocker arm mounted type lash adjuster.
(3) Remove the special tool and press the plunger. If the
plunger is hard to be pushed in, the lash adjuster is normal.
If the plunger can be pushed in all the way readily, bleed
the lash adjuster again and test again. If the plun ger
is still loose, replace the lash adjuster.
Caution
Upon completion of air bleeding, hold lash adjuster
upright to prevent inside diesel fuel from
TSB Revision
Page 143 of 2103
ENGINE OVERHAUL Cylinder Head and
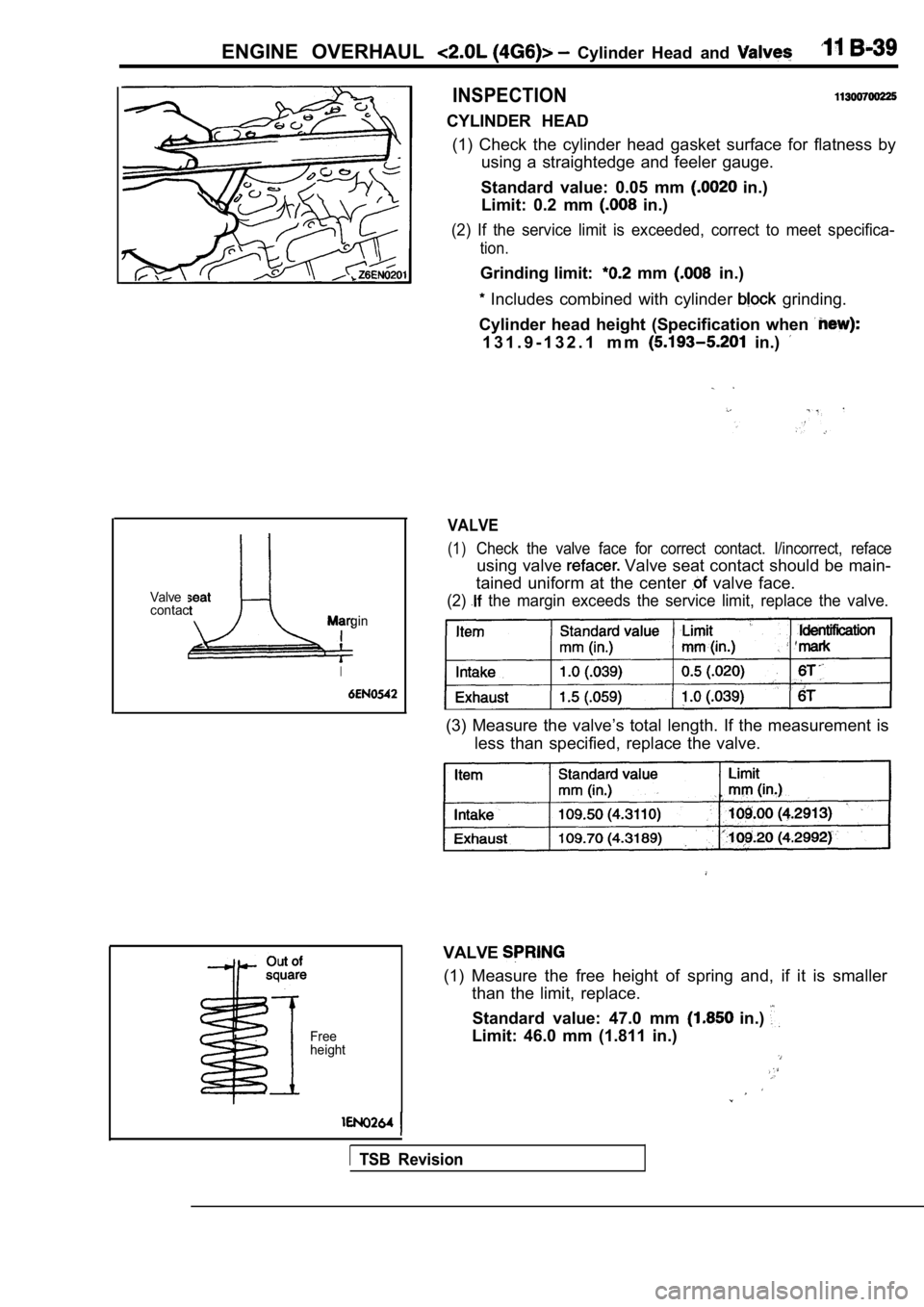
Valve seat
contact
Margin
I
I
Free
height
INSPECTION
CYLINDER HEAD (1) Check the cylinder head gasket surface for flat ness by
using a straightedge and feeler gauge.
Standard value: 0.05 mm
in.)
Limit: 0.2 mm
in.)
(2) If the service limit is exceeded, correct to me et specifica-
tion.
Grinding limit: mm in.)
Includes combined with cylinder grinding.
Cylinder head height (Specification when
1 3 1 . 9 - 1 3 2 . 1 m m in.)
VALVE
(1)Check the valve face for correct contact. I/incorre ct, reface
using valve Valve seat contact should be main-
tained uniform at the center
valve face.
(2) the margin exceeds the service limit, replace the valve.
(3) Measure the valve’s total length. If the measurement is
less than specified, replace the valve.
VALVE
(1) Measure the free height of spring and, if it is smaller
than the limit, replace.
Standard value: 47.0 mm
in.)
Limit: 46.0 mm (1.811 in.)
TSB Revision
Page 144 of 2103
ENGINE OVERHAUL Head and
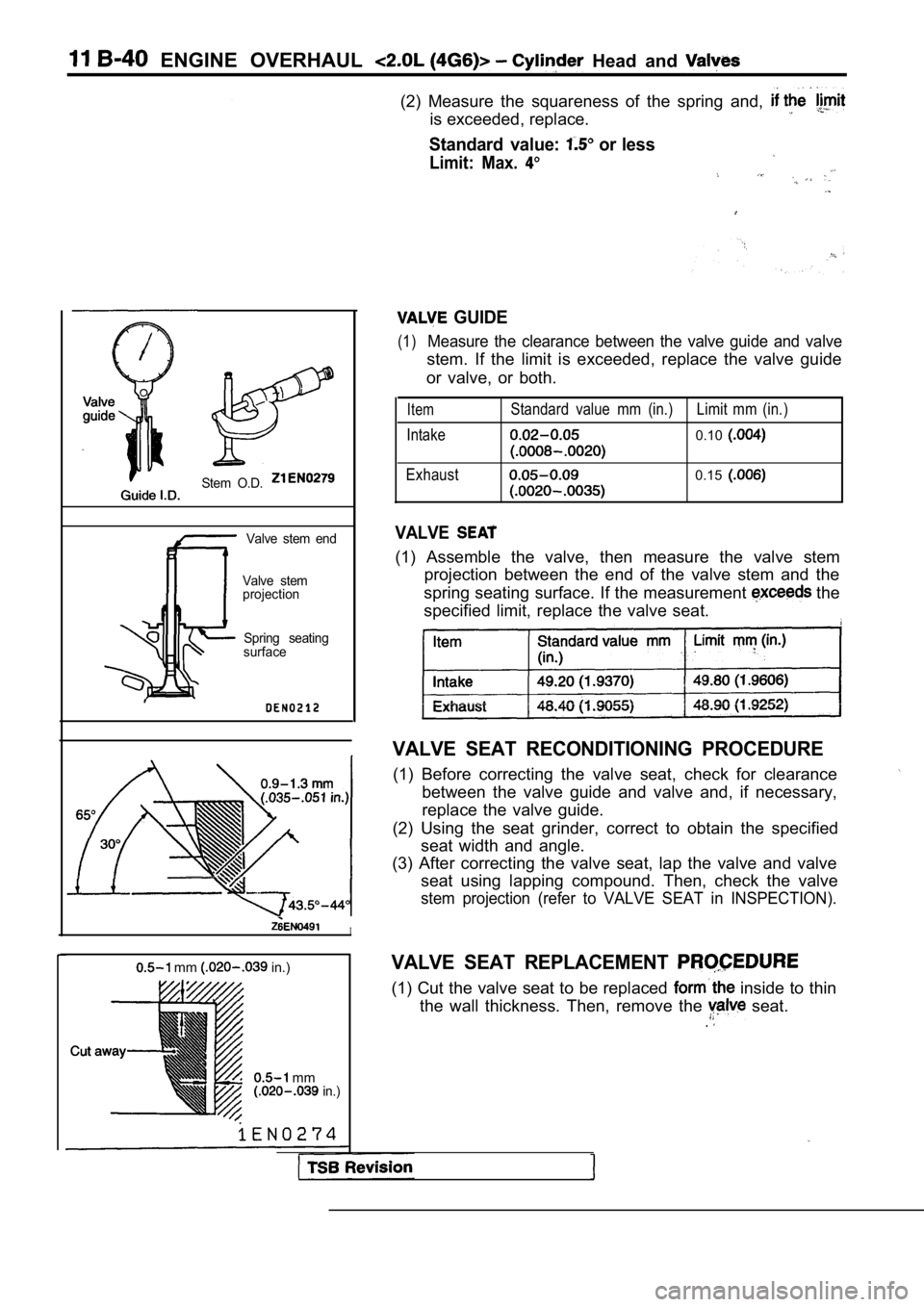
(2) Measure the squareness of the spring and,
is exceeded, replace.
Standard value: or less
Limit: Max.
Stem O.D.
Valve stem end
Valve stem
projection
Spring seating
surface
GUIDE
(1)Measure the clearance between the valve guide and v alve
stem. If the limit is exceeded, replace the valve guide
or valve, or both.
Item
Intake
Exhaust Standard value mm (in.) Limit mm (in.)0.10
0.15
VALVE
(1) Assemble the valve, then measure the valve stem
projection between the end of the valve stem and th e
spring seating surface. If the measurement
the
specified limit, replace the valve seat.
VALVE SEAT RECONDITIONING PROCEDURE
(1) Before correcting the valve seat, check for cle arance
between the valve guide and valve and, if necessary ,
replace the valve guide.
(2) Using the seat grinder, correct to obtain the s pecified
seat width and angle.
(3) After correcting the valve seat, lap the valve and valve
seat using lapping compound. Then, check the valve
stem projection (refer to VALVE SEAT in INSPECTION) .
VALVE SEAT REPLACEMENT
(1) Cut the valve seat to be replaced inside to thin
the wall thickness. Then, remove the
seat..
I
mm in.)
mm in.)
Page 145 of 2103
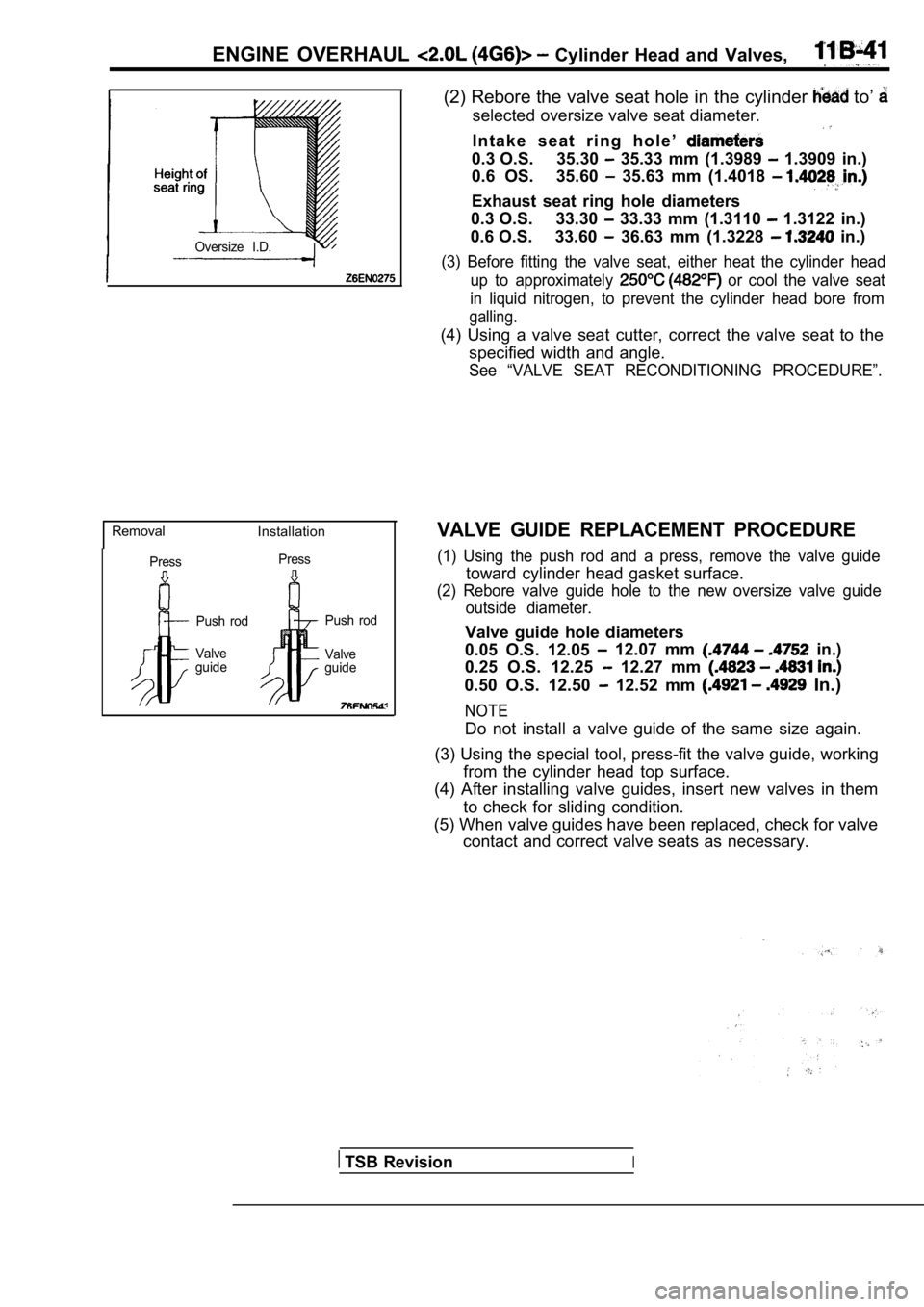
ENGINE OVERHAUL Cylinder Head and Valves,
Oversize I.D.
RemovalInstallation
PressPress
Push rod
Valve
guide Push rod
Valve
guide
(2) Rebore the valve seat hole in the cylinder to’
selected oversize valve seat diameter.
I n t a k e s e a t r i n g h o l e ’
0.3 O.S. 35.30 35.33 mm (1.3989 1.3909 in.)
0.6 OS. 35.60
35.63 mm (1.4018
Exhaust seat ring hole diameters
0.3 O.S. 33.30
33.33 mm (1.3110 1.3122 in.)
0.6 O.S. 33.60
36.63 mm (1.3228 in.)
(3) Before fitting the valve seat, either heat the cylinder head
up to approximately
or cool the valve seat
in liquid nitrogen, to prevent the cylinder head bo re from
galling.
(4) Using a valve seat cutter, correct the valve seat to the
specified width and angle.
See “VALVE SEAT RECONDITIONING PROCEDURE”.
VALVE GUIDE REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Using the push rod and a press, remove the valv e guide
toward cylinder head gasket surface.
(2) Rebore valve guide hole to the new oversize valve guide
outside diameter.
Valve guide hole diameters
0.05 O.S. 12.05
12.07 mm in.)
0.25 O.S. 12.25
12.27 mm
0.50 O.S. 12.50 12.52 mm In.)
NOTE
Do not install a valve guide of the same size again .
(3) Using the special tool, press-fit the valve gui de, working
from the cylinder head top surface.
(4) After installing valve guides, insert new valve s in them
to check for sliding condition.
(5) When valve guides have been replaced, check for valve
contact and correct valve seats as necessary.
TSB RevisionI
Page 154 of 2103

Front Case, Counterbalance
ENGINE Shaft and
INSPECTION
FRONT CASE
(1) Check oil holes for clogging and if necessary.
(2)’ Check left counterbalance shaft front bearing
for
Wear, damage and seizure. If there is anything wron g’
with the section, replace the front
(3) Check the front case for cracks and other damag e.
place cracked or damaged front case.
OIL SEAL
(1) Check the oil seal lip for wear and damage. Rep lace
oil seal if necessary.
(2) Check the oil seal lip for deterioration. Repla ce oil seal
if necessary.
I
COUNTERBALANCE SHAFT
(1) Check oil holes for clogging.
(2) Check journal for seizure, damage and contact w ith bear-
ing. If there is anything wrong with the journal, replace
counterbalance shaft, bearing or front case assembl y.
OIL PUMP
(1) Assemble the oil pump gear to the front case an d rotate
it to ensure smooth rotation with no looseness.
(2) Ensure that there is no ridge wear on the conta ct surface
between the front case and the gear surface of the oil
pump cover.
(3) Check the side clearance.
Standard value: Drive gear
mm
Driven gear mm in.)
TSB Revision
Page 157 of 2103
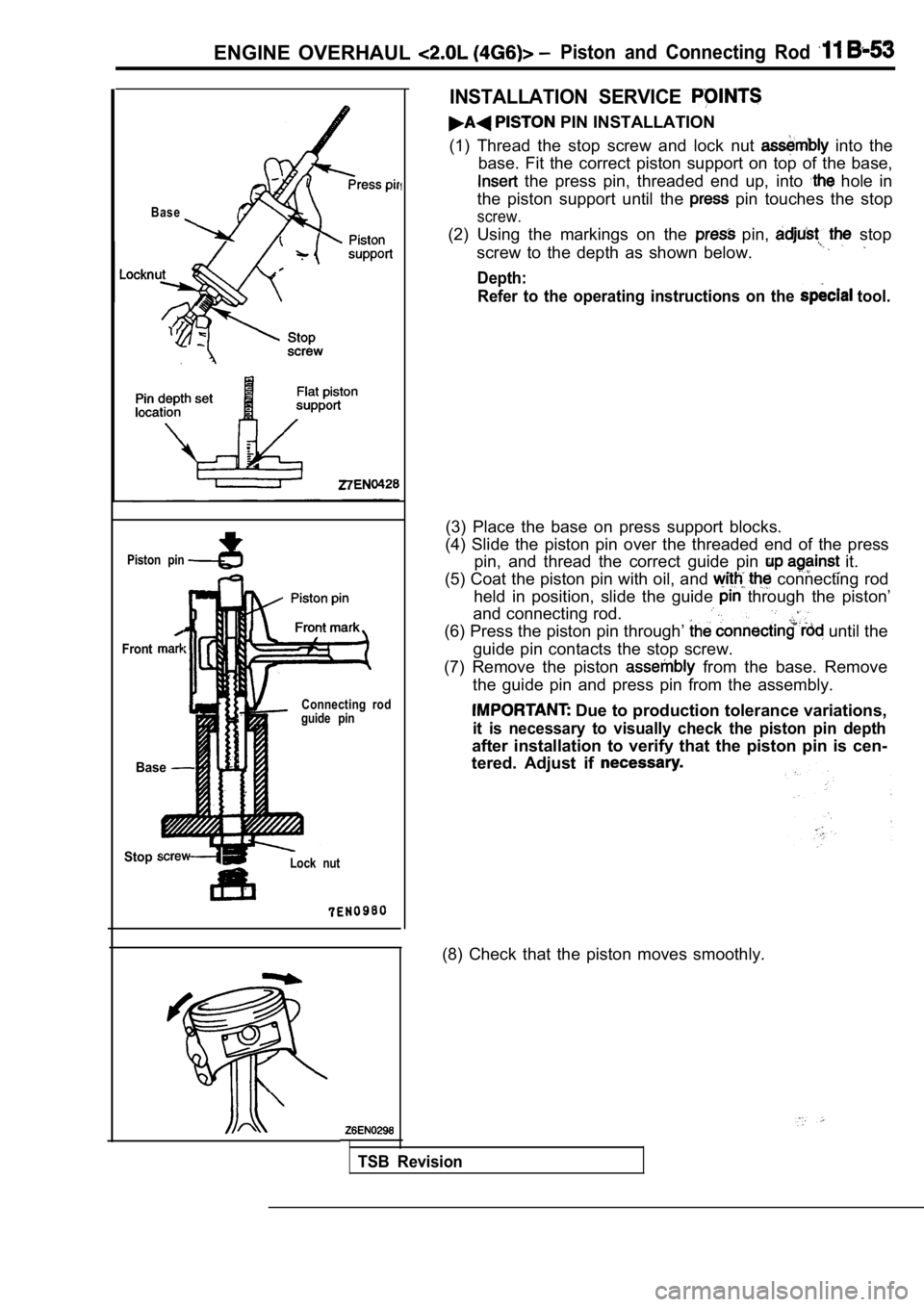
ENGINE OVERHAUL Piston and Connecting Rod
Piston pin
Base
Front
Base
Connecting rod
guide pin
StopLock nut
1
INSTALLATION SERVICE
PIN INSTALLATION
(1) Thread the stop screw and lock nut
into the
base. Fit the correct piston support on top of the base,
the press pin, threaded end up, into hole in
the piston support until the
pin touches the stop
screw.
(2) Using the markings on the pin, stop
screw to the depth as shown below.
Depth: Refer to the operating instructions on the
tool.
(3) Place the base on press support blocks.
(4) Slide the piston pin over the threaded end of t he press
pin, and thread the correct guide pin
it.
(5) Coat the piston pin with oil, and
connecting rod
held in position, slide the guide
through the piston’
and connecting rod.
(6) Press the piston pin through’ until the
guide pin contacts the stop screw.
(7) Remove the piston
from the base. Remove
the guide pin and press pin from the assembly.
Due to production tolerance variations,
it is necessary to visually check the piston pin de pth
after installation to verify that the piston pin is cen-
tered. Adjust if
(8) Check that the piston moves smoothly.
TSB Revision
Page 159 of 2103
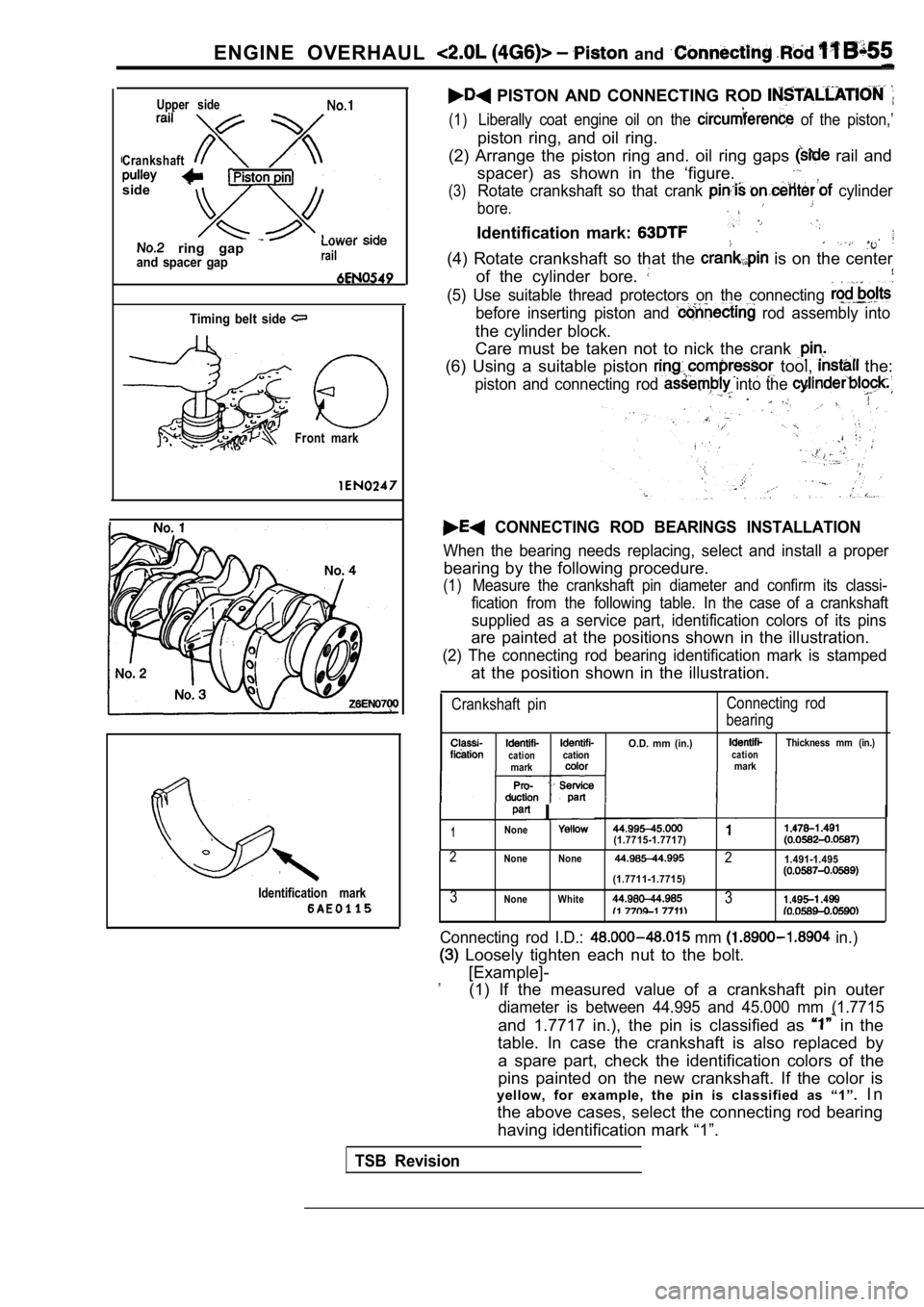
ENGINE OVERHAUL and
CrankshaftUpper side
side
ring gap and spacer gaprail
Timing belt side
Front mark
Identification mark
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD
(1)Liberally coat engine oil on the of the piston,’
piston ring, and oil ring.
(2) Arrange the piston ring and. oil ring gaps
rail and
spacer) as shown in the ‘figure.
(3)Rotate crankshaft so that crank cylinder
bore.
Identification mark:
(4) Rotate crankshaft so that the is on the center
of the cylinder bore.
(5) Use suitable thread protectors on the connectin g
before inserting piston and rod assembly into
the cylinder block.
Care must be taken not to nick the crank
(6) Using a suitable piston tool, the:
piston and connecting rod into the ,
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS INSTALLATION
When the bearing needs replacing, select and instal l a proper
bearing by the following procedure.
(1)Measure the crankshaft pin diameter and confirm its classi-
fication from the following table. In the case of a crankshaft
supplied as a service part, identification colors of its pins
are painted at the positions shown in the illustrat ion.
(2) The connecting rod bearing identification mark is stamped
at the position shown in the illustration.
Crankshaft pinConnecting rod
bearing
O.D. mm (in.)Thickness mm (in.)cationcationcationmarkmark
I
1None(1.7715-1.7717)
2None None21.491-1.495
(1.7711-1.7715)
3None White3
Connecting rod I.D.: mm in.)
Loosely tighten each nut to the bolt.
[Example]-
”(1) If the measured value of a crankshaft pin outer
diameter is between 44.995 and 45.000 mm (1.7715
and 1.7717 in.), the pin is classified as in the
table. In case the crankshaft is also replaced by
a spare part, check the identification colors of th e
pins painted on the new crankshaft. If the color is
yellow, for example, the pin is classified as “1”. I n
the above cases, select the connecting rod bearing having identification mark “1”.
TSB Revision