1988 PONTIAC FIERO turn signal
[x] Cancel search: turn signalPage 845 of 1825
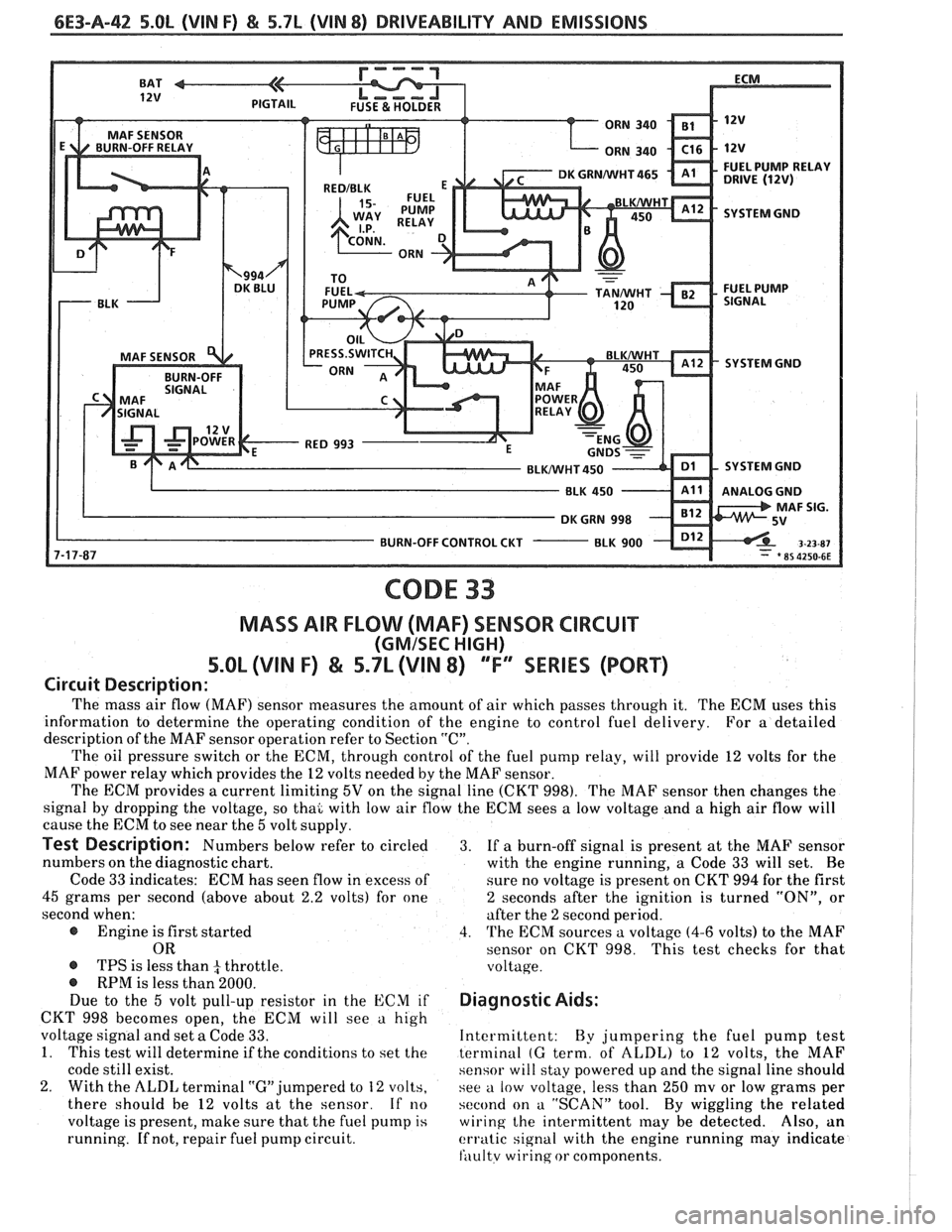
6E3-A-42 S.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
SYSTEM GND
SYSTEM GND
SYSTEM GND
ANALOG GND
BURN-OFF CONTROL CKT
-
CODE 33
MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR CIRCUIT
(GMISEC HIGH)
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) ""FY"IES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor measures the amount of air which passes through it. The ECM uses this
information to determine the operating condition of the engine to control fuel delivery.
For
a detailed
description of the MAF sensor operation refer to Section
"C".
The oil pressure switch or the ECM, through control of the fuel pump relay, will provide 12 volts for the
MAF power relay which provides the
12 volts needed by the MAF sensor.
The ECM provides
a current limiting 5V on the signal line (CKT 998). The MAF sensor then changes the
signal by dropping the voltage, so thai with low air flow the ECM sees
a low voltage and a high air flow will
cause the ECM to see near the
5 volt supply.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled 3. If a burn-off signal is present at the MAF sensor
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
with the engine running, a Code
33 will set. Be
Code
33 indicates: ECM has seen flow in excess of
sure no voltage is present on CKT 994 for the first
45 grams per second (above about 2.2 volts) for one 2 seconds after the ignition is turned "ON", or
second when: after the
2 second period.
@ Engine is first started 4. The ECM sources a voltage (4-6 volts) to the MAF
OR sensor on CKT 998. This test checks for that
@ TPS is less than 4 throttle. voltage. @ RPM is less than 2000.
Due to the 5 volt pull-up resistor in the ECM if Diagnostic Aids:
CKT 998 becomes open, the ECM will see a high
voltage signal and set
a Code 33. Intermittent:
By jumpering the fuel pump test
1. This test will determine if the conditions to set the terminal (G term, of ALDL) to 12 volts, the MAF
code still exist. sensor will stay powered up and the signal line should
2. With the ALDL terminal "G" jumpered to 12 volts,
see a low voltage, less than 250 mv or low grams per
there should be
12 volts at the sensor. If no second on a "SCAN" tool. By wiggling the related
voltage is present, make sure that the fuel pump
is wiring the intermittent may be detected. Also, an
running.
If not, repair fuel pump circuit. erratic signal with the engine running may indicate
fili~ltv wirinq or components.
Page 855 of 1825
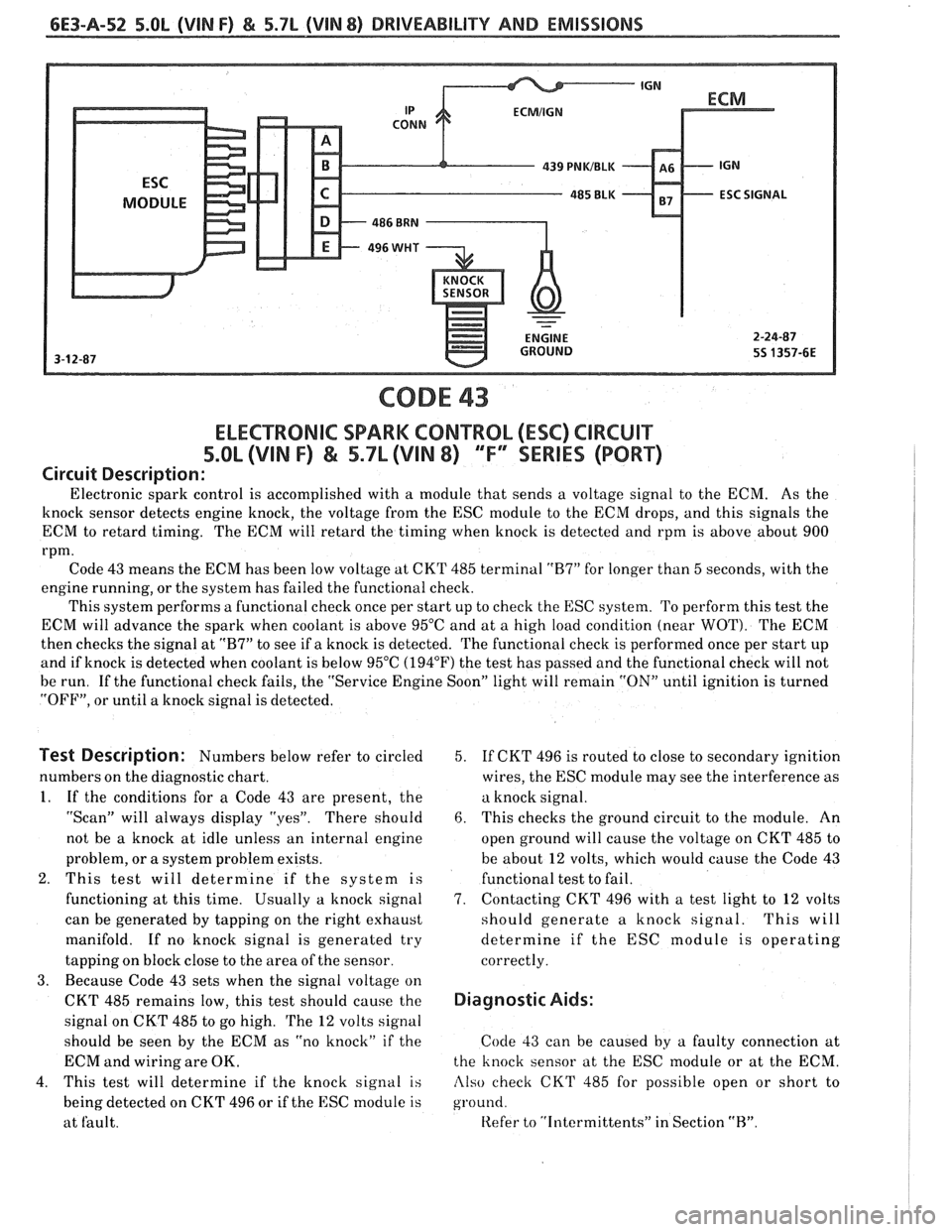
6E3-A-52 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CODE 43
ELECTRONIC SPARK CONTROL (ESC) ClRCUlT
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) 'TF" SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
Electronic spark control is accomplished with a module that sends a voltage signal to the ECM. As the
knock sensor detects engine knock, the voltage from the ESC module to the ECM drops, and this signals the
ECM to retard timing. The ECM will retard the timing when knock is detected and rpm is above about 900
rpm.
Code 43 means the ECM has been low voltage at CKT 485 terminal
"R7" for longer than 5 seconds, with the
engine running, or the system has failed the functional check.
This system performs a functional check once per start up to check the
ESC system. To perform this test the
ECM will advance the spark when coolant is above 95°C and at a high load condition (near
WOT). The ECM
then checks the signal at
"B7" to see if a knock is detected. The functional check is performed once per start up
and if knock is detected when coolant is below 95°C
(194°F') the test has passed and the functional check will not
be run. If the functional check fails, the "Service Engine Soon" light will remain
"ON" until ignition is turned
"OFF", or until a knock signal is detected.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. If the conditions for a Code 43 are present, the
"Scan" will always display "yes". There should
not be a knock at idle unless an internal engine
problem, or
a system problem exists.
2. This test will determine if the system is
functioning at this time. Usually
a knock signal
can be generated by tapping on the right exhaust
manifold. If no knock signal is generated try
tapping on block close to the area of the sensor.
3. Because Code 43 sets when the signal voltage on
CKT 485 remains low, this test should cause the
signal on CKT 485 to go high. The
12 volts signal
should be seen by the ECM as "no knock" if the
ECM and wiring are OK.
4. This test will determine if the knock signal
is
being detected on CKT 496 or if the ESC module is
at fault. 5.
If CKT
496 is routed to close to secondary ignition
wires, the ESC module may see the interference as
a knock signal.
6. This checks the ground circuit to the module. An
open ground will cause the voltage on CKT 485 to
be about
12 volts, which would cause the Code 43
functional test to fail.
7. Contacting CKT 496 with a test light to 12 volts
should generate a knock signal. This will
determine if the ESC module is operating
correctly.
Diagnostic Aids:
Code 33 can be caused by a faulty connection at
the knock sensor at the ESC module or at the ECM.
Also check CKT 485 for possible open or short to
ground.
Refer to "Intermittents" in Section "R".
Page 861 of 1825
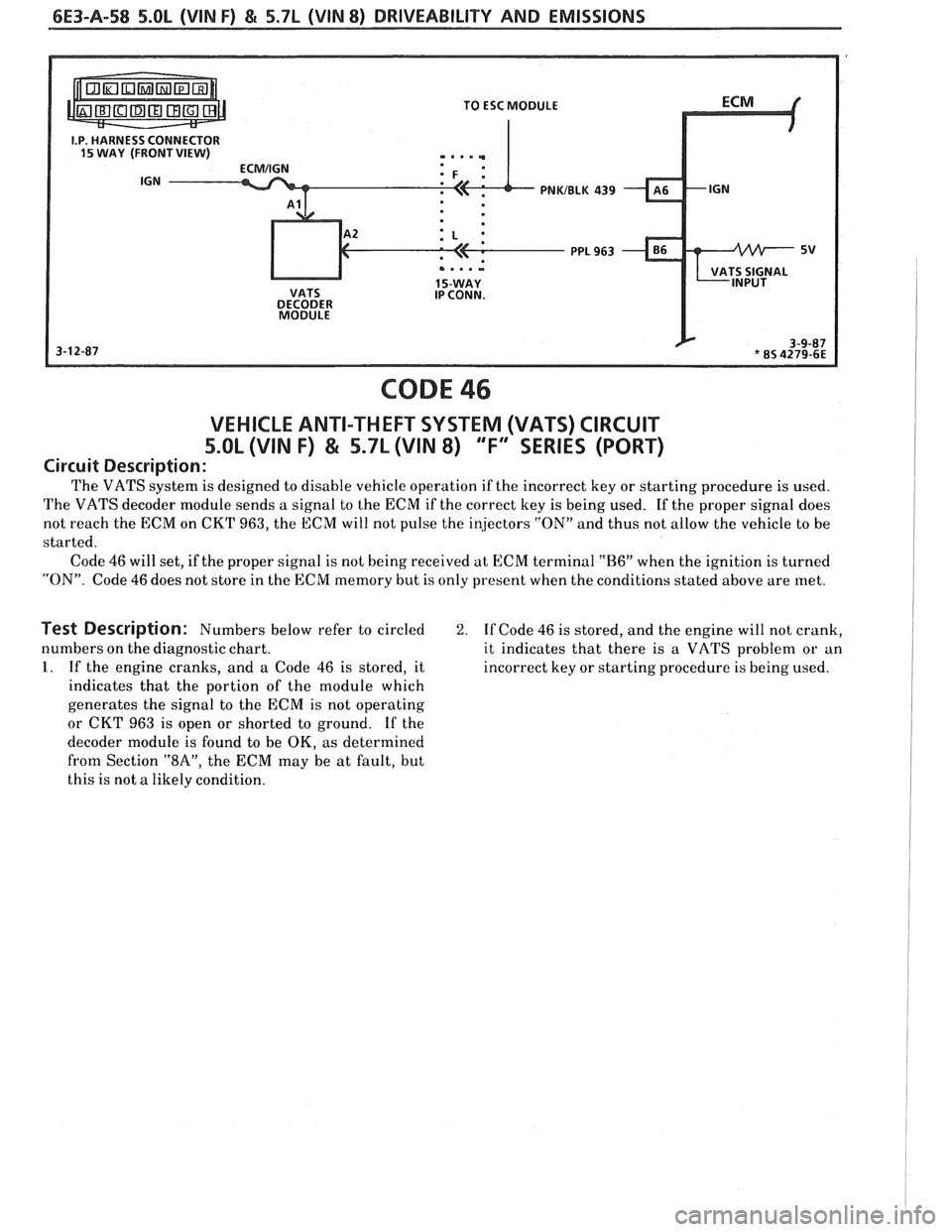
6E3-A-58 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PNKIBLK 439
PPL 963
5V
IP CONN.
DECODER
MODULE
CODE 46
VEHICLE ANTI-THEFT SYSTEM (VATS) CIRCUIT
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) 'TF'3SERlES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The VATS system is designed to disable vehicle operation if the incorrect key or starting procedure is used.
The VATS decoder module sends a signal to the ECM if the correct key is being used. If the proper signal does
not reach the ECM on CKT 963, the ECM will not pulse the injectors
"ON" and thus not allow the vehicle to be
started.
Code
46 will set, if the proper signal is not being received at ECM terminal "B6" when the ignition is turned
"ON". Code 46 does not store in the ECM memory but is only present when the conditions stated above are met.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled 2. If Code 46 is stored, and the engine will not crank,
numbers on the diagnostic chart. it indicates that there is a VATS problem or an
1. If the engine cranks, and a Code 46 is stored, it incorrect key or starting procedure is being used.
indicates that the portion of the module which
generates the signal to the ECM is not operating
or CKT 963 is open or shorted to ground. If the
decoder module is found to be
OK, as determined
from Section
"8AV, the ECM may be at fault, but
this is not a likely condition.
Page 863 of 1825
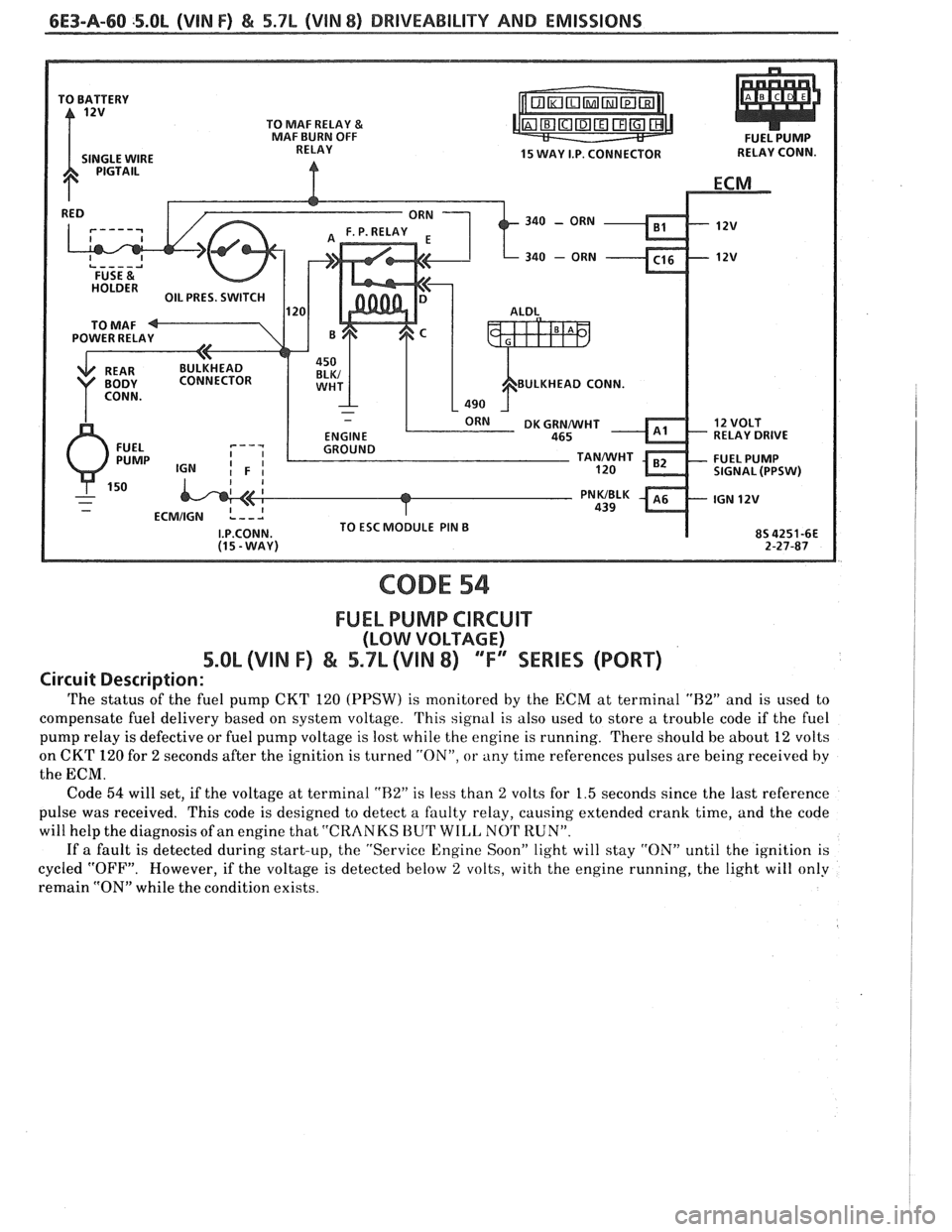
6E3-A-60 .5.0L (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
340 - ORN
BULKHEAD CONN.
RELAY DRIVE
CODE 54
FUEL PUMP CIRCUIT
(LOW VOLTAGE)
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIIN 8) "F" WRIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The status of the fuel pump CKT 120 (PPSW) is monitored by the ECM at terminal "H2" and is used to
compensate fuel delivery based on system voltage. This signal is also used to store a trouble code if the fuel
pump relay is defective or fuel pump voltage is lost while the engine is running. There should be about 12 volts
on CKT
120 for 2 seconds after the ignition is turned "ON", or any time references pulses are being received by
the ECM.
Code
54 will set, if the voltage at terminal "R2" is less than 2 volts for 1.5 seconds since the last reference
pulse was received. This code is designed to detect a faulty relay, causing extended crank time, and the code
will help the diagnosis of an engine that
"CRANKS BUT WILL NOT RUN".
If a fault is detected during start-up, the "Service Engine Soon" light will stay "ON" until the ignition is
cycled "OFF". However, if the voltage is detected below
2 volts, with the engine running, the light will only
remain "ON" while the condition exists.
Page 867 of 1825

6E3-B-2 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Problem may or may not turn "ON" the "Service Engine Soon" light, or store a code.
DO NOT use the Trouble Code Charts in
An intermittent "Service Engine Soon" light
Section A for intermittent problems. The fault must
with no stored code may be caused by:
be present to locate the problem. If a fault is
@ Ignition coil shorted to ground and arcing at
intermittent, use of Trouble Code Charts
may result
spark plug wires or plugs.
in replacement of good parts.
"Service Engine Soon" light wire to
ECM
@ Most intermittent problems are caused by
shorted to ground. (CKT 419).
faulty electrical connections or wiring. Perform
Diagnostic "Test" Terminal wire to ECM,
careful check as described at start of Section
shorted to
ground.(CKT 451)
"B". Check for:
@ ECM power grounds. See ECSI wiring
@ Poor mating of the connector halves, or diagrams.
terminals not fully seated in the connector
@ Loss of trouble code memory. To check,
body (backed out). disconnect TPS and idle engine until "Service
@ Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
Engine Soon" light comes on. Code 22 should be
All connector terminals in problem circuit
stored, and kept in memory when ignition is
should be carefully reformed or replaced to turned "OFF". If not, the ECM is faulty.
insure proper contact tension.
@ Check for an electrical system interference
@ Poor terminal to wire connection. This caused by a defective relay, ECM driven
requires removing the terminal from the
solenoid, or switch. They can cause a sharp
connector body to check. See "Introduction"
electrical surge. Normally, the problem will
to Section
"6E". occur when the faulty component is operated.
@ If a visual check does not find the cause of the @ Check for improper installation of electrical
problem, the car can be driven with a voltmeter
options, such as lights,
%way radios, etc.
connected to
a suspected circuit. A "Scan" tool
EST wires should be kept away from spark plug
can also be used for monitoring input signals to wires, distributor wires, distributor housing,
the ECM to help detect intermittent conditions. coil, and generator. Wire from
ECM to
An abnormal voltage, or "Scan" reading, when distributor
(CKT 453) should be a good
the problem occurs, indicates the problem
may connection.
be in that circuit. If the wiring and connectors
@ Check for open diode across AIC compressor
check OK and a Trouble Code was stored for a
clutch, and for other open diodes (see wiring
circuit having a sensor, except for Codes
43, 44, diagrams).
and 45, substitute a known good sensor and
recheck.
HARD START
Definition: Engine cranks OK, but does not start for a long
time. Does eventually run, or may start but immediately dies.
Perform careful check as described at start of
Section
"B".
@ Make sure driver is using correct starting
procedure.
@ CHECK:
- TPS for sticking or binding or a high TPS
voltage with the throttle closed (should read
less than
.700 volts).
- High resistance in coolant sensor circuit or
sensor itself. See Code 15 chart or with
a
"Scan" tool compare coolant temperature with
ambient temperature on a cold engine.
- Fuel pressure CHART A-7.
- Water contaminated fuel.
- EGR operation. Be sure valve seats properly and
is not staying open. See CHART C-7.
- Both injector fuses (visually inspect).
- Ignition system - Check distributor for:
Proper Output with ST-125.
Worn shaft.
Bare and shorted wires.
Pickup coil resistance and connections.
Loose ignition coil ground.
Moisture in distributor cap.
@ If problem exists in cold weather, check cold start
valve. See CHART A-9.
Page 871 of 1825

6E3-B-6 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
POOR FUEL ECONOMY
Definition: Fuel economy, as measured by an actual road test, is
noticeably lower than expected. Also, economy is noticeably lower than it
was on this car at one time, as previously shown by an actual road test.
@ Perform careful visual check as described at
start of Section "B".
@ CHECK:
- Coolant level.
- Engine thermostat for faulty part (always
open) or for wrong heat range. See Section
"6B".
- Compression
- Ignition timing. See Emission Control
Information label.
- TCC for proper operation. A "Scan" should
indicate an rpm drop when the TCC
is
commanded "ON". See CHART C-8.
- Induction system and crankcase for air leaks.
@ Check for exhaust restriction
See CHART
B-1.
DIESELING, RUN-ON
Definition: Engine continues to run after key is
turned off, but runs very roughly. If engine runs
smoothly, check ignition switch and adjustment.
@ Check injectors for leaking. See CHART A-7.
ROUGH, UNSTABLE, OR INCORRECT IDLE, STALLING
Definition: The engine runs unevenly at idle. If bad enough, the car may
shake. Also, the idle may vary in rpm (called "hunting"). Either condition
may be bad enough to cause stalling. Engine idles at incorrect speed.
@ Perform careful visual check as described at
start of Section "B".
e CHECK:
- Throttle linkage for sticking or binding.
- Ignition timing. See emission control
information label.
- ECM ground circuits.
- IAC system. See CHART C-2C.
- Generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9
or more than 16 volts.
- PIN switch circuit. See CHART C-lA, or use
"Scan" tool.
- Injector balance. See CHART C-2A.
- PCV valve for proper operation by placing
finger over inlet hole in valve end several
times. Valve should snap back. If not, replace
valve.
- Evaporative emission control system. CHART
C-3.
- A/C signal to ECM terminal "B8". "Scan" tool
should indicate
AIC is being requested when
ever
A/C is selected and the pressure cycling
switch is closed.
- Minimum idle speed. See Section "C2".
- Loose or damaged MAF sensor duct between
sensor and throttle body. Check
A.I.R. system. There should be no
A.1.R
to ports while in "Closed Loop". See CHART C6.
EGR valve: There should be no EGR at idle.
Run
a cylinder compression check-see Section
"6".
Inspect oxygen sensor for silicon contamination
from fuel, or use of improper RTV sealant. The
sensor will have a white, powdery coating, and
will result in a high but false signal voltage
(rich exhaust indication). The ECM will then
reduce the amount of fuel delivered to the
engine, causing a severe driveability problem.
Check for fuel in pressure regulator hose. If
present replace regulator assembly.
Check ignition system; wires, plugs, rotor, etc.
Check for loose or damaged air duct between
MAF sensor and throttle body.
Disconnect MAF sensor and if condition is
corrected replace sensor.
Clean injectors.
Monitoring block learn will help identify the
cause of the problem. If the system is runnig
lean (block learn greater than 1381, refer to
"Diagnostic Aids" on facing page of Code
44. If
the system is running rich (block learn less than
1 181, refer to "Diagnostic Aids" on facing page of
Code
45.
Page 878 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) 6E3-C1-3
The MAT sensor signal is used by the ECM to
delay
EGR until the manifold air temperature reaches
about 5°C
(40°F).
A failure in the MAT sensor circuit should set
either a Code
23 or Code 25.
Oxygen (02) Sensor
(Figure
€3-4)
The exhaust oxygen sensor (02) is mounted in the
exhaust system, where it can monitor the oxygen
content of the exhaust gas stream. The oxygen content
in the exhaust reacts with the sensor to produce a
voltage output. This voltage ranges from
approximately
.l volt (high 02 - lean mixture) to .9
volts (low 02 - rich mixture). This voltage can be
measured with a digital voltmeter having at least 10
meg ohms input impedance. Use of standard shop
type voltmeters will result in very inaccurate
readings.
By monitoring the voltage output of the 02 sensor,
the ECM will know what fuel mixture command to
give to the Injector (lean mixture-low
02 voltage= rich
command, rich mixture-high
O2 voltage = lean
command). The
02 sensor, if open, should set a Code 13. A low
voltage in the sensor circuit should set a Code
44. A
high voltage in the circuit should set a Code 45. Codes
44 and 45 could also be set as a result of fuel system
problems. See Code Charts.
EXHAUST OXYGEN (02)
10-2-86
* 45 0078-6E
Figure C1-4 E- xhaust Oxygen (Oz) Sensor
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
(Figure C1-5)
The throttle position sensor (TPS) is connected to
the throttle shaft on the throttle body. It is a
potentiometer with one end connected to
5 volts from
the ECM and the other to ECM ground.
A third wire
is connected to the ECM to measure the voltage from
the TPS. As the throttle valve angle is changed
(accelerator pedal moved), the output of the TPS also
changes. At a closed throttle position, the output of the TPS
is low (approximately
.5 volts). As the throttle
valve opens, the output increases so that, at wide-open
throttle, the output voltage should be approximately
5
volts.
By monitoring the output voltage from the
TPS,
the ECM can determine fuel delivery based on throttle
valve angle (driver demand).
A broken or loose 'I'PS
can cause intermittent bursts of fuel from the injector
and an unstable idle, because the ECM thinks the
throttle is moving.
A problem in any of the TPS
circuits will set either a Code
21 or 22. Once a trouble
code is set, the ECM will use an artificial default value
for TPS, and some vehicle perfhrmance will return.
See "On-Car Service" for replacement or
adjustment of
TPS.
10 THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY
20 THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)
Figure
C1-5 - Throttle Position Sensor
Knock Sensor
This sensor is used to control engine detonation
Refer to Section
"C5", for description.
Vehicle Speed Sensor
The vehicle speed sensor (VSS), part of the digital
cluster, sends a pulsing voltage signal to the ECM,
which the ECM converts to miles per hour.
This
sensor mainly controls the operation of the 'I'CC
system. See Code 24 or Section "C8" for more
information.
ParklNeutral Switch (Auto Only)
The parWneutra1 (PIN) switch indicates to the
ECM when the transmission is in park or neutral.
This information is used for the TCC and the
IAC
valve operation.
Important
Vehicle should not be driven with parklneutral
switch disconnected, as idle quality will be aft'ected
,ind a poss~hle false Code 24 (VSS).
Page 879 of 1825

6E3-C1-4 5.0L (VIN F) & 5.7L(VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
See Section "8A" for more information on the PIN
switch, which is part of the neutrallstart and backup
light switch assembly.
NC "ON" Signal
This signal tells the ECM that the NC selector
switch is turned "ON", and that the pressure cycling
switch is closed. The
ECM uses this to adjust the idle
speed when the air conditioning is working.
[f this signal is not available to the ECM, idle may
be rough, especially when the NC compressor cycles.
The voltage at ECM terminal "B8" should equal
battery voltage on a
C60 system and about 5 volts on a
C68 option, when
NC is requested and the pressure
cycling switch is closed.
Distributor Reference Signal
The distributor sends a signal to the ECM to tell it
both engine rpm and crankshaft position. See ignition
system Section
"C4" for further information.
DIAGNOSIS
To read the codes, use a "Scan" tool or ground the
diagnostic terminal with the engine not running and
the ignition "ON". The "Service Engine Soon" light
will flash Code 12 three times and then flash each code
stored in memory three times. All codes stored in
memory would have been read when Code 12 was
flashed again. No new codes can be stored when in the
diagnostics mode (diagnostics lead grounded). This
eliminates confusion while the system is being worked
on.
To clear the codes from memory:
@ Ignition "OFF".
@ Disconnect battery pigtail, located near the
battery, for 30 seconds.
Since the ECM can have a failure which may
affect only one circuit, following the diagnostic
procedures in this section will determine which circuit
has a problem and where it is.
If a diagnostic chart indicates that the
ECM
connections or ECM is the cause of a problem,and the
ECM is replaced, but does not correct the problem, one
of the following may be the reason:
-
@ There is a problem with the ECM terminal
connections.
- The diagnostic chart will say ECM
connections or ECM. The terminals may have to
be removed from the connector in order to check
them properly.
@ The ECM, or Mem-Cal is not correct for the
application.
- The incorrect components may cause
a malfunction and
may or may not set u code.
@ The problem is intermittent. - 'l'his means that the
problem is not present at the time the system is
being checked. In
this case, refer to the "Symptoms" portion
of the
manual and make a careful physical inspection
of
all portions of the system involved.
@ Shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness. - Solenoids
and relays are turned
"ON" and "OFF" by the
ECM, using internal electronic switches called
"Drivers".
A shorted solenoid, relay coil, or harness in a
GMP4 computer will not damage the ECM,
but will cause the circuit and controlled
component to be inoperative. When the
circuit fault is not present or has been
repaired, the
"Quad-Driver" will again
operate in a normal manner due to it's fault
protected design.
If a fault has been repaired
in a circuit controlled by a "Quad-Driver",
the original ECM should be reinstalled and
the circuit checked for proper operation.
ECM replacement will
not be necessary if the
repaired circuit or component now operates
correctly.
534636 or BT 8405 testers or equivalent provide a
fast, accurate means of checking for a shorted coil
or a short to battery voltage.
@ The Mem-Cal may be faulty. - Although these
rarely fail, it operates as part of the ECM.
Therefore, it could be the cause
of the problem.
Substitute a known good Mem-Cal.
@ The replacement ECM may be faulty - After the
ECM is replaced, the system should be rechecked
for proper operation. If the diagnostic chart again
indicates the ECM is the problem, substitute a
known good ECM. Although this is a rare
condition, it could happen.
ECM
A faulty ECM will be determined in the diagnostic
charts.
MEM-CAL
An incorrect or faulty Mem-Cal, which is part of
the ECM, may set a Code 41 or 52. Also, be sure Mem-
Cal is fully seated and latched in the socket.
ECM INPUTS
A11 of the sensors and input switches can be
diagnosed by the use of
a "Scan" tool. Following is a
short clescription of how the sensors and switches can
he diagnosed
by the use of a "Scan" tool. The "Scan"
can also be used to compare the values for a normal
running engine with the engine you're diagnosing.