1988 PONTIAC FIERO distributor
[x] Cancel search: distributorPage 397 of 1825
6A3-18 V-8 ENGINE
bore, remove remover and installer tool and
bearing from puller screw.
5. Remove remaining bearings (except front and
rear) in the same manner. It will be necessary to
index pilot in camshaft rear bearing to remove the
rear intermediate bearing.
6. Assemble remover
and installer tool on driver
handle and remove camshaft front and rear
bearings by driving towards center of cylinder
block.
lnstallation
The camshaft front and rear bearings should be
installed first. These bearings will act as guides for the
pilot and center the remaining bearings being pulled
into place.
1. Assemble remover
and installer tool on driver
handle and install camshaft front and rear
bearings by driving towards center of cylinder
block.
2. Using Tool Set J-6098, with nut then thrust
washer installed to end of threads, index pilot in
camshaft front bearing and install puller screw
through pilot.
3. Index camshaft bearing in bore (with oil hole
aligned as outlined below), then install remover
and installer tool on puller screw with shoulder
toward bearing.
e Number one cam bearing oil hole must be
positioned so that oil holes are equidistant
from 6 o'clock position.
e Number two through number four bearing
oil holes must be positioned at 5 o'clock
position (toward left side of engine and at a
position even with bottom of cylinder bore).
e Number five bearing oil hole must be in 12
o'clock position.
4. Using two wrenches, hold puller screw while
turning nut. After bearing has been pulled into
bore, remove the remover and installer tool from
puller screw and check alignment of oil hole in
camshaft bearing.
5. Install remaining bearings in the same manner. It
will be necessary to index pilot in the camshaft
rear bearing to install the rear intermediate
bearing.
6. Coat new camshaft rear plug O.D. with
# 1052080 sealant, or equivalent, and install
flush to 1/32"
(.80mm) deep.
OIL PAN
Removal
1. Disconnect battery negative cable.
2. Remove fan shroud.
3. Remove air cleaner and lay aside if equipped.
4. Remove distributor cap and lay aside.
5. Raise vehicle.
6. Drain crankcase.
7. Disconnect exhaust pipe at manifold.
8. Disconnect AIR pipe clamp.
9. Disconnect converter hanger bolts and allow
exhaust to hang down.
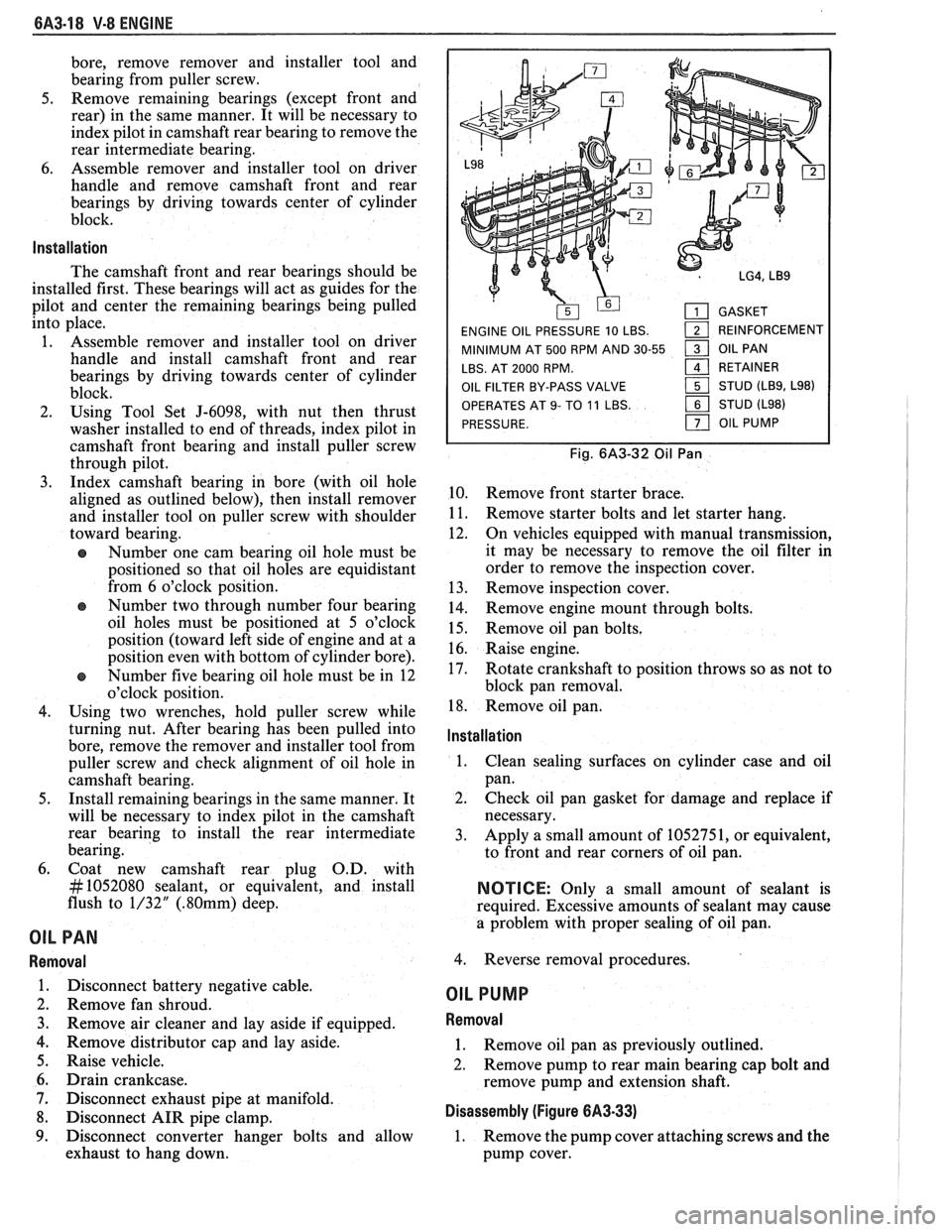
GASKET
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE 10 LBS.
1 REINFORCEMENT
MINIMUM AT 500 RPM AND 30-55
1 OIL PAN
LBS. AT 2000 RPM.
161 RETAINER
OIL FILTER BY-PASS VALVE STUD
(LB9, L98)
OPERATES
AT 9- TO 11 LBS. STUD (L98)
PRESSURE.
OIL PUMP
Fig. 6A3-32 Oil Pan
10. Remove front starter brace.
11. Remove starter bolts and let starter hang.
12. On vehicles equipped with manual transmission,
it may be necessary to remove the oil filter in
order to remove the inspection cover.
13. Remove inspection cover.
14. Remove engine mount through bolts.
15. Remove oil pan bolts.
16. Raise engine.
17. Rotate crankshaft to position throws so as not to
block pan removal.
18. Remove oil pan.
lnstallation
1.
Clean sealing surfaces on cylinder case and oil
pan.
2. Check oil pan gasket for damage and replace if
necessary.
3. Apply a small amount of 1052751, or equivalent,
to front and rear corners of oil pan.
NOTICE: Only a small amount of sealant is
required. Excessive amounts of sealant may cause
a problem with proper sealing of oil pan.
4. Reverse removal procedures.
OIL PUMP
Removal
1. Remove oil pan as previously outlined.
2. Remove pump to rear main bearing cap bolt and
remove pump and extension shaft.
Disassembly (Figure 6A3-33)
1. Remove the pump cover attaching screws and the
pump cover.
Page 398 of 1825
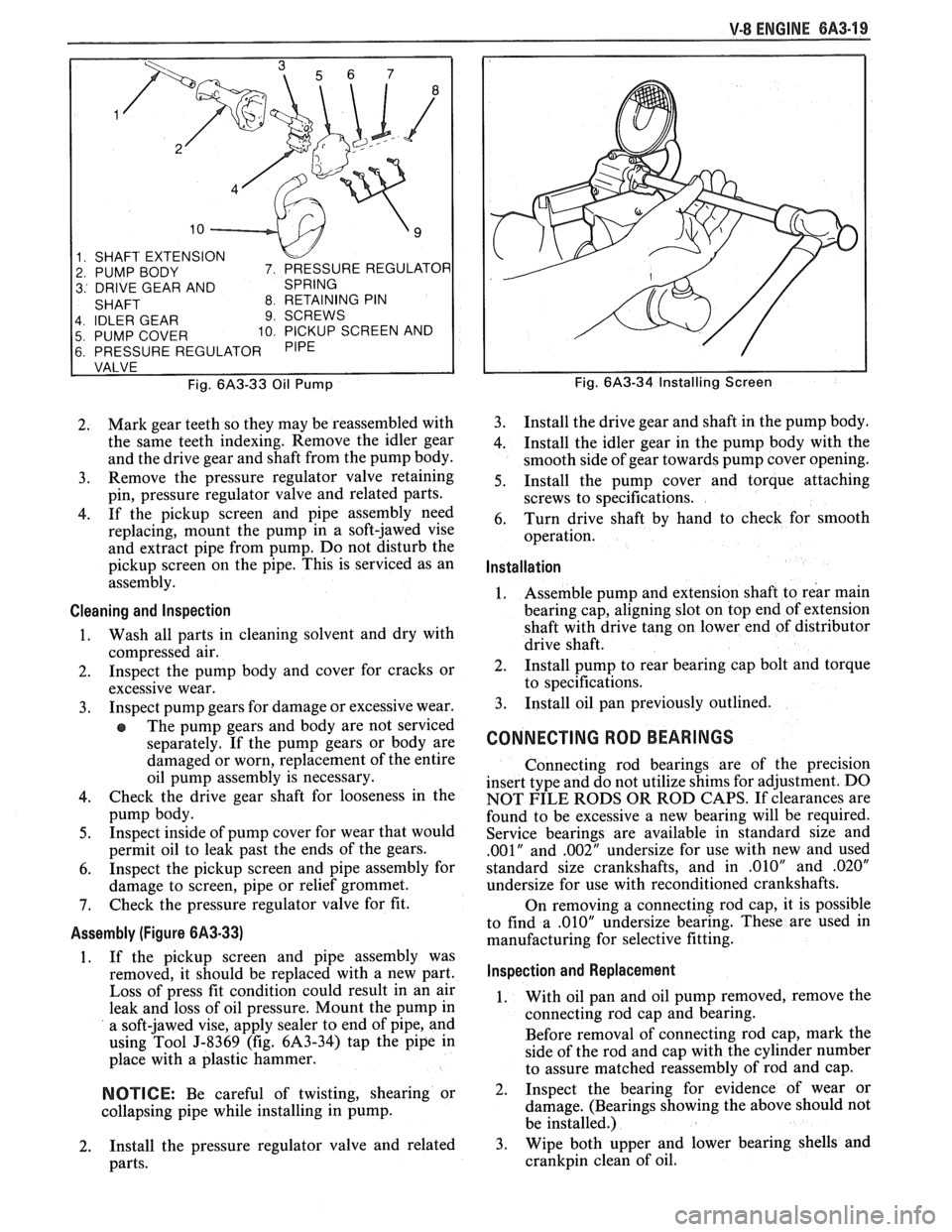
V-8 ENGINE 6A3-19
1 SHAFT EXTENSION
2 PUMP BODY
3 DRIVE GEAR AND
4 IDLER GEAR
9 SCREWS
5 PUMP COVER 10 PICKUP SCREEN AND
6 PRESSURE REGULATOR
Fig.
6A3-33 Oil Pump
2. Mark
gear teeth so they may be reassembled with
the same teeth indexing. Remove the idler gear
and the drive gear and shaft from the pump body.
3. Remove
the pressure regulator valve retaining
pin, pressure regulator valve and related parts.
4. If the pickup screen and pipe assembly need
replacing, mount the pump in a soft-jawed vise
and extract pipe from pump. Do not disturb the
pickup screen on the pipe. This is serviced as an
assembly.
Cleaning and lnspection
1. Wash all parts in cleaning solvent and dry with
compressed air.
2. Inspect the pump body and cover for cracks or
excessive wear.
3. Inspect
pump gears for damage or excessive wear.
The pump gears and body are not serviced
separately. If the pump gears or body are
damaged or worn, replacement of the entire
oil pump assembly is necessary.
4. Check the drive gear shaft for looseness in the
pump body.
5. Inspect inside of pump cover for wear that would
permit oil to leak past the ends of the gears.
6. Inspect the pickup screen and pipe assembly for
damage to screen, pipe or relief grommet.
7. Check the pressure regulator valve for fit.
Assembly (Figure 6A3-33)
1. If
the pickup screen and pipe assembly was
removed, it should be replaced with a new part.
Loss of press fit condition could result in an air
leak and loss of oil pressure. Mount the pump in
a soft-jawed vise, apply sealer to end of pipe, and
using Tool J-8369 (fig. 6A3-34) tap the pipe in
place with a plastic hammer.
NOTICE: Be careful of twisting, shearing or
collapsing pipe while installing in pump.
2. Install the
pressure regulator valve and related
parts.
Fig. 6A3-34 Installing Screen
3. Install the drive gear and shaft in the pump body.
4. Install
the idler gear in the pump body with the
smooth side of gear towards pump cover opening.
5. Install the pump cover and torque attaching
screws to specifications.
6. Turn
drive shaft by hand to check for smooth
operation.
Installation
1. Assemble
pump and extension shaft to rear main
bearing cap, aligning slot on top end of extension
shaft with drive tang on lower end of distributor
drive shaft.
2. Install
pump to rear bearing cap bolt and torque
to specifications.
3. Install
oil pan previously outlined.
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
Connecting rod bearings are of the precision
insert type and do not utilize shims for adjustment. DO
NOT FILE RODS OR ROD CAPS. If clearances are
found to be excessive a new bearing will be required.
Service bearings are available in standard size and
.001" and ,002" undersize for use with new and used
standard size crankshafts, and in
.010" and .020"
undersize for use with reconditioned crankshafts.
On removing a connecting rod cap, it is possible
to find a
.010" undersize bearing. These are used in
manufacturing for selective fitting.
lnspection and Replacement
1. With
oil pan and oil pump removed, remove the
connecting rod cap and bearing.
Before removal of connecting rod cap, mark the
side of the rod and cap with the cylinder number
to assure matched reassembly of rod and cap.
2. Inspect
the bearing for evidence of wear or
damage. (Bearings showing the above should not
be installed.)
3. Wipe both upper and lower bearing shells and
crankpin clean of oil.
Page 406 of 1825

V-8 ENGINE 6A3-27
3. When finish honing
a cylinder bore to fit a piston,
the hone should be moved up and down at a
sufficient speed to obtain very fine uniform
surface finish marks in a cross-hatch pattern of
approximately
45" to 65" included angle. The
finish marks should be clean but not sharp, free
from imbedded particles and torn or folded
metal.
4. Permanently mark
the piston for the cylinder to
which it has been fitted and proceed to hone
cylinders and fit the remaining pistons.
NOTICE: Handle the pistons with care and do not
attempt to force them through the cylinder until
the cylinder has been honed to correct size as this
type piston can be distorted through careless
handling.
5. Thoroughly
clean the bores with hot water and
detergent. Scrub well with a stiff bristle brush and
rinse thoroughly with hot water. It is extremely
essential that a good cleaning operation be
performed. If any of the abrasive material is
allowed to remain in the cylinder bores, it will
rapidly wear the new rings and cylinder bores in
addition to the bearings lubricated by the
contaminated oil, the bores should be swabbed
and then wiped with a clean dry cloth. Cylinder
should not be cleaned with kerosene or gasoline.
Clean the remainder of the cylinder block to
remove the excess material spread during the
honing operation.
Piston Selection
1. Check USED piston to cylinder bore clearance as
follows:
a. Measure
the "Cylinder Bore Diameter"
with a telescope gage
"2-1/2" (64mm) from
top of cylinder bore").
b. Measure
the
"Piston Diameter" (at skirt
across center line of piston pin).
c. Subtract
piston diameter from cylinder bore
diameter to determine "Piston to Bore
Clearance".
d. Determine if piston to bore clearance is in
the acceptable range.
2. If
used piston is not acceptable, check Piston Size
Chart and determine if a new piston can be
selected to fit cylinder bore within the acceptable
range.
3. If
cylinder bore must be reconditioned, measure
new piston diameter (across center line of piston
pin) then hone cylinder bore to correct clearance
(preferable range).
4. Mark the piston to identify the cylinder for which
it was fitted.
OIL FILTER BYPASS VALVE
Inspection and Replacement
With the oil filter removed, check the spring and
fibre valve for operation. Inspect for a cracked or
broken valve. If replacement is necessary, the oil filter
adapter and bypass valve assembly must be replaced as an
assembly. Clean valve chamber in cylinder block
thoroughly. Torque retaining screws to specifications.
ENGINE ASSEMBLY
Removal
1. Disconnect battery.
2. Remove air cleaner.
3. Remove hood.
4. Drain radiator.
5. Remove lower radiator hose.
6. Remove upper fan shroud.
7. Remove upper radiator hose and coolant
recovery hose.
8. Remove transmission cooler lines.
9. Remove radiator.
10. Remove fan assembly.
1 1. Remove heater hoses.
12. Disconnect
carburetor linkage, includes cruise
control detent cable.
13. Remove vacuum brake booster line.
14. Remove
distributor cap and lay wiring aside.
15. Disconnect necessary wires and hoses.
16. Remove power steering
pump and lay aside.
17. Raise vehicle.
18. Remove exhaust
pipes at exhaust manifold.
19. Remove dust cover.
20. Remove converter bolts.
2 1. Disconnect starter wires.
22. Remove bell housing bolts.
23. Remove
motor mount through bolts.
24. Disconnect fuel lines
at fuel pump.
25. Lower vehicle.
26. Support transmission.
27. Remove
A.I.R./Converter pipe bracket.
28. Remove engine, include removing wire
from
bracket at rear left of engine.
Installation
1. Position engine
assembly in vehicle.
2. Attach
motor mount to engine brackets and
lower engine in place.
3. Remove engine lifting device.
4. Remove transmission floor jack.
5. Raise vehicle on hoist.
6. Install mount "through" bolts. Torque to
specifications.
7. Install bell housing bolts. Torque to
specifications.
8. On vehicles with automatic transmissions, install
I
converter to flywheel attaching bolts. Torque to
specifications.
9. Install flywheel splash shield of converter
housing cover as applicable. Torque attaching
bolts to specifications.
I
10. Install starter wires.
1 1. Connect fuel lines.
12. Connect exhaust pipe at manifold.
13. Lower vehicle on hoist.
14. Reinstall power steering pump, if so equipped.
15. Connect necessary wires and hoses.
Page 410 of 1825
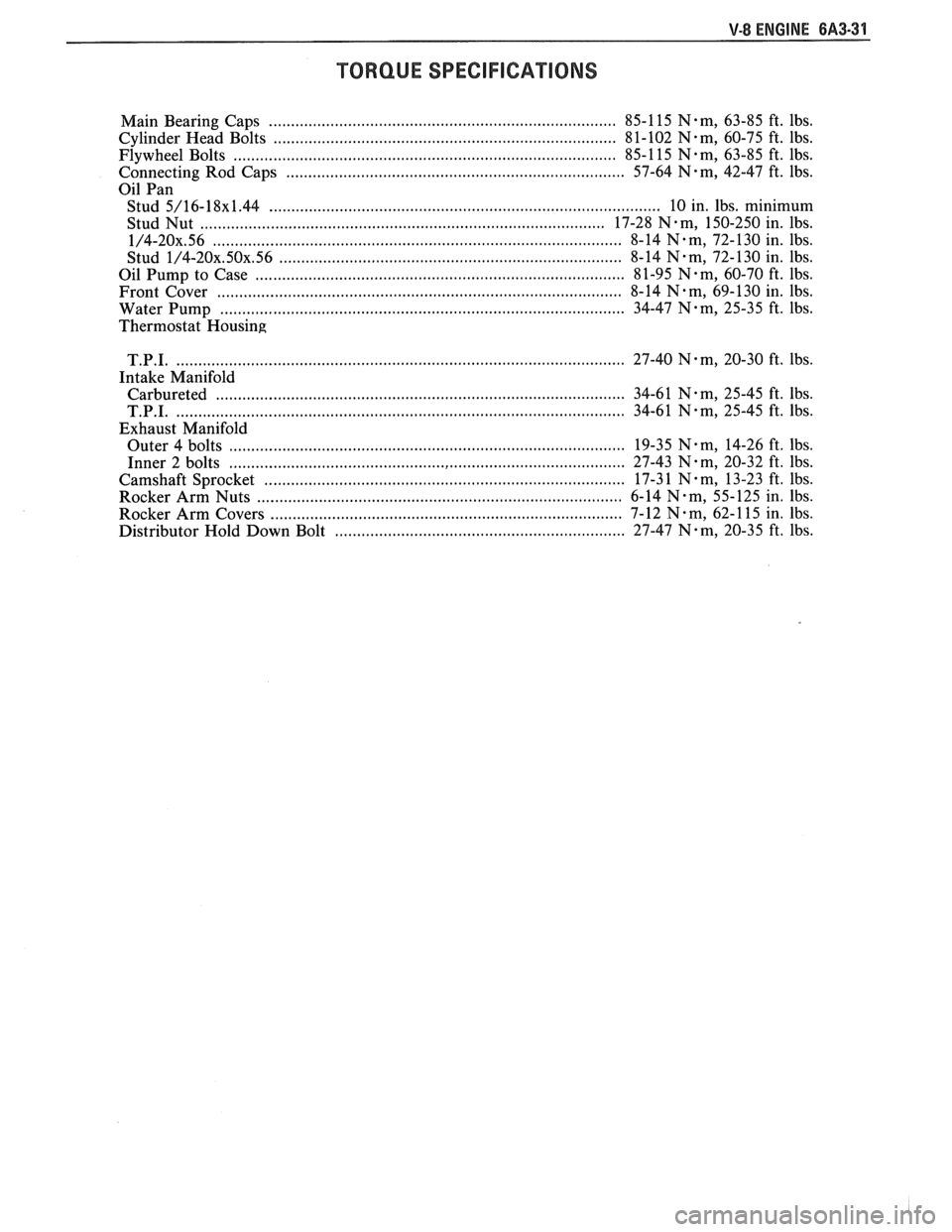
V-8 ENGINE 6A3-31
TORQUE SPECIFIGAUONS
Main Bearing Caps ............................................................................ 85-1 15 N-m, 63-85 ft. lbs.
Cylinder Head Bolts
.............................................................................. 81-102 N-m, 60-75 ft. lbs.
Flywheel Bolts
....................................................................................... 85-1 15 Nem, 63-85 ft. lbs.
........................................................................... Connecting Rod Caps 57-64 N-m, 42-47 ft. lbs.
Oil Pan
Stud
5/16-18~1.44 ....................................................................................... 10 in. lbs. minimum
Stud Nut
............................................................................................ 17-28 N-m, 150-250 in. lbs.
1/4-20x.56 ........................................................................................... 8-14 N-m, 72-130 in. lbs.
Stud
1/4-20x.50x.56 ............................................................................ 8-14 N.m, 72-130 in. lbs.
Oil Pump to Case
.................................................................................... 8 1-95 N . m, 60-70 ft. lbs.
Front Cover
............................................................................................ 8-14 N-m, 69-130 in. lbs.
Water Pump
........................................................................................... 34-47 N-m, 25-35 ft. lbs.
Thermostat Housing
T.P.I.
...................................................................................................... 27-40 N-m, 20-30 ft. Ibs.
Intake Manifold
Carbureted
............................................................................................. 34-61 N.m, 25-45 ft. Ibs.
T.P.I.
...................................................................................................... 34-61 N-m, 25-45 ft. Ibs.
Exhaust Manifold
Outer 4 bolts
.......................................................................................... 19-35 N-m, 14-26 ft. lbs.
Inner 2 bolts
........................................................................................ 27-43 N.m, 20-32 ft. Ibs.
Camshaft Sprocket
.................................................................................. 17-3 1 N-m, 13-23 ft. lbs.
Rocker Arm Nuts
................................................................................. 6-14 N-m, 55-125 in. Ibs.
Rocker Arm Covers
............................................................................. 7-12 N- m, 62- 11 5 in. Ibs.
Distributor Hold Down Bolt
.................................................................. 27-47 N-m, 20-35 ft. lbs.
Page 434 of 1825

ENGINE FUEL 6C.3
a Fuel feed and return pipes are secured to the
underbody with clamps and screw assemblies.
The pipes should be inspected occasionally for
leaks, kinks or dents.
e Follow the same routing as the original pipe.
e Pipes must be properly secured to the frame to
prevent chafing. A minimum of 6 mm
(1/4")
clearance must be maintained around a pipe to
prevent contact and chafing.
MPFl Fuel Pipes
Due to the fact that fuel pipes are under high
pressure, these systems require special consideration for service.
Many feed and return pipes use screw couplings
with
"0" Rings. Any time these fittings are loosened
to service or replace components, ensure that:
a A backup wrench is used while loosening and
tightening the fitting.
e Check all "0" rings at fitting locations (if
applicable) for cuts or any damage and replace
any that appear worn or damaged.
e Use correct torque when tightening fittings.
If pipes are replaced always use original
equipment parts, or parts that meet GM
specifications.
Fuel and Vapor Hoses
NOTICE: Fuel and vapor hoses are specially
manufactured. If replacement becomes necessary,
it is important to use only replacement hoses
meeting GM Specification 6163-M. These hoses
are identified with the words "Fluoroelastomer"
on them. Hoses not so marked could cause early
failure, or fail to meet emission standards.
e Do not use rubber hose within 4" of any part of
the exhaust system, or within
10" of the catalytic
converter.
FUEL PUMP
The electric fuel pump is in the fuel tank. The
tank has an outlet for a vapor return system. Any vapor
which forms is returned to the fuel tank along with hot
fuel through a separate line. This greatly reduces any
possibility of vapor lock by keeping cool fuel from the
tank constantly circulating through the fuel pump.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
To control fuel pump operation, a fuel pump
relay is used.
When the ignition switch is turned to "RUN"
position, the fuel pump relay activates the electric fuel
pump for
1.5 to 2.0 seconds to prime the injector(s). If
the ECM does not receive reference pulses from the
distributor after this time, the ECM signals the relay
to turn off the fuel pump. The relay will once again
activate the fuel pump when the
ECM receives
distributor reference pulses.
Fuel Filter
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of fire
and personal injury, it is necessary
to
relieve the fuel system pressure
before servicing fuel system
components. (See Fuel System
Pressure Relief.)
The inline filters can be found on the rear
crossmember of the vehicle. Always use a backup
wrench any time that the fuel filter is removed or
installed. Also make sure that a good
"0" Ring is used
at all screw couple locations. Torque on fittings is
30
N-m (22 lb. ft.).
FUEL TANK
The fuel tank is usually located under the rear of
the vehicle and a number of shapes and sizes are used
depending on the application.
The tank is held in place by two metal straps,
hinged (with a bolt through the hinge) and secured at
the opposite end with a nut and bolt assembly.
Anti-squeak pieces are used on top of the tank to
reduce rattles and other annoying noises.
The fuel tank, cap and lines should be inspected
for road damage, whch could cause leakage. Inspect
fuel cap for correct sealing and indications of physical
damage. Replace any damaged or malfunctioning
parts.
Before attempting service of any type on the fuel
tank, always
(1) remove negative battery cable from
battery, (2) place "no smoking" signs near work areas,
(3) be sure to have C02 fire extinguisher handy, (4)
wear safety glasses and
(5) siphon or pump fuel into an
explosion proof container.
Fuel Filler Gap
The fuel tank filler neck is equipped with a
screw-type cap. The threaded part of the cap requires
several turns counterclockwise to remove. The long
threaded area is designed to allow any remaining fuel
tank pressure to escape while the cap is being removed.
A built-in torque-limiting device prevents
overtightening. To install, turn the cap clockwise until
a clicking noise is heard. This signals that the correct
torque has been reached and the cap is fully seated.
N OTI G E: If a fuel filler cap requires replacement,
use only a cap with the same features. Failure to
use the correct cap can result in a serious
malfunction of the system.
Available on some models is an electric locking
fuel filler cap. Information on this option will be found
in Section
9E.
FUEL TANK FILLER NECK
To help prevent refueling with leaded gasoline,
the fuel filler neck on gasoline engine cars has a built-in
restrictor and deflector. The opening in the restrictor
will only admit the smaller unleaded gas nozzle spout,
which must be fully inserted to bypass the deflector.
Attempted refueling with a leaded gas nozzle or failure
Page 470 of 1825

IGNITION SYSTEM 6D4-1
ON SYSTEM
CONTENTS
General Description ............................... 6D4-1 Service Procedures ............................. 6D4-3
Ignition System .......................................... 6D4-1
Ignition System .......................................... 6D4-3
Distributor Ignition ................................ 6D4-1
Distributor Ignition ................................ 6D4 -3
Diannosis .................................................... 6D4-3 On-Car Service ......................................... 6D4-5 -
Ignition System .......................................... (334-3 Ignition System ........................... .. .............. 6D4-5
Distributor ................................................. 6D4 -7 HE1 Distributor .................................... 6D4-3
GENERAL DESCRIPION
The engine electrical system includes the battery,
ignition (primary and secondary), starter (and related
wiring) and the generator (and related wiring).
Diagnostic charts (see Section 6D) will aid in
trouble-shooting system faults. When a fault is traced
to a particular component, refer to that components'
section of the service manual.
IGNITION SYSTEM
Distributor Ignition
The ignition circuit consists of the battery,
distributor, ignition switch, spark plugs and primary
and secondary wiring. Refer to the Battery portion of
this section for battery information.
PIE1 Distributor
The Nigh Energy Ignition (HEI) distributor with
Electronic Spark Timing (EST), used on most engines,
combines all ignition components in one unit. The
ignition coil is in the distributor cap and connects
through a resistance brush to the rotor.
The distributor has an internal magnetic pick-up
assembly which contains a permanent magnet, a pole
piece with internal teeth and a pick-up coil. When the
teeth of the timer core, rotating inside the pole piece,
line up with the teeth of the pole piece, an induced
voltage in the pick-up coil signals the electronic module
to trigger the coil primary circuit. The primary current
decreases and a high voltage is induced in the ignition
coil secondary winding. This voltage is directed
through the rotor and secondary leads to fire the spark
plugs. The capacitor in the distributor is for radio noise
suppression,
All spark timing changes in the
HE1 (EST)
distributor are done electronically by an Electronic
Control Module (ECM), which monitors information
from various engine sensors, computes the desired
spark timing and signals the distributor to change the
timing accordingly.
A back-up spark advance system
is incorporated to signal the ignition module in case of
(ECM) failure. No vacuum or mechanical advance is
used. Further (EST) information is found in sections 6E
Emissions Control, and
8A Electrical
Troubleshooting.
Ignition Timing
Timing specifications for each engine are listed in
Section
6E. When using a timing light, connect an
adapter between the No. 1 spark plug and the No. 1
spark plug wire, or use an inductive type pick-up.
Do
not pierce the plug lead.
Once the insulation of the
spark plug cable has been broken, voltage will jump to
the nearest ground, and the spark plug will not fire
properly.
Always follow the tune-up label
procedures when adjusting timing.
Some engines will incorporate a magnetic timing
probe hole for use with special electronic timing
equipment. Fig.
1A shows a typical magnetic probe
hole. Consult manufacturer's instructions for use of
this equipment.
Secondary Wiring
The spark plug wiring used with ignition systems
is a carbon impregnated cord conductor, encased in an
8MM (5/16") diameter silicone rubber jacket. The
silicone jacket withstands very high temperatures and
also provides an excellent insulator for the higher
voltage of the
HE1 system. Silicone spark plug boots
form a tight seal on the plug.
The boot should be
twisted 1/2 turn before removing. Care should
also be exercised when connecting a timing light or
other pick-up equipment. Do not force anything
between the boot and wiring, or through the silicone
jacket. Connections should be made in parallel using
an adapter. DO NOT pull on the wire to remove. Pull
on the boot, or use a tool designed for this purpose.
Spark Plugs
Resistor type, tapered seat spark plugs are used
on all engines (except aluminum heads). No gasket is
used on these tapered seat plugs. See Figs.
1B and 1C
for an explanation of coding on spark plugs.
Normal service is assumed to be a mixture of
idling, slow speed, and high speed driving. Occasional
or intermittent high-speed driving is needed for good
Page 471 of 1825
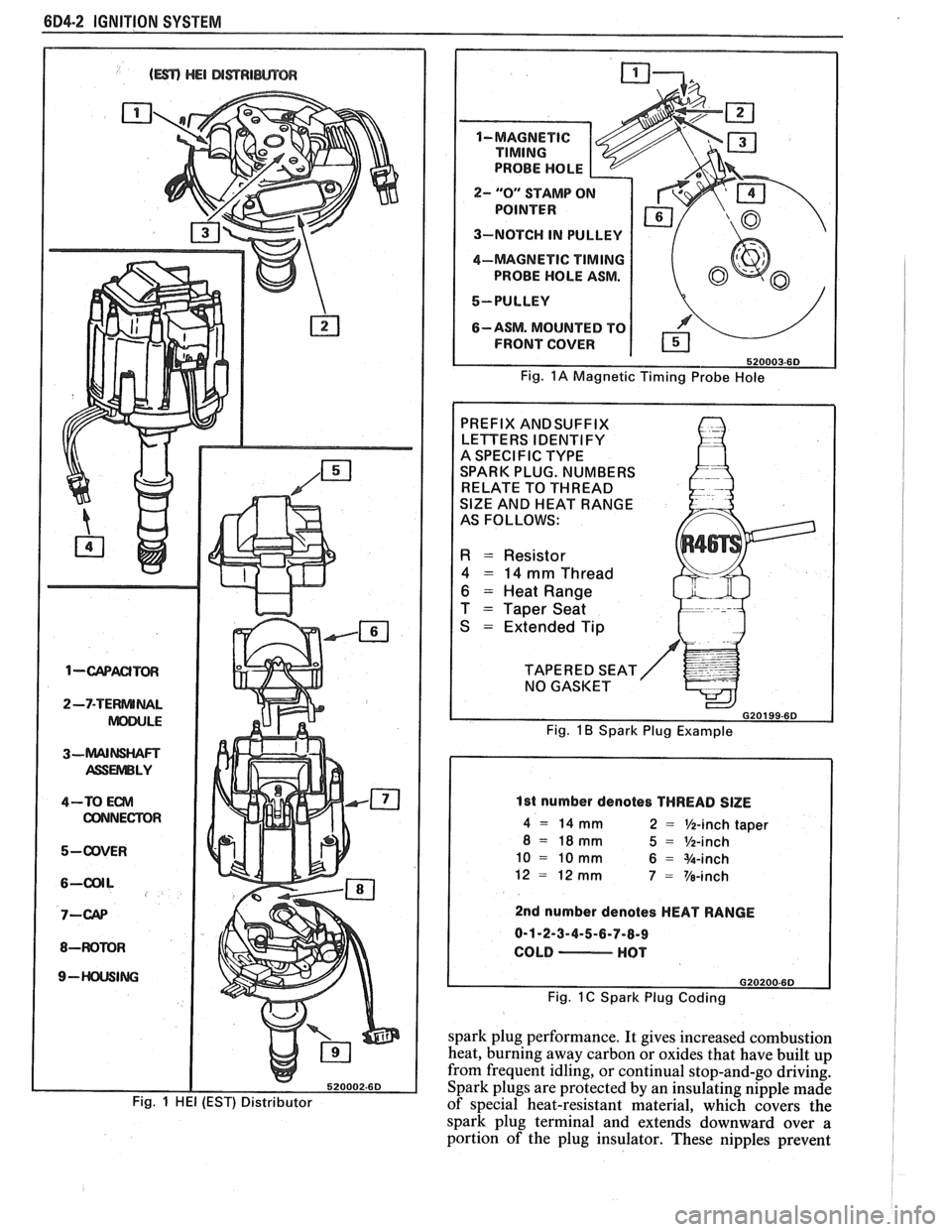
604-2 IGNITION SYSTEM
1-wACITm
2-7-TERNUNAL
ASSUVlBLY
4-TO Em
CONNECTOR
5-ODVER
8-WOMR
9- ING
Fig. 1 HE1 (EST) Distributor
2- "0" STAMP O
3-NOTCH IN PULLEY
4-MAGNETIC
TIMING
PROBE HOLE ASM.
5-PULLEY
6-ASM. MOUNTED TO
FRONT COVER
Fig. 1A Magnetic Timing Probe Hole
PREFIX ANDSUFFIX
LETTERS IDENTIFY
A SPECIFIC TYPE
SPARK PLUG. NUMBERS
RELATE TO THREAD
SlZE AND HEAT RANGE
AS FOLLOWS:
R = Resistor
4 = 14 mm Thread
6 = Heat Range
T
= Taper Seat
S
= Extended Tip
TAPERED SEAT NO GASKET
G20199-6D
Fig. 1 B Spark Plug Example
1st number denotes THREAD SlZE
4 = 14 mm 2 = %-inch taper
8 = 18mm 5 = %-inch
10 = 10 mm 6 = %-inch
12
= 12 mm 7 = Ve-inch
2nd number denotes HEAT RANGE
0-1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9
COLD
- HOT
Fig. 1 C Spark Plug Coding
spark plug performance. It gives increased combustion
heat, burning away carbon or oxides that have built up
from frequent idling, or continual stop-and-go driving.
Spark plugs are protected by an insulating nipple made
of special heat-resistant material, which covers the
spark plug terminal and extends downward over
a
portion of the plug insulator. These nipples prevent
Page 472 of 1825

IGNITION SYSTEM 6B4-3
flash-over, which causes engine misfiring. Do not
mistake corona discharge for flash-over, or a shorted
insulator. Corona is a steady blue light appearing
around the insulator, just above the shell crimp. It is
the visible evidence of a high-tension field and has no
effect on ignition performance. Usually it can be
detected only in darkness. This discharge may repel
dust particles, leaving a clear ring on the insulator just
above the shell. This ring is sometimes mistakenly
regarded as evidence that combustion gases have blown
out between shell and insulator.
lgnition Switch
The mechanical switch is located in the steering
column on the right hand side just below the steering
wheel. The electrical switching portion of the assembly
is separate from the key and lock cylinder. However,
both are synchronized and work in conjunction with
each other through the action of the actuator rod
assembly.
For a complete explanation of the key and lock
cylinder, and the actuator rod assembly, see
STEERING, Section
38. See Section 8 for electrical
switching.
DIAGNOSIS
IGNITION SYSTEM
Spark Plugs
Worn or dirty plugs may give satisfactory
operation at idling speed, but at higher RPM they
frequently fail. Faulty plugs are indicated in a number
of ways: poor fuel economy, power loss, loss of speed,
hard starting and generally poor engine performance.
Spark plugs may also fail due to carbon fouling,
excessive gap, or a broken insulator. Fouled plugs may
be indicated by black carbon
deposits. The black deposits are usually the result of
slow-speed driving and short runs, where sufficient
engine operating temperature is seldom reached. Worn
pistons, rings, faulty ignition, over-rich carburetion
and spark plugs which are too cold will also result in
carbon deposits.
Excessive gap wear, on plugs of low mileage,
usually indicates the engine is operating at high speeds,
or loads that are consistently greater than normal, or
that a plug which is too hot is being used. Electrode
wear may also be the result of plug overheating,
causcd
by combustion gases leaking past the threads due to
insufficient torquing of the spark plug. Excessively lean
carburetion will also result in accelerated electrode
wear.
Broken insulators are usually the result of
improper installation, or carelessness when regapping
the plug. Broken upper insulators usually result from
a poor fitting wrench, or an outside blow. The cracked
insulator may not show up right away, but will as soon
as oil or moisture penetrates the crack. The crack is
usually just below the crimped part of shell and may
not be visible.
Broken lower insulators usually result from
carelessness when regapping and generally are visible.
This type of break may result from the plug operating
too "hot", which may happen in periods of high-speed
operation or under heavy loads. When regapping a
spark plug, always make the gap adjustment by
bending the ground (side) electrode. Spark plugs with
broken insulators should always be replaced.
HE1 Distributor
See Unit Repair for distributor disassembly, test
and reassembly of individual distributor components,
when the distributor is removed from the vehicle. See
On-Car Service for distributor removal and installation
and for component removal with distributor in car. See
Section 6E for
HE1 and EST diagnosis.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
IGNITION SYSTEM
Distributor Ignition
NOTICE: This procedure is generally true for
most carlines. Where procedure is different, or
where additional information is required, see
"ON-CAR SERVICE" for specific
carline.
HE1 DISTRIBUTOR
Service Precautions
1. When making compression checks, disconnect
the ignition switch feed wire at the distributor.
When disconnecting this connector,
do not use
a screwdriver or tool to release the locking tab, as
it may break.
2. No periodic lubrication is required. Engine oil
lubricates the lower bushing and an oil-filled
reservoir provides lubrication for the upper
bushing. 3.
The tachometer (TACH) terminal is next to the
ignition switch (BAT) connector on the
distributor cap.
NOTICE: The tachometer terminal must
NEVER be allowed to touch ground, as damage
to the module and/or ignition coil can result.
Some tachometers currently in use may NOT be
compatible with the High Energy Ignition System.
Consult the manufacturer of the tachometer if
questions arise.
4. Dwell adjustment is controlled by the module,
and cannot be adjusted.
5. The material used to construct the spark plug
cables is very soft. This cable will withstand more
heat and carry a higher voltage, but scuffing and
cutting become easier. The spark plug cables
must be routed correctly to prevent
chafing or
cutting. See Spark Plug Section. When removing