1987 SUZUKI GRAND VITARA stop start
[x] Cancel search: stop startPage 24 of 962
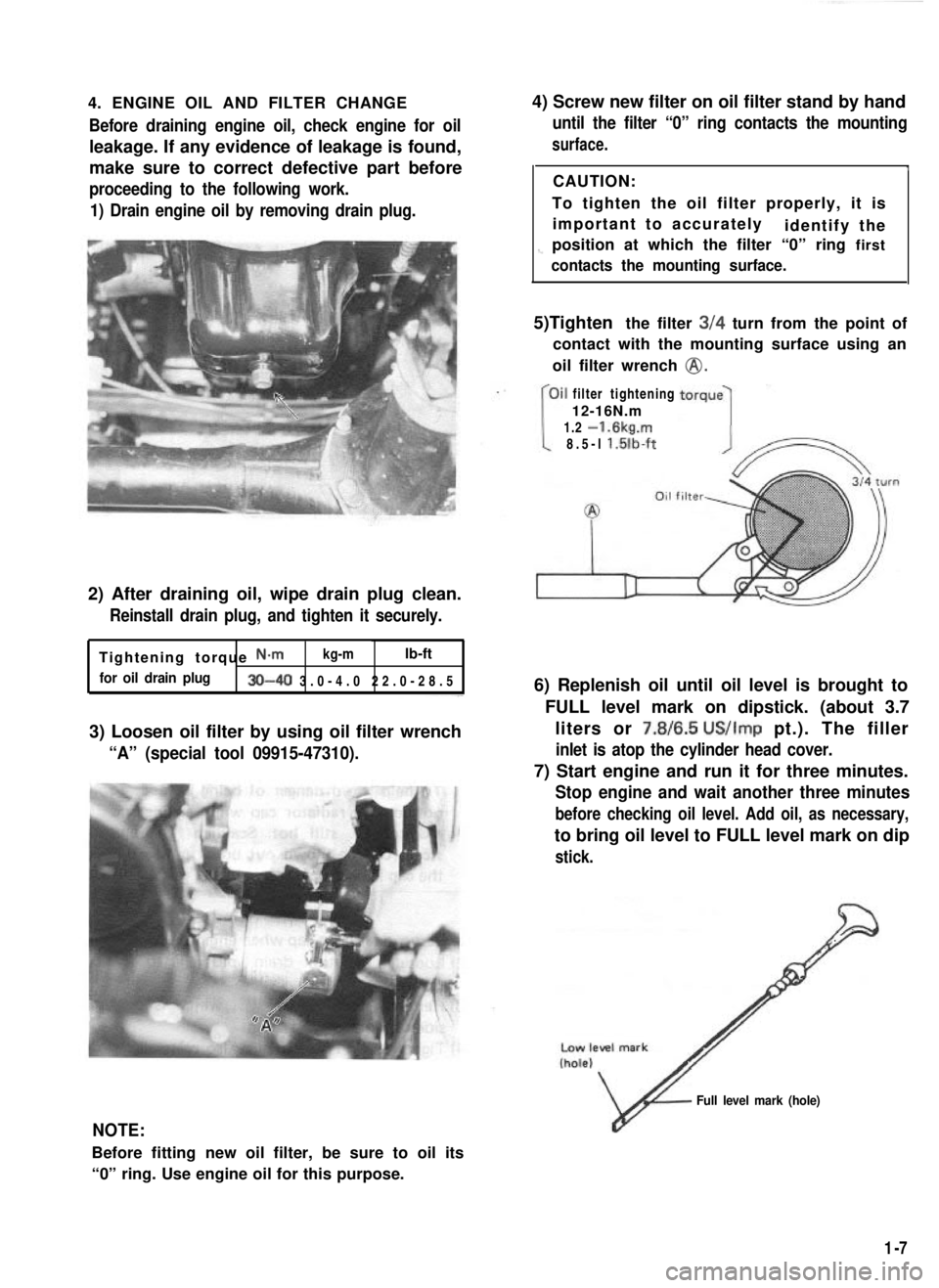
4. ENGINE OIL AND FILTER CHANGEBefore draining engine oil, check engine for oil
leakage. If any evidence of leakage is found,
make sure to correct defective part before
proceeding to the following work.
1) Drain engine oil by removing drain plug.
2) After draining oil, wipe drain plug clean.
Reinstall drain plug, and tighten it securely.
Tightening torque N-m kg-mlb-ft
for oil drain plug30-40 3.0-4.0 22.0-28.
5
3) Loosen oil filter by using oil filter wrench
“A” (special tool 09915-47310).
4) Screw new filter on oil filter stand by hand
until the filter “0” ring contacts the mounting
surface.
ICAUTION:
To tighten the oil filter properly, it is important to accurately identify the
1-position at which the filter “0” ring first
contacts the mounting surface.
5)Tighten the filter 3/4 turn from the point of
contact with the mounting surface using an
oil filter wrench
@.
filter tightening
12-16N.m
1.2
-1.6kg.m
8.5-l l.lilb-ft
6) Replenish oil until oil level is brought to
FULL level mark on dipstick. (about 3.7liters or 7.8/6.5
US/Imp pt.). The filler
inlet is atop the cylinder head cover.
7) Start engine and run it for three minutes.
Stop engine and wait another three minutes
before checking oil level. Add oil, as necessary,
to bring oil level to FULL level mark on dip
stick.
NOTE:
Before fitting new oil filter, be sure to oil its
“0” ring. Use engine oil for this purpose.
v
Full level mark (hole)
1-7
Page 28 of 962
1. During acceleration
2. During deceleration
3. Diaphragm
Movement of EGR valve diaphragm
14. ECM AND ASSOCIATED SENSORS
INSPECTION
1) Start engine and warm it up to normal operat-
ing temperature.
For Canadian specification vehicle, turn on
check switch.
2) Run engine at 1500 - 2000 r/min (t-pm).
In this state, make sure that “CHECK EON-
GINE” light flashes.
Flashing of light proves that ECM and associ-
ated sensors are in good condition.
If the light does not flash, check them and
replace or adjust as necessary. Refer to
SECTION 5 for checking procedure.
A
CHECKENGINE
“CHECK ENGINE” ligh t
3)Turn off “CHECK ENGINE” light cancel or
check switch on steering holder bracket.
4) Stop engine.
15. WIRING HARNESS AND CONNECTIONS
INSPECTION
1) Visually inspect all wires located in engine
compartment for evidence of breakage.
Inspect the condition of the insulation
(cracks). All clips and clamps should have
solid connections to wires.
2) Replace any wires in a deteriorated or other-
wise defective condition.
16. SPARK PLUGS REPLACEMENT
1) Disconnect high-tension cords from‘ spark
plugs. Make sure to pull only on spark plug
caps.
2) Using a spark plug wrench, loosen and remove
plugs.
0.7 - 0.8 mm(0.028 - 0.032 in.)
1-12
Page 32 of 962
1. Mixture adjusting screw pin
2. Rod
Mixture adjusting screw pin
10) With engine running at idle speed, adjust idle
mixture adjusting screw slowly in small incre-
ment allowing time for duty to stabilize after
turning screw to obtain duty of 10 - 50.
If duty is too low, back screw out; if too
high, screw it in. After obtaining duty of
10- 50, recheck idle speed, and adjust if
necessary.
NOTE:
If adjustment can’t be made because duty meter
indicator does not deflect, check feed baCk
system according to the checking procedure of
system described in section of Emission Control
System.
3) Reinstall carburetor following normal service
procedures.
Connect emission control system hoses and
lead wires. Make specified play on accelerator
cable and refill cooling system.
11) After adjustment, install seal rubber to duty
check coupler and drive in idle mixture
adjusting screw pin.
4) Place transaxle gear shift lever in “Neutral”,
set parking brake and block drive wheels.
5) Start engine, and warm it up to normal
operating temperature, stop engine.
6) Be sure to check the following before idle
mixutre adjustment.
l Fuel level is within round mark at the
center of level gauge.
l Valve lash is checked and adjusted accord-
ing to the maintenance schedule.
l Air cleaner has been properly installed
and is in good condition.
l All accessories (wipers, heater, lights etc)
are out of service.
29. CARBURETOR INSPECTION
Check each carburetor mounting nut for tight-
ness.
If it is found loose, tighten it securely.
Also, check where the carburetor and intake
manifold are mated and other parts of the
carburetor body for leakage. Be sure to correct
the cause for leakage, if any.
l Ignition timing is within specification.
l Choke valve opens fully.
l Idle-up actuator does not operate.
7) Check and adjust idle speed to specification
if necessary.
8) Remove seal rubber of duty check coupler
and connect positive terminal of duty
meter to“Blue/Red” wire and negative
terminal to “Black/Green” wire.
9) Run engine at 1,500 - 2,000 r/min for 30
seconds and bring it to idle speed.
1-16
Page 38 of 962
FINAL INSPECTION
Carry out road test in safe place.
WARNING:
When carrying out the following road
tests, select a safe place where no man or
no running car is seen so as to prevent any
accident.
1) Engine start
Check engine start for readiness.
2) Clutch
Check the following:
l that clutch is completely released when
depressing clutch pedal,
l that no slipping clutch occurs when releas-
ing pedal and accelerating,
l and that clutch itself is free from any
abnormal condition.
3) Gearshift Lever (Transmission and Transfer)
Check gearshift lever for smooth shifting
to all positions and for good performance of
transmission and transfer in any position.
4) Brake
[Foot brake]
Check the following when depressing brake
pedal while driving;
l that brake works properly,
l that it is free from noise,
l and that braking force applies equally on
all wheels.
[Parking brake]
Check to ensure that parking brake is fully
effective when the car is stopped on the slop
and brake lever is pulled all the way.
5) Steering
Check to ensure that steering wheel is free
from instability, or abnormally heavy feeling
while driving.
1-22
Page 55 of 962
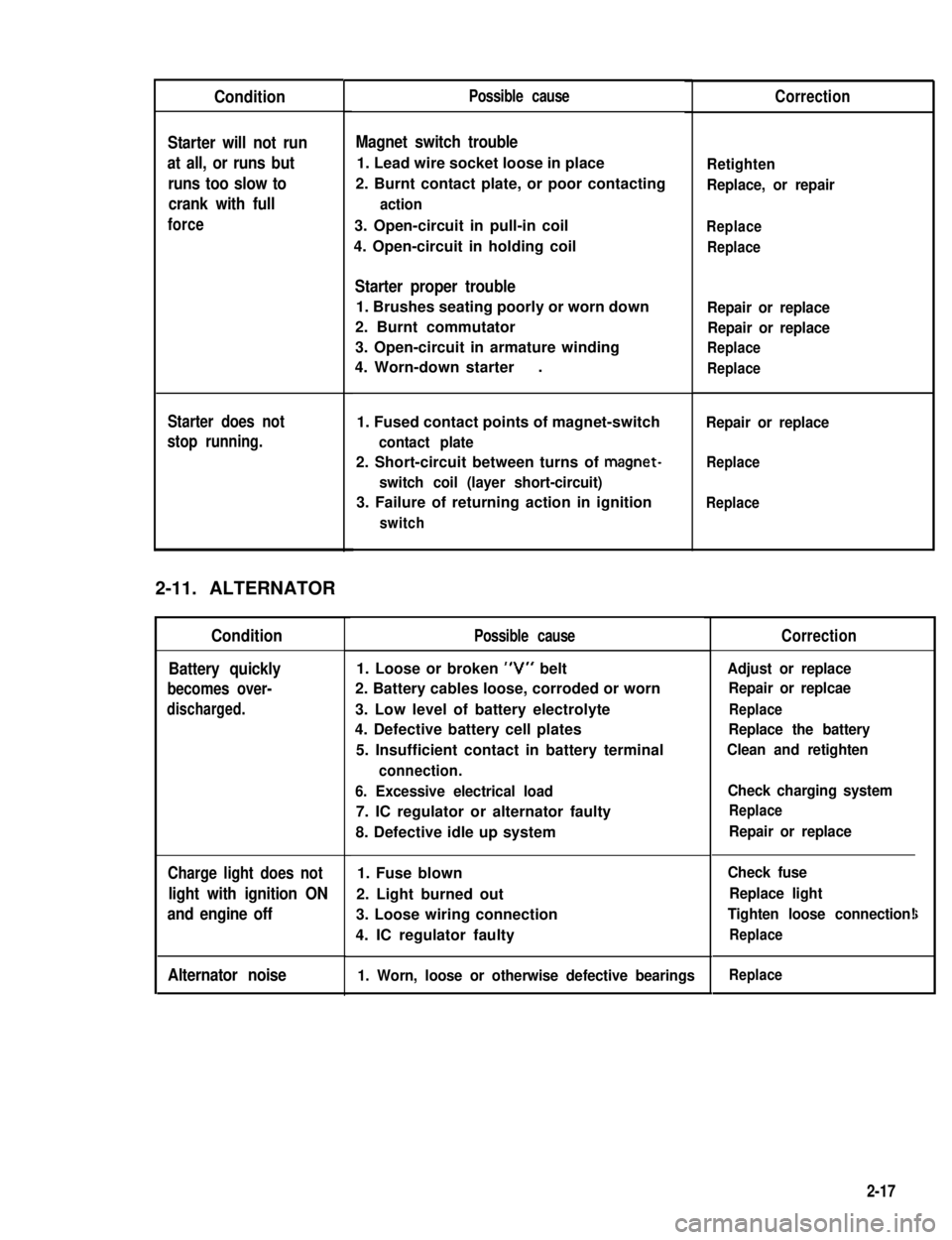
Condition
Starter will not run
at all, or runs but
runs too slow to
crank with full
force
Starter does not
stop running.
2-11. ALTERNATOR
Condition
Battery quickly
becomes over-
discharged.
Charge light does not
light with ignition ON
and engine off
Alternator noise
Possible cause
Magnet switch trouble
1. Lead wire socket loose in place
2. Burnt contact plate, or poor contacting
action
3. Open-circuit in pull-in coil
4. Open-circuit in holding coil
Starter proper trouble
1. Brushes seating poorly or worn down
2. Burnt commutator
3. Open-circuit in armature winding
4. Worn-down starter.
1. Fused contact points of magnet-switch
contact plate
2. Short-circuit between turns of magnet-
switch coil (layer short-circuit)
3. Failure of returning action in ignition
switch
Possible cause
1. Loose or broken “V” belt
2. Battery cables loose, corroded or worn
3. Low level of battery electrolyte
4. Defective battery cell plates
5. Insufficient contact in battery terminal
connection.
6. Excessive electrical load
7. IC regulator or alternator faulty
8. Defective idle up system
1. Fuse blown
2. Light burned out
3. Loose wiring connection
4. IC regulator faulty
1. Worn, loose or otherwise defective bearings
Correction
Retighten
Replace, or repair
Replace
Replace
Repair or replace
Repair or replace
Replace
Replace
Repair or replace
Replace
Replace
Correction
Adjust or replace
Repair or replcae
Replace
Replace the battery
Clean and retighten
Check charging system
Replace
Repair or replace
Check fuse
Replace light
Tighten loose connection!
Replace
i
Replace
2-17
Page 112 of 962
Engine Coolant
This subject is covered in SECTION 6 ENGINE
COOLING SYSTEM.
Exhaust Line and Muffler
Inspect each exhaust line connection for tight-
ness, and examine muffler and other parts for
evidence of breakage and leakage of gases.
Repair or replace defective parts, if any.
Compression Pressure Measurement
Check compression pressure on all four cylinders
as follows:
1) Warm up engine.
2) Stop engine after warming up.
3) Remove all spark plugs and disconnect
high tension cord from ignition coil.
4) Install compression gauge (special tool) into
spark plug hole.
5) Disengage clutch (to lighten starting load on
engine), and depress accelerator pedal all
the way to make throttle full-open.
6) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and
read the highest pressure on compression
gauge.
Standard
Limit
Max. difference
between any two
cylinders
Compression pressure
14.0 kg/cm2 (199.0 psi)
400 r/min
12.0 kg/cm2 (170.0 psi)
400 r/min
1 .O kg/cm2 (14.2 psi),
400 r/min
3
7) Carry out steps 4) through 6) on each cylin-
der to obtain four readings.
NOTE:
Compression pressure value is measured by using
compression gauge (Special tool 09915-64510).
Oil Pump Discharge Pressure Measurement
NOTE:
Prior to checking oil pressure, check the follow-
ing.
l Oil level in oil pan.
If level is low, add oil up to Full level hole on
oil level gauge.
0 Oil quality.
If oil is discolored, or deteriorated, change oil.
For particular oil to be used, refer to table on
p l-8 of SECTION 1.
l Oil leak.
If leak is found, repair it
1. Compression gauge (Special tool 09915-64510)
Fig. 3-8-7 Installing compression gauge
3-55
Page 113 of 962
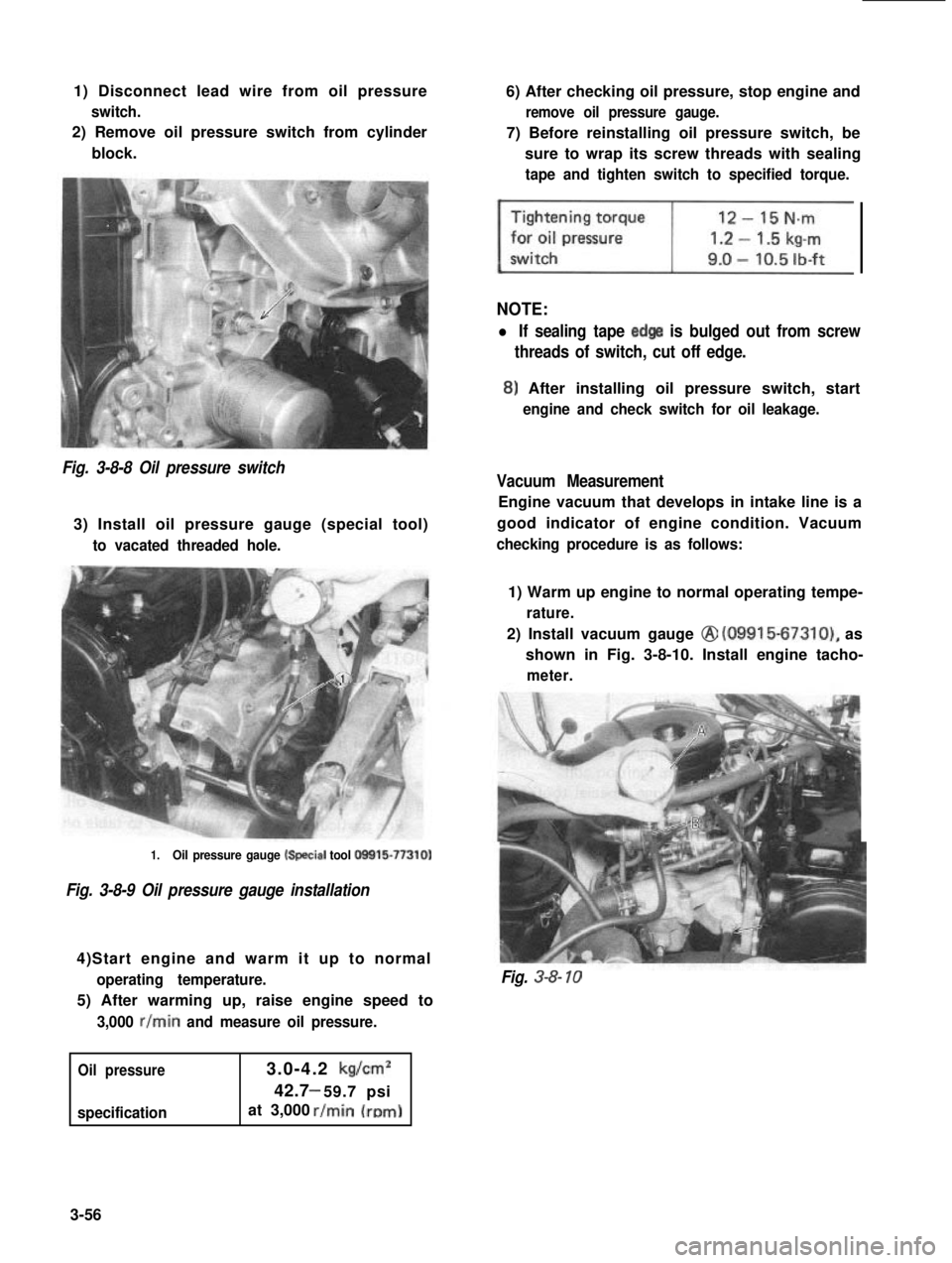
1) Disconnect lead wire from oil pressure
switch.
2) Remove oil pressure switch from cylinder
block.
6) After checking oil pressure, stop engine and
remove oil pressure gauge.
7) Before reinstalling oil pressure switch, be
sure to wrap its screw threads with sealing
tape and tighten switch to specified torque.
NOTE:
l If sealing tape edge is bulged out from screw
threads of switch, cut off edge.
8) After installing oil pressure switch, start
engine and check switch for oil leakage.
Fig. 3-8-8 Oil pressure switch
3) Install oil pressure gauge (special tool)
to vacated threaded hole.
Vacuum Measurement
Engine vacuum that develops in intake line is a
good indicator of engine condition. Vacuum
checking procedure is as follows:
1.Oil pressure gauge k+ecial tool O!Xil5-77310)
Fig. 3-8-9 Oil pressure gauge installation
4)Start engine and warm it up to normal
operating temperature.
5) After warming up, raise engine speed to
3,000 r/min and measure oil pressure.
Oil pressure
specification
3.0-4.2 kg/cm2
42.7 59.7 psi-
at 3,000
1) Warm up engine to normal operating tempe-
rature.
2) Install vacuum gauge @ (09915-67310), as
shown in Fig. 3-8-10. Install engine tacho-
meter.
Fig. 3-8- 10
3-56
Page 125 of 962
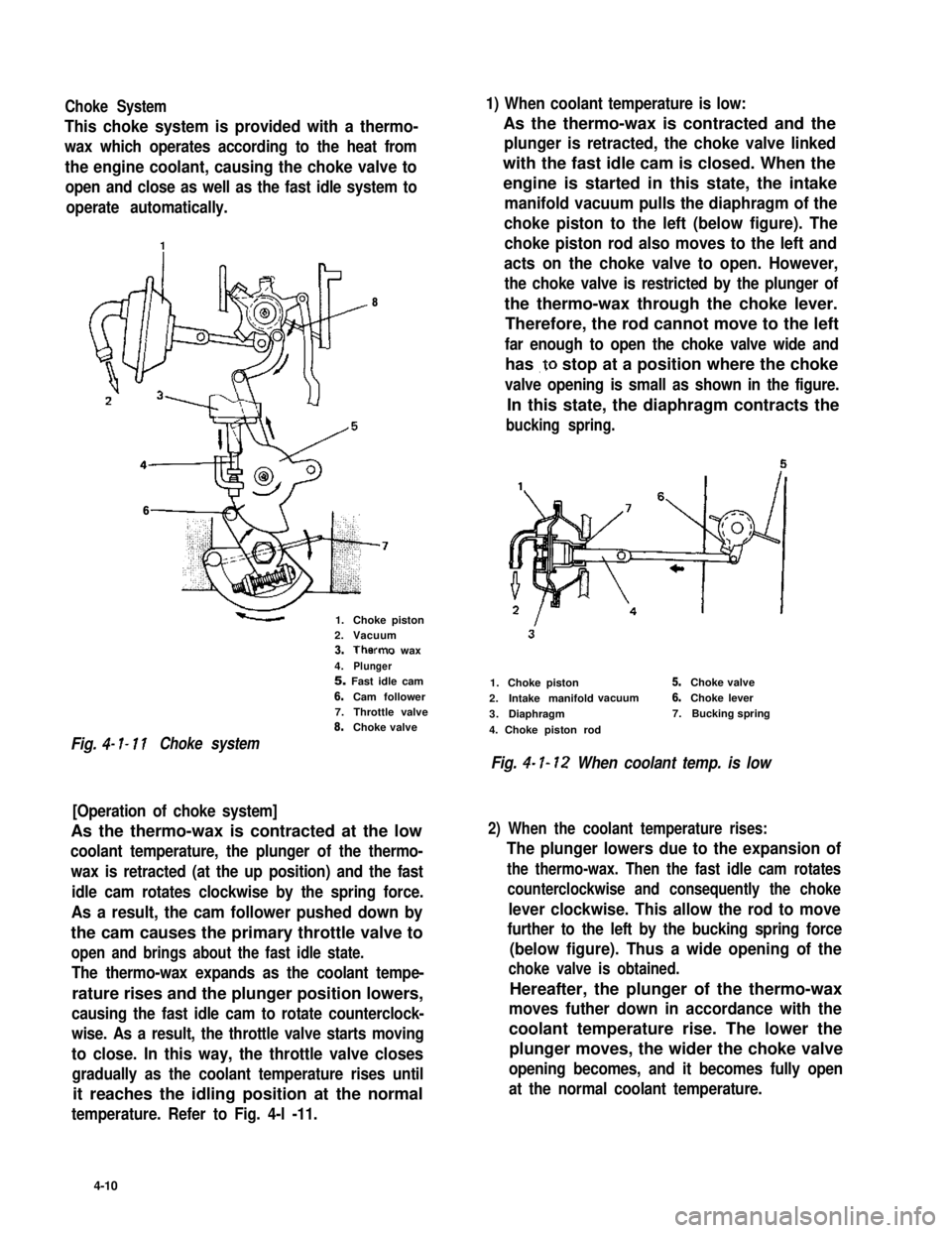
Choke System1) When coolant temperature is low:
This choke system is provided with a thermo-
wax which operates according to the heat from
the engine coolant, causing the choke valve to
open and close as well as the fast idle system to
operate automatically.
As the thermo-wax is contracted and the
plunger is retracted, the choke valve linked
with the fast idle cam is closed. When the
engine is started in this state, the intake
manifold vacuum pulls the diaphragm of the
choke piston to the left (below figure). The
choke piston rod also moves to the left and
acts on the choke valve to open. However,
the choke valve is restricted by the plunger of
the thermo-wax through the choke lever.
Therefore, the rod cannot move to the left
far enough to open the choke valve wide and
has .to stop at a position where the choke
valve opening is small as shown in the figure.
In this state, the diaphragm contracts the
bucking spring.
8
6
1.Choke piston2.Vacuum3.Therms wax
4.Plunger5. Fast idle cam
6.Cam follower7.Throttle valve8.Choke valve
Fig. 4- I- 11Choke system
[Operation of choke system]
As the thermo-wax is contracted at the low
coolant temperature, the plunger of the thermo-
wax is retracted (at the up position) and the fast
idle cam rotates clockwise by the spring force.
As a result, the cam follower pushed down by
the cam causes the primary throttle valve to
open and brings about the fast idle state.
The thermo-wax expands as the coolant tempe-
rature rises and the plunger position lowers,
causing the fast idle cam to rotate counterclock-
wise. As a result, the throttle valve starts moving
to close. In this way, the throttle valve closes
gradually as the coolant temperature rises until
it reaches the idling position at the normal
temperature. Refer to Fig. 4-l -11.
1.Choke piston
2.Intake manifoldvacuum
3.Diaphragm
4. Choke piston rod
5.Choke valve
6.Choke lever
7.Bucking spring
Fig. 4- I- 12 When coolant temp. is low
2) When the coolant temperature rises:
The plunger lowers due to the expansion of
the thermo-wax. Then the fast idle cam rotates
counterclockwise and consequently the choke
lever clockwise. This allow the rod to move
further to the left by the bucking spring force
(below figure). Thus a wide opening of the
choke valve is obtained.
Hereafter, the plunger of the thermo-wax
moves futher down in accordance with the
coolant temperature rise. The lower the
plunger moves, the wider the choke valve
opening becomes, and it becomes fully open
at the normal coolant temperature.
4-10