1985 FORD GRANADA check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 119 of 255

The ignition system is responsible for
igniting the fuel/air charge in each cylinder at
the correct moment. The components of the
system are the spark plugs, ignition coil,
distributor and connecting leads. Overall
control of the system is one of the functions of
the engine management module. Fuel-
injection models have a subsidiary ignition
module mounted on the distributor.
There are no contact breaker points in the
distributor. A square wave signal is generated
by the distributor electro-magnetically; this
signal is used by the engine management
module as a basis for switching the coil LT
current. Speed-related (centrifugal) advance is
also handled by the module. On carburettor
models, ignition timing is also advanced under
conditions of high inlet manifold vacuum.The engine management models are “black
boxes” which regulate both the fuel and the
ignition systems to obtain the best power,
economy and emission levels. The module
fitted to carburettor models is known as the
ESC II (Electronic Spark Control Mk II) module.
On fuel-injection models the more powerful
EEC IV (Electronic Engine Control Mk IV)
module is used.
Both types of module receive inputs from
sensors monitoring coolant temperature,
distributor rotor position and (on some
models) manifold vacuum. Outputs from the
module control ignition timing, inlet manifold
heating and (except on 1.8 litre models) idle
speed. The EEC IV module also has overall
control of the fuel-injection system, from
which it receives information.
Provision is made for the ignition timing to
be retarded to allow the use of low octane fuel
if necessary. On all except 1.8 litre models
there is also a facility for raising the idle speed.The EEC IV module contains self-test
circuitry which enables a technician with the
appropriate test equipment to diagnose faults
in a very short time. A Limited Operation
Strategy (LOS) means that the car is still
driveable, albeit at reduced power and
efficiency, in the event of a failure in the
module or its sensors.
Due to the complexity and expense of the
test equipment dedicated to the engine
management system, suspected faults should
be investigated by a Ford dealer, or other
competent specialist. This Chapter deals with
component removal and refitting, and with
some simple checks and adjustments.
On DOHC carburettor engines, the basic
operating principles of the ignition system are
as described above. A development of the
ESC II (Electronic Spark Control ll) system is
used to control the operation of the engine.
The ESC II module receives information from a
crankshaft speed/position sensor and an
1General information and
precautions
5•2Engine electrical systems
Ignition coil
Make . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Bosch, Femsa or Polmot
Primary resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.72 to 0.86 ohm
Secondary resistance:
All except DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.5 to 7.0 k ohms
DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.5 to 8.6 k ohms
Output voltage (open-circuit):
All except DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25 kV minimum
DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 kV minimum
HT leads
Maximum resistance per lead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 k ohms
Distributor
Make . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Bosch or Motorcraft
Rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Clockwise (viewed from above)
Automatic advance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Controlled by module
Dwell angle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Controlled by module
Ignition timing (see text)
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines:
Leaded fuel (97 octane):
Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10°BTDC
Fuel-injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12°BTDC
Unleaded fuel (95 octane):
Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6°BTDC
Fuel-injection models:
2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8°BTDC
2.8 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12°BTDC (no change)
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines:
Models with catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15°BTDC
Models without catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12°BTDC*
* Standard setting for 97 octane leaded fuel.
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Alternator adjusting strap:
To steering pump bracket (OHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2616 to 19
To front cover (V6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Spark plugs:
All models except 2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2815 to 21
2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 to 4022 to 30
Air charge temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Engine coolant temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Fuel rail temperature sensor (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Crankshaft speed/position sensor screw (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 to 52 to 4
procarmanuals.com
Page 121 of 255

1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead.
2Disconnect the battery positive leads. These
may be protected by a plastic cover. Do not
allow the spanner to bridge the positive and
negative terminals.
3Release the battery hold-down clamp. Lift
out the battery. Keep it upright and be careful
not to drop it - it is heavy.
4Commence by placing the battery in its tray,
making sure it is the right way round. Secure it
with the hold-down clamp.
5Clean the battery terminals if necessary
then reconnect them. Connect the positive
lead first, then the negative lead.
1Should it appear that the alternator is not
charging the battery, check first that the
drivebelt is intact and in good condition and
that its tension is correct. Also check the
condition and security of the alternator
electrical connections and the battery leads.
2Accurate assessment of alternator output
requires special equipment and a degree of
skill. A rough idea of whether output is
adequate can be gained by using a voltmeter
(range 0 to 15 or 0 to 20 volts) as follows.
3Connect the voltmeter across the battery
terminals. Switch on the headlights and note
the voltage reading: it should be between 12
and 13 volts.
4Start the engine and run it at a fast idle
(approx 1500 rpm). Read the voltmeter: it
should indicate 13 to 14 volts.
5With the engine still running at a fast idle,
switch on as many electrical consumers as
possible (heated rear window, heater blower
etc). The voltage at the battery should be
maintained at 13 to 14 volts. Increase the
engine speed slightly if necessary to keep the
voltage up.
6If alternator output is low or zero, check the
brushes. If the brushes are OK, seek expert
advice.7Occasionally the condition may arise where
the alternator output is excessive. Clues to this
condition are constantly blowing bulbs;
brightness of lights vary considerably with
engine speed; overheating of alternator and
battery, possible with steam or fumes coming
from the battery. This condition is almost
certainly due to a defective voltage regulator,
but expert advice should be sought.
8Note that the alternator voltage regulator
can be renewed without removing the
alternator from the vehicle. The procedure is
part of brush renewal.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the multi-plug from the rear of
the alternator. It may be secured by a wire clip.
3Slacken the alternator adjusting and pivot
nut(s), bolt(s)and washer(s)(see illustration).
Swing the alternator towards the engine and
slip the drivebelt(s) off the pulley.
4Support the alternator. Remove the
adjusting and pivot nuts, bolts and washers,
noting the fitted positions of the washers. Lift
out the alternator. Do not drop it, it is fragile.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Tension the drivebelt(s) then tighten the
adjustment strap bolt followed by the pivot nut
and bolt. If there are two pivot bolts, tighten
the front one first.
6Refit the multi-plug and reconnect the
battery.
1The alternator brushes can be inspected or
renewed without removing the alternator from
the vehicle, but disconnect the battery
negative lead first.
2From the rear of the alternator remove the
two screws which secure the voltage
regulator/brush carrier assembly. Withdraw
the assembly (see illustration).
3Measure the length of each brush
protruding from the carrier (see illustration). If
they are worn down to, or below, the minimumspecified, the old brushes will have to be
unsoldered and new ones soldered into place.
Some skill with a soldering iron will be
required; excess heat from the soldering iron
could damage the voltage regulator. When
fitted, the new brushes must move freely in
their holders.
4Clean the slip rings with a cloth moistened
with methylated spirit (see illustration). If they
are badly burnt or damaged, seek expert
advice.
5Refit the assembled brush carrier/voltage
regulator and secure it with the two screws. If
the alternator is on the vehicle, reconnect the
battery negative lead.
1If the starter motor fails to operate, first
check that the battery is charged by switching
on the headlights. If the headlights do not
come on, or rapidly become dim, the battery
or its connections are at fault.
2Check the security and condition of the
battery and starter solenoid connections.
Remember that the heavy lead to the solenoid
is always “live” - disconnect the battery
negative lead before using tools on the
solenoid connections.
8Starter motor - testing on the
vehicle7Alternator - brush renewal
6Alternator - removal and
refitting
5Alternator - testing on the
vehicle
4Battery - removal and refitting
5•4Engine electrical systems
7.3 Measuring brush protrusion7.4 Clean the slip rings (arrowed)
6.3 Alternator mounting details
A Large washer
B Small washer (not always fitted)
C Mounting bracket
D Alternator
Some models have a single pivot bolt
7.2 Removing the voltage regulator/brush
carrier
procarmanuals.com
Page 122 of 255

Solenoid check
3Disconnect the battery negative lead, and all
leads from the solenoid.
4Connect a battery and a 3 watt test lamp
between the solenoid body and the solenoid
motor terminal (see illustration).The test
lamp should light: if not, the solenoid windings
are open-circuit.
5Connect a battery and an 18 to 21 watt test
lamp across the solenoid motor and battery
terminals. Connect a further lead from the
battery positive terminal to the solenoid spade
terminal(see illustration).The solenoid
should be heard to operate and the test lamp
should light: if not, the solenoid contacts are
defective.
On load voltage check
6Remake the original connections to the
solenoid and reconnect the battery negative
lead. Connect a voltmeter across the battery
terminals, then disconnect the low tension
lead from the coil positive terminal and
operate the starter by turning the ignition
switch. Note the reading on the voltmeter
which should not be less than 10.5 volts.
7Now connect the voltmeter between the
starter motor terminal on the solenoid and the
starter motor body. With the coil low tension
lead still disconnected, operate the starter and
check that the recorded voltage is not more
than 1 volt lower than thatpreviously noted. If
the voltage drop is more than 1 volt a fault
exists in the wiring from the battery to the
starter.
8Connect the voltmeter between the battery
positive terminal and the terminal on the
starter motor. With the coil low tension lead
disconnected operate the starter for two or
three seconds. Battery voltage should be
indicated initially, then dropping to less than 1
volt. If the reading is more than 1 volt there is a
high resistance in the wiring from the battery
to the starter and the check in paragraph 9
should be made. If the reading is less than 1
volt proceed to paragraph 10.
9Connect the voltmeter between the two
main solenoid terminals and operate the
starter for two or three seconds. Batteryvoltage should be indicated initially then
dropping to less than 0.5 volt. If the reading is
more than 0.5 volt, the solenoid and
connections may be faulty.
10Connect the voltmeter between the
battery negative terminal and the starter motor
body, and operate the starter for two or three
seconds. A reading of less than 0.5 volt should
be recorded; however, if the reading is more,
the earth circuit is faulty and the earth
connections to the battery and body should be
checked.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead. Raise
and support the front of the vehicle.
2From underneath the vehicle, disconnect
the feed (heavy) cable from the solenoid.
3Disconnect the command lead from the
solenoid spade terminal.
4Undo the starter motor securing bolts and
(where fitted) the support bracket fastenings.
Withdraw the starter motor from the vehicle.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Check for correct operation on completion.
1Disconnect the motor lead from the
solenoid terminal.
2Remove the two screws which secure the
armature end cap. Remove the cap, the C-
washer and the plain washer(s).
3Remove the two through-bolts or studs.
4Remove the commutator end cover to
expose the brushgear. Carefully withdraw the
brushplate from the commutator. Be careful to
avoid damage to the brushes as they are
released.
5Examine the brushes: they should not beexcessively worn (see Specifications) and
must slide freely in their holders. Brush
renewal varies according to motor type as
follows:
Short frame - the brush lead must be
removed from the stand-off connector on the
brushplate, and the clip on the new brush lead
soldered to the connector.
Long frame - the old brush leads must be
cut and the new leads attached by soldering
Reduction gear - the brushplate must be
renewed complete with brushes, holders and
springs
6Reassembly is the reverse of dismantling
whilst noting the following:
7Clean the commutator with a rag moistened
with methylated spirit, then refit the
brushplate.
8Either clip the brushes in place after fitting
the plate, or use a tube of suitable diameter to
keep the brushes retracted during fitting.
9Make sure that the brushplate is correctly
positioned to allow the passage of through-
bolts or studs.
See Chapter 1, Section 20.
See Chapter 1, Section 39.
All engines except 2.4 & 2.9 litre V6
Note: The distributor should not be removed
without good cause, since the accuracy of
ignition timing achieved in production is
unlikely to be regained
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the distributor cap as described in
the previous Section. Depending on model, it
may be possible to move the cap aside
without disconnecting the HT leads.
3Using a spanner on the crankshaft pulley
bolt, turn the engine to bring No 1 cylinder to
firing point. (If the distributor cap is secured by
clips, make sure the clips stay clear of the
distributor moving parts.) No 1 cylinder is at
firing point when:
a)The timing marks are in alignment.
b)The tip of the rotor arm is pointing to the
place occupied by the No 1 HT lead
connector in the distributor cap (see
illustration).
4With No 1 cylinder at firing point, the tip of
the rotor arm should also be aligned with a
notch in the distributor body. Mark the notch
for reference when refitting.
5Depress the locking tab on the distributor
13Distributor - removal and
refitting
12HT leads, distributor cap and
rotor arm - removal, inspection
and refitting
11Spark plugs - removal,
inspection and refitting
10Starter motor - brush renewal
9Starter motor - removal and
refitting
Engine electrical systems 5•5
5
8.4 Solenoid winding check
A Battery terminal
B Motor terminalC Spade terminal
8.5 Solenoid contact check
A Battery terminal
B Motor terminalC Spade terminal
If the stud nuts are
inaccessible, lock two nuts
together on the stud and turn
them to unscrew it .
procarmanuals.com
Page 124 of 255

12When the distributor is at the firing point,
the leading edge of one of the vanes should be
in line with the rib on the sensor (see
illustration). Turn the distributor body slightly
if necessary to achieve this.
13Refit the clamp plate and bolt. Just nip up
the bolt for the time being. Tighten it finally
after checking the timing. Also secure the
support bracket, when fitted.
14Refit the rotor arm, distributor cap and HT
leads.
15Reconnect the distributor multi-plug.
16Reconnect the battery. Run the engine
and check the ignition timing as described in
the next Section.
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines
Note: The distributor should not be removed
or disturbed without good cause, since the
accuracy of timing achieved in production is
unlikely to be regained. If difficulty is
experienced in setting the timing after refitting,
or if a new distributor has been fitted, the
timing should be set by a Ford dealer using a
STAR (Self Test Automatic Readout) tester.
17Disconnect the battery negative lead.
18Disconnect the HT leads from the spark
plugs noting the correct fitted locations.
19Release the distributor cap and place it to
one side, complete with the HT leads.
20Turn the engine by means of the vibration
damper centre bolt until No 1 piston is at its
firing point (12°BTDC) (see illustration).
21If there is no mark visible, mark the rim of
the distributor body to indicate the point of
alignment of the contact end of the rotor.
22Mark the position of the distributor
mounting plate in relation to the cylinder
block.
23Disconnect the distributor wiring
connector.
24Scrape the sealant from around the
distributor clamp bolt then unscrew the bolt
and withdraw the distributor.
25Prior to refitting the distributor check that
the crankshaft is still set in the 12°BTDC
position for the No 1 piston.
26Hold the distributor over the hole so that
the mounting plinth and cylinder head marks
are aligned then align the rotor arm contact
end with the mark on the distributor rim (see
illustration).
27As the distributor is inserted, the rotor will
turn due to the meshing of the drive gears.
When the distributor is fully inserted, rotate the
distributor body until the rotor arm aligns with
mark C on the distributor rim.
28Once the rotor arm, cylinder head and
distributor alignment marks are all correctly
aligned, fit the clamp bolt and tighten it
securely.
29Refit the distributor cap then connect the
HT leads, reconnect the vacuum pipe and
wiring plug.
30Run the engine to normal operating
temperature and check the ignition timing,
bearing in mind the note made at the start of
this sub-Section.
All engines except DOHC
1Ignition timing is set very accurately in
production. It does not need to be checked or
adjusted on a routine basis. Adjustment will
only be necessary if the distributor, or an
associated component such as the timing belt,
has been disturbed.
2Before checking the timing, the following
conditions must be met:
a)The engine must be warmed up
b)On carburettor models, the vacuum pipe
must be disconnected from the manifold
and the manifold hole be plugged
c)Idle speed must be below 900 rpm
d)Any earthed “octane adjustment” wires
must be temporarily isolated
3Locate the timing marks. On SOHC engines
the timing scale is on the crankshaft pulley,
and a pointer on the timing cover must be
aligned with the appropriate mark on the
pulley (see illustration). Note that two
alternative types of pulley may be fitted (see
illustration).On V6 engines there is a single
notch on the pulley and the timing scale is on
the timing cover (see illustration).The desiredvalues are given in the Specifications.
Highlight the appropriate marks with white
paint.
4Connect a timing light (strobe) to No 1 HT
lead, following the maker’s instructions. Some
lights require additional power connections to
be made, either to the mains or to the battery.
5Run the engine at idle and shine the timing
light onto the marks. Take care not to get the
timing light leads, clothing etc tangled in the
fan blades or other moving parts. The timing
marks will appear stationary and (if the timing
is correct) in alignment.
14Ignition timing - checking
Engine electrical systems 5•7
5
13.12 Vane leading edge and sensor rib
(arrowed) are aligned at firing point13.20 Crankshaft pulley notch set to the 12°
BTDC position
14.3a Timing marks and pointer
Cast pulley shown
13.26 Rotor arm position before (1) and after (2) refitting the distributor
X = XC Notch
procarmanuals.com
Page 125 of 255
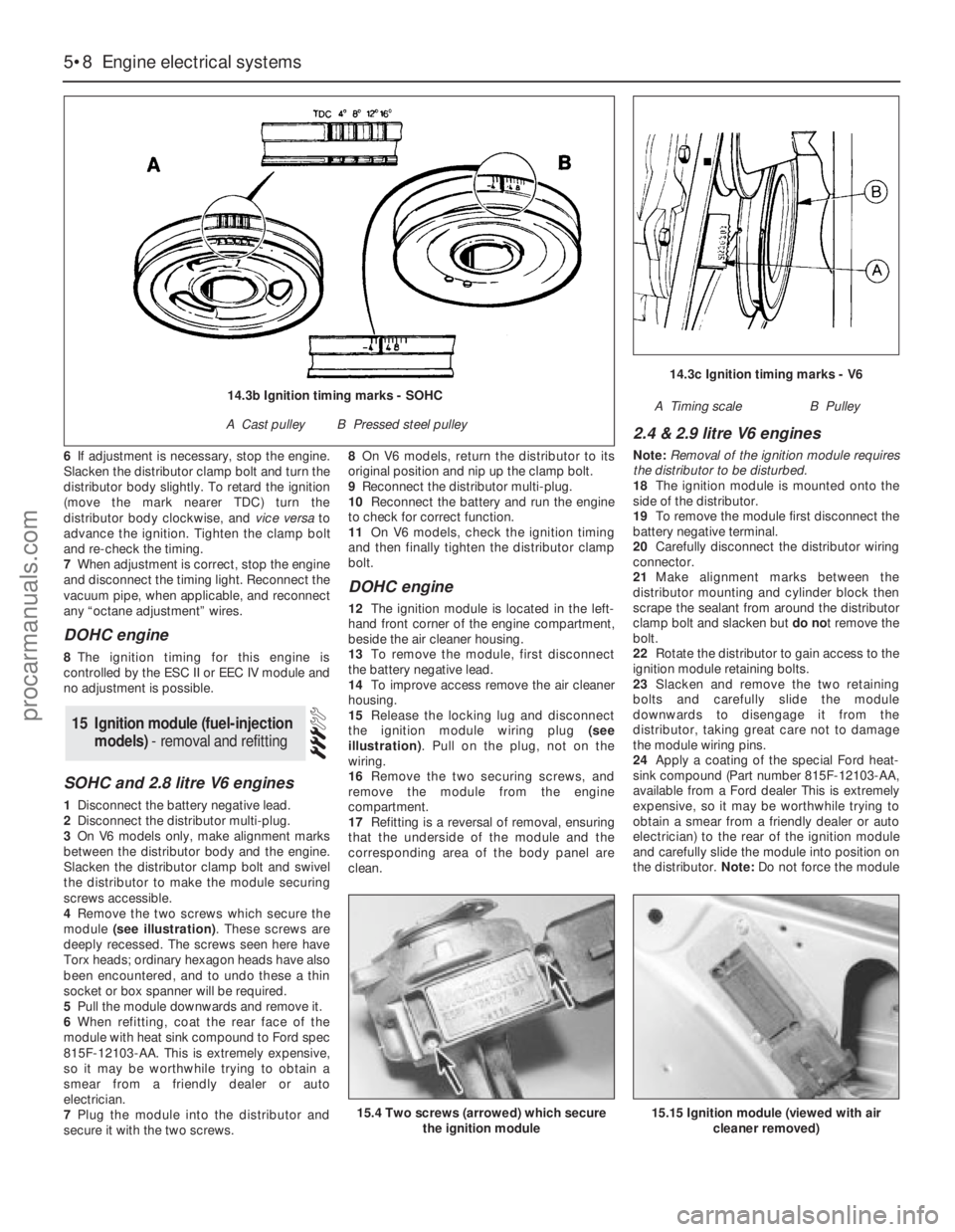
6If adjustment is necessary, stop the engine.
Slacken the distributor clamp bolt and turn the
distributor body slightly. To retard the ignition
(move the mark nearer TDC) turn the
distributor body clockwise, and vice versato
advance the ignition. Tighten the clamp bolt
and re-check the timing.
7When adjustment is correct, stop the engine
and disconnect the timing light. Reconnect the
vacuum pipe, when applicable, and reconnect
any “octane adjustment” wires.
DOHC engine
8The ignition timing for this engine is
controlled by the ESC II or EEC IV module and
no adjustment is possible.
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the distributor multi-plug.
3On V6 models only, make alignment marks
between the distributor body and the engine.
Slacken the distributor clamp bolt and swivel
the distributor to make the module securing
screws accessible.
4Remove the two screws which secure the
module (see illustration). These screws are
deeply recessed. The screws seen here have
Torx heads; ordinary hexagon heads have also
been encountered, and to undo these a thin
socket or box spanner will be required.
5Pull the module downwards and remove it.
6When refitting, coat the rear face of the
module with heat sink compound to Ford spec
815F-12103-AA. This is extremely expensive,
so it may be worthwhile trying to obtain a
smear from a friendly dealer or auto
electrician.
7Plug the module into the distributor and
secure it with the two screws.8On V6 models, return the distributor to its
original position and nip up the clamp bolt.
9Reconnect the distributor multi-plug.
10Reconnect the battery and run the engine
to check for correct function.
11On V6 models, check the ignition timing
and then finally tighten the distributor clamp
bolt.
DOHC engine
12The ignition module is located in the left-
hand front corner of the engine compartment,
beside the air cleaner housing.
13To remove the module, first disconnect
the battery negative lead.
14To improve access remove the air cleaner
housing.
15Release the locking lug and disconnect
the ignition module wiring plug (see
illustration). Pull on the plug, not on the
wiring.
16Remove the two securing screws, and
remove the module from the engine
compartment.
17Refitting is a reversal of removal, ensuring
that the underside of the module and the
corresponding area of the body panel are
clean.
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines
Note: Removal of the ignition module requires
the distributor to be disturbed.
18The ignition module is mounted onto the
side of the distributor.
19To remove the module first disconnect the
battery negative terminal.
20Carefully disconnect the distributor wiring
connector.
21Make alignment marks between the
distributor mounting and cylinder block then
scrape the sealant from around the distributor
clamp bolt and slacken but do not remove the
bolt.
22Rotate the distributor to gain access to the
ignition module retaining bolts.
23Slacken and remove the two retaining
bolts and carefully slide the module
downwards to disengage it from the
distributor, taking great care not to damage
the module wiring pins.
24Apply a coating of the special Ford heat-
sink compound (Part number 815F-12103-AA,
available from a Ford dealer This is extremely
expensive, so it may be worthwhile trying to
obtain a smear from a friendly dealer or auto
electrician) to the rear of the ignition module
and carefully slide the module into position on
the distributor. Note: Do not force the module
15Ignition module (fuel-injection
models) - removal and refitting
5•8Engine electrical systems
15.4 Two screws (arrowed) which secure
the ignition module15.15 Ignition module (viewed with air
cleaner removed)
14.3c Ignition timing marks - V6
A Timing scaleB Pulley14.3b Ignition timing marks - SOHC
A Cast pulleyB Pressed steel pulley
procarmanuals.com
Page 126 of 255

into position or the wiring pins will be
damaged.
25Refit the module retaining bolts and
tighten them securely.
26Rotate the distributor until the marks made
on removal are aligned then securely tighten
the clamp bolt.
27Reconnect the distributor wiring
connector and the battery negative terminal.
28Run the engine to normal operating
temperature and check the ignition timing.
All engines except DOHC fuel-
injection
1The ignition coil is mounted on the left-hand
side of the engine compartment (see
illustration). If it fails, there will be no spark
and the engine will stop.
2To test the coil an ohmmeter will be
required. Disconnect the LT and HT leads from
the coil and measure the resistance between
the two LT terminals (primary resistance), then
between the HT terminal and either LT
terminal (secondary resistance). Desired
values are given in the Specifications. In fact
most test gear will not be able to distinguish
between a normal primary resistance (which is
very low) and a short-circuit.
3In the absence of an ohmmeter, test the coil
by substitution of a known good unit.4To remove the coil, disconnect the LT and
HT leads, then remove the two screws which
secure the coil clamp. Lift out the coil.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
2.0 litre DOHC fuel-injection
engines
6Refer to the above paragraphs but note that
on some models the coil heat shield must be
removed for access to the coil securing bolts.
The heat shield is secured by two screws. An
earthing lead and/or a suppressor may also be
secured by one of the coil retaining screws
(see illustration).
1On carburettor models, a fuel trap is fitted in
the vacuum pipe between the inlet manifold
and the ESC II module.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Disconnect the vacuum pipes from the trap
and remove it. Dispose of it carefully, it may
contain fuel.
4When refitting, note that the end of the trap
marked CARB goes towards the manifold, and
the end marked DIST towards the module.
5Reconnect the battery.
ESC II module (carburettor
models)
SOHC engines
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Disconnect the vacuum pipe from the
module (see illustration).
3Release the locking catch and disconnect
the multi-plug from the module (see
illustration).
4Remove the three securing screws and
detach the module and bracket from the left-
hand inner wing.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Make sure that the multi-plug is securely fitted
and the locking catch engaged.Note: From January 1987, a new type of
module was fitted to the 1.8 litre engine. The
new module is smaller than the old unit and is
in the engine compartment mounted onto the
left-hand wing valance. The new module is
known as the ESC Hybrid Module.(see
illustration)
DOHC engine
6Removal and refitting is as above.
7The module is located on the left-hand side
of the engine compartment and is secured by
two screws.
EEC IV module (fuel-injection
models)
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines
8Disconnect the battery negative lead.
9Remove the under-dash trim on the
passenger side.
10Unclip the module and lower it onto the
vehicle floor.
11Remove the control bolt from the multi-
plug and disconnect the plug from the module.
12Refit by reversing the removal operations.
DOHC and 2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines
13The module is situated behind the
passenger side of the facia and is accessible
from underneath the glovebox.
14To remove the module first disconnect the
battery negative terminal.
15Reach up behind the glovebox and unclip
the module from the mounting bracket (see
illustration).
18Engine management control
module - removal and refitting
17Fuel trap (carburettor
models) - removal and refitting
16Ignition coil - testing, removal
and refitting
Engine electrical systems 5•9
5
16.1 Ignition coil location16.6 Suppresser secured by one of the coil
retaining screws
18.2 Disconnecting the ESC II module
vacuum pipe18.5 Engine management module - 1.8 litre
engine from January 198718.3 ESC II module multi-plug
procarmanuals.com
Page 127 of 255

16Undo the wiring connector retaining bolt
then carefully disconnect the wiring plug and
remove the module from the car (see
illustration).
17Refitting is a reverse of the removal
procedure ensuring that the wiring plug bolt is
securely tightened. On completion start the
engine and check that it runs correctly.
Note: Irregular idle is not necessarily caused
by a faulty or badly adjusted stepper motor.
Good electrical contact between the stepper
motor plunger and the adjusting screw is
essential. Before attempting adjustment or
renewal of the motor, try the effect of cleaning
the plunger and adjusting screw contact faces
with abrasive paper followed by switch
cleaning fluid. Switch cleaning fluid is available
from electronic component shops.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the air cleaner.
3Disconnect the multi-plug from the stepper
motor. Release the locking clip and pull on the
plug, not on the wires.
4Remove the four screws which secure the
stepper motor bracket to the carburettor.Remove the motor and bracket and separate
them (see illustration).
5Refit the motor and bracket to the
carburettor and secure with the four screws.
Reconnect the multi-plug.
6Make an initial adjustment to the throttle
lever adjusting screw if necessary so that it
protrudes from the lever by dimension X (see
illustration).
7Reconnect the air cleaner vacuum hose.
Position the air cleaner to one side so that
there is still access to the carburettor and
stepper motor.
8Connect a tachometer (rev. counter) to the
engine as instructed by the manufacturers.
Reconnect the battery.
9Run the engine. Check the idle mixture (CO
level) as described in Chapter 4 and adjust if
necessary.
10Switch off all electrical loads (headlights,
heater blower etc). If the idle speed adjustment
lead is earthed, temporarily isolate it. Make
sure that the automatic transmission selector is
in the N or P position (where applicable).
11Accelerate the engine to a speed greater
then 2500 rpm, allow it to return to idle, then
repeat. Insert a feeler blade of thickness 1.0
mm (0.04 in) between the stepper motor
plunger and the adjusting screw(see
illustration).With the feeler blade in place,
engine speed should be 875 ±25 rpm. 12If adjustment is necessary, remove the
tamperproof cap from the adjusting screw
locknut. Release the locknut, turn the
adjusting screw to achieve the correct speed
and tighten the locknut.
13Repeat paragraph 11 and check that the
speed is still correct. Readjust if necessary.
14Remove the feeler blade. Stop and restart
the engine, observing the stepper motor
plunger. Immediately after switching off, the
plunger should move to the “anti-dieseling”
position; after a few seconds it should extend
to the “vent manifold/start” position (see
illustration).
15Disconnect the test gear and refit the air
cleaner.
16Recheck the idle mixture.
17Fit new tamperproof plugs or caps if
necessary - see Chapter 4,
18Reconnect the idle speed adjustment lead
if it was earthed.
1The engine management system
temperature sensor is located on the underside
of the inlet manifold (SOHC engines), the side
of the manifold (DOHC engines) or on the front
face of the cylinder block (V6 engines).
20Coolant temperature sensor -
removal and refitting
19Carburettor stepper motor
(2.0 litre models) - removal,
refitting and adjustment
5•10Engine electrical systems
18.16 Disconnecting the EEC IV module
A Multi-plugB Securing bolt
19.6 Throttle lever initial adjustment
A Plunger
B Adjusting screw
C CapX 7.5 ±1.0 mm
(0.30 ±0.04 in)
19.11 Stepper motor adjustment
A LocknutB Feeler blade
19.14 Stepper motor plunger positions
A Vent manifold/start
B Anti-dieselingC Idle
19.4 Carburettor stepper motor and
mounting bracket18.15 Removing the engine management
modules (glovebox removed for clarity)
procarmanuals.com
Page 141 of 255

3Press the multi-plug locking lever,
disconnect the multi-plug and unhook it from
the module. Remove the module.
4Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Make sure that the multi-plug is properly
engaged before refitting the module.
Front
1Ensure that the handbrake is applied. Raise
and support the front of the vehicle.
2From under the bonnet disconnect the
wheel sensor wiring multi-plug. Unclip the
wiring, working towards the sensor.
3Remove the securing bolt and withdraw the
sensor from the stub axle carrier (see
illustration).
4Unclip the wire from the bracket on the
strut. Remove the sensor and its wiring (see
illustration).
5Clean any rust or debris from the sensor
bore in the stub axle carrier. Pack the bore
with clean wheel bearing grease.
6Renew the O-ring on the sensor and smear
it with grease.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Rear
8Chock the front wheels and release the
handbrake. Slacken the rear wheel nuts, raiseand support the rear of the vehicle and remove
the rear wheel.
9Fold the rear seat cushion forwards, remove
the side kick panel and roll back the carpet to
gain access to the sensor multi-plug (see
illustration).
10Disconnect the multi-plug, release the
floor grommet and pass the cable through the
floor.
11Unclip the handbrake cable from the
suspension lower arm.
12Remove the caliper front slide bolt and
pivot the caliper rearwards to gain access to
the sensor.
13Remove the sensor securing bolt and
withdraw the sensor.
14Clean up the sensor bore, pack it with
grease and renew the sensor O-ring.
15Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
2Disconnect the wiring plug then remove the
master cylinder reservoir cap; do not invert the
cap as hydraulic fluid could enter and damage
the reservoir level switch. Syphon the
hydraulic fluid from the reservoir. Note: Do not
syphon the fluid by mouth, as it is poisonous;
use a syringe or an old poultry baster.
Alternatively, open any convenient bleed
screw in the system and gently pump the
brake pedal to expel the fluid through a plastic
tube connected to the screw.
3Wipe clean the area around the brake pipe
unions on the right-hand side of the master
cylinder and place absorbent rags beneath the
pipe unions to catch any surplus fluid.
4To disconnect the plastic low pressure
hoses, use a small flat bladed screwdriver to
carefully press the flange of the collet into the
master cylinder then pull the hoses out from
the reservoir(see illustration).Unscrew the
two union nuts and disconnect the brake
pipes from master cylinder. Plug or tape over
the pipe/hose ends and master cylinder
orifices to minimise the loss of brake fluid and
to prevent the entry of dirt into the system.
Wash off any spilt fluid immediately with cold
water.5Slacken and remove the two nuts securing
the master cylinder to the vacuum servo unit
then withdraw the unit from the engine
compartment. Remove the O-ring from the
rear of master cylinder and discard it.
6If necessary remove the reservoir from the
master cylinder and withdraw the mounting
bush seals and O-rings. Note that the master
cylinder is a sealed unit with no spare parts
available separately. Therefore if it is faulty it
must be renewed as a unit.
7Fit new mounting bush seals and O-rings to
the master cylinder and refit the reservoir (if
removed). Remove all traces of dirt from the
master cylinder and servo unit mating surfaces
and fit a new O-ring onto the master cylinder
body.
8Fit the master cylinder to the servo unit
ensuring that the pushrod enters the servo unit
bore centrally. Refit the master cylinder
mounting nuts and tighten them to the
specified torque.
9Wipe clean the brake pipe/hose unions and
the master cylinder ports. Refit the pipes to
the master cylinder ports and tighten them
securely. Push the low pressure hoses into
position and check they are securely held by
their retaining collets.
10Refill the master cylinder reservoir with
new fluid and bleed the hydraulic system
1To test the operation of the servo unit
depress the footbrake several times to
exhaust the vacuum then start the engine
whilst keeping the pedal firmly depressed. As
the engine starts there should be a noticeable
“give” in the brake pedal as the vacuum builds
up. Allow the engine to run for at least two
minutes then switch it off. If the brake pedal is
now depressed it should feel normal, but
further applications should result in the pedal
feeling firmer, with the pedal stroke decreasing
with each application.
2If the servo does not operate as described,
inspect the servo unit check valve as
describedin paragraph 3 of Section 29.28Vacuum servo unit (April 1992
on) - testing, removal and
refitting
27Master cylinder (April 1992
on) - removal and refitting
26Wheel sensors - removal and
refitting
10•12Braking system
26.3 Removing a front sensor
27.4 Disconnecting the master cylinder low
pressure hoses (A) and brake pipes (B) -
models from April 1992
26.4 Unclipping the sensor wire from the
strut26.9 Rear wheel sensor multi-plug
(arrowed)
procarmanuals.com