1988 PONTIAC FIERO ignition
[x] Cancel search: ignitionPage 951 of 1825
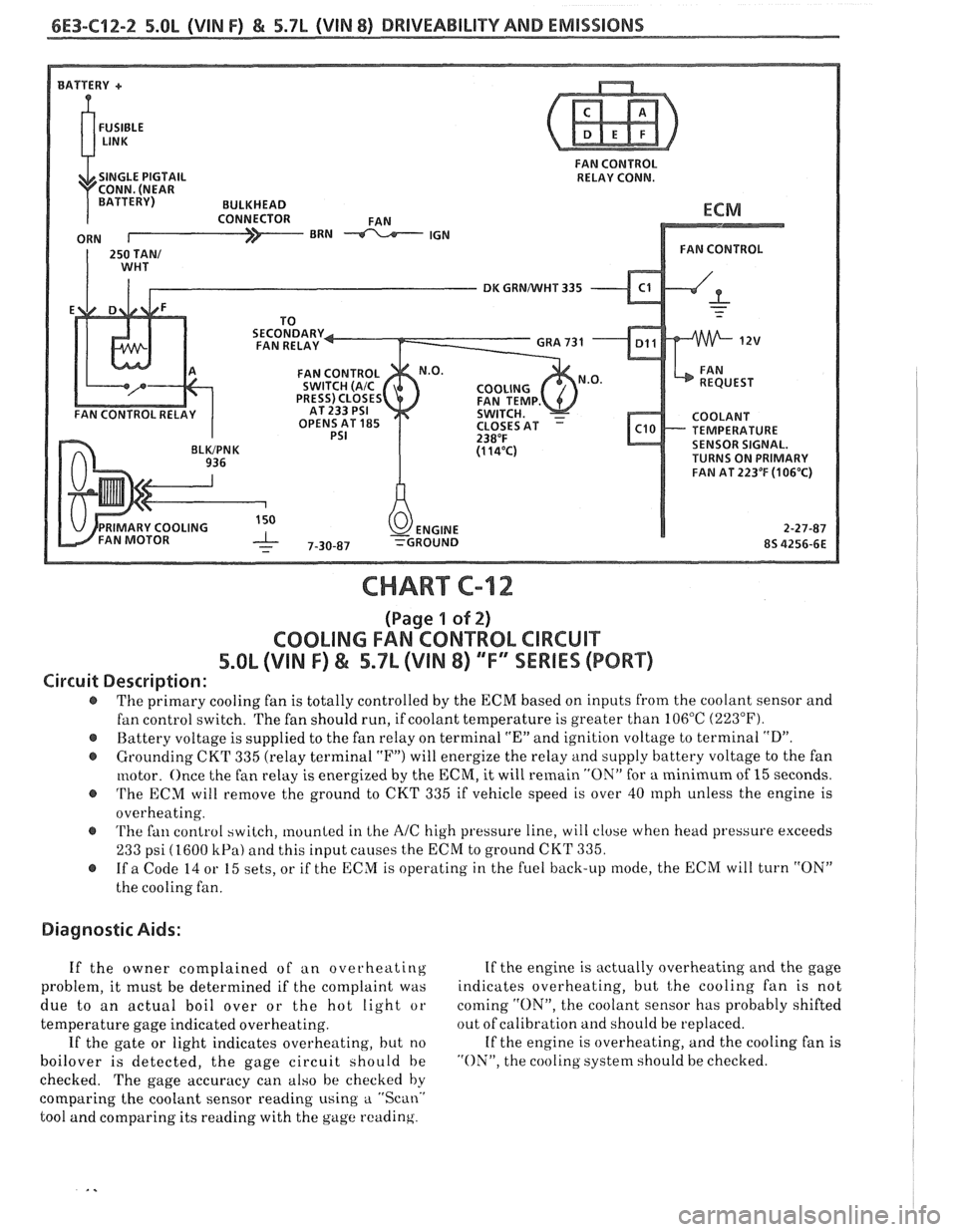
6E3-C12-2 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7b (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
FAN CONTROL
RELAY CONN.
DK GRNNVHT 335
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR SIGNAL.
TURNS ON PRIMARY
FAN AT
223OF (1 06'C)
CHART C-12
(Page 1 of 2)
COOLING FAN CONTROL CIRCUIT
5.8L (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) "F" SSERlES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The primary cooling fan is totally controlled by the ECM based on inputs from the coolant sensor and
fan control switch. The fan should run, if coolant temperature is greater than 106°C
(223°F).
@ Battery voltage is supplied to the fan relay on terminal "En and ignition voltage to terminal "D".
@ Grounding CKT 335 (relay terminal "F") will energize the relay and supply battery voltage to the fan
motor. Once the fan relay is energized by the
ECM, it will remain "ON" for a minimum of 15 seconds.
@ 'I'he ECM will remove the ground to CKT 335 if vehicle speed is over 40 rnph unless the engine is
overheating.
@ 'I'he fan control switch, mounted in Lhe AIC high pressure line, will close when head pressure exceeds
233 psi (1600 kPa) and this input causes the ECM to ground CKT 335.
@ If a Code 14 or 15 sets, or if the ECM is operating in the fuel back-up mode, the ECM will turn "ON"
the cooling fan.
Diagnostic Aids:
If the owner complained of an overheating If
the engine is actually overheating and the gage
problem, it must be determined if the complaint was indicates
overheating, but
t,he cooling fan is not
due to an actual boil over or the hot light or coming
"ON", the
coolant sensor has probably shifted
temperature gage indicated overheating. out
of calibration and should be replaced.
If the gate or light indicates overheating, but no If
the engine is overheating, and the cooling fan is
boilover is detected, the gage circuit should be "ON", the cooling system should be checked.
checked. The gage accuracy can also be checked by
comparing the coolant sensor reading using
a "Scan.'
tool and comparing its reading with the gage reading.
Page 953 of 1825
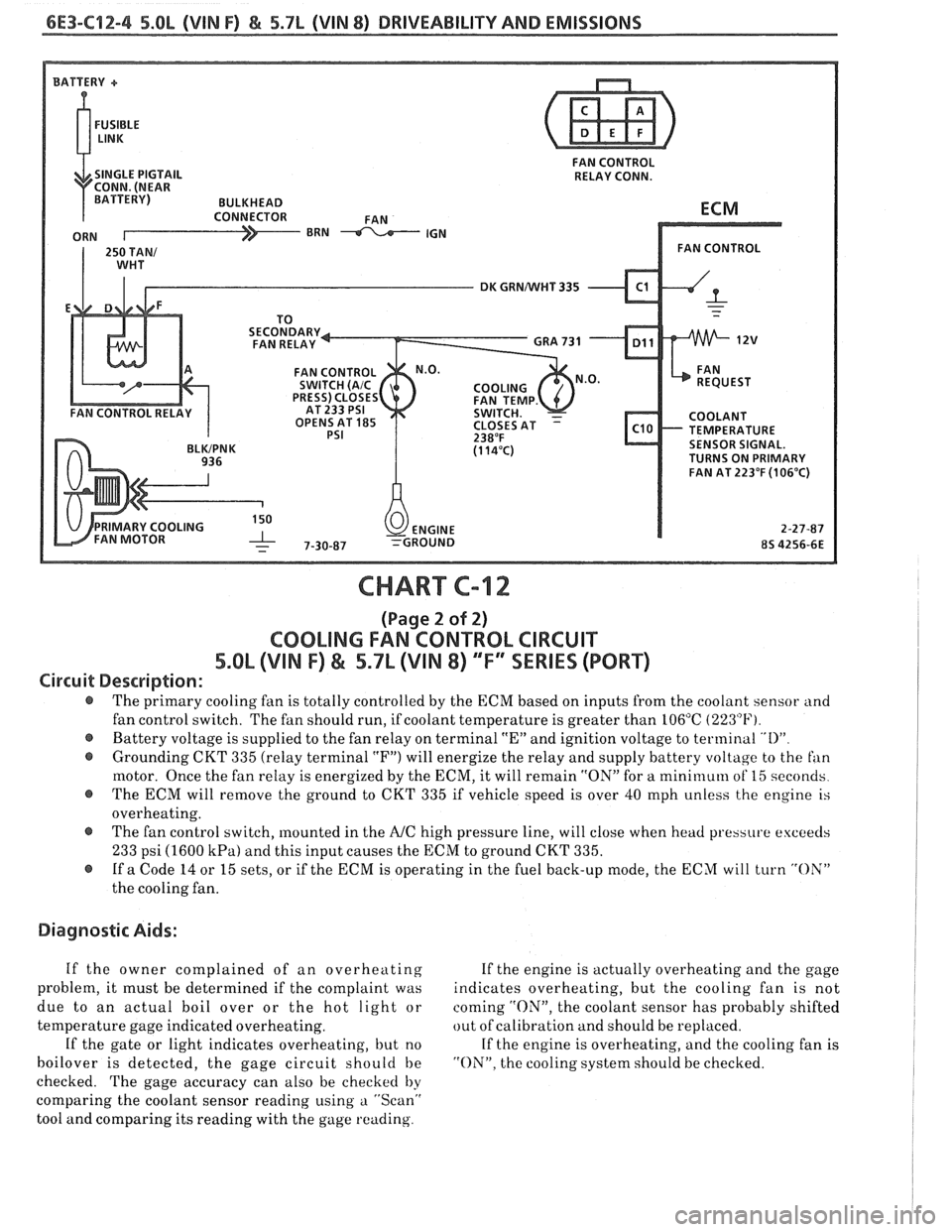
6E3-C12-4 5.8L (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
FAN CONTROL
SINGLE PIGTAIL RELAY CONN.
DK GRNNVHT 335
OPENS AT
185 TEMPERATURE SENSOR SIGNAL.
TURNS ON PRIMARY
FAN AT 223°F
(106°C)
CHART C-12
(Page 2 of 2)
COOLING FAN CONTROL CIRCUIT
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) ""FYSERlES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
@ The primary cooling fan is totally controlled by the ECM based on inputs from the coolant sensor and
fan control switch. The fan should run, if coolant temperature is greater than 106°C
(223°F).
@ Battery voltage is supplied to the fan relay on terminal "En and ignition voltage to terminal "I)"
@ Grounding CKT 335 (relay terminal "F") will energize the relay and supply battery voltage to the fan
motor. Once the fan relay is energized by the ECM, it will remain "ON" for a mini~nuln of 15 seconds
@ The ECM will remove the ground to CKT 335 if vehicle speed is over 40 mph unless the engine is
overheating.
@ The fan control switch, mounted in the A/C high pressure line, will close when head pressure exceeds
233 psi (1600 kPa) and this input causes the ECM to ground CKT 335.
@ If a Code 14 or 15 sets, or if the ECM is operating in the fuel back-up mode, the ECM will turn "OX"
the cooling fan.
Diagnostic Aids:
If the owner complained of an overheating If the engine is actually overheating and the gage
problem, it must be determined if the complaint was indicates overheating, but the cooling fan is not
due to an actual boil over or the hot light or coming
"ON", the coolant sensor has probably shifted
temperature gage indicated overheating. out
of calibration and should be replaced.
If the gate or light indicates overheating, but no If the engine is overheating, and the cooling fan is
boilover is detected, the gage circuit should be "ON". the cooling system should be checked.
checked. The gage accuracy can also be checked
by
comparing the coolant sensor reading using a "Scan"
tool and comparing its reading with the gage reading.
Page 958 of 1825

INDEX
SECTION PAGE
.................... Acceleration Mode C2-2
A/C On Signal
General Description
................. C1-4
......................... Diagnosis C1-5
Air Injection Check Valve
............... C6-4
Air Injection Control (Pedes) Valve
........ C6-1
Air Injection Reaction (A.I.R.) System
General Description
................. C6-1
......................... Diagnosis C6-2
Air Management Check (Pedes)
.......... C6-6
AirPump ........................... C6-2
........................... Service C6-3
...................... ALDL Connector A- 12
Automatic Transmission
Overdrive Switch Adjustment
.......... C8-3
Automatic Transmission Converter Clutch
(TCC) Electrical Diagnosis
.............. C8-6
Backfire
............................ B-5
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
......... C2-3
....................... Before Starting B-I
........................ Burnoff Relay C1-8
......................... Calpac Error 8-60
........................ Canister Hose C3-3
Canister Purge Solenoid
................ C3-3
Chart
A-1 :
.......... No Service Engine Soon Light A-1
0
Chart
A-2:
No ALDL Data. Or Won't Flash Code 12.
Or Service Engine Soon Light On Steady
. . A-1 2
Chart A-3:
Engine Cranks But Won't Run
.......... A-14
Chart A-7:
................ Fuel System Diagnosis A- 18
Chart A-9:
........... Cold Start Valve Circuit Test A-22
Chart
B-1:
Restricted Exhaust System Check ........ B-8
Chart
C-1A:
......... ParkINeutral Switch Diagnosis C1-10
Chart C-2A:
................. Injector Balance Test C2-18
Chart C-2C:
Idle Air Control (IAC) System Check ...... C2-20
SECTION PACE
Chart C-3:
........... Canister Purge Valve Check C3-4
Chart C-4:
................ Ignition System Check C4-4
Chart
6-5:
.......... Electronic Spark Control (ESC) C5-4
Chart C-6:
.............. Air Management Check C6-6
Chart C-7:
Exhaust Gas Recirculation
............. C7-4
Chart
C-8A:
Automatic Transmission Converter Clutch
............................. (TCC) C8-6
Chart C-8B:
Manual Transmission With Overdrive
.... C8-10
Chart C- 12
:
................. Cooling Fan Control C12-2
............................ Chuggle B-3
................... Clear Flood Mode.. C2-2
......................... Closed Loop C2-1
Code12
............................ C4-1
Code13
............................ A-24
Code14
............................ A-26
Code15
............................ A-28
Code21
............................ A-30
Code22
............................ A-32
Code23
............................ A-34
Code24
............................ A-36
Code25
............................ A-38
Code32
............................ A-40
Code33
............................ A-42
Code34
............................ A-44
Code36
............................ A-46
Code41
............................ A-48
Code42
............................ A-50 C4-2
Code43
............................ A-52
Code44
............................ A-54
Code45
............................ A-56
Code46
............................ A-58
Code54
............................ A-60
...................... Codes 51.52. 53 A-62
Cold Start Tube And Valve Assembly
...... C2-7
Cold Start Fuel
lnjection Sw~tch
.................. General Description C2-11
......................... Diagnosis A-22
.................. Component Location A-2
Coolant Temperature Sensor
.................. General Description C1-2
.......................... Diagnosis C1-4
A-26
........................... Service C1-7
Page 959 of 1825

INDEX
SECTION PAGE
Cooling Fan Control
................. General Description C12-1
........................ Diagnosis C12-2
........................... Cuts Out B-5
................... Cylinder Select Error A-48
.................... Deceleration Mode C2-3
......................... Detonation B-4
..................... Dieseling. Run On B-6
............. Distributor Reference Signal C1-4
...................... ECM Terminals A-7
.................. ECM Wiring Diagram A3-A6
EGR Control Valve
................. General Description C7-1
................. Valve Identification C7-2
................... Diagnosis. Service C7-2
A-40
.................. EGR Control Solenoid C7-3
......................... EGR Check C7-4
Electronic Control Module
................. General Description C1-1
......................... Diagnosis C1-4
............................ Service C1-5
..................... Function Check C1-7
Electronic Spark Control (ESC) System
................. General Description C5-1
................... Diagnosis. Service C5-4
Electronic Spark Timing EST
............. A-50
A-52
Engine Cranks But Won't Run
............ A-14
........................ Engine Knock C5-4
.......................... ESC Module C5-2
.......................... ESC Sensor C5-1
.................... ESC System Check C5-4
................... ESTllgnition System C4-1
Evaporative Emission Control System
................. General Description C3-1
.......................... Diagnosis C3-2
Exhaust Emissions Excessive (Odors)
....... B-7
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System
.... C7-1
Exhaust System Check Restricted
......... B-8
Fuel Control System
................. General Description C2- 1
......................... Diagnosis C2-5
..................... Fuel Cutoff Mode C2-3
SECTION PAGE
Fuel Injectors ........................
Fuel Pressure Connection Assy ............
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure ...........
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit .............
Fuel Pump Relay ......................
Fuel Rail
General Description
.................
........................... Service
Fuel System Diagnosis
..................
Fuel System Pressure Test ...............
Fuel Tank Pressure Control Valve .........
.......................... Hard Start B-2
.......... HE1 High Energy Ignition System C4-1
.......................... Hesitation
B-3
............ Idle Air Control System Check C2-20
.................. Idle Air
Control Valve C2-4
......................... Diagnosis C2-5
.................... Ignition System EST C4-1
........ Ignition System Check Integral Coil C4-4
........................ Incorrect Idle B-6
.................. Information Sensors C1.2. 9
.................. Injector
Balance Test C2-18
........................ lntermittents B-2
........................ Knock Sensor C1-3
........................ Lack Of Power B-4
......... Light. Manual Transmission Shift C8-6
.............. Light. Service Engine Soon A-10
MAF Sensor
.................. General Description C1-2
.......................... Diagnosis C1-5
A.42.44. 46
............................ Service C1-8
... Manual Transmission Electrical Diagnosis C8-10
MAT Sensor
.................. General Description C1-2
......................... Diagnosis C1-5
A.34. 38
Page 964 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - FUEL INJECTION 6E-3
VEHICLE EMISSION CONTROL INFORMATION
MBEL
The Vehicle Emission Control Information label
(Figure
1) contains important emission specifications
and setting procedures. In the upper left corner is
exhaust emission information which identifies the
year, the manufacturing division of the engine, the
displacement in liters of the engine, the class of
vehicle and type of fuel metering. Also there is an
illustrated emission component and vacuum hose
schematic. A similar label is located in the engine
compartment of every General Motors Corporation
vehicle. If the label has been removed, it can be
ordered from the parts division.
(WDDGM)
INTRODUCTION
Electronic Engine Control
Each engine has an electronic engine control
module
(ECM) to control the fuel system. The ECM
varies the
airlfuel ratio by controlling the fuel flow
through the
injectorb).
In addition, the ECM controls the ignition timing
as well as the fuel pump and other systems.
It is important to review the component sections
and wiring diagrams in Section
"6E2" and "6E3" for a
specific engine, to determine what is controlled by the
ECM and what systems are
non-ECM controlled.
What This Section Contains
Each General Motors engine has system controls
to reduce exhaust emissions while maintaining good
driveability and fuel economy. This section explains:
@ Wow to use the Driveability and Emission
Sections
"6E2" for TBI, and "6E3" for Port
Fuel engines.
A brief description of systems used to control
fuel and emissions.
@ Abbreviations that are used in "Driveability
and Emissions".
@ Wiring harness service information for
harnesses used with the ECM.
@ Special tools used to diagnosis and repair a
system. Before
checking the system, observe the following:
Blocking Drive Wheels
The vehicle drive wheels always should be
blocked, and parking brake firmly set, while checking
the system.
Cold Oxygen Sensor
On some engines, the oxygen sensor will cool off
after only a short period of operation at idle. This will
put the system into "Open Loop". To restore "Closed
Loop" operation, run the engine at part throttle and
accelerate from idle to part throttle a few times until
the system goes "Closed Loop".
VlSUAUPHYSlCAL UNDERHOOD
INSPE6"rON
This can often lead to fixing a problem without further
steps. Inspect all vacuum hoses for correct routing,
pinches, cuts, or disconnects. Be sure to inspect hoses
that are difficult to see beneath the air cleaner,
compressor, generator, etc. Inspect all the wires in the
engine compartment for correct and good connections,
burned or chafed spots, pinched wires, or contact with
sharp edges or hot exhaust manifolds. This
visual/physical inspection is very important. It must ,
be done carefully and thoroughly.
BASIC KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED
Before using this section of the service manual,
there are some areas that you should be familiar with.
Without this basic knowledge, you will have trouble
using the diagnostic procedures contained in this
section.
Basic Electric Circuits
You should understand the basic theory of
electricity, and know the meaning of voltage, amps,
ALL NEW GENERAL MOTORS VEHICLES ARE CERTIFIED BY THE UNITED STATES
ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
AGENCY AS CONFORMING TO THE REQUIREMENTS OF THE
REGULATIONS
FOR THE CONTROL OF AIR POLLUTION FROM NEW MOTOR VEHICLES. THlS
CERTIFICATION IS CONTINGENT OM CERTAIN ADJUSTMENTS BEING SET TO FACTORY
STANDARDS. IN MOST CASES, THESE ADJUSTMENT
POINTS EITHER HAVE BEEN
PERMANENTLY SEALED
AND/OR MADE INACCESSIBLE TO PREVENT INDISCRIMINATE OR
ROUTINE ADJUSTMENT IN THE FIELD. FOR
THlS REASON, "TI- FACTORY PROCEDURE FOR
TEMPORARILY REMOVING PLUGS, CAPS, ETC., FOR PURPOSES OF SERVICING THE PRODUCT,
MUST BE STRICTLY FOLLOWED AND, WHEREVER PRACTICABLE, RETURNED
TO WE
ORIGINAL INTENWF THE DESIGN.
Page 965 of 1825

6E-4 DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - FUEL INJECnON
and ohms. You should understand what happens in a
circuit with an open or a shorted wire. You should be
able to read and understand a wiring diagram. A
short to ground
is referred to as a ground to
distinguish it from a short between wires.
Use of Circuit Testing Tools
You should know how to use a test light, how to
connect and use
a tachometer, and how to use jumper
wires to by-pass components to test circuits. Care
should be taken to not deform the terminal when
testing.
Use of Digital Volt-Ohm Meter (DVM)
You should be familiar with the digital volt-ohm
Meter, particularly essential tool J-29125-A,
J34029A
or equivalent. You should be able to measure voltage,
resistance, and current, and know how to use the
meter correctly.
The digital volt-ohm meter is covered in the
"Special
ToolsJ'portion of this section.
DIAGNOSTIC INFORMATION
The electronic control module (ECM) is equipped
with a self-diagnosis system which detects system
failure and aids the technician by identifying the
circuit at fault via a trouble code. Below is
information about the way the ECM displays a
problem and how this corresponds to a trouble code in
the ECM. The ECM can also indicate an "Open Loop"
or "Closed Loop" mode.
"'Service Engine Soonw Light
This light is on the instrument panel, and has two
functions:
@ It is used to tell the driver that a problem has
occurred, and that the vehicle should be taken for
service as soon as reasonably possible.
@ It is used by the technician to read out "Trouble
CodesJ' to help diagnose system problems.
As a bulb and system check, the light will come
"ON" with the key "ON" and the engine not running.
When the engine is started, the light will turn "OFF".
If the light remains "ONJ', the self-diagnostic system
has detected a problem. If the problem goes away, the
light will go out in most cases after 10 seconds, but a
Trouble Code will remain stored in the ECM.
Intermittent "Service Engine Soon" Light
The diagnostic charts in Section "A" are set up to
check whether or not a stored trouble code is
"intermittent" or "hard". An
"intermittent" code is one which does not
always reset when the code setting parameters are
met, or is not present while you are working on the
vehicle. This is often caused by
a loose connection.
The facing page will contain diagnostic aids to help in
detecting
intermittents.
A "hard" code is one which is present when you
are working on the vehicle and the condition still
exists while working on the vehicle. The chart with
the stored trouble code number will lead you to the
cause of the problem.
Trouble Codes
The engine control module (ECM) is really a
computer. It uses sensors to look at many engine
operating conditions. It has
a memory and it knows
what certain sensor readings should be under certain
conditions. These conditions are described on the
facing page of each Trouble Code chart. If a sensor
reading is not what the ECM thinks it should be, the
ECM will turn "ON" the "Service Engine Soon" light
on the instrument panel, and will store a Trouble Code
in the memory. The Trouble Code tells which circuit
the trouble is in. A circuit consists of a sensor (such as
coolant temperature), the wiring and connectors to it,
and the ECM.
i
To get a Trouble Code out of the ECM, we use the
assembly line diagnostic link (ALDL) connector.
!
ALDL Connector I
I
The assembly line diagnostic link (ALDL) is a
diagnostic connector located in the passenger
compartment (Figure 2). It has terminals which are
used in the assembly plant to check that the engine is
operating properly before it leaves the plant.
Terminal "B" is the Diagnostic terminal, and it can be
connected to terminal
"A", or ground, to enter the
Diagnostic mode, or the Field Service Mode.
The ALDL connector is also used by "ScanJ' tools to
read information from the ECM via the Serial Data
Line. Serial Data information
is used extensively
throughout the manual.
Diagnostic Mode
1
If the Diagnostic terminal is grounded with the
ignition "ON" and the engine stopped, the system will
enter the Diagnostic Mode. In this mode the ECM
will:
1. Display a Code 12 by flashing the "Service Engine
Soon" light (indicating the system is operating). A
Code 12 consists of one flash, followed by a short
pause, then two flashes in quick succession. This
code will be flashed three times. If no other codes
Page 969 of 1825

6E-8 DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - FUEL INJECTION
Throttle Position Sensor (TPO) Coolant Q~erature
Values read will be the voltage as seen by the Engine
temperature is displayed in Celsius
ECM. The voltage should be the TPS specification degrees.
After the engine is started, temperature
with the throttle closed and go up to about 5 volts should
rise steadily to about
85-95" C, then stabilize
with throttle wide open
(WOT). when the thermostat opens.
Throttle Angle
Displayed, in percent, is the amount the throttle is
open. 0% is closed throttle, 100% is wide open throttle.
Oxygen (Of) Sensor
The reading will be read out in millivolts (mv)
with a range from 1 to 999 mv. If the reading is
consistently below 350 (350 mv), the fuel system
is
running lean as seen by the ECM; and if the reading is
consistently above 550 (550 mv), the system is
running rich.
In this position, information is used for assembly
verification only. PROM ID is useful only when the
vehicle
is equipped with the original ECM and PROM
or Mem-Cal.
Reading displays engine rpm. It is often useful if
extra reference pulses are suspected. A sudden high
rpm indication while at a steady throttle would
indicate electrical interference
(EMI) in the reference
circuit. This interference
is usually caused by ECM
wires too close to ignition secondary wires or an open
distributor ground circuit.
Displayed is vehicle speed, useful in checking TCC
application speed or speedometer accuracy.
MAF
This displays the amount of air passing the Mass
Air Flow
(MAF) sensor, in grams per second. It is
useful when comparing the airflow between a problem
vehicle and a known good one. Normal readings at
idle are about
4 to 8 grams. If a MAF code is set, this
reading will display the ECM default value.
This display should be the same as MAF when
there are no failures in the MAP sensor circuit. When
an MAF code is set, however, this value will not
change, and will indicate the
grn/sec that the failure
has detected.
Manifold Air Temperature (MAT) Sensor
This displays temperature of the intake manifold
air. It should read close to ambient air temperature
when the engine is cold, and rise as underhood and
engine temperatures increase.
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
The MAP sensor produces a low signal voltage
when manifold pressure is low (high vacuum) and a
high voltage when the pressure is high (low vacuum).
With the ignition "ON" and the engine stopped,
I
the manifold pressure is equal to atmospheric
pressure, and the signal voltage will be high. This 1
information is used by the ECM as an indication of
vehicle altitude and is referred to as BARO.
Comparison of this
BARO reading with a known good
vehicle with the same sensor is a good way to check
accuracy of a "suspect" sensor
*. Readings should be
the same
+ .4 volt. I
* A MAP sensor has a colored plastic insert visible I I
in the connector cavity. Sensors with the same insert I
color are identical in calibration. The harness I
I
electrical connector color also should be the same as 1 the sensor insert color.
I Vacuum (Differential Pressure) Sensor
The vacuum sensor produces a low signal voltage
when manifold vacuum is low, and a high voltage
when the vacuum is high.
With the ignition "ON" and the engine stopped,
there is no vacuum, so the voltage is low (under
1
volt). With the engine idling the vacuum is high so the
voltage is high (over
3 volts).
A vacuum sensor has a colored plastic insert
visible in the connector cavity. Sensors with the same
insert color are identical in calibration. The harness
electrical connector color also should be the same as
the sensor insert color.
This displays barometric pressure. The ECM uses
this information to adjust for altitude and pressure.
This value will vary depending on barometric
pressure and altitude. Some vehicles use a dedicated
bar0 sensor, while others take a MAP reading before
the engine is started, and at various times during
engine operation.
Page 970 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - FUEL INJECTION 6E-9
ParWNelatral Switch IAC (Idle Air Control)
The indication in this mode may vary with This system is used to control engine idle speed to
manufacturer so the type of reading for a particular the desired rpm, for different operating conditions. In
tool should be checked in the operator's manual. The this mode, the numbers will indicate the position to
important thing is that the the reading changes state which
the ECM has moved the valve pintle. The ECM
(switches) when the gear selector is moved from moves
the IAC in counts, or steps, and the number of
paridneutral to drive or reverse. these counts are displayed on a "Scan" tool.
"Trque Convertor Clutch (TCC)
In this position, the tool will indicate when the
TCC has been commanded by the ECM to turn "ONJ'.
This does not necessarily mean that the clutch was
engaged but only that the
ECM grounded the circuit
internally. The best way to determine if the clutch has
engaged is to monitor engine rpm when the TCC
comes "ON".
EGR (Duty Cycle)
The EGR system uses a valve to feed a small
amount of exhaust gas back into the intake manifold
to control formation of NO,. Like all ECM outputs, the
"Scan" tool only indicates that the ECM has
commanded the function, and does not indicate that
the function has really happened.
EGR Position
This indicates the position of the EGR pintle.
Integrator and Block Learn
Normal readings for these positions are around
128. If higher, it indicates that the ECM is adding fuel
to the base fuel calculation because the system is lean,
and if the numbers are below 128, the ECM is taking
out fuel from the base calculation because the system
is rich. The integrator gives short term corrective
action, while the block learn portion (which is a long
term correction) will only change if the integrator has
seen a condition which lasts for a calibrated period of
time.
Block Learn Multiplier (BLM) Cell - or -
Block Learn Memory (BLM)
There are up to sixteen different cells,
corresponding to ranges of rpm and engine load
(indicated by MAF or MAP signals), and other
conditions, such as
A/C or P/N switch "ON" or "OFF",
etc. The ECM learns how much adjustment is needed
in each cell, and retains it in memory, so that the
adjustment will immediately be made when the
engine operates in that cell (or
rpmlload range). This
parameter will display what cell the ECM is currently
using for the fuel calculation.
Desired RPM
This indicates the rpm to which the ECM is trying
to control the idle.
Shift Light
This displays "yes" when the ECM is commanding
the shift light to turn "ON".
PPSW (Pump Prime Switch)
This is the voltage on the fuel pump feed circuit.
The ECM will adjust fuel injector base pulse width
from this voltage value rather than from battery
voltage.
NC Request
The state of the A/C signal line to the ECM is
shown. It should read "yes" whenever the
IVC is
requested.
NC Clutch
"ON" is displayed when the ECM has commanded
the
A/C clutch "ON".
Knock Retard
This indicates the number of degrees the ECM is
retarding the electronic spark timing (EST).
Knock Signal
This displays a "yes" when knock is detected by
the ECM, and a "no" when knock is not detected.
Battery Voltage
This displays the battery voltage detected at the
ECM ignition input.
Fan
"ON" is displayed when the cooling fan has been
commanded "ON".