1985 FORD GRANADA jack points
[x] Cancel search: jack pointsPage 5 of 255

1•4Maintenance Schedule
1 Battery
2 Suspension turrets
3 Air cleaner cover
4 Vane airflow meters
5 Headlight covers
6 Tune-up label
7 Auxiliary driving light covers
8 Crankcase ventilation hoses
9 Throttle linkage cover
10 Throttle cable and kickdown switch
11 Plenum chamber
12 Idle speed control valve
13 Radiator top hose
14 Oil filler cap
15 Power steering fluid reservoir
16 Horn
17 Washer fluid level switch
18 Windscreen washer pump
19 Windscreen washer reservoir
20 Coolant level switch
21 Coolant expansion tank cap
22 Engine mounting
23 Heater hose
24 Brake hydraulic unit valve block
25 Brake fluid reservoir cap
26 Brake hydraulic unit accumulator
27 Main fuse/relay box
28 Wiper motor (behind cover)
29 Heater blower cover
30 Fuel pressure regulator
31 Distributor screening lid
32 Engine oil dipstick
33 Automatic transmission fluid dipstick Under-bonnet view of a 2.8 litre V6 Granada
1 Brake and fuel pipes
2 Transmission sump
3 Transmission crossmember
4 Speedometer sender unit
5 Propeller shaft coupling
6 Exhaust flanged joint
7 Exhaust mounting
8 Exhaust pipe
9 Jacking points
10 Anti-roll bar clamps
11 Anti-roll bar
12 Brake calipers
13 Brake flexible hoses
14 Suspension lower arms
15 Front crossmember
16 Track rods
17 Track rod ends
18 Steering rack bellows
19 Radiator bottom hose
20 Alternator
21 Transmission fluid cooler hoses
22 Crankshaft pulley
23 Fan
24 Oil filter
25 Sump drain plug
26 Starter motor
27 Starter motor solenoid Front underbody view of a 2.0 litre SOHC Granada with automatic transmission
procarmanuals.com
Page 6 of 255

1•5
1
Maintenance Schedule
1 Track rod end
2 Track rod
3 Steering gear gaiter
4 Water pump
5 Starter motor
6 Front suspension lower arm
7 Front suspension anti-roll bar
8 Exhaust downpipe
9 Exhaust gas oxygen (HEGO) sensor -
models with catalytic converter
10 Front suspension crossmember
11 Sump drain plug
12 Power steering pump
13 Washer fluid reservoir
14 Radiator cooling fans
15 Catalytic converter (where fitted)
16 Catalytic converter heatshield (where
fitted)
17 Transmission crossmember
18 Fuel feed and return pipes
19 Rear brake pipes
20 Steering gear feed and return hosesFront underbody view of a 2.0 litre DOHC Granada with automatic transmission
1 Rear silencer
2 Fuel pump (fuel-injection)
3 Fuel filter (fuel-injection)
4 Fuel tank
5 Fuel tank straps
6 Anti-roll bar clamps
7 Final drive rear mounting
8 Anti-roll bar
9 Driveshafts
10 Driveshaft joints
11 Final drive unit
12 Handbrake cables
13 Suspension lower arms
14 Crossmember
15 Exhaust hanger
16 Guide plates
17 Propeller shaft
18 Propeller shaft universal joint
19 Brake and fuel pipes
20 Shock absorber lower mountings
21 Jacking points
22 Intermediate silencer
23 Exhaust pipe
Rear underbody view of a 2.0 litre SOHC Granada with fuel-injection
procarmanuals.com
Page 54 of 255
6Disconnect the breather hose from the
camshaft cover, and unbolt the hose bracket
from the left-hand side of the cylinder head
(see illustration).
7Unscrew the securing bolt and disconnect
the earth lead from the left-hand rear of the
cylinder head.
8Remove the distributor cap and HT leads,
and the rotor arm and housing, as applicable.
If necessary, mark the HT leads to aid refitting.
9The cylinder head can be removed either
with or without the manifolds and fuel rail,
where applicable (it is easiest to remove the
head complete with the manifolds and fuel
rail). If desired, the inlet manifold and the fuel
rail can be unbolted and moved to one side,
leaving the wires, hoses, pipes and cables
connected, but care must be taken not to
place any strain on them.
10Unscrew the three securing nuts and
disconnect the exhaust downpipe from the
manifold. It may be necessary to jack up the
front of the vehicle to gain access to the nuts
(in which case apply the handbrake and
support the front of the vehicle securely on
axle stands) (see “Jacking”). Discard the
gasket.
11If the inlet manifold and the fuel rail (where
applicable) are to be removed with the cylinder
head, disconnect all relevant wires, hoses,
pipes and cables, otherwise, unbolt the
manifold and the fuel rail, and move them to
one side, ensuring that they are adequately
supported. If the fuel rail is unbolted, be
prepared for fuel spillage, and take adequate
fire precautions.
12Refer to the procedure described in
paragraphs 2 to 19 of Section 18 to complete
cylinder head removal.
13Commence refitting by referring to
paragraphs 20 to 55 of Section 18, then
reverse the procedure described in
paragraphs 1 to 11 of this Section, noting the
following points.
a)Use a new gasket when reconnecting the
exhaust downpipe to the manifold.
b)Ensure that the HT leads are reconnected
correctly.
c)Fill the cooling system.Note: New cylinder head bolts, a new cylinder
head gasket, a new timing chain tensioner
plunger assembly, a new upper timing chain
cover gasket, and a new camshaft cover
gasket and reinforcing sleeve sealing rings
must be used on refitting. It is essential that
the three smaller M8 bolts are of the latest type
with hexagonal heads, not the earlier Torx type
(see illustration).
1With the manifolds removed, proceed as
follows.
2Unscrew the eleven bolts and four nuts, and
remove the camshaft cover. Recover the gasket.
3Unscrew the four securing bolts and three
studs, and remove the upper timing chain
cover. Note the locations of the studs to aid
refitting.
4Using a spanner on the crankshaft pulley,
turn the crankshaft to bring No 1 piston to the
firing point (TDC). With No 1 piston at the firing
point, the timing marks on the camshaft
sprockets should be pointing away from each
other, and should be approximately level with
the top edge of the cylinder head. Timing
notches are provided in the camshaft
sprockets, and corresponding paint marks are
provided on the outside edges of the
sprockets (see illustration).
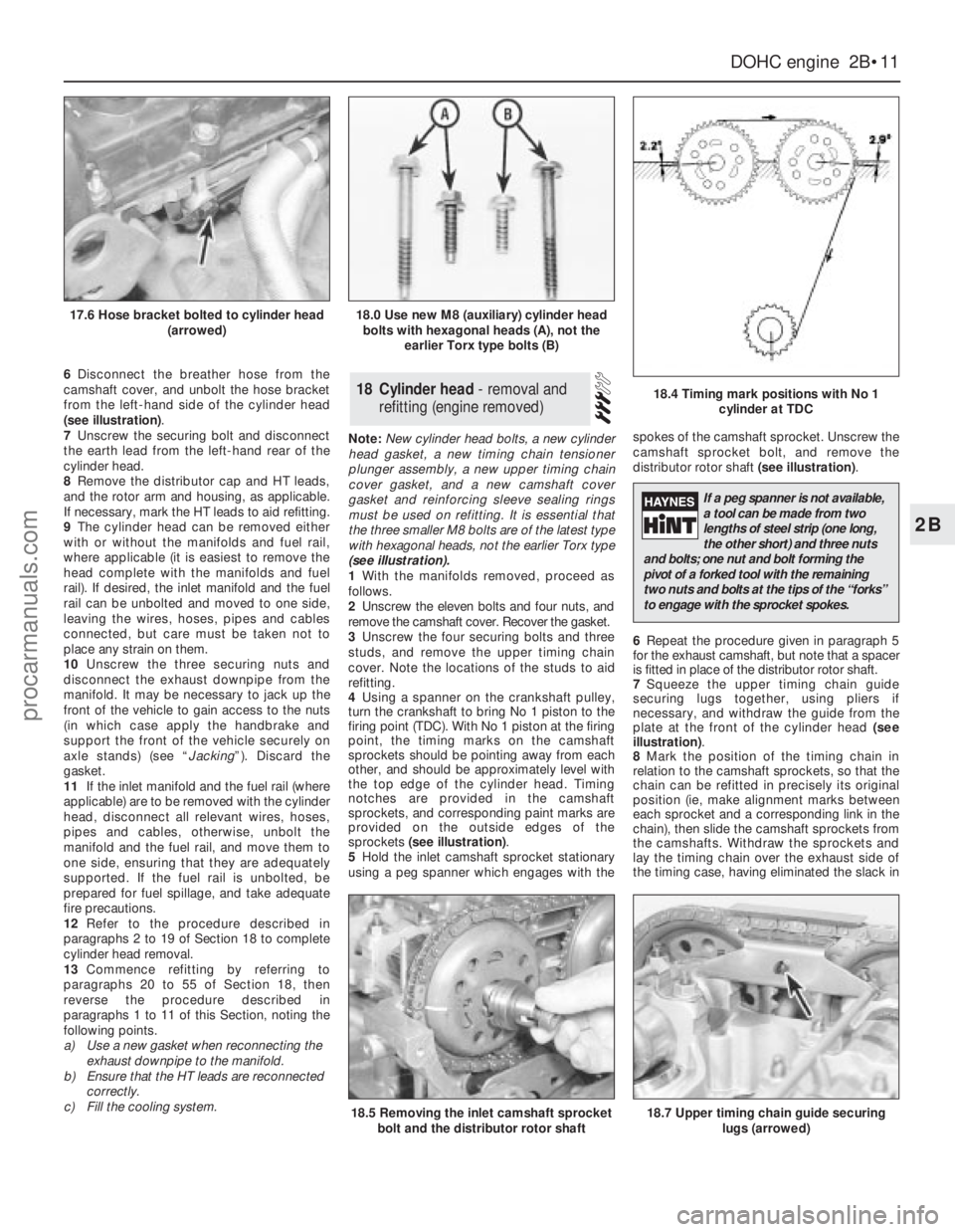
5Hold the inlet camshaft sprocket stationary
using a peg spanner which engages with thespokes of the camshaft sprocket. Unscrew the
camshaft sprocket bolt, and remove the
distributor rotor shaft (see illustration).
6Repeat the procedure given in paragraph 5
for the exhaust camshaft, but note that a spacer
is fitted in place of the distributor rotor shaft.
7Squeeze the upper timing chain guide
securing lugs together, using pliers if
necessary, and withdraw the guide from the
plate at the front of the cylinder head (see
illustration).
8Mark the position of the timing chain in
relation to the camshaft sprockets, so that the
chain can be refitted in precisely its original
position (ie, make alignment marks between
each sprocket and a corresponding link in the
chain), then slide the camshaft sprockets from
the camshafts. Withdraw the sprockets and
lay the timing chain over the exhaust side of
the timing case, having eliminated the slack in18Cylinder head - removal and
refitting (engine removed)
DOHCengine 2B•11
2B
17.6 Hose bracket bolted to cylinder head
(arrowed)18.0 Use new M8 (auxiliary) cylinder head
bolts with hexagonal heads (A), not the
earlier Torx type bolts (B)
18.4 Timing mark positions with No 1
cylinder at TDC
18.5 Removing the inlet camshaft sprocket
bolt and the distributor rotor shaft18.7 Upper timing chain guide securing
lugs (arrowed)
If a peg spanner is not available,
a tool can be made from two
lengths of steel strip (one long,
the other short) and three nuts
and bolts; one nut and bolt forming the
pivot of a forked tool with the remaining
two nuts and bolts at the tips of the “forks”
to engage with the sprocket spokes.
procarmanuals.com
Page 58 of 255

d)Disconnect the breather hose from the
camshaft cover.
e)Remove the distributor cap and HT leads,
and the rotor arm and housing. If
necessary, mark the HT leads to aid
refitting.
2Proceed as described in paragraphs 2 to 15
inclusive of Section 18.
3Examine the surfaces of the camshaft
journals and lobes and the contact surfaces of
the cam followers for wear. If wear is
excessive, considerable noise would have
been noticed from the top of the engine when
running, and new camshafts and followers
must be fitted. It is unlikely that this level of
wear will occur unless a considerable mileage
has been covered. Note that the cam followers
cannot be dismantled for renewal of individual
components.
4Check the camshaft bearing surfaces in the
cylinder head and the bearing caps for wear. If
excessive wear is evident, the only course of
action available is to renew the cylinder head
complete with bearing caps.
5Check the cam follower bores in the
cylinder head for wear. If excessive wear is
evident, the cylinder head must be renewed.
6Check the cam follower oil grooves and the
oil ports in the cylinder head for obstructions.
7Refit the cam followers and the camshafts as
described in paragraphs 27 to 55 of Section 18.
8If the engine is in the vehicle, reverse the
operations given in paragraph 1.
Refer to Part A, Section 15 of this Chapter,
noting the following points.
a)If the engine is in the car, refer to Chapter
6 when removing and refitting the clutch,
where applicable.
b)The flywheel/driveplate securing bolts
must be renewed on refitting; the new
bolts are supplied ready-coated with
thread-locking compound (see
illustration).
c)Check on the availability of new parts
before contemplating renewal of the ring
gear.Note: A suitable puller will be required to
remove the crankshaft pulley. A new
crankshaft pulley bolt and a new lower timing
chain cover gasket must be used on refitting.
1The crankshaft front oil seal is located in the
lower timing chain cover.
2If the engine is in the car, carry out the
following operations.
a)Disconnect the battery negative lead.
b)To improve access, remove the radiator. It
will be difficult to remove the crankshaft
pulley with the radiator in place.
c)On fuel-injection models, remove the air
inlet hose, plenum chamber, and air
cleaner lid as an assembly.
3Proceed as described in paragraphs 3 to 8
of Section 15.
4With the lower timing chain cover removed,
prise the old oil seal from the cover using a
screwdriver, and drive in the new seal using a
suitable metal tube. Make sure that the seal lip
faces into the engine. Take care not to
damage the timing chain cover. Note that the
seal should be fitted dry.
5Refit the lower timing chain cover as
described in paragraphs 32 to 40 of Section 15.
6If the engine is in the vehicle, reverse the
operations given in paragraph 2.
Note: New flywheel/driveplate bolts must be
used on refitting.
1Remove the flywheel/driveplate and the
engine adapter plate.
2Extract the seal using an oil seal removal tool
if available. It may also be possible to remove
the oil seal by drilling the outer face and using
self-tapping screws and a pair of grips.
3Clean the oil seal housing, then carefully
wind a thin layer of tape around the edge of
the crankshaft to protect the oil seal lip as the
seal is installed.
4Install a new oil seal. Make sure that the seal
lip faces into the engine (see illustration).5With the oil seal installed, carefully pull the
tape from the edge of the crankshaft.
6Refit the engine adapter plate and the
flywheel/driveplate.
Note: A new sump gasket will be required on
refitting, and suitable sealing compound will
be required to coat the sump and cylinder
block mating faces. Shims may be required
when mating the gearbox/transmission.
1Sump removal and refitting is far easier if
the engine is removed from the vehicle,
however if the engine is in the vehicle, proceed
as follows. If the engine has been removed
from the vehicle, proceed to paragraph 9.
2Remove the clutch or automatic
transmission, as applicable.
3Remove the flywheel/driveplate and the
engine adapter plate.
4Drain the engine oil into a suitable container.
5Ensure that the steering wheel is positioned
in the straight-ahead position then, using a
dab of paint or a marker pen, make alignment
marks between the intermediate shaft lower
clamp and steering gear pinion. Slacken and
remove the lower clamp bolt then disconnect
the intermediate shaft from the steering gear.
6Attach a suitable hoist to the engine lifting
brackets located at the front and rear of the
cylinder head, and carefully take the weight of
the engine.
7Detach the brake lines from the front
suspension crossmember.
8Support the crossmember with a jack, then
loosen the bolts securing the crossmember to
the underbody. Remove the bolts and carefully
lower the crossmember sufficiently to allow
the sump to be removed.
9If the engine has been removed, it is
preferable to keep it upright until the sump has
been removed to prevent sludge from entering
the engine internals.
10Unscrew the sump securing nuts and
bolts, and withdraw the sump from the engine.
Do not prise between the mating faces of the
sump and cylinder block. Discard the old
gasket.
11Thoroughly clean the mating faces of the
cylinder block and sump.
12Commence refitting by locating a new
gasket in the grooves in the sump.
25Sump - removal and refitting
24Crankshaft rear oil seal -
renewal
23Crankshaft front oil seal -
renewal
22Flywheel/driveplate - removal
inspection and refitting
DOHCengine 2B•15
2B
22.1 Improvised tool used to hold flywheel
when tightening securing bolts
24.4 Tool used to fit the oil seal
A Rear oil seal housing
B Special tool
A tool can be improvised using
a metal tube, a metal disc or
flat bar, and two flywheel
bolts.Draw the seal into
position using the two flywheel bolts.
If the sump is stuck, gently
tap it sideways to free it (the
sump will not move far
sideways, as it locates on
studs in the cylinder block).
procarmanuals.com
Page 68 of 255
meters and air inlet trunking. Also remove the
oil filler cap, which is connected to the
trunking by a crankcase ventilation hose.
5Release the securing clips and bolts and
remove the upper half of the fan shroud.
6Drain the cooling system and remove the
radiator.
7Disconnect the heater hoses from the
heater matrix and from the coolant outlet.
Unclip the hoses.
8Remove the fan and viscous clutch (where
fitted).
9Disconnect the following wiring:
a)Alternator
b)Temperature gauge sender
c)Engine management temperature sensor
d)Oil pressure switch
e)Idle speed control valve
f)Throttle position sensor
g)Injector nut-harness
h)Distributor multi-plug
i)Distributor-to-coil HT lead
10Disconnect the throttle cable. When
applicable, also disconnect the downshaft
cable or switch.
11Depressurise the fuel system and
disconnect the fuel supply and return lines
(see Chapter 4).
12Remove the steering pump and air
conditioning compressor drivebelts (as
applicable). Unbolt the steering pump and
compressor, move them aside within the limitsof their flexible hoses and support them by
wiring them to adjacent components.
13Remove the distributor cap and rotor.
14Remove the starter motor.
15Drain the engine oil. Unscrew the oil filter
with a strap or chain wrench and remove it; be
prepared for oil spillage.
16On manual gearbox models, disconnect
the clutch cable from the release lever.
17Unbolt the exhaust pipes from the
manifolds.
18On automatic transmission models, unbolt
the torque converter from the driveplate.
19Attach lifting tackle to the engine. If no
lifting eyes are fitted, pass ropes or chains
round the exhaust manifolds.
20Take the weight of the engine, then
remove the single nut on each side which
holds engine bearer to its mountings.
21From under the vehicle unbolt the engine
adapter plate from the bellhousing.
22Remove the engine-to-bellhousing bolts.
Also disconnect or unclip the battery negative
lead, the starter motor lead and the heat
shield.
23Support the transmission, preferably with
a trolley jack.
24Check that nothing has been overlooked,
then raise the engine and draw it forwards
clear of the transmission input shaft. Do not
allow the weight of the engine to hang on the
shaft, and do not lift the transmission by it.25With automatic transmission, make sure
that the torque converter stays engaged with
the oil pump in the transmission as the engine
is withdrawn.
26Lift the engine out of the engine bay and
take it to the bench.
2.4 & 2.9 litre engines
27The removal operations for these engines
are essentially as described for the 2.8 litre
version. Note the following points.
Coolant hoses
28Remove the hoses which run between the
thermostat housing and the water pump, and
the cooling system expansion tank.
29Remove the heater hoses which run
between the thermostat housing or coolant
distribution pipe and oil cooler (where fitted).
Vacuum hoses
30Disconnect the hose from the fuel
pressure regulator.
31Disconnect the hose from the plenum
chamber.
32Disconnect the hose from the throttle valve.
33Disconnect the hose from the T-piece
connector.
V6 engines 2C•7
2C
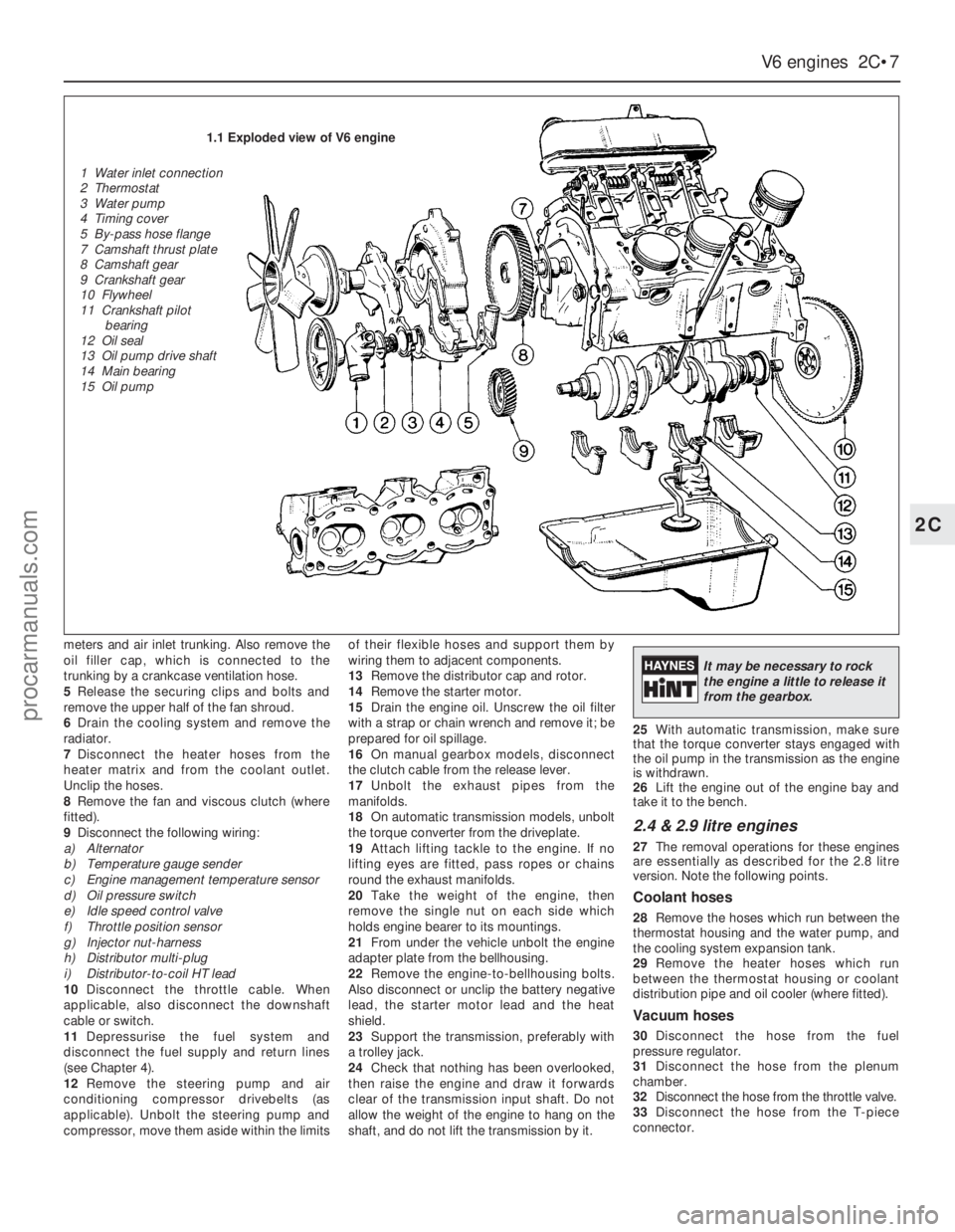
1.1 Exploded view of V6 engine
1 Water inlet connection
2 Thermostat
3 Water pump
4 Timing cover
5 By-pass hose flange
7 Camshaft thrust plate
8 Camshaft gear
9 Crankshaft gear
10 Flywheel
11 Crankshaft pilot
bearing
12 Oil seal
13 Oil pump drive shaft
14 Main bearing
15 Oil pump
It may be necessary to rock
the engine a little to release it
from the gearbox.
procarmanuals.com
Page 72 of 255
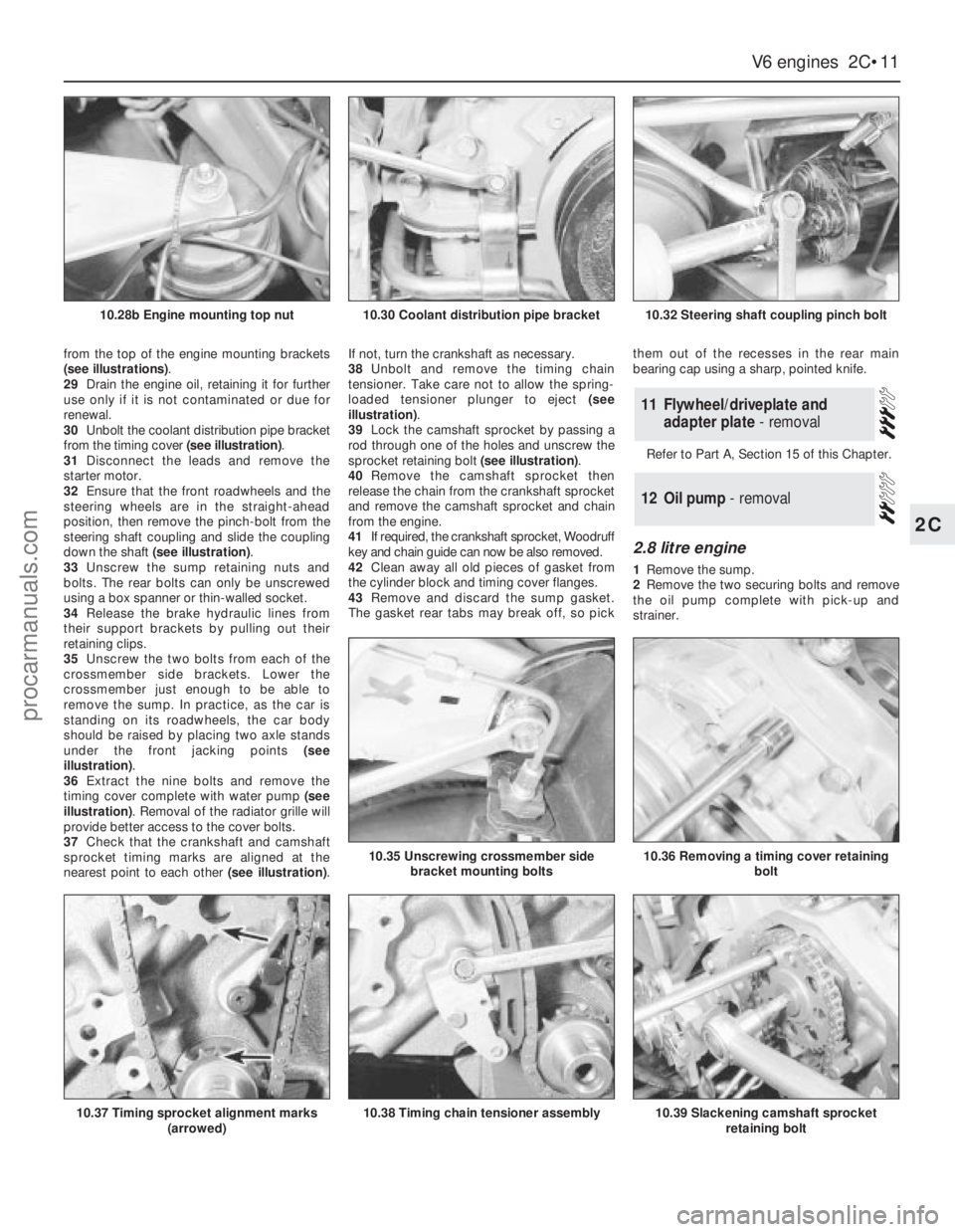
from the top of the engine mounting brackets
(see illustrations).
29Drain the engine oil, retaining it for further
use only if it is not contaminated or due for
renewal.
30Unbolt the coolant distribution pipe bracket
from the timing cover (see illustration).
31Disconnect the leads and remove the
starter motor.
32Ensure that the front roadwheels and the
steering wheels are in the straight-ahead
position, then remove the pinch-bolt from the
steering shaft coupling and slide the coupling
down the shaft (see illustration).
33Unscrew the sump retaining nuts and
bolts. The rear bolts can only be unscrewed
using a box spanner or thin-walled socket.
34Release the brake hydraulic lines from
their support brackets by pulling out their
retaining clips.
35Unscrew the two bolts from each of the
crossmember side brackets. Lower the
crossmember just enough to be able to
remove the sump. In practice, as the car is
standing on its roadwheels, the car body
should be raised by placing two axle stands
under the front jacking points (see
illustration).
36Extract the nine bolts and remove the
timing cover complete with water pump (see
illustration). Removal of the radiator grille will
provide better access to the cover bolts.
37Check that the crankshaft and camshaft
sprocket timing marks are aligned at the
nearest point to each other (see illustration).If not, turn the crankshaft as necessary.
38Unbolt and remove the timing chain
tensioner. Take care not to allow the spring-
loaded tensioner plunger to eject (see
illustration).
39Lock the camshaft sprocket by passing a
rod through one of the holes and unscrew the
sprocket retaining bolt (see illustration).
40Remove the camshaft sprocket then
release the chain from the crankshaft sprocket
and remove the camshaft sprocket and chain
from the engine.
41If required, the crankshaft sprocket, Woodruff
key and chain guide can now be also removed.
42Clean away all old pieces of gasket from
the cylinder block and timing cover flanges.
43Remove and discard the sump gasket.
The gasket rear tabs may break off, so pickthem out of the recesses in the rear main
bearing cap using a sharp, pointed knife.
Refer to Part A, Section 15 of this Chapter.
2.8 litre engine
1Remove the sump.
2Remove the two securing bolts and remove
the oil pump complete with pick-up and
strainer.
12Oil pump - removal
11Flywheel/driveplate and
adapter plate - removal
V6 engines 2C•11
2C
10.28b Engine mounting top nut10.30 Coolant distribution pipe bracket10.32 Steering shaft coupling pinch bolt
10.37 Timing sprocket alignment marks
(arrowed)
10.36 Removing a timing cover retaining
bolt10.35 Unscrewing crossmember side
bracket mounting bolts
10.38 Timing chain tensioner assembly10.39 Slackening camshaft sprocket
retaining bolt
procarmanuals.com
Page 97 of 255

The exhaust system fitted in production is
made of aluminised steel, with stainless steel
used in the endplates and baffles of the rear
silencer. Individual sections of the system are
easily renewed in service.
Emission control for the UK market is
achieved largely by the inherent efficiency of
the fuel, ignition and engine management
systems. A welcome spin-off from such
efficiency is remarkably good fuel economy for
a vehicle of such size and weight.
Precautions
Fuel
Many of the procedures in this Chapter
require the removal of fuel lines and
connections which may result in some fuel
spillage. Residual pressure in fuel-injection
systems will remain in the fuel lines long after
the vehicle was last used, therefore extra care
must be taken when disconnecting a fuel line
hose. Loosen any fuel hose slowly to avoid a
sudden release of pressure which may cause
fuel spray. As an added precaution place a rag
over each union as it is disconnected to catch
any fuel which is forcibly expelled. Before
carrying out any operation on the fuel system
refer to the precautions given in “Safety first!”
at the beginning of this Manual and follow
them implicitly. Petrol is a highly dangerous
and volatile liquid and the precautions
necessary when handling it cannot be
overstressed
Tamperproof adjustment screws
Certain adjustment points in the fuel system
(and elsewhere) are protected by tamperproof
caps, plugs or seals. The purpose of such
tamperproofing is to discourage, and to deter,
adjustment by unqualified operators.
In some EU countries (though not yet in the
UK) it is an offence to drive a vehicle with
missing or broken tamperproof seals. Before
disturbing a tamperproof seal, satisfy yourself
that you will not be breaking local or national
anti-pollution regulations by doing so. Fit a
new seal when adjustment is complete when
this is required by law.
Do not break tamperproof seals on a vehicle
which is still under warranty.
Catalytic converter
The catalytic converter is a reliable and
simple device which needs no maintenance in
itself, but there are some facts of which an
owner should be aware if the converter is to
function properly for the full service life.
a)DO NOT use leaded petrol in a car
equipped with a catalytic converter the
lead will coat the precious metals,
reducing their converting efficiency and
will eventually destroy the converter.
b)Always keep the ignition and fuel systems
well-maintained in accordance with the
manufacturer’s schedule - particularly,
ensure that the air cleaner filter element,
the fuel filter and the spark plugs are
renewed at the correct interval - if the inletair/fuel mixture is allowed to become too
rich due to neglect, the unburned surplus
will enter and burn in the catalytic
converter, overheating the element and
eventually destroying the converter.
c)If the engine develops a misfire, do not
drive the car at all (or at least as little as
possible) until the fault is cured - the
misfire will allow unburned fuel to enter
the converter, which will result in
overheating, as noted above.
d)DO NOT push- or tow-start the car - this
will soak the catalytic converter in
unburned fuel, causing it to overheat when
the engine does start - see b) above.
e)DO NOT switch off the ignition at high
engine speeds - if the ignition is switched
off at anything above idle speed,
unburnedfuel will enter the (very hot)
catalytic converter, with the possible risk
of igniting on the element and damaging
the converter.
f)DO NOT use fuel or engine oil additives -
these may contain substances harmful to
the catalytic converter.
g)DO NOT continue to use the car if the
engine burns oil to the extent of leaving a
visible trail of blue smoke - the unburned
carbon deposits will clog the converter
passages and reduce the efficiency; in
severe cases the element will overheat.
h)Remember that the catalytic converter
operates at very high temperatures -
hence the heat shields on the car’s
underbody and the casing will become hot
enough to ignite combustible materials
which brush against it - DO NOT,
therefore, park the car in dry undergrowth,
over long grass or piles of dead leaves.
i)Remember that the catalytic converter is
FRAGILE, do not strike it with tools during
servicing work, take great care when
working on the exhaust system, ensure
that the converter is well clear of any jacks
or other lifting gear used to raise the car
and do not drive the car over rough
ground, road humps, etc, in such a way as
to “ground” the exhaust system.
j)In some cases, particularly when the car is
new and/or is used for stop/start driving, a
sulphurous smell (like that of rotten eggs)may be noticed from the exhaust. This is
common to many catalytic converter-
equipped cars and seems to be due to the
small amount of sulphur found in some
petrols reacting with hydrogen in the
exhaust to produce hydrogen sulphide
(H
2S) gas; while this gas is toxic, it is not
produced in sufficient amounts to be a
problem. Once the car has covered a few
thousand miles the problem should
disappear - in the meanwhile a change of
driving style or of the brand of petrol used
may effect a solution.
k)The catalytic converter, used on a well-
maintained and well-driven car, should
last for between 50 000 and 100 000 miles
- from this point on, careful checks should
be made at all specified service intervals
of the CO level to ensure that the
converter is still operating efficiently - if
the converter is no longer effective it must
be renewed.
See Chapter 1, Section 38.
1On carburettor models only, the air cleaner
can take in both hot and cold air. Hot air is
obtained from a shroud bolted to the exhaust
manifold.
2A flap valve in the air cleaner spout
determines the mix of hot and cold air. The
valve is operated by a vacuum diaphragm.
Vacuum is obtained from the inlet manifold
and is applied via a heat-sensing valve, which
cuts off the vacuum as the temperature of the
incoming air rises. Thus the air cleaner takes in
only hot air on starting from cold, changing
progressively to cold air as the engine warms
up (see illustrations).
3If the system fails, either the engine will take
a long time to warm up (flap stuck in “cold”
position), or it may run roughly and not
develop full power when warm (flap stuck in
“hot” position). Check it as follows.
3Air cleaner temperature control
- description and testing
2Air cleaner and element -
removal and refitting
4•4Fuel and exhaust systems
3.2b Air cleaner heat sensor3.2a Air cleaner vacuum diaphragm unit
procarmanuals.com
Page 115 of 255

DOHC carburettor engine
8This procedure is essentially as described
above, noting the following points:
a)Note the plastic bush which is fitted to the
rear manifold stud. This must be removed
before the gasket can be withdrawn.
b)On refitting ensure that the mating
surfaces are clean and dry and fit new
gaskets.
c)Apply a thin coat of anti-seize compound
to the manifold studs to aid future
removal.
d)Tighten the manifold nuts to the specified
torque settings.
DOHC fuel-injection engine
9Disconnect the battery negative lead.
10Disconnect the wiring plug from the idle
speed control valve at the front of the plenum
chamber.
11Loosen the clamp, and detach the air inlet
hose from the air inlet tubing.
12Unscrew the securing nut, and release the
air inlet tube from the bracket on the engine
compartment front panel.
13Release the air cleaner lid securing clips,
then lift away the air inlet tube, plenum
chamber and air cleaner lid as an assembly,
disconnecting the breather hose from the air
inlet tube.
14On models fitted with a catalytic
converter, disconnect the exhaust gas oxygen
sensor wiring plug.
15Unscrew the securing nuts and disconnect
the exhaust downpipe from the manifold.
Recover the gasket. Support the exhaust
downpipe from underneath the vehicle (eg
with an axle stand) to avoid placing
unnecessary strain on the exhaust system.
16Unscrew the six securing nuts, and lift the
manifold from the cylinder head. Recover the
gasket.
17Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points.
a)Ensure that all mating faces are clean, and
use a new gasket.
b)Tighten the manifold securing nuts and
the downpipe securing nuts progressively
to the specified torque (where given).
SOHC and 2.8 litre V6 engines
1Periodically inspect the exhaust system for
freedom from corrosion and security of
mountings. Large holes will be obvious; small
holes may be found more easily by letting the
engine idle and partly obstructing the tailpipe
with a wad of cloth.
2Check the condition of the rubber
mountings by applying downward pressure on
the exhaust system and observing the
mountings for splits or cracks. Renew
deteriorated mountings.
3The exhaust systems fitted in production
have fewer sections than those available for
repair. Repair sections may be fitted to
production systems by cutting at the
appropriate point.
4The production exhaust systems are made
of aluminised and stainless steel. Repair
systems are available to the same standard, or
in standard quality (SQ) painted mild steel.
5It is recommended that the whole exhaust
system be removed even if only part requires
renewal, since separation of old joints, cutting
pipes etc is much easier away from the
vehicle. Proceed as follows.
6Disconnect the battery negative lead. Raise
and support the vehicle.
7Unbolt the manifold-to-downpipe flanged
joint(s).
8On V6 models, unbolt the left-hand front
silencer mounting.
9Release any earth straps.
10With the help of an assistant, unhook the
system from its mountings and remove it.
11Renew sections as necessary. Apply
exhaust jointing compound to sliding and
flanged joints, but do not tighten their clamps
yet. Use new sealing rings where necessary
(see illustration).
12Offer the system to the vehicle and hook it
onto the mountings.
13Refit any earth straps. On V6 models, also
refit the left-hand front silencer mounting.
14Loosely fit the manifold flange nuts.
Correct the alignment of the system, then
tighten all clamp nuts and bolts, starting at the
manifold flange(s) and working rearwards.
15Check that the system alignment is still
satisfactory then reconnect the battery. Run
the engine and check for leaks.
16When the system has warmed up, stop the
engine and carefully check the tightness of the
clamp nuts and bolts.
DOHC and 2.4 & 2.9 litre V6
engines
17Follow the above procedure, noting that
flanged joints incorporating gaskets may be
used to join exhaust sections on these
models. Where applicable, renew the gaskets
on refitting.
18On models fitted with a catalyticconverter, disconnect the battery negative
terminal and disconnect the exhaust gas
oxygen (HEGO) sensor wiring plug before
removing the downpipe.
DOHC engine
Note: The exhaust gas oxygen (HEGO) sensor
is delicate and will not work if it is dropped or
knocked, if the power supply is disrupted, or if
any cleaning materials are used on it. Never
touch the tip of the sensor as this can also
damage it.
1Ensure that the engine and the exhaust
system are cold.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle, and support it securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking”).
4Disconnect the sensor wiring plug halves by
releasing the locktabs and pulling on the plug
halves, not the wiring.
5Slide the heat shield (where fitted) from the
sensor.
6Bearing in mind the note made at the start
of this operation, unscrew the sensor from the
exhaust downpipe, and recover the sealing
ring (see illustration).
7Commence refitting by ensuring that the
sensor threads and the corresponding threads
in the downpipe are clean.
8Refit the sensor using a new sealing ring,
and tighten it to the specified torque.
9Further refitting is a reversal of removal, but
on completion start the engine, and check for
leaks around the sensor sealing ring.
V6 engines
10The sensors fitted to these models can be
removed and refitted using the information
given above, noting that on early models there
was only one sensor, which was fitted at the
point where the two downpipes meet below
the engine, and on some later models there
are two sensors, one in each downpipe.
43Exhaust gas oxygen (HEGO)
sensor (models with catalytic
converter) - removal and
refitting
42Exhaust system - inspection,
repair and renewal
4•22Fuel and exhaust systems
43.6 Exhaust gas oxygen (HEGO) sensor
(viewed from underneath)
42.11 Exhaust pipe flanged joint
A Sealing ring
B Flange
procarmanuals.com