1988 PONTIAC FIERO light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 610 of 1825
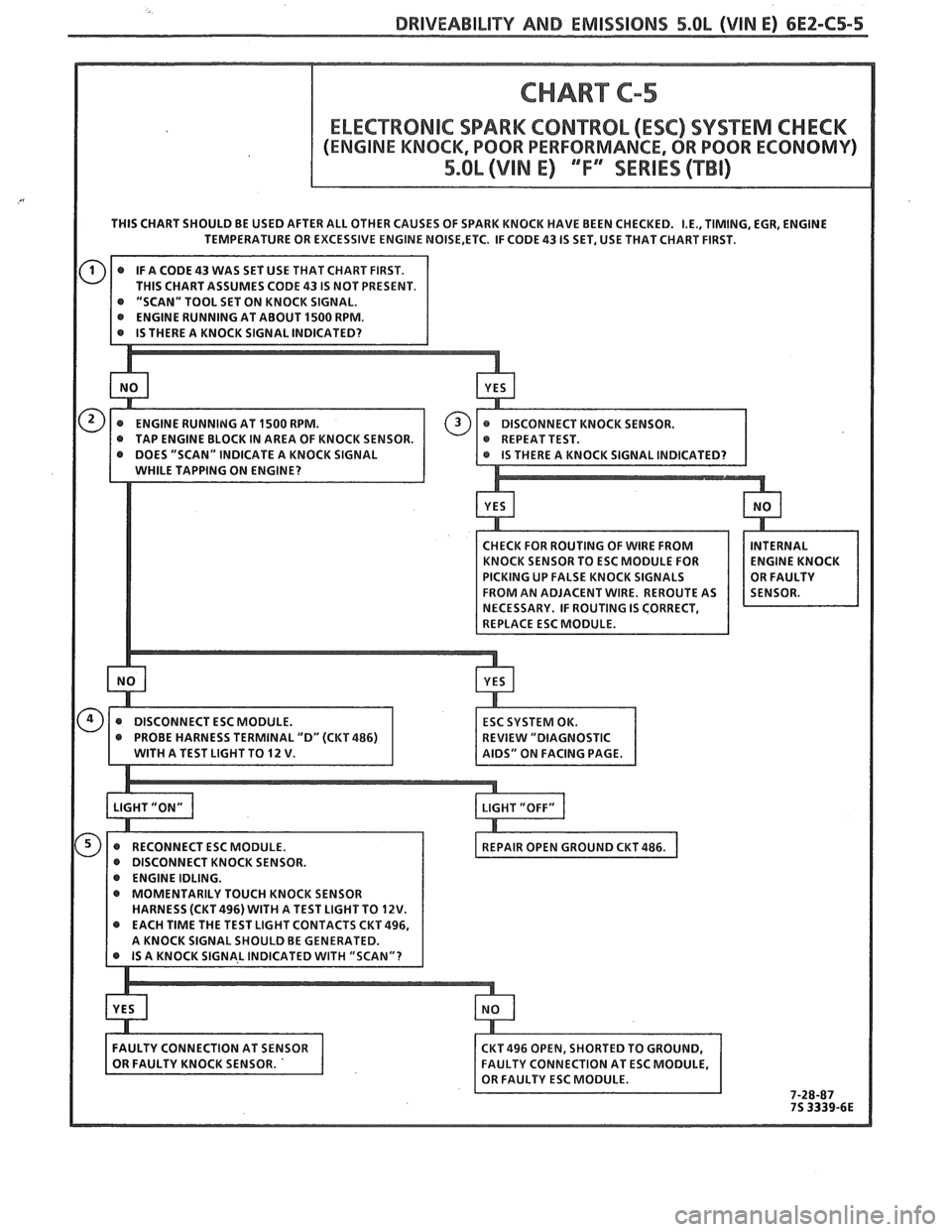
DRIVEABILIW AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN E) 6E2-C5-5
THIS CHART SHOULD BE USED AFTER ALL OTHER CAUSES OF SPARK KNOCK HAVE BEEN CHECKED. I.E., TIMING. EGR, ENGINE
TEMPERATURE OR EXCESSIVE ENGINE NOISE,ETC. IF CODE 43 IS SET, USE THAT CHART FIRST.
@ PROBE HARNESS TERMINAL "D" (CKT 486) EVlEW "DIAGNOSTIC
WITH A TEST LIGHT TO 12 V.
IDS" ON FACING PAGE
Page 613 of 1825
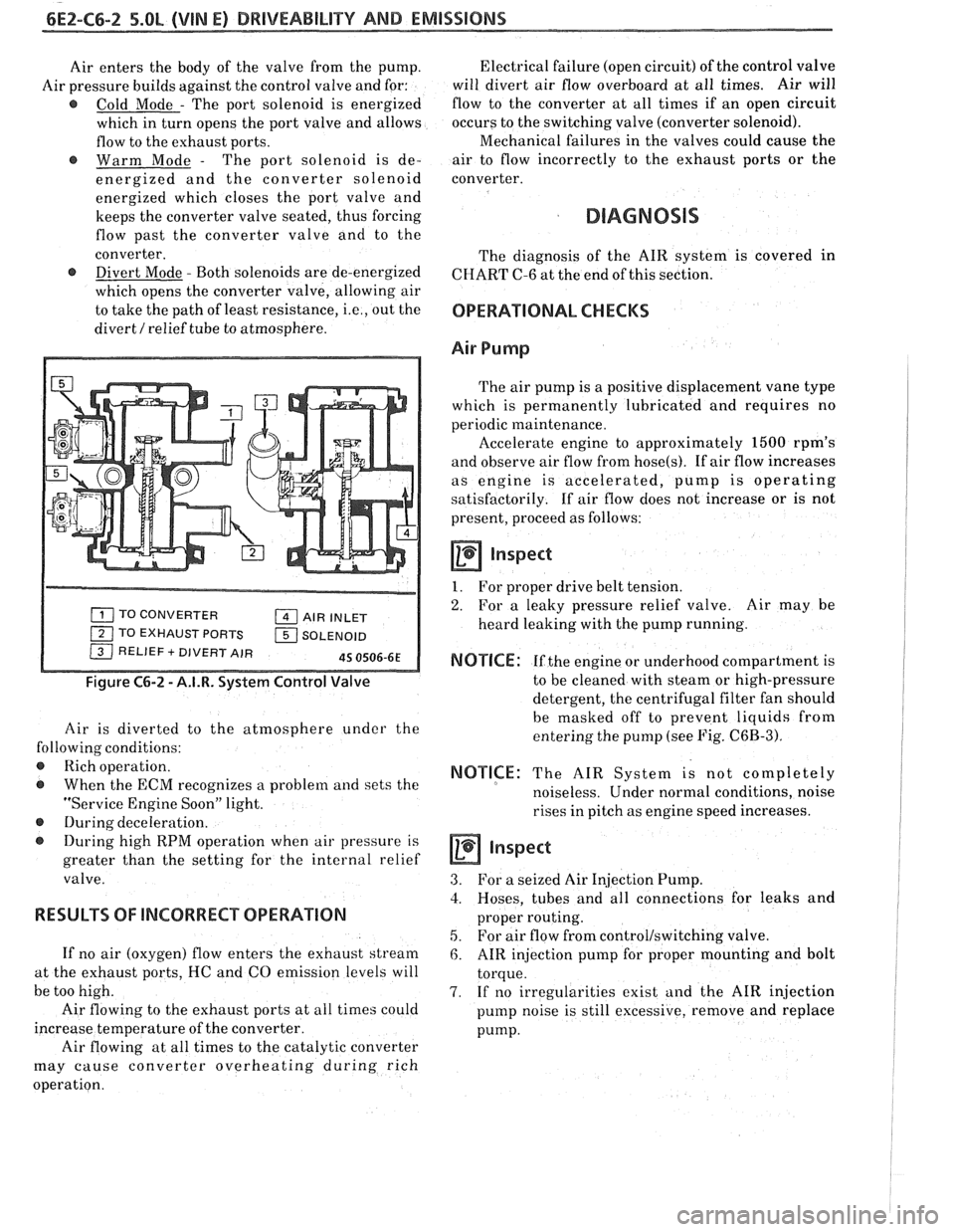
6EZ-C6-2 5.OL (VIN E) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Air enters the body of the valve from the pump.
Air pressure builds against the control valve and for:
@ Cold Mode - The port solenoid is energized
which in turn opens the port valve and allows
flow to the exhaust ports.
@ Warm Mode - The port solenoid is de-
energized and the converter solenoid
energized which closes the port valve and
keeps the converter valve seated, thus forcing
flow past the converter valve and to the
converter.
@ Divert Mode - Both solenoids are de-energized
which opens the converter valve, allowing air
to take the path of least resistance,
i.e., out the
divert
/ relief tube to atmosphere.
TO CONVERTER AIR INLET
1 TO EXHAUST PORTS 1 SOLENOID / RELIEF + DIVERT AIR 45 0506-6E
Figure C6-2 - A.I.R. System Control Valve
Air is diverted to the atmosphere under the
following conditions:
@ Rich operation.
@ When the ECM recognizes a problem and sets the
"Service Engine Soon" light.
@ During deceleration.
During high RPM operation when air pressure is
greater than the setting for the internal relief
valve.
RESULTS OF lNCORRECP OPERATION
If no air (oxygen) flow enters the exhaust stream
at the exhaust ports, HC and CO emission levels will
be too high.
Air flowing to the exhaust ports at all times could
increase temperature of the converter.
Air flowing at all times to the catalytic converter
may cause converter overheating during rich
operation. Electrical failure
(open circuit) of the control valve
will divert air flow overboard at all times. Air will
flow to the converter at all times if an open circuit
occurs to the switching valve (converter solenoid).
Mechanical failures in the valves could cause the
air to flow incorrectly to the exhaust ports or the
converter.
DIAGNOSIS
The diagnosis of the AIR system is covered in
CHART C-6 at the end of this section.
OPERATIONAL CHECKS
Air Pump
The air pump is a positive displacement vane type
which is permanently lubricated and requires no
periodic maintenance.
Accelerate engine to approximately
1500 rpm's
and observe air flow from
hose(s). If air flow increases
as engine is accelerated, pump is operating
satisfactorily. If air flow does not increase or is not
present, proceed as follows:
a Inspect
1. For proper drive belt tension.
2. For a leaky pressure relief valve. Air may be
heard leaking with the pump running.
NOTICE: If the engine or underhood compartment is
to be cleaned with steam or high-pressure
detergent, the centrifugal filter fan should
be masked off to prevent liquids from
entering the pump (see Fig.
C6B-3).
NOTICE: The AIR System is not completely
noiseless. Under normal conditions, noise
rises in pitch as engine speed increases.
inspect
3. For a seized Air Injection Pump.
3. Hoses, tubes and all connections for leaks and
proper routing.
5. For air flow from control/switching valve.
6. AIR injection pump for proper mounting and bolt
torque.
7. If no irregularities exist and the AIR injection
pump noise is still excessive, remove and replace
pump.
Page 617 of 1825
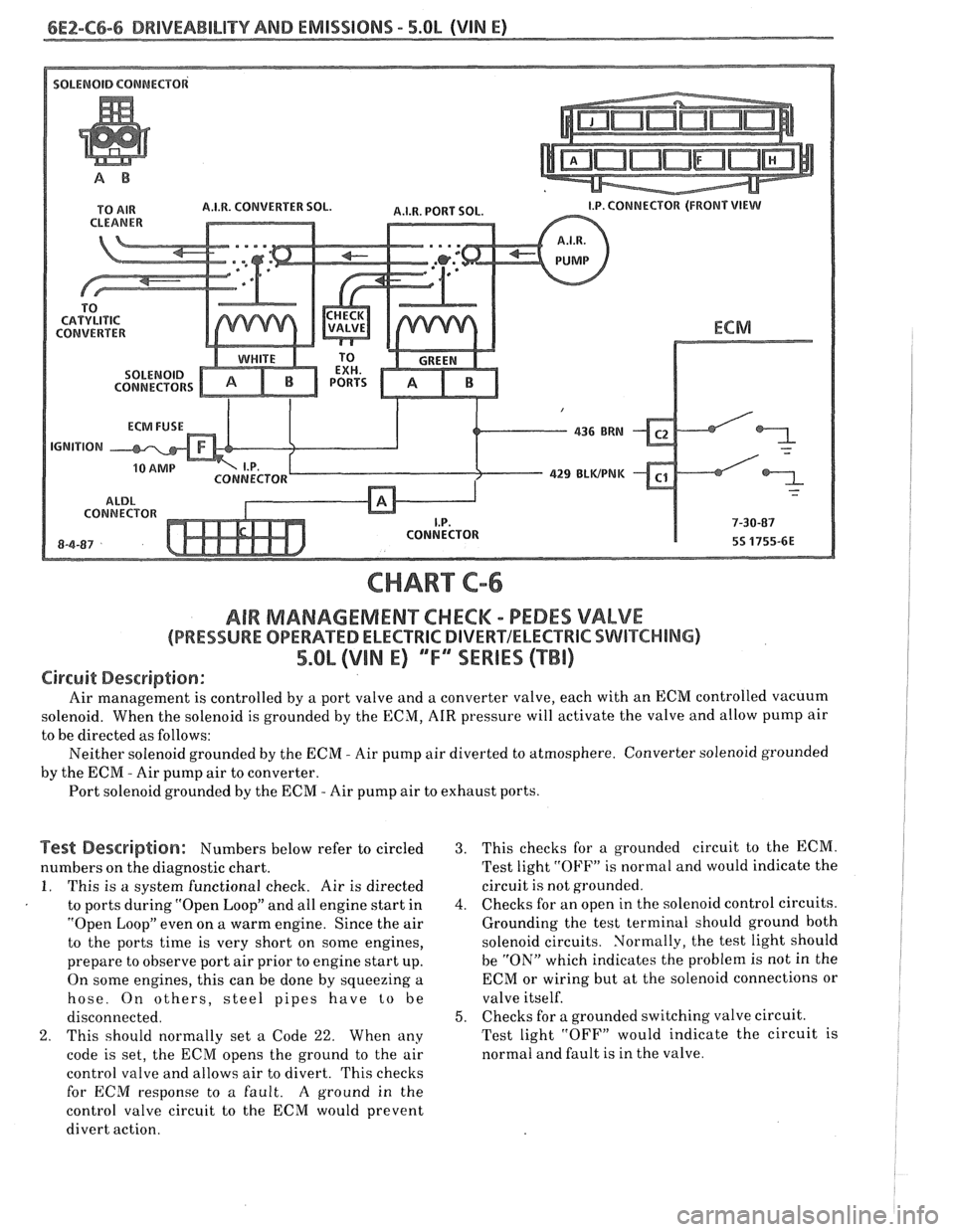
6E2-C6-6 DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - 5.OL (VIN E)
A.I.W. CONVERTER SOL.
CONNECTORS
429 BLWPNK
CONNECTOR CONNECTOR
CHART C-6
AIR MAMAGEMENKHECM - PEDES VALVE
(PRESSURE OPERATED ELECTRlC DIVERVELECTRIC SWITCHING)
5.Qb (VIN E) ""FYSERIES (TBI)
Circuit Description:
Air management is controlled by a port valve and a converter valve, each with an ECM controlled vacuum
solenoid. When the solenoid is grounded by the ECM,
AIR pressure will activate the valve and allow pump air
to be directed as follows:
Neither solenoid grounded by the
ECM - Air pump air diverted to atmosphere. Converter solenoid grounded
by the
ECIM - Air pump air to converter.
Port solenoid grounded by the ECM
- Air pump air to exhaust ports.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
I. This is a system functional check. Air is directed
to ports during "Open Loop" and all engine start in
"Open Loop" even on a warm engine. Since the air
to the ports time is very short on some engines,
prepare to observe port air prior to engine start up.
On some engines, this can be done by squeezing a
hose. On others, steel pipes have
to be
disconnected.
2. This should normally set a Code 22. When any
code is set, the
ECM opens the ground to the air
control valve and allows air to divert. This checks
for
ECM response to a fault. A ground in the
control valve circuit to the ECM would prevent
divert action.
3. This checks for a grounded circuit to the ECM.
Test light
"OFF" is normal and would indicate the
circuit
is not grounded.
4. Checks for an open in the solenoid control circuits.
Grounding the test terminal should ground both
solenoid circuits. Normally, the test light should
be "ON" which indicates the problem is not in the
ECM or wiring but at the solenoid connections or
valve itself.
5. Checks for a grounded switching valve circuit.
Test light "OFF" would indicate the circuit is
normal and fault is in the valve.
Page 620 of 1825
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - 5.OL (VIN E) 6E2-C7-1
SECTION C7
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULAVON (EGR) SYSEENO
GENERAL DESCRIPTION ...............
........................ PURPOSE
OPERATION
......................
EGR CONTROL .....................
...... NEGATIVE BACKPRESSURE VALVE
.......... EGR VALVE IDENTIFICATION
RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION
. . , .
CONTENTS
......................... C7-1 DIAGNOSIS C7-2
..................... C7-1 ON-CAR SERVICE C7-2
....................... C7-1 EGRVALVE C7-2
............. C7-1 EGR Manifold Passage C7-2
C7-1
EGR CONTROL SOLENOID ............. C7-3
C7-2 PARTS INFORMATION
................. C7-3
C7-2
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
PURPOSE
The EGR system is used to lower NO, (oxides of
nitrogen) emission levels caused by high combustion
temperatures.
It does this by decreasing combustion
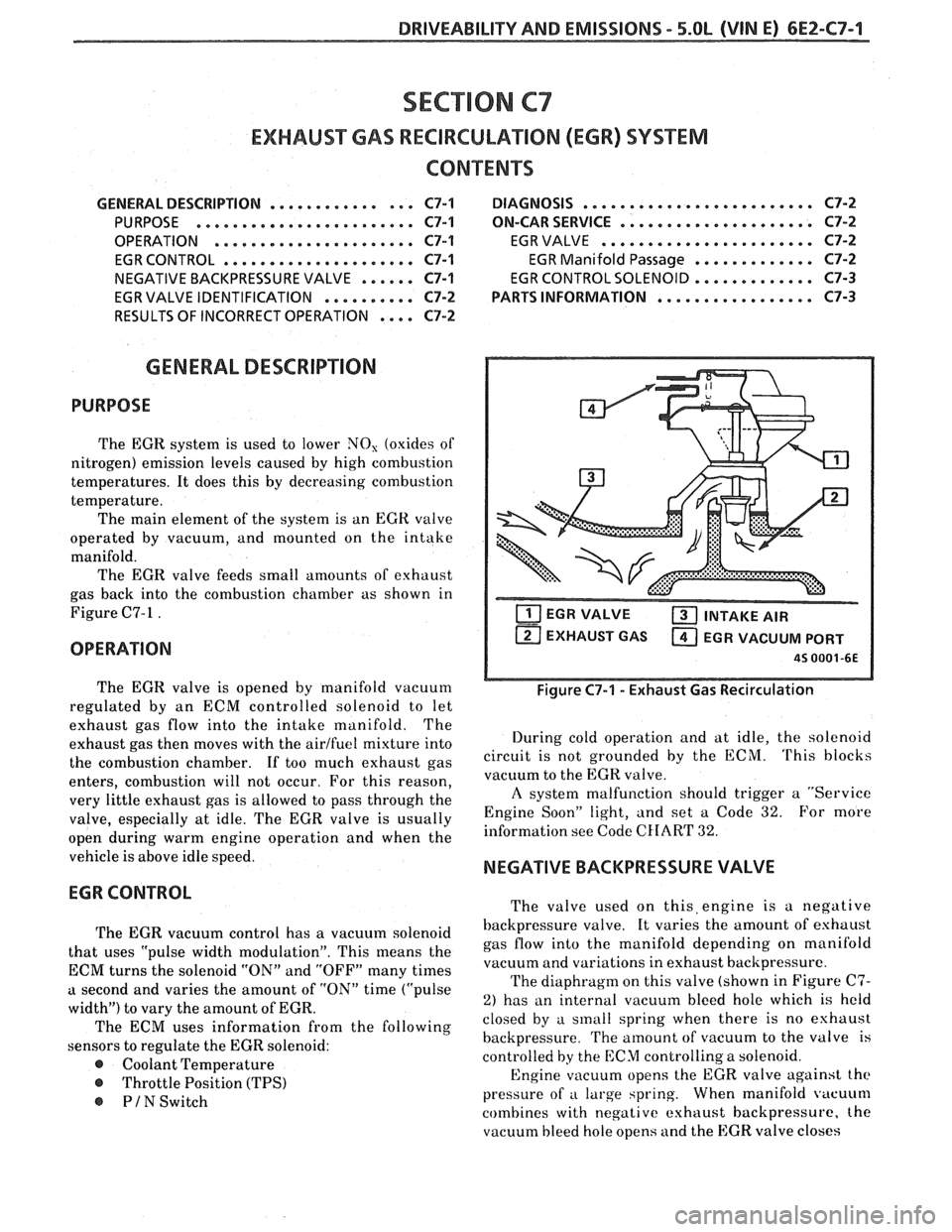
temperature. The main element of the system is an
EGR valve
operated by vacuum, and mounted on the intake
manifold. The EGR valve feeds small amounts of exhaust
gas back into the combustion chamber as shown in
Figure C7-1
.
OPERATION
The EGR valve is opened by manifold vacuum
regulated by an ECM controlled solenoid to let
exhaust gas flow into the intake manifold. The
exhaust gas then moves with the
airlfuel mixture into
the combustion chamber.
If too much exhaust gas
enters, combustion will not occur. For this reason,
very little exhaust gas is allowed to pass through the
valve, especially at idle. The EGR valve is usually
open during warm engine operation and when the
vehicle is above idle speed.
EGR CONTROL
The EGR vacuum control has a vacuum solenoid
that uses "pulse width modulation". This means the
ECM turns the solenoid "ON" and "OFF" many times
a second and varies the amount of "ON" time ("pulse
width") to vary the amount of EGR.
The ECM uses information from the following
sensors to regulate the EGR solenoid:
@ Coolant Temperature
@ Throttle Position (TPS)
PIN Switch
T'IT] EGR VALVE a INTAKE AIR
EXHAUST GAS
a EGR VACUUM PORT
45 0001 -6E
Figure C7-1 - Exhaust Gas Recirculation
During cold operation and at idle, the solenoid
circuit is not grounded by the ECM.
'I'his blocks
vacuum to the EGR valve.
A system malfunction should trigger a "Service
Engine Soon" light, and set a Code
32. For more
information see Code
CHAR'I' 32.
NEGATIVE BACKPRESSURE VALVE
The valve used on this,engine is a negative
backpressure valve. It varies the amount of eshaust
gas flow into the manifold depending on manifold
vacuum and variations in exhaust backpressure.
The diaphragm on this valve (shown in Figure
C7-
2) has an internal vacuum bleed hole which is held
closed by a sinall spring when there is no eshaust
backpressure.
The amount of vacuum to the valve is
controlled
by the ECM controlling a solenoid.
Engine vacuum opens the EGR valve against
the
pressure of a large spring. When manifold vacuum
combines with negative exhaust backpressure, the
vacuum bleed hole opens and the EGR valve closes
Page 630 of 1825
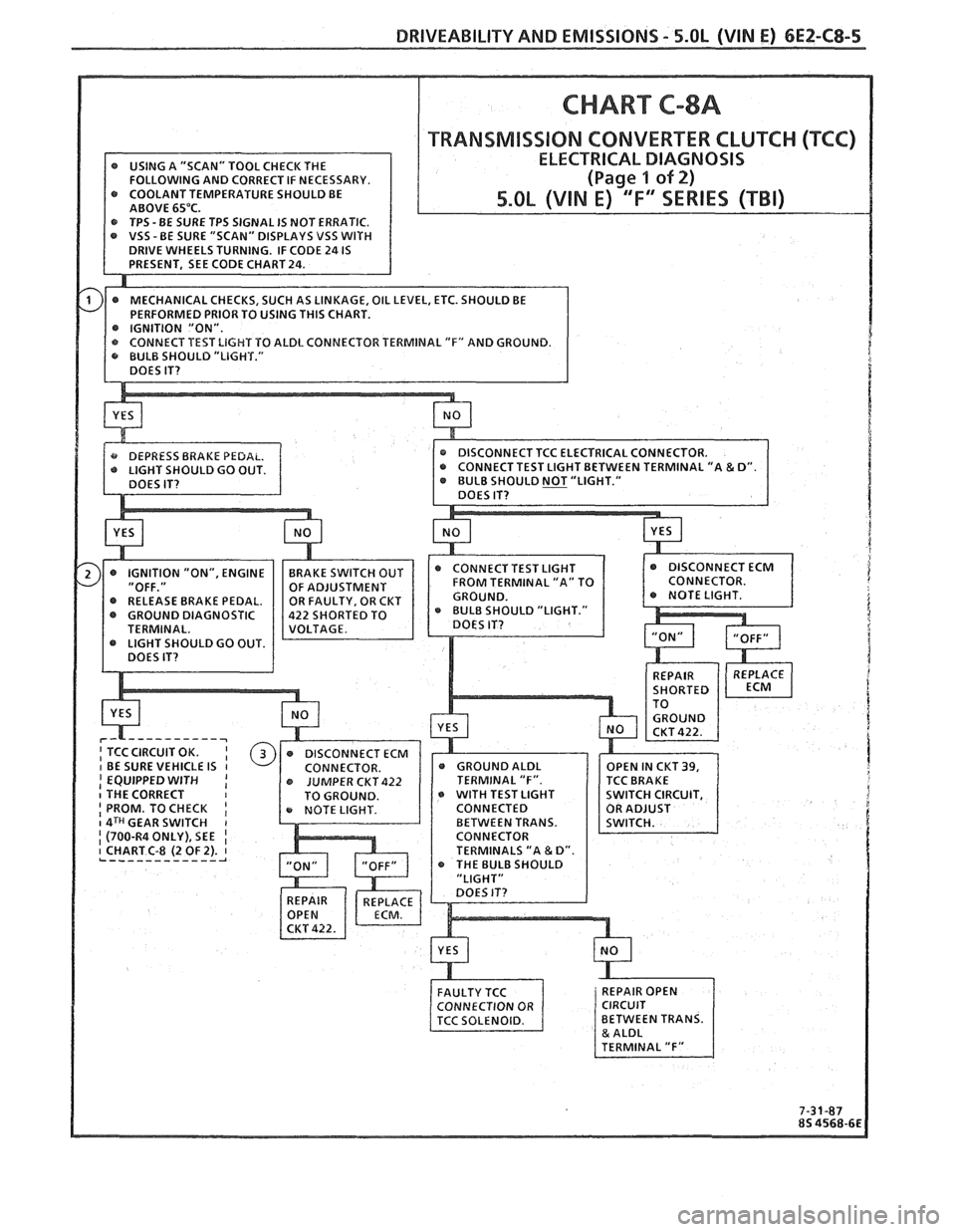
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - 5.8L (VIN E) 6EZ-C8-5
TRANSMlSSlON CONVERTER CLUTCI-I (KC)
@ GROUND DIAGNOSTIC 22 SHORTED TO
I EQUIPPED WITH I I THE CORRECT o WITH TEST LIGHT I PROM. TO CHECK I CONNECTED I 4TCI GEAR SWITCH I I (700-R4ONLY),SEE I CHART C-8 (2 OF 2). 1 L ------------ A
Page 633 of 1825
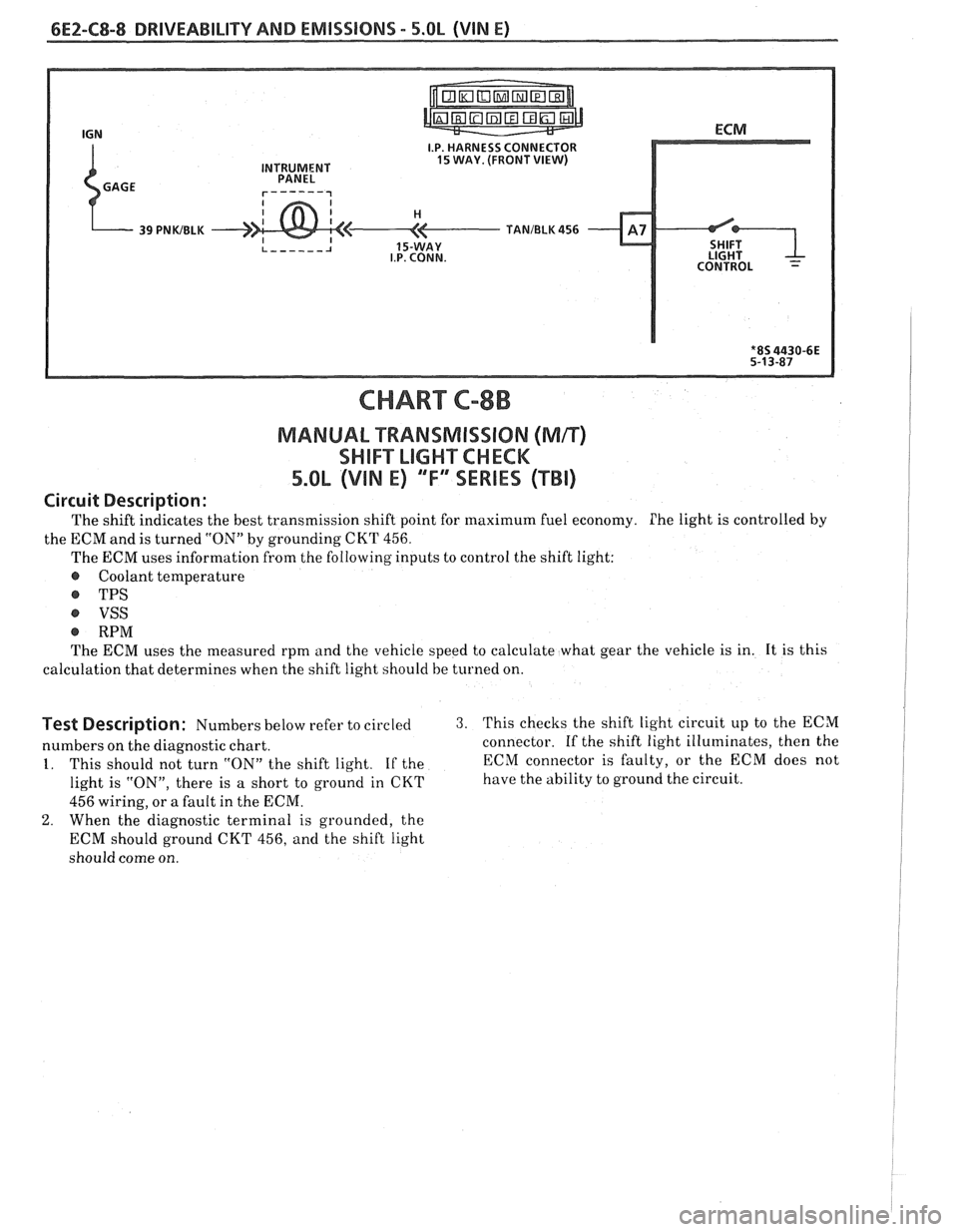
6E2-C8-8 DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - 5.OL (VIN E)
I.P. HARNESS CONNECTOR
INTRUMENT 15 WAY. (FRONT VIEW)
CHART C-8B
MANUAL "TRANSMISSION (Mn)
SWIFT LIGHXCHCK
5.OL (VIN E) "F" "SERIES ("Ti)
Circuit Description:
The shift indicates the best transmission shift point for maximum fuel economy. Phe light is controlled by
the ECM and is turned "ON" by grounding
CKT 456.
The ECM uses information from the following inputs to control the shift light:
@ Coolant temperature
@ TPS
VSS
@ RPM
The ECM uses the measured rpm and the vehicle speed to calculate what gear the vehicle is in. It is this
calculation that determines when the shift light should be
turned on.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled 3. This checks the shift light circuit up to the ECM
numbers on the diagnostic chart. connector.
If the shift light illuminates, then the
1. This should not turn "ON" the shift light. If the ECM
connector is faulty, or the ECM does not
light is "ON", there is
a short to ground in CKT have the ability to ground the circuit.
456 wiring, or a fault in the ECM.
2. When the diagnostic terminal is grounded, the
ECM should ground CKT 456, and the shift light
should come on.
Page 634 of 1825
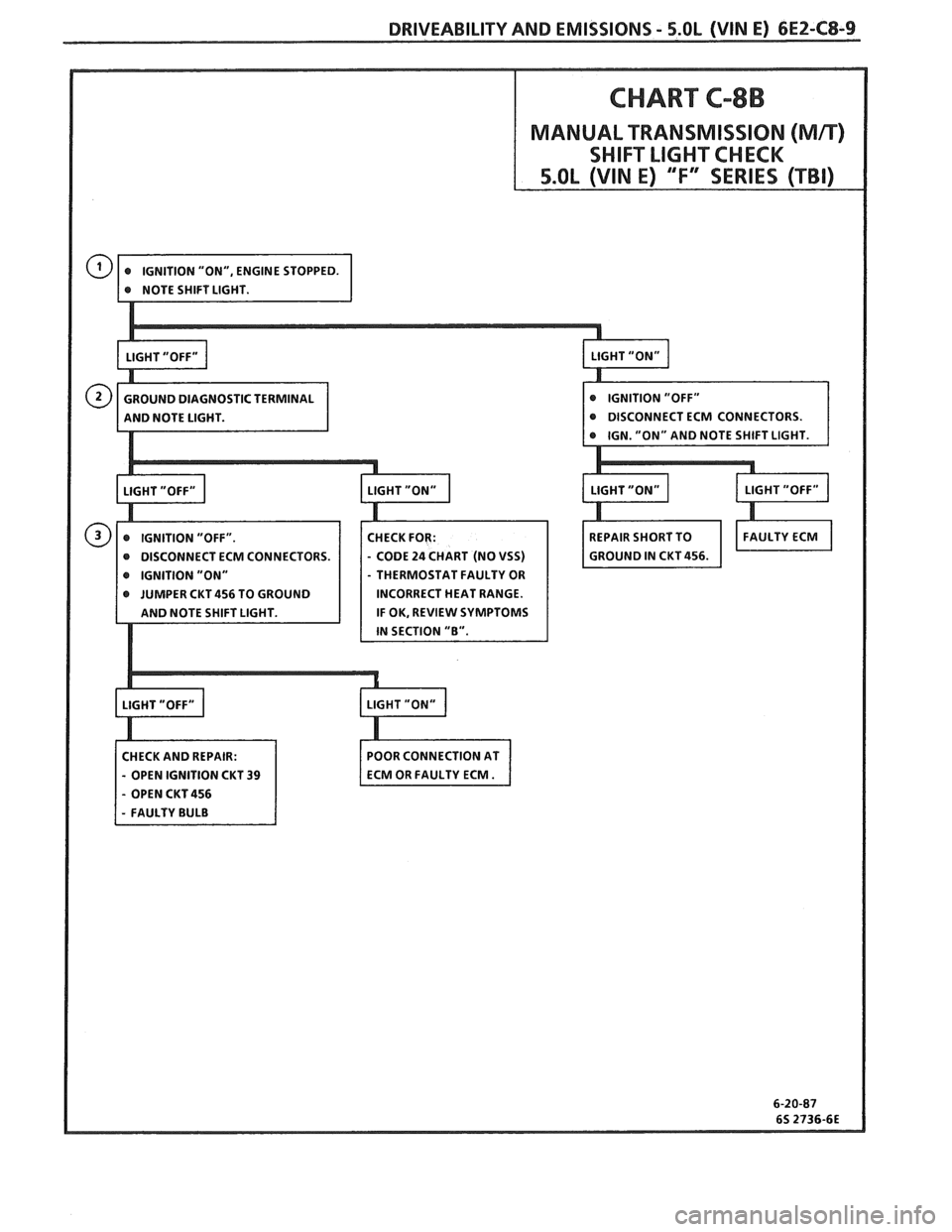
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS - S.OL (WIN E) 6EZ-CS-9
CHART C-8B
MANUAL TRANSMISSION (Mn)
SHIFT LIGHT CHECK
CM CONNECTORS.
IGNITION "ON" THERMOSTAT FAULTY OR
JUMPER CKT 456 TO GROUND INCORRECT HEAT RANGE.
IF OK, REVIEW SYMPTOMS
CHECK AND REPAIR:
- OPEN IGNITION CKT 39
- OPEN CKT 456
Page 642 of 1825
SECTION PAGE
A
Acceleration Mode .................... C2-2
AIC Request Signal
General Description
................. C1-4
Diagnosis ......................... C1-5
Air Injection Check Valve C6-3
Air Injection Control (Pedes) Valve
........ C6-3
Air
lnjection Reaction (A.I.R.) System
General Description
.................. C6- 1
Diagnosis ......................... C6-2
Part Information
.................... C6-4
Air Management Check (Pedes)
.......... C6-6
Air Pump
............................ C6-2
........................... Service C6-3
ALDL Connector ....................... A-1 2
Automatic Transmission Converter Clutch
(TCC) Electrical Diagnosis
.............. C8-4
C8-6
B
Backfire ............................ 6-6
......... Battery Voltage Correction Mode C2-2
Before
Start~ng ...................... B-1
C
Cal Pak General
Descript~on ................. C1-2
Service
........................... C1-8
Canister Control Valve
................. C3-2
Canister Hoses
....................... C3-3
Canister Purge Solenoid
................ C3-3
Canister Purge Valve Check
............. C3-6
Chart A-
I :
No Service Engine Soon Light .......... A-10
Chart A-2:
No ALDL Data. Or Won't Flash Code 12.
Or Service Engine Soon Light On Steady
. . A-1 2
Chart A-3:
Engine Cranks But Won't Run
.......... A-14
Chart A-7:
Fuel System Diagnosis
................ A-1 8
Chart
B-1:
Restricted Exhaust System Check ........ 6-7
Chart C-IA:
ParkINeutral Switch Diagnosis ......... Cl-12
Chart C-16:
Crank Signal
....................... C1-14
Chart C-1 D
.................. MAP Output Check C1-16
SECTION
Chart C-2C:
Idle Air Control (IAC) System Check ...... C2-18
Chart C-3:
Canister Purge Valve Check
........... C3-6
Chart C-4B:
Ignition System Check
................ C4-4
Chart C-5:
Electronic Spark Control
(ESC) .......... C5-4
Chart C-66:
Air Management Check
.............. C6-6
Chart C-7:
Exhaust Gas Recirculation
............. C7-4
Chart
C-$A:
Transmission Converter Clutch (TCC) .... C8-4
Chart
C-8A
700-4R Transmission Electrical Diagnosis . . C8-6
Chart
C-86:
Shift Light ......................... C8-8
Chuggle
............................ B-3
Clear Flood Mode
..................... C2-2
Closed Loop
......................... C2-2
Code12
............................ C4-2
Code13
............................ A-22
Code14
............................ A-24
Code43
............................ A-42
Code44
............................ A-44
Code45
............................ A-46
Code54
............................ A-48
Codes 5 1.52. 55
...................... A-50
Component Location
.................. A-2
Control Valves
....................... C3-3
Coolant Temperature Sensor
General Description
.................. C1-2
Diagnosis
.......................... Cl-5
Service
........................... C1-8
Cuts Out ............................ 6-4
Crank Signal General Description
................. C1-4
Diagnosis
......................... C1-14
D
Deceleration Mode .................... C2-2