1988 PONTIAC FIERO distributor
[x] Cancel search: distributorPage 493 of 1825
6E2-A-2 5.OL (VIN E) DRIVEABILIW AND EMISSIONS
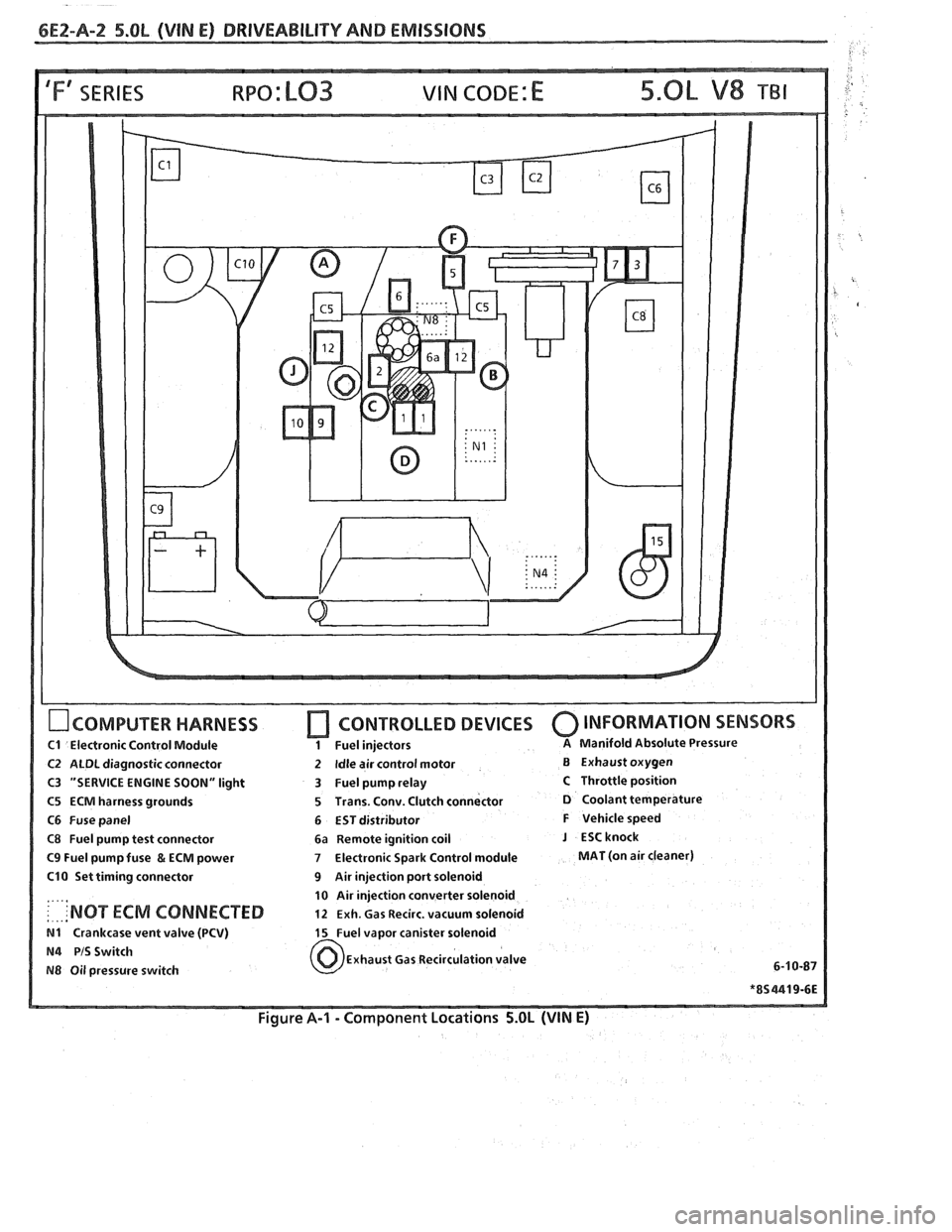
IFf SERIES VIN CODE: E
OCOMPUTER HARNESS
C1 Electronic Control Module
C2 ALDL diagnostic connector
C3 "SERVICE ENGINE SOON" light
C5 ECM harness grounds
C6 Fuse panel
C8 Fuel pump test connector
C9 Fuel pump fuse & ECM power
C10 Set timing connector
....,
: . ... 'NOT ECM CONNECTED
N1 Crankcase vent valve (PCV)
N4 PIS Switch
N8 Oil pressure switch
[7 CONTROLLED DEVICES 0 INFORMATION SENSORS
1 Fuel injectors A Manifold Absolute Pressure
2 Idle air control motor B Exhaust oxygen
3 Fuel pump relay
C Throttle position
5 Trans. Conv. Clutch connector
D Coolant temperature
6 EST distributor
F Vehicle speed
6a Remote ignition coil
J ESCknock
7 Electronic Spark Control module MAT (on air cleaner)
9 Air injection port solenoid
10 Air injection converter solenoid
12 Exh. Gas Recirc. vacuum solenoid
15 Fuel vapor canister solenoid
Exhaust Gas Recirculation valve
6-1
0-87
Figure A-I - Component Locations 5.OL (VIN E)
Page 535 of 1825
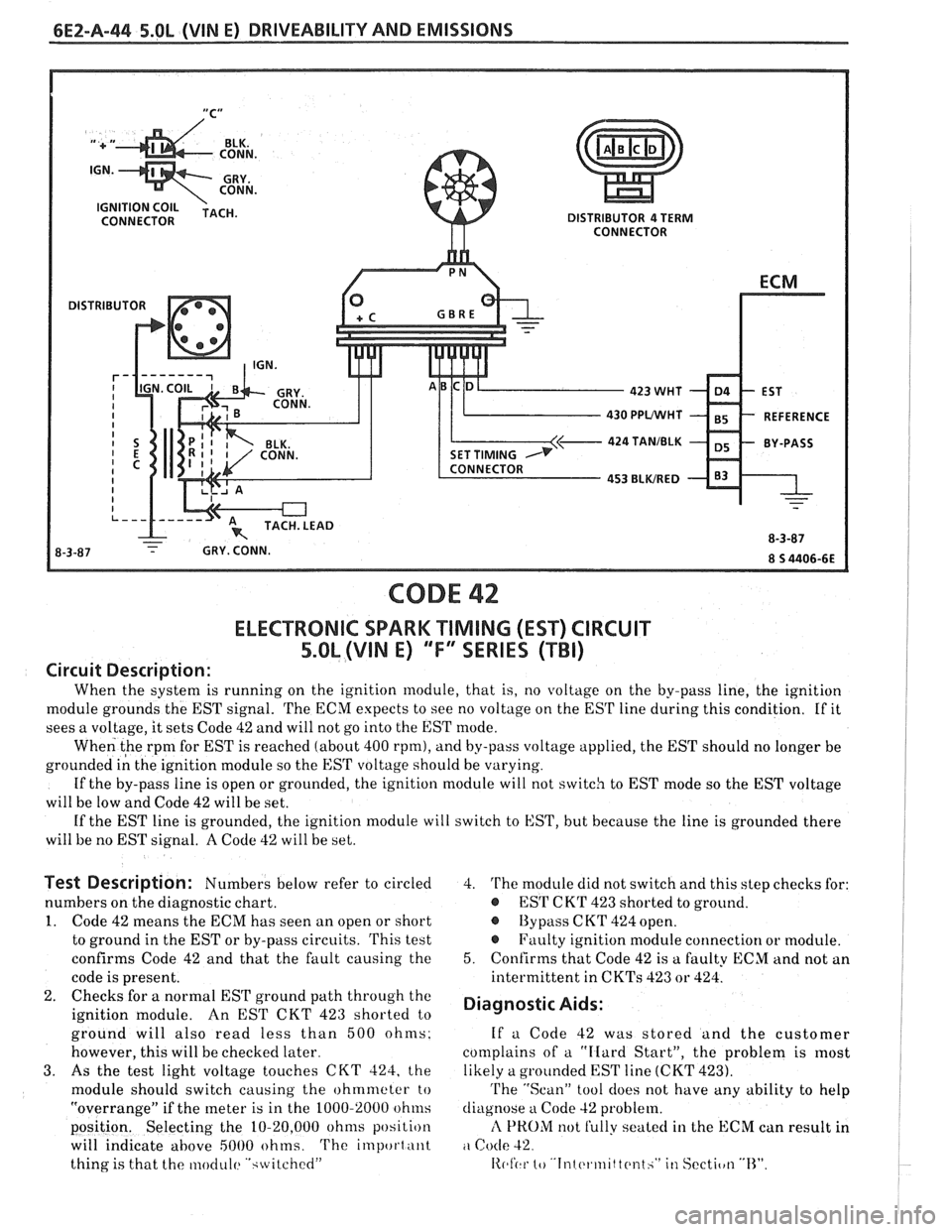
6E2-A-44 5.OL (WIN E) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DISTRIBUTOR 4 TERM
CONNECTOR
DISTRIBUTOR
430 PPVWHT
424 TANIBLK
CODE 42
ELECTRONlC SPARK TIMING (EST) CIRCUIT
5.OL (VIN E) ""FYSERIES (TBI)
Circuit Description:
When the system is running on the ignition module, that is, no voltage on the by-pass line, the ignition
module grounds the EST signal. The ECM expects to see no voltage on the EST line during this condition. If it
sees a voltage, it sets Code 42 and will not go into the EST mode.
When the
rpm for EST is reached (about 400 rpm), and by-pass voltage applied, the EST should no longer be
grounded
i; the ignition module so the EST voltage should be varying.
If the by-pass line is open or grounded, the ignition module will not
switcli to EST mode so the EST voltage
will be low and Code 42 will be set.
If the EST line is grounded, the ignition module
will switch to EST, but because the line is grounded there
will be no EST signal.
A Code 42 will be set.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. Code 42 means the ECM has seen an open or short
to ground in the EST or by-pass circuits. This test
confirms Code 42 and that the fault causing the
code is present.
2. Checks for a normal EST ground path through the
ignition module.
An EST CKT 423 shorted to
ground will also read less than 500 ohms.
however, this will be checked later.
3. As the test light voltage touches CKT 424, the
module should switch causing the ohmmeter
to
"overrange" if the meter is in the 1000-2000 ohnls
position. Selecting the 10-20,000 ohms position
will indicate
above 5000 ohms. The important
thing is that the moclul(~ ".;~vitched"
4. The module did not switch and this step checks for:
@ ES'I' CKT 423 shorted to ground.
@ By pass C KT 424 open.
@ Faulty ignition module connection or module.
5. Confirms that Code 42 is a faulty ECM and not an
intermittent in
CKTs 423 or 424.
Diagnostic Aids:
If a Code 42 was stored and the customer
complains of
a "IIard Start", the problem is most
likely a grounded EST line (CKT 423).
'I'he "Scan" tool does not have any ability to help
diagnose
a Code 42 problem.
rl PROM not Sully seated in the ECM can result in
Code 42
11~1'(.1- 10 '.In1 c.l.lnlt tc~nth" in Sectiotl "13".
Page 549 of 1825

6EZ-B-2 5.OL (VIN E) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Problem may or may not turn "ON" the "Service Engine Soon" light, or store a code.
DO NOT use the trouble code charts in Section
"A" for intermittent problems. The fault must be
present to locate the problem. If a fault is
intermittent, use of trouble code charts may result
in replacement of good parts.
@ Most intermittent problems are caused by faulty
electrical connections or wiring. Perform
careful check of suspect circuits for:
- Poor mating of the connector halves, or
terminals, not fully seated in the connector
body (backed out).
I - Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
All connector terminals in problem circuit
should be carefully reformed to increase
contact tension.
- Poor terminal to wire connection. This
requires removing the terminal from the
connector body to check as outlined in the
Introduction to Section
"6E".
@ If a visual (physical) check does not find the
cause of the problem, the car can be driven with
a voltmeter connected to a suspected circuit or a
"Scan" tool may be used. An abnormal voltage
reading, when the problem occurs, indicates the
problem may be in that circuit. If the wiring
and connectors check OK, and a trouble code was
stored for a circuit having a sensor, except
for Codes 44 and 45, substitute a known good
sensor and recheck.
@ Loss of trouble code memory. To check,
disconnect TPS and idle engine until "Service
Engine Soon" light comes
"ON". Code 22 should
be stored, and kept in memory, when ignition is
turned "OFF" for at least 10 seconds. If not, the
ECM
is faulty.
@ An intermittent "SES" light, and no trouble
codes, may be caused by:
- Electrical system interference caused by a
defective relay, ECM driven solenoid, or switch.
They can cause a sharp electrical surge.
Normally, the problem will occur when the
faulty component is operated.
- Improper installation of electrical options, such
as lights, 2-way radios, etc.
- EST wires should be routed away from spark
plug wires, ignition system components, and
generator. Wire for CKT 453 from ECM to
ignition system should be a good ground.
- Ignition secondary shorted to ground.
- CKTs 419 ("SES" light) or 451 (Diagnostic Test)
intermittently shorted to ground.
- ECM power grounds.
HARD START
Definition: Engine cranks OK, but does not start for a long
time. Does eventually run, or may start but immediately dies.
, <
@ CHECK: 4. Connect a radiator test pump to the line and
- For water contaminated fuel. apply 103 kPa (15 psi) pressure. If the
- Fuel system pressure CHART A-7. pressure will hold for 60 seconds, the check
- TPS for sticking or binding should read less than
valve is OK.
1.25 volts on a "Scan" tool. @ Check ignition system for:
- No crank signal; see CHART C-1B. - Proper output with ST-125.
- EGR operation; CHART C-7. - Worn shaft.
- Fuel System - CHART A-7. - Rare and shorted wires.
- For a faulty in-tank fuel pump check valve, - Pickup coil resistance and connections.
which would allow the fuel in the lines to drain
- Loose ignition coil connections.
back to the tank after the engine is stopped. To
- Moisture in distributor cap.
check for this condition:
- Spark plugs, wet plugs, cracks, wear,
1. Ignition "OFF".
improper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy
2. Disconnect fuel line at the filter
deposits.
3. Remove the tank filler cap. @ If engine starts but then, immediately stalls,
open distributor bypass line. If engine then
starts, and runs OK, replace distributor pickup
coil.
@ Check CKT 423 (EST) for short to ground.
Page 551 of 1825

6EZ-B-4 5.OL (VIN E) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DEWNATION 1 SPARK KNOCK
Definition: A mild to severe ping, usually worse under acceleration. The
engine makes sharp metallic knocks that change with throttle opening.
@ CHECK for obvious overheatingproblems. - For proper transmission shift points. See Section
- Low coolant. "7".
- Loose water pump belt. - TCC operation. See CHART C-8.
- Restricted air flow to radiator, or restricted - For incorrect basic engine parts such as cam,
water flow thru radiator. heads,
pistons, etc.
- Faulty or incorrect thermostat. - Excessive oil entering combustion chamber.
- Coolant sensor, which has shifted in value. @ Remove carbon with top engine cleaner. Follow
- Correct coolant solution - should be a 50150 instructions on can.
mix of GM
#lo52753 anti-freeze coolant (or @ If there is spray from only one injector, then there
equiv.) and water. is
a malfunction in the injector assembly, or in the
@ CHECK: signal to the injector assembly. The malfunction
- For poor fuel quality, proper octane rating. can be isolated by switching the injector
- For correct PROM. connectors. If the problem remains with the
- Spark plugs for correct heat range.
original injector, after switching the connector,
- ESC system opeation. See CHART C-5.
then the injector is defective. Replace the injector.
- Ignition timing. See Vehicle Emission Control
If the problem moves with the injector connector,
Information label. then the
problem is an improper signal in the
- Fuel system for low pressure. See CHART A-7.
injector circuits. See CHART A-3.
- Check EGR svstem. - CHART C-7.
HESITATION, SAG, STUMBLE
Definition: Momentary lack of response as the accelerator is pushed down.
Can occur at all car speeds.
C'sually most severe when first trying to make the car
move, as from a stop sign.
May cause the engine to stall if severe enough.
@ Perform careful visual (physical) check, as Information" label.
described at start of Section
"B". - Generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9 or
@ CHECK: more than 16 volts.
- Fuel pressure. See CHART A-7. - For open ignition system ground, CKT 453.
- Water contaminated fuel. - Canister purge system for proper operation. See
- TPS for binding or sticking.
Section "C3".
- Ignition timing. See "Emission Control - EGR valve operation, CHART C-7.
CU"F OUT, MISSES
Definition: Steady pulsation or jerking that follows engine
speed, usually more pronounced as engine load increases. The
exhaust has a steady spitting sound at idle or low speed.
@ Perform careful visual (physical) check, us
described at start of Section
"B".
@ If ignition system is suspected of causing a miss
at idle or cutting, out under load:
@ Check for missing cylinder by:
1. Disconnect IAC motor. Start engine.
Remove one spark plug wire at a time, using
insulated pliers.
2. If there is an rpm drop on all cylinders, (equal
to within 50
rpm), go to "Rough, Unstable, Or
Incorrect Idle, Or Stalling" symptom.
Reconnect
IAC motor.
3. If there is no rpm drop on one or more
cylinders, or excessive variation in drop, check
for spark, on the suspected
cylinder(s) with J
26792 (ST-1251 spark tester or equivalent. If no
spark, see Section
"6D" for "Intermittent Operation
or Miss". If there is spark, remove spark plug(s) in
these cylinders and check for:
- Cracks
- Wear
- Improper gap
- Burned electrodes
- Heavy deposits
- Perform compression check on
questionable cylinder.
@ Check wire resistance (shoulcl not exceed 30,000
ohms), also, check rotor and distributor cap.
Page 553 of 1825

6E2-8-6 5.OL (VIN E) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
- MAP Sensor - Ignition "ON", engine stopped.
Compare MAP voltage with known good vehicle.
-
Voltage should be the same + 400 mV (.4 volts).
OR
Start and idle engine. Disconnect
sensor
electrical connector. If idle improves, substitute
a known good sensor and recheck.
- A/C refrigerant pressure too high. Check for
overcharge or faulty pressure switch.
- PCV valve for proper operation by placing finger
over inlet hole in valve end several times. Valve
should snap back. If not, replace valve.
Run a cylinder compression check See Section
" 6".
Inspect oxygen sensor for silicon contamination
from fuel, or use of improper RTV sealant. The
sensor will have a white, powdery coating, and
will result in a high but false signal voltage (rich
exhaust indication). The ECM will then reduce
the amount of fuel delivered to the engine,
causing a severe driveability problem.
EXCESSIVE EXHAUST EMISSIONS OR ODORS
Definition: Vehicle fails an emission test. Vehicle has excessive "rotten egg"
smell. Excessive odors do not necessarily indicate excessive emissions.
@ Perform "Diagnostic Circuit Check".
@ IF TEST SHOWS EXCESSIVE CO AND HC, (or
also has excessive odors)
@ Check items that will cause engine to run
RICH.
e Make sure engine is at normal operating
temperature.
o CHECK:
- Fuel pressure. See CHART A-7.
- Incorrect timing. See Vehicle Emission
Control Information label.
- Canister for fuel loading. See CHART C-3.
- PCV valve for being plugged, stuck or blocked
PCV hose or fuel in the crankcase.
- Spark plugs, plug wires, and ignition
components. See Section
"6D".
- Check for lead contamination of catalytic
converter (look for removal of fuel filler neck
restrictor).
- Check for properly installed fuel cap.
@ If the system is running rich, (block learn less
than
1181, refer to "Diagnostic Aids" on facing
page of Code
45.
o IF TEST SHOWS EXCESSIVE NOx:
@ Check items which cause car to run LEAN, or
to run too hot.
- EGR valve for not opening. See CHART C-7.
- Vacuum leaks. - Coolant system and coolant fan for proper
operation. See
CHART C-12.
- Remove carbon with top engine cleaner.
Follow instructions on can.
- Check ignition timing for excessive base
advance. See Emission Control Information
label.
@ If the system is running lean, (block learn greater
than
138) refer to "Diagnostic Aids" on facing
page of Code
44.
DIESELING, RUN-ON
Definition: Engine continues to run after key is turned "OFF", but runs very roughly.
Ifengine runs smoothly, check ignition switch and adjustment.
@ Check injector for leaking. Apply 12 volts to fuel Visually check injector and TBI assembly for fuel
pump test terminal to turn "ON" fuel pump and leakage.
pressurize fuel system.
BACKFIRE
Definition: Fuel ignites in intake manifold, making a loud popping noise.
@ CHECK: - For faulty spark plugs and/or plug wires or
- EGR operation for being open all the time. See
hoots.
CHART C-7. - Faulty A.I.R. check valve.
- Output voltage of ignition coil. @ Perform a compression check - look for sticking or
- For crossfire between spark plugs (distributor leaking valves.
cap, spark plug wires, and proper routing' of plug
- For proper valve timing.
wires).
- Broken or worn valve train parts.
- Engine timing - See Emission Control
Information label.
Page 556 of 1825
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN El 6EZ-C1-1
SECTION Cl
ELECTWONllC CONTROL MODULE (ECM) AND SENSORS
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-1 Coolant Temperature Sensor . . . . . . . . C1-5
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULE (ECM) . . C1-1 MAT Sensor. . . . . . . . . . . .. . . ... . . . . $1 -5
PROM ........................... C1-1 MAP Sensor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1 -6
CALPAK.........,................ C1-2 Oxygen (02) Sensor. . . . . . ... . . . a C1-6
ECM FUNCTION . . . , . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-2 Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) . . . . . . . . C1-6
INFORMATION SENSORS . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-2 Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) . . . . . . . . . C1-6
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor . . C1-2 PIN Switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-6
MAP Sensor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-2 (PSPS) . . . . . ... .. . . . ... . . .. .. . . . C1-6
MAT Sensor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-3 AJC Request Signal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-6
Oxygen (Oz) Sensor. . . . . . . . . .. . . . . . C1-3 Distributor Reference Signal . . . . . . . . . C1-6
Throttle Posit~on Sensor (TPS) . . . . . . . . C1-3 Knock Signal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-6
Knock Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-4 ON-CAR SERVICE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-6
Park Neutral Switch (Auto Only) . . . . . . C1-4 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULE . . . . . . . 61-6
Crank Signal . . . . . . , . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-4 PROM ........................... C1-7
A/C "On" Signal . . . , . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-4 Functional Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-8
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) . . . . . . . . . C1-4 CALPAK...................,...... C1-8
Distributor Reference Signal . . . . . . . . . C1-4 COOLANTSENSOR .. . . . . . . . , . . . . . . . . . C1-9
(PSPS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-4 MAPSENSOR ..... ........ ... . .. . .* C1-9
DIAGNOSIS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-5 OXYGEN (02) SENSOR . . . . . . . . . a . . a . . C1-9
ECM ............................. C1-5 THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS) . . . . . C1-10
PROM ........................... C1-5 PARKINEUTRALSWITCH . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-10
ECM INPUTS.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . , . . . . . C1-5 PARTS
INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C1-10
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
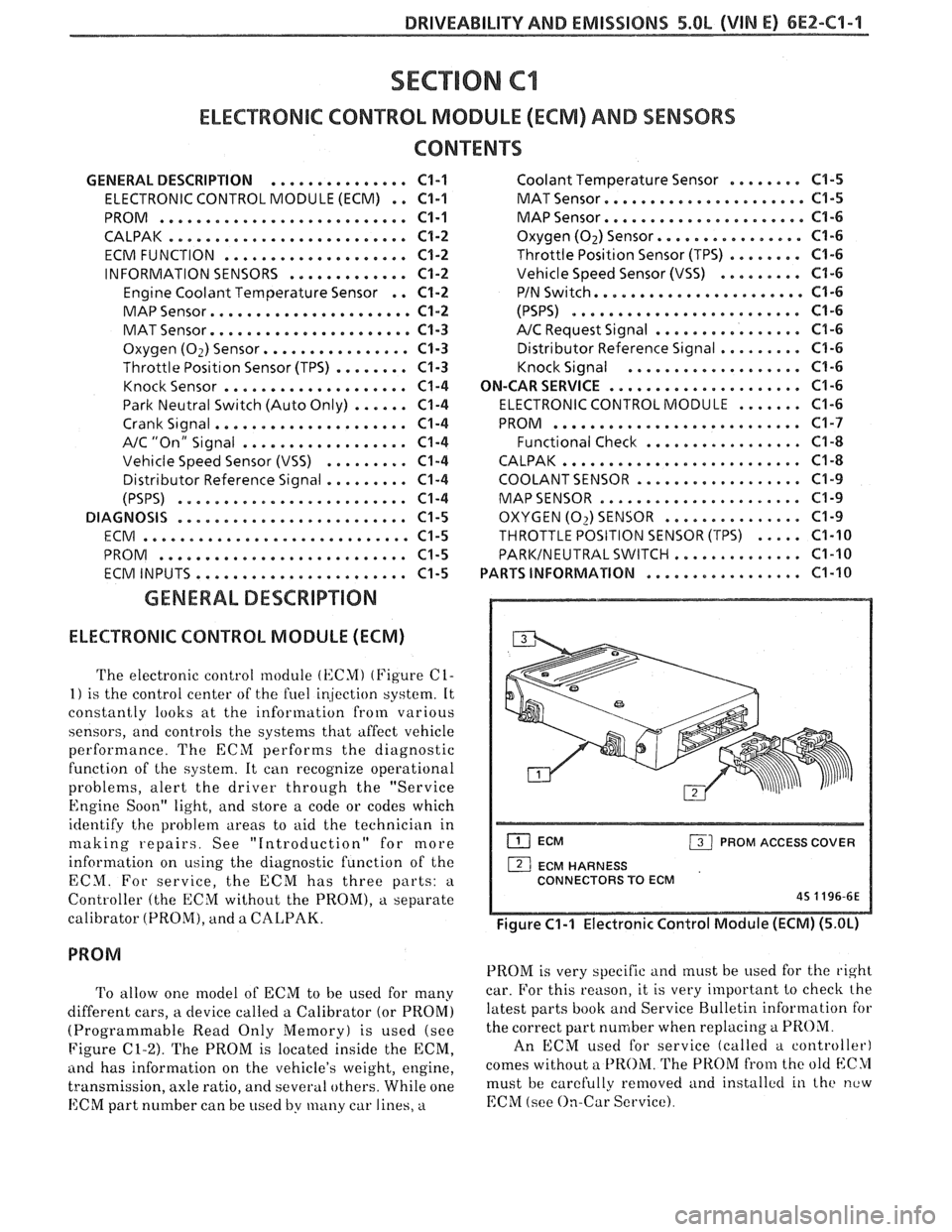
The electronic control module (KCMI (Figure C1-
1) is the control center of the fuel ir!jection system. It
constantly looks at the information from various
sensors, and controls the systems that affect vehicle
performance. The ECM performs the diagnostic
function of the system. It can recognize operational
problems, alert the driver through the "Service
Engine Soon" light, and store a code or codes which
identify the problem areas to aid the technician in
making repairs. See "Introduction" for more
information on using the diagnostic function of the
ECM. For service, the ECM has three parts:
a
Controller (the ECM without the PROM), a separate
calibrator (PROM), and a
CALPAK.
To allow one model of ECM to be used for many
different cars, a device called a Calibrator (or PROM)
(Programmable Read Only Memory) is used (see
Figure
C1-2). The PROM is located inside the ECM,
ancl has information on the vehicle's weight, engine,
transmission, axle ratio, and several others. While one
ECM part number can be used by many car lines, a
ECM PROM ACCESS COVER
1 ECM HARNESS
CONNECTORS TO ECM
45 1196-6E
Figure C1-1 Electronic Control Module (ECM) (5.OL)
PROM is very specific and must be used for the right
car. For this reason, it is very important to checlc the
latest parts book and Service Bulletin information for
the correct part number when replacing
a PROM.
An ECM used for service (called a controller)
comes without a
PROM. The PROM from the old blC>1
must be carefully removed and installctl in the new
EChI (see On-Car Service).
Page 559 of 1825

6EZ-C1-4 S.OL (VIN E) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
THROTTLE VALVE
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM)
THROTTLE POSITION
(TPS)
8P 0321.
Figure C1-7 - Throttle Position Sensor (Typical)
A brolten or loose TPS can cause intermittent bursts of
fuel from the injector, and an unstable idle, because
the ECM thinks the throttle is moving. Once a trouble
code is set, the ECM will use an artificial value for
TPS, and some vehicle performance will return.
On all engines, the TPS is not adjustable. The
ECM uses the reading at idle for the zero reading, so
no adjustment is necessary.
Knock Sensor
The knock sensor is mounted in the engine block.
When abnormal engine vibrations (spark knock) are
present, the sensor produces a voltage signal, which is
sent to the ESC module.
See Section
"C5" for further information on the
electornic spark control
(ESC) system.
ParklNeutral Switch (Auto Only)
The parWneutra1 (PIN) switch indicates to the
ECM when the transmission is in park or neutral.
This information is used for the TCC
, and the IAC
valve operation.
Important
Vehicle should not be driven with parklneutral
switch disconnected as idle quality will be affected
and a possible false Code
24 VSS.
See Section
"8A" for more information on the PIN
switch, which is part of the neutrallstart and
backup light switch assembly.
Crank Signal
The ECM looks at the starter solenoid to tell when
the engine is cranking. It uses this to tell when the car
is in the Starting Mode.
If this signal is not available, car may be hard to
start in extremely cold weather.
AIC Request Signal
This signal tells the ECM that the AJC selector
switch is turned
"ON", and that the pressure cycling
switch is closed. The ECM uses this to adjust the idle
speed when the air conditioning is working.
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
The vehicle speed sensor (VSS) sends a pulsing
voltage signal to the ECM, which the ECM converts to
miles per hour. This sensor mainly controls the
operation of the TCC system. See "TCC System" for
more information.
Distributor Reference Signal
The distributor sends a signal to the ECM to tell it
both engine rpm and crankshaft position. See "EST
System" for further information.
Power Steering Pressure Switch (PSPS)
I
This switch tells the ECM that the vehicle is in a
parking maneuver.
The ECM uses this information to
compensate for the additional engine load by moving
the IAC valve. The ECM will, also, turn
"OFF" the
A/C clutch when high pressure is detected.
( POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH
Figure C'I-8 - Power Steering Pressure Switch (PSPS)
Page 560 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN E) 6EZ-C1-5
DIAGNOSIS
Since the ECM can have a failure which may
effect only one circuit, following the diagnostic
procedures in this section can reliably tell when a
failure has occurred in the ECM. Also,
a Code
55 in
dicates a failure of the ECM.
If a diagnostic chart indicates that the ECM
connections or ECM is the cause of a
problem,and the
ECM is replaced, but does not correct the problem, one
of the following may be the reason:
e
connections. - The diagnostic chart will say "ECM
Connections or ECM". The terminals mav have to be
removed from the connector in order to check them
properly.
@ The ECM or PROM is not correct for the
. - The incorrect ECM or PROM may cause
a malfunction and may or may not set a code.
. - This means that
time the system is
being checked. In this case, refer to the "Symptoms"
portion of the manual and make a careful physical
Solenoids and relays are turned "ON" and "OFF" by
the ECM, using internal electronic switches called
"Drivers".
A shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness in a
GMP4 computer will not damage the ECM,
but will cause the circuit and controlled
component to be inoperative. When the
circuit fault is not present or has been
repaired, the "Quad-Driver" will again
operate in a normal manner due to it's fault
protected design. If a fault has been repaired
in a circuit controlled
by a "Quad-Driver", the
original
ECM should be reinstalled and the
circuit checked for proper operation.
ECM
replacement will not be necessary if the
repaired circuit or component now operates
correctly.
534636 or BT8405 testers or equivalent provide a
fast, accurate means of checking for a shorted coil or a
short to battery voltage.
e , - Although the
PROM rarely
fails,it operates as part of the ECM.
Therefore, it could be the cause of the problem.
Substitute a known good PROM.
o . - After the
ECM is replaced, the system should be rechecked for
proper operation. If the diagnostic chart again
indicates the ECM is the problem, substitute a known
good ECM. Although this is a rare condition, it could
happen. The
components or circuits and the codes or
charts, related to them are:
@ Code 55 indicates a failure of the ECM.
@ PROM - Code 51.
@ Coolant Temperature Sensor - CHARTS 14 -
15.
@ MAP sensor - CHART 33 or 34. To check the
sensor with no code set, use CHART
C-1D.
e TPS - CHARTS 21 or 22.
e PIN switch - CHART C-1A
@ Crank Signal - CHART C-1B
@ O2 Sensor - CHARTS 13,44,45.
@ VSS - CHART 24 and in TCC System.
e Distributor - CHART 42 and in EST system.
@ Distributor - Chart and in the EST system.
ECM
A faulty ECM will be determined in the diagnostic
charts, or by a Code 55.
PROM
An incorrect or faulty PROM, which is part of the
ECM, may set a Code 51.
ECM INPUTS
All of the sensors and input switches can be
diagnosed by the use of a "Scan" tool. Following is
a
short description of how the sensors and switches can
be diagnosed by the use of "a Scan" tool. The
"Scan"
tool can also by used to compare the values for a
normal running engine with the engine you're
diagnosing.
Coolant Temperature Sensor
A "Scan" tool displays engine temp. in degrees
centigrade. After the engine is started, the
temperature should rise steadily to about
90°C, then
stabilize when thermostat opens.
A fault in the
coolant sensor circuit should set a Code 14 or 15. The
code charts also contain a chart to check for sensor
resistance values relative to temperature.
MAT Sensor
A "Scan" tool displays temperature of the air
entering the engine and should read close ambient air
temperature, when engine is cold, and rise
as
underhood temperature increases. If the engine has
not been run for several hours (overnight), the MAT
sensor temperature and coolant temperature should
read close to each other.