1985 FORD GRANADA set clock
[x] Cancel search: set clockPage 14 of 255

DOHC engines
12On this engine, the coolant/alternator
drivebelt also drives the power steering pump
and (where applicable) the air conditioning
compressor. The drivebelt tension is set by an
automatic tensioner assembly.
13The condition of the drivebelt should be
checked as described above.
14An idea of the amount of wear which has
taken place on the belt can be gained from the
position of indicator mark (A) on the mounting
bracket in relation to the block (B) on the
tensioner arm (see illustration).When the belt
is new the mark should be aligned with the top
of the tensioner block. As the belt wears, the
tensioner arm moves and the block on the arm
will move slowly up in relation to the mark on
the bracket. When the mark aligns with the
bottom of the tensioner arm block the belt can
be regarded as worn and should be replaced
(see illustration).
15To renew the belt, turn the automatic
tensioner arm clockwise, using a 17 mm
socket and a wrench on the boss in the centre
of the pulley, and slide the belt from the
pulleys, then slowly release the tensioner.
16To fit a new belt, rotate the tensioner
clockwise as during removal, then slide the
belt over the pulleys. With the belt correctly
located, slowly release the tensioner; the
tensioner will automatically set the correct
drivebelt tension.
Caution:Before carrying out any work on the
vehicle battery, read through the precautions
given in “Safety first!” at the beginning of this
manual.
1The battery fitted as original equipment is
“maintenance-free”, and requires no
maintenance apart from having the case kept
clean, and the terminals clean and tight.
2To clean the battery terminals disconnect
them, after having first removed the cover
(later models) -negative earth first. Use a wire
brush or abrasive paper to clean the terminals.
Bad corrosion should be treated with a
solution of bicarbonate of soda, applied with
an old toothbrush. Do not let this solution get
inside the battery.3Coat the battery terminals with petroleum
jelly or a proprietary anti-corrosive compound
before reconnecting them. Reconnect and
tighten the positive (live) lead first, followed by
the negative (earth) lead. Do not overtighten.
4Keep the top of the battery clean and dry.
Periodically inspect the battery tray for
corrosion, and make good as necessary.
5Further information on the battery, charging
and jump-starting can be found in Chapter 5,
and in the preliminary Sections of this manual.
SOHC engines
1Valve clearances are checked with the
engine cold.
2On carburettor models, remove the air cleaner.
3On fuel-injection models, remove the
bracing strap which connects the inlet
manifold to the right-hand side of the engine.
4On all models, identify the HT leads and
disconnect them from the spark plugs. Unclip
the leads from the rocker cover.
5Although not essential, it will make the
engine easier to turn if the spark plugs are
removed.
6Remove the ten bolts which secure the
rocker cover, noting the location of the
different shapes of reinforcing plates. Remove
the cover and gasket.7One of the cam lobes will be seen to be
pointing upwards. Measure the clearance
between the base of this cam and the cam
follower, finding the thickness of feeler blade
which gives a firm sliding fit(see illustration).
8The desired valve clearances are given in
the Specifications. Note that the clearances
for inlet and exhaust valves are different.
Numbering from the front (sprocket) end of the
camshaft, the exhaust valves are 1, 3, 5 and 7,
and the inlet valves 2, 4, 6 and 8.
9If adjustment is necessary, slacken the ball-
pin locknut and screw the ball-pin up or down
until the clearance is correct. Hold the ball-pin
stationary and tighten the locknut(see
illustration).Recheck the clearance after
tightening the locknut in case the ball-pin has
moved.
10Turn the engine to bring another cam lobe
to the vertical position and repeat the above
procedure. Carry on until all eight valves have
been checked.
11Access to some of the ball-pins is made
difficult by the carburettor or fuel-injection inlet
manifold. To avoid having to remove the
offending components, double cranked
spanners or cutaway socket spanners can be
used (see illustration).
12When adjustment is complete, refit the
rocker cover using a new gasket. Make sure
that the dovetail sections of the gasket fit
together correctly.
13Fit the rocker cover bolts and reinforcing
plates. Tighten the bolts as described in
Chapter 2A Section 44, paragraph 11.
23Engine valve clearance check
22Battery terminal check
1•13
1
Every 12 000 miles or 12 months
21.14a Water pump/alternator drivebelt
tensioner indicator position - DOHC engine
A Indicator markB Block
21.14b Water pump/alternator drivebelt
tensioner wear indicator location (arrowed)
- DOHC engine21.8 Tightening the alternator strap bolt
23.7 Measuring a valve clearance - SOHC
engine23.9 Adjusting a valve clearance - SOHC
engine
procarmanuals.com
Page 29 of 255

14Take the weight of the engine and remove
the two engine bearer-to-mounting nuts.
15Lift the engine/transmission, at the same
time lowering the trolley jack. Draw the unit
forwards and lift it out of the engine bay.
16Temporarily refit the anti-roll bar if the
vehicle is to be moved.
1With the engine and gearbox on the bench,
remove the starter motor.
2Remove the bolt from the engine adapter plate.
3Remove the bracing strap and the
remaining engine-to-bellhousing bolts.
4With the aid of an assistant draw the
gearbox off the engine. Do not allow the weight
of the gearbox to hang on the input shaft.
1It is best to mount the engine on a
dismantling stand, but if this is not available,
stand the engine on a strong bench at a
comfortable working height. Failing this, it will
have to be stripped down on the floor.
2Cleanliness is most important, and if the
engine is dirty, it should be cleaned with
paraffin while keeping it in an upright position.
3Avoid working with the engine on a concrete
floor, as grit can be a real source of trouble.
4As parts are removed, clean them in paraffin.
However, do not immerse parts with internal
oilways in paraffin as it is difficult to remove,
usually requiring a high pressure hose.
5It is advisable to have suitable containers to
hold small items according to their use, as this
will help when reassembling the engine and
also prevent possible losses.
6Always obtain complete sets of gaskets
when the engine is being dismantled, but
retain the old gaskets with a view of using
them as a pattern to make a replacement if a
new one is not available.7When possible, refit nuts, bolts and washers
in their location after being removed, as this
helps protect the threads and will also be
helpful when reassembling the engine.
8Retain unserviceable components in order
to compare them with the new parts supplied.
9A Torx key, size T55, will be needed for
dealing with the cylinder head bolts. A 12-
spline key (to fit bolt size M8) will be needed
for the oil pump bolts. Other Torx and 12-
spline bolts may be encountered; sets of the
keys required to deal with them are available
from most motor accessory shops and tool
factors.
10Another tool which is useful, though by no
means essential, is a valve spring compressor
of the type which hooks under the camshaft
(see illustration). As a Ford tool this bears the
number 21-005-A; proprietary versions may
also be available.
Before dismantling the engine into its main
components, the following ancillary
components can be removed. The actual
items removed, and the sequence of removal,
will depend on the work to be done:
Inlet manifold and associated items
Exhaust manifold
Fuel pump (mechanical type) and pushrod
Alternator
Distributor, HT leads and spark plugs
Fan, water pump and thermostat
Oil pressure switch
(see illustration)
Temperature gauge senderOil filter and dipstick
Engine bearer arms (see illustration)
Crankcase ventilation components
Clutch
Alternator mounting bracket (see
illustration)
1If the engine is still in the vehicle, carry out
the following preliminary operations:
a)Disconnect the battery negative lead
b)Drain the cooling system
c)Remove the inlet and exhaust manifolds
d)Disconnect the radiator top hose from the
thermostat housing, and the spur from the
expansion tank
e)Disconnect the wiring from the
temperature gauge sender
f)Remove the distributor cap, HT leads and
spark plugs
2Unscrew the bolts and withdraw the timing
cover (see illustration). Note the location of
the cover in the special bolt.
3Using a socket on the crankshaft pulley bolt.
turn the engine clockwise until the TDC (top
dead centre) notch on the pulley is aligned
with the pointer on the crankshaft front oil seal
housing, and the pointer on the camshaft
sprocket is aligned with the indentation on the
cylinder head (see illustrations).Note the
position of the distributor rotor arm, and mark
its contact end in relation to the rim of the
distributor body.
4Slacken the timing belt tensioner bolts. Pivot
10Cylinder head - removal
9Ancillary components - removal
8Engine dismantling - general
information
7Engine - separation from
manual gearbox
2A•6SOHCengines
9.1a Engine oil pressure switch (arrowed)
9.1b Removing an engine bearer arm9.1c Removing the alternator bracket
8.10 This valve spring compressor is used
by hooking it under the camshaft
Clean oilways with nylon pipe
cleaners.
10.2 Removing the timing cover
procarmanuals.com
Page 102 of 255

1Check the cost and availability of spare parts
before deciding to dismantle the carburettor. If
the unit has seen much service, fitting a new or
reconditioned carburettor may prove more
satisfactory than any attempt at overhaul.
2Obtain a carburettor repair kit, which will
contain the necessary gaskets, diaphragms
and other renewable items.
3With the carburettor removed from the
vehicle, clean it thoroughly externally and
place it on a clean worksurface.
4 Referringto the exploded view of the
carburettor(see illustration),remove each
component part whilst making a note of its
fitted position. Make alignment marks on
linkages etc.
5Reassemble in the reverse order to
dismantling, using new gaskets, O-rings etc.
6To check the choke pull-down after
reassembly, position the fast idle screw on the
highest step of the cam. Press the pull-down
adjusting screw towards the pull-down
diaphragm and measure the choke valve
opening with a twist drill or gauge rod of the
specified diameter. Adjust if necessary using
a 2 mm Allen key (see illustration).
7After refitting the throttle damper, adjust its
position in the bracket so that with a 2 mm
(0.08 in) feeler blade inserted between the idle
speed adjusting screw and the throttle lever,
the damper plunger is just touching the
actuating lever(see illustration).
8Adjust the idle speed and mixture, and if
necessary the fast idle speed, after refitting the
carburettor.
9Recheck the throttle damper adjustment,
when applicable.
1This is not a routine operation. It should only
be necessary after overhaul, or when a new
carburettor is fitted.
2The idle speed and mixture must be
correctly set and the engine must be at
operating temperature.3Remove the air cleaner and plug the
manifold vacuum connection.
4With the engine running, position the fast
idle screw on the second highest step of the
fast idle cam(see illustration).Measure the
engine speed and compare it with that given in
the Specifications.
5If adjustment is necessary, remove the
tamperproof plug from the fast idle screw by
crushing it with pliers. Stop the engine and
open the throttle to gain access to the screw
with a small screwdriver. Turn the screw a
small amount clockwise to increase the speed,
anti-clockwise to reduce it, then reseat the
screw on the second highest step of the cam
and recheck the engine speed. Repeat as
necessary.
6Fit a new tamperproof cap where this is
required by law, then refit the air cleaner.
Idle speed cannot be adjusted in the usual
way on this carburettor, as it is controlled by
the ESC ll module.
If mixture adjustment is required, proceed
as described in Chapter 1, Section 16.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the air cleaner.3Disconnect the choke and stepper motor
wiring. The stepper motor multi-plug locking
device must be depressed to release the plug
(seeillustration).
4Unclip the throttle arm from the throttle lever
and remove the throttle cable bracket.
5Disconnect the fuel hose from the
carburettor and plug it. If a crimped type hose
clip is fitted, cut it off and use a worm drive
clip when refitting.
6Disconnect the vacuum pipe(s) from the
carburettor, noting their connecting points if
there is any possibility of confusion.
7Remove the four carburettor-to-manifold
nuts. Check that nothing has been overlooked,
then lift off the carburettor. Recover the
gasket.
8Clean the carburettor and manifold mating
faces, being careful not to sweep dirt into the
manifold.
9Refit by reversing the removal operations. If
the stepper motor has been disturbed, refer to
Chapter 5, Section 19 for the initial
adjustment.
1Check the cost and availability of spare
parts before deciding to dismantle the
carburettor. If the unit has seen much service,
fitting a new or reconditioned carburettor may
prove more satisfactory than any attempt at
overhaul.
2Obtain a carburettor repair kit, which will
contain the necessary gaskets, diaphragms
and other renewable items.
3With the carburettor removed from the
vehicle, clean it thoroughly externally and
place it on a clean worksurface.
4 Referringto the exploded view of the
carburettor(see illustration),remove each
component part whilst making a note of its
fitted position. Make alignment marks on
linkages etc.
5Reassemble in the reverse order to
dismantling, using new gaskets, O-rings etc.
Be careful not to kink the diaphragms.
17Weber 2V carburettor -
dismantling and reassembly
16Weber 2V carburettor -
removal and refitting
15Weber 2V carburettor - idle
speed and mixture adjustments
14Pierburg 2V carburettor - fast
idle adjustment
13Pierburg 2V carburettor -
dismantling and reassembly
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•9
4
14.4 Fast idle adjustment - Pierburg 2V
Tip of fast idle screw is arrowed
13.6 Choke pull-down adjustment13.7 Throttle damper adjustment - Pierburg
2V carburettor
A Actuating lever
B Damper plungerC Damper locknut
D Feeler blade
16.3 Depress locking clip (arrowed) when
disconnecting stepper motor multi-plug
procarmanuals.com
Page 119 of 255

The ignition system is responsible for
igniting the fuel/air charge in each cylinder at
the correct moment. The components of the
system are the spark plugs, ignition coil,
distributor and connecting leads. Overall
control of the system is one of the functions of
the engine management module. Fuel-
injection models have a subsidiary ignition
module mounted on the distributor.
There are no contact breaker points in the
distributor. A square wave signal is generated
by the distributor electro-magnetically; this
signal is used by the engine management
module as a basis for switching the coil LT
current. Speed-related (centrifugal) advance is
also handled by the module. On carburettor
models, ignition timing is also advanced under
conditions of high inlet manifold vacuum.The engine management models are “black
boxes” which regulate both the fuel and the
ignition systems to obtain the best power,
economy and emission levels. The module
fitted to carburettor models is known as the
ESC II (Electronic Spark Control Mk II) module.
On fuel-injection models the more powerful
EEC IV (Electronic Engine Control Mk IV)
module is used.
Both types of module receive inputs from
sensors monitoring coolant temperature,
distributor rotor position and (on some
models) manifold vacuum. Outputs from the
module control ignition timing, inlet manifold
heating and (except on 1.8 litre models) idle
speed. The EEC IV module also has overall
control of the fuel-injection system, from
which it receives information.
Provision is made for the ignition timing to
be retarded to allow the use of low octane fuel
if necessary. On all except 1.8 litre models
there is also a facility for raising the idle speed.The EEC IV module contains self-test
circuitry which enables a technician with the
appropriate test equipment to diagnose faults
in a very short time. A Limited Operation
Strategy (LOS) means that the car is still
driveable, albeit at reduced power and
efficiency, in the event of a failure in the
module or its sensors.
Due to the complexity and expense of the
test equipment dedicated to the engine
management system, suspected faults should
be investigated by a Ford dealer, or other
competent specialist. This Chapter deals with
component removal and refitting, and with
some simple checks and adjustments.
On DOHC carburettor engines, the basic
operating principles of the ignition system are
as described above. A development of the
ESC II (Electronic Spark Control ll) system is
used to control the operation of the engine.
The ESC II module receives information from a
crankshaft speed/position sensor and an
1General information and
precautions
5•2Engine electrical systems
Ignition coil
Make . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Bosch, Femsa or Polmot
Primary resistance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.72 to 0.86 ohm
Secondary resistance:
All except DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.5 to 7.0 k ohms
DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4.5 to 8.6 k ohms
Output voltage (open-circuit):
All except DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25 kV minimum
DOHC fuel-injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 kV minimum
HT leads
Maximum resistance per lead . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 k ohms
Distributor
Make . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Bosch or Motorcraft
Rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Clockwise (viewed from above)
Automatic advance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Controlled by module
Dwell angle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Controlled by module
Ignition timing (see text)
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines:
Leaded fuel (97 octane):
Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10°BTDC
Fuel-injection models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12°BTDC
Unleaded fuel (95 octane):
Carburettor models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6°BTDC
Fuel-injection models:
2.0 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8°BTDC
2.8 litre . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12°BTDC (no change)
2.4 & 2.9 litre V6 engines:
Models with catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15°BTDC
Models without catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12°BTDC*
* Standard setting for 97 octane leaded fuel.
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Alternator adjusting strap:
To steering pump bracket (OHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2616 to 19
To front cover (V6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41 to 5130 to 38
Spark plugs:
All models except 2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2815 to 21
2.8 litre V6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30 to 4022 to 30
Air charge temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Engine coolant temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Fuel rail temperature sensor (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Crankshaft speed/position sensor screw (DOHC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 to 52 to 4
procarmanuals.com
Page 151 of 255
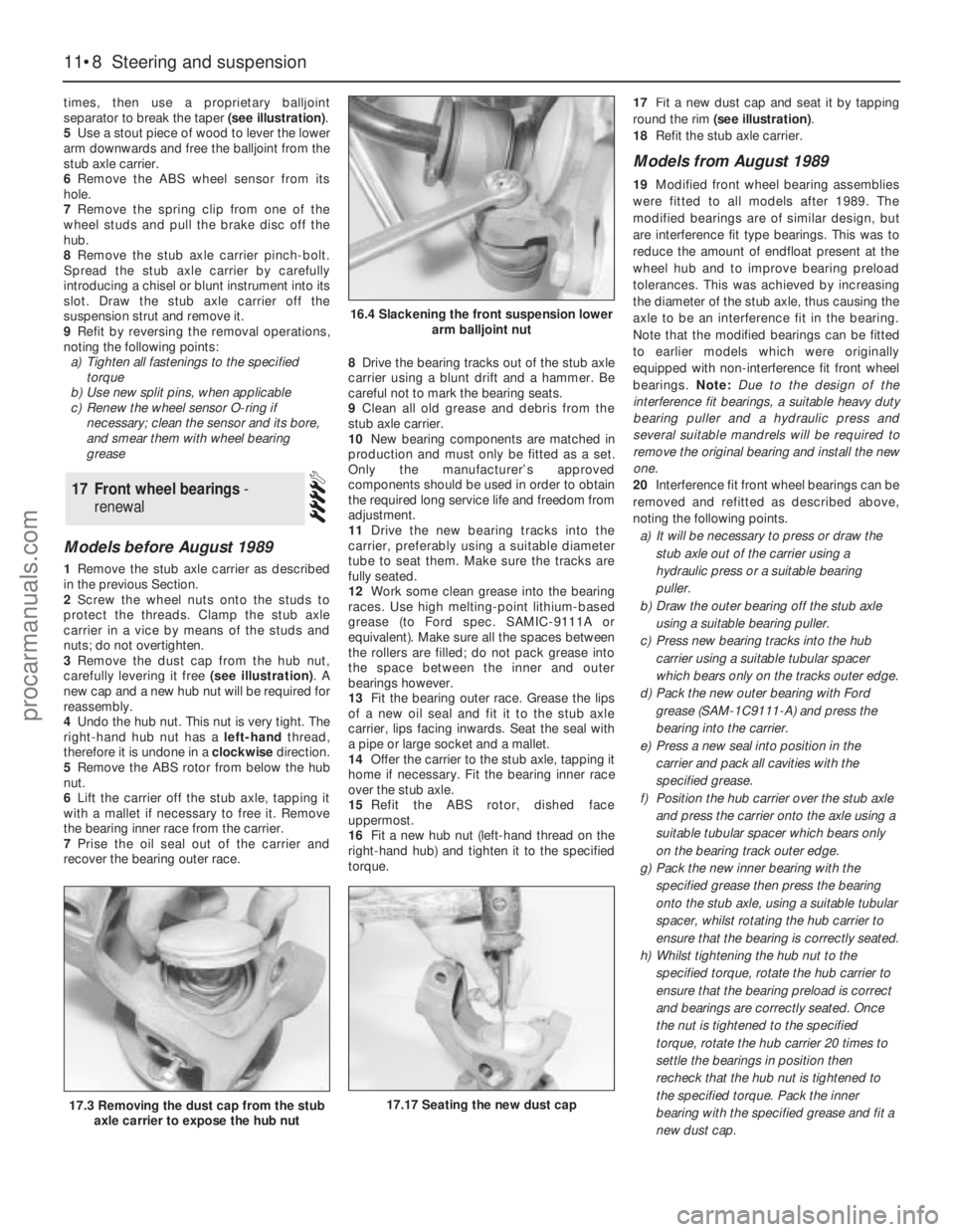
times, then use a proprietary balljoint
separator to break the taper (see illustration).
5Use a stout piece of wood to lever the lower
arm downwards and free the balljoint from the
stub axle carrier.
6Remove the ABS wheel sensor from its
hole.
7Remove the spring clip from one of the
wheel studs and pull the brake disc off the
hub.
8Remove the stub axle carrier pinch-bolt.
Spread the stub axle carrier by carefully
introducing a chisel or blunt instrument into its
slot. Draw the stub axle carrier off the
suspension strut and remove it.
9Refit by reversing the removal operations,
noting the following points:
a)Tighten all fastenings to the specified
torque
b)Use new split pins, when applicable
c)Renew the wheel sensor O-ring if
necessary; clean the sensor and its bore,
and smear them with wheel bearing
grease
Models before August 1989
1Remove the stub axle carrier as described
in the previous Section.
2Screw the wheel nuts onto the studs to
protect the threads. Clamp the stub axle
carrier in a vice by means of the studs and
nuts; do not overtighten.
3Remove the dust cap from the hub nut,
carefully levering it free (see illustration). A
new cap and a new hub nut will be required for
reassembly.
4Undo the hub nut. This nut is very tight. The
right-hand hub nut has a left-handthread,
therefore it is undone in a clockwisedirection.
5Remove the ABS rotor from below the hub
nut.
6Lift the carrier off the stub axle, tapping it
with a mallet if necessary to free it. Remove
the bearing inner race from the carrier.
7Prise the oil seal out of the carrier and
recover the bearing outer race.8Drive the bearing tracks out of the stub axle
carrier using a blunt drift and a hammer. Be
careful not to mark the bearing seats.
9Clean all old grease and debris from the
stub axle carrier.
10New bearing components are matched in
production and must only be fitted as a set.
Only the manufacturer’s approved
components should be used in order to obtain
the required long service life and freedom from
adjustment.
11Drive the new bearing tracks into the
carrier, preferably using a suitable diameter
tube to seat them. Make sure the tracks are
fully seated.
12Work some clean grease into the bearing
races. Use high melting-point lithium-based
grease (to Ford spec. SAMIC-9111A or
equivalent). Make sure all the spaces between
the rollers are filled; do not pack grease into
the space between the inner and outer
bearings however.
13Fit the bearing outer race. Grease the lips
of a new oil seal and fit it to the stub axle
carrier, lips facing inwards. Seat the seal with
a pipe or large socket and a mallet.
14Offer the carrier to the stub axle, tapping it
home if necessary. Fit the bearing inner race
over the stub axle.
15Refit the ABS rotor, dished face
uppermost.
16Fit a new hub nut (left-hand thread on the
right-hand hub) and tighten it to the specified
torque.17Fit a new dust cap and seat it by tapping
round the rim (see illustration).
18Refit the stub axle carrier.
Models from August 1989
19Modified front wheel bearing assemblies
were fitted to all models after 1989. The
modified bearings are of similar design, but
are interference fit type bearings. This was to
reduce the amount of endfloat present at the
wheel hub and to improve bearing preload
tolerances. This was achieved by increasing
the diameter of the stub axle, thus causing the
axle to be an interference fit in the bearing.
Note that the modified bearings can be fitted
to earlier models which were originally
equipped with non-interference fit front wheel
bearings. Note: Due to the design of the
interference fit bearings, a suitable heavy duty
bearing puller and a hydraulic press and
several suitable mandrels will be required to
remove the originalbearing and install the new
one.
20Interference fit front wheel bearings can be
removed and refitted as described above,
noting the following points.
a)It will be necessary to press or draw the
stub axle out of the carrier using a
hydraulic press or a suitable bearing
puller.
b)Draw the outer bearing off the stub axle
using a suitable bearing puller.
c)Press new bearing tracks into the hub
carrier using a suitable tubular spacer
which bears only on the tracks outer edge.
d)Pack the new outer bearing with Ford
grease (SAM-1C9111-A) and press the
bearing into the carrier.
e)Press a new seal into position in the
carrier and pack all cavities with the
specified grease.
f)Position the hub carrier over the stub axle
and press the carrier onto the axle using a
suitable tubular spacer which bears only
on the bearing track outer edge.
g)Pack the new inner bearing with the
specified grease then press the bearing
onto the stub axle, using a suitable tubular
spacer, whilst rotating the hub carrier to
ensure that the bearing is correctly seated.
h)Whilst tightening the hub nut to the
specified torque, rotate the hub carrier to
ensure that the bearing preload is correct
and bearings are correctly seated. Once
the nut is tightened to the specified
torque, rotate the hub carrier 20 times to
settle the bearings in position then
recheck that the hub nut is tightened to
the specified torque. Pack the inner
bearing with the specified grease and fit a
new dust cap.
17Front wheel bearings -
renewal
11•8Steering and suspension
16.4 Slackening the front suspension lower
arm balljoint nut
17.17 Seating the new dust cap17.3 Removing the dust cap from the stub
axle carrier to expose the hub nut
procarmanuals.com
Page 178 of 255
Chapter 13
Body electrical system
Anti-theft alarm system components - removal and refitting . . . . . .36
Auxiliary warning system components - testing, removal and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Central locking motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Cigarette lighter - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Clock - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Electrical fault-finding - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Exterior lights - bulb renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Exterior light units - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Fuel computer components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Fuses, relays and control units - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .16
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Headlight beam alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Heater blower motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Horn - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Horn switch plate, slip rings and brushes - removal and refitting . .12
Ignition/starter switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Instrument cluster - dismantling and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Instrument cluster - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Interior lights - bulb renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6Joystick fader control - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Loudspeakers (original equipment) - removal and refitting . . . . . . .31
Radio aerial pre-amplifier (original equipment) - removal and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Radio or radio/cassette player (original equipment) - removal and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Rear entertainment console - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Rear headphone relay - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Rear window wiper motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Seat adjusting motors - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Seat heating elements - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Sliding roof motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Speed control system components - removal and refitting . . . . . . .28
Speedometer sender unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Switches - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Window operating motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Windscreen, rear window and headlight washer components -
removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Windscreen wiper motor and linkage - removal and refitting . . . . .23
Wiper arms and blades - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
General
System type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 volt, negative earth
Light bulbs (typical)Fitting Wattage
Headlights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . H4 60/55
Auxiliary driving lights and front foglights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . H3 55
Side/parking lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Glass base 5
Direction indicators, reversing light and rear foglight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bayonet 21
Stop and tail lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bayonet 21/5
Door open/kerb illumination lights, luggage area light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bayonet 5
Number plate lights, reading light and footwell lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Glass base 5
Engine bay light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bayonet 10
Interior lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Festoon 10
Vanity mirror light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Festoon 3
Glovebox light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Glass base 3
Ashtray light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Glass base 1.2
Instrument illumination, pilot and warning lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Glass base 1.2/2.5
Heater control light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Glass base 1
Automatic transmission selector light and clock light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bayonet 1.4
Fuses and circuit breakers- main fuse box
Fuse No Rating (A) Circuit(s) protected
1 20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . LH main beam, LH auxiliary driving light
2 20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . RH main beam, LH auxiliary driving light
3 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . LH dipped beam
4 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . RH dipped beam
5 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . LH side and tail lights
6 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . RH side and tail lights
13•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanicDifficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
13
procarmanuals.com
Page 181 of 255

the circuit between the relevant connector and
the battery is problem-free.
13Continue to check the remainder of the
circuit in the same fashion.
14When a point is reached at which no
voltage is present, the problem must lie
between that point and the previous test point
with voltage. Most problems can be traced to
a broken, corroded or loose connection.
Finding a short-circuit
15To check for a short-circuit, first disconnect
the load(s) from the circuit (loads are the
components which draw current from a circuit,
such as bulbs, motors, heating elements, etc).
16Remove the relevant fuse from the circuit,
and connect a circuit tester or voltmeter to the
fuse connections.
17Switch on the circuit, bearing in mind that
some circuits are live only when the ignition
switch is moved to a particular position.
18If voltage is present (indicated either by
the tester bulb lighting or a voltmeter reading),
this means that there is a short-circuit.
19If no voltage is present, but the fuse still
blows with the load(s) connected, this
indicates an internal fault in the load(s).
Finding an earth fault
20The battery negative terminal is connected
to “earth” - the metal of the engine/transmission
and the car body - and most systems are wired
so that they only receive a positive feed, the
current returning via the metal of the car body.
This means that the component mounting andthe body form part of that circuit. Loose or
corroded mountings can therefore cause a range
of electrical faults, ranging from total failure of a
circuit, to a puzzling partial fault. In particular,
lights may shine dimly (especially when another
circuit sharing the same earth is in operation),
motors (eg wiper motors or the radiator cooling
fan motor) may run slowly, and the operation of
one circuit may have an apparently-unrelated
effect on another. Note that on many vehicles,
earth straps are used between certain
components, such as the engine/transmission
and the body, usually where there is no metal-to-
metal contact between components, due to
flexible rubber mountings, etc.
21To check whether a component is properly
earthed, disconnect the battery, and connect
one lead of an ohmmeter to a known good
earth point. Connect the other lead to the wire
or earth connection being tested. The
resistance reading should be zero; if not,
check the connection as follows.
22If an earth connection is thought to be
faulty, dismantle the connection, and clean
back to bare metal both the bodyshell and the
wire terminal, or the component’s earth
connection mating surface. Be careful to
remove all traces of dirt and corrosion, then
use a knife to trim away any paint, so that a
clean metal-to-metal joint is made. On
reassembly, tighten the joint fasteners
securely; if a wire terminal is being refitted, use
serrated washers between the terminal and
the bodyshell, to ensure a clean and secure
connection. When the connection is remade,
prevent the onset of corrosion in the future byapplying a coat of petroleum jelly or silicone-
based grease, or by spraying on (at regular
intervals) a proprietary ignition sealer, or a
water-dispersant lubricant.
Headlight
1Open and prop the bonnet. Remove the
cover from the rear of the headlight unit by
twisting it anti-clockwise.
2Disconnect the wiring plug from the
headlight bulb. Release the spring clip by
squeezing its legs together and move it clear
of the bulb (see illustration).
3Remove the headlight bulb (see
illustration). Caution: If the lights have just
been in use, the bulb may be extremely hot.
4When handling the new bulb, use a tissue or
clean cloth to avoid touching the glass with
the fingers. If the glass is accidentally touched,
wipe it clean using methylated spirit. Moisture
and grease from the skin can cause
blackening and rapid failure of the new bulb.
5Fit the new bulb, making sure that the legs
and cut-outs in the bulb base and the reflector
match up. Secure with the spring clip.
6Reconnect the wiring plug. Check the
headlight for correct operation, then refit and
secure the rear cover.
Front parking light (sidelight)
7Gain access as for the headlight bulb, then
pull the parking light bulbholder from the
headlight reflector.
8Extract the wedge base bulb from the
holder (see illustration). Fit the new bulb, refit
the bulbholder and check for correct
operation.
Auxiliary driving light (when fitted)
9From above the auxiliary light unit, release
the cover spring clip and remove the cover
(see illustration).
10Release the spring clip from the bulb.
Withdraw the bulb and unplug its wiring
connector (see illustration). Caution: If the
lights have just been in use, the bulb may be
extremely hot.
11Do not touch the glass of the new bulb
with the fingers.
3Exterior lights - bulb renewal
13•4Body electrical system
3.2 Squeeze the spring clip legs (arrowed)
to remove the headlight bulb3.3 Removing a headlight bulb
3.8 Removing the front parking light bulb
from the holder3.9 Auxiliary driving light cover3.10 Removing the auxiliary driving light
bulb
procarmanuals.com
Page 187 of 255

1With the instrument cluster removed, a
particular gauge or other component can be
renewed by following the appropriate parts of
this Section.
2Remove all the light bulbs and holders from
the rear of the panel by twisting them anti-
clockwise.
3To remove the printed circuit, unclip and
remove the two multi-plug terminal retainers.
Remove all the nuts and washers from the
printed circuit terminals, then unclip and
remove the printed circuit. Be careful with it, it
is fragile (see illustration).
4To remove the instrument cluster glass,
release the two securing clips from thebottom
edge of the glass. Swing the glass upwards
and remove it.
5With the glass removed, the speedometer,
fuel and temperature gauges can be removed
individually after undoing their securing nuts or
screws. To remove the clock or tachometer,
the printed circuit must be removed as well.
6When fitted, the low fuel/high temperature
warning light bulbs can be renewed after
removing the combined gauge unit. Use
tweezers to extract the old bulb and to fit the
new one.
7The graphic display module, when fitted,
can be removed after undoing its two securing
screws.
8Reassemble the instrument cluster by
reversing the dismantling operations.
1To remove the clock from the instrument
panel, refer to the previous Section.
2To remove the clock from the overhead
console, first remove the console.
3Remove the clock rear cover, which is
secured by two screws.
4Remove the two screws which secure the
clock itself, then withdraw the clock.
5Refit by reversing the removal operations.1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
Front lighter
2On models with high level trim, pull the
centre console surround away from the radio
to gain access to the lighter. On models with
low level trim, remove the radio/cassette unit.
3Disconnect the wires from the cigarette
lighter and push it out of the illuminated ring.
4Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Rear lighter
5Pull off the rear heater control lever knob.
6Remove the rear console panel, which is
secured by two screws.
7Disconnect the wires from the lighter and
push it out of the illuminated ring.
8Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1Two horns are fitted as standard. The high
tone horn is located to the right of the radiator
and is accessible from under the bonnet. The
low tone horn is located below and to the left
of the radiator and is accessible from below.
2Remove the horn securing nut or bolt and
recover the shakeproof washer.
3Disconnect the wiring and remove the horn.4When refitting the horn, make sure it is
correctly positioned before tightening the
securing nut or bolt.
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
Switch plate
2Pull off the steering wheel centre cover.
3Undo the three screws which retain the
switch plate. Disconnect and remove the
switch plate (see illustration).
4Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Slip rings
5Remove the steering wheel.
6Release the tangs which secure the slip
rings to the underside of the steering wheel.
Disconnect the slip rings from the switch plate
and remove them.
7Refit by reversing the removal operations.
Brushes
8Remove the steering wheel.
9Remove the steering column upper and
lower shrouds.
10Disconnect the wiring from the horn
brushes. Carefully lever out the brush unit,
using a thin screwdriver inserted into the
bottom edge of the unit(see illustration).
11Refit by reversing the removal operations.
1Remove the seat.
2Remove the seat cushion or backrest trim.
3Note which way round the heating element
is facing (see illustration),then remove the
wire clips and adhesive tape which secure it to
the seat. Retrieve the tie-rod and fit it to the
new element.
4Fit the new element with the thermostat
facing the cushion foam. Secure the element
with wire clips and tape, ensuring that it is not
too tight - it must be able to flex under load.
5Refit the cushion or backrest trim.
6Refit the seat and check the heating
elements for correct operation.
13Seat heating elements -
removal and refitting
12Horn switch plate, slip rings
and brushes - removal and
refitting
11Horn - removal and refitting
10Cigarette lighter - removal
and refitting
9Clock - removal and refitting
8Instrument cluster - dismantling
and reassembly
13•10Body electrical system
8.3 Instrument cluster printed circuit
Unclip retainers at their top ends (arrowed)
13.3 Seat heating element
Thermostat (arrowed) must face the foam
12.3 Three screws (arrowed) secure the
horn switch plate12.10 Removing the horn brush unit
procarmanuals.com