1988 PONTIAC FIERO fuel pressure
[x] Cancel search: fuel pressurePage 14 of 1825
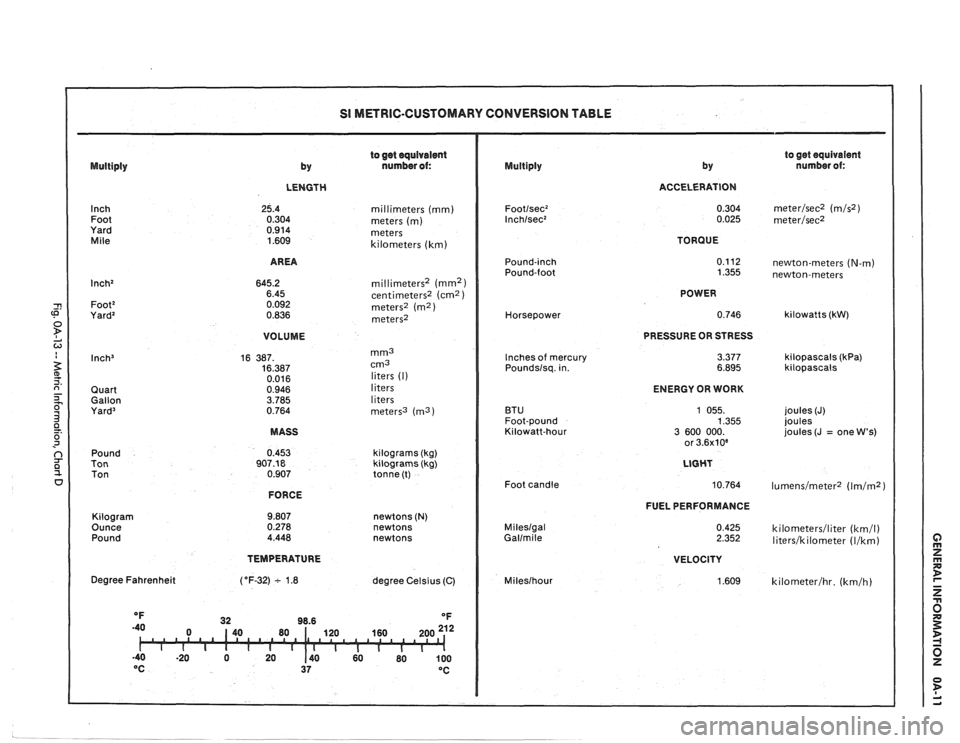
SI METRIC-CUSTOMARY CONVERSION TABLE
to get equivalent
by nurnber of: Multiply
to get equivalent
by number ol: Multiply
LENGTH ACCELERATION
Inch Foot
Yard
Mile millimeters (mm)
meters (m) meters
kilometers (km) TORQUE
AREA
newton-meters (N-m) newton-meters
millimeters2 (mm2) centimeters2 (cm2 ) meters' (m2) meters2
POWER
Horsepower
VOLUME PRESSURE
OR STRESS
3.377 6.895
mm3 cm3
liters (I)
liters
liters
meters3
(ma)
Inches of mercury
Poundslsq. in. kilopascals (kPa) kilopascals
Quart
Gallon
Yard3
ENERGY OR WORK
BTU
Foot-pound
Kilowatt-hour joules
(J)
joules
joules (J
= one W's) MASS
Pound
Ton Ton kilograms
(kg)
kilograms (kg)
tonne (t)
Foot candle
FORCE
FUEL PERFORMANCE
Kilogram
Ounce Pound newtons (N) newtons
newtons Mileslgal Gallmile kilometerslliter (km/l) literslkilometer (Ilkm)
TEMPERATURE
VELOCITY
1.609 Degree Fahrenheit
degree Celsius (C) Mileslhour
Page 16 of 1825

- -
GENERAL INFORMATION OA-13
LIST OF AUTOMOTIVE ABBREVIATIONS
WHICH MAY
BE USED IN THIS MANUAL
A-6 - Axial 6 Cyl. A C Compressor AIC - Air Conditioning
ACC - Auto'matic Climate Control
EMF
- Electromotive Force PAIR - Pulse Air Injection Reaction System
EMR - Electronic Module Retard
P B - Power Brakes
EOS - Exhaust Oxygen Sensor
PCV - Positive Crankcase Ventilation
ESC - Electronic Spark Control
PECV - Power Enrichment Control Valve
APT
- Adjustable Part Throttle
AT - Automatic Transmission
ATC - Automatic Temperature Control
ATDC
- After Top Dead Center
FMVSS
- Federal Motor Vehicle Safety BAR0 - Barometric Absolute Pressure Sensor
Ft. Lb. - Foot Pounds (Torque)
Bat. + - Positive Terminal FWD - Front Wheel Drive
- Four Wheel Drive
BHP - Brake Horsepower 4 x 4 - Four Wheel Drive
BP - Back Pressure
BTDC - Before Top Dead Center
HD - Heavy Duty HE1 - High Energy Ignition
Cat. Conv. - Catalytic Converter
CC - Catalytic Converter
- Cubic Centimeter - Converter Clutch
CCC - Computer Command Control
HVM
- Heater-Vent-Module
IAC
- ldle Air Control CCOT - Cycling Clutch (Orifice) Tube IC - Integrated Circuit CCP - Controlled Canister Purge
ID - Identification
C.E. - Check Engine - Inside Diameter
CEAB - Cold Engine Airbleed ILC - Idle Load Compensator
CEMF - Counter Electromotive Force I/P - Instrument Panel
CID - Cubic Inch Displacement ISC - Idle Speed Control CLOOp - Closed Loop
CLCC - Closed Loop Carburetor Control km - Kilometers
CP
- Canister Purge kmiL - Kilometers Liter (mpg) Cu. In. - Cubic Inch kPa - Kilopascals
CV - Constant Velocity
Cyl.
- Cylinder(s)
L-4 - Four Cylinder In-Line (Engine)
DBB - Dual Bed Bead L-6 - Six Cylinder In-Line (Engine)
DBM - Dual Bed Monolith
LF - Left Front DEFl - Digital Electronic Fuel Injection LR - Left Rear DFI - Digital Fuel Injection
Diff. - Differential Man. Vac. - Manifold Vacuum Distr. - Distributor MAP - Manifold Absolute Pressure
EAC
- Electric Air Control Valve
EAS - Electric Air Switching Valve MPG - Miles Per Gallon
ECC - Electronic Comfort Control
MPH - Miles Per Hour
ECM - Electronic Control Module MT - Manual Transmission
N.m - Newton Metres (Torque)
Emission Control
Fig. 014-15 -- Common Abbreviations
Page 21 of 1825

OB-4 MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION
Tire and wheel operation - Be alert to a vibra-
tion of the steering wheel or seat at normal highway
speeds. This may mean a wheel balance is needed. Also, a
pull right or left on a straight, level road may show the
need for
a tire pressure adjustment or wheel alignment.
Steering system operation - Be alert to
changes in steering action. An inspection is needed when
the steering wheel is harder to turn or has too much free
play or if unusual sounds are noted when turning or
parking.
Headlight aim operation - Take note of light
pattern occasionally. If beam aim doesn't look right,
headlights should be adjusted.
AT EACH FUEL FILL
Engine oil level check - Check engine oil level
and add if necessary. See your Owner's
Manual for further
details.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Engine coolant level and condition - Check
engine coolant level in coolant reservoir tank and add if
necessary. Replace if dirty or rusty. See your Owner's
Manual for further details.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Windshield washer fluid level check -- Check
washer fluid level in container and add if necessary.
Hood latch operation - When opening hood on
cars equipped with hoods that open from the front, note
the operation of secondary latch. It should keep hood from
opening all the way when primary latch is released. Make
sure that hood closes firmly.
AT LEAST MONTI-ILY
Tire and wheel inspection and pressure
check--
Check tires for abnormal wear or damage. Also,
check for damaged wheels. Keep pressures as shown on
Tire Placard on the driver's door (include spare unless it is
a stowaway). Pressure should b\: checked when tires are
"cold". See "Tires" in Owner's Manual for further
infomation.
Light operation check - Check operation of
license plate light, side-marker lights, headlights includ-
ing high beams, parking lights, taillights, brake lights.
turn signals, backup lights, instrument panel and interior
lights and hazard warning flashers.
Fluid leak check - After the car has been parked
for a while, inspect the surface beneath the car for water,
oil, fuel or other fluids. Water dripping from the air
conditioning system after use is normal. If you notice fuel
leaks or fumes, the cause should be found and corrected at
once.
AT LEAST TWICE A YEAR (FOR EXAMPLE,
EVERY SPRING AND FALL)
Power steering pump fluid level check --
Check power steering pump fluid level in accordance with
Owner's Manual instructions and keep at proper level.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Brake master cylinder reservoir fluid level
check ---- Check fluid and keep at proper level. Note: It is
normal for the brake fluid level to go down slightly as the
brake pads wear
- so be sure to keep reservoir filled.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have
it inspected and repaired at once.
Clutch system service --- manual transmis-
sionltransaxle --- For cars equipped with hydraulic
clutch system, check the reservoir fluid level and add fluid
as required. All others, check clutch pedal free travel and
adjust as necessary. See your Owner's Manual for further
details.
~
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Weatherstrip Lubrication - Clean surface and
then apply a thin film of silicone grease with a clean cloth.
EACH TIME OIL IS CHANGED
Automatic and manual transmissionltrans-
axle fluid level check - Check transmission/transaxle
fluid level and add as required. (Corvette only) if equipped
with manual transmission
- check fluid in the overdrive
unit and add as required.
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have
it inspected and repaired at once.
Brake systems inspection - For convenience,
the following should be done when wheels are removed
for rotation: Inspect lines and hoses for proper hookup,
binding, leaks, cracks, chafing, etc. Inspect disc brake
pads for wear and rotors for surface condition. Also in-
spect drum brake linings for wear and cracks. Inspect
other brake parts, including drums, wheel cylinders, park-
ing brake, etc. at the same time. Check parking brake
adjustment.
INSPECT BRAKES MORE OFTEN IF DRIVING
HABITS OR CONDITIONS RESULT IN FREQUENT
BRAKING.
Steering, suspension and front drive axle
boot and seal inspection
- Inspect front and rear
suspension and steering system for damaged, loose or
missing parts, signs of wear or lack of lubrication. Inspect
power steering lines and hoses for proper hookup, bind-
ing, leaks, cracks, chafing, etc. (On cars equipped with
manual steering gear, check for seal leakage.) On
front-
wheel-drive cars, clean then inspect drive axle boot seals
for damage, tears or leakage. Replace seals if necessary.
Exhaust system inspection - Inspect complete
system. Inspect body near the exhaust system. Look for
broken, damaged, missing or out-of-position parts as well
as open seams, holes, loose connections or other condi-
tions which could cause a heat buildup in the tloor pan or
could let exhaust fumes seep into the trunk or passenger
compartment.
Page 22 of 1825

MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION OB-5
Throttle linkage inspection -- Inspect for inter-
ference, binding, damaged or missing parts.
Engine drive belts inspection - Inspect all
belts for cracks, fraying and wear. Adjust or replace as
needed.
Rear axle service (if equipped) - Check gear
lubricant level and add if needed. For cars equipped with a
limited slip rear axle, fluid does not require changing
(except Caprice and Corvette
- change fluid and required
additive at first
7,500 miles (12 500 km). See your
Owner's Manual or "Recommended Fluids
& Lubricants
Chart" in this section.
IF YOU USE YOUR GAR TO PULL A TRAILER,
CHANGE GEAR LUBRICANT EVERY 7,500 MILES
(12 500 KM).
NOTICE: A large loss in this system may indicate a
problem. Have it inspected and repaired at once.
Power antenna - Clean and then lubricate power
antenna mast. The proper lubricant as shown in Figure
OB-2 should be used.
AT LEAST ONCE A YEAR
Lap and shoulder belts condition and opera-
tion
- Inspect belt system, including webbing, buckles,
latch plates, retractors, guide loops and anchors.
Moveable head restraint operation - On cars
with moveable restraints, make sure restraints stay in the
desired position. (See adjustment instructions in your
Owner's Manual.)
Seatback latch and recliner operation on
cars equipped
with recliner seat --- Be sure seat-
backs latch on those cars with folding seats using mechan-
ical latches. Make sure the recliner is holding by pushing
and pulling on the top of the
seatback while it is reclined.
See your Owner's Manual for seat operating information.
Spare tire and jack storage- Be alert to rattles
in rear of car. Make sure the space tire, all jacking equip-
ment, any tire inflator and any covers or doors are securely
stowed at all times. Oil jack ratchet or screw mechanism
after each use.
Key lock service - Lubricate key lock cylinder at
least annually.
Body lubrication service - Lubricate all body
door hinges including the tailgate or hatchback lid (if
equipped). Also lubricate the body hood, fuel door and
rear compartment hinges and latches including interior
glove box and counsel doors, and any folding seat
hardware.
"Fansmissionltransaxle neutral or clutch
starl switch operation
CAUnON: Before pedorming the follow-
ing safety switch check, be sure to have
enough room around the car. Then, firmly
apply both the parking brake (see your
Owner's Manual for procedure) and the
regular brakes. Do not use the accelerator pedal.
If the engine
starls, be ready to turn
off the ignition promptly. Take these pre-
cautions because the car could move
without warning and possibly cause per-
sonal injury or properly damage. On auto-
matic transmissionltransaxle cars, try to
starl the engine in each gear. The starler
should crank only in "Park" or "Neutral."
On manual transmissionltransaxle cars,
place the
shiR lever in "Neutral," push the
clutch halfway and try to starl. The starler
should crank only when the clutch is fully
depressed.
Steering column lock operation
- While
parked, try to turn key to "Lock" in each gear range. The
key should turn to "Lock" only when gear is in "Park" on
automatic or "Reverse" on manual
transmissionltransax-
le. On cars with key release lever, try to turn key toULock"
without depressing the lever. The key should turn to
"Lock" only with the key lever depressed. On all vehicles,
the key should come out only in "Lock."
Parking brake and transmissionltransaxle
"Park" mechanism operation
CAUT1ON:Before checking the holding
ability of the parking brake and automatic
transmissionltransaxle "Park" mecha-
nism, park on a fairly steep hill with
enough room for movement in the down-
hill direction. To reduce the risk of person-
al injury or property damage, be prepared
to apply the regular brakes promptly if the
car begins to move.
To check the parking brake, with the engine running and
transmission/transaxle in "Neutral." slowly remove foot
pressure from the regular brake pedal (until the car is held
by only the parking brake).
To check the automatic transmissionltransaxle "Park"
mechanism holding ability, release all brakes after shift-
ing the transmissionltransaxle to "Park."
ljnderbody flushing - At least every spring,
tlush from the underbody with plain water any corrosive
materials used for ice and snow removal and dust control.
Take care to thoroughly clean any areas where mud and
other debris can collect.
Sediment packed in closed areas
of the vehicle should be loosened before being flushed.
Engine cooling system service - Inspect
coolant and freeze protection. If dirty or rusty, drain, flush
and refill with new coolant. Keep coolant
at the proper
mixture as specified in your Owner's Manual. This pro-
vides proper freeze protection. corrosion inhibitor level
and engine operating temperature. Inspect hoses and re-
place if cracked. swollen or deteriorated. Tighten hose
clamps. Clean outside of radiator and air conditioning
condensor. Wash radiator filler cap and neck.
To help
ensure proper operation. a pressure test of both the cooling
system and cap is also recommended. (See maintenance
schedule charts in Figure
OB-l for the recommended
coolant change interval.)
Page 234 of 1825
TIRES AND WHEELS 3E-3
METRIC WHEEL NUTS AND STUDS
Some models use metric wheel nuts and wheel
studs. The nut will have the word "metric" stamped on
its face and the stud will have the letter
"M" stamped
into the threaded end. The word "metric" is stamped
on its head.
The thread size of the metric wheel nuts and
wheel studs are
"MI2 x 1.5". These stand for:
M = Metric
12
= Diameter in millimeters
1.5
= Millimeters per thread
If a broken stud is found, see Section 3C (Front
Suspension) or Section 3D (Rear Suspension) for
replacement procedure.
INFLATION OF TIRES
The pressure recommended for any model is
carefully calculated to give a satisfactory ride,
handling, tread life and load carrying capacity.
Tire pressure, with tires cold, (after car has set for
three hours or more, or driven less than one mile)
should be checked monthly or before any extended trip
and set to the specifications on the tire placard located
on rear face of driver's door. Tire inflation pressure is
also given in Section OB.
Valve caps or extensions should be on the valves
to keep dust and water out.
1. For sustained driving at speeds up to 85
mph (140 km/h), in countries where such
speeds are allowed by law, your tires should be set
at the pressures recommended on your tire
placard.
Sustained driving at speeds
faster than
85 mph (140 km/h), where
permitted
by law, is not advised unless
your car has special high speed tires available
from many tire dealers.
2. Tire pressures may increase as much as 6 psi
when hot.
3. Higher
than recommended pressure can cause:
o Hard ride
o Tire bruising or carcass damage
Rapid tread wear at center of tire
4. Lower
than
recommended pressure can cause:
@ Tire squeal on turns
@ Hard steering
o Rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the
tread
Tire rim bruises and rupture
e Tire cord breakage
o High tire temperatures
o Reduced handling
High fuel consumption
5. Unequal pressure on same axle can cause:
Uneven braking
o Steering lead
o Reduced handling
e Swerve on acceleration
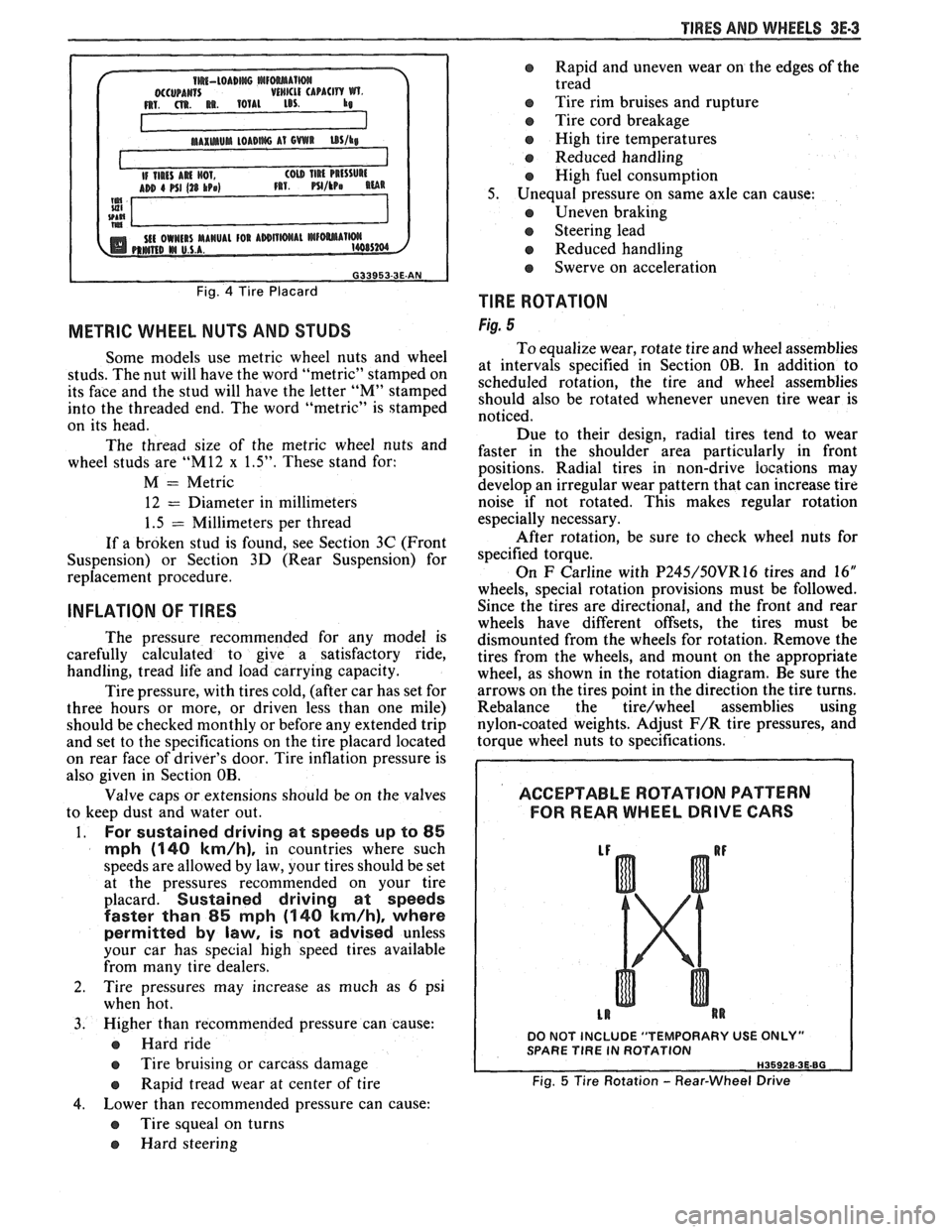
TlRE ROTATION
Fig. 5
To equalize wear, rotate tire and wheel assemblies
at intervals specified in Section OB. In addition to
scheduled rotation, the tire and wheel assemblies
should also be rotated whenever uneven tire wear is
noticed.
Due to their design, radial tires tend to wear
faster in the shoulder area particularly in front
positions. Radial
tires in non-drive
iocations may
develop an irregular wear pattern that can increase tire
noise if not rotated. This makes regular rotation
especially necessary.
After rotation, be sure to check wheel nuts for
specified torque.
On
F Carline with P245/50VR16 tires and 16"
wheels, special rotation provisions must be followed.
Since the tires are directional, and the front and rear
wheels have different offsets, the tires must be
dismounted from the wheels for rotation. Remove the
tires from the wheels, and mount on the appropriate
wheel, as shown in the rotation diagram. Be sure the
arrows on the tires point in the direction the tire turns.
Rebalance the
tire/wheel assemblies using
nylon-coated weights. Adjust
F/R tire pressures, and
torque wheel nuts to specifications.
ACCEPTABLE ROTATION PATTERN
FOR REAR WHEEL
DRIVE GARS
DO NOT INCLUDE "TEMPORARY USE ONLY" SPARE TlRE IN ROTATION
Fig. 5 Tire Rotation - Rear-Wheel Drive
Page 348 of 1825

ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION 6-3
B, Section 6E2 - Fuel Injection (TBI)
B, Section 6E3 - Fuel Injection (Ported)
ENGINE MECHANICAL DIAGNOSIS
The following diagnostic information covers common problems and possible causes. When
the proper diagnosis is made, the problem should be corrected by adjustment, repair or part
replacement as required. Refer to the appropriate section of the manual for these procedures.
EXCESSIVE OIL LOSS
B, External oil leaks. Tighten bolts and/or replace o Continuous high speed driving, and/or severe
gaskets and seals as necessary. usage
such as trailer hauling, will normally cause
decreased oil mileage.
e Improper reading of dipstick. Check oil with car PCV system malfunctioning. on a level surface and allow adequate drain-down Valve guides and/or valve stem seals worn, or time.
seals omitted. Ream guides and install oversize
service valves and/or new valve stem seals.
Improper Use S.A'E' Piston rings broken, worn, or not seateded. Allow viscosity for prevailing temperatures. See
adequate time for rings to seat. Replace broken
Owner's Manual for proper specifications.
or worn rings, as necessary.
Piston improperly installed or misfitted.
LOW OIL PRESSURE
Slow idle speed. Set idle speed to correct
specification, if not ECM controlled.
Incorrect, or malfunctioning, oil pressure switch.
Incorrect, or malfunctioning, oil pressure gage.
Replace with proper gage.
.*
Improper oil viscosity, or diluted oil. install oil of
proper viscosity for expected temperature, or
install new oil if diluted with moisture or
unburned fuel mixtures.
o Oil pump worn or dirty.
e Plugged oil filter.
e Oil pickup screen loose or plugged.
B, Hole in oil pickup tube.
e Excessive bearing clearance. Replace if necessary.
o Cracked, porous or plugged oil galleys. Repair or
replace block.
o Galley plugs missing or misinstalled. Install
plugs, or repair as necessary.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE
e Low oil pressure. Repair as necessary. (See o Broken valve spring.
preceding diagnosis for low oil pressure.)
o Sticking valves.
o Loose rocker arm attachments. Inspect and B, Lifters worn, dirty, or defective. Clean, inspect,
test and replace as necessary.
repair as necessary.
o Camshaft worn, or poor machining. Replace
o Worn rocker arm and/or pushrod. camshaft.
B, Worn valve guides.
ENGINE KNOCK DIAGNOSIS
KNOCKS COLD AND CONTINUES FOR TWO TO THREE MINUTES
INCREASES
WITH TORQUE
o Vacuum operated EFE engines may have valve o Excessive piston to bore clearance. Replace
knock. Replace EFE valve. piston.
e Flywheel contacting splash shield. Reposition
splash shield.
e Loose or broken balancer or drive pulleys.
Tighten, or replace as necessary. Cold engine piston knock usually
disappears when the cylinder is grounded
out. Cold engine piston knock which
disappears in 1.5 minutes should be
considered acceptable.
Page 349 of 1825

6-4 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION
Bent connecting rod.
HEAVY KNOCK H0"FVVI"F TORQUE APPLIED
Broken balancer, or pulley hub. Replace parts as e Exhaust system grounded. Reposition as
necessary. necessary.
Loose torque converter bolts. Flywheel
cracked.
e Excessive main bearing clearance. Replace as
Accessory belts too tight or nicked. Replace
necessary.
and/or tension to specs as necessary.
e Excessive rod bearing clearance. Replace as
necessary.
LIGHT KNOCK HOT
Detonation or spark knock. Check operation of e Loose torque converter bolts.
EST or ESC (See Section
6D or 6E). Check e Exhaust leak at manifold. Tighten bolts and/or
engine timing and fuel quality.
replace gasket.
8 Excessive rod bearing clearance. Replace
bearings as necessary.
KNOCKS ON INITIAL START-UP BUT ONLY LASTS A FEW SECONDS
Noisy mechanical fuel pump. Replace pump.
When the engine is stopped, some valves
will be open. Spring pressure against lifters
Improper oil viscosity. Install proper oil viscosity will
tend to bleed lifter down. Attempts to
for expected temperatures. See Owner's Manual. repair
should be made only if the problem
is consistent.
Hydraulic lifter bleed down. Clean, test and @ Excessive crankshaft end clearance. Replace
replace as necessary. crankshaft
thrust bearing.
@ Excessive front main bearing clearance. Replace
worn parts.
KNOCKS AT IDLE HOT
Loose or worn drive belts. Tension and/or @ Excessive piston pin clearance. Ream and install
replace as necessary. oversize pins. (VIN R and 2) or replace piston
A/C Compressor or generator bearing. Replace and
pin.
as necessary.
e Connecting rod alignment. Check and replace
rods as necessary.
Noisy mechanical fuel pump. Replace pump.
8 Insufficient piston to bore clearance. Hone bore
Valve train. Replace parts as necessary. and
fit new piston.
@ Loose crankshaft balancer. Torque and/or
Improper oil viscosity. Install proper viscosity oil
replace worn parts.
for expected temperature4 See Owner" e Piston pin offset to wrong side. Install correct
ENGINE OVERHEATS
Coolant system leak, oil cooler system leak, or
2. Belt slipping or damaged. Replace tensioner, or
coolant recovery system not operating. Check for belt, as required.
leaks and correct as required. Check coolant
3. Thermostat stuck closed. Check and replace if
recovery tank, hose and radiator cap.
required.
4. Electrical cooling fan operation. See the
ELECTRICAL TROUBLESHOOTING
MANUAL.
5. Head gasket leaking. Check and repair as
required.
Page 352 of 1825

2.8 LITER V-6 BA2-1
TER V-6 V N CODES RPO
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION ........................ 6A2- 1
ENGINE LUBRICATIONS ......................... 6A2- 1
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE ............................. 6A2-7
Powertrain Mounts .................................... 6A2-7
Rocker Arm Cover .................................... 6A2-8
Intake Manifold .......................................... 6A2-9
Exhaust Manifold ................................... 6A2-9
Rocker Arm and Push Rod ....................... 6A2- 10
Valve Mechanism
....................................... 6A2- 10
Valve Stem Oil Seal and/or Valve
Spring
.................... .. .. ... ................... 6A2- 10
Valve Lifters
............................................. 6A2- l l
Cylinder Head ............................................ 6A2- 12
Rocker Arm Studs
.................................... 6A2- 13
Valve Guides
........................................... 6A2- 13
Valve Seats
................................................ 6A2- 14
Valves
......................................................... 6A2- 14
Torsional Damper
..................................... 6A2- 14 Crankcase
Front Cover
.............................. 6A2- 15
Oil Seal (Front Cover)
........................... .... 6A2- 15
Timing Chain
& Sprocket .......................... 6A2- 15
Camshaft
................................................... 6A2- 16
Camshaft Bearings
................................... 6A2- 16
Oil Pan
........................................................ 6A2- 17
Oil Pump
.................................................. 6A2- 18
Connecting Rod Bearings .......................... 6A2- 18
Main Bearings
............................................ 6A2- 19
Oil Seal (Rear Main)
.................................. 6A2-2 1
Pistons, Rings & Connecting Rods ........... 6A2-2 1
Honing or Reboring Cylinders .................. 6A2-23
Fitting Pistons ............................................ 6A2-24
.............................................. Piston Rings 6A2-24
Engine Assembly ...................................... 6A2-25
.................................................. Crankshaft 6A2-25
........................................ Sprocket or Gear 6A2-26
..................................... SPECIFICATIONS 6A2-26
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
CYLINDER BLOCK
The cylinder block is made of alloy cast iron and
has 6 cylinders arranged in a "V" shape with 3
cylinders in each bank. The cylinder banks are set at
a
60" angle from each other.
The right bank cylinders are
1, 3, 5. Cylinders 2,
4, 6 are on the left bank.
Four main bearings support the crankshaft which
is retained by bearing caps that are machined with the
block for proper alignment and clearances.
CYLINDER HEAD
The cast alloy iron cylinder heads have individual
intake and exhaust ports for each cylinder. Valve
guides are integral, and rocker arms are retained on
individual threaded studs.
CRANKSHAFT AND BEARINGS
The crankshaft is cast nodular iron with deep
rolled fillets on all six crankpins and two center main
journals. Four steel backed aluminum bearings are
used, with
#3 bearing being the end-thrust bearing.
CAMSHAFT AND DRIVE
sprocket is also hardened sintered iron, and is pressed
onto the nose of the crankshaft.
A rubber snubber is
used to dampen chain motion.
PISTONS AND CONNECTING RODS
The pistons are cast aluminum with steel struts
using two compression rings and one coil control ring.
The piston pin is offset
1.5mm towards the major
thrust side. This allows a gradual change in thrust
pressure against the cylinder wall as the piston travels
its path. Pins are chromium steel and have a floating
fit in the pistons. They are retained in the connecting
rods by a press fit.
Connecting rods are made of forged steel. Full
pressure lubrication is directed to the connecting rods
by drilled oil passages from the adjacent main bearing
journal.
VALVE TRAIN
A very simple ball pivot-type train is used.
Motion is transmitted from the camshaft through the
hydraulic lifter and push rod to the rocker arm. The
rocker arm
~ivots on its ball and transmits the
camshaft
mot'ion to the valve. The rocker arm ball
locates on a stud, threaded into the head, and is
The camshaft is cast alloy iron with tapered 13. by a nut. The push rod is located by a guide
2mm wide lobes, offset from the lifters and tapered to plate held under the rocker arm stud, assuring that the
provide positive valve lifter rotation. The camshaft is arm Operates in the plane the
support& by four journals and includes a
distributor/oil pump drive gear, and fuel pump INTAKE MANIFOLD - - eccentric.
The intake manifold is a three piece cast
A
3/8" pitch chain drives the camshaft through
aluminum unit. It centrally supports a fuel rail with 6
a hardened sintered iron sprocket. The crankshaft
fuel injectors.