1988 PONTIAC FIERO turn signal
[x] Cancel search: turn signalPage 21 of 1825

OB-4 MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION
Tire and wheel operation - Be alert to a vibra-
tion of the steering wheel or seat at normal highway
speeds. This may mean a wheel balance is needed. Also, a
pull right or left on a straight, level road may show the
need for
a tire pressure adjustment or wheel alignment.
Steering system operation - Be alert to
changes in steering action. An inspection is needed when
the steering wheel is harder to turn or has too much free
play or if unusual sounds are noted when turning or
parking.
Headlight aim operation - Take note of light
pattern occasionally. If beam aim doesn't look right,
headlights should be adjusted.
AT EACH FUEL FILL
Engine oil level check - Check engine oil level
and add if necessary. See your Owner's
Manual for further
details.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Engine coolant level and condition - Check
engine coolant level in coolant reservoir tank and add if
necessary. Replace if dirty or rusty. See your Owner's
Manual for further details.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Windshield washer fluid level check -- Check
washer fluid level in container and add if necessary.
Hood latch operation - When opening hood on
cars equipped with hoods that open from the front, note
the operation of secondary latch. It should keep hood from
opening all the way when primary latch is released. Make
sure that hood closes firmly.
AT LEAST MONTI-ILY
Tire and wheel inspection and pressure
check--
Check tires for abnormal wear or damage. Also,
check for damaged wheels. Keep pressures as shown on
Tire Placard on the driver's door (include spare unless it is
a stowaway). Pressure should b\: checked when tires are
"cold". See "Tires" in Owner's Manual for further
infomation.
Light operation check - Check operation of
license plate light, side-marker lights, headlights includ-
ing high beams, parking lights, taillights, brake lights.
turn signals, backup lights, instrument panel and interior
lights and hazard warning flashers.
Fluid leak check - After the car has been parked
for a while, inspect the surface beneath the car for water,
oil, fuel or other fluids. Water dripping from the air
conditioning system after use is normal. If you notice fuel
leaks or fumes, the cause should be found and corrected at
once.
AT LEAST TWICE A YEAR (FOR EXAMPLE,
EVERY SPRING AND FALL)
Power steering pump fluid level check --
Check power steering pump fluid level in accordance with
Owner's Manual instructions and keep at proper level.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Brake master cylinder reservoir fluid level
check ---- Check fluid and keep at proper level. Note: It is
normal for the brake fluid level to go down slightly as the
brake pads wear
- so be sure to keep reservoir filled.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have
it inspected and repaired at once.
Clutch system service --- manual transmis-
sionltransaxle --- For cars equipped with hydraulic
clutch system, check the reservoir fluid level and add fluid
as required. All others, check clutch pedal free travel and
adjust as necessary. See your Owner's Manual for further
details.
~
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Weatherstrip Lubrication - Clean surface and
then apply a thin film of silicone grease with a clean cloth.
EACH TIME OIL IS CHANGED
Automatic and manual transmissionltrans-
axle fluid level check - Check transmission/transaxle
fluid level and add as required. (Corvette only) if equipped
with manual transmission
- check fluid in the overdrive
unit and add as required.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have
it inspected and repaired at once.
Brake systems inspection - For convenience,
the following should be done when wheels are removed
for rotation: Inspect lines and hoses for proper hookup,
binding, leaks, cracks, chafing, etc. Inspect disc brake
pads for wear and rotors for surface condition. Also in-
spect drum brake linings for wear and cracks. Inspect
other brake parts, including drums, wheel cylinders, park-
ing brake, etc. at the same time. Check parking brake
adjustment.
INSPECT BRAKES MORE OFTEN IF DRIVING
HABITS OR CONDITIONS RESULT IN FREQUENT
BRAKING.
Steering, suspension and front drive axle
boot and seal inspection
- Inspect front and rear
suspension and steering system for damaged, loose or
missing parts, signs of wear or lack of lubrication. Inspect
power steering lines and hoses for proper hookup, bind-
ing, leaks, cracks, chafing, etc. (On cars equipped with
manual steering gear, check for seal leakage.) On
front-
wheel-drive cars, clean then inspect drive axle boot seals
for damage, tears or leakage. Replace seals if necessary.
Exhaust system inspection - Inspect complete
system. Inspect body near the exhaust system. Look for
broken, damaged, missing or out-of-position parts as well
as open seams, holes, loose connections or other condi-
tions which could cause a heat buildup in the tloor pan or
could let exhaust fumes seep into the trunk or passenger
compartment.
Page 47 of 1825

18-4 AIR CONDITIONING
If replacement of the pressure cycling switch is
necessary, it is important to note that this may be done
without removing the refrigerant charge.
A Schrader-
type valve is located in the pressure switch fitting.
During replacement of the pressure switch, a new
oiled O-ring must be installed and the switch assem-
bled to the specified torque of
6- 13 N*m (5- 10 lb. ft.).
Power Steering Gut-OH, or Anticipate
Switch
Engine idle quality on some cars is maintained
by cutting off the compressor (switch normally
closed) when high power steering loads are imposed.
On other cars the switch (normally open) provides a
signal to the ECM to allow engine control systems to
compensate for high-power steering loads.
Wide-Open Tkroale (WOT) Compressor
Cut-Out
Switch
A switch located on the throttle corltrols of some
carburetor equipped cars opens the circuit to the com-
pressor clutch during full throttle acceleration. The
switch activates a relay that controls the compressor
clutch. During full throttle acceleration
on cars
equipped with TBI or
Em, the TPS sends a signal to
the ECM, thereby controlling the compressor clutch.
Air Conditioning Time Delay Relay
This relay on some cars controls the current to
the entire air conditioning system and provides a short
delay of air conditioning operation upon start-up.
Constant Run Relay
Engine idle quality on some cars is maintained
by a "constant run" system (constant run relay) that
eliminates compressor cycling during engine idle for a
predetermined time after the vehicle has come to rest
from road speed.
If the idle period continues for an
extended time, the
A/C system may return to a con-
ventional C.C.O.T. mode for a short time to prevent
system freeze-up. The
A/C control relay and constant
run relays are both controlled by the Electronic Con-
trol Module (ECM) which determines operating con-
ditions by evaluating input from the distributor
(engine speed), vehicle speed sensor, air sensor and
A/C compressor "on" signal.
5-PRESSURE CYCLING 8-EXPANSION TUBE
SWITCH (ORIFICE)
6-DESSICANT BAG O-LIQUID LINE
7-OIL BLEED HOLE
10-PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
@ ee LOW PRESSURE LIQUID HIGH PRESSURE LIQUID LOW PRESURE VAPOR HIGH PRESSURE VAPOR
Figure 2 A/C System - Typical
Page 126 of 1825

STEERING, SUSPENSION, f IRES AND WHEELS DIAGNOSIS 3.1
SECVION 3
STEER NG, SUSPENS
WHEELS
AGNOS
CONTENTS
........................................... General Information 3- 1 ............................................ General Diagnosis 3- 1
Power Recirculating Ball .................................. 3-3
................. Steering Linkage ........................ .. 3-3
Power Steering Pump ................... ... ............ 3-4
Steering Column
Lock System
........................... ... ................ 3-4
Column ............................................................ 3-5
........................................ Turn Signal Switch 3-6
Ignition Switch .............................................. 3-7
Key Reminder .............................................. 3-7
Dimmer Switch .................... ... ................ 3-10
Pivot and Switch Assembly ............................ 3-10
Steering Gear and Pump Leaks .......................... 3- 10
Seal Replacement Recommendations ................. 3- 10
Power Steering System Test Procedure .............. 3-12
................ Strut Dampener and Shock Absorber 3- 12
Tires ........................ .. ..................................... 3- 13
Vibrations .......................... .............. .................... 3- 14
.......................... Tapered Roller Bearings .. .... 3- 14
Trim Height .............................................. 3-14
GENERAL INFORMATION Abnormal or Excessive Tire Wear
Since the problems in steering, suspension, tires
and wheels involve several systems, they must all be
considered when diagnosing a complaint. To avoid
e Front-wheel or rear-wheel alignment
using the wrong symptom, always road test the car
o Sagging or broken springs
first. Proceed with the following preliminary checks
Tire out of balance and correct any substandard conditions which are worn strut dampener or shock absorber found. o Hard driving
--
e Tires for wrong pressure and uneven wear
o Joints from the column to the steering gear for
loose connectors or wear
o Front and rear suspension, and the steering gear
or linkage for loose or damaged parts
Out-of-round or out-of-balance tires, bent wheels,
and loose and/or rough wheel bearings
@ Power steering system for leaks. Also check the
power steering fluid level and the pump drive belt
tension
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS
Car Pulls (Leads)
Inspect
Mismatched or uneven tires
Broken or sagging springs
Radial tire lateral force
Front-wheel or rear-wheel alignment
o Steering gear valve off center (unbalanced)
e Front brakes dragging
a Overloaded car
e Not rotating tires
Scuffed Tires
o Toe incorrect
e Excessive speed on turns
o Suspension arm bent or twisted
Wheel Tramp
Inspect
o Blister or bump on tire
o Improper strut dampener or shock absorber
action
Shimmy, Shake or Vibration
inspect
e Tire or wheel out of balance
e Worn wheel bearings
a Worn tie rod ends
o Worn lower ball joints
Page 128 of 1825

STEERING, SUSPENSION, VIBES AND WHEELS DIAGNOSIS 3-3
Steering Wheel Kick-Back (Power)
Inspect
e Air in system
e Loose steering gear mounting
e Joints from column to steering gear loose or worn
e Tie rod ends loose
Worn or missing check valve
(800 series)
e Wheel bearings worn
e See "Too Much Play In Steering" for other
possible causes.
Steering Wheel Surges Or Jerks (Power)
Inspect
Hydraulic system - Make pressure test with gage
J 5176-D or
J 25323
e Sluggish steering gear valve
Loose pump drive belt
Cupped Tires
Inspect
Front-wheel or rear-wheel alignment
e Strut dampeners or shock absorbers weak
e Wheel bearing worn
e Excessive tire or wheel runout
e Worn ball joint
a Loose steering gear adjustment
POWER RECIRCULATING BALL
SEERING GEAR DIAGNOSIS
Hissing Noise
There is some noise in all power steering systems.
One of the most common is a hissing sound when the
steering wheel is turned and the car is not moving. This
noise will be most evident when turning the wheel
while the brakes are applied. There is no relationship
between this noise and steering performance. Do not
replace the valve unless the "hissing" noise is extremely
objectionable. A replacement valve will also have a
slight noise, and is not always a cure for the condition.
Check that the intermediate shaft joints are not loose.
Rattle or Chucking Noise
Inspect -
Pressure hose grounding out
e Tie rod ends loose
e Steering gear attachment loose
a Loose pitman shaft "over-center" adjustment.
A slight rattle may occur on turns because of
increased clearance off the "high point". This is
normal and clearance must not be reduced below
specified limits to eliminate this slight rattle.
Poor Return of Steering Wheel to Center
Front-wheel alignment
Wheel bearing worn
Tie rod end binding
Ball joint binding
Steering wheel rubbing against turn signal
housing
Steering gear adjustments
Tight or frozen intermediate steering shaft
Sticky or plugged spool valve
Momentary Increase in Effort Whsn Turning
Wheel Fast to Right or Left
Inspect
High internal leakage
Steering Wheel Surges or Jerks When Turning
With
Engine Running Especially During Parking
ln8pe~t
e Insufficient pump pressure
Sticky flow control valve
Excessive Wheel Kickback or Loose Steering
Air in system
Steering gear attachment loose
Tie rod ends loose
Wheel bearings worn
Steering gear flexible coupling loose on shaft or
rubber disc mounting nuts loose
Loose thrust bearing preload adjustment
Excessive "over-center" lash
Worn pressure port check valve
Hard Steering or Lack of Assist
(Especially During Parking)
-
Brakes applied while turning steering wheel
Intermediate shaft damaged or worn
e Sticky flow control valve
Insufficient pump pressure
Excessive internal pump leakage
Excessive internal steering gear leakage
STEERING LINKAGE DIAGNOSIS
Excessive Play or Looseness in Steering Systern
inspect
r, Worn upper ball joints
e Steering gear worm bearings loosely adjusted
Page 131 of 1825

3-6 STEERING, SUSPENSION, TIRES AND WHEELS DIAGNOSIS
Steering Wheel Loose
lnspect
Excessive clearance between holes in support or
housing and pivot pin diameters
e Damaged or missing anti-lash spring in spheres
e Upper bearing not seated in housing
e Upper bearing inner race seal missing
e Loose support screws
e Bearing preload spring missing or broken
Steering Wheel Loose (Every Other Tilt Position)
lnspect
e Loose fit between shoe and shoe pivot pin
e Shoe not free in slot
Steering Column Not Locking In Any Tilt
Position
lnspect
e Shoe seized on its pivot pin
e Shoe grooves may have burrs or dirt
e Shoe lock spring weak or broken
Steering Wheel Fails To Return To Top Tilt
Position
Inspect
e Pivot pins are bound up
e Wheel tilt spring is broken or weak
e Turn signal switch wires too tight
Noise When Tilting Column
Inspect
e Upper tilt bumpers worn
e Tilt spring rubbing in housing
TURN SIGNAL SWITCH
This diagnosis covers mechanical problems only
See Section
8A for turn signal switch electrical diagnosis.
Turn Signal Will Not Stay In Turn Position
lnspect
e Foreign material or loose parts impeding
movement of yoke
e Broken or missing detent or cancelling spring
s None of the above, replace switch
Turn Signal Will Not Cancel
lnspect
a Loose switch mounting screws
e Switch or anchor bosses broken
e Broken, missing or out of position detent, return
or cancelling spring
Worn cancelling cam
Turn Signal Difficult To Operate
0 Inspect
e Turn signal switch arm loose
e Yoke broken or distorted, replace switch
e Loose or misplaced springs
e Foreign parts andlor material
o Loose turn signal switch mounting screws
Turn Signal Will Not Indicate Lane Change
a Inspect
e Broken lane change pressure pad or spring
hanger
e Broken, missing or misplaced lane change spring
e Jammed base or wires
Hazard Switch Cannol: Be Turned Off
a Inspect
e Foreign material between hazard support
cancelling leg and yoke
e If no foreign material is found, replace turn signal
switch.
Hazard Switch Will Not Stay On or Difficult To
Turn Off
e Loose turn signal switch
a Interference with other components
e Foreign material interference
e None of the above, replace turn signal switch
No Turn Signal Lights
lnspect
e Electrical failure in chassis harness
e Inoperative turn signal flasher
e Loose chassis-to-column connector. Disconnect
column-to-chassis connector and connect new
turn signal switch to chassis and operate switch
by hand.
A. If car lights now operate normally, turn
signal switch is inoperative.
B. If
car lights do not operate, refer to Section 8A
for electrical diagnosis.
Turn Indicator Lights On, But Not Flashing
a Inspect
e Inoperative turn signal flasher
Loose chassis-to-column connection
Inoperative turn signal switch
Page 132 of 1825

STEERING, SUSPENSION, TIRES AND WHEELS DIAGNOSIS 3-7
e To determine if turn signal switch is inoperative,
substitute new turn signal switch into circuit and
operate switch by hand.
If the car's lights operate
normally, turn signal switch is inoperative.
Front Or Rear Turn Signal Lights Not Flashing
Inspect
s Burned-out or damaged turn signal bulb
e High resistance conection to ground at bulb
socket
s Loose chassis-to-column connector. Disconnect
column-to-chassis connector and connect new
turn signal switch into system and operate switch
by hand.
A. If turn signal lights are now on and flashing,
turn signal switch is inoperative.
B. If car lights do not operate, refer to Section
8A
for electrical diagnosis.
Turn Indicator Panel Lights
Inspect
Burned out bulbs or opens, grounds in the wiring
harness from the front turn signal bulb socket to the
indicator lights. Refer to Section
8A for electrical
diagnosis.
Stop Light Mot On When Turn Indicated
Inspect
s Loose column-to-chassis connection
e Disconnect the column-to-chassis connector and
connect the new turn signal switch into the
system and operate the switch by hand.
A. If the brake lights work when the switch is
in the turn position, the turn signal switch
is inoperative.
B. If the brake lights do not work, refer to Section
8A for electrical diagnosis.
Turn Signal Lights Flash Very Slowly
e Loose chassis-to-column connection
a Disconnect the column-to-chassis connector and
connect a new turn signal switch into the system
and operate the switch by hand.
A. If the lights flash at a normal rate, the turn
signal switch is inoperative.
B. If the Lights still flash very slowly, refer to
Section
8A for electrical diagnosis.
Hazard Signal Lights Will Not Flash - Turn
Signal Functions Normally
~"SPBC~
a Blown fuse
Inoperative hazard warning flasher
e Loose chassis-to-column connection
s Disconnect the column-to-chassis connector and
connect a new turn signal switch into the system,
then press in the hazard warning button and
watch the hazard warning lights.
A. If the lights now work normally, the turn
signal switch is inoperative.
B. If the lights do not flash, check the wiring
harness. Refer to Section
8A for electrical
diagnosis.
IGNITION SWITCH
Electrical System Will Not Function
Damaged ign~rion switch
e Ignition switch not adjusted properly
e Loose connector at the ignition switch
Switch Will Not Turn
Inspect
Damaged ignition switch
Switch Cannot Be Set Correctly
Inspect
Switch actuator rod deformed
e Sector to rack engaged in wrong tooth
KEY REMINDER
Figs. 1 through 11 ,
Weminder Continues To Operate With Key Out,
But Stops When Driver's Door Is Closed
e Chips, foreign material in lock cylinder bore
Sticky lock cylinder actuator tip
Damaged or broken reminder switch
Reminder Does Not Sound With Key Fully
Inserted In Lock Cylinder And The Driver's Door
Open
Inspect
1. Power not available to reminder. Refer to Sec-
tion
8A for electrical diagnosis.
2. Open in chassis wiring. Check by separating
chassis-to-column connector. Connect terminals
"E" and "F" female contacts on the chassis
connector (a bent paper clip will work). If the
reminder sounds, repair chassis wiring. If the
reminder does not sound, go to Step
A.
A. Connect a continuity meter (light) to the
male
"E" and "F" column connector
contacts. Push the key all the way into the
lock cylinder. If the light is on when the key
Page 133 of 1825
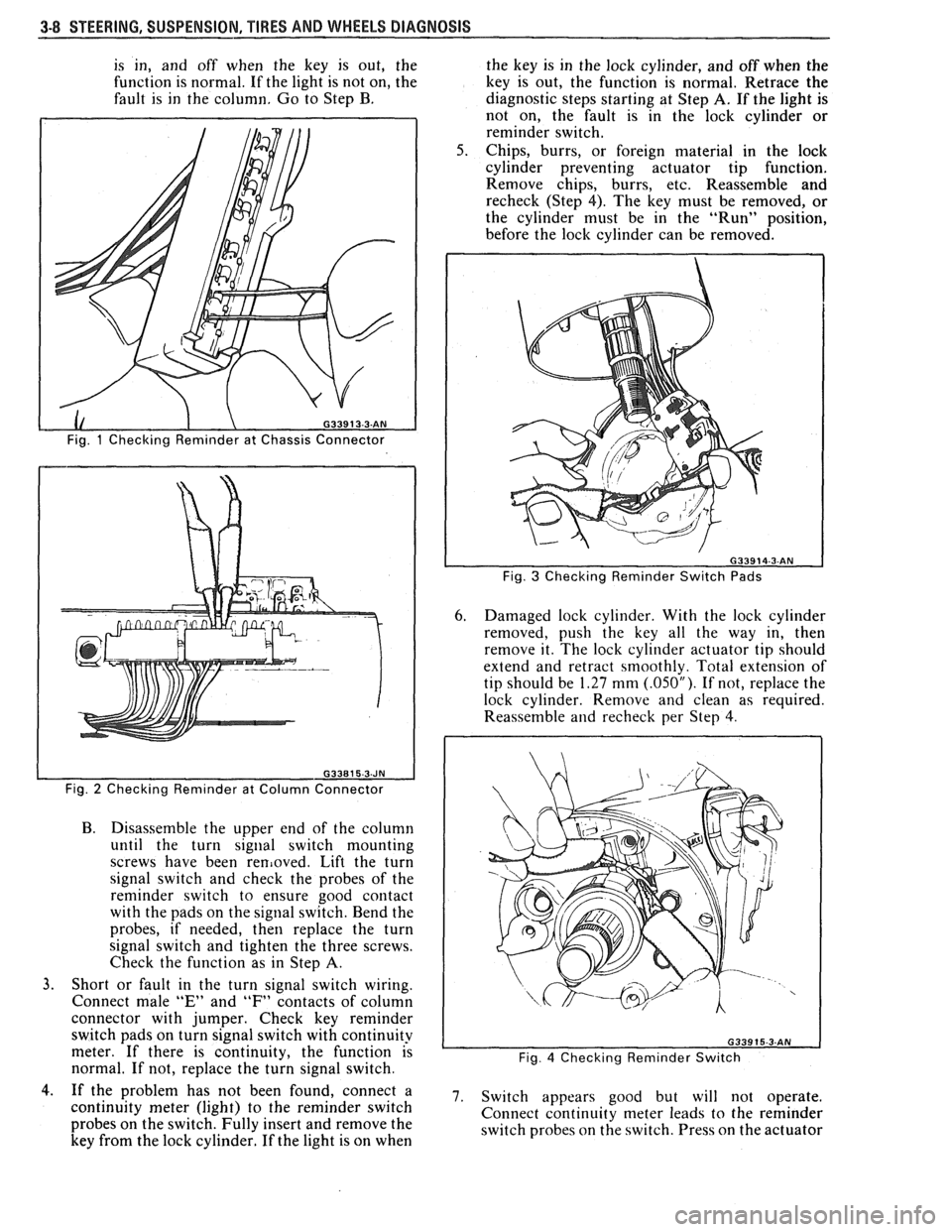
3-8 STEERING. SUSPENSION. TIRES AND WHEELS DIAGNOSIS
is in, and off when the key is out, the
function is normal. If the light is not on, the
fault is in the column. Go to Step B.
Fig. 1 Checking Reminder at Chassis Connector
Fig.
2 Checking Reminder at Column Connector
B. Disassemble the upper end of the column
until the turn
signal switch mounting
screws have been
removed. Lift the turn
signal switch and check the probes of the
reminder switch to ensure good contact
with the pads on the signal switch. Bend the
probes, if needed, then replace the turn
signal switch and tighten the three screws.
Check the function as in Step
A.
3. Short or fault in the turn signal switch wiring.
Connect male
"E" and "F" contacts of column
connector with jumper. Check key reminder
switch pads on turn signal switch with continuity
meter. If there is continuity, the function is
normal. If not, replace the turn signal switch. the
key is in the lock cylinder, and off when the
key is out, the function is normal. Retrace the
diagnostic steps starting at Step
A. If the light is
not on, the fault is in the lock cylinder or
reminder switch.
Chips, burrs, or foreign material in the lock
cylinder preventing actuator tip function.
Remove chips, burrs, etc. Reassemble and
recheck (Step 4). The key must be removed, or
the cylinder must be in the "Run" position,
before the lock cylinder can be removed.
Fig. 3 Checking Reminder Switch Pads
6. Damaged lock cylinder. With the lock cylinder
removed, push the key all the way in, then
remove it. The lock cylinder actuator tip should
extend and retract smoothly. Total extension of
tip should be
1.27 mm (.05OU). If not, replace the
lock cylinder. Remove and clean as required.
Reassemble
and recheck per Step 4.
Fig. 4 Checking Reminder Switch
4.. If the problem has not been found, connect a 7. switch appears good but will not operate, continuity meter (light) to the reminder switch
Connect continuity meter leads to the reminder
probes on the switch. Fully insert and remove the
switch probes on the switch. Press on the actuator
key from the lock cylinder. If the light is on when
Page 135 of 1825

3-10 STEERING, SUSPENSION, TIRES AND WHEELS DIAGNOSIS
Reminder Keeps Operating With Key In Lock
Cylinder, Driver's Door Open Or Closed; Ceases
When Key Is Removed
Inspect
s Door jamb switch on driver's side misadjusted or
inoperative.
e Wire from signal switch to door jamb switch
shorted.
A. This condition indicates the lock cylinder or
the reminder switch is at fault. To verify,
check for continuity at the
"E" and "F"
male column connector contacts, with the
key removed from the lock cylinder. If
continuity exists, the fault is in the column.
B. Insert the key into the lock, then turn the
lock toward the "Start" position. If the
reminder stops when the key is in the
"Run" position or when it is turned past
"Run" toward "Start," the problem is a
sticky lock cylinder actuator.
COLUMN-MOUNTED DIMMER SWITCH
No "Low" or "High" Beam
Inspect
e Loose connector at dimmer switch
e Improper adjustment
e Internally damaged or worn switch. Check the
continuity on the switch at the It. green and at the
tan switch terminals by pushing in the plunger all
the way.
A click should be heard. If there is no
continuity, replace the dimmer switch. If there is
continuity, refer
to'section 8A for electricaldiag-
nosis.
PIVOT AND SWITCH ASSEMBLY
Switch Inoperative: No "Low," "High" and/or
"Wash"
e Loose body-to-switch connector
a Broken or damaged switch
Internally damaged or worn switch. Connect a
new switch without removing the old one. If the
system functions, replace the switch. If the
system doesn't function, refer to Section
8A for
electrical diagnosis.
STEERING GEAR AND PUMP LEAKS
General Procedure
Inspect
s Overfilled reservoir
s Fluid aeration and overflow
e , Hose connections
Verify exact point of leakage Example:
Torsion bar, stub shaft and
adjuster seals are close together; the exact
spot where the system is leaking may not be
clear.
Example: The point from which the fluid is
dripping is not necessarily the point where
the system is leaking; fluid overflowing from
the reservoir, for instance.
e When service is required:
A. Clean leakage area upon disassembly.
B. Replace leaking seal.
C. Check component sealing surfaces for
damage.
D. Reset bolt torque to specifications, where
required.
Some complaints about the power steering system
may be reported as:
A. Fluid leakage on garage floor
B. Fluid leaks visible on steering gear or pump
C. Growling noise, especially when parking or
when engine is cold
D. Loss of power steering when parking
E. Heavy steering effort
When troubleshooting these kinds of complaints,
check for an external leak in the power steering system.
For further diagnosis of leaks, refer to External
Leakage Check in this section.
External Leakage Check
Fig. 12
The purpose of this procedure is to pinpoint the
location of the leak.
In some cases, the leak can easily be located. But,
seepage-type leaks may be more difficult to isolate. To
locate seepage leaks, use the following method.
1. With the engine off, wipe dry the complete power
steering system.
2. Check the fluid level in the pump's reservoir. Add
fluid if necessary.
3. Start the engine, then turn the steering wheel
from stop to stop several times. Do not hold it at
a stop for any length of time, as this can damage
the power steering pump. It is easier if someone
else operates the steering wheel while you search
for the seepage.
4. Find the exact area of the leak and repair leak.
SEAL REPLACEMENT
RECOMMENDATIONS
Lip seals, which seal rotating shafts, require
special treatment. This type of seal is used on the
steering gear and on the drive shaft of the pump. When
there is a leak in one of these areas, always replace the
seal(s), after inspecting and thoroughly cleaning the
sealing surfaces. Replace the shaft only if very severe
pitting is found. If the corrosion in the lip seal contact
zone is slight, clean the surface of the shaft with crocus
cloth. Replace the shaft only if the leakage cannot be
stopped by first smoothing with crocus cloth.